c815ec8e48b83b24ee25387df726ef19.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 POSTEC Lecture Network Management Chapter 6 NGN Management June 9 -12, 2008 Masayoshi Ejiri Japan
POSTEC Lecture Network Management Chapter 6 NGN Management June 9 -12, 2008 Masayoshi Ejiri Japan
 Agenda 1. ICT Operations and Management - Service Industries - ICT Services and Networks— - Target of the Management 2, Architecture , Function , Information Model and Business Process - ITU-T TMN( Telecommunications Management Network) - Tele. Management Forum Telecommunications Operations Map ( TOM) - Multi domain management and System Integration - Standardization 3. OSS( Operations Support System ) Development - Software Architecture , Key Technologies and Product Evaluation— 4. SLA( Service Level Agreement) and Qo. S( Quality of Service) - SLA Definition , reference point and policy based negotiation 5, IP/e. Business Management - Paradigm shift , Architecture beyond TMN and enhanced TOM 6. NGN( Next Generation Networks) Management - NGN Networks and Services , New Paradigm of ICT Business and Management
Agenda 1. ICT Operations and Management - Service Industries - ICT Services and Networks— - Target of the Management 2, Architecture , Function , Information Model and Business Process - ITU-T TMN( Telecommunications Management Network) - Tele. Management Forum Telecommunications Operations Map ( TOM) - Multi domain management and System Integration - Standardization 3. OSS( Operations Support System ) Development - Software Architecture , Key Technologies and Product Evaluation— 4. SLA( Service Level Agreement) and Qo. S( Quality of Service) - SLA Definition , reference point and policy based negotiation 5, IP/e. Business Management - Paradigm shift , Architecture beyond TMN and enhanced TOM 6. NGN( Next Generation Networks) Management - NGN Networks and Services , New Paradigm of ICT Business and Management
 Chapter 6 Agenda • • • ICT status in Japan Converged Market and New Paradigm Service Delivery on SOA and Saa. S NGN strategy and architecture NGN Management
Chapter 6 Agenda • • • ICT status in Japan Converged Market and New Paradigm Service Delivery on SOA and Saa. S NGN strategy and architecture NGN Management
 Business on Converged Market Services : • • • Triple/Quadruple services consuming Interactive BB. By Convergence Communications, Broadcast and Contents Create/ Delivery players and customer participation To Proactive customers SP’s Target : • • • Establish NGN ( Next Generation Network) and Managed Ubiquitous BB and Location Services Attractive Services by Collaborating with inter/intra industries and customers. Ensure Revenue Assurance Scheme Operations and Management : • • • Customer self/ responsible Operations and Management. Customer represented Operations Management NGN 2. 0 and Web 2. 0
Business on Converged Market Services : • • • Triple/Quadruple services consuming Interactive BB. By Convergence Communications, Broadcast and Contents Create/ Delivery players and customer participation To Proactive customers SP’s Target : • • • Establish NGN ( Next Generation Network) and Managed Ubiquitous BB and Location Services Attractive Services by Collaborating with inter/intra industries and customers. Ensure Revenue Assurance Scheme Operations and Management : • • • Customer self/ responsible Operations and Management. Customer represented Operations Management NGN 2. 0 and Web 2. 0
 U-Japan Ubiquitous • Universal : on universal design concept, where anyone can easily enjoy participate in social activities. • Use Oriented : from complete user perspective, offer services for user needs and convenience. • Unique : bring human power to create business and services for local area revitalization
U-Japan Ubiquitous • Universal : on universal design concept, where anyone can easily enjoy participate in social activities. • Use Oriented : from complete user perspective, offer services for user needs and convenience. • Unique : bring human power to create business and services for local area revitalization
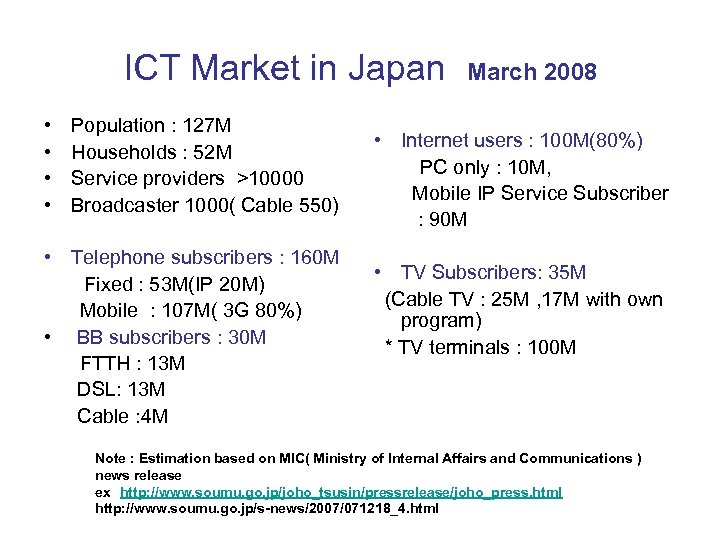 ICT Market in Japan • • Population : 127 M Households : 52 M Service providers >10000 Broadcaster 1000( Cable 550) • Telephone subscribers : 160 M Fixed : 53 M(IP 20 M) Mobile : 107 M( 3 G 80%) • BB subscribers : 30 M FTTH : 13 M DSL: 13 M Cable : 4 M March 2008 • Internet users : 100 M(80%) PC only : 10 M, Mobile IP Service Subscriber : 90 M • TV Subscribers: 35 M (Cable TV : 25 M , 17 M with own program) * TV terminals : 100 M Note : Estimation based on MIC( Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications ). news release ex http: //www. soumu. go. jp/joho_tsusin/pressrelease/joho_press. html http: //www. soumu. go. jp/s-news/2007/071218_4. html
ICT Market in Japan • • Population : 127 M Households : 52 M Service providers >10000 Broadcaster 1000( Cable 550) • Telephone subscribers : 160 M Fixed : 53 M(IP 20 M) Mobile : 107 M( 3 G 80%) • BB subscribers : 30 M FTTH : 13 M DSL: 13 M Cable : 4 M March 2008 • Internet users : 100 M(80%) PC only : 10 M, Mobile IP Service Subscriber : 90 M • TV Subscribers: 35 M (Cable TV : 25 M , 17 M with own program) * TV terminals : 100 M Note : Estimation based on MIC( Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications ). news release ex http: //www. soumu. go. jp/joho_tsusin/pressrelease/joho_press. html http: //www. soumu. go. jp/s-news/2007/071218_4. html
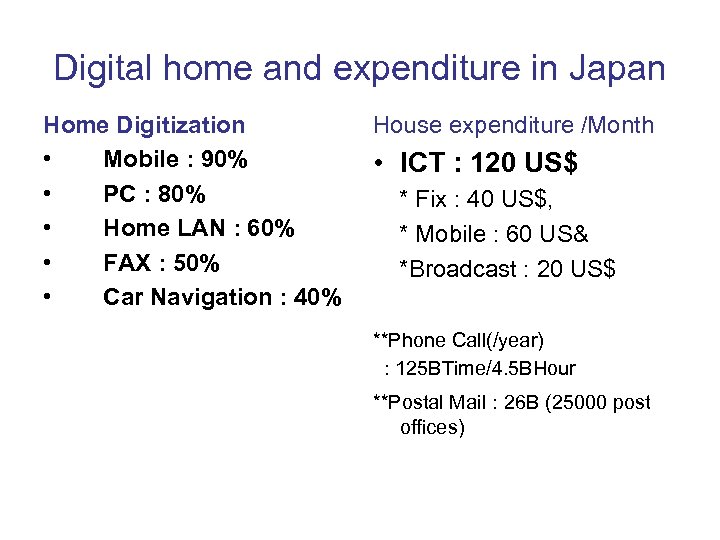 Digital home and expenditure in Japan Home Digitization • Mobile : 90% • PC : 80% • Home LAN : 60% • FAX : 50% • Car Navigation : 40% House expenditure /Month • ICT : 120 US$ * Fix : 40 US$, * Mobile : 60 US& *Broadcast : 20 US$ **Phone Call(/year) : 125 BTime/4. 5 BHour **Postal Mail : 26 B (25000 post offices)
Digital home and expenditure in Japan Home Digitization • Mobile : 90% • PC : 80% • Home LAN : 60% • FAX : 50% • Car Navigation : 40% House expenditure /Month • ICT : 120 US$ * Fix : 40 US$, * Mobile : 60 US& *Broadcast : 20 US$ **Phone Call(/year) : 125 BTime/4. 5 BHour **Postal Mail : 26 B (25000 post offices)
