691c7e51f3dd48993c6df49dbe6fac20.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Popular protocols for serving media 4 Network transmission control < RTP – Realtime Transmission Protocol = RTCP – Realtime Transmission Control Protocol 4 Session control < Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) < Session Description Protocol (SDP) – textual representation of sesion 4 VOIP – Session Initiation Protocol < Signaling for IP Telephony 4 SAP – Session announcement protocol for multicast sessions 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 1
Popular protocols for serving media 4 Network transmission control < RTP – Realtime Transmission Protocol = RTCP – Realtime Transmission Control Protocol 4 Session control < Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) < Session Description Protocol (SDP) – textual representation of sesion 4 VOIP – Session Initiation Protocol < Signaling for IP Telephony 4 SAP – Session announcement protocol for multicast sessions 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 1
 RTP and RTSP 4 RTP usage – in several application audio and video tools (vat, vic) 4 RTP follows the principle of application level framing and integrated layer processing 4 RTP/UDP/IP is being used by the current streaming session protocols such as RTSP 4 Session protocols are actually negotiation/session establishment protocols that assist multimedia applications 4 Multimedia applications such as Quick. Time, Real Player and others use them 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 2
RTP and RTSP 4 RTP usage – in several application audio and video tools (vat, vic) 4 RTP follows the principle of application level framing and integrated layer processing 4 RTP/UDP/IP is being used by the current streaming session protocols such as RTSP 4 Session protocols are actually negotiation/session establishment protocols that assist multimedia applications 4 Multimedia applications such as Quick. Time, Real Player and others use them 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 2
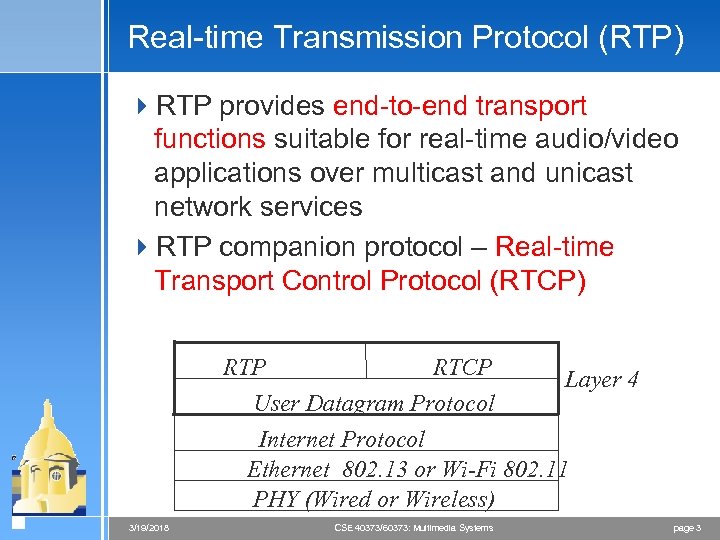 Real-time Transmission Protocol (RTP) 4 RTP provides end-to-end transport functions suitable for real-time audio/video applications over multicast and unicast network services 4 RTP companion protocol – Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) RTP RTCP Layer 4 User Datagram Protocol Internet Protocol Ethernet 802. 13 or Wi-Fi 802. 11 PHY (Wired or Wireless) 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 3
Real-time Transmission Protocol (RTP) 4 RTP provides end-to-end transport functions suitable for real-time audio/video applications over multicast and unicast network services 4 RTP companion protocol – Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) RTP RTCP Layer 4 User Datagram Protocol Internet Protocol Ethernet 802. 13 or Wi-Fi 802. 11 PHY (Wired or Wireless) 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 3
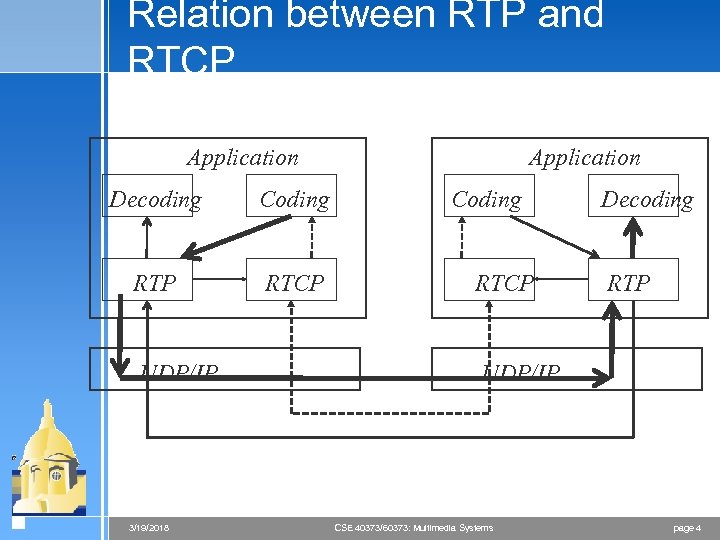 Relation between RTP and RTCP Application Decoding Coding RTP RTCP UDP/IP 3/19/2018 Application Coding RTCP Decoding RTP UDP/IP CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 4
Relation between RTP and RTCP Application Decoding Coding RTP RTCP UDP/IP 3/19/2018 Application Coding RTCP Decoding RTP UDP/IP CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 4
