8d81294e33662c8d8d5c9d1432c5bdf6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 104
 Post World War II Cold War (1945 – 1989) • Korean War (1950 – 1953) • Civil Rights Era (1945 – 1975) • Vietnam Era (1954 – 1976)
Post World War II Cold War (1945 – 1989) • Korean War (1950 – 1953) • Civil Rights Era (1945 – 1975) • Vietnam Era (1954 – 1976)
 Post WWII n GI Bill of Rights ¡ “government issue” ¡ 1944 Congressional act which gave veterans money to spend on businesses, homes, and schooling n n Helped more than 2 million former soldiers attend college to prepare for new careers Baby Boom ¡ Increased birthrate following WWII
Post WWII n GI Bill of Rights ¡ “government issue” ¡ 1944 Congressional act which gave veterans money to spend on businesses, homes, and schooling n n Helped more than 2 million former soldiers attend college to prepare for new careers Baby Boom ¡ Increased birthrate following WWII
 Post WWII n Philippines ¡ n 1946, U. S. gave Filipinos their independence State of Israel ¡ May 14, 1948 n an independent nation
Post WWII n Philippines ¡ n 1946, U. S. gave Filipinos their independence State of Israel ¡ May 14, 1948 n an independent nation
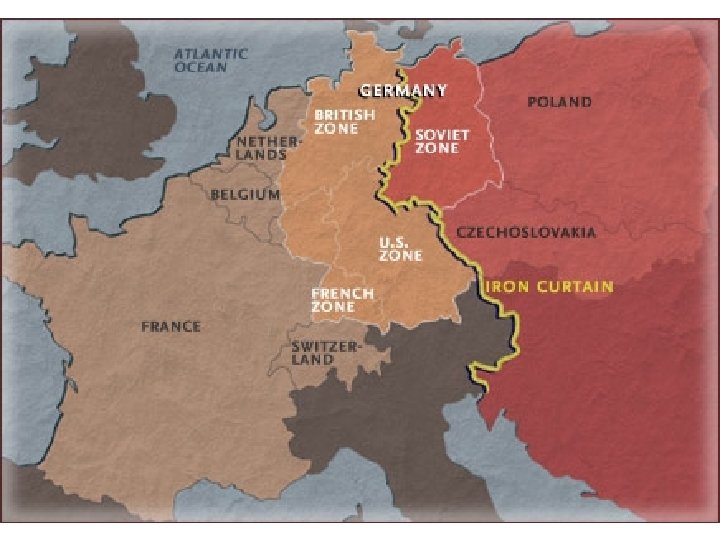
 WWII – Review n Yalta Conference ¡ Allies agreed to divide Germany & Berlin into 4 zones controlled by Americans, British, French & Soviets ¡ Stalin promised to hold free elections in parts of Eastern Europe under his control
WWII – Review n Yalta Conference ¡ Allies agreed to divide Germany & Berlin into 4 zones controlled by Americans, British, French & Soviets ¡ Stalin promised to hold free elections in parts of Eastern Europe under his control
 Atlantic Charter – Review n Franklin Roosevelt and Winston Churchill agreed to seek no territorial gain from the war n FDR and Churchill pledged to support the “right of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they will live. ” (self-determination) n The Charter called for a “permanent system of general security, ” such as an organization like the League of Nations (United Nations)
Atlantic Charter – Review n Franklin Roosevelt and Winston Churchill agreed to seek no territorial gain from the war n FDR and Churchill pledged to support the “right of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they will live. ” (self-determination) n The Charter called for a “permanent system of general security, ” such as an organization like the League of Nations (United Nations)
 Post WWII n United Nations ¡ ¡ ¡ June 26, 1945 Keep the peace Gather food & supplies for needy nations Homes for war victims Help developing nations with problems of health, farming, and education
Post WWII n United Nations ¡ ¡ ¡ June 26, 1945 Keep the peace Gather food & supplies for needy nations Homes for war victims Help developing nations with problems of health, farming, and education
 Post WWII n United Nations ¡ General Assembly n ¡ No way to enforce decisions Security Council n n More powerful 15 members ¡ 5 permanent members n U. S. , Russia, China, Britain, France n If only one permanent member vetoes, Security Council cannot act
Post WWII n United Nations ¡ General Assembly n ¡ No way to enforce decisions Security Council n n More powerful 15 members ¡ 5 permanent members n U. S. , Russia, China, Britain, France n If only one permanent member vetoes, Security Council cannot act
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Truman (like FDR) believed in self-determination ¡ U. S. demanded free elections be held throughout Eastern Europe n n Much was occupied by the Soviet Union Stalin promised to allow free elections, but went back on his word after WWII ¡ He wanted military security for the Soviet Union, and for his country to be the dominant world power
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Truman (like FDR) believed in self-determination ¡ U. S. demanded free elections be held throughout Eastern Europe n n Much was occupied by the Soviet Union Stalin promised to allow free elections, but went back on his word after WWII ¡ He wanted military security for the Soviet Union, and for his country to be the dominant world power