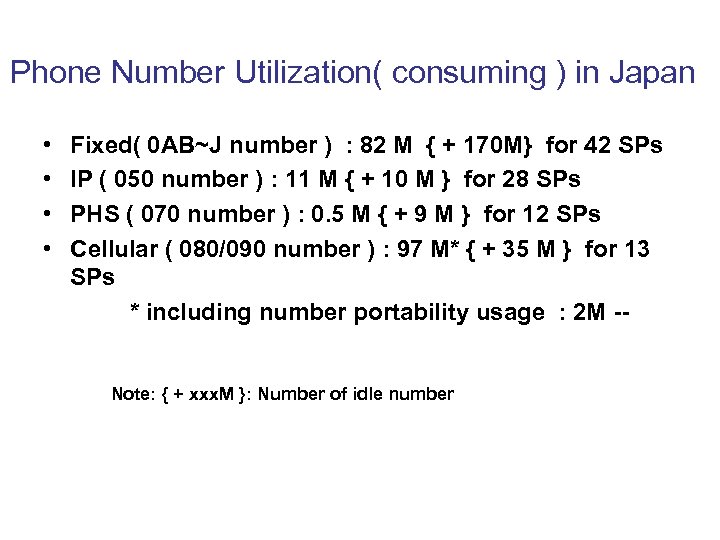 Phone Number Utilization( consuming ) in Japan • • Fixed( 0 AB~J number ) : 82 M { + 170 M} for 42 SPs IP ( 050 number ) : 11 M { + 10 M } for 28 SPs PHS ( 070 number ) : 0. 5 M { + 9 M } for 12 SPs Cellular ( 080/090 number ) : 97 M* { + 35 M } for 13 SPs * including number portability usage : 2 M -Note: { + xxx. M }: Number of idle number
Phone Number Utilization( consuming ) in Japan • • Fixed( 0 AB~J number ) : 82 M { + 170 M} for 42 SPs IP ( 050 number ) : 11 M { + 10 M } for 28 SPs PHS ( 070 number ) : 0. 5 M { + 9 M } for 12 SPs Cellular ( 080/090 number ) : 97 M* { + 35 M } for 13 SPs * including number portability usage : 2 M -Note: { + xxx. M }: Number of idle number
 New Paradigm (1) Customer Participation BGM CGM BGM ( Back Ground Music) • Contents provider generate and /or distribute messages • Customers reactively enjoy them. CGM* ( Customer Generated Message) • Customer proactively generate( create /mash up ) and enjoy messages • Provider assist/coordinate message generation/ distribution and owner of archive Ex. You. Tube, Google Map, My space, SNS etc. * Consumer Generated Media
New Paradigm (1) Customer Participation BGM CGM BGM ( Back Ground Music) • Contents provider generate and /or distribute messages • Customers reactively enjoy them. CGM* ( Customer Generated Message) • Customer proactively generate( create /mash up ) and enjoy messages • Provider assist/coordinate message generation/ distribution and owner of archive Ex. You. Tube, Google Map, My space, SNS etc. * Consumer Generated Media
 New Paradigm (2) Broadband , Ubiquitous and Location • IPTV and FTTH • Home networking • Location management Security vs Privacy --Human activities are informed/checked/ logged by location – Identifier : GPS , Base station , Wireless LAN, RFID, Terminal
New Paradigm (2) Broadband , Ubiquitous and Location • IPTV and FTTH • Home networking • Location management Security vs Privacy --Human activities are informed/checked/ logged by location – Identifier : GPS , Base station , Wireless LAN, RFID, Terminal
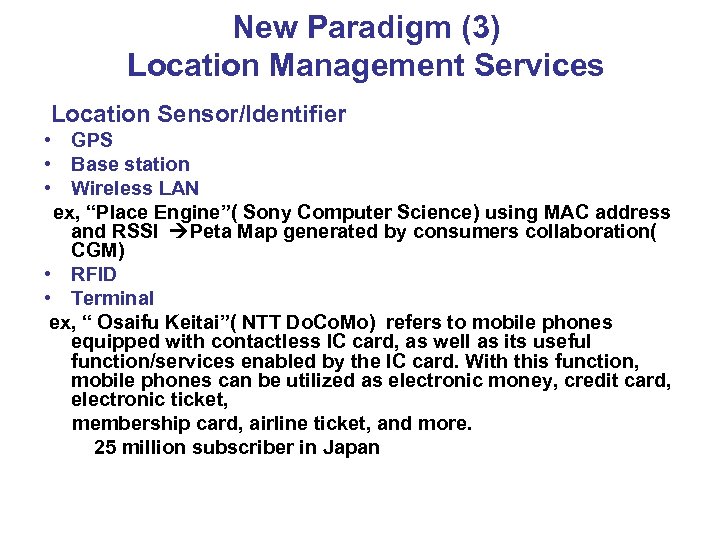 New Paradigm (3) Location Management Services Location Sensor/Identifier • GPS • Base station • Wireless LAN ex, “Place Engine”( Sony Computer Science) using MAC address and RSSI Peta Map generated by consumers collaboration( CGM) • RFID • Terminal ex, “ Osaifu Keitai”( NTT Do. Co. Mo) refers to mobile phones equipped with contactless IC card, as well as its useful function/services enabled by the IC card. With this function, mobile phones can be utilized as electronic money, credit card, electronic ticket, membership card, airline ticket, and more. 25 million subscriber in Japan
New Paradigm (3) Location Management Services Location Sensor/Identifier • GPS • Base station • Wireless LAN ex, “Place Engine”( Sony Computer Science) using MAC address and RSSI Peta Map generated by consumers collaboration( CGM) • RFID • Terminal ex, “ Osaifu Keitai”( NTT Do. Co. Mo) refers to mobile phones equipped with contactless IC card, as well as its useful function/services enabled by the IC card. With this function, mobile phones can be utilized as electronic money, credit card, electronic ticket, membership card, airline ticket, and more. 25 million subscriber in Japan
 Location Services and Management Security vs Privacy --Human activities are informed/checked/ logged by location – • • GPS Mobile phone location service to identify /notice his/her location and automatic notice of entry/exit of predefined areas. Secure Pass by informing child ‘s parent mobile phone the event where a child passes ticket gate by commune pass, Human/Car move tracking services using GPS based location/speed/direction /time/status information every few seconds. Check doubtful action and compliance , Lost mobile phone security by checking the location matching of owner and terminal Location Value Chain • • Provide Local Utility information ( Shopping , Restaurant. . ) NGN CSF(Convergence Services Framework), CC-FE( Convergence Coordination Functional Entity) Coordinate location information with services. Seek( Recruit) available persons in the best location on demand, real time deal. “ Location Call” : Area limited special services with no charge Context aware management • TPO ( Time , Place and Occasion )awareness
Location Services and Management Security vs Privacy --Human activities are informed/checked/ logged by location – • • GPS Mobile phone location service to identify /notice his/her location and automatic notice of entry/exit of predefined areas. Secure Pass by informing child ‘s parent mobile phone the event where a child passes ticket gate by commune pass, Human/Car move tracking services using GPS based location/speed/direction /time/status information every few seconds. Check doubtful action and compliance , Lost mobile phone security by checking the location matching of owner and terminal Location Value Chain • • Provide Local Utility information ( Shopping , Restaurant. . ) NGN CSF(Convergence Services Framework), CC-FE( Convergence Coordination Functional Entity) Coordinate location information with services. Seek( Recruit) available persons in the best location on demand, real time deal. “ Location Call” : Area limited special services with no charge Context aware management • TPO ( Time , Place and Occasion )awareness
 New Paradigm (4) Revenue Assurance Scheme Toward Free of Charge Mind • Who will pay for Communications Mechanism ( Broad band, Traffic, Storage, Wire and wireless Access, etc. ) • Who will pay for Contents on Internet ( Customer enjoy as consumer and also as contents provider -- create, mash up, copy, etc. and share contents on internet --) • Customer will pay for Logical/Physical Access facilities to ensure their service contract ( mostly by Fix sum) • Advertisement can not cover NGN and ICT investment.
