f9ab1f53023aec1930f1d7d4b1638952.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Positive Behavioral Interventions & Supports: School-based Prevention George Sugai OSEP Center on PBIS Center for Behavioral Education & Research University of Connecticut George. sugai@uconn. edu www. pbis. org www. scalingup. org www. cber. org
www. p bis. or g
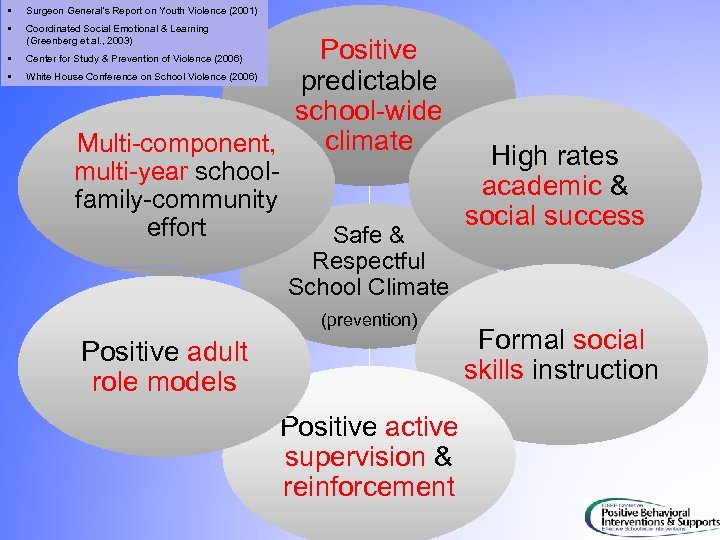
• Surgeon General’s Report on Youth Violence (2001) • Coordinated Social Emotional & Learning (Greenberg et al. , 2003) • Center for Study & Prevention of Violence (2006) • White House Conference on School Violence (2006) Positive predictable school-wide climate Multi-component, multi-year schoolfamily-community effort Safe & Respectful School Climate (prevention) Positive adult role models High rates academic & social success Formal social skills instruction Positive active supervision & reinforcement

PBIS is about…. Improving classroom & school climate Integrating Decreasing academic & reactive behavior management initiatives Improving Maximizing support for academic students w/ achievement EBD
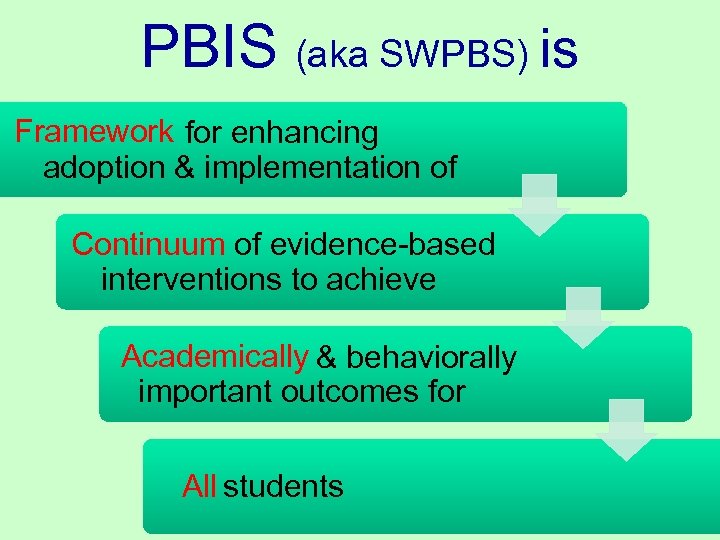
