857e32d03e5f838b7da320c4c7dfdb52.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61
 POSTEC Lecture Network Management Chapter 3 OSS Development April 15 -May 1, 2008 Masayoshi Ejiri Japan 1
POSTEC Lecture Network Management Chapter 3 OSS Development April 15 -May 1, 2008 Masayoshi Ejiri Japan 1
 Agenda 1. ICT Operations and Management - Service Industries - ICT Services and Networks— - Target of the Management 2, Architecture , Function , Information Model and Business Process - ITU-T TMN( Telecommunications Management Network) - Tele. Management Forum Telecommunications Operations Map ( TOM) - Multi domain management and System Integration - Standardization 3. OSS( Operations Support System ) Development - Software Architecture , Key Technologies and Product Evaluation— 4. SLA( Service Level Agreement) and Qo. S( Quality of Service) - SLA Definition , reference point and policy based negotiation 5, IP/e. Business Management - Paradigm shift , Architecture beyond TMN and enhanced TOM 6. NGN( Next Generation Networks) Management - NGN Networks and Services , New Paradigm of ICT Business and Management 2
Agenda 1. ICT Operations and Management - Service Industries - ICT Services and Networks— - Target of the Management 2, Architecture , Function , Information Model and Business Process - ITU-T TMN( Telecommunications Management Network) - Tele. Management Forum Telecommunications Operations Map ( TOM) - Multi domain management and System Integration - Standardization 3. OSS( Operations Support System ) Development - Software Architecture , Key Technologies and Product Evaluation— 4. SLA( Service Level Agreement) and Qo. S( Quality of Service) - SLA Definition , reference point and policy based negotiation 5, IP/e. Business Management - Paradigm shift , Architecture beyond TMN and enhanced TOM 6. NGN( Next Generation Networks) Management - NGN Networks and Services , New Paradigm of ICT Business and Management 2
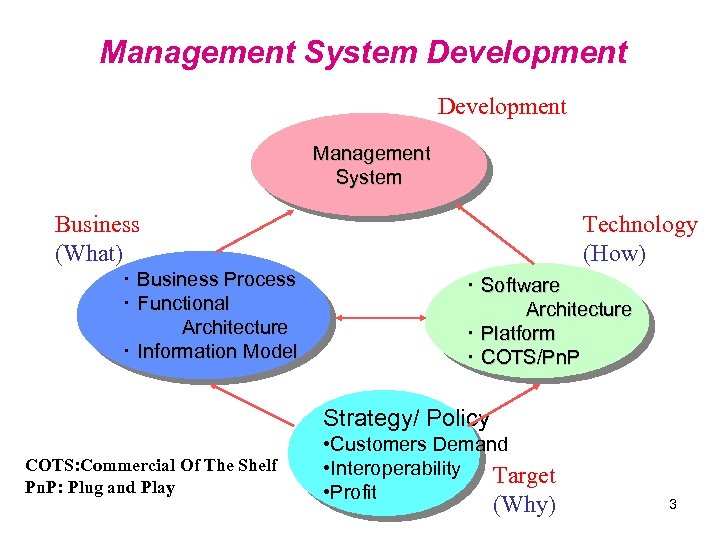 Management System Development Management System Business (What) ・ Business Process ・ Functional Architecture ・ Information Model Technology (How) ・ Software Architecture ・ Platform ・ COTS/Pn. P Strategy/ Policy COTS: Commercial Of The Shelf Pn. P: Plug and Play • Customers Demand • Interoperability Target • Profit (Why) 3
Management System Development Management System Business (What) ・ Business Process ・ Functional Architecture ・ Information Model Technology (How) ・ Software Architecture ・ Platform ・ COTS/Pn. P Strategy/ Policy COTS: Commercial Of The Shelf Pn. P: Plug and Play • Customers Demand • Interoperability Target • Profit (Why) 3
 OSS Development • • • Target Software Architecture and Foundation TMF Goal and NGOSS Products evaluation Proof of Interoperability 4
OSS Development • • • Target Software Architecture and Foundation TMF Goal and NGOSS Products evaluation Proof of Interoperability 4
 OSS Development - from Built to Assemble- Software Manufacturing Package integration, Use Tools Proprietary BP and Interface Common BP and Standards interface Software Module Software Component (Atomic Component and Objects ? ? ) 5
OSS Development - from Built to Assemble- Software Manufacturing Package integration, Use Tools Proprietary BP and Interface Common BP and Standards interface Software Module Software Component (Atomic Component and Objects ? ? ) 5
 For Faster, Cheaper and Better OSS Consensus of Business Process and OSS ・COTS: Commercial Off the Shelf Software ・Proof of Interoperability Globally Acceptable Software Packages and OSS ----> Not Built but Buy 6
For Faster, Cheaper and Better OSS Consensus of Business Process and OSS ・COTS: Commercial Off the Shelf Software ・Proof of Interoperability Globally Acceptable Software Packages and OSS ----> Not Built but Buy 6
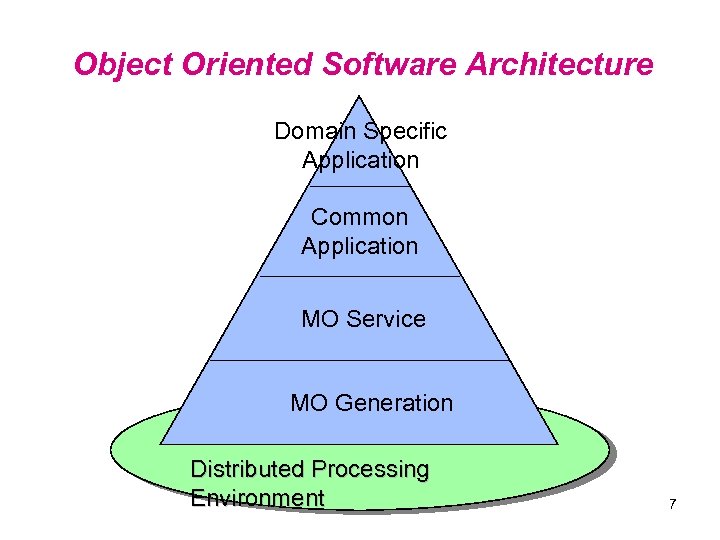 Object Oriented Software Architecture Domain Specific Application Common Application MO Service MO Generation Distributed Processing Environment 7
Object Oriented Software Architecture Domain Specific Application Common Application MO Service MO Generation Distributed Processing Environment 7
