5ba9bdb35263278a0b251d4e52af24e6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95

POSTEC Lecture Network Management Chapter 5 IP/e. Business Management May 29 -June 5, 2008 Masayoshi Ejiri Japan 1

Agenda 1. ICT Operations and Management - Service Industries - ICT Services and Networks— - Target of the Management 2, Architecture , Function , Information Model and Business Process - ITU-T TMN( Telecommunications Management Network) - Tele. Management Forum Telecommunications Operations Map ( TOM) - Multi domain management and System Integration - Standardization 3. OSS( Operations Support System ) Development - Software Architecture , Key Technologies and Product Evaluation— 4. SLA( Service Level Agreement) and Qo. S( Quality of Service) - SLA Definition , reference point and policy based negotiation 5, IP/e. Business Management - Paradigm shift , Architecture beyond TMN and enhanced TOM 6. NGN( Next Generation Networks) Management - NGN Networks and Services , New Paradigm of ICT Business and Management 2

Agenda • Paradigm shift • IP/e. Business management beyond TMN • e. TOM : enhanced Telecom Operation Map Process components Process flow Process and function ( Rec. M 3400) ITIL ( IT Infrastructure Library ) 3
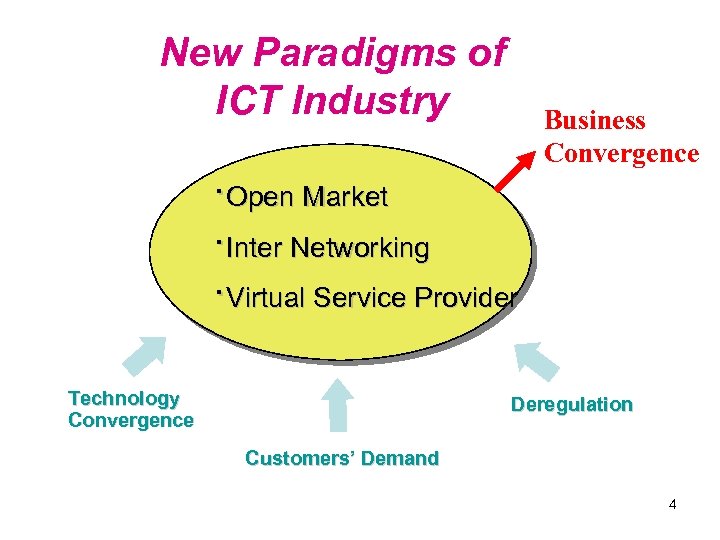
New Paradigms of ICT Industry ·Open Market ·Inter Networking ·Virtual Service Provider Technology Convergence Business Convergence Deregulation Customers’ Demand 4

ICT Market Trend • Past(~1985): Monopoly, Regulated Market. PSTN based telephone services by mega carriers to Reactive customers • Current(~2005 ): Competitive , Deregulated Market. Dominant PSTN plus Explosive Mobile and Internet based telephone +Date services by new/old service providers to personalized but still Reactive customers • Future(2010~) Converged Market by removing industry boundary and customer/provider scheme. NGN based ubiquitous triple/quadruple services by provider/customer collaboration to Proactive end users 5

ICT Management Target Past : • Bottom up approach for robust and interoperable resource management • TMN Architecture and FCAPS Current • Top down approach for Customer retention and profit conscious resource management. • Process evolution for customer self operations • N 3 B(Not Built Buy) OSS by COTS and Pn. P Future • Customer driven services and operation using Web 2. 0 • Context, Contents and SLA aware management 6

1, Monopoly, Regulated Market ( 1890’s -1980’s) Services • POTS on PSTN • by mega carriers (ROC: Recognized Operating Company) • SP( Service Provider) centric SP’s Targets • Establish nation wide ubiquitous telephone network by automated SW network • On Demand subscription. Operations and OSS • NEsupervise and Control by on site maintenance, then Centralized NE maintenance • Random , Individual and Proprietary OSS Development • Human and paper based CC&B (Customer Care and Billing) POTS : Plane Old Telephone Service PSTN : Public Switched Telephone Network NE : Network Element 7

2, Competitive, Deregulated Market ( 1985~) Services: • • • Telephone on PSTN and Mobile by competition among conventional carriers and new comers To reactive customers but Price Down Pressure ( Price Competition ) SP’s Target : • • • CAPEX/OPEX cost down for price down Up Graded CC&B for customer retention Competitive but Interoperable Operations among SPs Operations and OSS • • Operations Mission and Positioning Customer Oriented Top Down approach Systematic and Standardized OSS development on TMN Vertical process integration ( FAB) 8

ITU-T TMN Recommendations • • • TMN Functional Architecture LLA : Logical Layered Architecture TMN Information Architecture TMN Physical Architecture TMN Management Area TMN Management Services 9
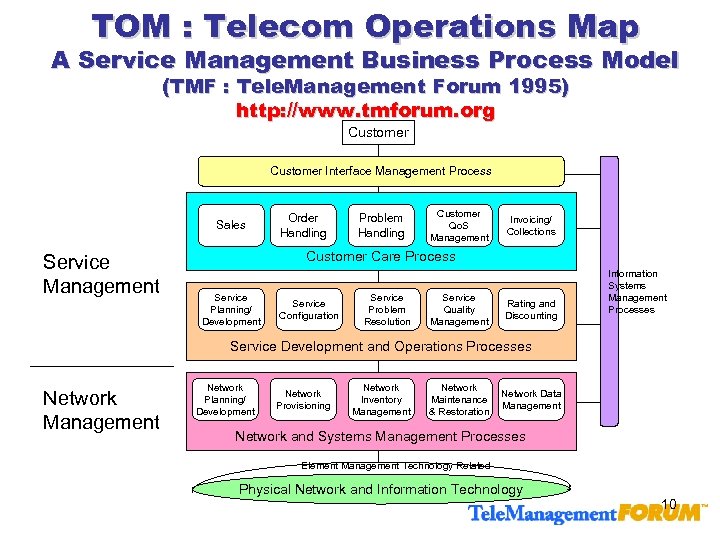
TOM : Telecom Operations Map A Service Management Business Process Model (TMF : Tele. Management Forum 1995) http: //www. tmforum. org Customer Interface Management Process Sales Service Management Order Handling Problem Handling Customer Qo. S Management Invoicing/ Collections Customer Care Process Service Planning/ Development Service Configuration Service Problem Resolution Service Quality Management Rating and Discounting Information Systems Management Processes Service Development and Operations Processes Network Management Network Planning/ Development Network Provisioning Network Inventory Management Network Maintenance & Restoration Network Data Management Network and Systems Management Processes Element Management Technology Related Physical Network and Information Technology 10
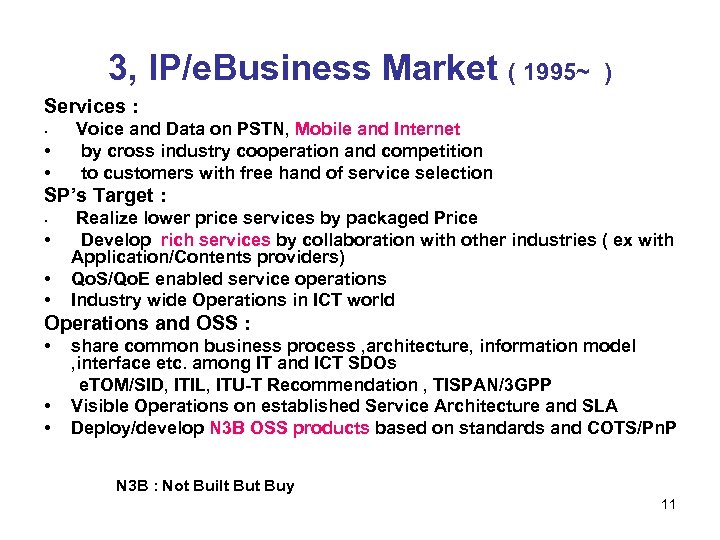
3, IP/e. Business Market ( 1995~ ) Services : • • • Voice and Data on PSTN, Mobile and Internet by cross industry cooperation and competition to customers with free hand of service selection SP’s Target : • • Realize lower price services by packaged Price Develop rich services by collaboration with other industries ( ex with Application/Contents providers) Qo. S/Qo. E enabled service operations Industry wide Operations in ICT world Operations and OSS : • • • share common business process , architecture, information model , interface etc. among IT and ICT SDOs e. TOM/SID, ITIL, ITU-T Recommendation , TISPAN/3 GPP Visible Operations on established Service Architecture and SLA Deploy/develop N 3 B OSS products based on standards and COTS/Pn. P N 3 B : Not Built Buy 11
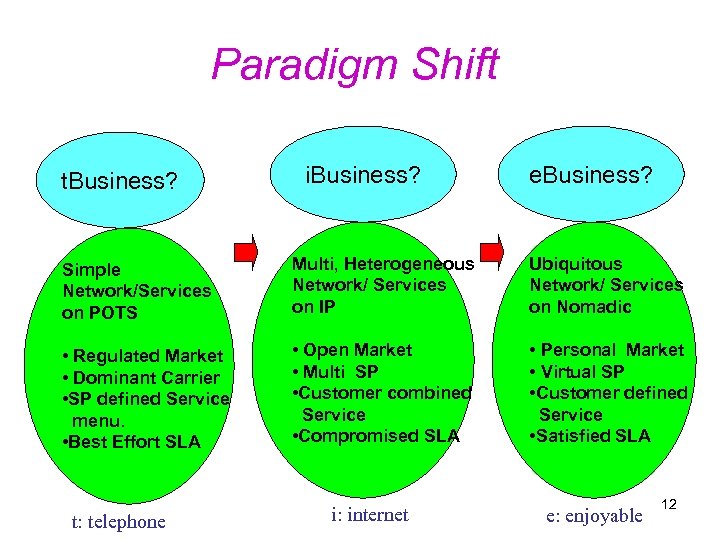
Paradigm Shift t. Business? i. Business? e. Business? Simple Network/Services on POTS Multi, Heterogeneous Network/ Services on IP Ubiquitous Network/ Services on Nomadic • Regulated Market • Dominant Carrier • SP defined Service menu. • Best Effort SLA • Open Market • Multi SP • Customer combined Service • Compromised SLA • Personal Market • Virtual SP • Customer defined Service • Satisfied SLA t: telephone i: internet e: enjoyable 12

IP Services --for Speed, Simple and Smile e. Business-Customers’ Demand Providers’ Solution • Speedy / Easy Subscription On Line, Real Time Provisioning • Non Stop Services Reliable & Scalable Networks / Systems • Quick Response High Throughput Mechanism • Secure Services Security Level Agreement • Price Performance Negotiation 13
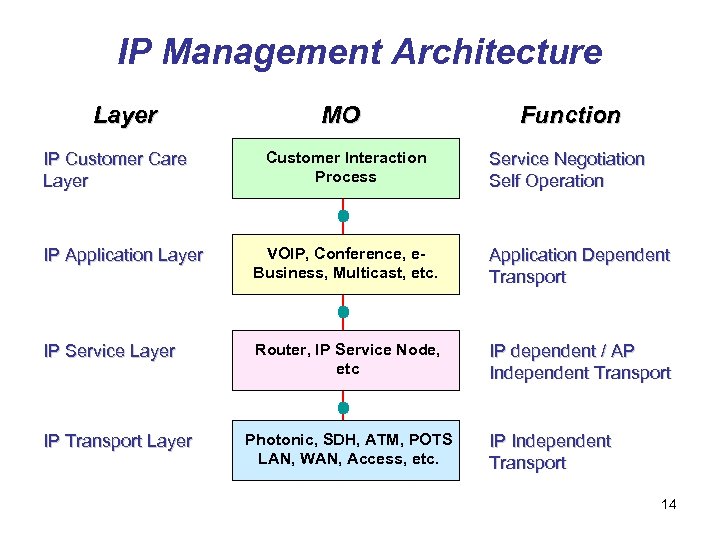
IP Management Architecture Layer IP Customer Care Layer MO Customer Interaction Process Function Service Negotiation Self Operation IP Application Layer VOIP, Conference, e. Business, Multicast, etc. Application Dependent Transport IP Service Layer Router, IP Service Node, etc IP dependent / AP Independent Transport IP Transport Layer Photonic, SDH, ATM, POTS LAN, WAN, Access, etc. IP Independent Transport 14
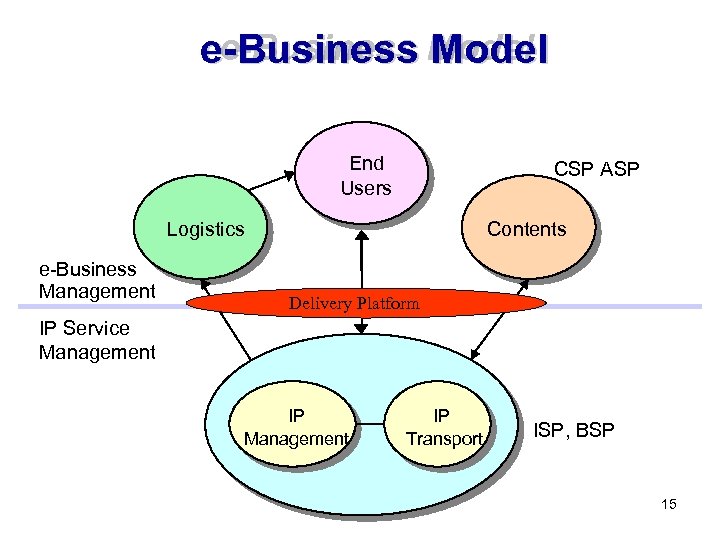
e-Business Model End Users CSP ASP Logistics e-Business Management Contents Delivery Platform IP Service Management IP Transport ISP, BSP 15
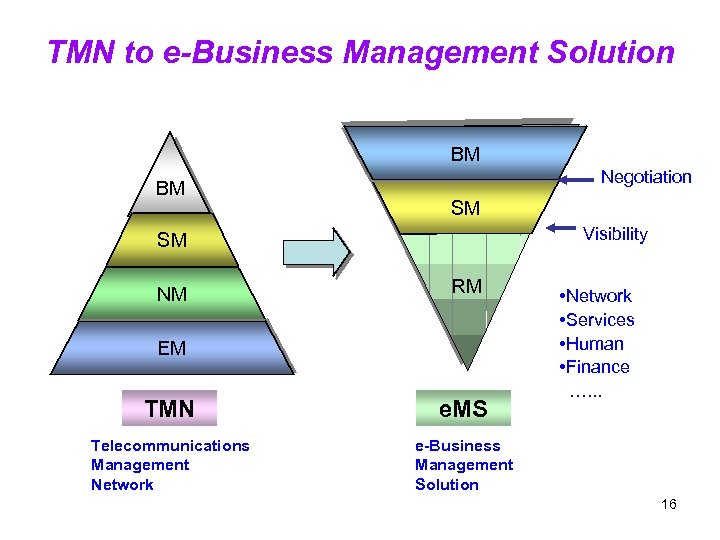
TMN to e-Business Management Solution BM Negotiation NM BM SM Visibility SM NM RM EM TMN e. MS Telecommunications Management Network • Network • Services • Human • Finance …. . . e-Business Management Solution 16