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n n Ideological conflict ¡ Fought with words & ideas Primarily between U. S. and Soviet Union Communism vs. Democracy Dominated world politics
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n n Ideological conflict ¡ Fought with words & ideas Primarily between U. S. and Soviet Union Communism vs. Democracy Dominated world politics
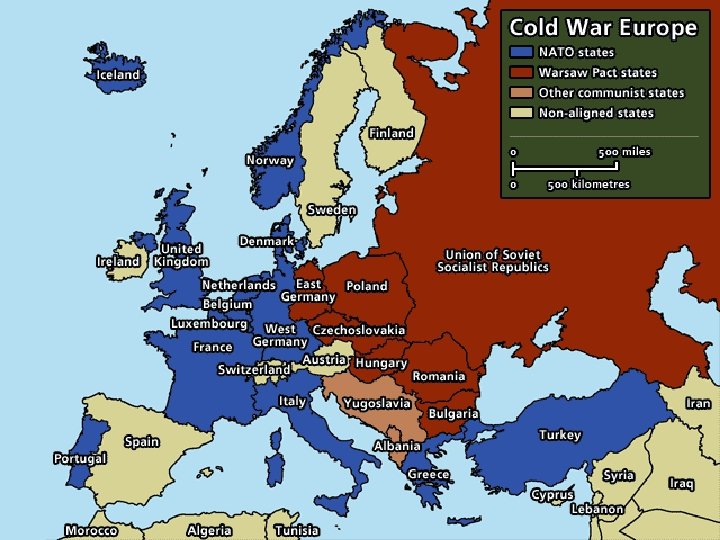
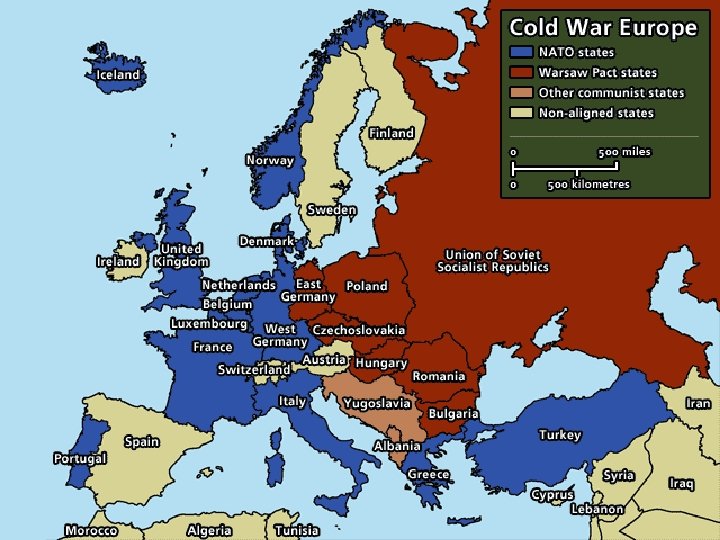
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n International Organizations ¡ United Nations ¡ NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) n n n ¡ April 1949 U. S. and other Western nations Military alliance – collective defense against a Soviet attack Warsaw Pact n n 1955 Soviet Union and satellite nations
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n International Organizations ¡ United Nations ¡ NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) n n n ¡ April 1949 U. S. and other Western nations Military alliance – collective defense against a Soviet attack Warsaw Pact n n 1955 Soviet Union and satellite nations
 Cold War 1945 – 1989
Cold War 1945 – 1989
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n “A freely elected government in any of the Eastern European countries would be anti-Soviet, and that we cannot allow. ” – Josef Stalin n By 1948, the government of most nations in Eastern Europe were satellites of Soviet Union ¡ Nations dominated politically or economically by a more powerful nation
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n “A freely elected government in any of the Eastern European countries would be anti-Soviet, and that we cannot allow. ” – Josef Stalin n By 1948, the government of most nations in Eastern Europe were satellites of Soviet Union ¡ Nations dominated politically or economically by a more powerful nation
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Winston Churchill ¡ ¡ Warned Americans of the Soviet threat in a speech on March 5, 1946, at Westminster College in Fulton, MO An “iron curtain has descended across the continent”, walling off Soviet-dominated nations from the rest of the world
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Winston Churchill ¡ ¡ Warned Americans of the Soviet threat in a speech on March 5, 1946, at Westminster College in Fulton, MO An “iron curtain has descended across the continent”, walling off Soviet-dominated nations from the rest of the world
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Truman Doctrine ¡ March 1947 ¡ Containment n Limit or block expansion of Soviet Communism
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Truman Doctrine ¡ March 1947 ¡ Containment n Limit or block expansion of Soviet Communism
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Marshall Plan ¡ ¡ ¡ June 1947 Proposed by Secy. of State George Marshall Provided money to help European nations rebuild after WWII n ¡ Factories, schools, hospitals, railroads, bridges, farms Huge success n 1948 -1951, U. S. loaned >$12 billion to Western European countries 16
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Marshall Plan ¡ ¡ ¡ June 1947 Proposed by Secy. of State George Marshall Provided money to help European nations rebuild after WWII n ¡ Factories, schools, hospitals, railroads, bridges, farms Huge success n 1948 -1951, U. S. loaned >$12 billion to Western European countries 16
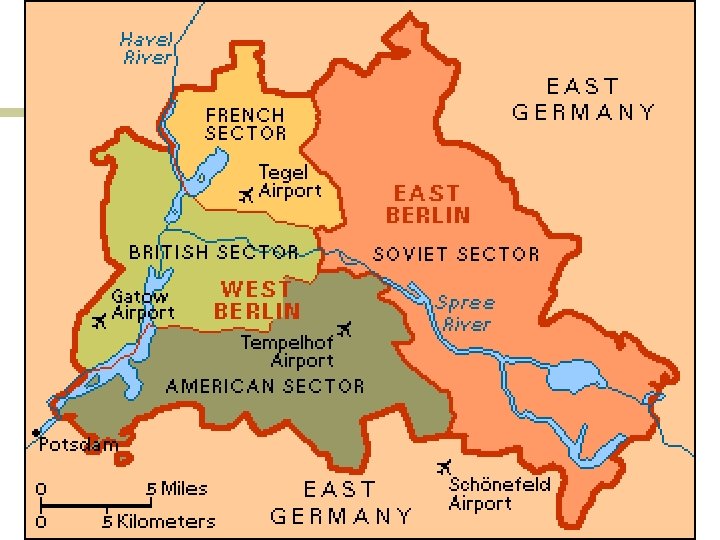
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Germany & Berlin ¡ Divided into 4 parts n East Germany – Communist ¡ Soviet Union n West Germany – Democracy ¡ Great Britain ¡ France ¡ U. S.
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Germany & Berlin ¡ Divided into 4 parts n East Germany – Communist ¡ Soviet Union n West Germany – Democracy ¡ Great Britain ¡ France ¡ U. S.