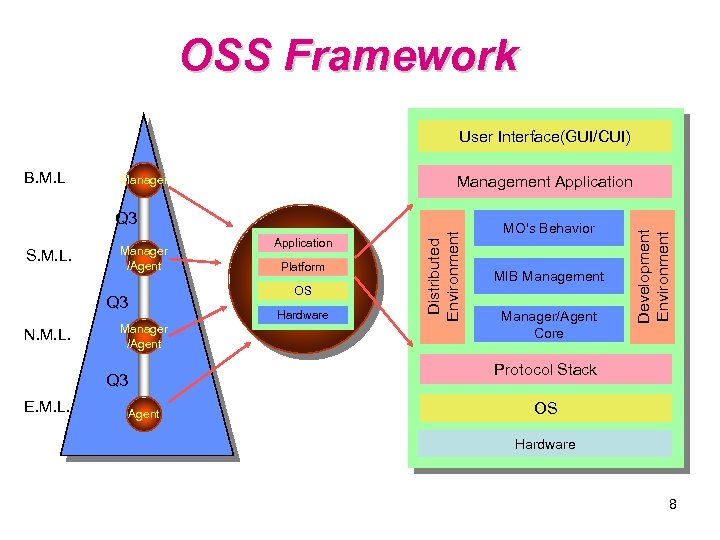 OSS Framework User Interface(GUI/CUI) Management Application Manager S. M. L. Manager /Agent Hardware Manager /Agent MO's Behavior MIB Management Manager/Agent Core Protocol Stack Q 3 E. M. L. Platform OS Q 3 N. M. L. Application Distributed Environment Q 3 Development Environment B. M. L Agent OS Hardware 8
OSS Framework User Interface(GUI/CUI) Management Application Manager S. M. L. Manager /Agent Hardware Manager /Agent MO's Behavior MIB Management Manager/Agent Core Protocol Stack Q 3 E. M. L. Platform OS Q 3 N. M. L. Application Distributed Environment Q 3 Development Environment B. M. L Agent OS Hardware 8
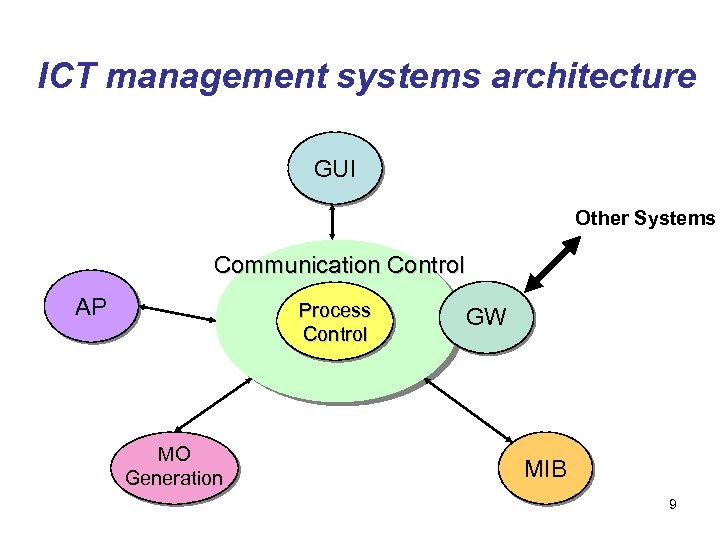 ICT management systems architecture GUI Other Systems Communication Control AP Process Control MO Generation GW MIB 9
ICT management systems architecture GUI Other Systems Communication Control AP Process Control MO Generation GW MIB 9
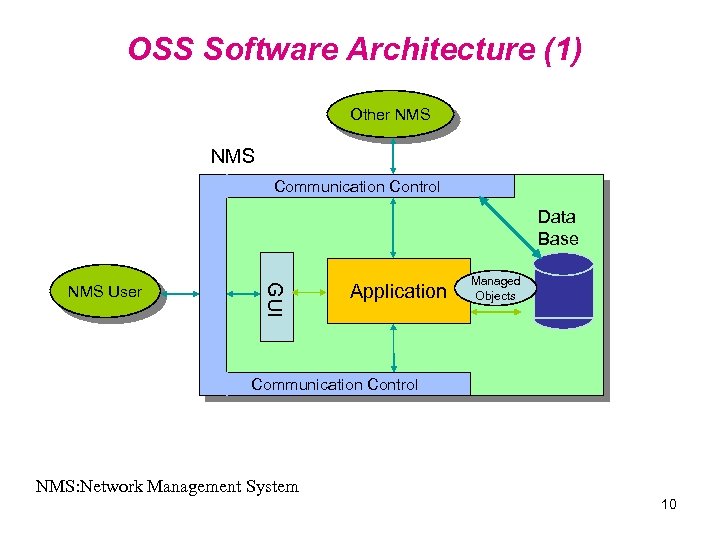 OSS Software Architecture (1) Other NMS Communication Control Data Base GUI NMS User Application Managed Objects Communication Control NMS: Network Management System 10
OSS Software Architecture (1) Other NMS Communication Control Data Base GUI NMS User Application Managed Objects Communication Control NMS: Network Management System 10
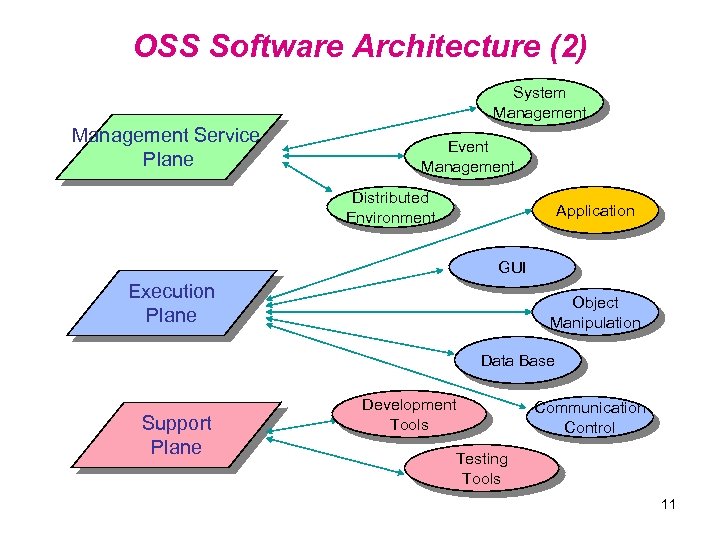 OSS Software Architecture (2) System Management Service Plane Event Management Distributed Environment Application GUI Execution Plane Object Manipulation Data Base Support Plane Development Tools Communication Control Testing Tools 11
OSS Software Architecture (2) System Management Service Plane Event Management Distributed Environment Application GUI Execution Plane Object Manipulation Data Base Support Plane Development Tools Communication Control Testing Tools 11
 Requirements for the Platform • Operability – Easy Operation, End User Computing Oriented, Easy GUI • Interoperability – Provide seamless information exchange between applications • Portability – Software package • Scalability – Easy to extend • Flexibility – Evolution of Business Process and Operability 12
Requirements for the Platform • Operability – Easy Operation, End User Computing Oriented, Easy GUI • Interoperability – Provide seamless information exchange between applications • Portability – Software package • Scalability – Easy to extend • Flexibility – Evolution of Business Process and Operability 12
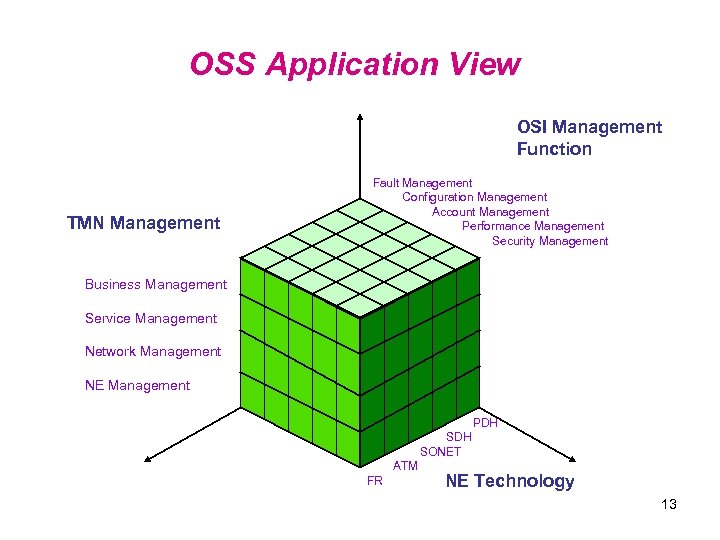 OSS Application View OSI Management Function TMN Management Fault Management Configuration Management Account Management Performance Management Security Management Business Management Service Management Network Management NE Management PDH SONET ATM FR NE Technology 13
OSS Application View OSI Management Function TMN Management Fault Management Configuration Management Account Management Performance Management Security Management Business Management Service Management Network Management NE Management PDH SONET ATM FR NE Technology 13
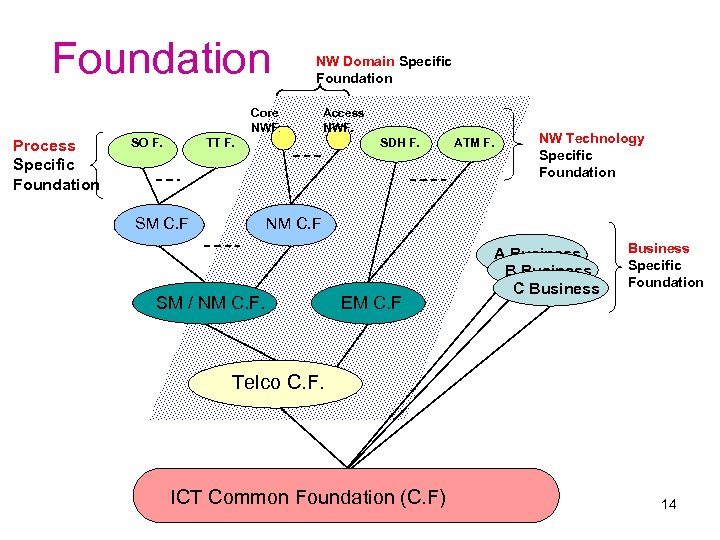 Foundation NW Domain Specific Foundation Core NWF. Process Specific Foundation SO F. Access NWF. TT F. SM C. F SDH F. ATM F. NW Technology Specific Foundation NM C. F SM / NM C. F. EM C. F A Business B Business C Business Specific Foundation Telco C. F. ICT Common Foundation (C. F) 14
Foundation NW Domain Specific Foundation Core NWF. Process Specific Foundation SO F. Access NWF. TT F. SM C. F SDH F. ATM F. NW Technology Specific Foundation NM C. F SM / NM C. F. EM C. F A Business B Business C Business Specific Foundation Telco C. F. ICT Common Foundation (C. F) 14
 TMF Tele. Management Forum? • Non-profit global organization of 600+ service providers, systems integrators, ISV and NE vendors, established 1988 • TM Forum Events - TMW( Tele. Management Forum) : General Meeting , Twice a year with Discussion, Education, Catalyst projects and Products Exhibition - TAW( Team Action Week) : Experts Meeting, 4 times a year and additional meeting and frequent Conference Call , defines de facto standards 15
TMF Tele. Management Forum? • Non-profit global organization of 600+ service providers, systems integrators, ISV and NE vendors, established 1988 • TM Forum Events - TMW( Tele. Management Forum) : General Meeting , Twice a year with Discussion, Education, Catalyst projects and Products Exhibition - TAW( Team Action Week) : Experts Meeting, 4 times a year and additional meeting and frequent Conference Call , defines de facto standards 15