 RTCP: Control and Management 4 Out-of-band control information for RTP flow. < Monitors Qo. S for RTP in the delivery and packaging of multimedia data < Used periodically to transmit control packets to participants in a streaming multimedia session. < Provides feedback on the quality of service being provided by RTP < Gathers statistics on media connection = Bytes sent, packets sent, lost packets, jitter, feedback and round trip delay = Application may use this information to increase the quality of service, perhaps by limiting flow or using a different codec 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 5
RTCP: Control and Management 4 Out-of-band control information for RTP flow. < Monitors Qo. S for RTP in the delivery and packaging of multimedia data < Used periodically to transmit control packets to participants in a streaming multimedia session. < Provides feedback on the quality of service being provided by RTP < Gathers statistics on media connection = Bytes sent, packets sent, lost packets, jitter, feedback and round trip delay = Application may use this information to increase the quality of service, perhaps by limiting flow or using a different codec 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 5
 RTCP Functions 4 There are several type of RTCP packets: < Sender report packet, < Receiver report packet, < Source Description RTCP Packet, < Goodbye RTCP Packet and < Application Specific RTCP packets. 4 RTCP itself does not provide any flow encryption or authentication means. SRTCP protocol can be used for that purpose. 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 6
RTCP Functions 4 There are several type of RTCP packets: < Sender report packet, < Receiver report packet, < Source Description RTCP Packet, < Goodbye RTCP Packet and < Application Specific RTCP packets. 4 RTCP itself does not provide any flow encryption or authentication means. SRTCP protocol can be used for that purpose. 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 6
 RTP Services 4 Payload Type Identification < Determination of media coding < Source identification < RTP works with Profiles = Profile defines a set of payload type codes and their mappings to payload formats 4 Sequence numbering < Error detection 4 Time-stamping < Time monitoring, synchronization, jitter calculation 4 Delivery monitoring 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 7
RTP Services 4 Payload Type Identification < Determination of media coding < Source identification < RTP works with Profiles = Profile defines a set of payload type codes and their mappings to payload formats 4 Sequence numbering < Error detection 4 Time-stamping < Time monitoring, synchronization, jitter calculation 4 Delivery monitoring 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 7
 RTP Services – Support of heterogeneity 4 Mixer service < Allows for resynchronization of incoming audio packets < Reconstructs constant 20 ms spacing generated by sender < Mixes reconstructed audio streams into single stream < Translated audio encoding to lower bandwidth < Forwards lower bandwidth packet streams 4 Translator service < Allows for translation between IP and other high speed protocols < May change encoding data 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 8