Lessons Learnt from Logistic Industry • Basic Service : ex. Collection of goods from location A and deliver to location B - Transport services • Associated services : Convenience Store acts as a mediator for collection. Deliveries be arranged in agreed time and traceable. - Operations Services • Value added Services : Perishable goods ( fish, fruit) be transported using a cold storage , delicate good be transported using hanging - Contents Aware Delivery Services 17
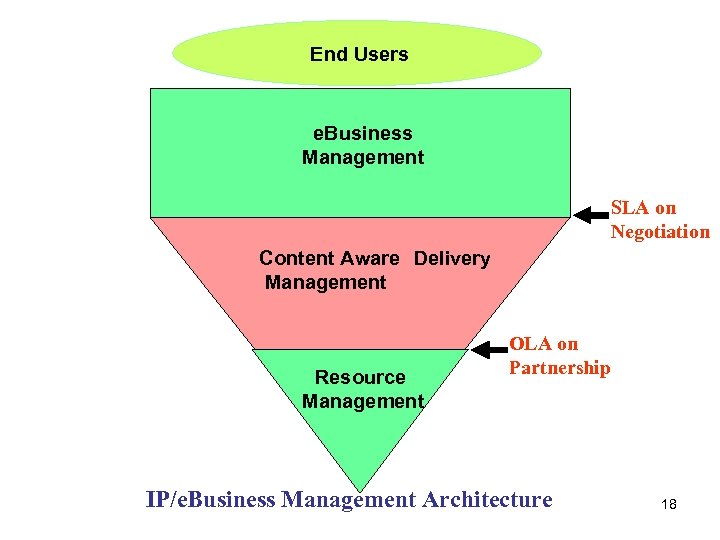
End Users e. Business Management SLA on Negotiation Content Aware Delivery Management Resource Management OLA on Partnership IP/e. Business Management Architecture 18
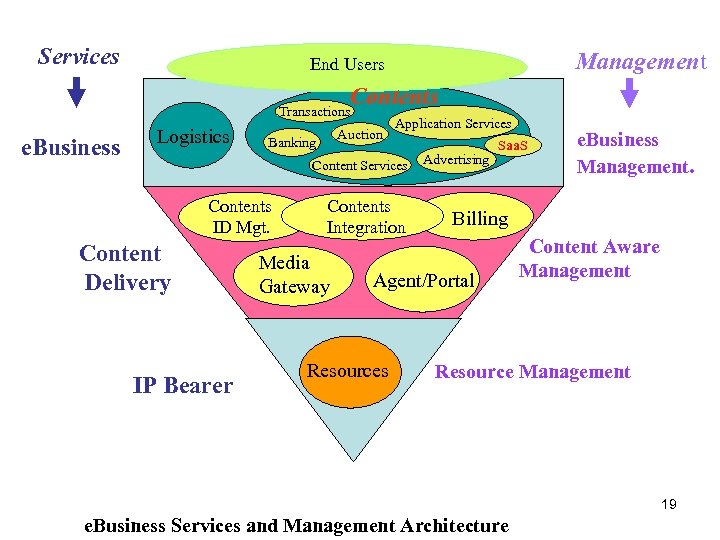
Services Management End Users Contents Transactions e. Business Logistics Auction Banking Application Services Contents ID Mgt. Content Delivery IP Bearer Contents Integration Media Gateway Advertising Saa. S Billing Agent/Portal Resources e. Business Management. Content Aware Management Resource Management 19 e. Business Services and Management Architecture
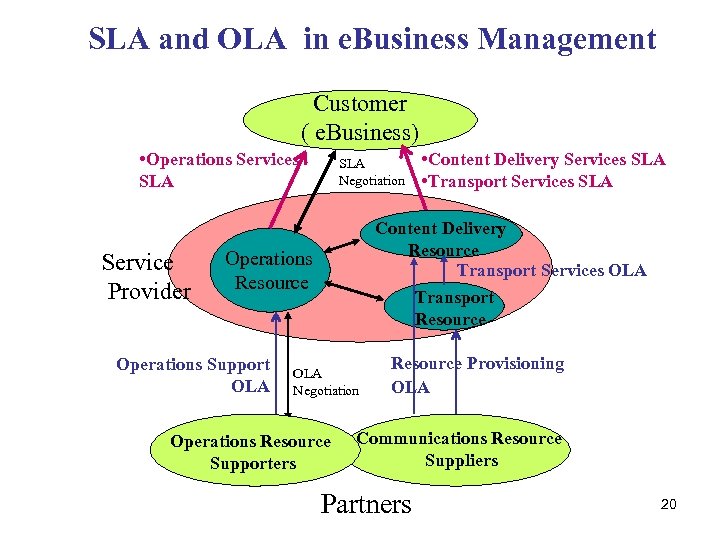
SLA and OLA in e. Business Management Customer ( e. Business) • Operations Services SLA Service Provider SLA Negotiation Content Delivery Resource Transport Services OLA Transport Resource Operations Support OLA • Content Delivery Services SLA • Transport Services SLA OLA Negotiation Operations Resource Supporters Resource Provisioning OLA Communications Resource Suppliers Partners 20

Key Words for IP/e. Business management • Partnership : Common BP & Interface • • • TMN to e. MS(e. Business Management Solutions) Adaptive & Customer Driven Business Process Consensus among Industries and Customers • Negotiation & SLA • • • : Differentiation Policy Based Negotiation Management Customer Self Operations Qo. S oriented Secure & Customer perceptible SLA 21

IP/e. Business Management Why ? Support e. Business by Competitive Service Creation in New Paradigm What ? Negotiation for Customer Defined Services and SLA How ? Policy Based Management and COTS/ Pn. P OSS 22

Business Process -TOM to e. TOM- • • e. Business Oriented TOM Open , Visible Process for Customer retention Common Business process for Partnership Enterprise Management for Total Solution 23

Business Process in TMN • The business process approach has built on the concepts of management services and functions in order to develop a reference framework for categorizing all the business activities that a service provider will use. 24

Related TMN Rec. • ITU-T Recommendation M. 3010 Principles for a telecommunications management network. • ITU-T Recommendation M. 3020 TMN interface specification methodology. • ITU-T Recommendation M. 3200 TMN management services and telecommunications managed areas: overview. • ITU-T Recommendation M. 3400 TMN management functions. 25