 TMF Direction • Interoperable OSS: as the de-facto standard. – Multi-Service Providers, Vendors, Technologies, . … – Common Business process and Components • Source of new technologies for OSS developments. – COTS, CORBA, XML, SOAP, JINI, … • International Promotion for OSS products. – Catalyst Showcase,Product Expo… 16
TMF Direction • Interoperable OSS: as the de-facto standard. – Multi-Service Providers, Vendors, Technologies, . … – Common Business process and Components • Source of new technologies for OSS developments. – COTS, CORBA, XML, SOAP, JINI, … • International Promotion for OSS products. – Catalyst Showcase,Product Expo… 16
 TMF Goals TMF is committed to enabling: • Real world solutions • Implementation Tested models • Available COTS products that plug and play Lead industry in definition and realization of New Generation OSS Development less than 3 Months ? ? ? 17
TMF Goals TMF is committed to enabling: • Real world solutions • Implementation Tested models • Available COTS products that plug and play Lead industry in definition and realization of New Generation OSS Development less than 3 Months ? ? ? 17
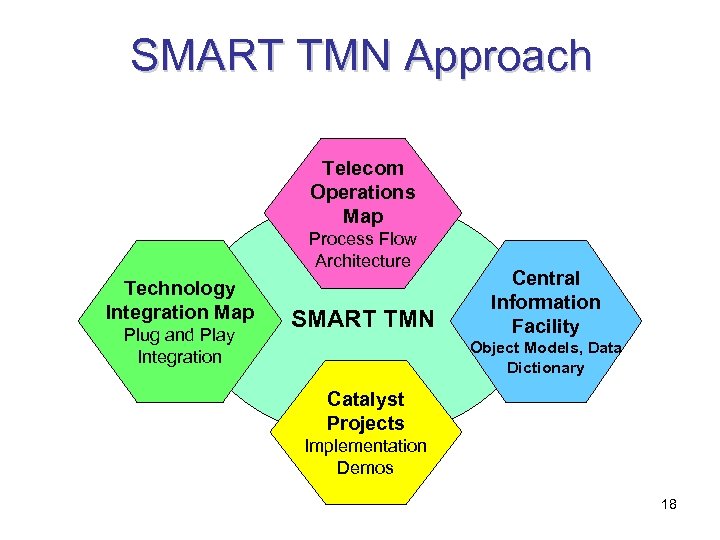 SMART TMN Approach Telecom Operations Map Process Flow Architecture Technology Integration Map Plug and Play Integration SMART TMN Central Information Facility Object Models, Data Dictionary Catalyst Projects Implementation Demos 18
SMART TMN Approach Telecom Operations Map Process Flow Architecture Technology Integration Map Plug and Play Integration SMART TMN Central Information Facility Object Models, Data Dictionary Catalyst Projects Implementation Demos 18
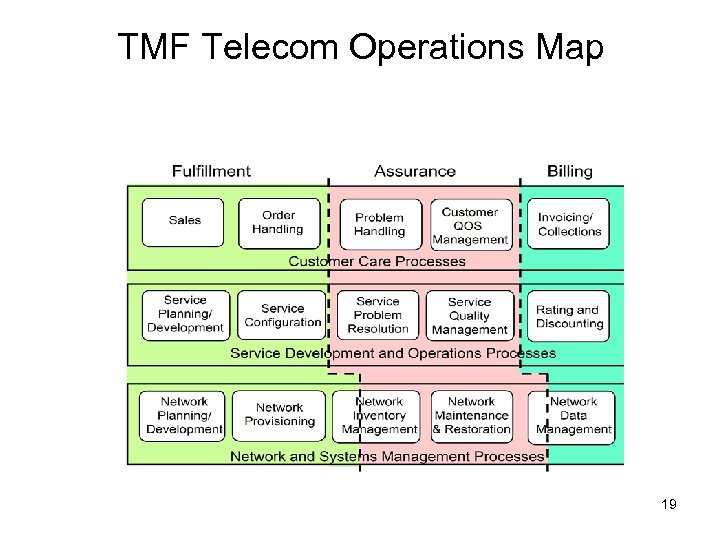 TMF Telecom Operations Map 19
TMF Telecom Operations Map 19
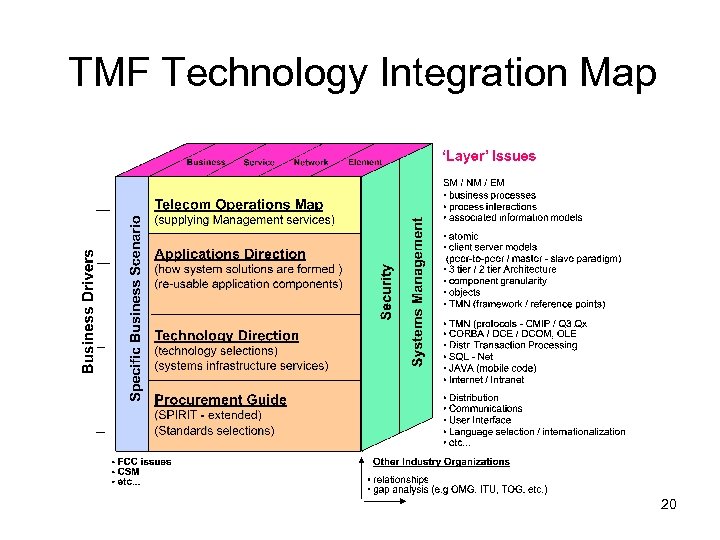 TMF Technology Integration Map 20
TMF Technology Integration Map 20
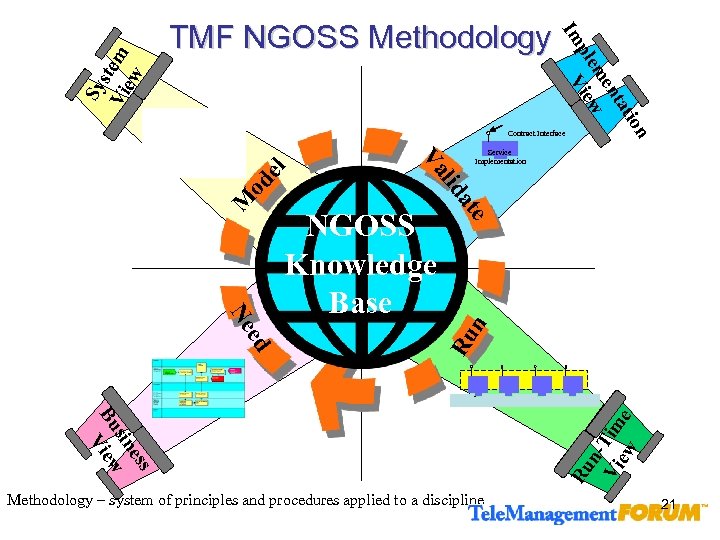 Sy s Vi tem ew ati nt me ple View Im TMF NGOSS Methodology on at n e n. Vi Tim ew e s es sin Bu iew V Methodology – system of principles and procedures applied to a discipline Ru ed Ne NGOSS Knowledge Base Ru od lid M Service Implementation Va el Contract Interface 21
Sy s Vi tem ew ati nt me ple View Im TMF NGOSS Methodology on at n e n. Vi Tim ew e s es sin Bu iew V Methodology – system of principles and procedures applied to a discipline Ru ed Ne NGOSS Knowledge Base Ru od lid M Service Implementation Va el Contract Interface 21
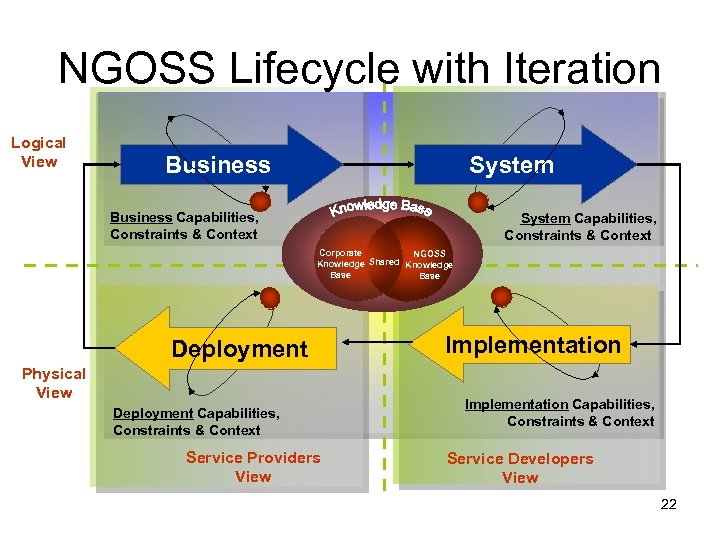 NGOSS Lifecycle with Iteration Logical View Business System Business Capabilities, Constraints & Context System Capabilities, Constraints & Context Corporate NGOSS Knowledge Shared Knowledge Base Deployment Physical View Deployment Capabilities, Constraints & Context Service Providers View Implementation Capabilities, Constraints & Context Service Developers View 22
NGOSS Lifecycle with Iteration Logical View Business System Business Capabilities, Constraints & Context System Capabilities, Constraints & Context Corporate NGOSS Knowledge Shared Knowledge Base Deployment Physical View Deployment Capabilities, Constraints & Context Service Providers View Implementation Capabilities, Constraints & Context Service Developers View 22
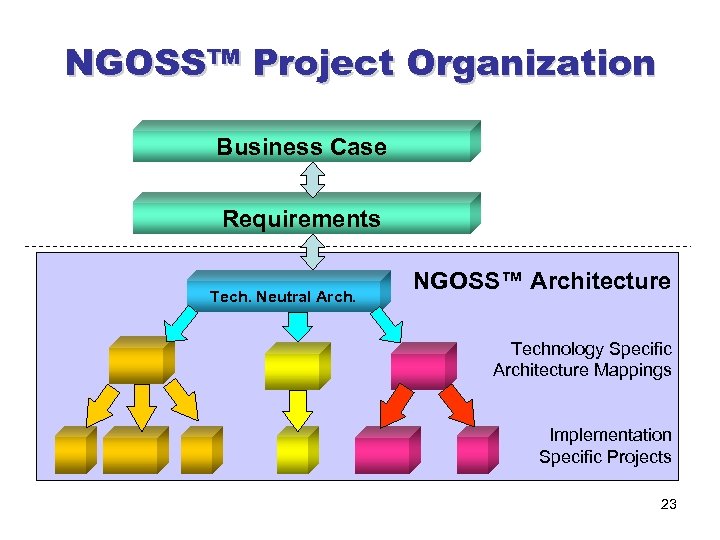 NGOSS™ Project Organization Business Case Requirements Tech. Neutral Arch. NGOSS™ Architecture Technology Specific Architecture Mappings Implementation Specific Projects 23
NGOSS™ Project Organization Business Case Requirements Tech. Neutral Arch. NGOSS™ Architecture Technology Specific Architecture Mappings Implementation Specific Projects 23
 NGOSS New Generation Operations Systems and Software • Define and rationalize the new generation of architectures and frameworks • NGOSS™ is the term the TMF uses to describe • a “loosely coupled” distributed component architecture • along with “business aware” application components • upon which ICSP business can run. • The components interact through a common information bus • The components can be programmed through the use of a process management tool to control the business processes of the service provider using the functionality provided by the components. 24
