politicalparties-10010.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Political Parties §What is the difference between the Republicans and the Democrats? §Why are political parties important in a democracy?
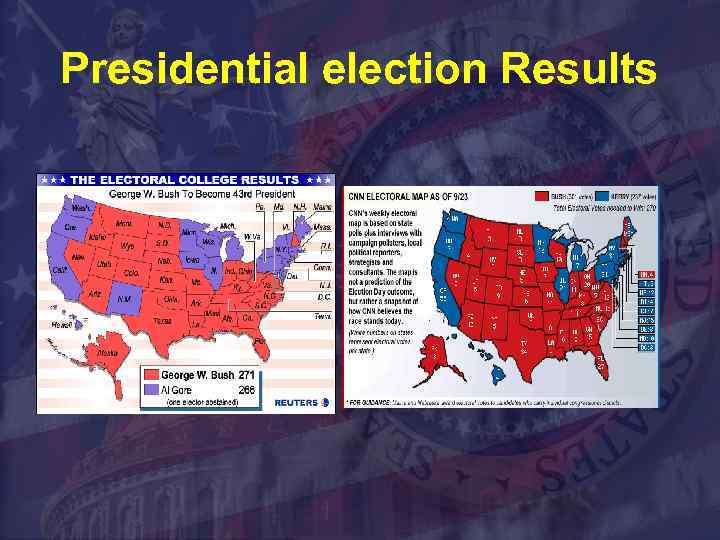
Presidential election Results

Political Socialization § Source of political beliefs and attitudes § Family and the Social Environment § Education § Peers § Leaders’ Influence § Media § Political events § Example: – The Great Depression – 60’s and the Vietnam War Era

What are political parties? § Definition § Political party is an organization that seeks to attain political power within a government § § Usually by participating in electoral campaigns. Parties often support a certain ideology § Subgroups interests are integrated

Institutional Constraints on Political Parties § Structure and Strength of Parties: Majoritarian or Proportional Representation § History § Presidential or Parliamentary System § Laws and Constitution §

Theory: Lipset and Rokkan § Theory on Political Cleavages § Parties that were formed in the aftermath of political, religious, and economic revolutions are frozen. State vs. Church § Worker vs. Owner § Land vs. Industry § Center vs. Periphery (Fed vs. State) § § These have and will continue to exist in the political arena despite new issues and challenges.

The Constitution § Says nothing about political parties. § Why? Founding fathers felt parties were wicked and corrupt. § Did not want parties to control politics. § Did not want to pervade the entire country and create factions. §

Today’s Major US Political Parties and Ideology § Republican Party (GOP)Considered the more socially conservative and economically neoliberal. § Laissez-Faire Economics § Party Chairman- Ken Mehlman § § Democratic Party. Considered more socially liberal and economically interventionist. § Party Chairman- Howard Dean §

US Parties: First Party System (before 1824) American Revolution Federalist • Founded by Hamilton • Supported strong central government • Commercial interest: merchants and large planters Anti federalist • Founded by Jefferson • Supported more state autonomy • Also known as the Republicans Jackson split into a Democratic party Adams remained in the Republican party, but latter called the Whigs Hamiltonian vision for modernizing the United States

Era of Good Feelings (1817 -1825) § One Party Dominance (the Republicans) Federalist virtually collapsed in 1816 § 1817 -1825 no real competition § Republicans opposed big government §
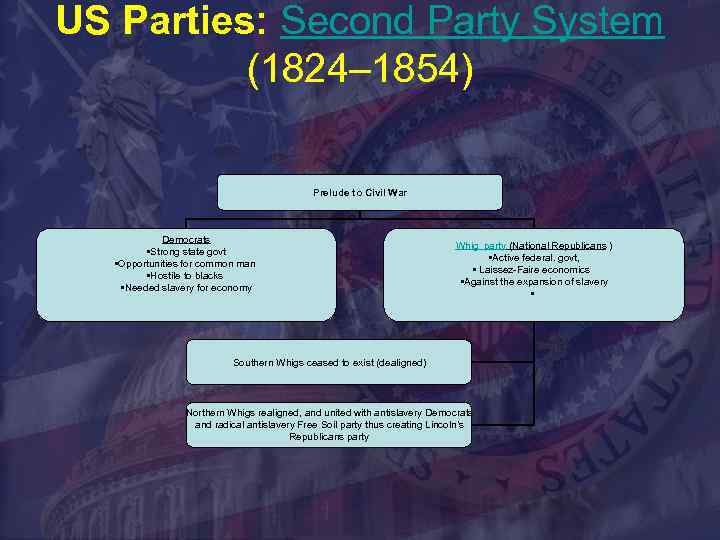
US Parties: Second Party System (1824– 1854) Prelude to Civil War Democrats • Strong state govt • Opportunities for common man • Hostile to blacks • Needed slavery for economy Whig party (National Republicans ) • Active federal. govt, • Laissez-Faire economics • Against the expansion of slavery Southern Whigs ceased to exist (dealigned) Northern Whigs realigned, and united with antislavery Democrats and radical antislavery Free Soil party thus creating Lincoln’s Republicans party •