ITU-T Rec. M 3050 series • • • M 3050. 0 : e. TOM-Introduction M 3050. 1 : e. TOM-The business process framework M 3050. 2 : e. TOM-Process decomposition and descriptions M 3050. 3 : e. TOM-Representative procces flows M 3050. 4 : B 2 B integration: Using B 2 B inter-enterprise integration with the e. TOM M 3050 Supplement 1: e. TOM-An Interim View of and Interpreter’s Guide for e. TOM and ITIL Practicioners M 3050 Supplement 2: e. TOM-Public B 2 B Business Operations Map( BOM) M 3050 Supplement 3: e. TOM to M 3400 mapping M 3050 Supplement 4: An e. TOM Primer 26
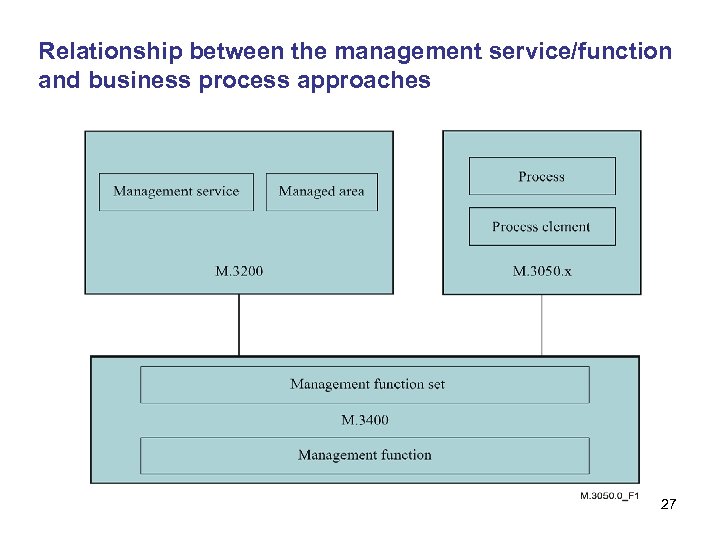
Relationship between the management service/function and business process approaches 27
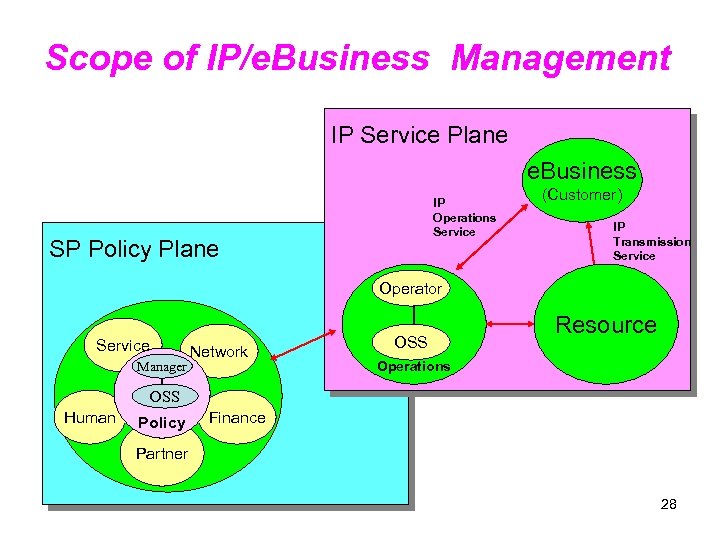
Scope of IP/e. Business Management IP Service Plane e. Business IP Operations Service SP Policy Plane (Customer) IP Transmission Service Operator Service Manager Network OSS Resource Operations OSS Human Policy Finance Partner 28
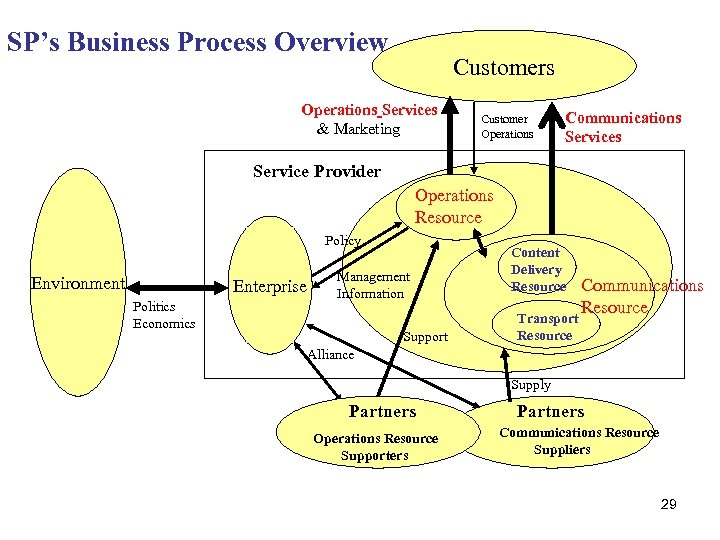
SP’s Business Process Overview Customers Operations Services & Marketing Customer Operations Communications Service Provider Operations Resource Policy Environment Enterprise Politics Economics Management Information Support Content Delivery Resource Transport Resource Communications Resource Alliance Supply Partners Operations Resource Supporters Partners Communications Resource Suppliers 29
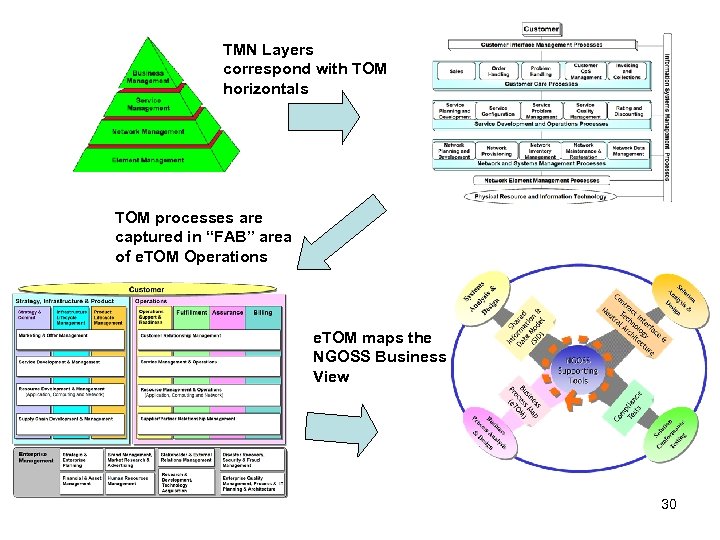
TMN Layers correspond with TOM horizontals TOM processes are captured in “FAB” area of e. TOM Operations e. TOM maps the NGOSS Business View 30
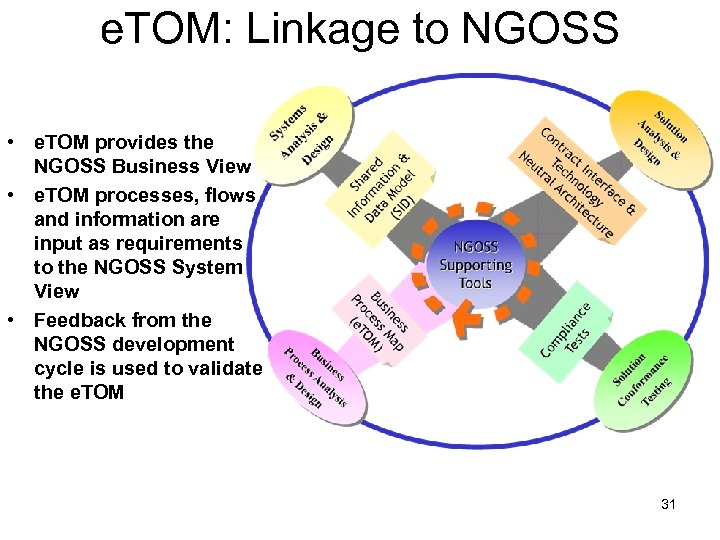
e. TOM: Linkage to NGOSS • e. TOM provides the NGOSS Business View • e. TOM processes, flows and information are input as requirements to the NGOSS System View • Feedback from the NGOSS development cycle is used to validate the e. TOM 31
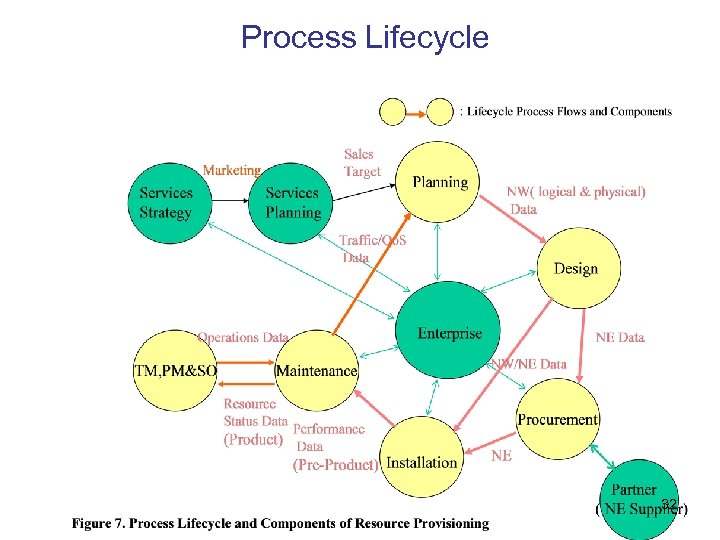
Process Lifecycle 32
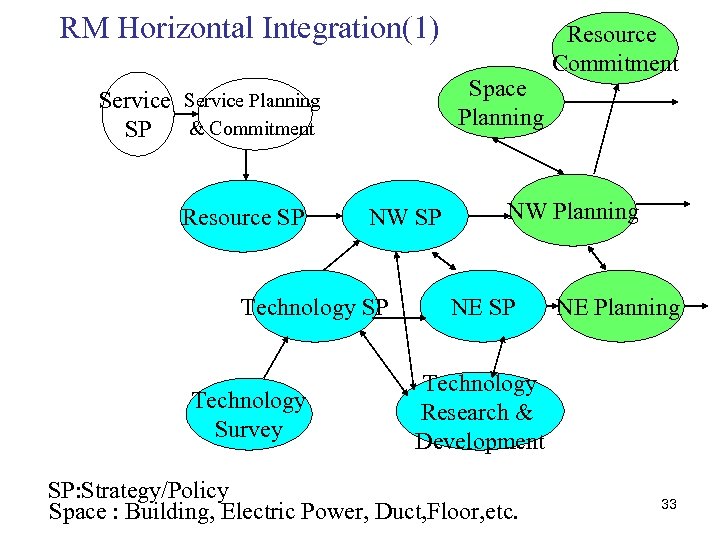
RM Horizontal Integration(1) Space Planning Service Planning & Commitment SP Resource SP NW SP Technology Survey Resource Commitment NW Planning NE SP NE Planning Technology Research & Development SP: Strategy/Policy Space : Building, Electric Power, Duct, Floor, etc. 33
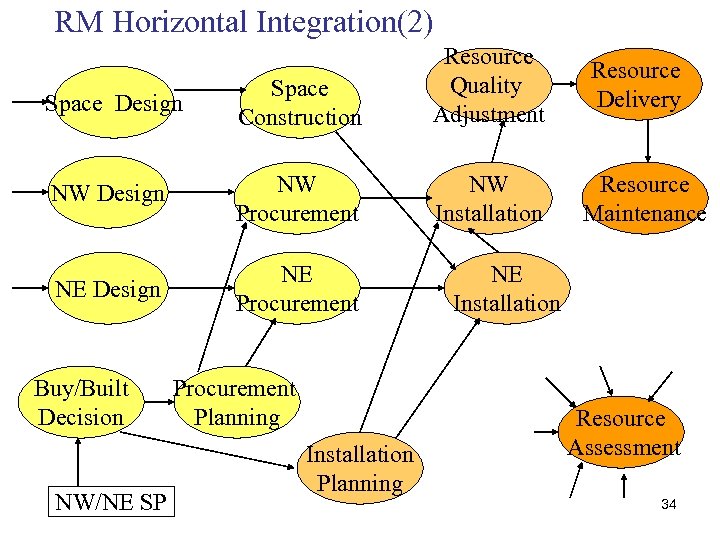
RM Horizontal Integration(2) Space Design Space Construction Resource Quality Adjustment NW Design NW Procurement NW Installation NE Design NE Procurement Buy/Built Decision NW/NE SP Procurement Planning Installation Planning Resource Delivery Resource Maintenance NE Installation Resource Assessment 34
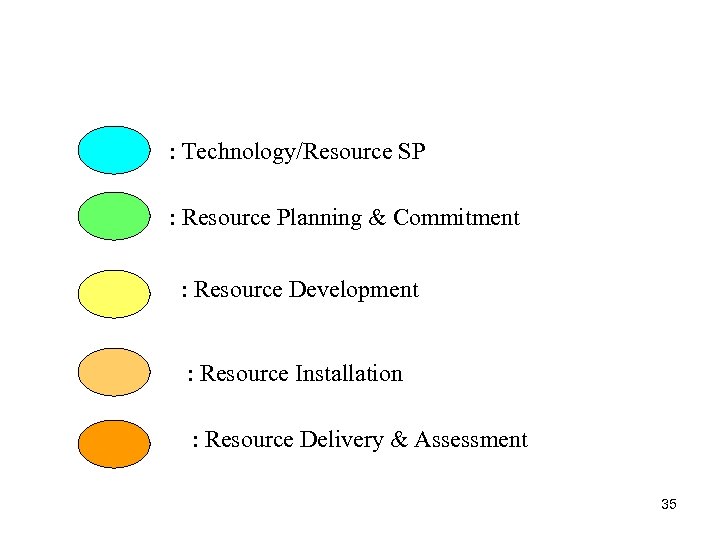
: Technology/Resource SP : Resource Planning & Commitment : Resource Development : Resource Installation : Resource Delivery & Assessment 35
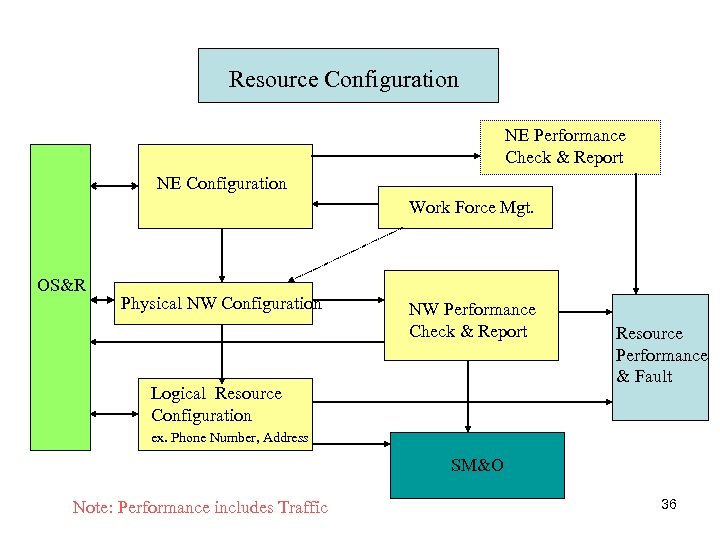
Resource Configuration NE Performance Check & Report NE Configuration Work Force Mgt. OS&R Physical NW Configuration NW Performance Check & Report Logical Resource Configuration Resource Performance & Fault ex. Phone Number, Address SM&O Note: Performance includes Traffic 36
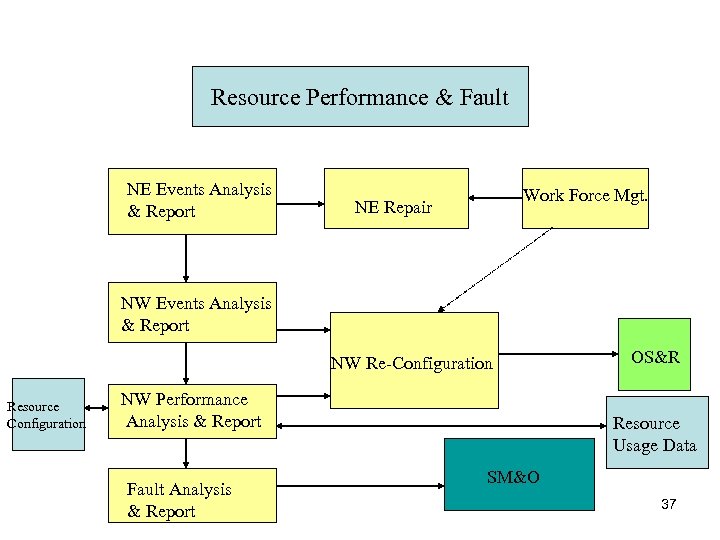
Resource Performance & Fault NE Events Analysis & Report Work Force Mgt. NE Repair NW Events Analysis & Report NW Re-Configuration Resource Configuration NW Performance Analysis & Report Fault Analysis & Report OS&R Resource Usage Data SM&O 37
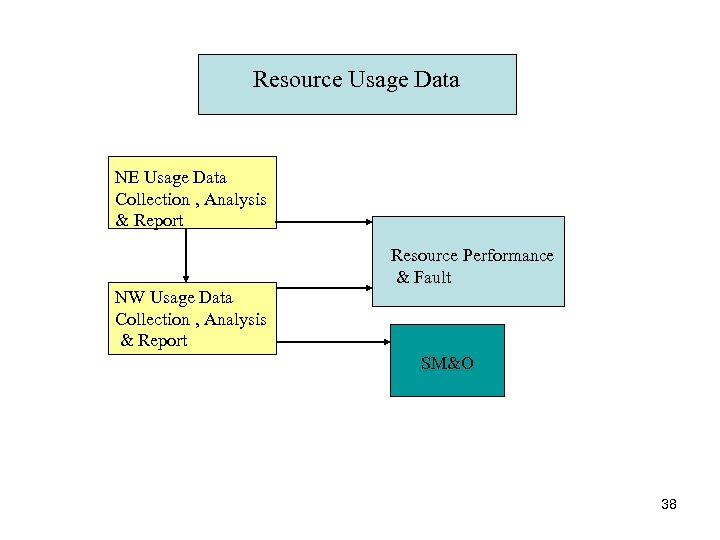
Resource Usage Data NE Usage Data Collection , Analysis & Report Resource Performance & Fault NW Usage Data Collection , Analysis & Report SM&O 38
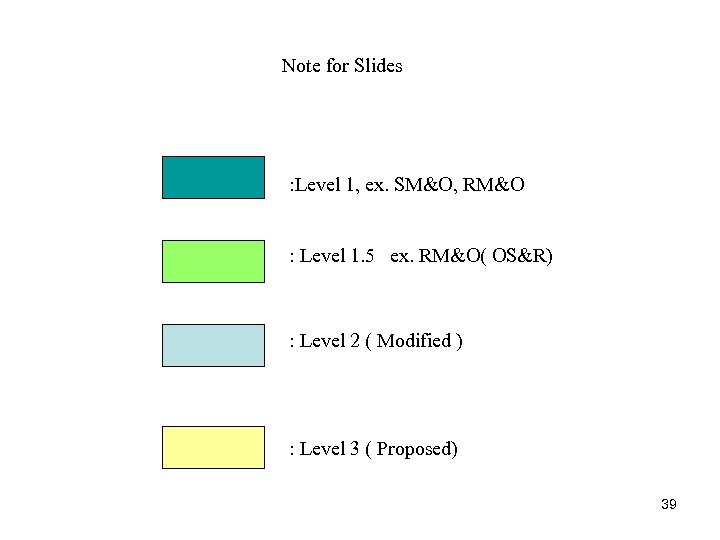
Note for Slides : Level 1, ex. SM&O, RM&O : Level 1. 5 ex. RM&O( OS&R) : Level 2 ( Modified ) : Level 3 ( Proposed) 39
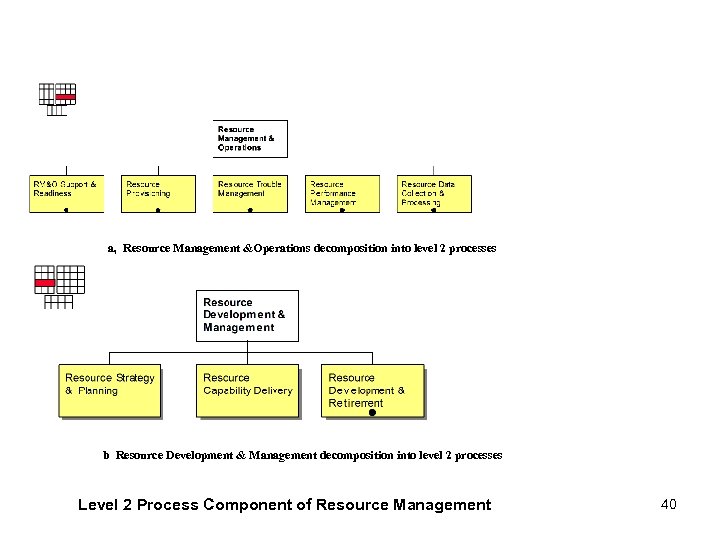
a, Resource Management &Operations decomposition into level 2 processes b Resource Development & Management decomposition into level 2 processes Level 2 Process Component of Resource Management 40
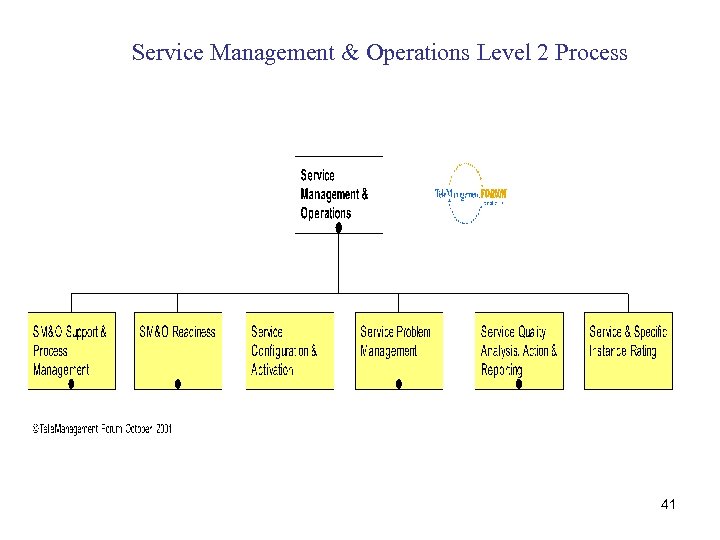
Service Management & Operations Level 2 Process 41
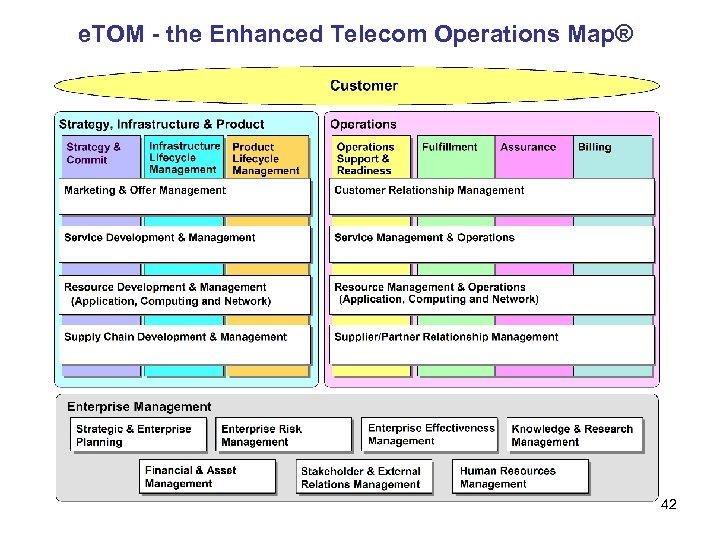
e. TOM - the Enhanced Telecom Operations Map® 42
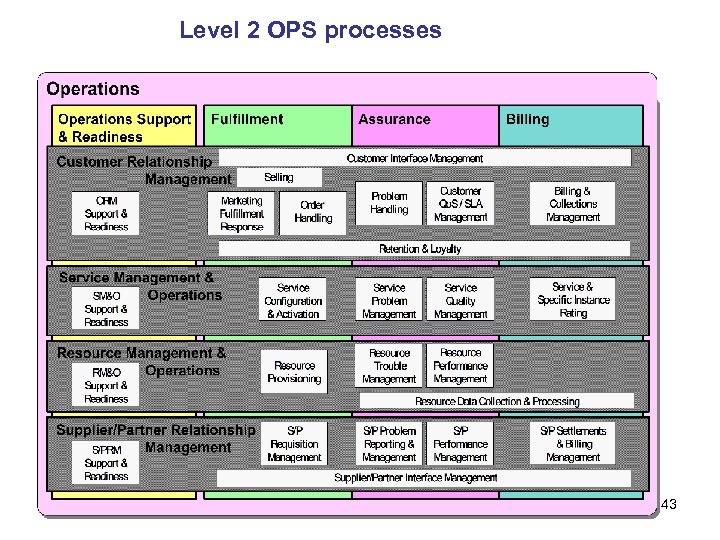
Level 2 OPS processes 43