NGOSS New Generation Operations Systems and Software • Define and rationalize the new generation of architectures and frameworks • NGOSS™ is the term the TMF uses to describe • a “loosely coupled” distributed component architecture • along with “business aware” application components • upon which ICSP business can run. • The components interact through a common information bus • The components can be programmed through the use of a process management tool to control the business processes of the service provider using the functionality provided by the components. 24
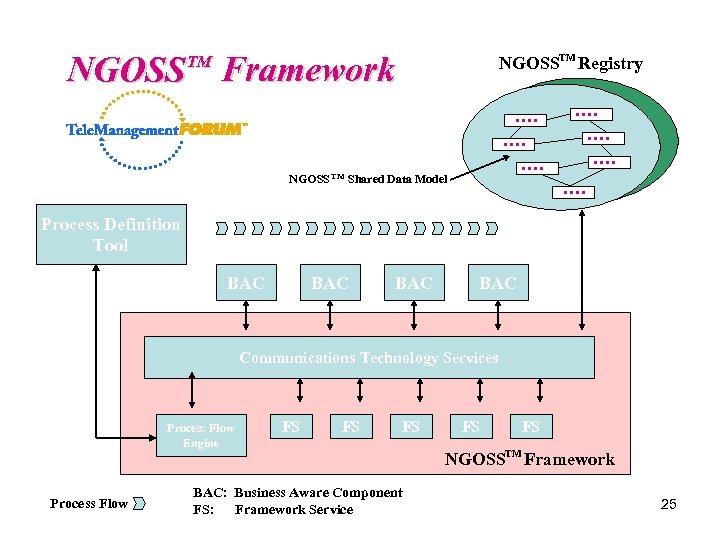 NGOSS Framework NGOSSTM Registry TM NGOSS TM Shared Data Model Process Definition Tool BAC BAC Communications Technology Services Process Flow Engine Process Flow FS FS FS BAC: Business Aware Component FS: Framework Service FS FS NGOSSTM Framework 25
NGOSS Framework NGOSSTM Registry TM NGOSS TM Shared Data Model Process Definition Tool BAC BAC Communications Technology Services Process Flow Engine Process Flow FS FS FS BAC: Business Aware Component FS: Framework Service FS FS NGOSSTM Framework 25
 Business Requirements for Industry Stakeholders • Service Provider – – Richer Services Offerings Faster Time to Market Buy vs. Build Multi- vendor ・ Systems Integrator – – Faster/ Complete Solution Predictable Outcomes/ Costs Grow the Market • Independent Software Vendor – – – Build Once, Sell Many Less Custom Development Customizable Software Components Grow the Market • Network Equipment Provider – More/ Faster Equipment Sales 26
Business Requirements for Industry Stakeholders • Service Provider – – Richer Services Offerings Faster Time to Market Buy vs. Build Multi- vendor ・ Systems Integrator – – Faster/ Complete Solution Predictable Outcomes/ Costs Grow the Market • Independent Software Vendor – – – Build Once, Sell Many Less Custom Development Customizable Software Components Grow the Market • Network Equipment Provider – More/ Faster Equipment Sales 26
 OSS Requirements • • • Interoperability Scalability Evolvability/ Migration Modularity/ Distribution Backward Compatibility Reliability, Availability, Survivability Flexibility Manageability/ Serviceability Data Accessibility Security etc. 27
OSS Requirements • • • Interoperability Scalability Evolvability/ Migration Modularity/ Distribution Backward Compatibility Reliability, Availability, Survivability Flexibility Manageability/ Serviceability Data Accessibility Security etc. 27
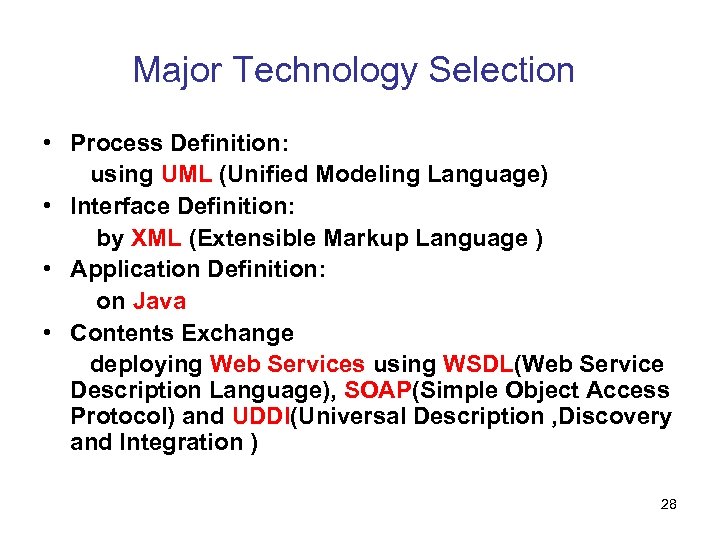 Major Technology Selection • Process Definition: using UML (Unified Modeling Language) • Interface Definition: by XML (Extensible Markup Language ) • Application Definition: on Java • Contents Exchange deploying Web Services using WSDL(Web Service Description Language), SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol) and UDDI(Universal Description , Discovery and Integration ) 28
Major Technology Selection • Process Definition: using UML (Unified Modeling Language) • Interface Definition: by XML (Extensible Markup Language ) • Application Definition: on Java • Contents Exchange deploying Web Services using WSDL(Web Service Description Language), SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol) and UDDI(Universal Description , Discovery and Integration ) 28
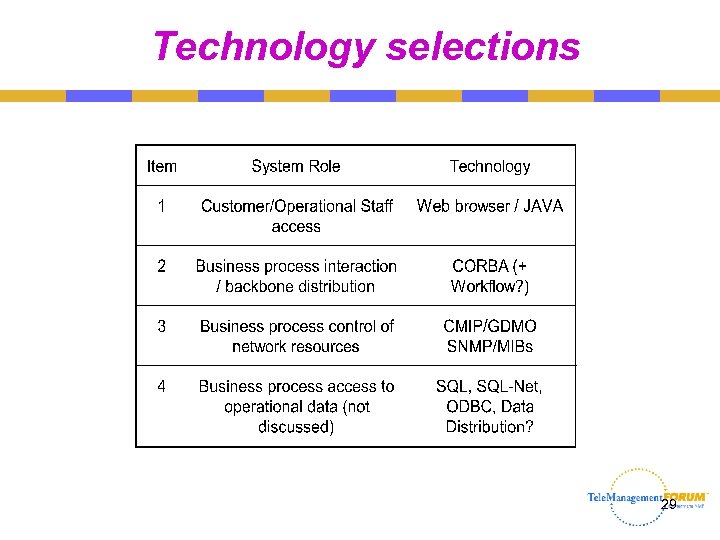 Technology selections 29
Technology selections 29
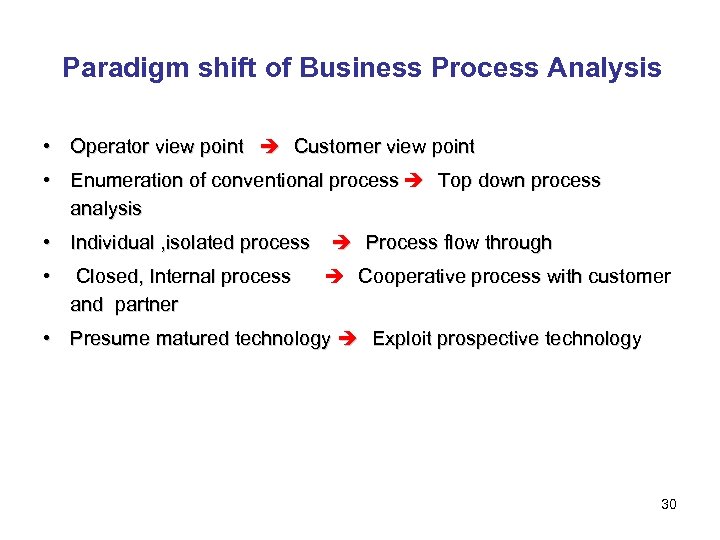 Paradigm shift of Business Process Analysis • Operator view point Customer view point • Enumeration of conventional process Top down process analysis • Individual , isolated process Process flow through • Closed, Internal process Cooperative process with customer and partner • Presume matured technology Exploit prospective technology 30
Paradigm shift of Business Process Analysis • Operator view point Customer view point • Enumeration of conventional process Top down process analysis • Individual , isolated process Process flow through • Closed, Internal process Cooperative process with customer and partner • Presume matured technology Exploit prospective technology 30
 New Business process Optimized Process Agility process for daily business transformation by process components. based flexible BPM 31
New Business process Optimized Process Agility process for daily business transformation by process components. based flexible BPM 31