US Parties: Third Party System: Post Civil War (1854– 1896) Post Civil War Democrats • Feared strong central govt • Did not want to give free slaves rights • Dominated the white south for decades Democrats embraced populism. Advocated for small farmers Sought high inflation for debt relief. Republicans • Sought to increase the power of the federal govt • Promoted economic growth and businesses • Promoted evangelical protestant morals and values • Public schools w/ protestant curriculum • Inflation in check to maintain working class wages • Limited/prohibited the sale of alcohol

US Parties: Fourth Party System/ Progressive Era (1896– 1932) Industrial Revolution Democrats • Traditional small govt. policy was realigned and opened to govt. intervention in the economy • Wilson was able to win presidency because the Republican split Republicans • Honest Impartial Govt could regulate the economy more effectively 1912 split : T. Roosevelt ran on the Bull Moose Ticket The platform based non progressive ideals. Protect women, children, and immigrants. Reform corrupt govt, and give people more voice.

US Parties: New Deal and Fifth Party System Great Depression and New Deal Republicans Laissez Faire State govt and private organizations To ease the suffering Democrats United whites and blacks Both sought relief from hardships Strong federal govt 60’s Democrats split from economic and social Conservatives in south into republican base 60’s social progressives African Americans remained Democrats

Function of Political Parties § § § To mobilize the public in an organization Organize and run elections Recruit Candidates (strategy: TO WIN) Presenting alternative policies Accepting responsibility for the operation of govt. (advocating party agenda) § Acting as opposition to party in power
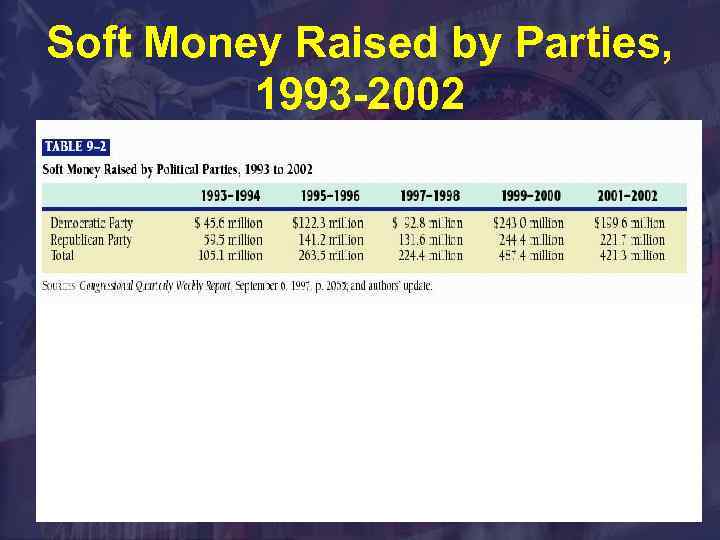
Soft Money Raised by Parties, 1993 -2002

Parties: Party Structure § National Level § § Pres. controls National Convention Party Chairperson National Committee § State level § § Governor controls State Conventions State party chairperson Party Boss § Local Level (Grassroots) § § § County Committee County Chairperson District Leaders Precinct or ward captains Party Workers

Political Cartoon

Primary Elections § Candidates official nomination process § All parties will select their candidate for the general election Presidential or gubernatorial candidates § First Tuesday in the month of June before the general election in November § Front-Loading: § § State determines the date for its primary or caucus § Early primaries are more influential – States compete to schedule their primaries as early as possible – New Hampshire (first presidential primary) – Iowa (first caucus)

Parties in Action § Meetings § § § Quadrennial Nominate presidential candidate Reveals party platform Introduces new and upcoming stars Establishes party momentum § Government Provides funding for candidates § Whips legislators § § Finances § Fund raising

Political Cartoon

Accountability to the Voters § Presidential and Parliamentary Systems § Viable third parties

Role of the Citizen

Quiz § Why are political parties important in to fulfilling democracy?
politicalparties-10010.ppt