Level 2 SIP Processes 44
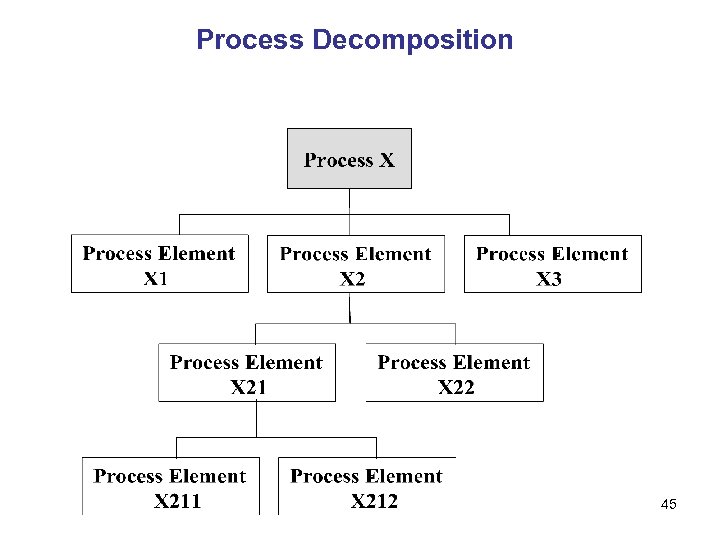
Process Decomposition 45

Process Decomposition • Concept and Overview : Level 0: • Common Process Oriented Components ( Entities) Process Groups ( V/H) for common understanding: Level 1 Components for Common Process: Level 2 • Software Reuse Oriented Components common in Level 1 and specific in Level 2: Level 3 Components common in Level 2 and specific in Level 3: Level 4 Atomic Components ? 46
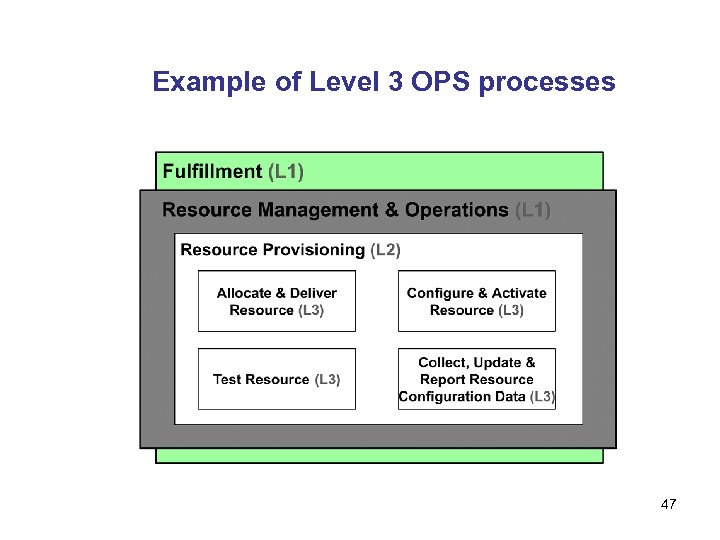
Example of Level 3 OPS processes 47
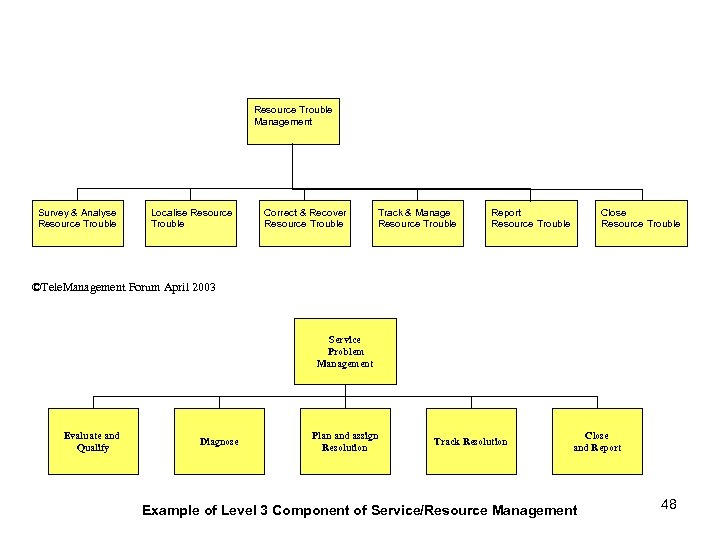
Resource Trouble Management Survey & Analyse Resource Trouble Localise Resource Trouble Correct & Recover Resource Trouble Track & Manage Resource Trouble Close Resource Trouble Report Resource Trouble ©Tele. Management Forum April 2003 Service Problem Management Evaluate and Qualify Diagnose Plan and assign Resolution Track Resolution Close and Report Example of Level 3 Component of Service/Resource Management 48
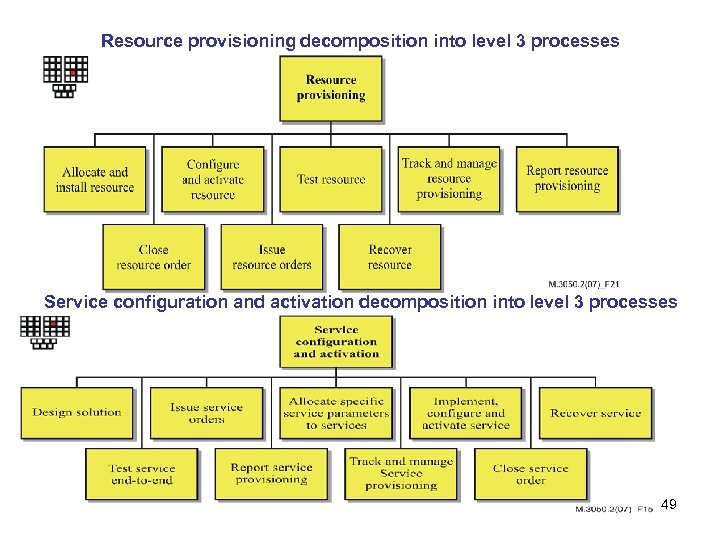
Resource provisioning decomposition into level 3 processes Service configuration and activation decomposition into level 3 processes 49
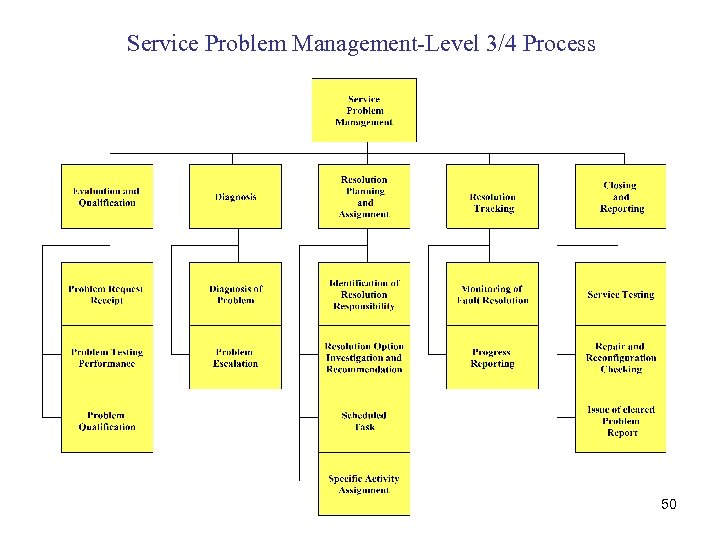
Service Problem Management-Level 3/4 Process 50
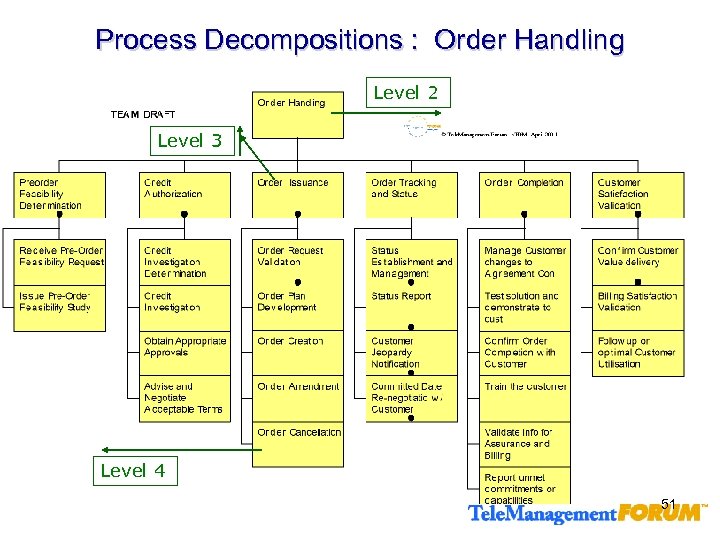
Process Decompositions : Order Handling Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 51
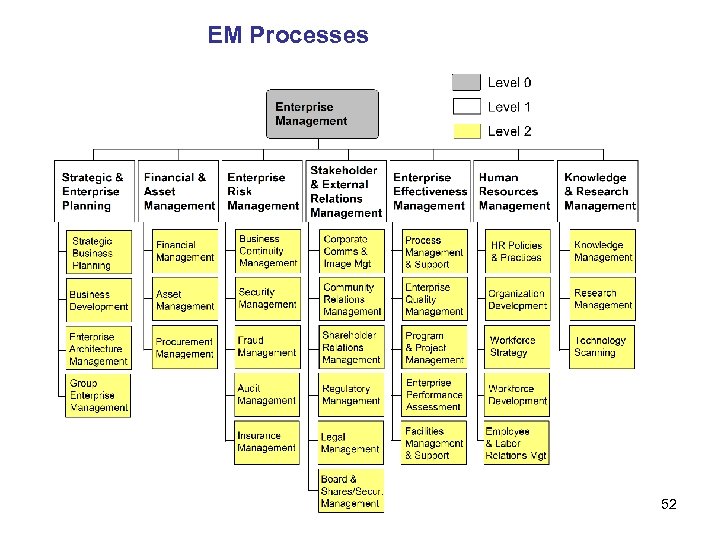
EM Processes 52
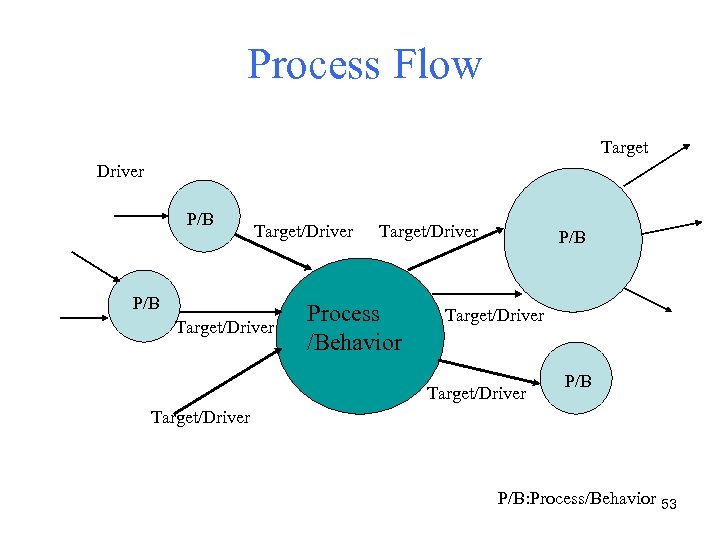
Process Flow Target Driver P/B Target/Driver Process /Behavior P/B Target/Driver P/B: Process/Behavior 53
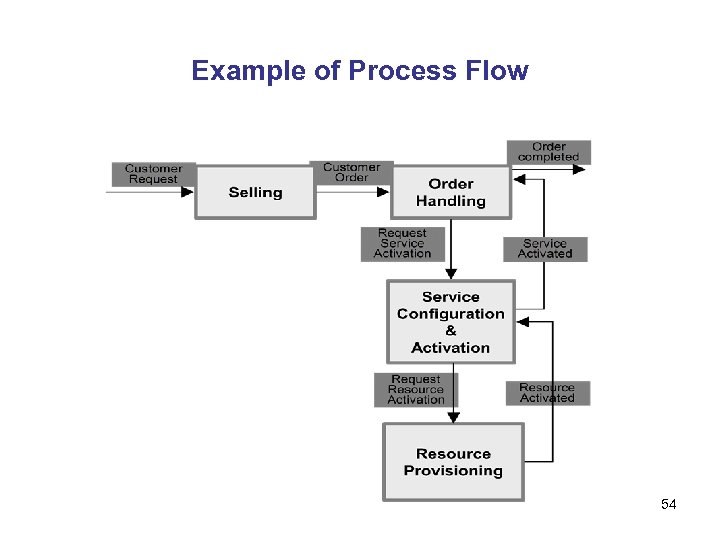
Example of Process Flow 54
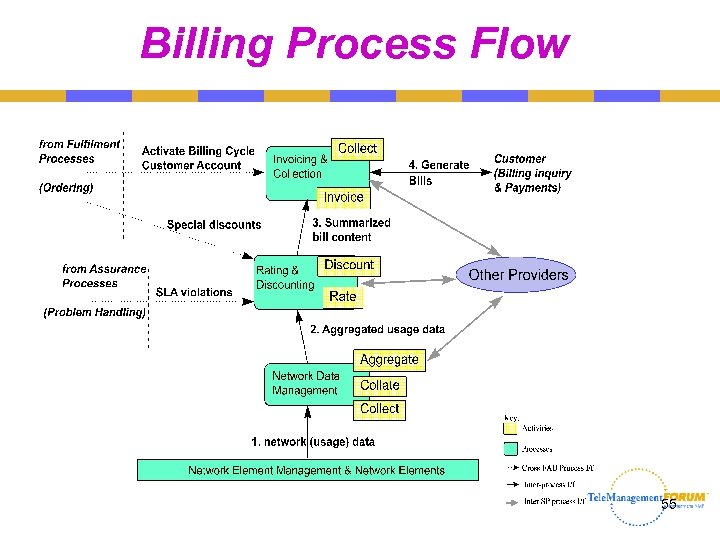
Billing Process Flow 55