 Cold War 1945 – 1989
Cold War 1945 – 1989
 Cold War 1945 – 1989
Cold War 1945 – 1989
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n n n Western powers decided it was time to reunite Germany in 1948, but Stalin was opposed June 1948, Soviets set up a blockade around Berlin and prevented delivery of Allied supplies Berlin Airlift ¡ ¡ n Cargo planes delivered tons of food and supplies to 2 M people in West Berlin >200, 000 flights from June 1948 – May 1949, Soviets call off blockade
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n n n Western powers decided it was time to reunite Germany in 1948, but Stalin was opposed June 1948, Soviets set up a blockade around Berlin and prevented delivery of Allied supplies Berlin Airlift ¡ ¡ n Cargo planes delivered tons of food and supplies to 2 M people in West Berlin >200, 000 flights from June 1948 – May 1949, Soviets call off blockade
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) Berlin Airlift
Cold War (1945 – 1989) Berlin Airlift
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n n October 1949, U. S. , Britain, & France combine their zones into one country – West Germany A divided Germany and Berlin remained a focus of Cold War tensions Between 1949 and 1961, thousands of East Germans fled to West Berlin, then into West Germany Berlin Wall ¡ ¡ ¡ Built in August 1961 Separated East and West Germany Stood for 28 years as a symbol of a divided Germany and Europe
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n n October 1949, U. S. , Britain, & France combine their zones into one country – West Germany A divided Germany and Berlin remained a focus of Cold War tensions Between 1949 and 1961, thousands of East Germans fled to West Berlin, then into West Germany Berlin Wall ¡ ¡ ¡ Built in August 1961 Separated East and West Germany Stood for 28 years as a symbol of a divided Germany and Europe
 Berlin Wall
Berlin Wall
 Berlin Wall
Berlin Wall
 Berlin Wall Westminster College Fulton, MO
Berlin Wall Westminster College Fulton, MO
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Election of 1948 ¡ Chicago Tribune mistakenly declared Thomas Dewey the winner over Harry Truman
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Election of 1948 ¡ Chicago Tribune mistakenly declared Thomas Dewey the winner over Harry Truman
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n People’s Republic of China ¡ In late 1949, Chinese Communists take control of China ¡ Mao Zedong – leader
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n People’s Republic of China ¡ In late 1949, Chinese Communists take control of China ¡ Mao Zedong – leader
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Election of 1952 ¡ ¡ ¡ Truman decides not to run Democrat Adlai Stevenson, Gov. of IL Dwight D. Eisenhower Republican war hero n n “I like Ike” Landslide victory
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Election of 1952 ¡ ¡ ¡ Truman decides not to run Democrat Adlai Stevenson, Gov. of IL Dwight D. Eisenhower Republican war hero n n “I like Ike” Landslide victory
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ 1950 s n People live longer thanks to new medicines (antibiotics) and polio vaccine n Suburbs grew by 50% ¡ n Poor & less educated stayed in inner cities By end of decade: ¡ ¡ ¡ 6 of 10 families owned homes 3 out of 4 had cars Almost every home had a TV
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ 1950 s n People live longer thanks to new medicines (antibiotics) and polio vaccine n Suburbs grew by 50% ¡ n Poor & less educated stayed in inner cities By end of decade: ¡ ¡ ¡ 6 of 10 families owned homes 3 out of 4 had cars Almost every home had a TV
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ 1950 s n Television ¡ ¡ ¡ n I Love Lucy, most popular show Howdy Doody popular with kids Frozen dinners Rock-and-Roll ¡ ¡ Elvis Presley, “The King” “Rock Around the Clock” by Bill Haley and the Comets
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ 1950 s n Television ¡ ¡ ¡ n I Love Lucy, most popular show Howdy Doody popular with kids Frozen dinners Rock-and-Roll ¡ ¡ Elvis Presley, “The King” “Rock Around the Clock” by Bill Haley and the Comets
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Dwight D. Eisenhower ¡ President 1953 -1961 ¡ Vice President – Richard Nixon ¡ Interstate Highway Act of 1956 n One of Eisenhower’s greatest achievements
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Dwight D. Eisenhower ¡ President 1953 -1961 ¡ Vice President – Richard Nixon ¡ Interstate Highway Act of 1956 n One of Eisenhower’s greatest achievements
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) Korean War (1950 – 1953) • Officially a “police action, ” not a war
Cold War (1945 – 1989) Korean War (1950 – 1953) • Officially a “police action, ” not a war
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean Peninsula ¡ Occupied & ruled harshly by Japan since 1910 n After Japan’s defeat in WWII, Korea was divided at the 38 th parallel latitude n North Korean troops invaded South Korea ¡ June 25, 1950
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean Peninsula ¡ Occupied & ruled harshly by Japan since 1910 n After Japan’s defeat in WWII, Korea was divided at the 38 th parallel latitude n North Korean troops invaded South Korea ¡ June 25, 1950
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 - 1953 ¡ North Korea (communist) n ¡ Helped by Communist China and backed by Soviet Union South Korea (non-communist) n Helped by United Nations and backed by the U. S.
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 - 1953 ¡ North Korea (communist) n ¡ Helped by Communist China and backed by Soviet Union South Korea (non-communist) n Helped by United Nations and backed by the U. S.
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ War against communism ¡ U. N. voted to send military troops – 90% were American ¡ Pres. Truman appointed Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur to lead the troops
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ War against communism ¡ U. N. voted to send military troops – 90% were American ¡ Pres. Truman appointed Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur to lead the troops