 Check points of OSS development • What advantage customer can expect ? • The business process developed is applicable in the market ? ( Modify process to meet market products and trend) • How flexibility and expandability are guaranteed to meet unknown change in short time ? • Can be interface clarified on system ground plan ? Can related systems agree it ? • List up and evaluate reusable /available components and tools ? • Evaluate current/future technologies ? Deployed technologies will become mainstream ? • Can you sell the developed package ? • Can you release within 6 months ? 32
Check points of OSS development • What advantage customer can expect ? • The business process developed is applicable in the market ? ( Modify process to meet market products and trend) • How flexibility and expandability are guaranteed to meet unknown change in short time ? • Can be interface clarified on system ground plan ? Can related systems agree it ? • List up and evaluate reusable /available components and tools ? • Evaluate current/future technologies ? Deployed technologies will become mainstream ? • Can you sell the developed package ? • Can you release within 6 months ? 32
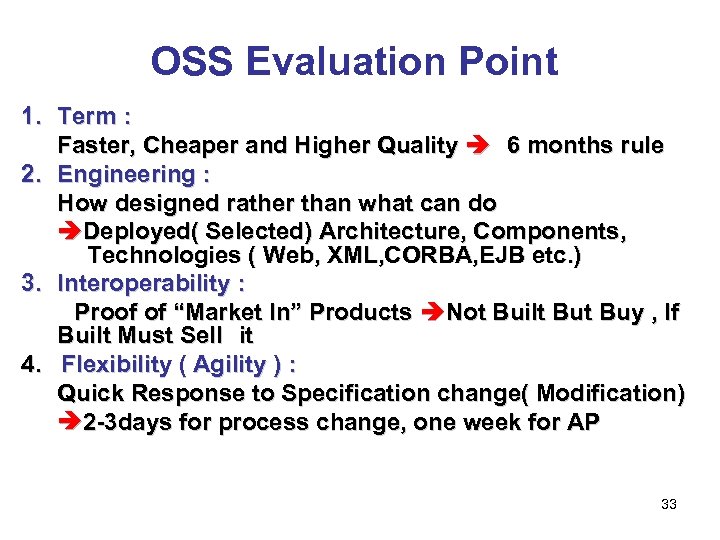 OSS Evaluation Point 1. Term : Faster, Cheaper and Higher Quality 6 months rule 2. Engineering : How designed rather than what can do Deployed( Selected) Architecture, Components, Technologies ( Web, XML, CORBA, EJB etc. ) 3. Interoperability : Proof of “Market In” Products Not Built Buy , If Built Must Sell it 4. Flexibility ( Agility ) : Quick Response to Specification change( Modification) 2 -3 days for process change, one week for AP 33
OSS Evaluation Point 1. Term : Faster, Cheaper and Higher Quality 6 months rule 2. Engineering : How designed rather than what can do Deployed( Selected) Architecture, Components, Technologies ( Web, XML, CORBA, EJB etc. ) 3. Interoperability : Proof of “Market In” Products Not Built Buy , If Built Must Sell it 4. Flexibility ( Agility ) : Quick Response to Specification change( Modification) 2 -3 days for process change, one week for AP 33
 Productivity of Software Vendor( Organization ) 1. Technology and Connoisseur 2. Common Information Model and Architecture ( Reusable Components) 3. Platform Selection, Stock of Software components 4. Development Environment and Tools 5. Personal Productivity 34
Productivity of Software Vendor( Organization ) 1. Technology and Connoisseur 2. Common Information Model and Architecture ( Reusable Components) 3. Platform Selection, Stock of Software components 4. Development Environment and Tools 5. Personal Productivity 34
 Requirements to SE/SI group for analysis and design • Vision and insight to grasp business as a whole. • Foresight to depict what is essence and substantial. • Ability of abstraction , description and presentation. • Engineering ability to embody concept to products. 35
Requirements to SE/SI group for analysis and design • Vision and insight to grasp business as a whole. • Foresight to depict what is essence and substantial. • Ability of abstraction , description and presentation. • Engineering ability to embody concept to products. 35
 Project Management • Control of CQD(Cost, Quality and Delivery) Does work , do things right • Manage CQD, Technology, User support, Change management , Time in Market etc. Does contribute , do right things 36
Project Management • Control of CQD(Cost, Quality and Delivery) Does work , do things right • Manage CQD, Technology, User support, Change management , Time in Market etc. Does contribute , do right things 36
 Project Management • PMBOK(Project Management Body of Knowledge) 5 basic process group: Initiating. Planning, Executing, Controlling, Closing 9 knowledge areas: Integration, Scope, Time, Cost, Quality, Human Resource, Communications, Risk, Procurement, • PMP(Project Management Professional )qualification by PMI( Project Management Institute /USA) 37
Project Management • PMBOK(Project Management Body of Knowledge) 5 basic process group: Initiating. Planning, Executing, Controlling, Closing 9 knowledge areas: Integration, Scope, Time, Cost, Quality, Human Resource, Communications, Risk, Procurement, • PMP(Project Management Professional )qualification by PMI( Project Management Institute /USA) 37