Order Handling Process Flow at Level 3 56
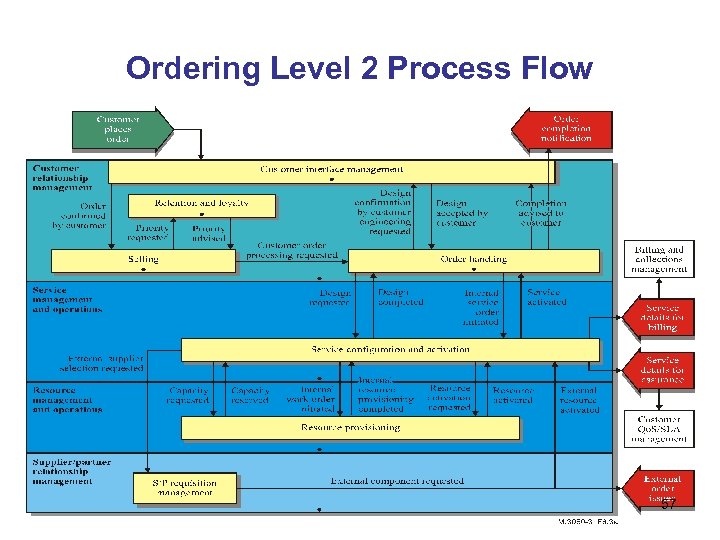
Ordering Level 2 Process Flow 57

Why use e. TOM? • e. TOM makes available a standard structure, terminology and classification scheme for describing business processes and their constituent building blocks • e. TOM supplies a foundation for applying enterprise-wide discipline to the development of business processes • e. TOM provides a basis for understanding and managing portfolios of IT applications in terms of business process requirements • e. TOM enables creation of consistent and high-quality end-to-end process flows, with opportunities for cost and performance improvement, and for re-use of existing processes and systems • e. TOM use across the industry will increase the likelihood that off-the -shelf applications will be readily integrated into the enterprise, at a lower cost than custom-built applications 58

