2110709bb7977c88145b6f0bf7776eab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Political Redistricting By Saad Padela

The American Political System Legislative bicameralism Number of seats in lower house is proportional to population Single-member districts First-past-the-post (or plurality) voting “One man, one vote”
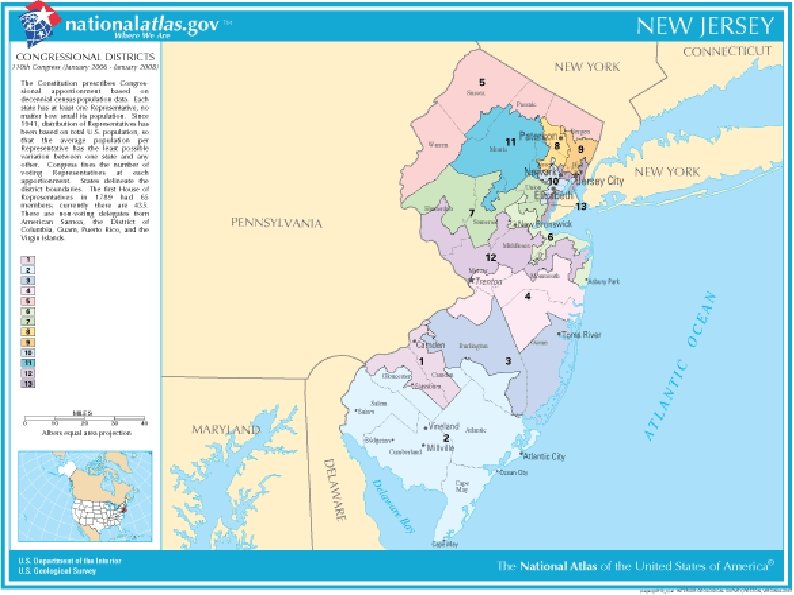

The Case for Redistricting New Census data every 10 years # of Representatives = α * Population 0<α<1 # of Representatives = # of Districts Population rises => More seats Districts must be redrawn

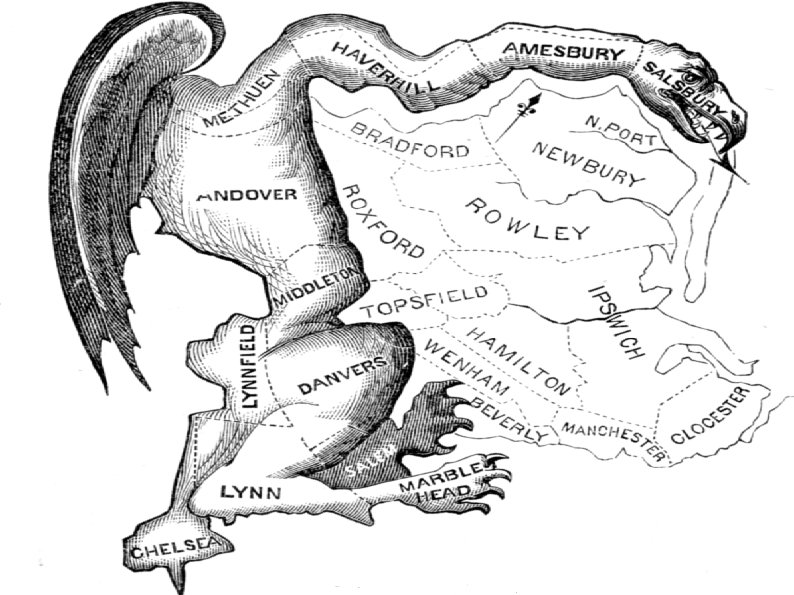
Gerrymandering

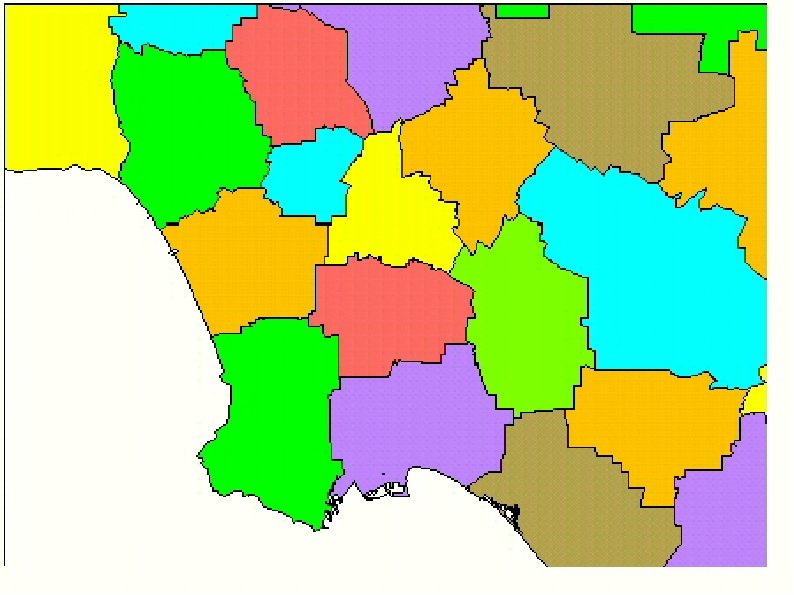
Types of Gerrymandering Partisan Bipartisan Incumbents vs. Challengers Racial and ethnic Democrats vs. Republicans Majority vs. Minority groups “Benign” In favor of minority groups

