1196b4d0798b4b7a17196f0029d90e88.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Polyuria-polydipsia Central diabetes insipidus Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Psychogenic water drinking Diabetes mellitus

Survey of diabetes insipidus History n quantitation of daily fluid intake and output w noturia or enuresis n detailed dietary history w avoid foods with a high protein content n n n acuteness of onset drug growth and development

Survey of diabetes insipidus Lab n n 24 h I/O Urine: specific gravity or osmo. , glucose Serum sodium and osmo. definite diagnosis: water deprivation test

Water deprivation test Prcedure n n morning: empty bladder & weigh pt NPO blood: Na, K, Ca, Crea, osmo. , vasopressin q 1 h check: w BW w Urine: vol. , specific gravity(sg), osmolality w Serum: Na, osmolality

Water deprivation test Ending (one of following) n n BW > 3% serum Na > 150 mmol/L or osmo. > 300 mmol/L Uosmo reaches 850 mmol/kg for 2 consecutive tests Uosmo stablized ( < 30 mmol/kg between the last 2 collections) Empty bladder Blood: osmo. , Na, and vasopressin DDAVP (2 ug) s. c. or 10 ug (0. 1 ml) intranasal, and drink as desired Uosmo and Sosmo q 30 min x 2, (x 4 if intranasal)
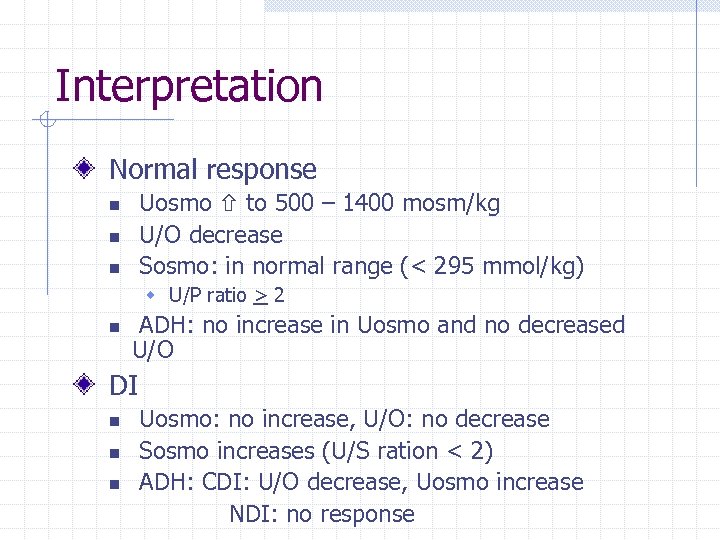
Interpretation Normal response Uosmo to 500 – 1400 mosm/kg U/O decrease Sosmo: in normal range (< 295 mmol/kg) n n n w U/P ratio > 2 n ADH: no increase in Uosmo and no decreased U/O DI n n n Uosmo: no increase, U/O: no decrease Sosmo increases (U/S ration < 2) ADH: CDI: U/O decrease, Uosmo increase NDI: no response
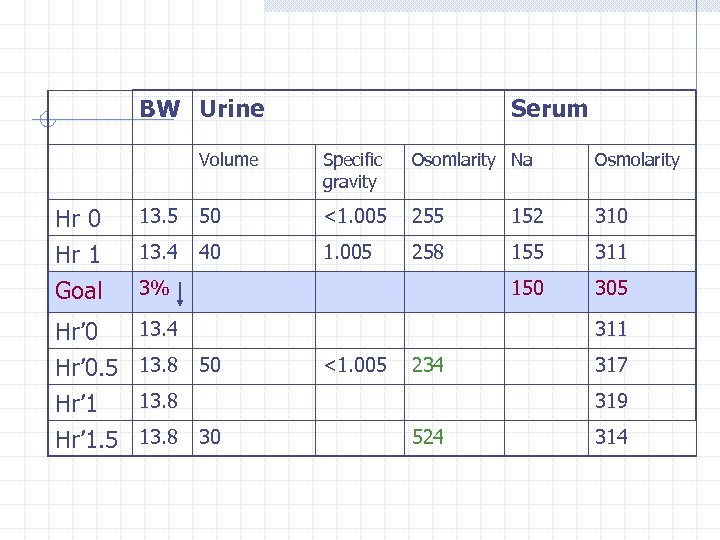
BW Urine Serum Volume Specific gravity Osomlarity Na Osmolarity Hr 0 13. 5 50 <1. 005 255 152 310 Hr 1 Goal 13. 4 40 1. 005 258 155 311 150 305 Hr’ 0. 5 Hr’ 1. 5 13. 4 3% 13. 8 311 50 <1. 005 234 13. 8 317 319 30 524 314
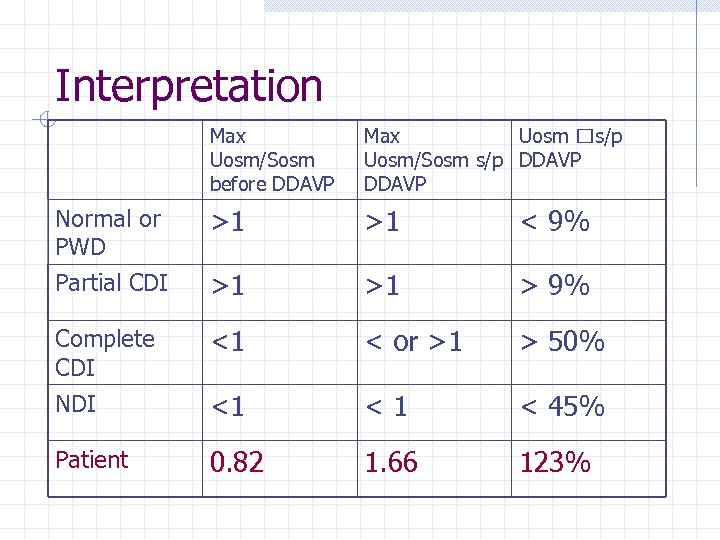
Interpretation Max Uosm/Sosm before DDAVP Max Uosm s/p Uosm/Sosm s/p DDAVP Normal or PWD >1 >1 < 9% Partial CDI >1 >1 > 9% Complete CDI NDI <1 < or >1 > 50% <1 <1 < 45% Patient 0. 82 1. 66 123%