RTP Services – Support of heterogeneity 4 Mixer service < Allows for resynchronization of incoming audio packets < Reconstructs constant 20 ms spacing generated by sender < Mixes reconstructed audio streams into single stream < Translated audio encoding to lower bandwidth < Forwards lower bandwidth packet streams 4 Translator service < Allows for translation between IP and other high speed protocols < May change encoding data 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 8
 Payload Formats 4 Static Payload formats < Established in RTP Profile < Payload type 0 : = µ-law audio codec 4 Dynamic Payload formats < Applications agree per session on payload format < H. 263, JPEG, MPEG 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 9
Payload Formats 4 Static Payload formats < Established in RTP Profile < Payload type 0 : = µ-law audio codec 4 Dynamic Payload formats < Applications agree per session on payload format < H. 263, JPEG, MPEG 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 9
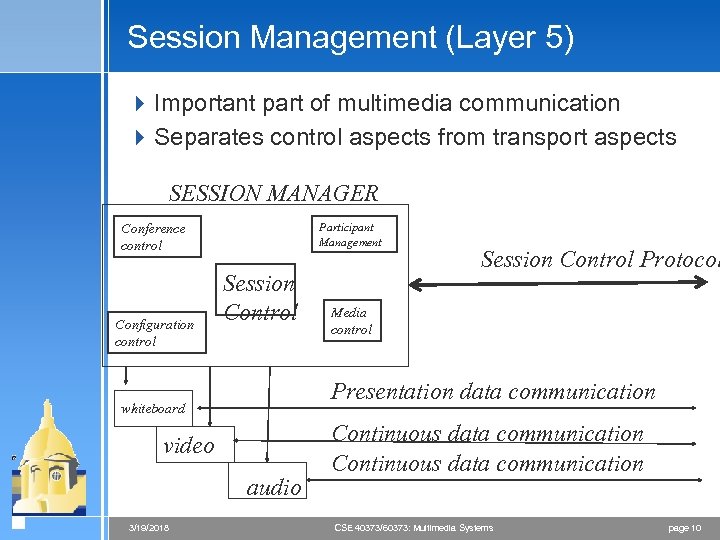 Session Management (Layer 5) 4 Important part of multimedia communication 4 Separates control aspects from transport aspects SESSION MANAGER Participant Management Conference control Configuration control Session Control Media control Presentation data communication whiteboard video audio 3/19/2018 Session Control Protocol Continuous data communication CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 10
Session Management (Layer 5) 4 Important part of multimedia communication 4 Separates control aspects from transport aspects SESSION MANAGER Participant Management Conference control Configuration control Session Control Media control Presentation data communication whiteboard video audio 3/19/2018 Session Control Protocol Continuous data communication CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 10
 Session Manager 4 Tasks: < Membership control < Monitoring of shared workspace < Coordination of Media control management < Exchange of Qo. S parameters < Conference control management – establishment, modification, termination 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 11
Session Manager 4 Tasks: < Membership control < Monitoring of shared workspace < Coordination of Media control management < Exchange of Qo. S parameters < Conference control management – establishment, modification, termination 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 11
 Session Control 4 Session Described by < Session state = Name of session, start, valid policies 4 Session management – two steps for state processing < Establishment of session < Modification of session 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 12
Session Control 4 Session Described by < Session state = Name of session, start, valid policies 4 Session management – two steps for state processing < Establishment of session < Modification of session 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 12
 Session Control 4 Conference Control < Centralized or distributed approach 4 Media Control < Synchronization 4 Configuration Control < Negotiation of Qo. S parameters, admission control and reservation/allocation of resources 4 Membership Control < Invitation of users; registration of users, change of membership 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 13