Recent Reports on e. TOM Adoptions (SPs) 59

Recent Reports on e. TOM Adoptions (Vendors, SIs, etc) Reorganized existing BPM and Best Practices around e. TOM, with strategic decision to increase participation in e. TOM team work. Introduced internal e. TOM training, with e. TOM as a common language and reference throughout the company. Mapped Amdocs products to e. TOM, and used as sales tool. Used e. TOM to map existing industry processes, analyze business drivers and pains, and guide the design of new processes. Also, as a framework for ISV & SI Partnerships Have developed Telecom Reference Business Model based on e. TOM (Levels 1, 2 & 3), and extended to Levels 5 & 6 for business scenario investigation, legacy system gap analysis, new OSS/BSS specification, consultancy support, etc Used e. TOM for internal product training, product features cross - referencing nd functional gap analysis, marketing analysis (competitors/partners), customer communication (incl. RFI/RFP), workflow “seed” processes Used e. TOM for mapping Motorola products and managed services, for gap analysis of solution portfolio and for partnership communications 60
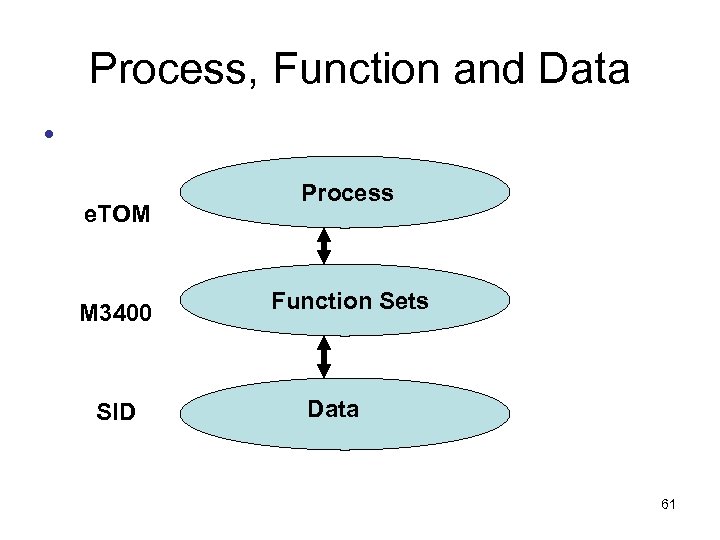
Process, Function and Data • e. TOM M 3400 SID Process Function Sets Data 61
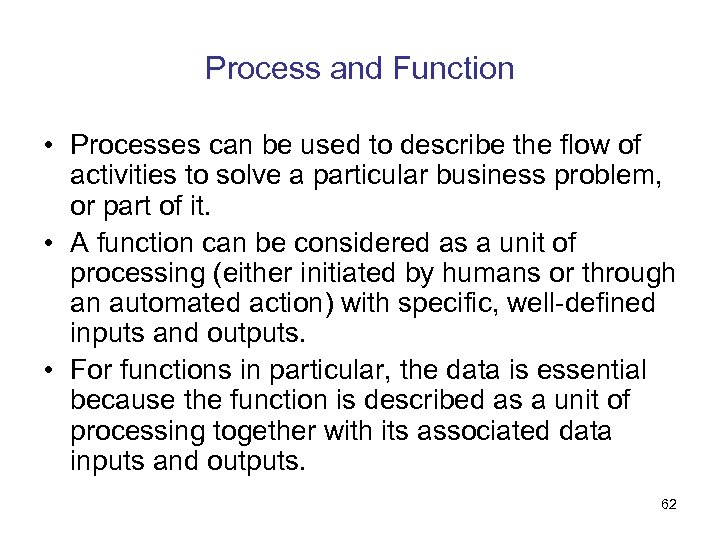
Process and Function • Processes can be used to describe the flow of activities to solve a particular business problem, or part of it. • A function can be considered as a unit of processing (either initiated by humans or through an automated action) with specific, well-defined inputs and outputs. • For functions in particular, the data is essential because the function is described as a unit of processing together with its associated data inputs and outputs. 62
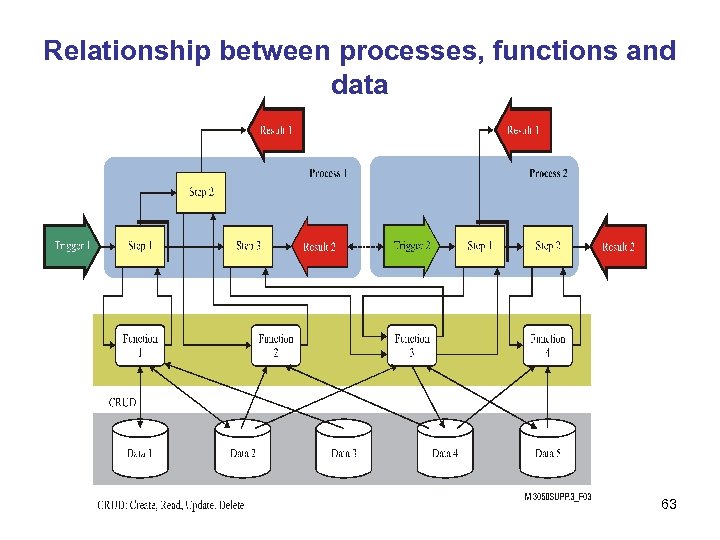
Relationship between processes, functions and data 63
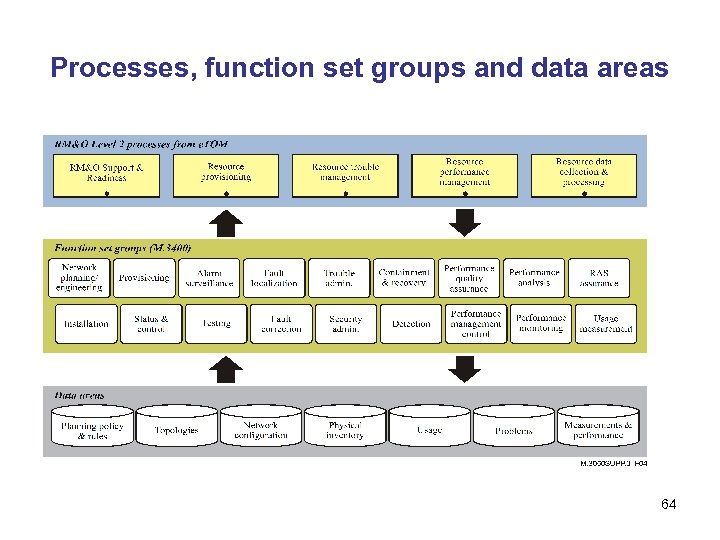
Processes, function set groups and data areas 64
Objectives of mapping e. TOM to M. 3400 • Facilitate the linkage from process view to functional view; • Provide a framework for level of granularity and abstraction for the interface definitions; • Get a better handle on what should be implemented in systems in terms of: –Reusable software components; –Boundaries of what to implement; • Understand what are the interfaces between processes at the indicated levels; • Identify the needs for standardization. 65
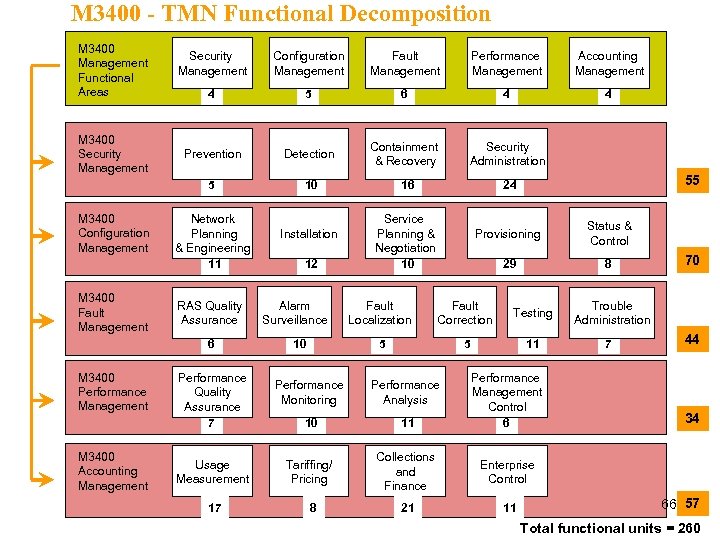
M 3400 - TMN Functional Decomposition M 3400 Management Functional Areas M 3400 Configuration Management M 3400 Fault Management Configuration Management Fault Management Performance Management Accounting Management 4 5 6 4 4 Prevention Detection Containment & Recovery Security Administration 5 M 3400 Security Management 10 Network Planning & Engineering 11 RAS Quality Assurance 6 M 3400 Performance Management M 3400 Accounting Management Performance Quality Assurance 7 Usage Measurement 17 Installation 12 Alarm Surveillance 16 55 24 Service Planning & Negotiation 10 Provisioning Status & Control 29 8 Fault Correction Testing 5 10 Fault Localization 5 11 Performance Management Control 6 Performance Monitoring Performance Analysis 10 11 Tariffing/ Pricing Collections and Finance 11 Trouble Administration 7 44 Enterprise Control 21 70 8 34 66 57 Total functional units = 260
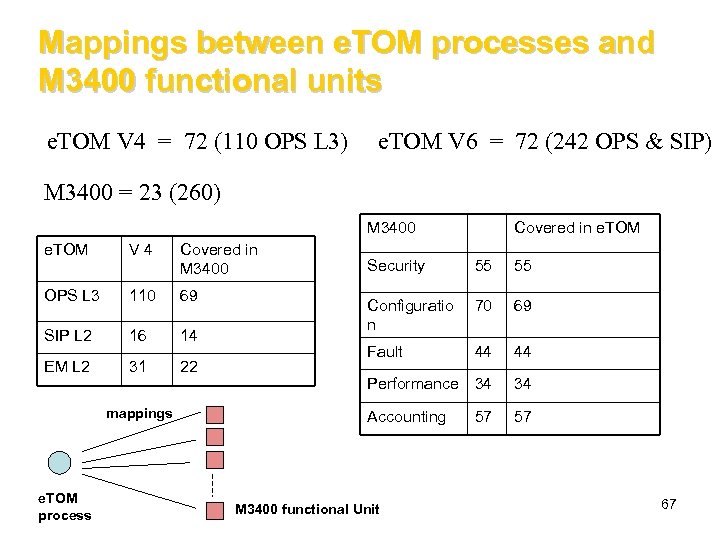
Mappings between e. TOM processes and M 3400 functional units e. TOM V 4 = 72 (110 OPS L 3) e. TOM V 6 = 72 (242 OPS & SIP) M 3400 = 23 (260) M 3400 e. TOM V 4 Covered in M 3400 OPS L 3 110 69 SIP L 2 16 14 EM L 2 31 22 mappings e. TOM process Covered in e. TOM Security 55 55 Configuratio n 70 69 Fault 44 44 Performance 34 34 Accounting 57 M 3400 functional Unit 57 67
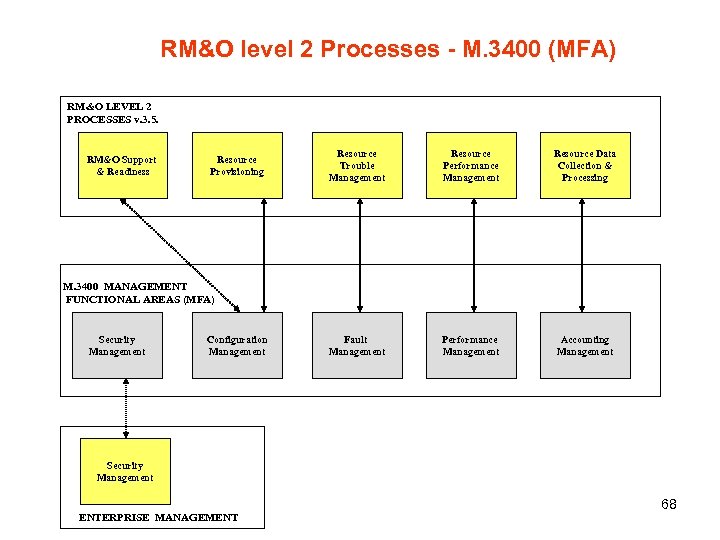
RM&O level 2 Processes - M. 3400 (MFA) RM&O LEVEL 2 PROCESSES v. 3. 5. RM&O Support & Readiness Resource Provisioning Resource Trouble Management Resource Performance Management Resource Data Collection & Processing Fault Management Performance Management Accounting Management M. 3400 MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONAL AREAS (MFA) Security Management Configuration Management Security Management ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT 68
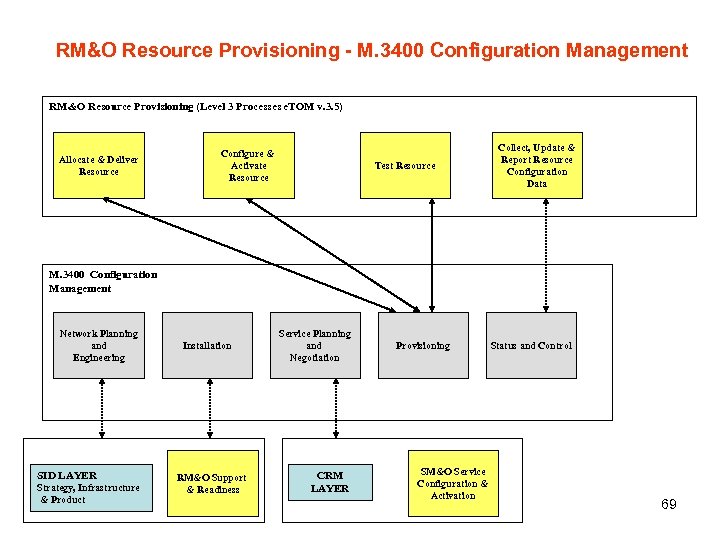
RM&O Resource Provisioning - M. 3400 Configuration Management RM&O Resource Provisioning (Level 3 Processes e. TOM v. 3. 5) Allocate & Deliver Resource Configure & Activate Resource Test Resource Collect, Update & Report Resource Configuration Data M. 3400 Configuration Management Network Planning and Engineering SID LAYER Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Installation RM&O Support & Readiness Service Planning and Negotiation CRM LAYER Provisioning SM&O Service Configuration & Activation Status and Control 69
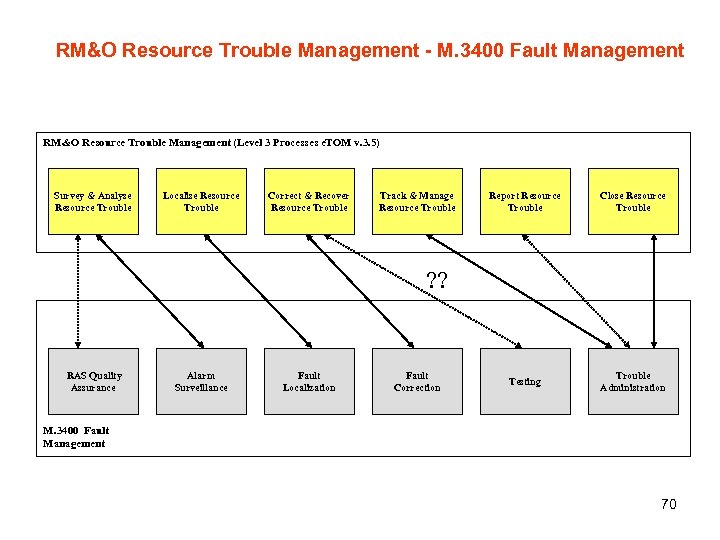
RM&O Resource Trouble Management - M. 3400 Fault Management RM&O Resource Trouble Management (Level 3 Processes e. TOM v. 3. 5) Survey & Analyse Resource Trouble Localise Resource Trouble Correct & Recover Resource Trouble Track & Manage Resource Trouble Report Resource Trouble Close Resource Trouble Testing Trouble Administration ? ? RAS Quality Assurance Alarm Surveillance Fault Localization Fault Correction M. 3400 Fault Management 70
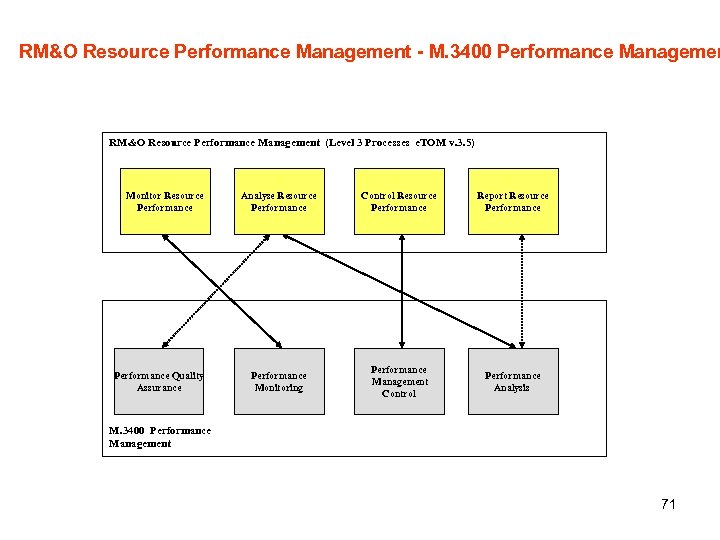
RM&O Resource Performance Management - M. 3400 Performance Managemen RM&O Resource Performance Management (Level 3 Processes e. TOM v. 3. 5) Monitor Resource Performance Quality Assurance Analyse Resource Performance Control Resource Performance Report Resource Performance Monitoring Performance Management Control Performance Analysis M. 3400 Performance Management 71
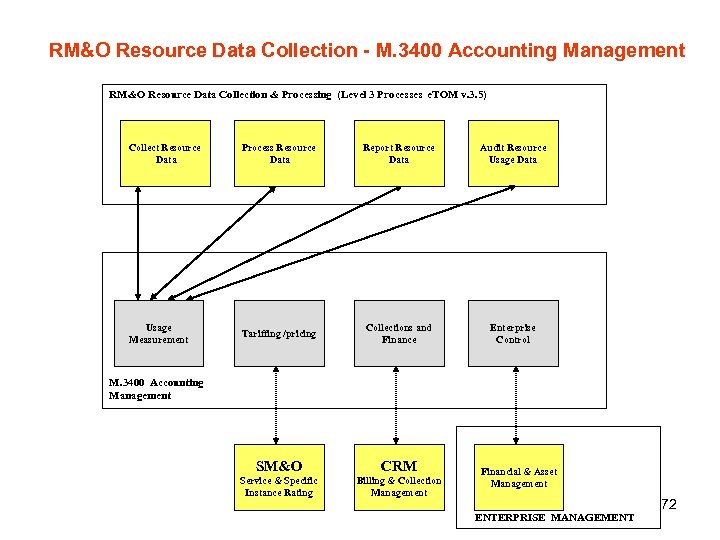
RM&O Resource Data Collection - M. 3400 Accounting Management RM&O Resource Data Collection & Processing (Level 3 Processes e. TOM v. 3. 5) Collect Resource Data Process Resource Data Report Resource Data Audit Resource Usage Data Usage Measurement Tariffing /pricing Collections and Finance Enterprise Control M. 3400 Accounting Management SM&O CRM Service & Specific Instance Rating Billing & Collection Management Financial & Asset Management ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT 72
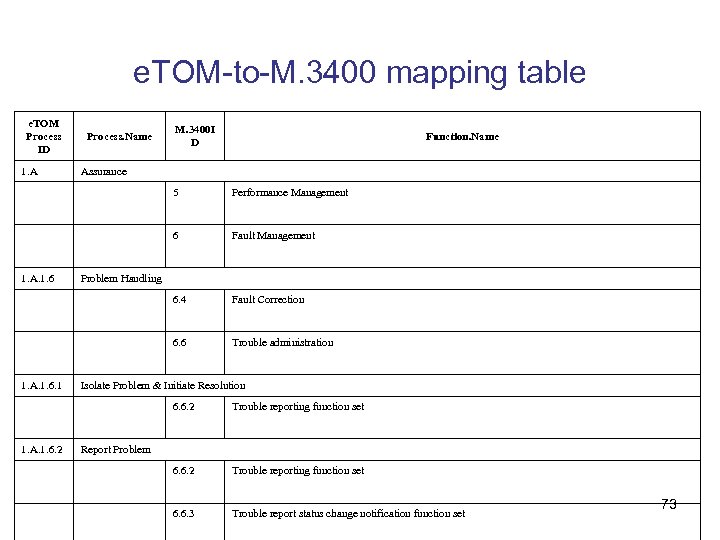
e. TOM-to-M. 3400 mapping table e. TOM Process ID 1. A Process. Name M. 3400 I D Function. Name Assurance 5 6 Fault Correction 6. 6 1. A. 1. 6. 1 Fault Management 6. 4 1. A. 1. 6 Performance Management Trouble administration Problem Handling Isolate Problem & Initiate Resolution 6. 6. 2 1. A. 1. 6. 2 Trouble reporting function set 6. 6. 3 Trouble report status change notification function set Report Problem 73
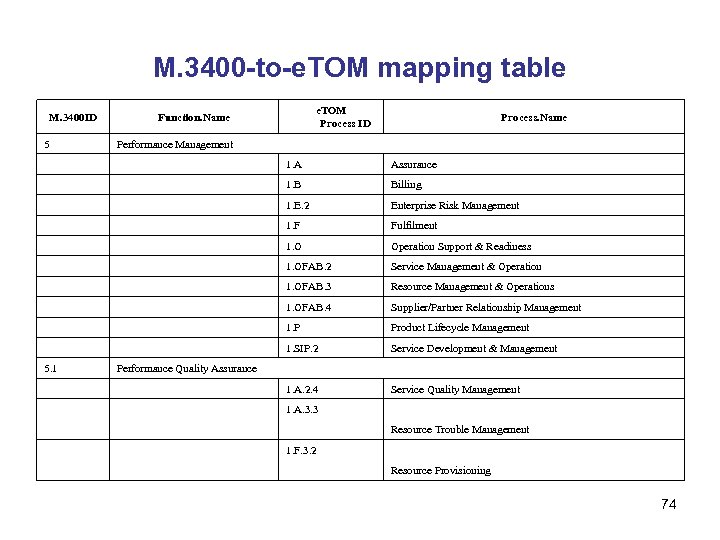
M. 3400 -to-e. TOM mapping table M. 3400 ID 5 e. TOM Process ID Function. Name Process. Name Performance Management 1. A 1. B Billing 1. E. 2 Enterprise Risk Management 1. F Fulfilment 1. O Operation Support & Readiness 1. OFAB. 2 Service Management & Operation 1. OFAB. 3 Resource Management & Operations 1. OFAB. 4 Supplier/Partner Relationship Management 1. P Product Lifecycle Management 1. SIP. 2 5. 1 Assurance Service Development & Management 1. A. 2. 4 Service Quality Management Performance Quality Assurance 1. A. 3. 3 Resource Trouble Management 1. F. 3. 2 Resource Provisioning 74