PBIS (aka SWPBS) is Framework for enhancing adoption & implementation of Continuum of evidence-based interventions to achieve Academically & behaviorally important outcomes for All students

Prevention Logic for All Redesign of teaching environments…not students Prevention Objectives Prevention Actions Prevent Decrease worsening & Eliminate Add triggers Teach, development reduce triggers & & monitor, & of new intensity of maintainers acknowledge prosocial problem existing of problem of prosocial behaviors problem behaviors E ENC D INCI CE N VALE E PR Biglan, 1995; Mayer, 1995; Walker et al. , 1996
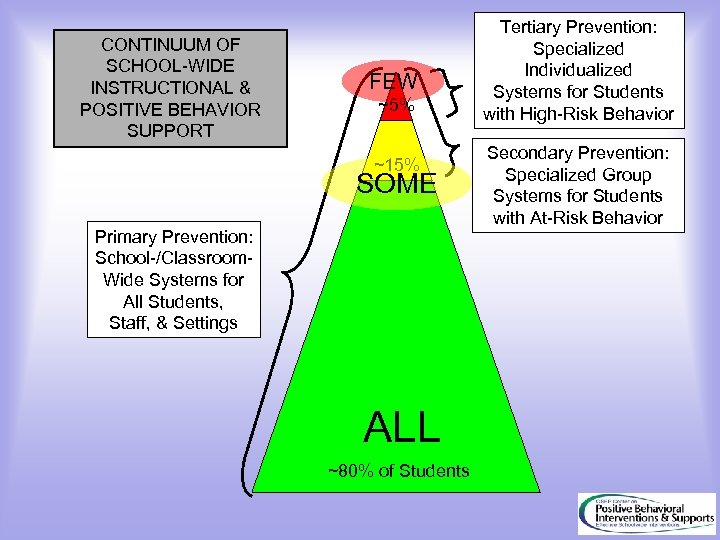
CONTINUUM OF SCHOOL-WIDE INSTRUCTIONAL & POSITIVE BEHAVIOR SUPPORT FEW ~5% ~15% SOME Primary Prevention: School-/Classroom. Wide Systems for All Students, Staff, & Settings ALL ~80% of Students Tertiary Prevention: Specialized Individualized Systems for Students with High-Risk Behavior Secondary Prevention: Specialized Group Systems for Students with At-Risk Behavior
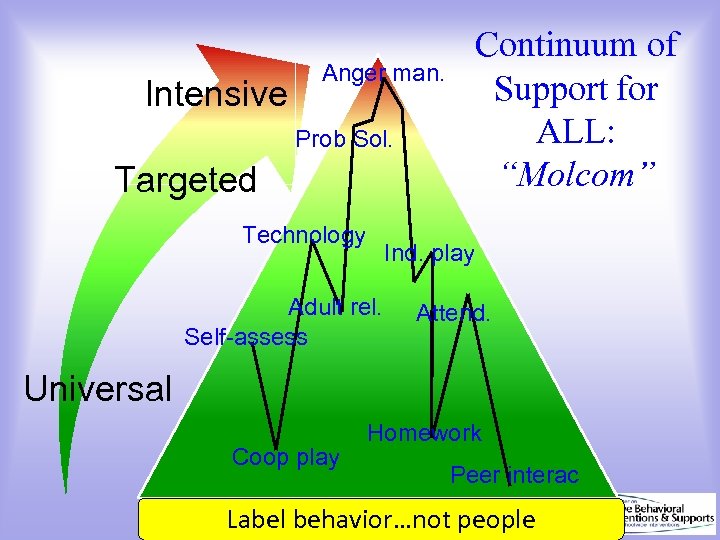
Intensive Continuum of Support for ALL: “Molcom” Anger man. Prob Sol. Targeted Technology Ind. play Adult rel. Self-assess Attend. Universal Coop play Homework Peer interac Label behavior…not people Dec 7, 2007
