fdb29c27b2355291b9ea63aa5d508393.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
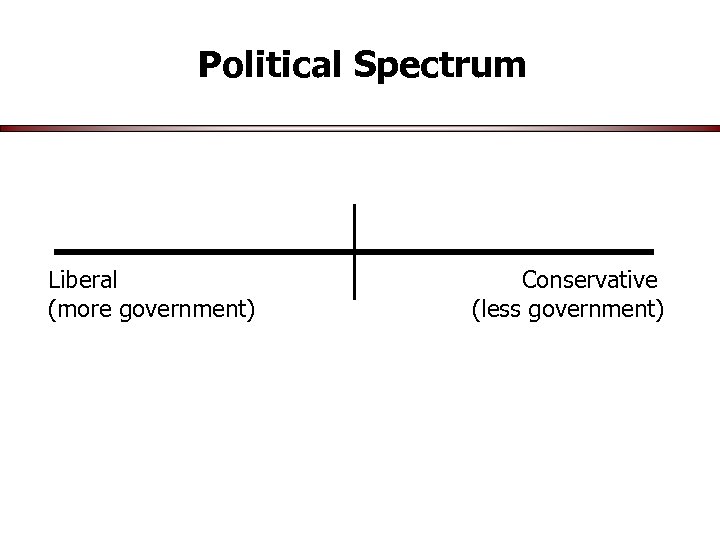
Political Spectrum Liberal Conservative (more government) (less government)

Politics of the Minority v Find allies issue by issue. Not philosophy by philosophy v Build coalitions, compromise, find common ground v Be positive, reasonable, work within system v Base case on facts, not myths or emotions v Adopt non-partisan strategy