Gerrymandering Strategies Different election objectives To win a single district To win a majority of many districts Partisan Own votes Win districts by the smallest margin possible Minimize wasted votes in losing districts Opponent's votes Fragment them into different districts Concentrate them into a single district

Gerrymandering Strategies Bipartisan Racial and ethnic Maximize number of “safe” districts Fragment supporters of minority candidates “Benign” Maximize chances of minority representation by concentrating them into single districts

A Linear Programming Formulation? Easy to see Small scholarly literature Those who are involved in it like to keep their work secret

Detection of Gerrymandering A rich literature Hess, S. W. 1965. “Nonpartisan Political Redistricting by Computer. ” Operations Research, 13 (6), 998 -1006.

Good Districts are. . . Equally populous Contiguous Compact
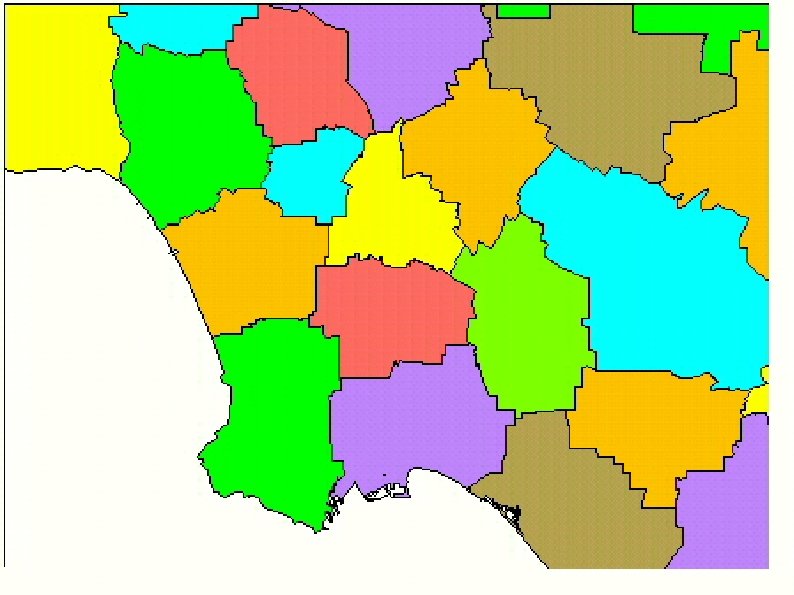