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ North Korea invaded South Korea and occupied most of the peninsula ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur and UN forces counterattacked, pushing North Koreans back across the 38 th parallel ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur continues into North Korea, almost to China n UN goal was to reunify Korea
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ North Korea invaded South Korea and occupied most of the peninsula ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur and UN forces counterattacked, pushing North Koreans back across the 38 th parallel ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur continues into North Korea, almost to China n UN goal was to reunify Korea
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Angered Chinese government sent troops to assist North Korea n ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur wanted to attack China n ¡ China pushed UN forces beyond the 38 th parallel and back into South Korea and the war became a stalemate He believed this was the only way to win the Korean War Pres. Truman did not want to attack China n He feared this might lead to another world war
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Angered Chinese government sent troops to assist North Korea n ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur wanted to attack China n ¡ China pushed UN forces beyond the 38 th parallel and back into South Korea and the war became a stalemate He believed this was the only way to win the Korean War Pres. Truman did not want to attack China n He feared this might lead to another world war
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur publicly called for the bombing of China ¡ Pres. Truman warned Gen. Mac. Arthur against making further public statements ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur disregarded Pres. Truman’s warnings n ¡ Mac. Arthur publicly argued that he could not win the war because of Washington politicians A furious Pres. Truman fired Gen. Mac. Arthur
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur publicly called for the bombing of China ¡ Pres. Truman warned Gen. Mac. Arthur against making further public statements ¡ Gen. Mac. Arthur disregarded Pres. Truman’s warnings n ¡ Mac. Arthur publicly argued that he could not win the war because of Washington politicians A furious Pres. Truman fired Gen. Mac. Arthur
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Peace talks began in July 1953, but fighting continued ¡ Fighting ended in July 1953 with a cease-fire ¡ The border between North and South Korea is almost exactly where it was before the war n ¡ Tensions between North and South Korea continue today North and South Korea agreed to establish a demilitarized zone n An area from which military forces are prohibited
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Peace talks began in July 1953, but fighting continued ¡ Fighting ended in July 1953 with a cease-fire ¡ The border between North and South Korea is almost exactly where it was before the war n ¡ Tensions between North and South Korea continue today North and South Korea agreed to establish a demilitarized zone n An area from which military forces are prohibited
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Korea was the first attempt by the U. S. to stop communism in Asia n n 2 M Koreans died, mostly civilians 30, 000 Americans died & thousands from other nations ¡ Officially, it was a “police action, ” not a war ¡ Korea is the last communist hot spot n It developed nuclear weapons at the beginning of the 21 st century
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Korean War: 1950 – 1953 ¡ Korea was the first attempt by the U. S. to stop communism in Asia n n 2 M Koreans died, mostly civilians 30, 000 Americans died & thousands from other nations ¡ Officially, it was a “police action, ” not a war ¡ Korea is the last communist hot spot n It developed nuclear weapons at the beginning of the 21 st century
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Red scare in America ¡ Many Americans fear Communist sympathizers and spies might be secretly working to overthrow the U. S. government
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Red scare in America ¡ Many Americans fear Communist sympathizers and spies might be secretly working to overthrow the U. S. government
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Alger Hiss ¡ Former State Dept. official ¡ Accused of passing government secrets to Soviet agents in 1930 s n ¡ The “pumpkin papers” Convicted of perjury, spent several years in prison
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Alger Hiss ¡ Former State Dept. official ¡ Accused of passing government secrets to Soviet agents in 1930 s n ¡ The “pumpkin papers” Convicted of perjury, spent several years in prison
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Julius and Ethel Rosenberg ¡ Found guilty of passing secrets of the atomic bomb to Soviets ¡ Sentenced to death and executed in 1953
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Julius and Ethel Rosenberg ¡ Found guilty of passing secrets of the atomic bomb to Soviets ¡ Sentenced to death and executed in 1953
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n U. S. government released papers in 1990 s indicating that Hiss and the Rosenbergs had been spies
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n U. S. government released papers in 1990 s indicating that Hiss and the Rosenbergs had been spies
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy ¡ Built his career by exposing alleged Communists in U. S. government ¡ Without evidence, sensationally accused people of being Communists ¡ Many Americans were eager to believe him
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Senator Joseph Mc. Carthy ¡ Built his career by exposing alleged Communists in U. S. government ¡ Without evidence, sensationally accused people of being Communists ¡ Many Americans were eager to believe him