New Paradigm (4) Revenue Assurance Scheme Toward Free of Charge Mind • Who will pay for Communications Mechanism ( Broad band, Traffic, Storage, Wire and wireless Access, etc. ) • Who will pay for Contents on Internet ( Customer enjoy as consumer and also as contents provider -- create, mash up, copy, etc. and share contents on internet --) • Customer will pay for Logical/Physical Access facilities to ensure their service contract ( mostly by Fix sum) • Advertisement can not cover NGN and ICT investment.
 Advertisement in 2007( estimated) Total Expenditure 63 B $ -Mass Communication 32 B $ TV: 18 B$, News Paper : 8. 5 B$, Internet 5. 5 B$ ( 9%) Magazine: 4 B$, Radio : 1. 5$ - Promotion media : 25 B$ Note : Communications /Broadcasting Industry’s Market ( Revenue) : 170 B$ -Communications : 135 B$ - Broadcast : 35 B$ Note : Based on Dentsu report 1$=110 JPY
Advertisement in 2007( estimated) Total Expenditure 63 B $ -Mass Communication 32 B $ TV: 18 B$, News Paper : 8. 5 B$, Internet 5. 5 B$ ( 9%) Magazine: 4 B$, Radio : 1. 5$ - Promotion media : 25 B$ Note : Communications /Broadcasting Industry’s Market ( Revenue) : 170 B$ -Communications : 135 B$ - Broadcast : 35 B$ Note : Based on Dentsu report 1$=110 JPY
 New paradigm ( 5) Service delivery: Xaa. S: XXX as a Service • Saa. S( Software as a Service) Software Service Product : Web 2. 0 • Aaa. S( Access as a Service) Access Mechanism Service Contract : NGN 2. 0 • Paa. S (Platform as a Service ) : Salesforce. com • Paa. S ( Product as a Service) Function & Application Service Component : SOA • Paa. S (Process as a Service) Work flow Service aggregation : e. TOM & SDP Licence Agreement Service Level Agreement
New paradigm ( 5) Service delivery: Xaa. S: XXX as a Service • Saa. S( Software as a Service) Software Service Product : Web 2. 0 • Aaa. S( Access as a Service) Access Mechanism Service Contract : NGN 2. 0 • Paa. S (Platform as a Service ) : Salesforce. com • Paa. S ( Product as a Service) Function & Application Service Component : SOA • Paa. S (Process as a Service) Work flow Service aggregation : e. TOM & SDP Licence Agreement Service Level Agreement
 SOA • • De-composite into general purpose component Business Function=Component=Service Loose coupled Find-Bind composite service • Service( system) development free from ( independent of ) IT infrastructure, platform, technology and etc. • Deploy general purpose interface like Web services
SOA • • De-composite into general purpose component Business Function=Component=Service Loose coupled Find-Bind composite service • Service( system) development free from ( independent of ) IT infrastructure, platform, technology and etc. • Deploy general purpose interface like Web services
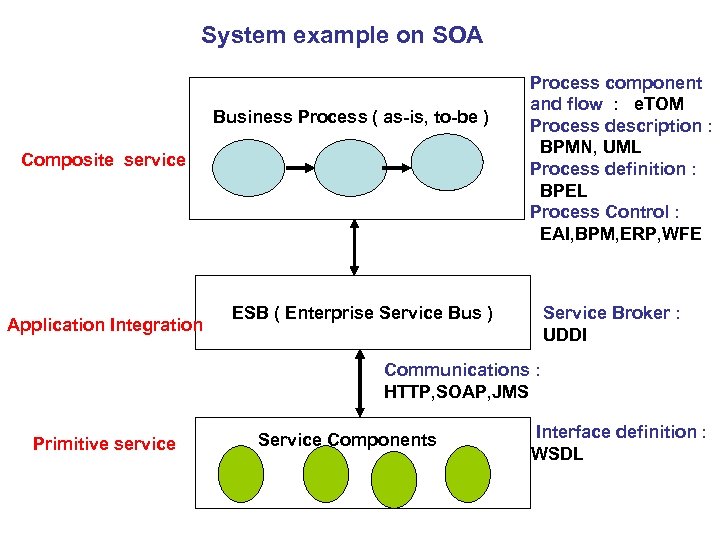 System example on SOA Business Process ( as-is, to-be ) Composite service Application Integration Process component and flow : e. TOM Process description : BPMN, UML Process definition : BPEL Process Control : EAI, BPM, ERP, WFE ESB ( Enterprise Service Bus ) Service Broker : UDDI Communications : HTTP, SOAP, JMS Primitive service Service Components Interface definition : WSDL
System example on SOA Business Process ( as-is, to-be ) Composite service Application Integration Process component and flow : e. TOM Process description : BPMN, UML Process definition : BPEL Process Control : EAI, BPM, ERP, WFE ESB ( Enterprise Service Bus ) Service Broker : UDDI Communications : HTTP, SOAP, JMS Primitive service Service Components Interface definition : WSDL