Equal population Easy to write as a constraint

Contiguity Highly intuitive Sometimes tedious to code

Compactness Ambiguous Difficult to measure Niemi et al. 1990. “Measuring Compactness and the Role of a Compactness Standard in a Test for Partisan and Racial Gerrymandering. ” The Journal of Politics, 52 (4), 1155 -1181. “A Typology of Compactness Measures” (Table 1) Dispersion Perimeter Population
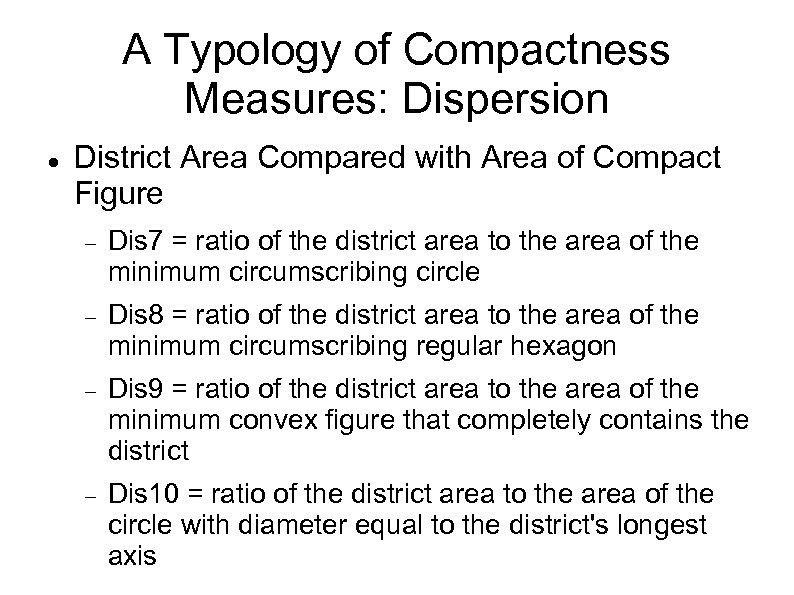
A Typology of Compactness Measures: Dispersion District Area Compared with Area of Compact Figure Dis 7 = ratio of the district area to the area of the minimum circumscribing circle Dis 8 = ratio of the district area to the area of the minimum circumscribing regular hexagon Dis 9 = ratio of the district area to the area of the minimum convex figure that completely contains the district Dis 10 = ratio of the district area to the area of the circle with diameter equal to the district's longest axis
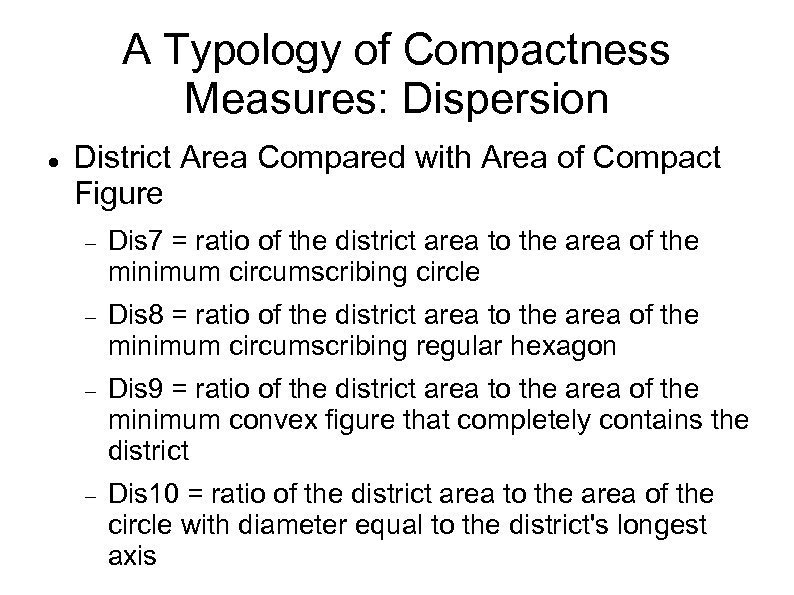
A Typology of Compactness Measures: Dispersion District Area Compared with Area of Compact Figure Dis 7 = ratio of the district area to the area of the minimum circumscribing circle Dis 8 = ratio of the district area to the area of the minimum circumscribing regular hexagon Dis 9 = ratio of the district area to the area of the minimum convex figure that completely contains the district Dis 10 = ratio of the district area to the area of the circle with diameter equal to the district's longest axis
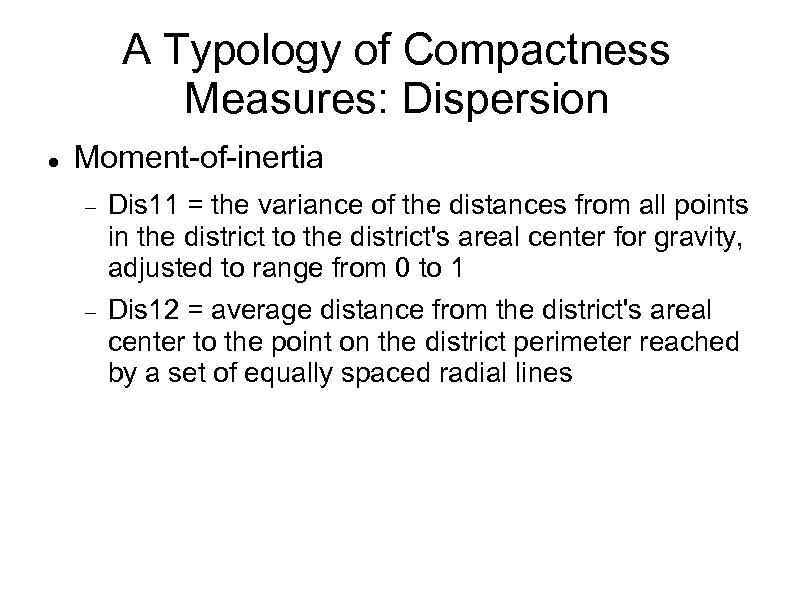
A Typology of Compactness Measures: Dispersion Moment-of-inertia Dis 11 = the variance of the distances from all points in the district to the district's areal center for gravity, adjusted to range from 0 to 1 Dis 12 = average distance from the district's areal center to the point on the district perimeter reached by a set of equally spaced radial lines
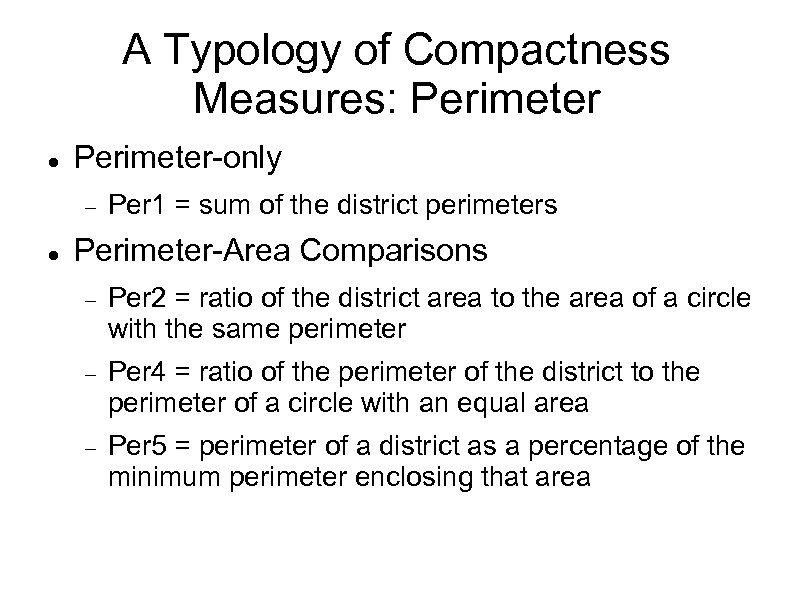
A Typology of Compactness Measures: Perimeter-only Per 1 = sum of the district perimeters Perimeter-Area Comparisons Per 2 = ratio of the district area to the area of a circle with the same perimeter Per 4 = ratio of the perimeter of the district to the perimeter of a circle with an equal area Per 5 = perimeter of a district as a percentage of the minimum perimeter enclosing that area
A Typology of Compactness Measures: Population District Population Compared with Population of Compact Figure Pop 1 = ratio of the district population to the population of the minimum convex figure that completely contains the district Pop 2 = ratio of the district population to the population in the minimum circumscribing circle Moment-of-inertia Pop 3 = population moment of inertia, normalized from 0 to 1