Session Control 4 Conference Control < Centralized or distributed approach 4 Media Control < Synchronization 4 Configuration Control < Negotiation of Qo. S parameters, admission control and reservation/allocation of resources 4 Membership Control < Invitation of users; registration of users, change of membership 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 13
 RTSP 4 Enables controlled, on-demand delivery of real-time data such as audio and video 4 Intends to control multiple data delivery sessions 4 Provides means for choosing delivery channels < UDP < Multicast UDP, < TCP 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 14
RTSP 4 Enables controlled, on-demand delivery of real-time data such as audio and video 4 Intends to control multiple data delivery sessions 4 Provides means for choosing delivery channels < UDP < Multicast UDP, < TCP 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 14
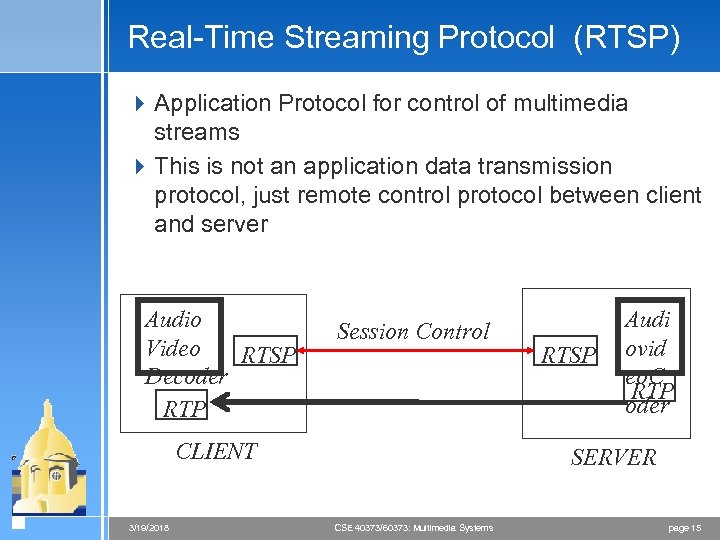 Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) 4 Application Protocol for control of multimedia streams 4 This is not an application data transmission protocol, just remote control protocol between client and server Audio Video RTSP Decoder RTP Session Control CLIENT 3/19/2018 RTSP Audi ovid eo. C RTP oder SERVER CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 15
Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) 4 Application Protocol for control of multimedia streams 4 This is not an application data transmission protocol, just remote control protocol between client and server Audio Video RTSP Decoder RTP Session Control CLIENT 3/19/2018 RTSP Audi ovid eo. C RTP oder SERVER CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 15
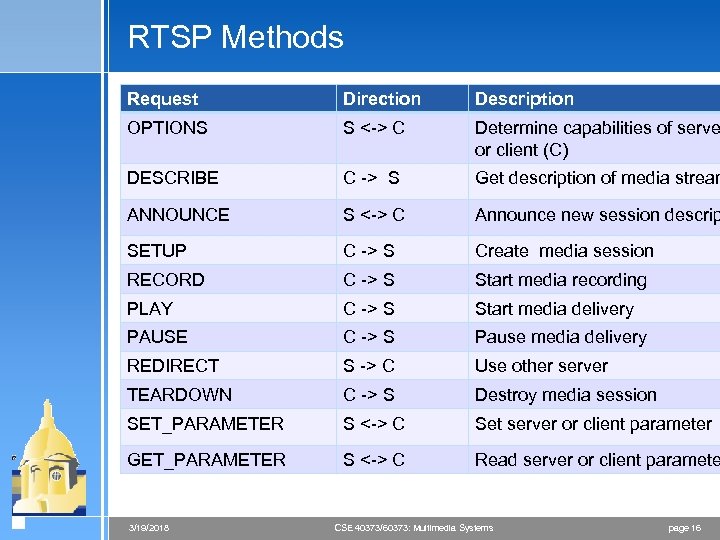 RTSP Methods Request Direction Description OPTIONS S <-> C Determine capabilities of serve or client (C) DESCRIBE C -> S Get description of media stream ANNOUNCE S <-> C Announce new session descrip SETUP C -> S Create media session RECORD C -> S Start media recording PLAY C -> S Start media delivery PAUSE C -> S Pause media delivery REDIRECT S -> C Use other server TEARDOWN C -> S Destroy media session SET_PARAMETER S <-> C Set server or client parameter GET_PARAMETER S <-> C Read server or client paramete 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 16
RTSP Methods Request Direction Description OPTIONS S <-> C Determine capabilities of serve or client (C) DESCRIBE C -> S Get description of media stream ANNOUNCE S <-> C Announce new session descrip SETUP C -> S Create media session RECORD C -> S Start media recording PLAY C -> S Start media delivery PAUSE C -> S Pause media delivery REDIRECT S -> C Use other server TEARDOWN C -> S Destroy media session SET_PARAMETER S <-> C Set server or client parameter GET_PARAMETER S <-> C Read server or client paramete 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 16