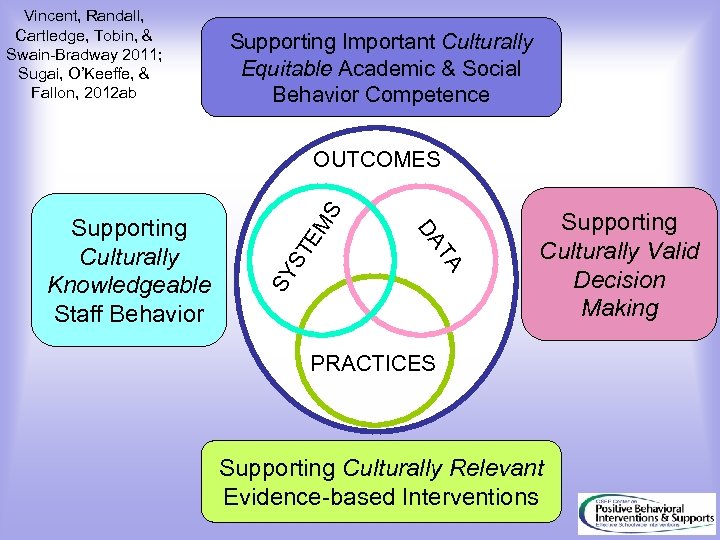
Vincent, Randall, Cartledge, Tobin, & Swain-Bradway 2011; Sugai, O’Keeffe, & Fallon, 2012 ab Supporting Important Culturally Equitable Academic & Social Behavior Competence ST EM SY TA DA Supporting Culturally Knowledgeable Staff Behavior S OUTCOMES Supporting Culturally Valid Decision Making PRACTICES Supporting Culturally Relevant Evidence-based Interventions
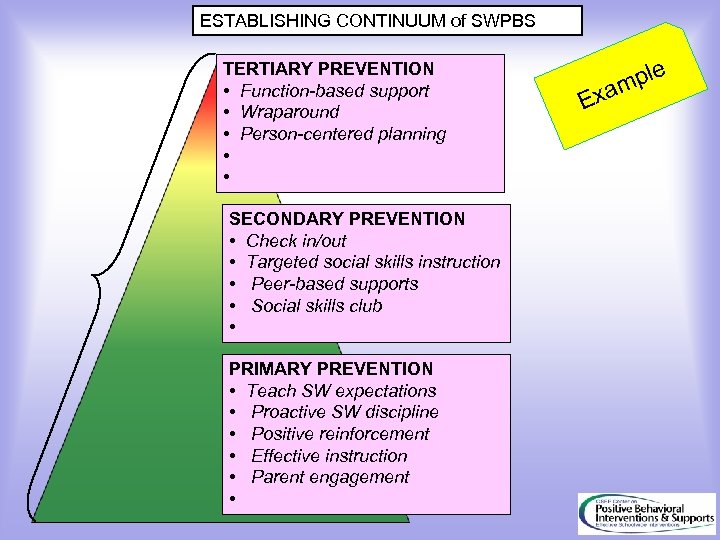
ESTABLISHING CONTINUUM of SWPBS TERTIARY PREVENTION • Function-based support • Wraparound • Person-centered planning • • SECONDARY PREVENTION • Check in/out • Targeted social skills instruction • Peer-based supports • Social skills club • PRIMARY PREVENTION • Teach SW expectations • Proactive SW discipline • Positive reinforcement • Effective instruction • Parent engagement • Exa ple m
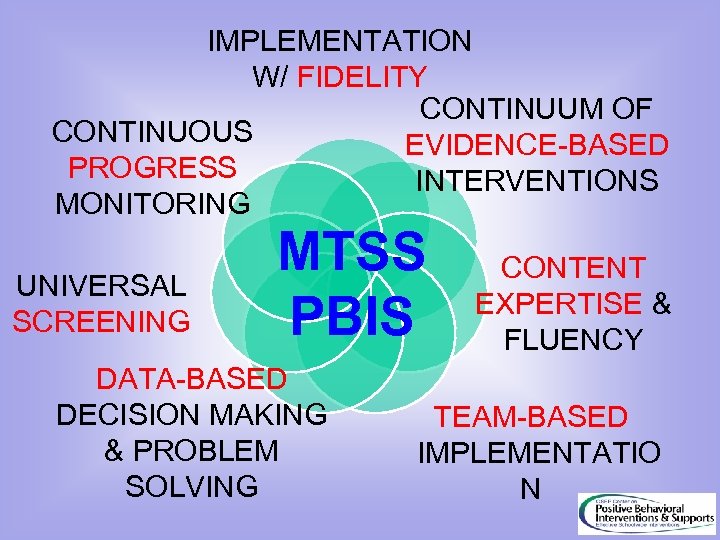
IMPLEMENTATION W/ FIDELITY CONTINUUM OF CONTINUOUS EVIDENCE-BASED PROGRESS INTERVENTIONS MONITORING UNIVERSAL SCREENING MTSS PBIS DATA-BASED DECISION MAKING & PROBLEM SOLVING CONTENT EXPERTISE & FLUENCY TEAM-BASED IMPLEMENTATIO N