 Note of project management • “Object oriented “ is a methodology effective only when project team well understands what is it. • Only the objects which intentionally developed for the purpose of reuse can be reused. • Water fall model can be applied to the objects small enough that one person can understand. • Take enough time before starting programming. • High technologies soon become consensus and low technologies in the next step. 38
Note of project management • “Object oriented “ is a methodology effective only when project team well understands what is it. • Only the objects which intentionally developed for the purpose of reuse can be reused. • Water fall model can be applied to the objects small enough that one person can understand. • Take enough time before starting programming. • High technologies soon become consensus and low technologies in the next step. 38
 Case Study • NTT Service front support system • Fujitsu Service Management system ( FLEXER –SM) 39
Case Study • NTT Service front support system • Fujitsu Service Management system ( FLEXER –SM) 39
 Target of Service Front Issues : • In the explosion of variety of services, heterogeneous technologies and competition • Urgent to Establish total customer center for any services and claims • By Realizing quick and accurate response to customers for 24/7/365 Kaizen : • Develop Business process and OSS to concentrate necessary information to service front operator -> networking • Training and team work reinforcement to operators 40
Target of Service Front Issues : • In the explosion of variety of services, heterogeneous technologies and competition • Urgent to Establish total customer center for any services and claims • By Realizing quick and accurate response to customers for 24/7/365 Kaizen : • Develop Business process and OSS to concentrate necessary information to service front operator -> networking • Training and team work reinforcement to operators 40
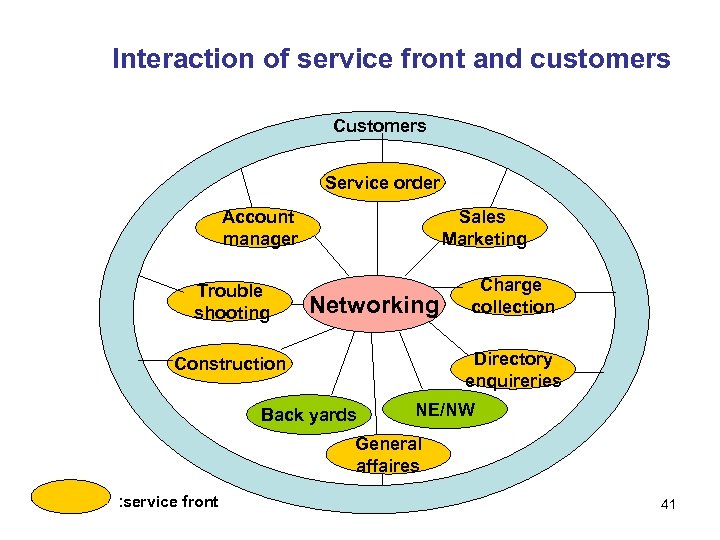 Interaction of service front and customers Customers Service order Account manager Trouble shooting Sales Marketing Networking Charge collection Directory enquireries Construction Back yards NE/NW General affaires : service front 41
Interaction of service front and customers Customers Service order Account manager Trouble shooting Sales Marketing Networking Charge collection Directory enquireries Construction Back yards NE/NW General affaires : service front 41
 Business process ( networking and organization) • Reform of “ 113” test center of service claims to total customer service center • Responsible HQ department create DB of service /products information accessible from any center operators. ( visual and text ) • Network status information is to be reported to /can be accessed by the operators for both intra office and nationwide events. • Share the knowledge and useful experiences among centers by email exchange, accumulate knowledge DB and help desk. • Rule based control of information handling for security. 42
Business process ( networking and organization) • Reform of “ 113” test center of service claims to total customer service center • Responsible HQ department create DB of service /products information accessible from any center operators. ( visual and text ) • Network status information is to be reported to /can be accessed by the operators for both intra office and nationwide events. • Share the knowledge and useful experiences among centers by email exchange, accumulate knowledge DB and help desk. • Rule based control of information handling for security. 42
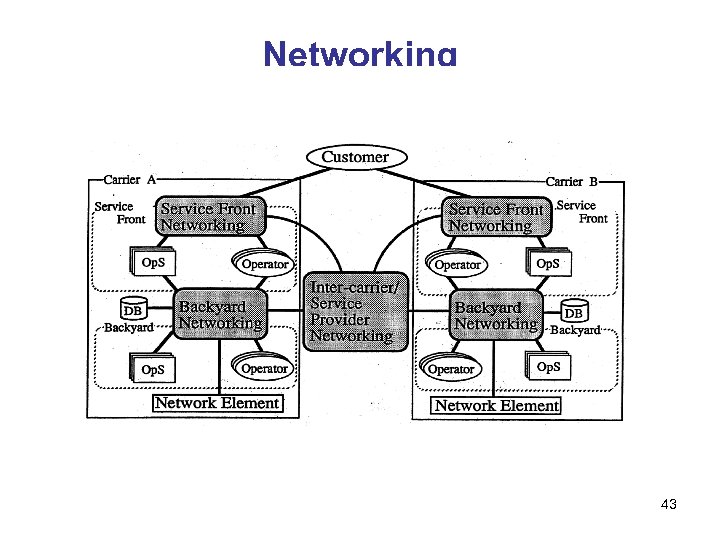 Networking 43
Networking 43
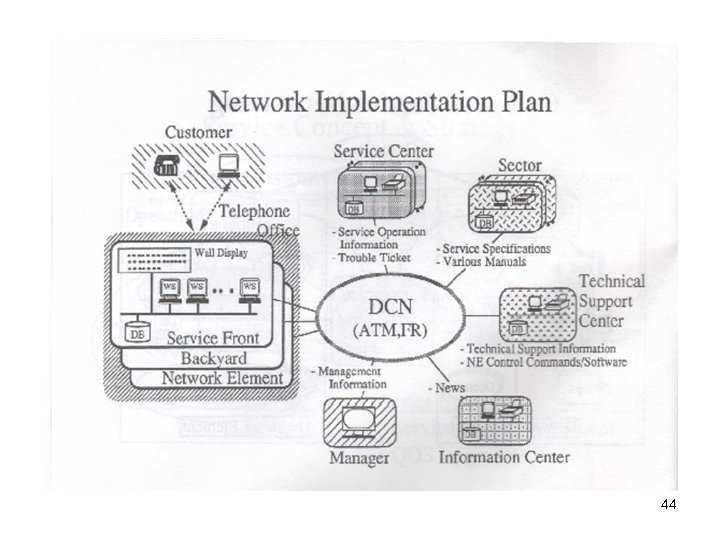 44
44
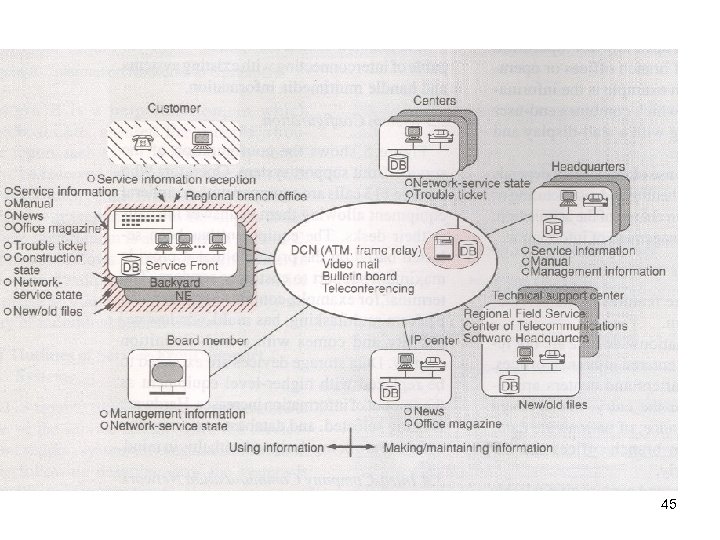 45
45
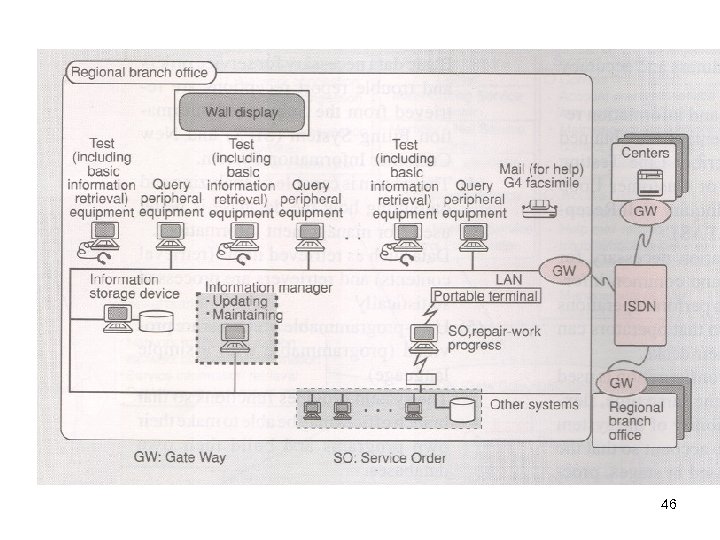 46
46
 OSS development • Received the order at April 1993 and introduced the OSS to 90 main centers at March 1994 • Process analysis , design and technology assessment for 6 months collaborating OSS developers and business practitioners( operators) • Software development for 6 months. Initial OSS cut off ( first introduction ) started January 1994. • Deploy Sun Solaris , embedded mail function and package middleware. • Deploy end user programmable GUI and local DB. 47