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ ¡ n Mc. Carthy bullied witnesses before his Senate committee and made exaggerated charges He ruined many lives and careers Mc. Carthyism ¡ Accusing someone of disloyalty without having any evidence
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ ¡ n Mc. Carthy bullied witnesses before his Senate committee and made exaggerated charges He ruined many lives and careers Mc. Carthyism ¡ Accusing someone of disloyalty without having any evidence
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Nikita Khrushchev ¡ 1953, became leader of Soviet Union when Josef Stalin died ¡ Predicted Communism would destroy Western democracies
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Nikita Khrushchev ¡ 1953, became leader of Soviet Union when Josef Stalin died ¡ Predicted Communism would destroy Western democracies
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n U. S. and Soviet Union began arms race ¡ n Contest in which nations compete to build powerful weapons U. S. exploded first hydrogen bomb in 1952 (H-bomb) ¡ Followed in next few years by Soviet Union, China, United Kingdom, and France
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n U. S. and Soviet Union began arms race ¡ n Contest in which nations compete to build powerful weapons U. S. exploded first hydrogen bomb in 1952 (H-bomb) ¡ Followed in next few years by Soviet Union, China, United Kingdom, and France
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Sputnik I ¡ Launched October 4, 1957 by Soviet Union ¡ World’s 1 st artificial satellite ¡ 1 st man-made object to orbit the Earth n n ¡ 184 lbs. About the size of a basketball Took about 98 minutes to orbit the Earth at 18, 000 mph
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Sputnik I ¡ Launched October 4, 1957 by Soviet Union ¡ World’s 1 st artificial satellite ¡ 1 st man-made object to orbit the Earth n n ¡ 184 lbs. About the size of a basketball Took about 98 minutes to orbit the Earth at 18, 000 mph
 Sputnik I – launched by Soviet Union
Sputnik I – launched by Soviet Union
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Start of the Space Age and the – U. S. S. R. space race ¡ n U. S. Control outer space Led directly to creation of NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Admin. )
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Start of the Space Age and the – U. S. S. R. space race ¡ n U. S. Control outer space Led directly to creation of NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Admin. )
 Cold War 1945 - 1989 • Explorer I Launched by the U. S. January 31, 1958 ¡ 1 st U. S. satellite ¡ Officially known as Satellite 1958 Alpha ¡ 30. 66 lbs.
Cold War 1945 - 1989 • Explorer I Launched by the U. S. January 31, 1958 ¡ 1 st U. S. satellite ¡ Officially known as Satellite 1958 Alpha ¡ 30. 66 lbs.
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Fidel Castro ¡ Communist ¡ In a 1959 revolution, took control of Cuba ¡ U. S. glad to see Fulgencio Batista ousted ¡ Castro took land belonging to American companies ¡ U. S. started a trade embargo against Cuba
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Fidel Castro ¡ Communist ¡ In a 1959 revolution, took control of Cuba ¡ U. S. glad to see Fulgencio Batista ousted ¡ Castro took land belonging to American companies ¡ U. S. started a trade embargo against Cuba
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Castro asked Soviet Union for help ¡ People left Cuba for the U. S. ¡ In April 1961, Cuban exiles returned with U. S. support n n ¡ Landed at Bay of Pigs Invasion failed, many were captured U. S. – Cuban government relations strained
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Castro asked Soviet Union for help ¡ People left Cuba for the U. S. ¡ In April 1961, Cuban exiles returned with U. S. support n n ¡ Landed at Bay of Pigs Invasion failed, many were captured U. S. – Cuban government relations strained
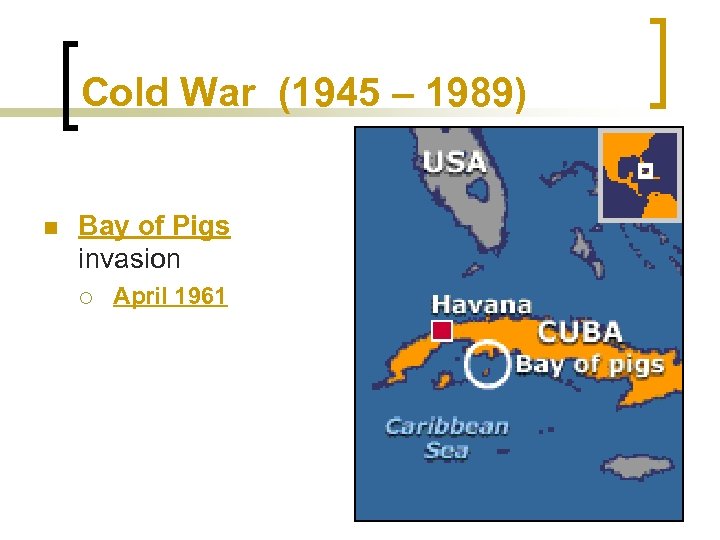 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Bay of Pigs invasion ¡ April 1961
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Bay of Pigs invasion ¡ April 1961
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Election of 1960 ¡ Richard M. Nixon n ¡ Vice President & Republican candidate John F. Kennedy n n Democrat candidate Narrowly wins election ¡ Vice President – Lyndon Johnson
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Election of 1960 ¡ Richard M. Nixon n ¡ Vice President & Republican candidate John F. Kennedy n n Democrat candidate Narrowly wins election ¡ Vice President – Lyndon Johnson
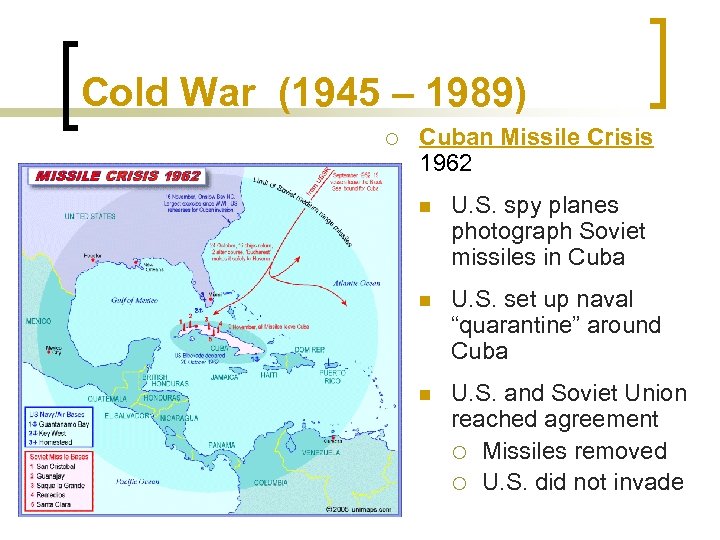 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Cuban Missile Crisis 1962 n U. S. spy planes photograph Soviet missiles in Cuba n U. S. set up naval “quarantine” around Cuba n U. S. and Soviet Union reached agreement ¡ Missiles removed ¡ U. S. did not invade
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Cuban Missile Crisis 1962 n U. S. spy planes photograph Soviet missiles in Cuba n U. S. set up naval “quarantine” around Cuba n U. S. and Soviet Union reached agreement ¡ Missiles removed ¡ U. S. did not invade
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) Vietnam Era • Officially a “conflict, ” not a war
Cold War (1945 – 1989) Vietnam Era • Officially a “conflict, ” not a war
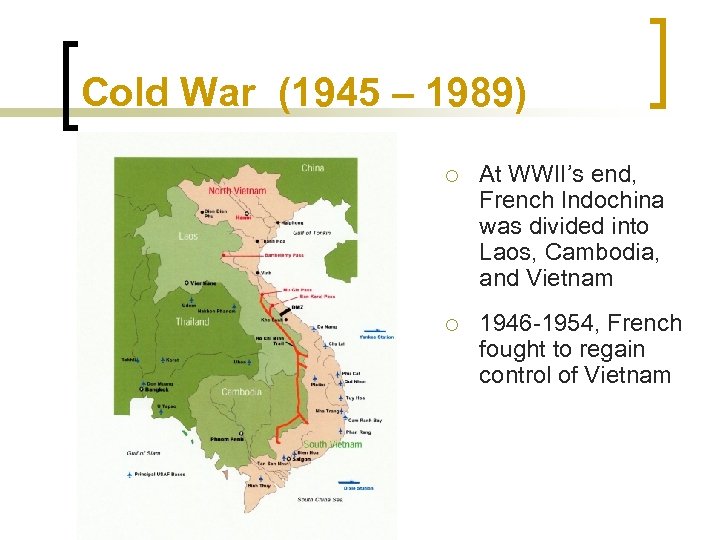 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ At WWII’s end, French Indochina was divided into Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam ¡ 1946 -1954, French fought to regain control of Vietnam
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ At WWII’s end, French Indochina was divided into Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam ¡ 1946 -1954, French fought to regain control of Vietnam
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Ho Chi Minh drove out the French and set up a Communist government in northern Vietnam ¡ Vietnam became divided into North and South, and civil war broke out