 RTSP Extensions 4 Timing < RTSP needs to hide latency variations < PLAY request may contain information about when request is to be executed 4 Three types of timestamps < SMPTE (the same as in TV production) = Format: hours: minutes: seconds: frames < Normal play time = Measured relative to beginning of stream and expressed in ours, minutes, seconds and fractions of second < Absolute time = Wall clock 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 17
RTSP Extensions 4 Timing < RTSP needs to hide latency variations < PLAY request may contain information about when request is to be executed 4 Three types of timestamps < SMPTE (the same as in TV production) = Format: hours: minutes: seconds: frames < Normal play time = Measured relative to beginning of stream and expressed in ours, minutes, seconds and fractions of second < Absolute time = Wall clock 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 17
 Session Description Protocol (SDP) 4 Text format for describing multimedia sessions 4 Not really a protocol (similar to markup language like HTML) 4 Can be carried in any protocol, e. g. , RTSP or SIP 4 Describes unicast and multicast sessions 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 18
Session Description Protocol (SDP) 4 Text format for describing multimedia sessions 4 Not really a protocol (similar to markup language like HTML) 4 Can be carried in any protocol, e. g. , RTSP or SIP 4 Describes unicast and multicast sessions 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 18
 SDP 4 There are five terms related to multimedia session description: < Conference: It is a set of two or more communicating users along with the software they are using. < Session : Session is the multimedia sender and receiver and the flowing stream of data. < Session Announcement: A session announcement is a mechanism by which a session description is conveyed to users in a proactive fashion, i. e. , the session description was not explicitly requested by the user. < Session Advertisement : same as session announcement < Session Description : A well defined format for conveying sufficient information to discover and participate in a multimedia session. 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 19
SDP 4 There are five terms related to multimedia session description: < Conference: It is a set of two or more communicating users along with the software they are using. < Session : Session is the multimedia sender and receiver and the flowing stream of data. < Session Announcement: A session announcement is a mechanism by which a session description is conveyed to users in a proactive fashion, i. e. , the session description was not explicitly requested by the user. < Session Advertisement : same as session announcement < Session Description : A well defined format for conveying sufficient information to discover and participate in a multimedia session. 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 19
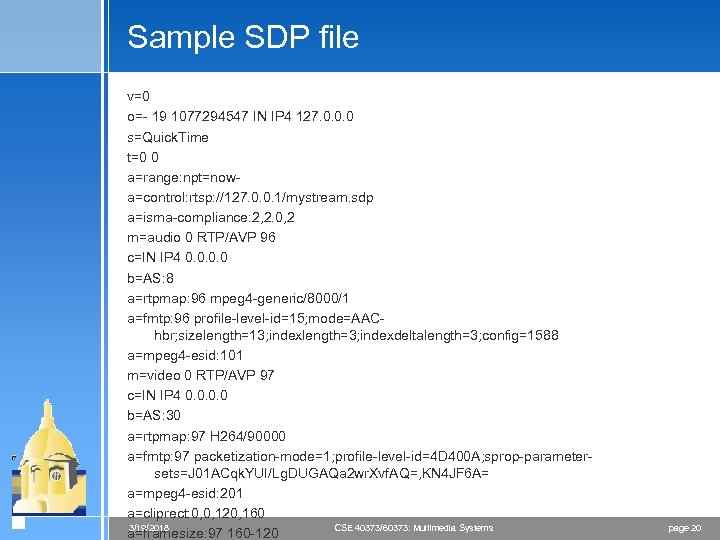 Sample SDP file v=0 o=- 19 1077294547 IN IP 4 127. 0. 0. 0 s=Quick. Time t=0 0 a=range: npt=nowa=control: rtsp: //127. 0. 0. 1/mystream. sdp a=isma-compliance: 2, 2. 0, 2 m=audio 0 RTP/AVP 96 c=IN IP 4 0. 0 b=AS: 8 a=rtpmap: 96 mpeg 4 -generic/8000/1 a=fmtp: 96 profile-level-id=15; mode=AAChbr; sizelength=13; indexlength=3; indexdeltalength=3; config=1588 a=mpeg 4 -esid: 101 m=video 0 RTP/AVP 97 c=IN IP 4 0. 0 b=AS: 30 a=rtpmap: 97 H 264/90000 a=fmtp: 97 packetization-mode=1; profile-level-id=4 D 400 A; sprop-parametersets=J 01 ACqk. YUI/Lg. DUGAQa 2 wr. Xvf. AQ=, KN 4 JF 6 A= a=mpeg 4 -esid: 201 a=cliprect: 0, 0, 120, 160 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems 3/19/2018 a=framesize: 97 160 -120 page 20