OSS development • Received the order at April 1993 and introduced the OSS to 90 main centers at March 1994 • Process analysis , design and technology assessment for 6 months collaborating OSS developers and business practitioners( operators) • Software development for 6 months. Initial OSS cut off ( first introduction ) started January 1994. • Deploy Sun Solaris , embedded mail function and package middleware. • Deploy end user programmable GUI and local DB. 47
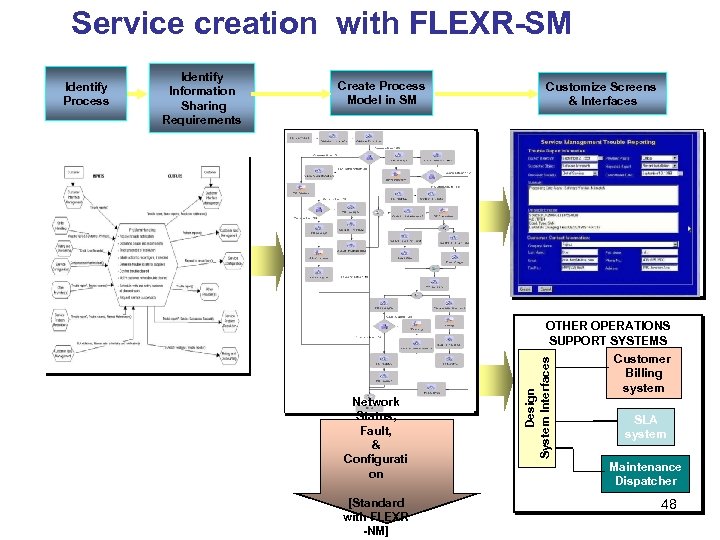 Service creation with FLEXR-SM Identify Information Sharing Requirements Create Process Model in SM Customize Screens & Interfaces OTHER OPERATIONS SUPPORT SYSTEMS Customer Billing system Network Status, Fault, & Configurati on [Standard with FLEXR -NM] Design System Interfaces Identify Process SLA system Maintenance Dispatcher 48
Service creation with FLEXR-SM Identify Information Sharing Requirements Create Process Model in SM Customize Screens & Interfaces OTHER OPERATIONS SUPPORT SYSTEMS Customer Billing system Network Status, Fault, & Configurati on [Standard with FLEXR -NM] Design System Interfaces Identify Process SLA system Maintenance Dispatcher 48
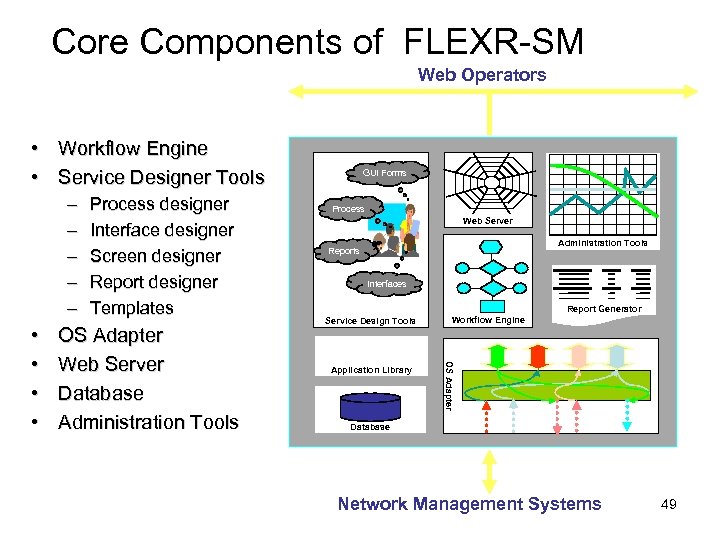 Core Components of FLEXR-SM Web Operators • Workflow Engine • Service Designer Tools – – – OS Adapter Web Server Database Administration Tools Process Web Server Administration Tools Reports Interfaces Report Generator Service Design Tools Application Library Workflow Engine OS Adapter • • Process designer Interface designer Screen designer Report designer Templates GUI Forms Database Network Management Systems 49
Core Components of FLEXR-SM Web Operators • Workflow Engine • Service Designer Tools – – – OS Adapter Web Server Database Administration Tools Process Web Server Administration Tools Reports Interfaces Report Generator Service Design Tools Application Library Workflow Engine OS Adapter • • Process designer Interface designer Screen designer Report designer Templates GUI Forms Database Network Management Systems 49
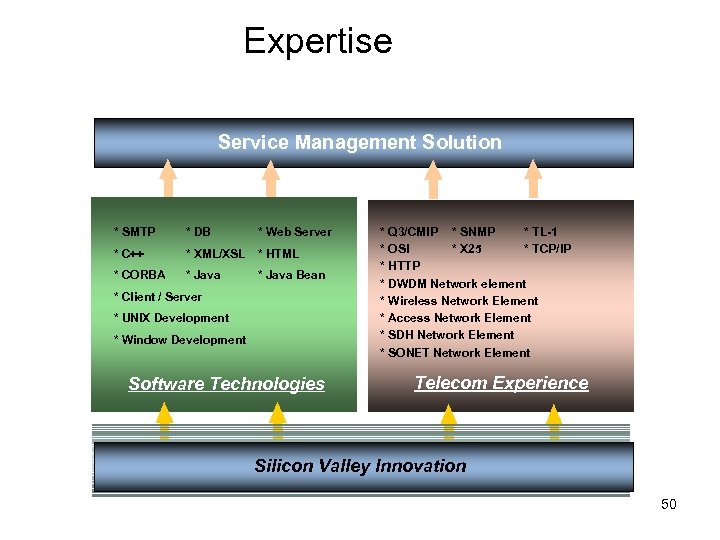 Expertise New Technology and Experience provide Flexible Solution Service Management Solution * SMTP * DB * Web Server * C++ * XML/XSL * HTML * CORBA * Java Bean * Client / Server * UNIX Development * Window Development Software Technologies * Q 3/CMIP * SNMP * TL-1 * OSI * X 25 * TCP/IP * HTTP * DWDM Network element * Wireless Network Element * Access Network Element * SDH Network Element * SONET Network Element Telecom Experience Silicon Valley Innovation 50
Expertise New Technology and Experience provide Flexible Solution Service Management Solution * SMTP * DB * Web Server * C++ * XML/XSL * HTML * CORBA * Java Bean * Client / Server * UNIX Development * Window Development Software Technologies * Q 3/CMIP * SNMP * TL-1 * OSI * X 25 * TCP/IP * HTTP * DWDM Network element * Wireless Network Element * Access Network Element * SDH Network Element * SONET Network Element Telecom Experience Silicon Valley Innovation 50
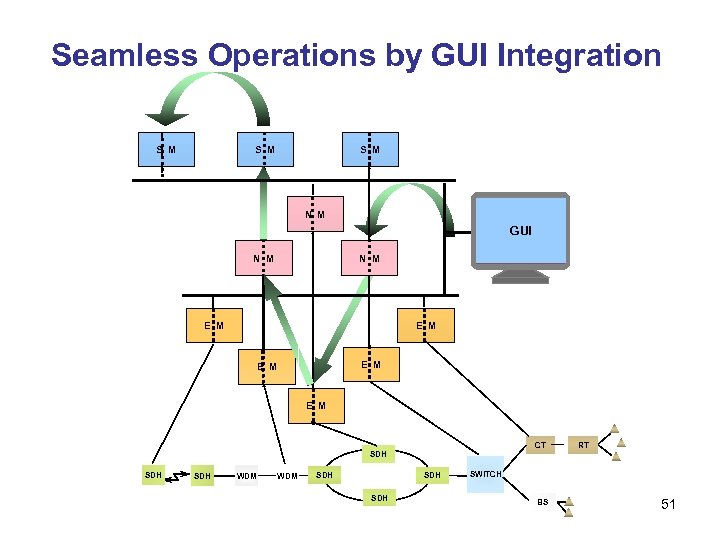 Seamless Operations by GUI Integration S M S M N M EM GUI NM Screen N M E M E M E M CT SDH SDH WDM SDH SDH RT SWITCH BS 51
Seamless Operations by GUI Integration S M S M N M EM GUI NM Screen N M E M E M E M CT SDH SDH WDM SDH SDH RT SWITCH BS 51
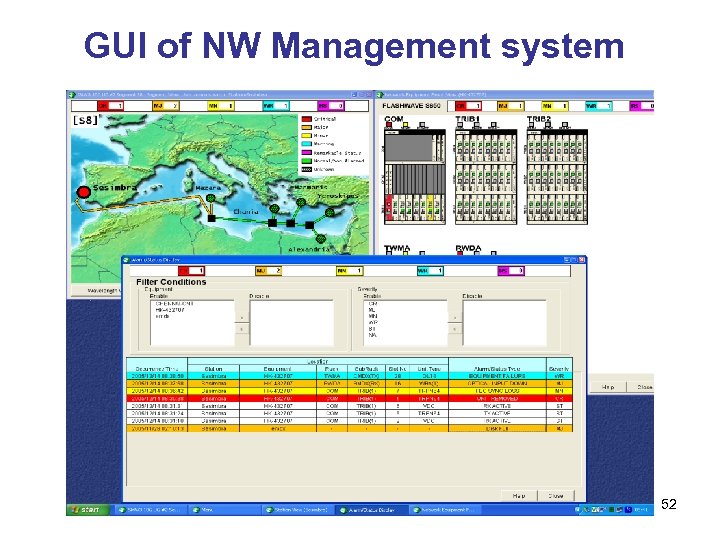 GUI of NW Management system 52
GUI of NW Management system 52
 Benefit to customer • Web-based Business Process Management System – Reduce Operators Skills / Training – Prevent Operators Mistakes (Enforce Procedures and Policies to ensure quality work ) – Coordination (Different People and Applications work together to do a task) • Process Monitor and Control for Customer Satisfaction – Process/application monitoring allows the operation to be streamlined – Work distribution among operators allows escalation and automatic distribution of tasks. • Fully integrated to Fujitsu NMS – Accurate Real-time Information of Network Condition and Inventory. • Flexible Integration to Other Systems / Applications – Seamless Information Flow between People, Application and Network – Extensible and Customizable Installation and Configuration 53
