 Portfolio Management Summary of Defensive and Offensive strategies Presented by Sept. Stock Selection Committee
Portfolio Management Summary of Defensive and Offensive strategies Presented by Sept. Stock Selection Committee
 Agenda n n n What portfolio management is NOT Price pitfalls Defensive summary Offensive summary Tool overview
Agenda n n n What portfolio management is NOT Price pitfalls Defensive summary Offensive summary Tool overview
 Portfolio Management is NOT Passively tracking prices to benchmark performance; tracking is postmortem. n Selling holdings when they reach pre-defined price targets. n Selling (or buying) holdings based on short term price fluctuations. n
Portfolio Management is NOT Passively tracking prices to benchmark performance; tracking is postmortem. n Selling holdings when they reach pre-defined price targets. n Selling (or buying) holdings based on short term price fluctuations. n
 Price Pitfalls “When you buy stocks you buy companies—or at least shares in them. So portfolio management involves monitoring companies, not their stock prices. This is a major distinction and one that you must embrace. ” n n n Short term price fluctuations are more often attributable to “soft” speculation than to fact-based fundamentals such as sales, profit, and earnings. Short term price is affected by rumors, stories, analysts’ upgrades/downgrades, and bad/positive media coverage. Price is linked to investor confidence. More often than not, loss of confidence (low price) is groundless when dealing with good-quality companies.
Price Pitfalls “When you buy stocks you buy companies—or at least shares in them. So portfolio management involves monitoring companies, not their stock prices. This is a major distinction and one that you must embrace. ” n n n Short term price fluctuations are more often attributable to “soft” speculation than to fact-based fundamentals such as sales, profit, and earnings. Short term price is affected by rumors, stories, analysts’ upgrades/downgrades, and bad/positive media coverage. Price is linked to investor confidence. More often than not, loss of confidence (low price) is groundless when dealing with good-quality companies.
 What is Portfolio Management? Portfolio management is a proactive process where you periodically evaluate the health of your companies by looking at the fundamentals and attempt to maximize return. n n n Managing size and diversification (10 -25 holdings) Defending your portfolio from loss Offensively searching out lower-risk alternatives with higher rates of return
What is Portfolio Management? Portfolio management is a proactive process where you periodically evaluate the health of your companies by looking at the fundamentals and attempt to maximize return. n n n Managing size and diversification (10 -25 holdings) Defending your portfolio from loss Offensively searching out lower-risk alternatives with higher rates of return
 Defensive Strategy “You may discover that you have one of the one-out-offive companies the Rule of Five warns you about. You’ll want to get rid of it before it does major damage to your portfolio. ” n n n Check sales growth; should be most stable Check pre-tax profit; ultimately affect earnings, but companies can sometimes delay effects in bottom line; (e. g. reduce shares outstanding) Check earnings
Defensive Strategy “You may discover that you have one of the one-out-offive companies the Rule of Five warns you about. You’ll want to get rid of it before it does major damage to your portfolio. ” n n n Check sales growth; should be most stable Check pre-tax profit; ultimately affect earnings, but companies can sometimes delay effects in bottom line; (e. g. reduce shares outstanding) Check earnings
 Defensive Actions n n Investigate reasons behind the decline; the 10 -Q is a good source. Do nothing: Declines are normal in aging companies that have above average growth rates Wait: Allow management to correct performance Sell, but do so almost as a last resort
Defensive Actions n n Investigate reasons behind the decline; the 10 -Q is a good source. Do nothing: Declines are normal in aging companies that have above average growth rates Wait: Allow management to correct performance Sell, but do so almost as a last resort
 Offensive Strategy “Offensive strategy doesn’t share the urgency of defense. Here, you’re concerned not so much with preventing loss as you are with enhancing the value of your holdings” n n n Stock prices go up for reasons other than fundamentals If the price rises so high that no growth potential exists, it may need to be replaced Favor existing holdings
Offensive Strategy “Offensive strategy doesn’t share the urgency of defense. Here, you’re concerned not so much with preventing loss as you are with enhancing the value of your holdings” n n n Stock prices go up for reasons other than fundamentals If the price rises so high that no growth potential exists, it may need to be replaced Favor existing holdings
 Offensive Actions n n n Perform an optimistic evaluation of current holdings Use risk index to help gauge overvaluation Consider replacement when risk index > 67% Maintain a watch-list of high-quality stocks Consider cost of replacement: cost of trade, number of shares, value, and projected value Replacement calculations n n value = shares * (price – (cost of trade/ shares)) FV = value * ( 1 + ( annual_return ) )5
Offensive Actions n n n Perform an optimistic evaluation of current holdings Use risk index to help gauge overvaluation Consider replacement when risk index > 67% Maintain a watch-list of high-quality stocks Consider cost of replacement: cost of trade, number of shares, value, and projected value Replacement calculations n n value = shares * (price – (cost of trade/ shares)) FV = value * ( 1 + ( annual_return ) )5
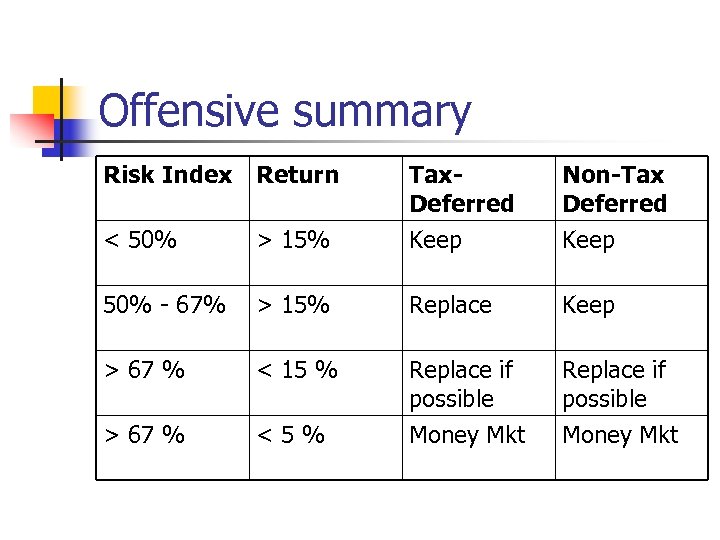 Offensive summary Risk Index Return Tax. Deferred Non-Tax Deferred < 50% > 15% Keep 50% - 67% > 15% Replace Keep > 67 % < 15 % Replace if possible > 67 % <5% Money Mkt
Offensive summary Risk Index Return Tax. Deferred Non-Tax Deferred < 50% > 15% Keep 50% - 67% > 15% Replace Keep > 67 % < 15 % Replace if possible > 67 % <5% Money Mkt
 The End Questions?
The End Questions?