Sample SDP file v=0 o=- 19 1077294547 IN IP 4 127. 0. 0. 0 s=Quick. Time t=0 0 a=range: npt=nowa=control: rtsp: //127. 0. 0. 1/mystream. sdp a=isma-compliance: 2, 2. 0, 2 m=audio 0 RTP/AVP 96 c=IN IP 4 0. 0 b=AS: 8 a=rtpmap: 96 mpeg 4 -generic/8000/1 a=fmtp: 96 profile-level-id=15; mode=AAChbr; sizelength=13; indexlength=3; indexdeltalength=3; config=1588 a=mpeg 4 -esid: 101 m=video 0 RTP/AVP 97 c=IN IP 4 0. 0 b=AS: 30 a=rtpmap: 97 H 264/90000 a=fmtp: 97 packetization-mode=1; profile-level-id=4 D 400 A; sprop-parametersets=J 01 ACqk. YUI/Lg. DUGAQa 2 wr. Xvf. AQ=, KN 4 JF 6 A= a=mpeg 4 -esid: 201 a=cliprect: 0, 0, 120, 160 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems 3/19/2018 a=framesize: 97 160 -120 page 20
 VOIP 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 21
VOIP 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 21
 Signaling for IP Telephony 4 Internet Telephone – needs ability of one party to signal to other party to initiate a new call 4 Call – association between a number of participants < Note: there is no physical channel or network resources associated with the session layer connection, the connection exists only as signaling state at two end points 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 22
Signaling for IP Telephony 4 Internet Telephone – needs ability of one party to signal to other party to initiate a new call 4 Call – association between a number of participants < Note: there is no physical channel or network resources associated with the session layer connection, the connection exists only as signaling state at two end points 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 22
 IP Telephony Signaling Protocol (Requirements) 4 Name translations and user location < Mapping between names of different levels of abstraction = Email address to IP address of host 4 Feature negotiation < Group of end systems must agree on what media to exchange ad their respective parameters = Different encodings, rates 4 Call Participant Management = Invite participants to existing call, transfer call and hold other users 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 23
IP Telephony Signaling Protocol (Requirements) 4 Name translations and user location < Mapping between names of different levels of abstraction = Email address to IP address of host 4 Feature negotiation < Group of end systems must agree on what media to exchange ad their respective parameters = Different encodings, rates 4 Call Participant Management = Invite participants to existing call, transfer call and hold other users 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 23
 IP Telephony Signaling (Requirements) 4 Feature change < Adjust composition of media sessions during the course of call = Add or reduce functionality = Impose or remove constraints due to addition or removal of participants 4 Two signaling protocols: < SIP (IETF Standard) < H. 323 (ITU Standard) 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 24