 BPML : Business Process Model Notation Developed by BPMI( Business Process Management Initiative) , maintained by OMG ( Open Management Group) Basic 4 elements • Flow Objects : Events, Activities, Gateways • • • Connecting Objects : Sequence Flow, Message Flow, Association Swim lane : Pool, Lane Artifacts ; Data Objects, Group, Annotation
BPML : Business Process Model Notation Developed by BPMI( Business Process Management Initiative) , maintained by OMG ( Open Management Group) Basic 4 elements • Flow Objects : Events, Activities, Gateways • • • Connecting Objects : Sequence Flow, Message Flow, Association Swim lane : Pool, Lane Artifacts ; Data Objects, Group, Annotation
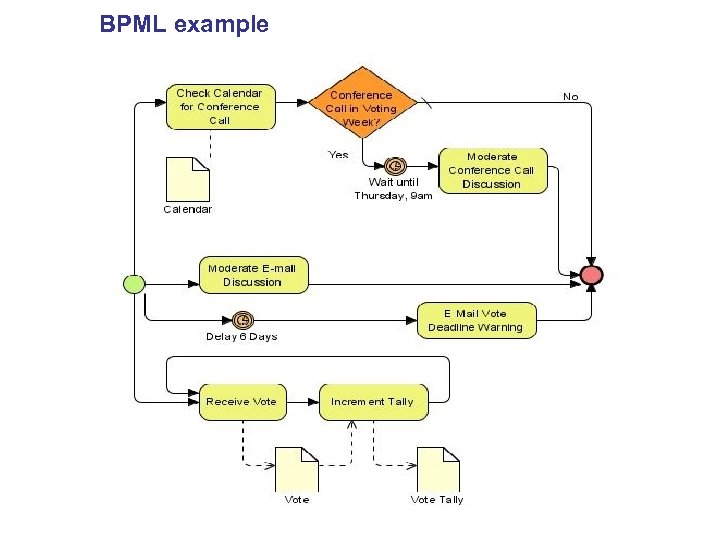 BPML example
BPML example
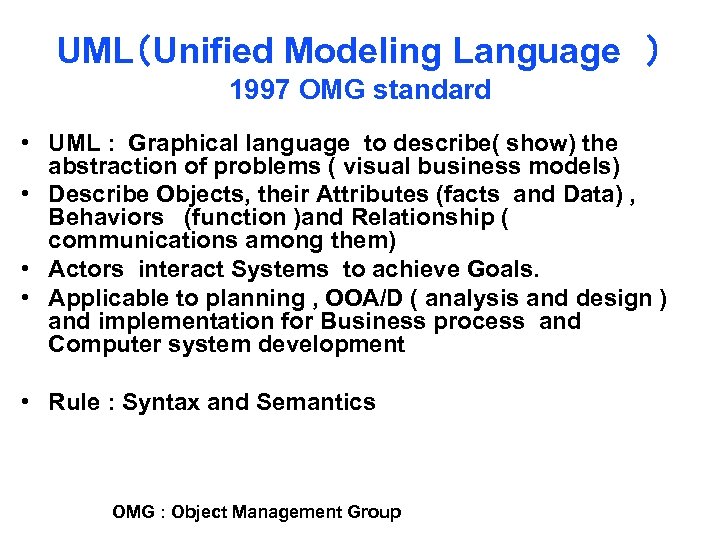 UML(Unified Modeling Language ) 1997 OMG standard • UML : Graphical language to describe( show) the abstraction of problems ( visual business models) • Describe Objects, their Attributes (facts and Data) , Behaviors (function )and Relationship ( communications among them) • Actors interact Systems to achieve Goals. • Applicable to planning , OOA/D ( analysis and design ) and implementation for Business process and Computer system development • Rule : Syntax and Semantics OMG : Object Management Group
UML(Unified Modeling Language ) 1997 OMG standard • UML : Graphical language to describe( show) the abstraction of problems ( visual business models) • Describe Objects, their Attributes (facts and Data) , Behaviors (function )and Relationship ( communications among them) • Actors interact Systems to achieve Goals. • Applicable to planning , OOA/D ( analysis and design ) and implementation for Business process and Computer system development • Rule : Syntax and Semantics OMG : Object Management Group
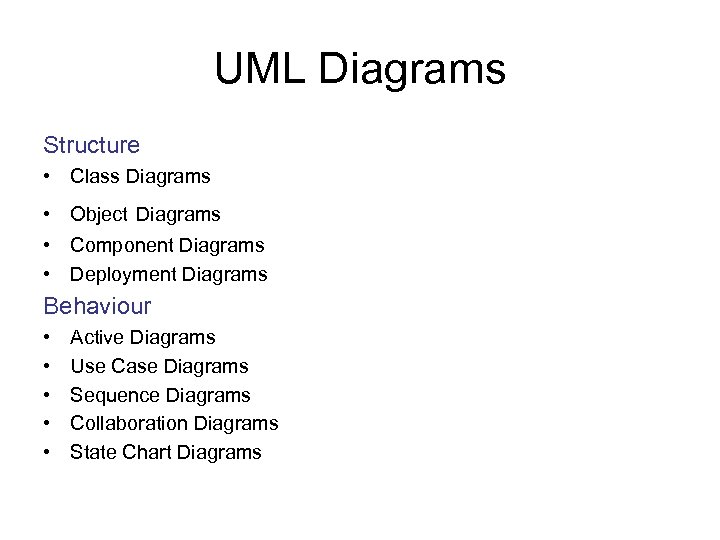 UML Diagrams Structure • Class Diagrams • Object Diagrams • Component Diagrams • Deployment Diagrams Behaviour • • • Active Diagrams Use Case Diagrams Sequence Diagrams Collaboration Diagrams State Chart Diagrams
UML Diagrams Structure • Class Diagrams • Object Diagrams • Component Diagrams • Deployment Diagrams Behaviour • • • Active Diagrams Use Case Diagrams Sequence Diagrams Collaboration Diagrams State Chart Diagrams
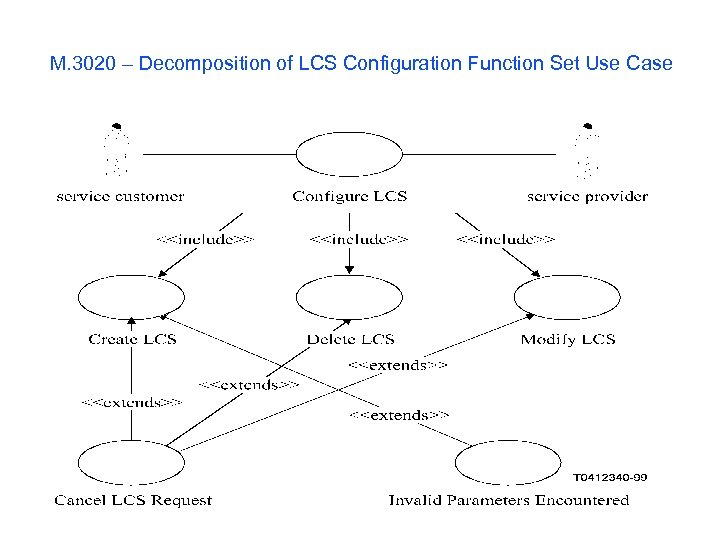 M. 3020 – Decomposition of LCS Configuration Function Set Use Case
M. 3020 – Decomposition of LCS Configuration Function Set Use Case
 WS-BPEL : Web Service Business Process Execution Language • Developed by OASIS( Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards) • XML-based language for executable and abstract business processes. • Web service orchestration by interacting partner web services /process • Automated process integration by defining an interoperable integration model Cf. Web Service Choreography : XML based business process modeling language specified by W 3 C
WS-BPEL : Web Service Business Process Execution Language • Developed by OASIS( Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards) • XML-based language for executable and abstract business processes. • Web service orchestration by interacting partner web services /process • Automated process integration by defining an interoperable integration model Cf. Web Service Choreography : XML based business process modeling language specified by W 3 C