Where is The Power in Agricultural and Food Policy? • Agriculture’s iron triangle • Government – Executive Branch – Legislative Branch – Judicial Branch • Other Organizations – – General farm organizations Commodity organizations Agribusinesses Public interest groups • Other departments
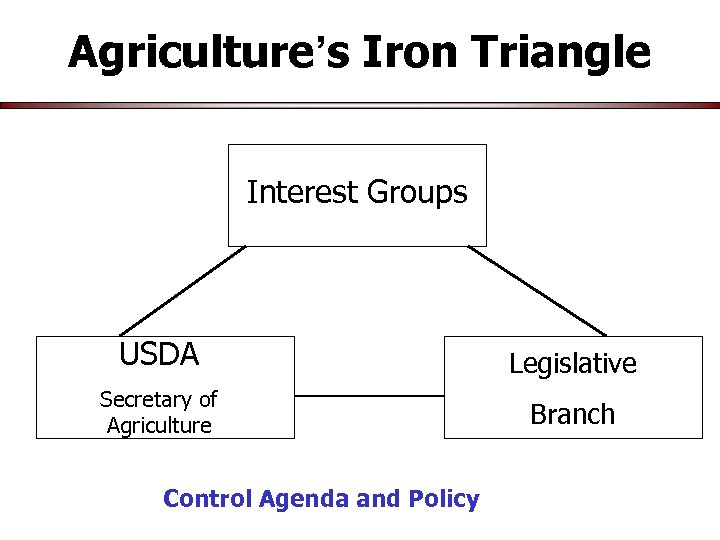
Agriculture’s Iron Triangle Interest Groups USDA Legislative Secretary of Agriculture Branch Control Agenda and Policy
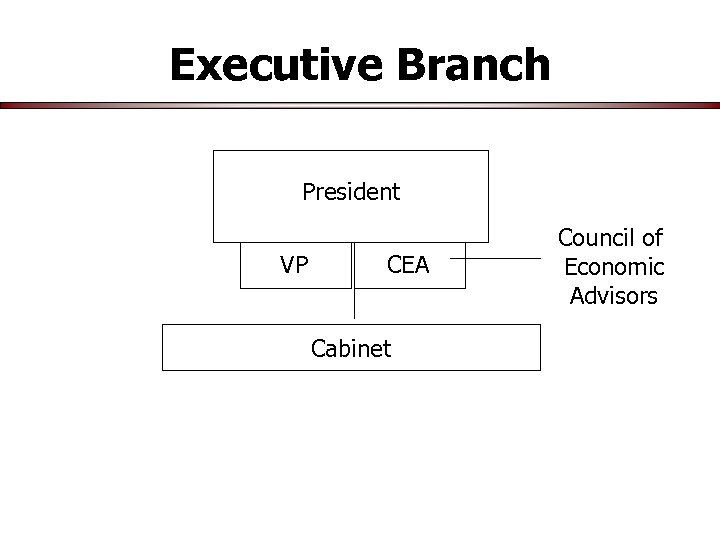
Executive Branch President VP CEA Cabinet Council of Economic Advisors
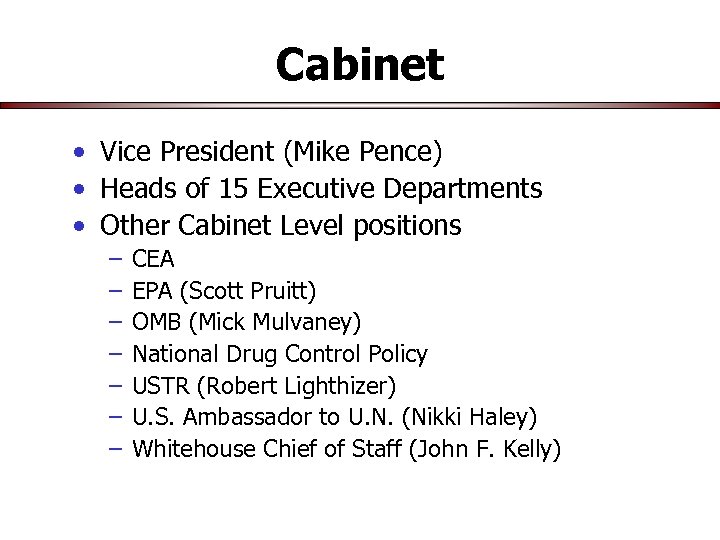
Cabinet • Vice President (Mike Pence) • Heads of 15 Executive Departments • Other Cabinet Level positions – – – – CEA EPA (Scott Pruitt) OMB (Mick Mulvaney) National Drug Control Policy USTR (Robert Lighthizer) U. S. Ambassador to U. N. (Nikki Haley) Whitehouse Chief of Staff (John F. Kelly)

Executive Departments • • • • Agriculture (USDA) (Sonny Perdue) Commerce (DOC) Defense (DOD) Education Energy (DOE) Health & Human Services (HHS) Homeland Security Housing & Urban Development (HUD) Interior (DOI) Justice (DOJ) Labor (DOL) State (DOS) Transportation (DOT) Treasury Veteran Affairs
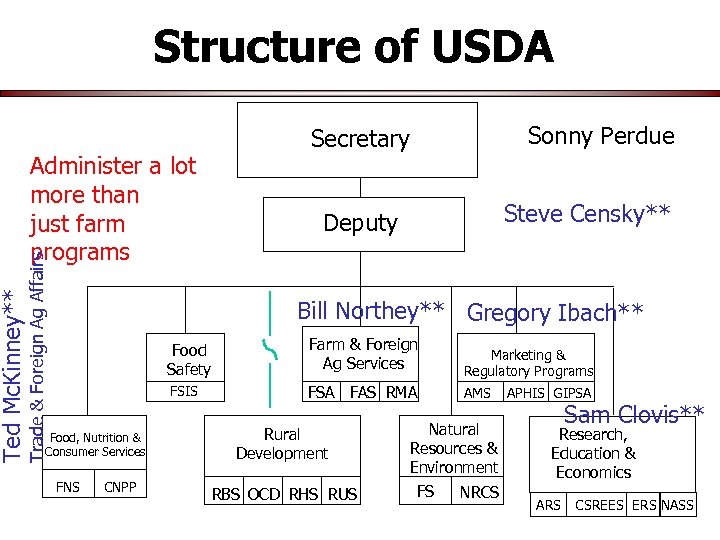
Structure of USDA Administer a lot more than just farm programs Trade & Foreign Ag Affairs Ted Mc. Kinney** Sonny Perdue Secretary Steve Censky** Deputy Bill Northey** Gregory Ibach** Food Safety FSIS Food, Nutrition & Consumer Services FNS CNPP Farm & Foreign Ag Services FSA FAS RMA Rural Development RBS OCD RHS RUS Marketing & Regulatory Programs AMS Natural Resources & Environment FS NRCS APHIS GIPSA Sam Clovis** Research, Education & Economics ARS CSREES ERS NASS

