faaeffa1b7b475cdabd3f7bc65fc9b02.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Population-Based Epidemiologic Safety Studies: Overview and Challenges Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee Silver Spring, Maryland June 19, 2005 David J. Graham, MD, MPH Office of Drug Safety Center for Drug Evaluation and Research

Why Postmarketing Safety Studies? • Residual uncertainty at approval • New safety signal post-approval Beyond case reports Serious Potentially large exposure Potentially large excess risk Potentially “safer” alternatives “Less serious” indication • Inappropriate off-label use Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 2

Mechanisms for Performing Postmarketing Drug Safety Studies • Phase 4 • Ad hoc postmarketing studies Performed by Companies Existing national data Cooperative Agreement Program Performed by GPRD ODS Special projects: Kaiser Permanente, California Veterans’ Administration database Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 3

National Data Resources • NHANES QT prolongation in general population • NHDS Pancreatitis in children AMI in children • NAMCS Prevalence of drug therapy Prevalence of diagnosed diseases • NCHS statistics Age-specific denominators Cause of death Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 4
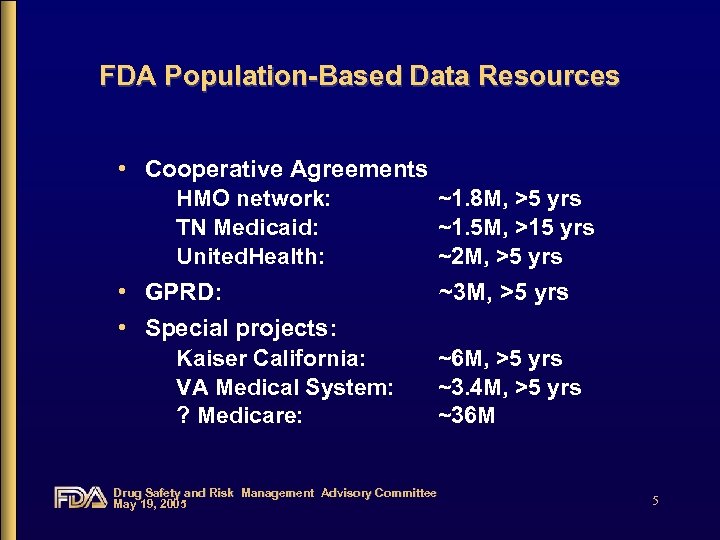
FDA Population-Based Data Resources • Cooperative Agreements HMO network: TN Medicaid: United. Health: ~1. 8 M, >5 yrs ~1. 5 M, >15 yrs ~2 M, >5 yrs • GPRD: • Special projects: Kaiser California: VA Medical System: ? Medicare: ~3 M, >5 yrs ~6 M, >5 yrs ~3. 4 M, >5 yrs ~36 M Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 5

Basic Database Features • • Population-based “Large” Longitudinal Automated claims Pharmacy Provider-encounters Procedures • Record-linkage capacity Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 6

FDA Funding Costs of Resources • National resources • Cooperative Agreements $0 $900 K per yr • GPRD $500 K per yr • Special projects VA medical system Kaiser Permanente Medicare $10 K $60 K Could be $$$ Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 7

Cooperative Agreement Program • Access to 3 population-based data resources with research expertise • Longitudinal Outpatient prescriptions Diagnosis & procedure claims Medical record linkage No routine death ascertainment • Ability to study Patterns of use w/in database Exposure-outcome Effects of regulatory interventions Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 8

Claims Data Quality • Pharmacy claims High validity 95% complete within 2 mos • Diagnosis claims Outpatient: low validity Inpatient: it depends 95% complete within 6 mos • Procedure claims High validity 95% complete within 6 mos Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 9

Proposed Changes in Cooperative Agreement • Shift from grant to contract Growing pains • Intention to fund multiple databases • Focus on safety-related issues important to FDA • Retain collaborative relationship Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 10

General Practice Research Database • UK-based electronic medical record • GP-centered, longitudinal Low turnover GP visits, health measures Consultant referrals and hospitalizations Labs, procedures ± results Computer-generated outpatient prescriptions Death ascertainment • Complex relational file structure • In-house access via Internet Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 11

Unique Limitations • UK population - not US • National formulary - cost containment • Different health care standards and practice • Different prescribing patterns • Very large data files • In-house resource requirements Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 12

Other Population-Based Resources • VA medical system Moving to EMR Males, older, sicker Some acute hospitalizations missed Some lab data • Kaiser Permanente Large HMO Closed system, integrated Some formulary restrictions Computerized lab data Death ascertainment Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 13

Types of Studies • Patterns of drug use Persistency Co-prescribing • Case series • Prevalence cohort • Inception cohort • Case-control • Nested case-control • Patient surveys Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 14

Study Examples • Factors associated with QTc prolongation • Predictors of COX-2 inhibitor use • Birth defect incidence with an antibiotic • Incidence of severe liver injury with a diabetes drug • Chronic use of corticosteroids in children • Incidence of rhabdomyolysis with lipid-lowering drugs • Compliance with contraindicated use labeling • Compliance with liver enzyme monitoring recommendations Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 15
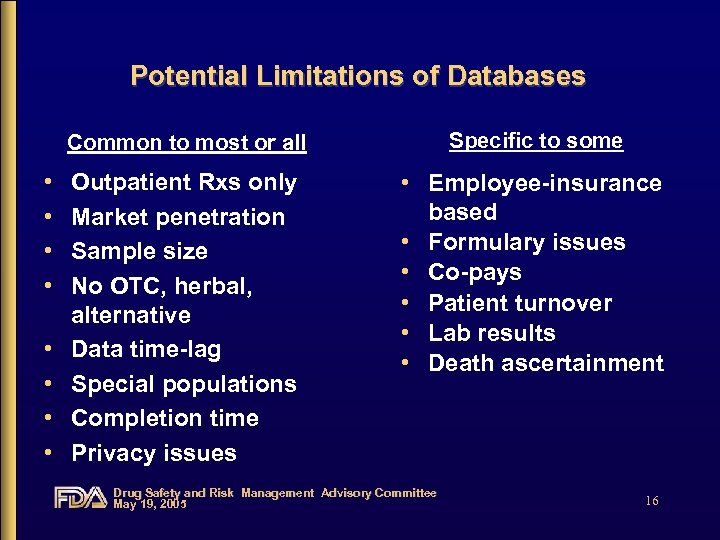
Potential Limitations of Databases Common to most or all • • Specific to some Outpatient Rxs only Market penetration Sample size No OTC, herbal, alternative Data time-lag Special populations Completion time Privacy issues • Employee-insurance based • Formulary issues • Co-pays • Patient turnover • Lab results • Death ascertainment Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 16

Challenges (1) • Budgetary Databases Operation • Infrastructure Personnel Training Hardware/software • Methodologic Study design Proper covariates Power Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 17

Challenges (2) • Topic identification & selection • Matching question & data resource • Prioritization • Use for regulatory purposes Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee May 19, 2005 18
faaeffa1b7b475cdabd3f7bc65fc9b02.ppt