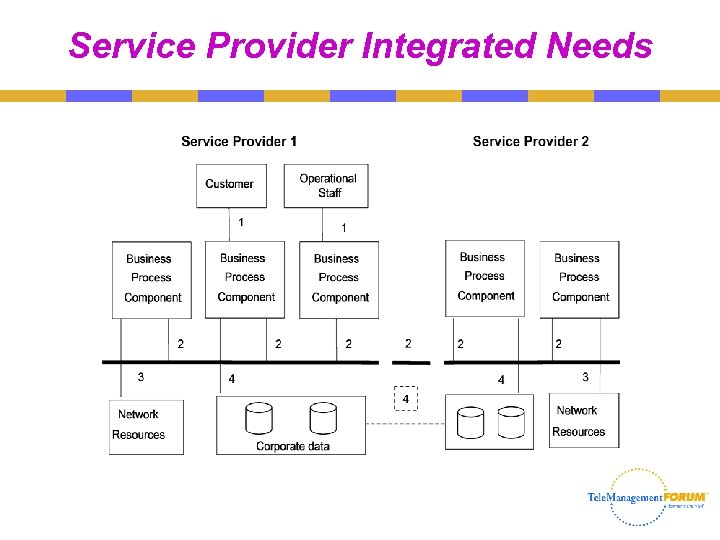 Service Provider Integrated Needs
Service Provider Integrated Needs
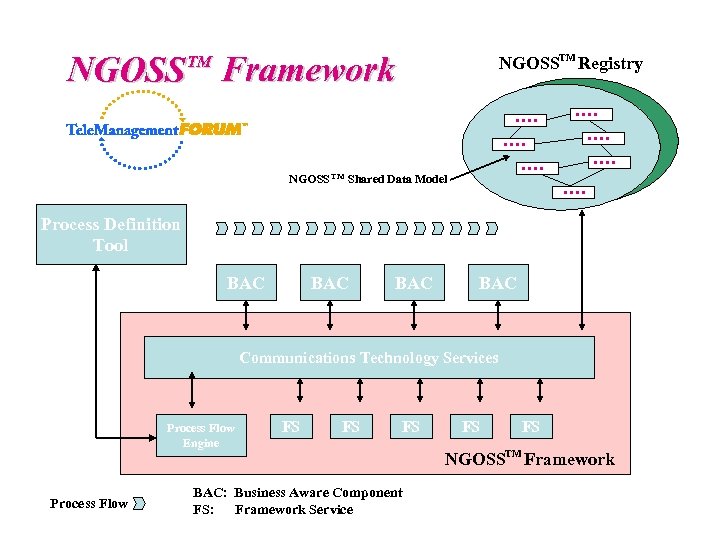 NGOSS Framework NGOSSTM Registry TM NGOSS TM Shared Data Model Process Definition Tool BAC BAC Communications Technology Services Process Flow Engine Process Flow FS FS FS BAC: Business Aware Component FS: Framework Service FS FS NGOSSTM Framework
NGOSS Framework NGOSSTM Registry TM NGOSS TM Shared Data Model Process Definition Tool BAC BAC Communications Technology Services Process Flow Engine Process Flow FS FS FS BAC: Business Aware Component FS: Framework Service FS FS NGOSSTM Framework
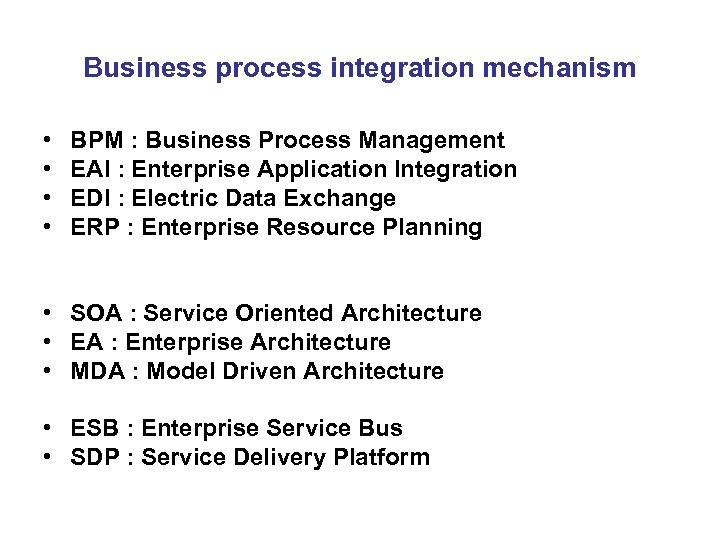 Business process integration mechanism • • BPM : Business Process Management EAI : Enterprise Application Integration EDI : Electric Data Exchange ERP : Enterprise Resource Planning • SOA : Service Oriented Architecture • EA : Enterprise Architecture • MDA : Model Driven Architecture • ESB : Enterprise Service Bus • SDP : Service Delivery Platform
Business process integration mechanism • • BPM : Business Process Management EAI : Enterprise Application Integration EDI : Electric Data Exchange ERP : Enterprise Resource Planning • SOA : Service Oriented Architecture • EA : Enterprise Architecture • MDA : Model Driven Architecture • ESB : Enterprise Service Bus • SDP : Service Delivery Platform
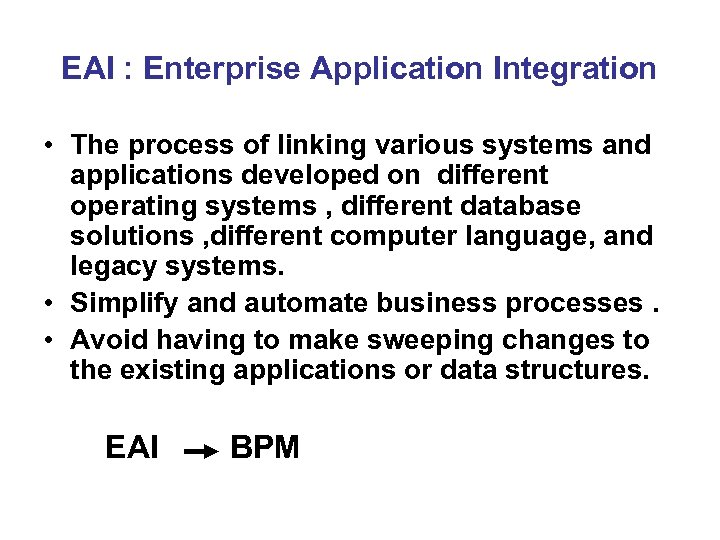 EAI : Enterprise Application Integration • The process of linking various systems and applications developed on different operating systems , different database solutions , different computer language, and legacy systems. • Simplify and automate business processes. • Avoid having to make sweeping changes to the existing applications or data structures. EAI BPM
EAI : Enterprise Application Integration • The process of linking various systems and applications developed on different operating systems , different database solutions , different computer language, and legacy systems. • Simplify and automate business processes. • Avoid having to make sweeping changes to the existing applications or data structures. EAI BPM
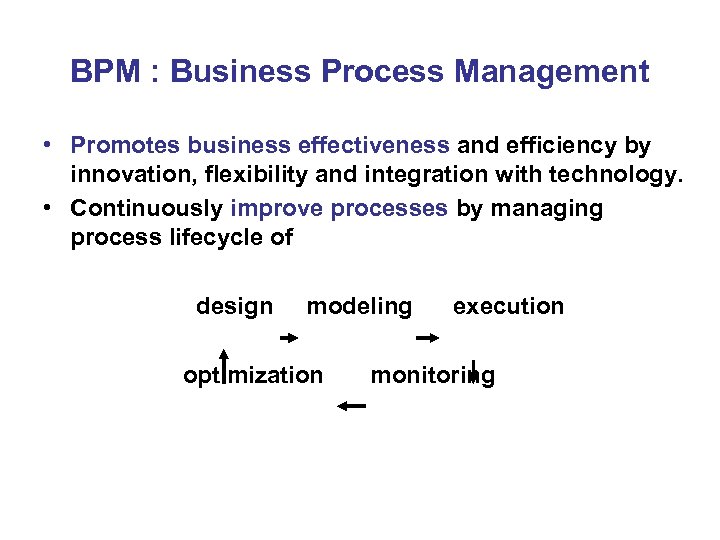 BPM : Business Process Management • Promotes business effectiveness and efficiency by innovation, flexibility and integration with technology. • Continuously improve processes by managing process lifecycle of design modeling optimization execution monitoring
BPM : Business Process Management • Promotes business effectiveness and efficiency by innovation, flexibility and integration with technology. • Continuously improve processes by managing process lifecycle of design modeling optimization execution monitoring
 ERP : Enterprise Resource Planning • Integrates into a unified system based on common database and modular software design. • A common database allows to store and retrieve information in real-time resulting information to be more reliable, accessible, and easily shared. • A modular software design improves the business by adding functionality, mixing and matching programs from different vendors ERP Package on SOA