Legislative Branch • “All Legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives. ” Article I, Section 1 • Membership – House • 435 elected for 2 year terms • Census determines number from each state – Senate • 100 elected for 6 year terms

Functions of Congress • Authorization (legislation/programs) • Appropriation (who gets what? ) • Oversight (keep an eye on Executive Branch)
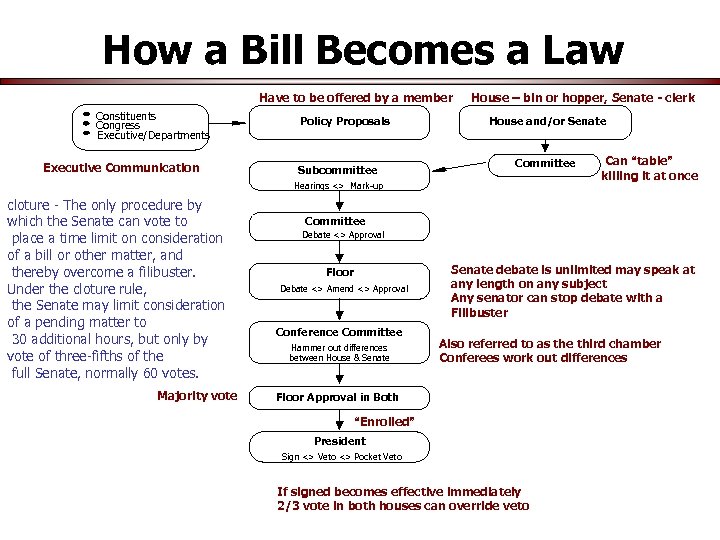
How a Bill Becomes a Law Have to be offered by a member Constituents Congress Executive/Departments Executive Communication Policy Proposals Subcommittee House – bin or hopper, Senate - clerk House and/or Senate Committee Hearings <> Mark-up cloture - The only procedure by which the Senate can vote to place a time limit on consideration of a bill or other matter, and thereby overcome a filibuster. Under the cloture rule, the Senate may limit consideration of a pending matter to 30 additional hours, but only by vote of three-fifths of the full Senate, normally 60 votes. Majority vote Can “table” killing it at once Committee Debate <> Approval Floor Debate <> Amend <> Approval Conference Committee Hammer out differences between House & Senate debate is unlimited may speak at any length on any subject Any senator can stop debate with a Filibuster Also referred to as the third chamber Conferees work out differences Floor Approval in Both “Enrolled” President Sign <> Veto <> Pocket Veto If signed becomes effective immediately 2/3 vote in both houses can override veto
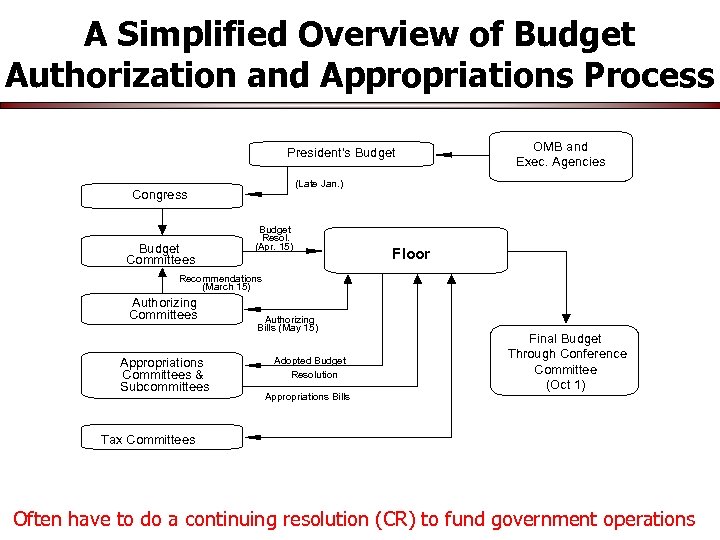
A Simplified Overview of Budget Authorization and Appropriations Process President's Budget (Late Jan. ) Congress Budget Committees OMB and Exec. Agencies Budget Resol. (Apr. 15) Floor Recommendations (March 15) Authorizing Committees Appropriations Committees & Subcommittees Authorizing Bills (May 15) Adopted Budget Resolution Appropriations Bills Final Budget Through Conference Committee (Oct 1) Tax Committees Often have to do a continuing resolution (CR) to fund government operations