IP Telephony Signaling (Requirements) 4 Feature change < Adjust composition of media sessions during the course of call = Add or reduce functionality = Impose or remove constraints due to addition or removal of participants 4 Two signaling protocols: < SIP (IETF Standard) < H. 323 (ITU Standard) 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 24
 SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) 4 SIP Goal: invite new participants to call 4 Client-Server protocol at the application level 4 Protocol: < User/Client creates requests and sends to server; < User agent server responds; 4 SIP requests can traverse many proxy servers 4 Server may act as redirect server 4 Proxies or redirect servers cannot accept/reject requests, only user agent server can 4 Requests/Responses are textual 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 25
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) 4 SIP Goal: invite new participants to call 4 Client-Server protocol at the application level 4 Protocol: < User/Client creates requests and sends to server; < User agent server responds; 4 SIP requests can traverse many proxy servers 4 Server may act as redirect server 4 Proxies or redirect servers cannot accept/reject requests, only user agent server can 4 Requests/Responses are textual 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 25
 SIP - Message 4 Calls in SIP – have unique call ID (carried in Call-ID header field of SIP message) 4 Call identifier is created by the caller and used by all participants 4 SIP messages have information < Logical connection source < Logical connection destination < Media capabilities (use SDP) 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 26
SIP - Message 4 Calls in SIP – have unique call ID (carried in Call-ID header field of SIP message) 4 Call identifier is created by the caller and used by all participants 4 SIP messages have information < Logical connection source < Logical connection destination < Media capabilities (use SDP) 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 26
 SIP – Addressing and Naming 4 To be invited and identified, called party must be named 4 SIP chooses email-like identifier < user@domain < user@host < user@IPaddress < phone-number@gateway 4 SIP’s address: part of SIP URL < sip: j. doe@example. com < URL can be placed on web page 4 Interactive audio/video requests translation < name@domain to host@host 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 27
SIP – Addressing and Naming 4 To be invited and identified, called party must be named 4 SIP chooses email-like identifier < user@domain < user@host < user@IPaddress < phone-number@gateway 4 SIP’s address: part of SIP URL < sip: j. doe@example. com < URL can be placed on web page 4 Interactive audio/video requests translation < name@domain to host@host 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 27
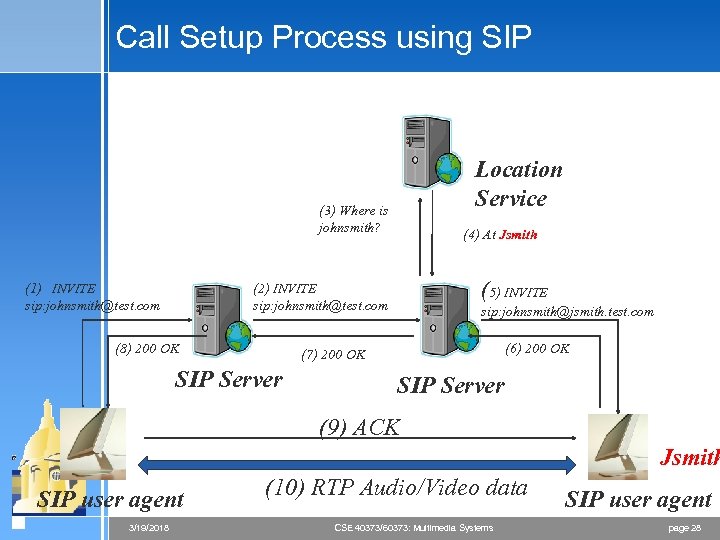 Call Setup Process using SIP Location Service (3) Where is johnsmith? (1) INVITE sip: johnsmith@test. com (4) At Jsmith (5) INVITE (2) INVITE sip: johnsmith@test. com (8) 200 OK sip: johnsmith@jsmith. test. com (6) 200 OK (7) 200 OK SIP Server (9) ACK Jsmith SIP user agent 3/19/2018 (10) RTP Audio/Video data CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems SIP user agent page 28