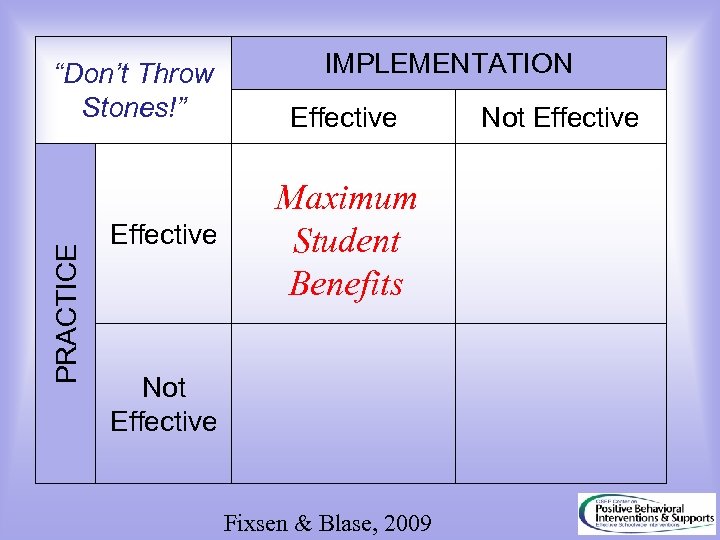
PRACTICE “Don’t Throw Stones!” Effective IMPLEMENTATION Effective Maximum Student Benefits Not Effective Fixsen & Blase, 2009 Not Effective
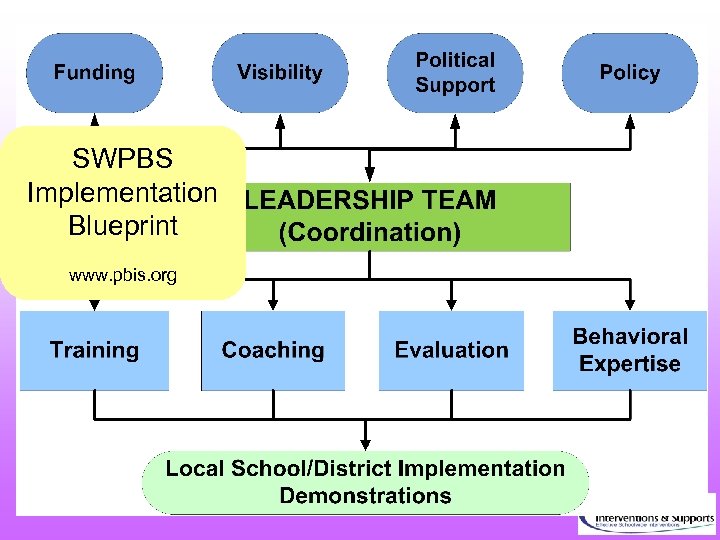
SWPBS Implementation Blueprint www. pbis. org
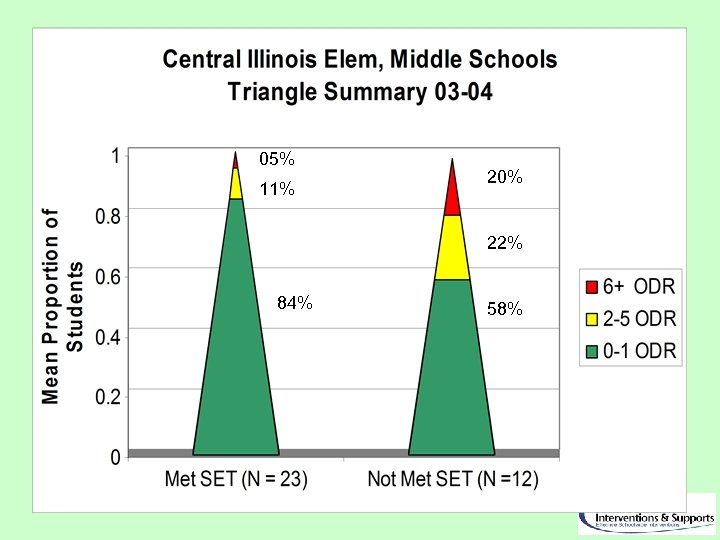
05% 11% 20% 22% 84% 58%
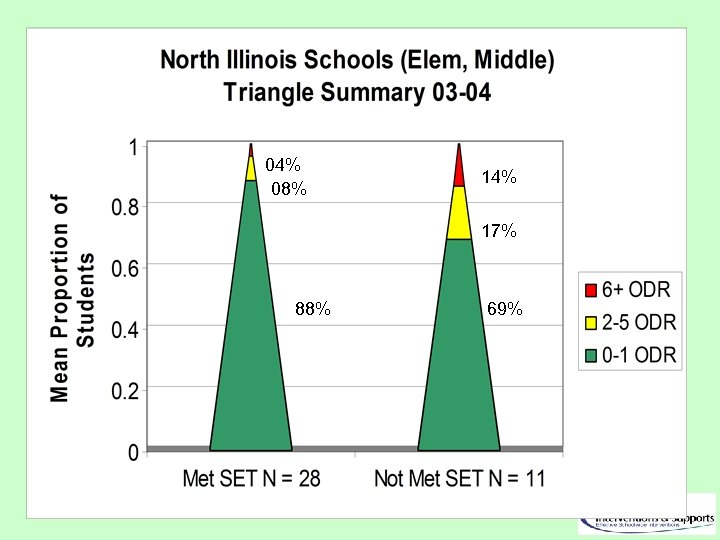
04% 08% 14% 17% 88% 69%
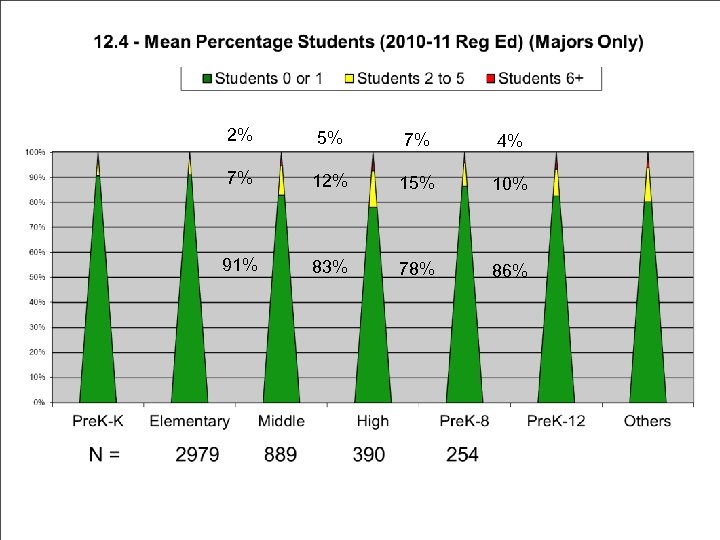
2% 5% 7% 4% 7% 12% 15% 10% 91% 83% 78% 86%
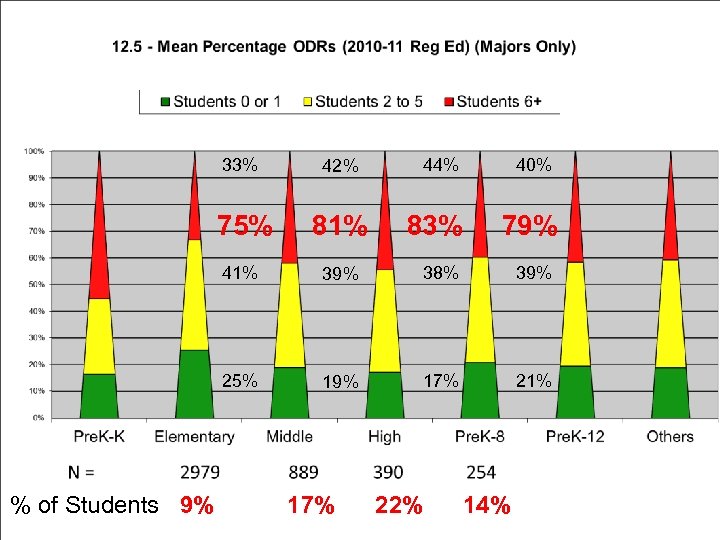
33% 75% 81% 41% 39% 38% 39% 25% % of Students 9% 42% 19% 17% 21% 17% 44% 83% 22% 40% 79% 14%
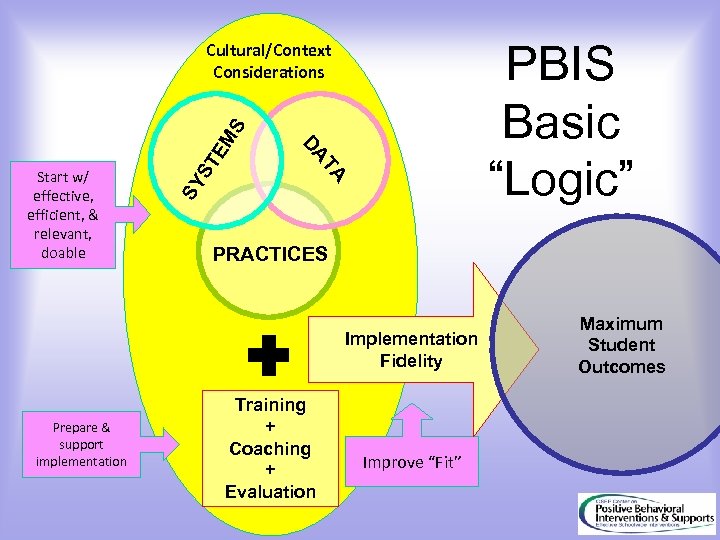
PBIS Basic “Logic” TE SY S Start w/ effective, efficient, & relevant, doable TA DA MS Cultural/Context Considerations PRACTICES Implementation Fidelity Prepare & support implementation Training + Coaching + Evaluation Improve “Fit” Maximum Student Outcomes
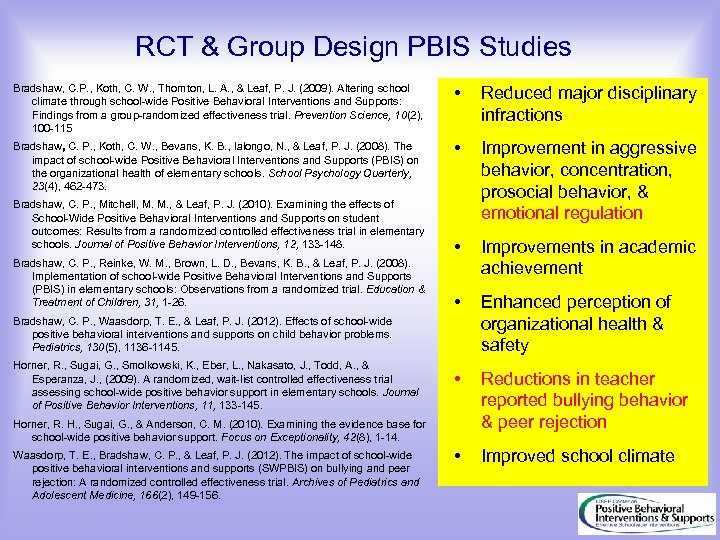
RCT & Group Design PBIS Studies Bradshaw, C. P. , Koth, C. W. , Thornton, L. A. , & Leaf, P. J. (2009). Altering school climate through school-wide Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports: Findings from