Warehouse Location model Hess, S. W. 1965. “Nonpartisan Political Redistricting by Computer. ” Operations Research, 13 (6), 998 -1006. Garfinkel, R. S. And G. L. Nemhauser. 1970. “Optimal Political Districting By Implicit Enumeration techniques. ” Management Science, 16 (8). Hojati, Mehran. 1996. “Optimal Political Districting. ” Computers and Operations Research, 23 (12), 1147 -1161. All these formulations have class NP

Heuristic Methods Hess, S. W. 1965. Garfinkel, R. S. And G. L. Nemhauser. 1970. Hojati, Mehran. 1996. Bozkaya, B. , Erkut, E. , and G. Laporte. 2003. “A tabu search heuristic and adaptive memory procedure for political districting. ” European Journal of Operational Research, 144, 12 -26.

Statistical physics? Chou, C. and S. P. Li. 2006. “Taming the Gerrymander – Statistical physics approach to Political Districting Problem. ”

Criticisms of Compactness Altman, Micah. 1998. “Modeling the effect of mandatory district compactness on partisan gerrymanders. ” Political Geography, 17 (8), 989 -1012. Nonlinear effects – “electoral manipulation is much more severely constrained by high compactness than by moderate compactness” Context-dependent, and purely relative Asymmetrical effects on different political groups Compactness can also disadvantage geographically concentrated minorities

More Sophisticated Measures Niemi, R. and J. Deegan. 1978. “A Theory of Political Districting. ” American Political Science Review, 72 (4), 1304 -1323. Neutrality Range of Responsiveness % range of the total popular vote over which seats change from one party to the other Constant Swing Ratio v% of the popular vote results in s% of the seats rate at which a party gains seats per increment in votes Competitiveness % of districts in which the “normal” vote is close to 50%

Balinksi, Michel. 2008. “Fair Majority Voting (or How to Eliminate Gerrymandering). ” The American Mathematical Monthly, 115 (2), 97114.
2110709bb7977c88145b6f0bf7776eab.ppt