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Ho Chi Minh drove out the French and set up a Communist government in northern Vietnam ¡ Vietnam became divided into North and South, and civil war broke out
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n U. S. political leaders feared Communist takeover in Southeast Asia n Domino theory ¡ If one country fell to the Communists, neighboring countries would follow
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n U. S. political leaders feared Communist takeover in Southeast Asia n Domino theory ¡ If one country fell to the Communists, neighboring countries would follow
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ U. S. sent money and weapons to South Vietnam, and trained its soldiers ¡ U. S. advisers began fighting in Vietnam ¡ Guerrilla warfare fighters for the North came to be called the Vietcong n Supported by Soviet Union and China with arms and supplies
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ U. S. sent money and weapons to South Vietnam, and trained its soldiers ¡ U. S. advisers began fighting in Vietnam ¡ Guerrilla warfare fighters for the North came to be called the Vietcong n Supported by Soviet Union and China with arms and supplies
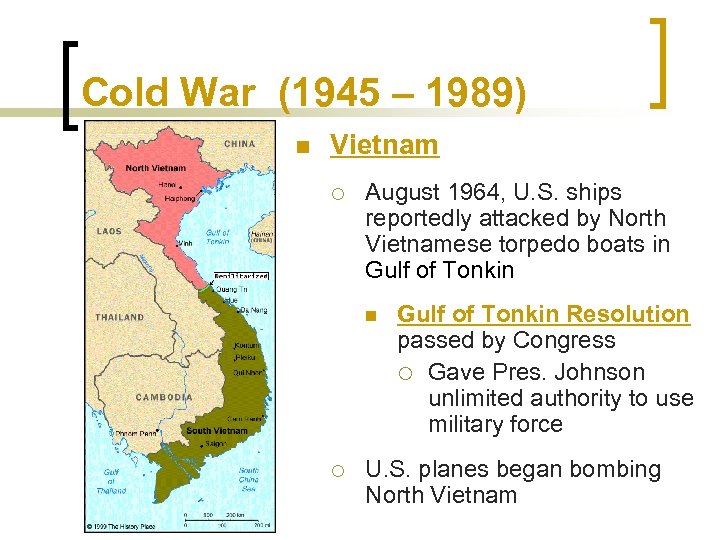 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ August 1964, U. S. ships reportedly attacked by North Vietnamese torpedo boats in Gulf of Tonkin n ¡ Gulf of Tonkin Resolution passed by Congress ¡ Gave Pres. Johnson unlimited authority to use military force U. S. planes began bombing North Vietnam
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ August 1964, U. S. ships reportedly attacked by North Vietnamese torpedo boats in Gulf of Tonkin n ¡ Gulf of Tonkin Resolution passed by Congress ¡ Gave Pres. Johnson unlimited authority to use military force U. S. planes began bombing North Vietnam
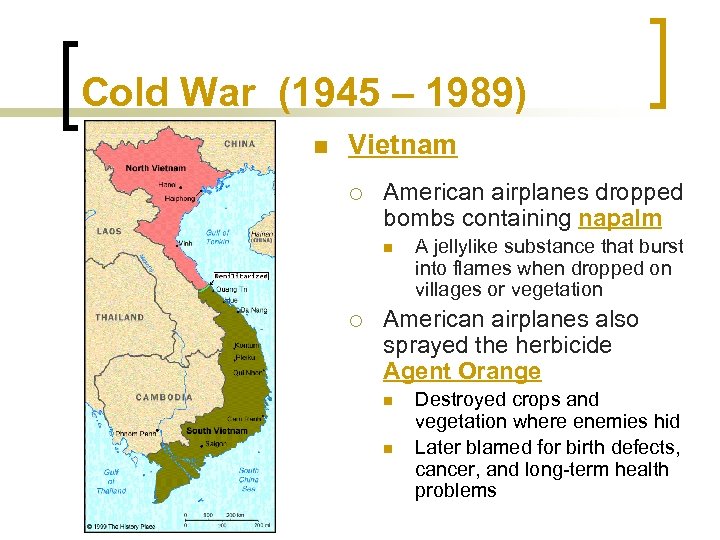 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ American airplanes dropped bombs containing napalm n ¡ A jellylike substance that burst into flames when dropped on villages or vegetation American airplanes also sprayed the herbicide Agent Orange n n Destroyed crops and vegetation where enemies hid Later blamed for birth defects, cancer, and long-term health problems
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ American airplanes dropped bombs containing napalm n ¡ A jellylike substance that burst into flames when dropped on villages or vegetation American airplanes also sprayed the herbicide Agent Orange n n Destroyed crops and vegetation where enemies hid Later blamed for birth defects, cancer, and long-term health problems
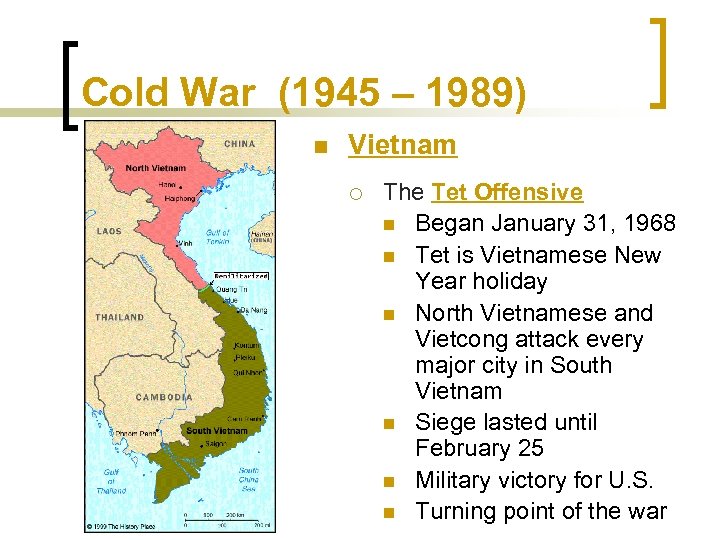 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ The Tet Offensive n Began January 31, 1968 n Tet is Vietnamese New Year holiday n North Vietnamese and Vietcong attack every major city in South Vietnam n Siege lasted until February 25 n Military victory for U. S. n Turning point of the war
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ The Tet Offensive n Began January 31, 1968 n Tet is Vietnamese New Year holiday n North Vietnamese and Vietcong attack every major city in South Vietnam n Siege lasted until February 25 n Military victory for U. S. n Turning point of the war
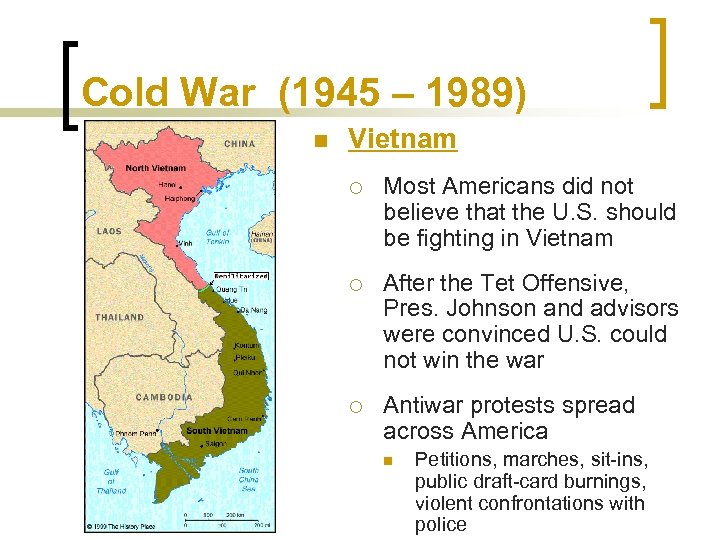 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Most Americans did not believe that the U. S. should be fighting in Vietnam ¡ After the Tet Offensive, Pres. Johnson and advisors were convinced U. S. could not win the war ¡ Antiwar protests spread across America n Petitions, marches, sit-ins, public draft-card burnings, violent confrontations with police
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Most Americans did not believe that the U. S. should be fighting in Vietnam ¡ After the Tet Offensive, Pres. Johnson and advisors were convinced U. S. could not win the war ¡ Antiwar protests spread across America n Petitions, marches, sit-ins, public draft-card burnings, violent confrontations with police
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Pres. Nixon expanded the war into Cambodia and Laos to attack North Vietnamese bases and disrupt their supply lines along the Ho Chi Minh Trail
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Pres. Nixon expanded the war into Cambodia and Laos to attack North Vietnamese bases and disrupt their supply lines along the Ho Chi Minh Trail
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Kent State University, Kent, OH n Worst, deadly antiwar protest in America – May 4, 1970
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Kent State University, Kent, OH n Worst, deadly antiwar protest in America – May 4, 1970
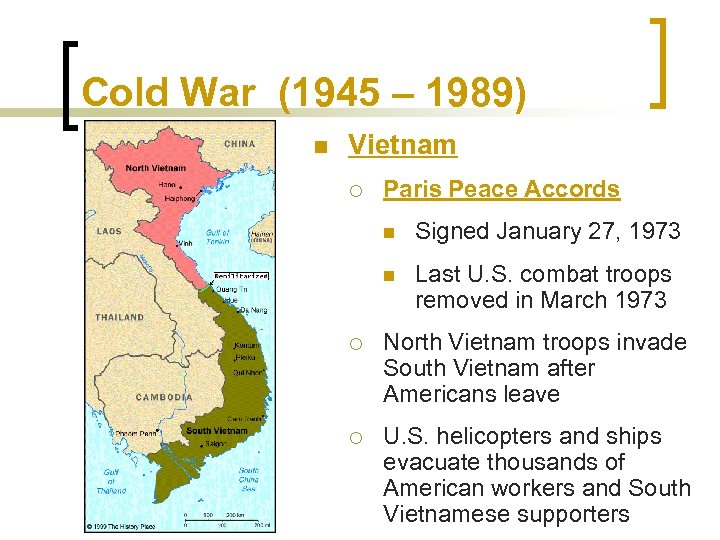 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Paris Peace Accords n Signed January 27, 1973 n Last U. S. combat troops removed in March 1973 ¡ North Vietnam troops invade South Vietnam after Americans leave ¡ U. S. helicopters and ships evacuate thousands of American workers and South Vietnamese supporters
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Paris Peace Accords n Signed January 27, 1973 n Last U. S. combat troops removed in March 1973 ¡ North Vietnam troops invade South Vietnam after Americans leave ¡ U. S. helicopters and ships evacuate thousands of American workers and South Vietnamese supporters
 Cold War 1945 – 1989 n Vietnam ¡ April 30, 1975, South Vietnamese government formally surrendered ¡ Vietnam united under a Communist government ¡ Saigon renamed Ho Chi Minh City ¡ More than 1 M people fled the new regime n Boat people attempted to escape in small boats ¡ 200, 000 died at sea or in refugee camps ¡ U. S. and other nations took in many refugees
Cold War 1945 – 1989 n Vietnam ¡ April 30, 1975, South Vietnamese government formally surrendered ¡ Vietnam united under a Communist government ¡ Saigon renamed Ho Chi Minh City ¡ More than 1 M people fled the new regime n Boat people attempted to escape in small boats ¡ 200, 000 died at sea or in refugee camps ¡ U. S. and other nations took in many refugees