ITIL Initially developed by UK government CCTA ( Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency ) in 1980’s. OGC ( Office of Government Commerce) • • Service Support : 308 Pages Service Delivery : 376 Pages Application Management : ; 158 Pages Planning to Implement Service Management : 208 Pages ICT Infrastructure Management : 283 Pages Security Management : 124 Pages Business Perspective : NA 75
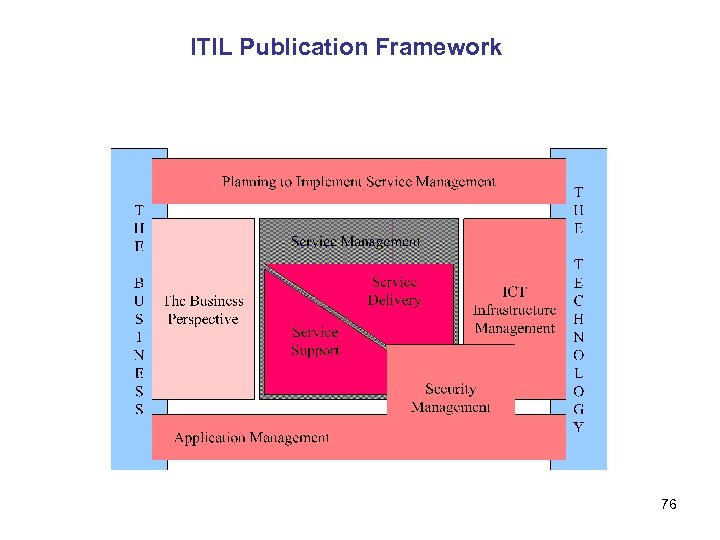
ITIL Publication Framework 76
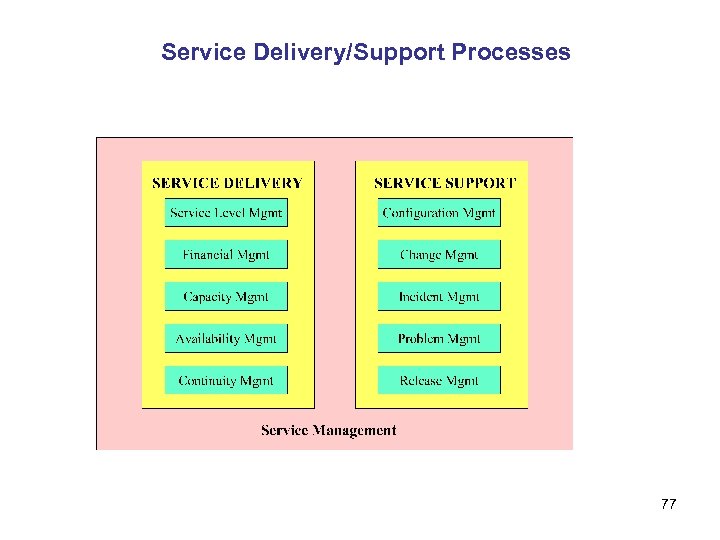
Service Delivery/Support Processes 77
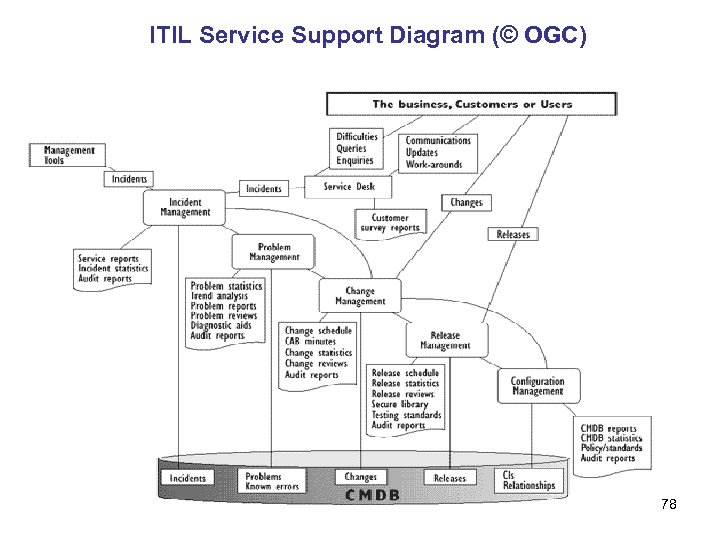
ITIL Service Support Diagram (© OGC) 78
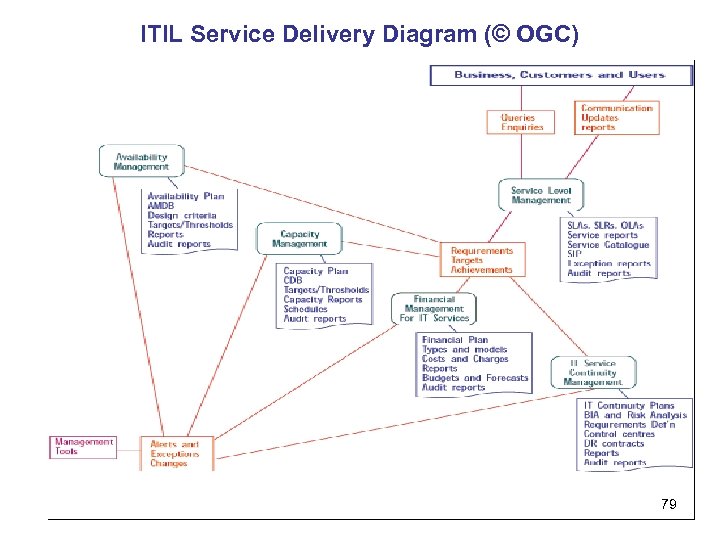
ITIL Service Delivery Diagram (© OGC) 79
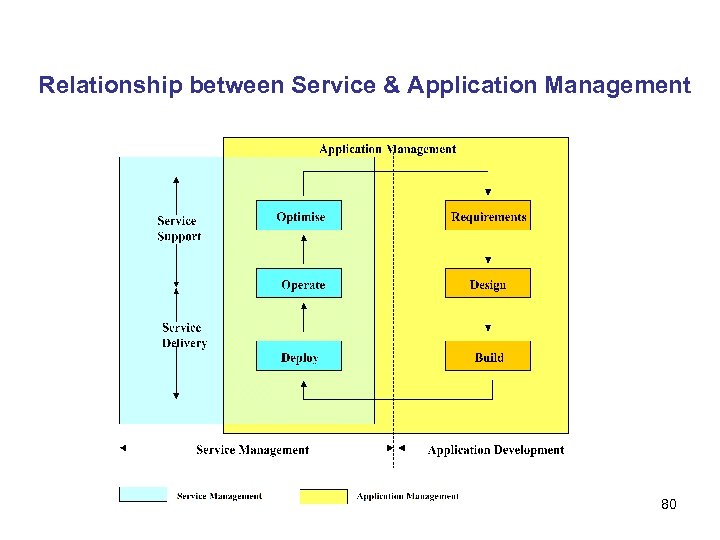
Relationship between Service & Application Management 80
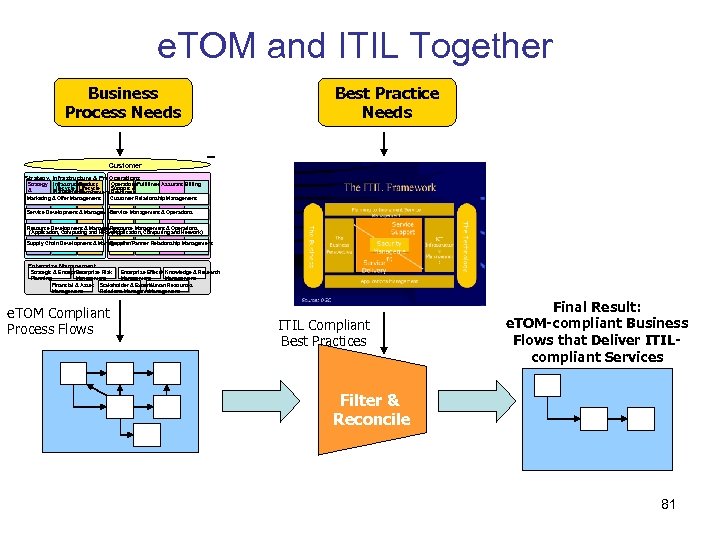
e. TOM and ITIL Together Business Process Needs Best Practice Needs Customer Strategy, Infrastructure & Product Operations Strategy Infrastructure Product Operations. Fulfillment Assurance Billing Lifecycle Support & & Management Readiness Commit Marketing & Offer Management Customer Relationship Management Service Development & Management Service Management & Operations Resource Development & Management Resource Management & Operations (Application, Computing and Network) Supply Chain Development & Management Supplier/Partner Relationship Management Enterprise Effectiveness Strategic & Enterprise Risk Knowledge & Research Management Planning Management Financial & Asset Stakeholder & External Human Resources Management Relations Management e. TOM Compliant Process Flows ITIL Compliant Best Practices Final Result: e. TOM-compliant Business Flows that Deliver ITILcompliant Services Filter & Reconcile 81

e. TOM • Business context is a total enterprise model for telcos. • International standard through ITU. • Constitutes the Business View section of NGOSS, TMF’s initiative on OSS / BSS solutions. • A common language for business processes. • A hierarchy of process definitions. • A repository of process elements at various levels of detail that can be combined and applied in specific applications. • Provides examples of process flows. • Flow diagrams are used in e. TOM to illustrate end to end processes e. g. Fulfillment. • Technical content now mature, with an i 82