Call Setup Process using SIP Location Service (3) Where is johnsmith? (1) INVITE sip: johnsmith@test. com (4) At Jsmith (5) INVITE (2) INVITE sip: johnsmith@test. com (8) 200 OK sip: johnsmith@jsmith. test. com (6) 200 OK (7) 200 OK SIP Server (9) ACK Jsmith SIP user agent 3/19/2018 (10) RTP Audio/Video data CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems SIP user agent page 28
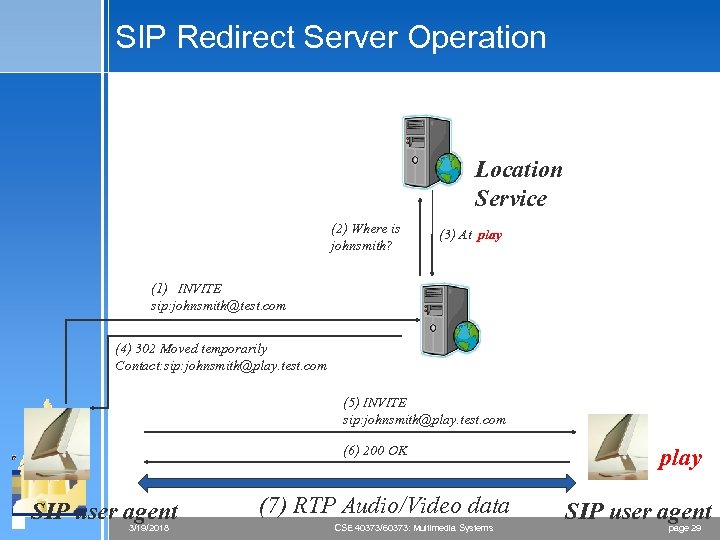 SIP Redirect Server Operation Location Service (2) Where is johnsmith? (3) At play (1) INVITE sip: johnsmith@test. com (4) 302 Moved temporarily Contact: sip: johnsmith@play. test. com (5) INVITE sip: johnsmith@play. test. com (6) 200 OK SIP user agent 3/19/2018 (7) RTP Audio/Video data CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems play SIP user agent page 29
SIP Redirect Server Operation Location Service (2) Where is johnsmith? (3) At play (1) INVITE sip: johnsmith@test. com (4) 302 Moved temporarily Contact: sip: johnsmith@play. test. com (5) INVITE sip: johnsmith@play. test. com (6) 200 OK SIP user agent 3/19/2018 (7) RTP Audio/Video data CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems play SIP user agent page 29
 SIP Requests/Methods 4 INVITE—Indicates a client is being invited to participate in a call session. 4 ACK—Confirms that the client has received a final response to an INVITE request. 4 BYE—Terminates a call and can be sent by either the caller or the callee. 4 CANCEL—Cancels any pending searches but does not terminate a call that has already been accepted. 4 OPTIONS—Queries the capabilities of servers. 4 REGISTER—Registers the address listed in the To header field with a SIP server. 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 30
SIP Requests/Methods 4 INVITE—Indicates a client is being invited to participate in a call session. 4 ACK—Confirms that the client has received a final response to an INVITE request. 4 BYE—Terminates a call and can be sent by either the caller or the callee. 4 CANCEL—Cancels any pending searches but does not terminate a call that has already been accepted. 4 OPTIONS—Queries the capabilities of servers. 4 REGISTER—Registers the address listed in the To header field with a SIP server. 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 30
 SAP – Session Announcement Protocol 4 RTSP and SIP are designed for one-on-one session 4 SAP is multicast announcement protocol 4 Protocol < Distributed servers periodically send multicast packets (advertisements) containing descriptions of sessions generated by local sources < Advertisements are received by multicast receivers on well-known , static multicast address/port 4 Advertisement contains SDP information to start media tools needed in the session 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 31
SAP – Session Announcement Protocol 4 RTSP and SIP are designed for one-on-one session 4 SAP is multicast announcement protocol 4 Protocol < Distributed servers periodically send multicast packets (advertisements) containing descriptions of sessions generated by local sources < Advertisements are received by multicast receivers on well-known , static multicast address/port 4 Advertisement contains SDP information to start media tools needed in the session 3/19/2018 CSE 40373/60373: Multimedia Systems page 31