ERP : Enterprise Resource Planning • Integrates into a unified system based on common database and modular software design. • A common database allows to store and retrieve information in real-time resulting information to be more reliable, accessible, and easily shared. • A modular software design improves the business by adding functionality, mixing and matching programs from different vendors ERP Package on SOA
 UDDI: Universal Description Discovery and Integration • An open industry initiative, sponsored by OASIS. • Platform independent XML based registry Publish service listings and discover each other Define how the services or software applications interact over the internet. • Three components: White page — address, contact, and known identifiers. Yellow Page — industrial categorizations. Green Pages— technical information about services
UDDI: Universal Description Discovery and Integration • An open industry initiative, sponsored by OASIS. • Platform independent XML based registry Publish service listings and discover each other Define how the services or software applications interact over the internet. • Three components: White page — address, contact, and known identifiers. Yellow Page — industrial categorizations. Green Pages— technical information about services
 ASP & Saa. S • • Buy Software function , not license Web browsing : easy to use Function integration : SOA, Ad on soft Price down of high speed communications ( BB) Multi tenant ( share server , DB etc) Customize : parameterized AP Secure outsourcing Utility Pricing
ASP & Saa. S • • Buy Software function , not license Web browsing : easy to use Function integration : SOA, Ad on soft Price down of high speed communications ( BB) Multi tenant ( share server , DB etc) Customize : parameterized AP Secure outsourcing Utility Pricing
 Paa. S of Force. com • Application Exchange : AP Upload, download • User Interface as a Service : GUI components • Logic as a Service : WF, On demand language, Report, Dash board • Integration as a Service : SOA, ERP, Office • Database as a Service : DB built by GUI • Global, Trusted, Secure Infrastructure : User, access, log Mgt. Data back up
Paa. S of Force. com • Application Exchange : AP Upload, download • User Interface as a Service : GUI components • Logic as a Service : WF, On demand language, Report, Dash board • Integration as a Service : SOA, ERP, Office • Database as a Service : DB built by GUI • Global, Trusted, Secure Infrastructure : User, access, log Mgt. Data back up
 ASP & Saa. S • • Buy Software function , not license Web browsing : easy to use Function integration : SOA, Ad on soft Price down of high speed communications ( BB) Multi tenant ( share server , DB etc) Customize : parameterized AP Secure outsourcing Utility Pricing
ASP & Saa. S • • Buy Software function , not license Web browsing : easy to use Function integration : SOA, Ad on soft Price down of high speed communications ( BB) Multi tenant ( share server , DB etc) Customize : parameterized AP Secure outsourcing Utility Pricing
 Paa. S of Force. com • Application Exchange : AP Upload, download • User Interface as a Service : GUI components • Logic as a Service : WF, On demand language, Report, Dash board • Integration as a Service : SOA, ERP, Office • Database as a Service : DB built by GUI • Global, Trusted, Secure Infrastructure : User, access, log Mgt. Data back up