Action is in Committees (House and Senate) • Overall Congressional Leadership – Senate Majority: Mitch Mc. Connell (KY) – Minority: Chuck Schumer (NY) – Speaker of the House: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority: Kevin Mc. Carthy (CA) Minority: Nancy Pelosi (CA) • Budget Committee (sets limits on spending) – Senate Majority: Mike Enzi (WY) Minority: Bernie Sanders (VT) – House Majority: Diane Black (TN) Minority: John Yarmuth (KY)

Action is in Committees (cont. ) • Agriculture Committee (authorizes ag and nutrition, etc legislation) – Senate Majority: Pat Roberts (KS) Minority: Debbie Stabenow (MI) – House Majority: Mike Conaway (TX) Minority: Collin Peterson (MN) • Agriculture appropriations subcommittee (decides what/who gets money) – Senate Majority: John Hoeven (ND) Minority: Jeff Merkley (OR) – House Majority: Robert Aderholt (AL) Minority: Sanford Bishop (GA)
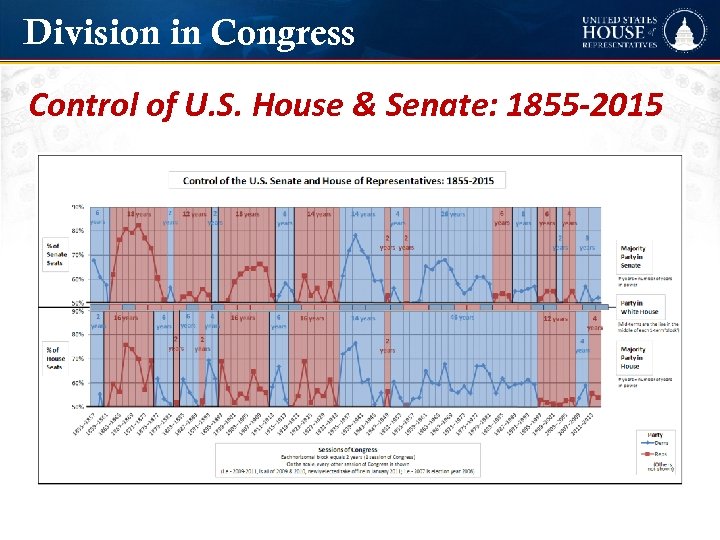
Division in Congress Control of U. S. House & Senate: 1855 -2015