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Longest war in U. S. history, lasted for 10 years n Eisenhower was president when the war began, Nixon was president when it ended ¡ First foreign war the U. S. did not win ¡ U. S. never officially declared war in Vietnam
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Longest war in U. S. history, lasted for 10 years n Eisenhower was president when the war began, Nixon was president when it ended ¡ First foreign war the U. S. did not win ¡ U. S. never officially declared war in Vietnam
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Vets were not welcomed home with cheering and parades ¡ 1. 8 M American men drafted ¡ 58, 000 Americans died in combat ¡ 300, 000 Americans wounded ¡ $200 billion price tag n Damaged U. S. economy for years
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Vets were not welcomed home with cheering and parades ¡ 1. 8 M American men drafted ¡ 58, 000 Americans died in combat ¡ 300, 000 Americans wounded ¡ $200 billion price tag n Damaged U. S. economy for years
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Undermined the nation’s trust in the government and its leaders ¡ Pentagon Papers n Published in 1971 by leading newspapers n Secret government documents showing how government officials concealed actions and misled Americans
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Vietnam ¡ Undermined the nation’s trust in the government and its leaders ¡ Pentagon Papers n Published in 1971 by leading newspapers n Secret government documents showing how government officials concealed actions and misled Americans
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n War Powers Act ¡ Passed by Congress in 1973 to curb President’s power ¡ President cannot send military forces into action for longer than 60 days without congressional approval
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n War Powers Act ¡ Passed by Congress in 1973 to curb President’s power ¡ President cannot send military forces into action for longer than 60 days without congressional approval
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n 26 th Amendment to the Constitution ¡ Passed in 1971 ¡ Lowered voting age to 18 n If 18 -year-olds were old enough to fight and die in Vietnam, they were old enough to vote
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n 26 th Amendment to the Constitution ¡ Passed in 1971 ¡ Lowered voting age to 18 n If 18 -year-olds were old enough to fight and die in Vietnam, they were old enough to vote
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy ¡ 1961 Peace Corps created by Congress n Program to build relationships between Americans and peoples of other nations ¡ ¡ Sharing skills and knowledge Encourage economic growth in developing countries
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy ¡ 1961 Peace Corps created by Congress n Program to build relationships between Americans and peoples of other nations ¡ ¡ Sharing skills and knowledge Encourage economic growth in developing countries
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President F. Kennedy ¡ Assassinated Nov. 22, 1963 n In Dallas, TX John
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President F. Kennedy ¡ Assassinated Nov. 22, 1963 n In Dallas, TX John
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President F. Kennedy John ¡ Assassinated Nov. 22, 1963 ¡ Lee Harvey Oswald n Arrested for killing Kennedy
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President F. Kennedy John ¡ Assassinated Nov. 22, 1963 ¡ Lee Harvey Oswald n Arrested for killing Kennedy
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Lee Harvey Oswald ¡ Shot and killed by Jack Ruby
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Lee Harvey Oswald ¡ Shot and killed by Jack Ruby
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Lyndon B. Johnson ¡ 1963 -1969 ¡ Democrat ¡ Vice President – Hubert H. Humphrey 1965 - 1969
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Lyndon B. Johnson ¡ 1963 -1969 ¡ Democrat ¡ Vice President – Hubert H. Humphrey 1965 - 1969
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy’s New Frontier ¡ ¡ ¡ Space Age Russians – first astronauts in space Alan Shepard n 1 st American in space, 1961
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy’s New Frontier ¡ ¡ ¡ Space Age Russians – first astronauts in space Alan Shepard n 1 st American in space, 1961
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy’s New Frontier ¡ Space Age ¡ John Glenn n 1 st American to orbit Earth, 1962
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy’s New Frontier ¡ Space Age ¡ John Glenn n 1 st American to orbit Earth, 1962
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy’s New Frontier – Space Age ¡ ¡ Apollo 11 mission Eagle lunar module July 20, 1969 Neil Armstrong n 1 st man on moon
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Kennedy’s New Frontier – Space Age ¡ ¡ Apollo 11 mission Eagle lunar module July 20, 1969 Neil Armstrong n 1 st man on moon
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Columbia ¡ 1 st Space shuttle ¡ Launched April 1981
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Columbia ¡ 1 st Space shuttle ¡ Launched April 1981
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Richard Nixon ¡ ¡ 1969 – 1974 Vice Presidents n n Spiro T. Agnew Gerald R. Ford
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Richard Nixon ¡ ¡ 1969 – 1974 Vice Presidents n n Spiro T. Agnew Gerald R. Ford
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Watergate scandal n 1972 election n Democratic Party offices break-in n Pres. Nixon’s aides involved in break-in n Pres. Nixon cover-up
Cold War (1945 – 1989) ¡ Watergate scandal n 1972 election n Democratic Party offices break-in n Pres. Nixon’s aides involved in break-in n Pres. Nixon cover-up
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Spiro T. Agnew ¡ Pres. Nixon’s Vice President Charged with accepting bribes as Gov. of Maryland V. P. of U. S. ¡ Resigned as V. P. ¡ October 1973 n Gerald Ford appointed as V. P.