Paa. S of Force. com • Application Exchange : AP Upload, download • User Interface as a Service : GUI components • Logic as a Service : WF, On demand language, Report, Dash board • Integration as a Service : SOA, ERP, Office • Database as a Service : DB built by GUI • Global, Trusted, Secure Infrastructure : User, access, log Mgt. Data back up
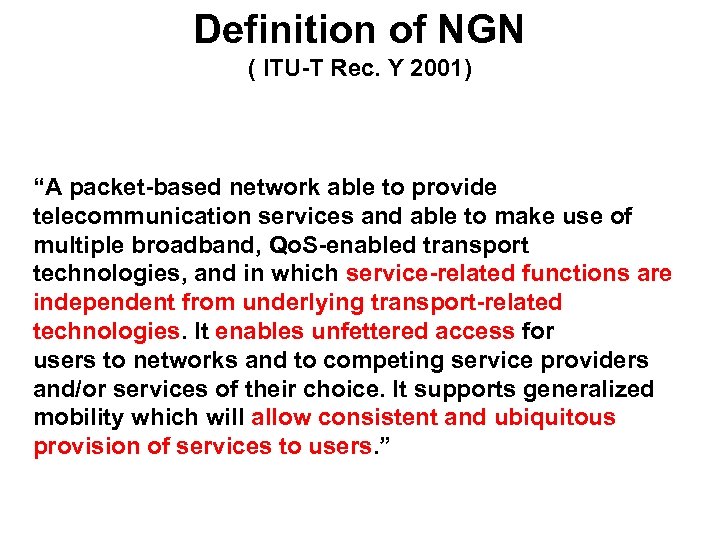 Definition of NGN ( ITU-T Rec. Y 2001) “A packet-based network able to provide telecommunication services and able to make use of multiple broadband, Qo. S-enabled transport technologies, and in which service-related functions are independent from underlying transport-related technologies. It enables unfettered access for users to networks and to competing service providers and/or services of their choice. It supports generalized mobility which will allow consistent and ubiquitous provision of services to users. ”
Definition of NGN ( ITU-T Rec. Y 2001) “A packet-based network able to provide telecommunication services and able to make use of multiple broadband, Qo. S-enabled transport technologies, and in which service-related functions are independent from underlying transport-related technologies. It enables unfettered access for users to networks and to competing service providers and/or services of their choice. It supports generalized mobility which will allow consistent and ubiquitous provision of services to users. ”
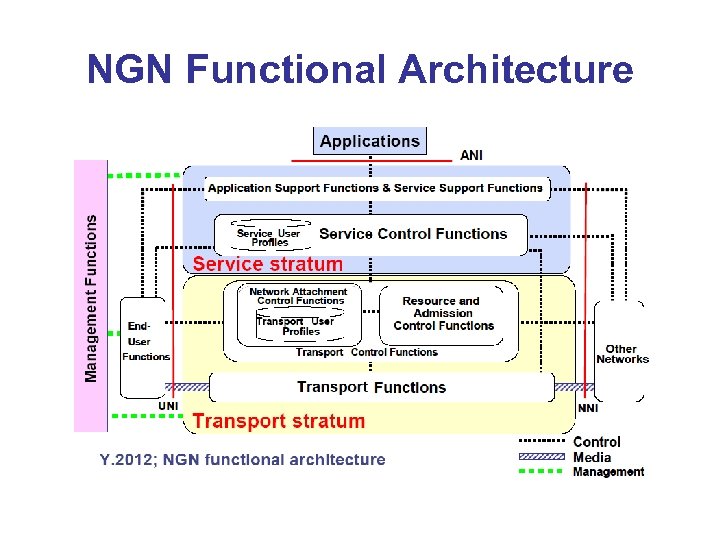 NGN Functional Architecture
NGN Functional Architecture
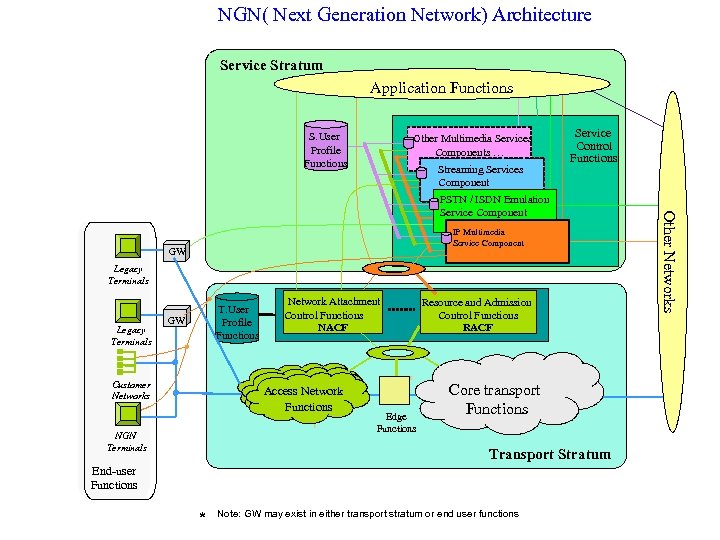 NGN( Next Generation Network) Architecture Service Stratum Application Functions S. User Profile Functions Other Multimedia Services Other Multimedia Components … Streaming Services Component Service Control and Functions Control Functions IP Multimedia Component Service Component &PSTN/ISDN Simulation GW GW Legacy Terminals T. User Profile Functions GW Customer Networks Network Attachment Network Access Control Functions Attachment Functions NACF NAAF Access Transport Network Functions NGN Terminals Edge Functions Resource and Admission Control Functions RACF Core transport Functions Transport Stratum End-user Functions * Note: GW may exist in either transport stratum or end user functions Other Networks PSTN / ISDN Emulation Service Component
NGN( Next Generation Network) Architecture Service Stratum Application Functions S. User Profile Functions Other Multimedia Services Other Multimedia Components … Streaming Services Component Service Control and Functions Control Functions IP Multimedia Component Service Component &PSTN/ISDN Simulation GW GW Legacy Terminals T. User Profile Functions GW Customer Networks Network Attachment Network Access Control Functions Attachment Functions NACF NAAF Access Transport Network Functions NGN Terminals Edge Functions Resource and Admission Control Functions RACF Core transport Functions Transport Stratum End-user Functions * Note: GW may exist in either transport stratum or end user functions Other Networks PSTN / ISDN Emulation Service Component
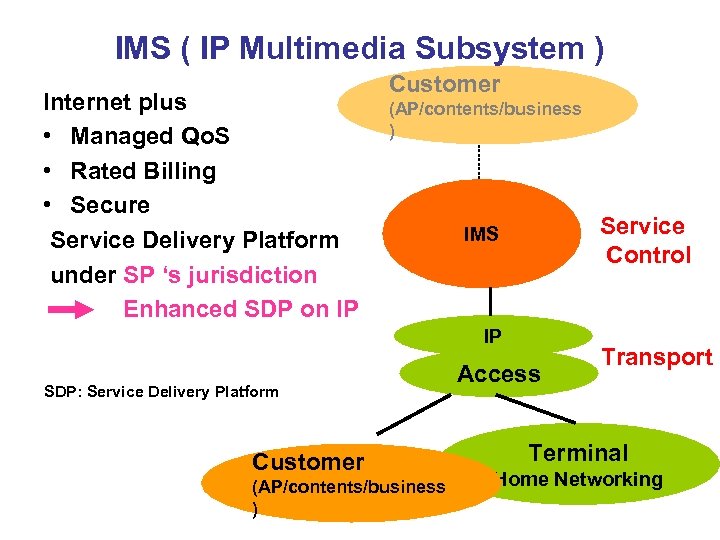 IMS ( IP Multimedia Subsystem ) Internet plus • Managed Qo. S • Rated Billing • Secure Service Delivery Platform under SP ‘s jurisdiction Enhanced SDP on IP Customer (AP/contents/business ) Service Control IMS IP SDP: Service Delivery Platform Customer (AP/contents/business ) Access Transport Terminal Home Networking