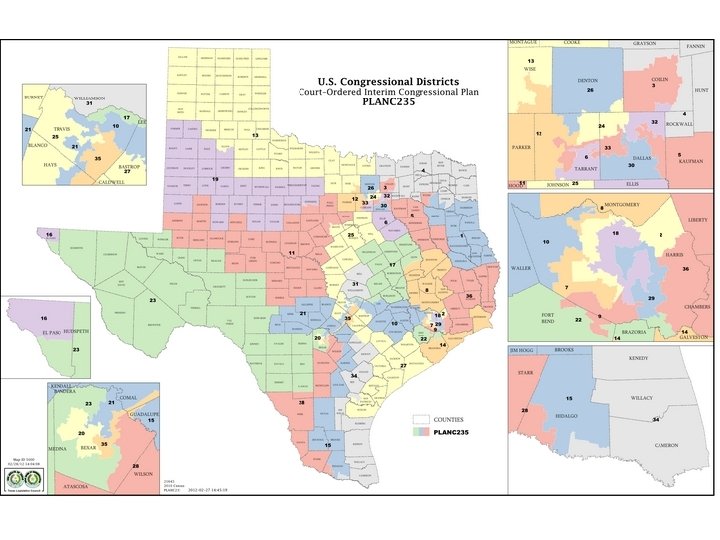
Texas Redistricting • • • Every decade presents different challenges and reflects the wills of the various players involved during that period. The history of the redistricting process during the 1980 s, 1990 s, 2000 s, and of the 2010 s process to date, illustrates some of the different courses decennial redistricting can take. The timing and legal requirements, however, dictate that the basic process likely takes the following course, which is described in more detail in the associated sections. Census population data is delivered to the legislature no later than April 1 of the year following the decennial census, and perhaps as much as six weeks earlier. As soon as the census data is loaded in the computer systems, the members of the legislature, their designees, and other interested parties begin drawing plans. Bills to enact new redistricting plans follow the same path through the legislature as other legislation. If Texas senate or house districts are not enacted during the first regular session following the publication of the decennial census, the Texas Constitution requires that the Legislative Redistricting Board (LRB) meet and adopt its own plan. The LRB has jurisdiction only in the months following the legislature's first redistricting effort. Any legislative or LRB plan must be submitted to the U. S. Department of Justice or the U. S. District Court for the District of Columbia for preclearance under Section 5 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
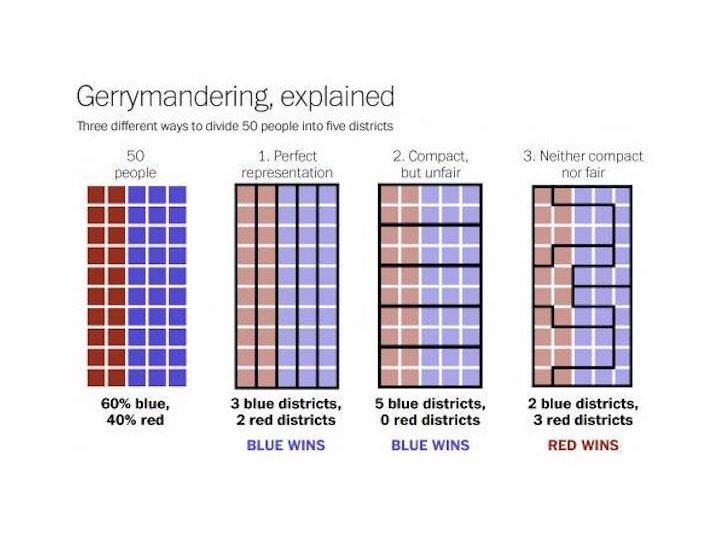

Majority is really important • Elects leadership of Congress (control agenda) • Has majority membership of committees and subcommittees • Elects chairs of committees and subcommittees (control agenda) • Has the most staff (bigger offices, etc)
fdb29c27b2355291b9ea63aa5d508393.ppt