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Spiro T. Agnew ¡ Pres. Nixon’s Vice President Charged with accepting bribes as Gov. of Maryland V. P. of U. S. ¡ Resigned as V. P. ¡ October 1973 n Gerald Ford appointed as V. P.
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Richard Nixon ¡ 1 st President to resign the office, August 1974 n Resigned before being impeached because of Watergate scandal
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Richard Nixon ¡ 1 st President to resign the office, August 1974 n Resigned before being impeached because of Watergate scandal
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Gerald Ford ¡ 1974 – 1977 ¡ 1 st and only President not elected to the office ¡ Pardoned former president Nixon
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Gerald Ford ¡ 1974 – 1977 ¡ 1 st and only President not elected to the office ¡ Pardoned former president Nixon

 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Jimmy Carter ¡ 1977 – 1981 ¡ Democrat n Inexperienced with Washington politics ¡ Vice President n Walter Mondale
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Jimmy Carter ¡ 1977 – 1981 ¡ Democrat n Inexperienced with Washington politics ¡ Vice President n Walter Mondale
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Iran Hostage Crisis ¡ Iranian radicals seized American embassy in Tehran on Nov 4, 1979 n Held 52 hostages for 444 days ¡ Released them minutes after Ronald Reagan was inaugurated
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n Iran Hostage Crisis ¡ Iranian radicals seized American embassy in Tehran on Nov 4, 1979 n Held 52 hostages for 444 days ¡ Released them minutes after Ronald Reagan was inaugurated
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Ronald Reagan ¡ 1981 – 1989 ¡ Republican n Great Communicator ¡ Vice President – George H. W. Bush ¡ Popular
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Ronald Reagan ¡ 1981 – 1989 ¡ Republican n Great Communicator ¡ Vice President – George H. W. Bush ¡ Popular
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Reagan ¡ ¡ “Government is not the solution to our problems. Government is the problem. ” Reaganomics n Reduced government spending & lowered taxes ¡ In 1981, persuaded Congress to lower taxes by 25%
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President Reagan ¡ ¡ “Government is not the solution to our problems. Government is the problem. ” Reaganomics n Reduced government spending & lowered taxes ¡ In 1981, persuaded Congress to lower taxes by 25%
 Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President George H. W. Bush ¡ 1989 – 1993 ¡ Republican ¡ Vice President n J. ¡ Danforth Quayle 1991 Gulf War n Operation Storm ¡ Desert 1991 recession
Cold War (1945 – 1989) n President George H. W. Bush ¡ 1989 – 1993 ¡ Republican ¡ Vice President n J. ¡ Danforth Quayle 1991 Gulf War n Operation Storm ¡ Desert 1991 recession
 Cold War Ends (1945 – 1989) n 1979 Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan ¡ n President Carter imposed trade restrictions and pulled U. S. from 1980 Olympic Games in Moscow President Reagan increased defense spending ¡ Soviets tried to keep up with U. S. on military spending (arms race), but did not have the money – this weakened Soviet economy
Cold War Ends (1945 – 1989) n 1979 Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan ¡ n President Carter imposed trade restrictions and pulled U. S. from 1980 Olympic Games in Moscow President Reagan increased defense spending ¡ Soviets tried to keep up with U. S. on military spending (arms race), but did not have the money – this weakened Soviet economy
 Cold War Ends (1945 – 1989) n Mikhail Gorbachev ¡ 1985, became leader of Soviet Union ¡ Soviet Union lost interest in supporting unpopular Communist leaders in Eastern European countries
Cold War Ends (1945 – 1989) n Mikhail Gorbachev ¡ 1985, became leader of Soviet Union ¡ Soviet Union lost interest in supporting unpopular Communist leaders in Eastern European countries
 Cold War Ends (1945 – 1989) n 1989 ¡ n 1990 ¡ n Fall of Berlin Wall Reunification of Germany 1991 ¡ Fall of Soviet Union
Cold War Ends (1945 – 1989) n 1989 ¡ n 1990 ¡ n Fall of Berlin Wall Reunification of Germany 1991 ¡ Fall of Soviet Union
 Modern America n President Bill Clinton ¡ 1993 – 2001 ¡ Democrat ¡ Vice President n Albert Gore, Jr.
Modern America n President Bill Clinton ¡ 1993 – 2001 ¡ Democrat ¡ Vice President n Albert Gore, Jr.
 Modern America n President Bill Clinton ¡ Federal budget surpluses 1998 -2001 ¡ December 1998, impeached by House n Senate did not convict Clinton, he remained in office
Modern America n President Bill Clinton ¡ Federal budget surpluses 1998 -2001 ¡ December 1998, impeached by House n Senate did not convict Clinton, he remained in office
 Modern America n 2000 Election ¡ Al Gore – Democrat candidate n Won ¡ George W. Bush – Republican candidate n Won ¡ popular vote electoral vote Democrats challenged results in court n First time Supreme Court ruled in Presidential election n Bush declared winner
Modern America n 2000 Election ¡ Al Gore – Democrat candidate n Won ¡ George W. Bush – Republican candidate n Won ¡ popular vote electoral vote Democrats challenged results in court n First time Supreme Court ruled in Presidential election n Bush declared winner
 Modern America n President George Bush ¡ 2001 – 2009 ¡ Republican ¡ Vice President n Richard Cheney ¡ Cut taxes to offset surplus ¡ No Child Left Behind ¡ 2003 Iraq War
Modern America n President George Bush ¡ 2001 – 2009 ¡ Republican ¡ Vice President n Richard Cheney ¡ Cut taxes to offset surplus ¡ No Child Left Behind ¡ 2003 Iraq War
 Modern America n President Barack Obama ¡ 2009 – Present ¡ Democrat ¡ Vice President n Joe ¡ Biden Health Care Reform
Modern America n President Barack Obama ¡ 2009 – Present ¡ Democrat ¡ Vice President n Joe ¡ Biden Health Care Reform