ITIL • Business context is IT / ICT Service Management. • Included in various national standards, and slated to be adopted by ISO in 2005 / 06. • A comprehensive and consistent set of best practices. • A set of methods for delivering controlled and optimizable services. • Common language • Aim is to provide high quality services with a particular focus on Customer relationships. • Is built on agreements where the IT organization should provide whatever is mutually agreed with Customers. • Service Delivery processes are partially concerned with setting up agreements and monitoring the targets within these agreements. On the operational level, the Service Support processes can be viewed as delivering service as laid down in these agreements. • Flow charts are used in ITIL. • Inclusion of closed feedback quality loops for continuous improvement. • It supports and drives ‘quality’ or repeatability 83
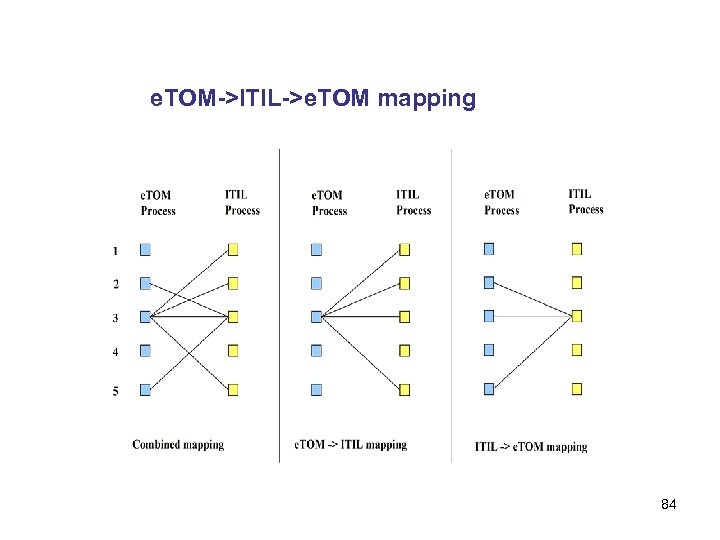
e. TOM->ITIL->e. TOM mapping 84
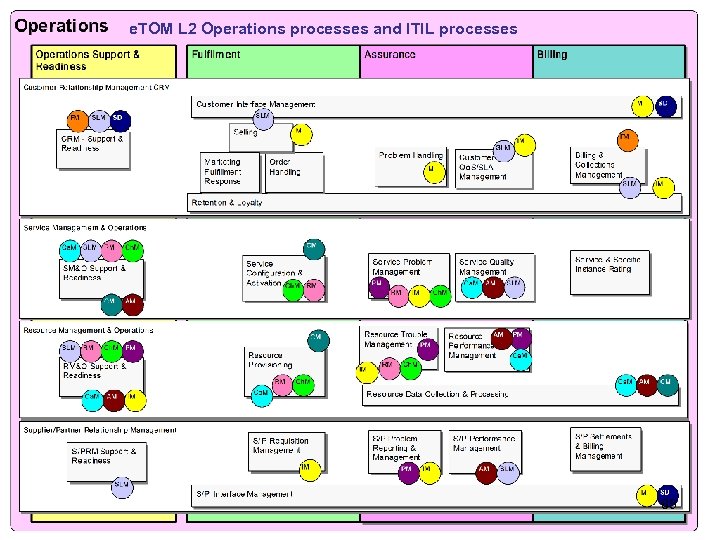
e. TOM L 2 Operations processes and ITIL processes 85
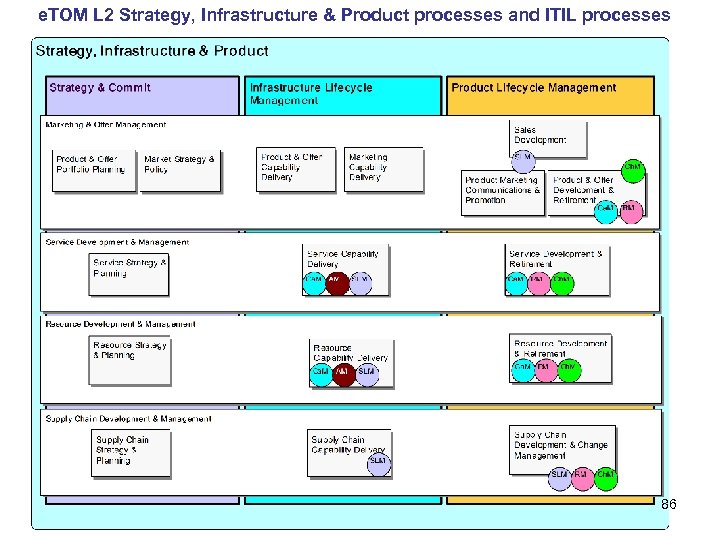
e. TOM L 2 Strategy, Infrastructure & Product processes and ITIL processes 86
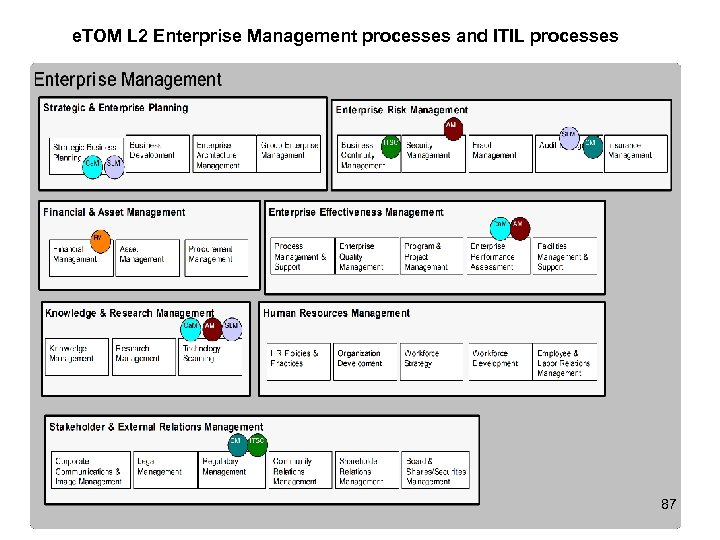
e. TOM L 2 Enterprise Management processes and ITIL processes 87
88
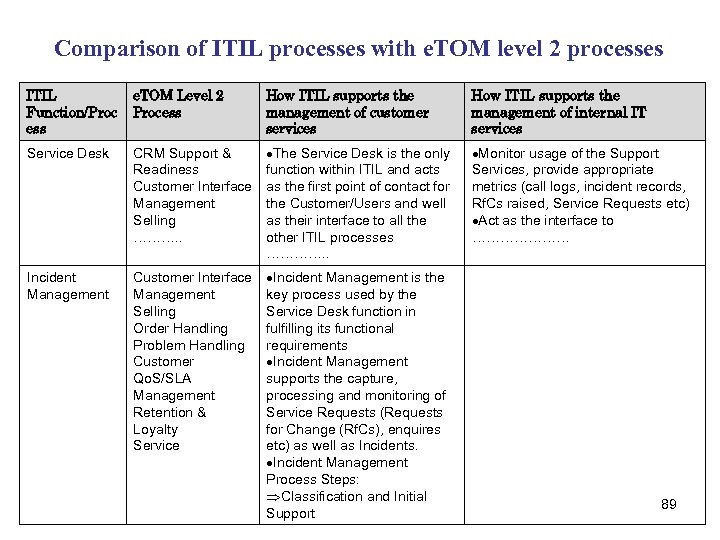
Comparison of ITIL processes with e. TOM level 2 processes ITIL Function/Proc ess e. TOM Level 2 Process How ITIL supports the management of customer services How ITIL supports the management of internal IT services Service Desk CRM Support & Readiness Customer Interface Management Selling ………. . The Service Desk is the only function within ITIL and acts as the first point of contact for the Customer/Users and well as their interface to all the other ITIL processes …………. . Monitor usage of the Support Services, provide appropriate metrics (call logs, incident records, Rf. Cs raised, Service Requests etc) Act as the interface to ………………… Incident Management Customer Interface Management Selling Order Handling Problem Handling Customer Qo. S/SLA Management Retention & Loyalty Service Incident Management is the key process used by the Service Desk function in fulfilling its functional requirements Incident Management supports the capture, processing and monitoring of Service Requests (Requests for Change (Rf. Cs), enquires etc) as well as Incidents. Incident Management Process Steps: Classification and Initial Support 89
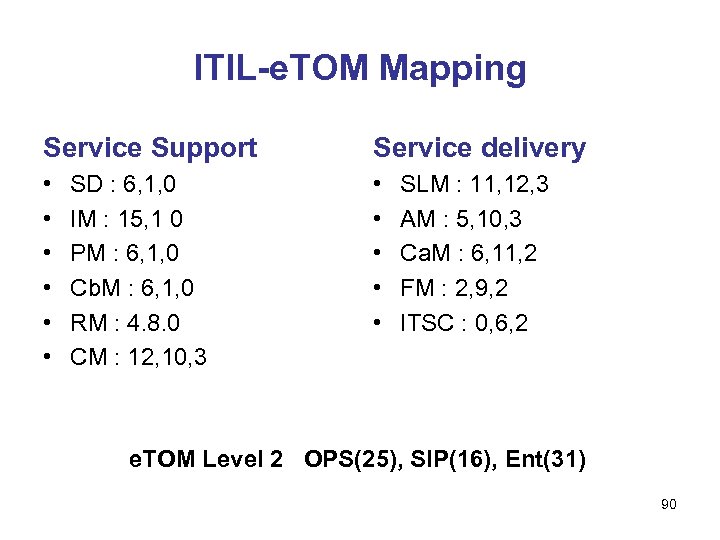
ITIL-e. TOM Mapping Service Support Service delivery • • • SD : 6, 1, 0 IM : 15, 1 0 PM : 6, 1, 0 Cb. M : 6, 1, 0 RM : 4. 8. 0 CM : 12, 10, 3 SLM : 11, 12, 3 AM : 5, 10, 3 Ca. M : 6, 11, 2 FM : 2, 9, 2 ITSC : 0, 6, 2 e. TOM Level 2 OPS(25), SIP(16), Ent(31) 90
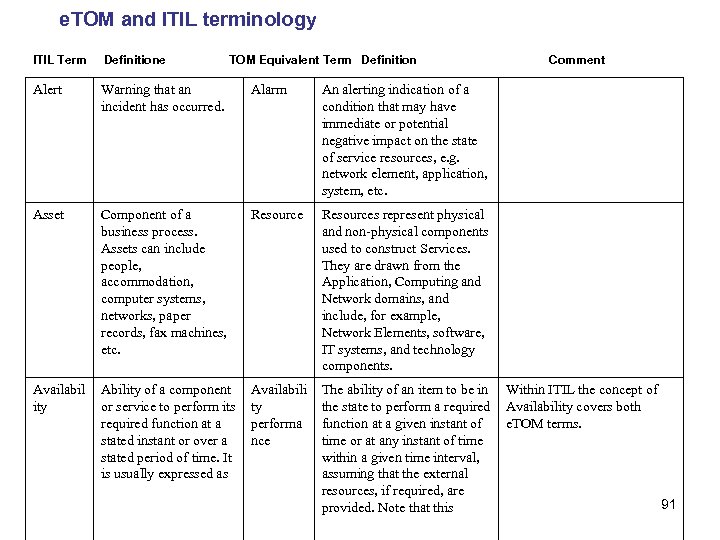
e. TOM and ITIL terminology ITIL Term Definitione TOM Equivalent Term Definition Comment Alert Warning that an incident has occurred. Alarm An alerting indication of a condition that may have immediate or potential negative impact on the state of service resources, e. g. network element, application, system, etc. Asset Component of a business process. Assets can include people, accommodation, computer systems, networks, paper records, fax machines, etc. Resources represent physical and non-physical components used to construct Services. They are drawn from the Application, Computing and Network domains, and include, for example, Network Elements, software, IT systems, and technology components. Availabil ity Ability of a component or service to perform its required function at a stated instant or over a stated period of time. It is usually expressed as Availabili ty performa nce The ability of an item to be in Within ITIL the concept of the state to perform a required Availability covers both function at a given instant of e. TOM terms. time or at any instant of time within a given time interval, assuming that the external resources, if required, are 91 provided. Note that this
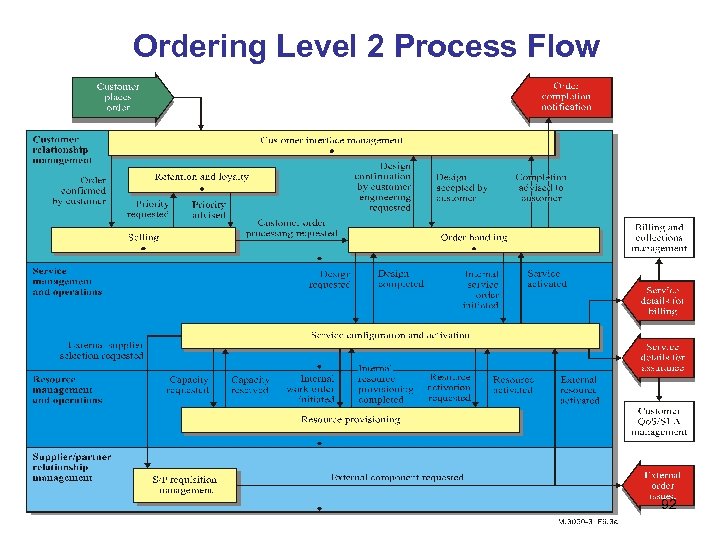
Ordering Level 2 Process Flow 92
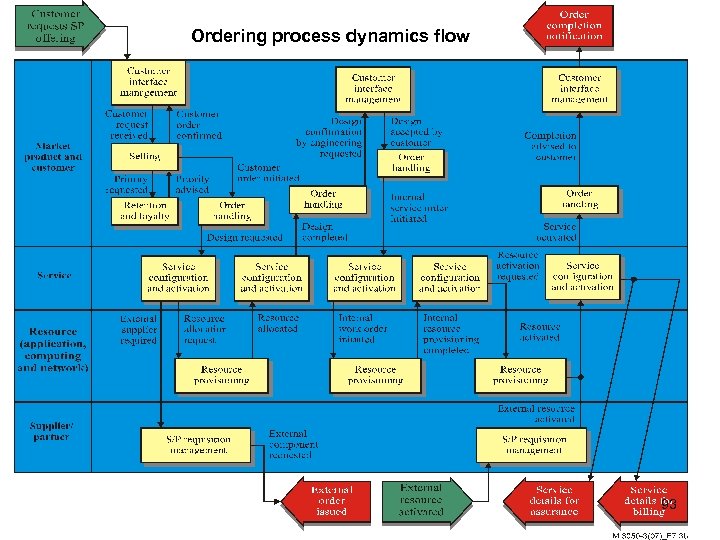
Ordering process dynamics flow 93
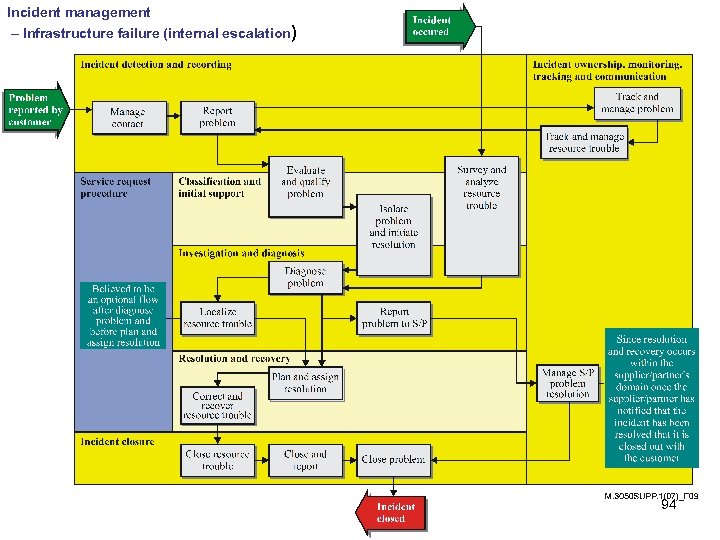
Incident management – Infrastructure failure (internal escalation) 94
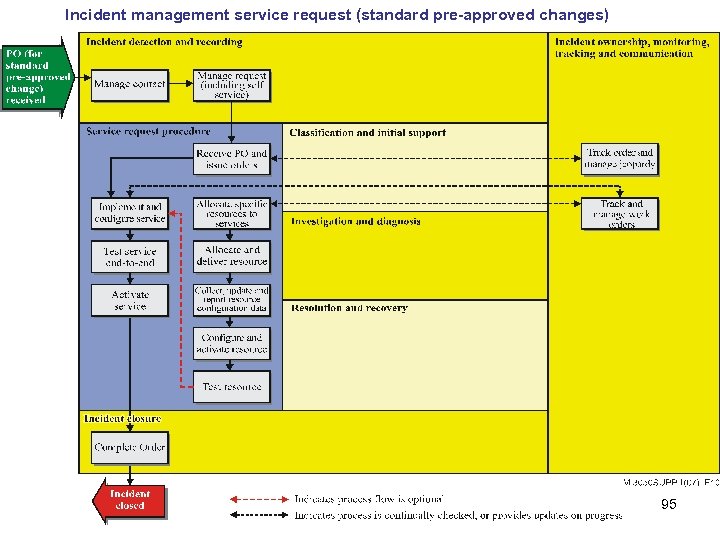
Incident management service request (standard pre-approved changes) 95
5ba9bdb35263278a0b251d4e52af24e6.ppt