Central diabetes insipidus Cause n n n brain tumor idiopathic neurosurgery head trauma HIE histiocytosis Survey: skull x-ray or head CT Tx: hormonal replacement

Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Cause n n n congenital acquired: chronic renal Dz e- disorder: hypokalemia, hypercalcemia sickle cell trait adrenal insufficiency drug w lithiium, colchicine, constrast, diuretics n diet w protein starvation, chronic salt depletion, chronic high water intake

Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Survey n n electrolyte renal echo Treatment n n low sodium diet (< 1 mmol/kg/24 h) adequate protein (2 g/kg/day) 300 -400 ml/kg water drug: w thiazide (hydrochlorothiazide 2 -4 mg/kg/d): 注意 hypokalemia, 可與 amiloride併用 w indocin (2 mg/kg/d): 亦可與 thiazide併用

Water deprivation test Prcedure n n morning: empty bladder & weigh pt NPO blood: Na, K, Ca, Crea, osmo. , vasopressin q 1 h check: w BW w Urine: vol. , specific gravity(sg), osmolality w Serum: Na, osmolality

Water deprivation test Ending (one of following) n n BW > 5% (or 3%) serum Na > 150 mmol/L and plasma osmo. > 305 mmol/kg Uosmo reaches 850 mmol/kg for 2 consecutive tests Uosmo stablized ( < 30 mmol/kg between the last 2 collections) Empty bladder Blood: osmo. , Na, and vasopressin DDAVP (2 ug) use, and drink as desired Uosmo and Sosmo q 30 min x 2
1196b4d0798b4b7a17196f0029d90e88.ppt