a group-randomized effectiveness trial. Prevention Science, 10(2), 100 -115 • Reduced major disciplinary infractions Bradshaw, C. P. , Koth, C. W. , Bevans, K. B. , Ialongo, N. , & Leaf, P. J. (2008). The impact of school-wide Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) on the organizational health of elementary schools. School Psychology Quarterly, 23(4), 462 -473. • Improvement in aggressive behavior, concentration, prosocial behavior, & emotional regulation • Improvements in academic achievement • Enhanced perception of organizational health & safety • Reductions in teacher reported bullying behavior & peer rejection • Improved school climate Bradshaw, C. P. , Mitchell, M. M. , & Leaf, P. J. (2010). Examining the effects of School-Wide Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports on student outcomes: Results from a randomized controlled effectiveness trial in elementary schools. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 12, 133 -148. Bradshaw, C. P. , Reinke, W. M. , Brown, L. D. , Bevans, K. B. , & Leaf, P. J. (2008). Implementation of school-wide Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) in elementary schools: Observations from a randomized trial. Education & Treatment of Children, 31, 1 -26. Bradshaw, C. P. , Waasdorp, T. E. , & Leaf, P. J. (2012). Effects of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports on child behavior problems. Pediatrics, 130(5), 1136 -1145. Horner, R. , Sugai, G. , Smolkowski, K. , Eber, L. , Nakasato, J. , Todd, A. , & Esperanza, J. , (2009). A randomized, wait-list controlled effectiveness trial assessing school-wide positive behavior support in elementary schools. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 11, 133 -145. Horner, R. H. , Sugai, G. , & Anderson, C. M. (2010). Examining the evidence base for school-wide positive behavior support. Focus on Exceptionality, 42(8), 1 -14. Waasdorp, T. E. , Bradshaw, C. P. , & Leaf, P. J. (2012). The impact of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports (SWPBIS) on bullying and peer rejection: A randomized controlled effectiveness trial. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 166(2), 149 -156.
Common Language & Behaviors Effective Organizations Common Vision/Values Common Experience Quality Leadership
f9ab1f53023aec1930f1d7d4b1638952.ppt