IMS ( IP Multimedia Subsystem ) Internet plus • Managed Qo. S • Rated Billing • Secure Service Delivery Platform under SP ‘s jurisdiction Enhanced SDP on IP Customer (AP/contents/business ) Service Control IMS IP SDP: Service Delivery Platform Customer (AP/contents/business ) Access Transport Terminal Home Networking
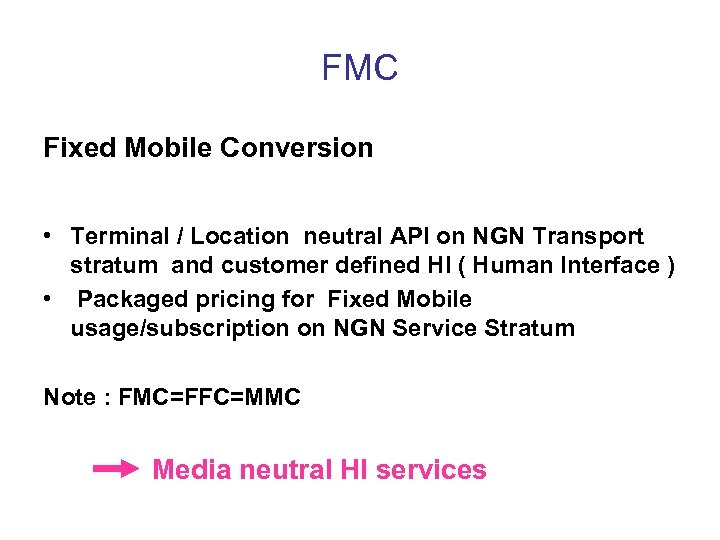 FMC Fixed Mobile Conversion • Terminal / Location neutral API on NGN Transport stratum and customer defined HI ( Human Interface ) • Packaged pricing for Fixed Mobile usage/subscription on NGN Service Stratum Note : FMC=FFC=MMC Media neutral HI services
FMC Fixed Mobile Conversion • Terminal / Location neutral API on NGN Transport stratum and customer defined HI ( Human Interface ) • Packaged pricing for Fixed Mobile usage/subscription on NGN Service Stratum Note : FMC=FFC=MMC Media neutral HI services
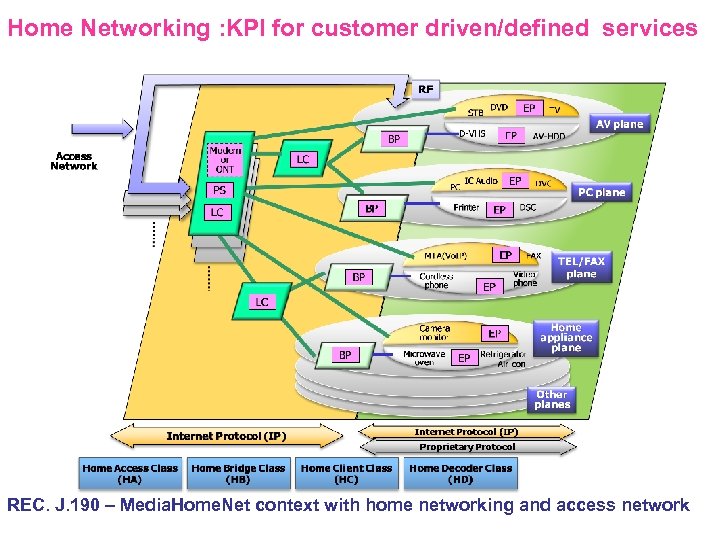 Home Networking : KPI for customer driven/defined services REC. J. 190 – Media. Home. Net context with home networking and access network
Home Networking : KPI for customer driven/defined services REC. J. 190 – Media. Home. Net context with home networking and access network
 NGN Services and Management • • Contents aware services Context aware services Customer aware services HI aware services Location aware services Media aware services Service aware services Customer( User, Provider, AP , Contents, Business ) driven /defined Services • • • Self adaptation Self control Self management Self organization Self operations Customer ( User, Provider, AP , Contents, Business ) driven /defined Management
NGN Services and Management • • Contents aware services Context aware services Customer aware services HI aware services Location aware services Media aware services Service aware services Customer( User, Provider, AP , Contents, Business ) driven /defined Services • • • Self adaptation Self control Self management Self organization Self operations Customer ( User, Provider, AP , Contents, Business ) driven /defined Management
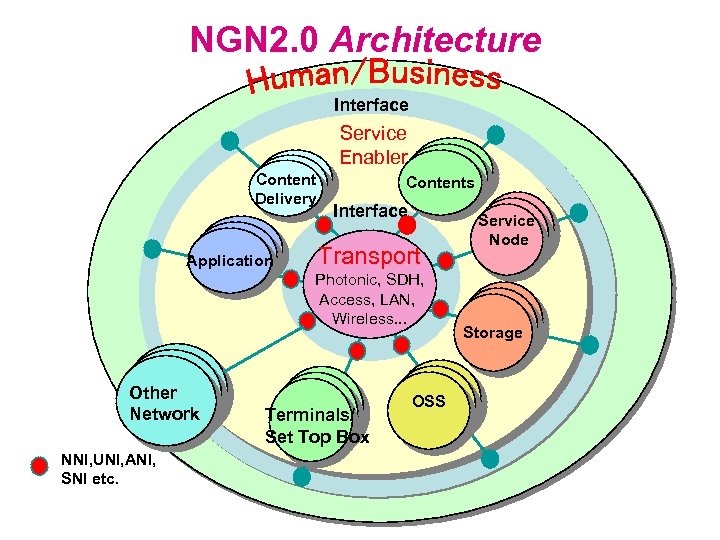 NGN 2. 0 Architecture Interface Clients Content WSs Delivery Clients WSs Application WSs Other Network Service Enabler IN IN nodes Contents nodes Interface Transport Photonic, SDH, Access, LAN, Wireless. . . Set Top Terminals/ Boxes Set Top Box NNI, UNI, ANI, SNI etc. Service SWs Node Servers Storage OSS OSS Elements
NGN 2. 0 Architecture Interface Clients Content WSs Delivery Clients WSs Application WSs Other Network Service Enabler IN IN nodes Contents nodes Interface Transport Photonic, SDH, Access, LAN, Wireless. . . Set Top Terminals/ Boxes Set Top Box NNI, UNI, ANI, SNI etc. Service SWs Node Servers Storage OSS OSS Elements
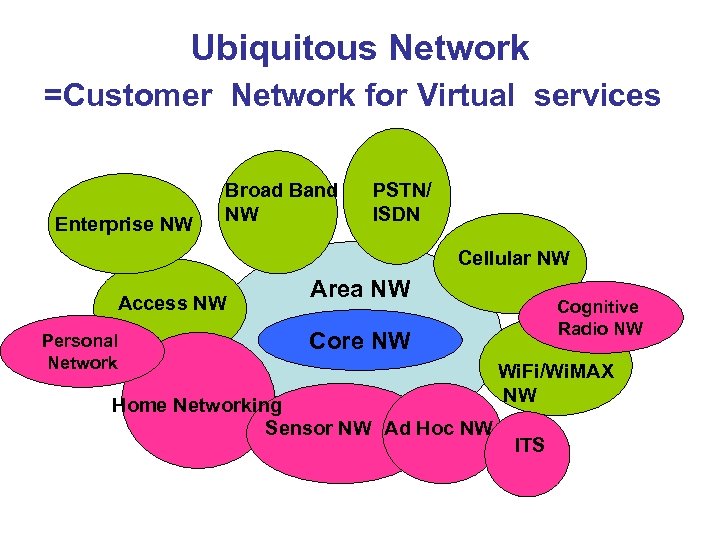 Ubiquitous Network =Customer Network for Virtual services Enterprise NW Broad Band NW PSTN/ ISDN Cellular NW Access NW Personal Network Area NW Cognitive Radio NW Core NW Home Networking Sensor NW Ad Hoc NW Wi. Fi/Wi. MAX NW ITS
Ubiquitous Network =Customer Network for Virtual services Enterprise NW Broad Band NW PSTN/ ISDN Cellular NW Access NW Personal Network Area NW Cognitive Radio NW Core NW Home Networking Sensor NW Ad Hoc NW Wi. Fi/Wi. MAX NW ITS
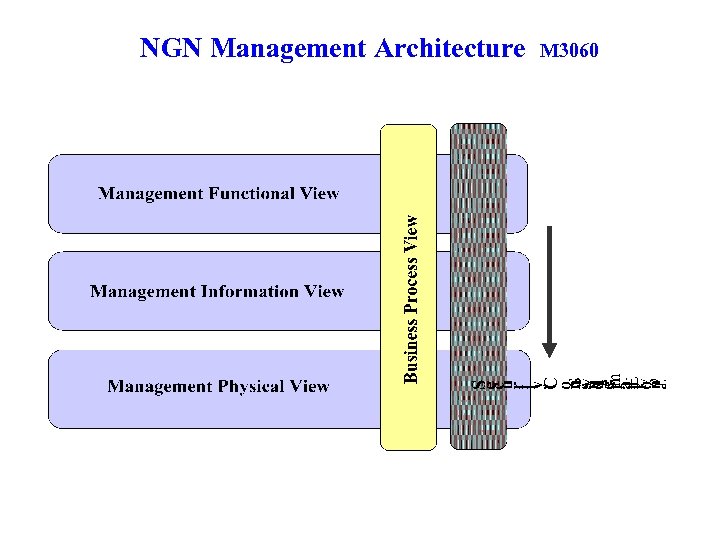 NGN Management Architecture M 3060
NGN Management Architecture M 3060
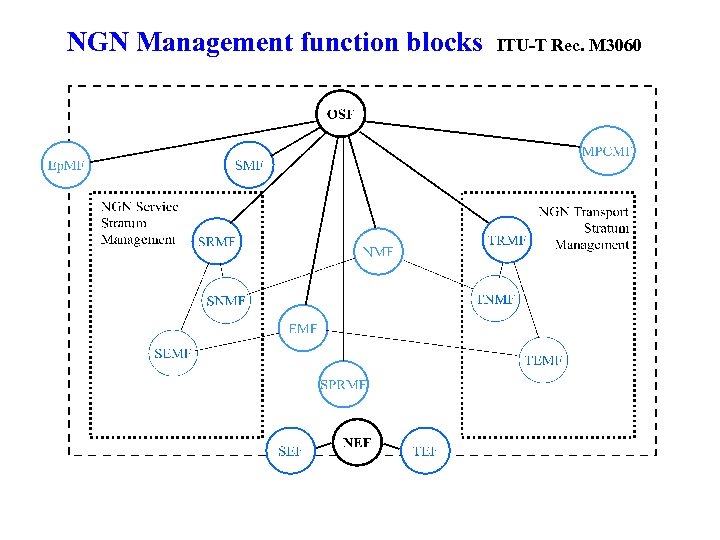 NGN Management function blocks ITU-T Rec. M 3060
NGN Management function blocks ITU-T Rec. M 3060
 M 3060 • Abbreviation
M 3060 • Abbreviation