Benefit to customer • Web-based Business Process Management System – Reduce Operators Skills / Training – Prevent Operators Mistakes (Enforce Procedures and Policies to ensure quality work ) – Coordination (Different People and Applications work together to do a task) • Process Monitor and Control for Customer Satisfaction – Process/application monitoring allows the operation to be streamlined – Work distribution among operators allows escalation and automatic distribution of tasks. • Fully integrated to Fujitsu NMS – Accurate Real-time Information of Network Condition and Inventory. • Flexible Integration to Other Systems / Applications – Seamless Information Flow between People, Application and Network – Extensible and Customizable Installation and Configuration 53
 Proof of interoperability - TMF Catalyst Project • Business Challenges • Objectives • Benefit to Industry – Network Operators and Service Providers – Equipment Vendors – End Customers • Scenarios • Participants 54 Copyright © FUJITSU LIMITED, 1998
Proof of interoperability - TMF Catalyst Project • Business Challenges • Objectives • Benefit to Industry – Network Operators and Service Providers – Equipment Vendors – End Customers • Scenarios • Participants 54 Copyright © FUJITSU LIMITED, 1998
 Catalyst Project Teams • Common Interconnect Gateway Platform • Connection Management • Customer-Provided Trouble Ticket Management • Plug & Play End-to-End Service Assurance • Plug & Play Service Fulfillment 55
Catalyst Project Teams • Common Interconnect Gateway Platform • Connection Management • Customer-Provided Trouble Ticket Management • Plug & Play End-to-End Service Assurance • Plug & Play Service Fulfillment 55
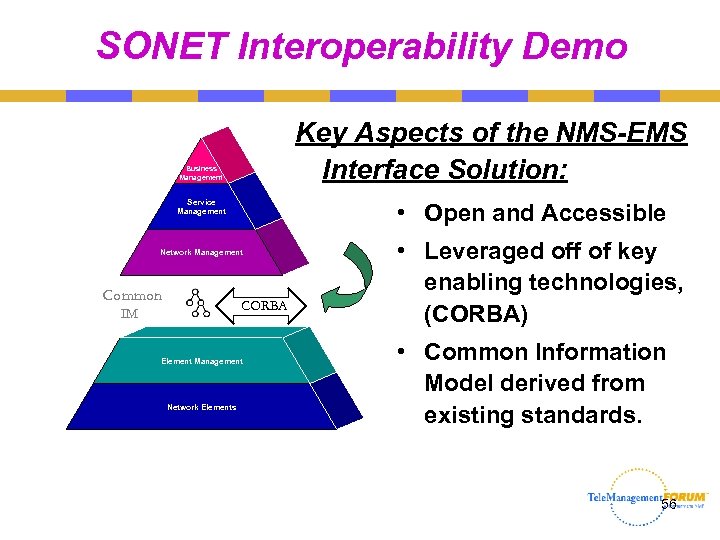 SONET Interoperability Demo Key Aspects of the NMS-EMS Interface Solution: Business Management Service Management • Open and Accessible Network Management Common CORBA IM Element Management Network Elements • Leveraged off of key enabling technologies, (CORBA) • Common Information Model derived from existing standards. 56
SONET Interoperability Demo Key Aspects of the NMS-EMS Interface Solution: Business Management Service Management • Open and Accessible Network Management Common CORBA IM Element Management Network Elements • Leveraged off of key enabling technologies, (CORBA) • Common Information Model derived from existing standards. 56
 SONET Interoperability Demo • Objective: Enable Network Manageability of Complex SONET Networks Composed of Multi-Vendor, Multi-Technology, Heterogeneous Equipment. • Solution: Define Common, Open Interface at the NMLEML Reference Point. • Demonstration: Illustrate End-to-End Connection Management across a real SONET network 57
SONET Interoperability Demo • Objective: Enable Network Manageability of Complex SONET Networks Composed of Multi-Vendor, Multi-Technology, Heterogeneous Equipment. • Solution: Define Common, Open Interface at the NMLEML Reference Point. • Demonstration: Illustrate End-to-End Connection Management across a real SONET network 57
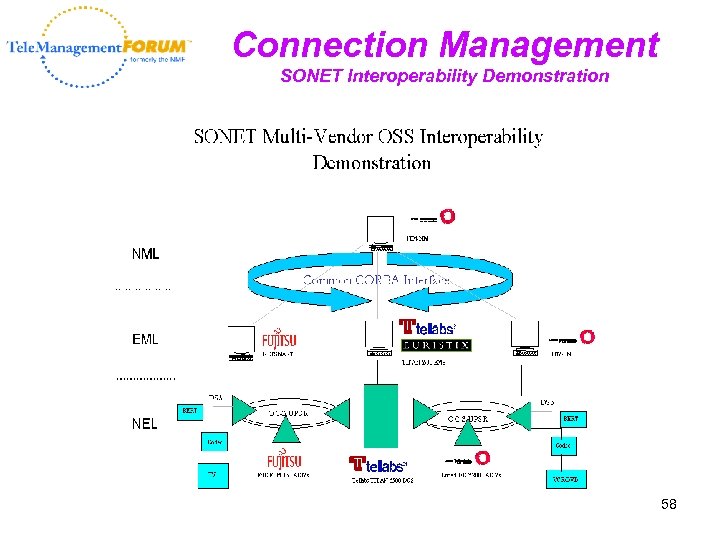 Connection Management SONET Interoperability Demonstration 58
Connection Management SONET Interoperability Demonstration 58
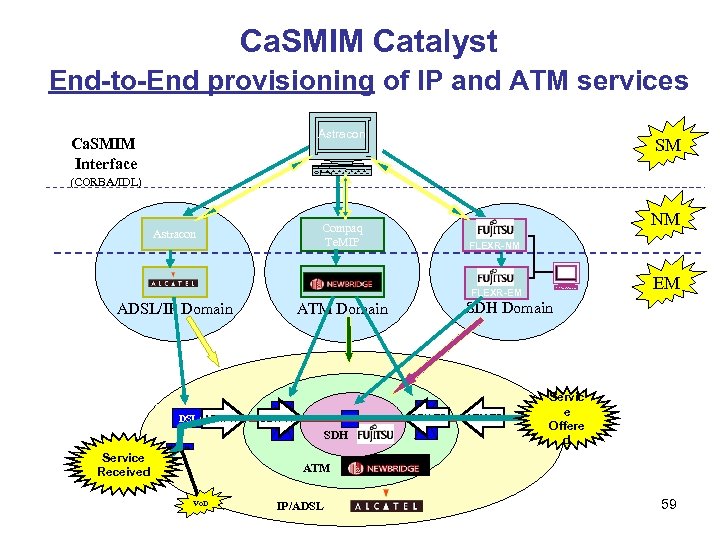 Ca. SMIM Catalyst End-to-End provisioning of of IP and ATM End-to-End provisioning IP and ATM services Astracon Ca. SMIM Interface SM (CORBA/IDL) NM Compaq Te. MIP Astracon FLEXR-NM EM FLEXR-EM ADSL/IP Domain DSLAM TP ATM SDH TP SDH Modem Service IP Web TP Received SDH Domain ATM TP Servic e IP ISPTP Offere d ATM Vo. D IP/ADSL 59
Ca. SMIM Catalyst End-to-End provisioning of of IP and ATM End-to-End provisioning IP and ATM services Astracon Ca. SMIM Interface SM (CORBA/IDL) NM Compaq Te. MIP Astracon FLEXR-NM EM FLEXR-EM ADSL/IP Domain DSLAM TP ATM SDH TP SDH Modem Service IP Web TP Received SDH Domain ATM TP Servic e IP ISPTP Offere d ATM Vo. D IP/ADSL 59
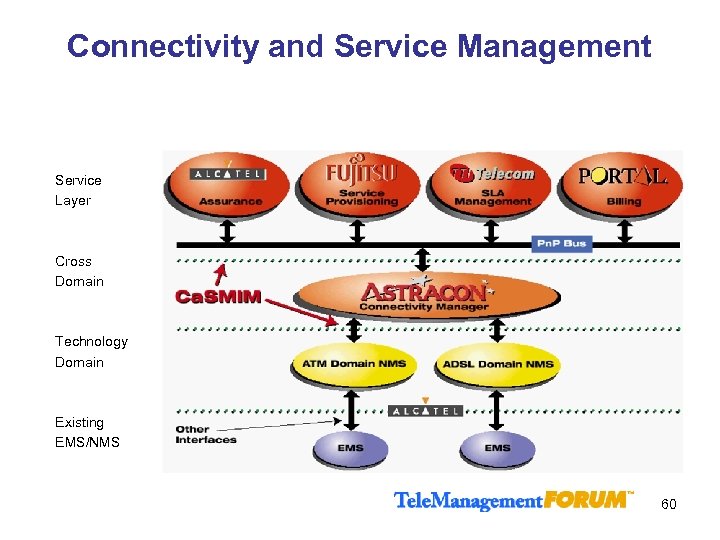 Connectivity and Service Management Service Layer Cross Domain Technology Domain Existing EMS/NMS 60
Connectivity and Service Management Service Layer Cross Domain Technology Domain Existing EMS/NMS 60
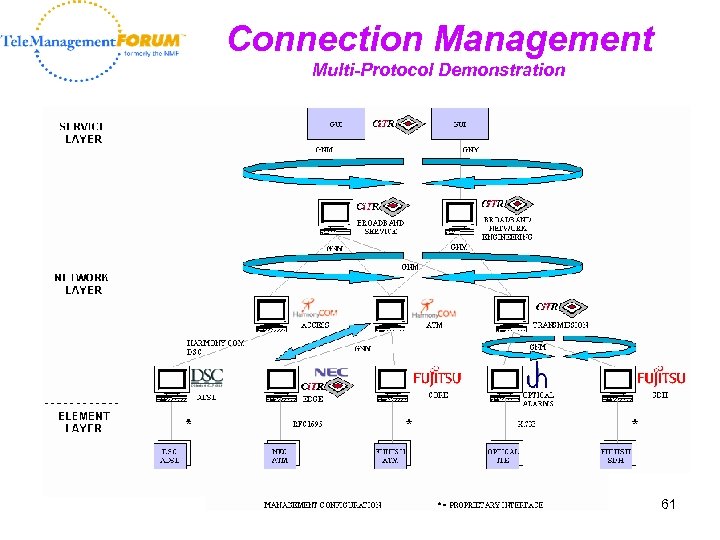 Connection Management Multi-Protocol Demonstration 61
Connection Management Multi-Protocol Demonstration 61


