968d3bbeb1ac7b1b727db8c0ffcebe45.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Political Parties
Political Parties
 Functions of political parties • 1) Nominating candidates- Who should be the party’s nominees? Parties not only provide a mechanism for nominations (primaries, a caucus) but they also recruit candidates. • For local offices, there is often an interview process
Functions of political parties • 1) Nominating candidates- Who should be the party’s nominees? Parties not only provide a mechanism for nominations (primaries, a caucus) but they also recruit candidates. • For local offices, there is often an interview process
 • 2) Structuring the Voting Choice- parties give us a limited number of candidates to choose from. • This helps to streamline the effort needed to vote (and yet we don’t vote all that much!)
• 2) Structuring the Voting Choice- parties give us a limited number of candidates to choose from. • This helps to streamline the effort needed to vote (and yet we don’t vote all that much!)
 • 3) Proposing alternative government programs • Tax policy • Environmental policy • Debt reduction • Entitlements
• 3) Proposing alternative government programs • Tax policy • Environmental policy • Debt reduction • Entitlements
 • 4) Coordinating the actions of public officials • The President is the leader of his party and the Congressional members tend to follow his lead. • The Speaker and/or Senate Majority Leader (or Minority leaders) lead the opposition. (in our current case John Boehner is SOH)
• 4) Coordinating the actions of public officials • The President is the leader of his party and the Congressional members tend to follow his lead. • The Speaker and/or Senate Majority Leader (or Minority leaders) lead the opposition. (in our current case John Boehner is SOH)
 History of US Party Politics • I. Pre-party period • Parties were seen as divisive. Federalist No. 10 argued that a federal system would weed out factionalism • During the Am. Rev. there were “loyalists” or “tories” and “Whigs” or “patriots” • During the debate on the Constitution there were “Federalists” and “Anti-federalists” • The President and VP were chosen by the electoral college. The electors were initially chosen by state legislatures (as were Senators)
History of US Party Politics • I. Pre-party period • Parties were seen as divisive. Federalist No. 10 argued that a federal system would weed out factionalism • During the Am. Rev. there were “loyalists” or “tories” and “Whigs” or “patriots” • During the debate on the Constitution there were “Federalists” and “Anti-federalists” • The President and VP were chosen by the electoral college. The electors were initially chosen by state legislatures (as were Senators)
 History of US Party Politics • I. Pre-party period • Parties were seen as divisive. Federalist No. 10 argued that a federal system would weed out factionalism • During the Am. Rev. there were “loyalists” or “tories” and “Whigs” or “patriots” • During the debate on the Constitution there were “Federalists” and “Anti-federalists” • The President and VP were chosen by the electoral college. The electors were initially chosen by state legislatures (as were Senators)
History of US Party Politics • I. Pre-party period • Parties were seen as divisive. Federalist No. 10 argued that a federal system would weed out factionalism • During the Am. Rev. there were “loyalists” or “tories” and “Whigs” or “patriots” • During the debate on the Constitution there were “Federalists” and “Anti-federalists” • The President and VP were chosen by the electoral college. The electors were initially chosen by state legislatures (as were Senators)
 • Candidates for other offices were chosen by a Caucus of political leaders • President Washington was above politics altogether, he was WASHINGTON
• Candidates for other offices were chosen by a Caucus of political leaders • President Washington was above politics altogether, he was WASHINGTON
 The First Party System • Election of 1796 - Adams (Fed) beats Jefferson (Rep) but Jefferson becomes VP. Yikes!! • Election of 1800 - Jefferson and Burr (Rep) beat Adams and Pinckney (Fed). However, the electors must cast 2 votes and Jefferson and Burr are tied. Yikes!! The House eventually votes for Jefferson as President • 12 th Amendment- separate elections for President and VP
The First Party System • Election of 1796 - Adams (Fed) beats Jefferson (Rep) but Jefferson becomes VP. Yikes!! • Election of 1800 - Jefferson and Burr (Rep) beat Adams and Pinckney (Fed). However, the electors must cast 2 votes and Jefferson and Burr are tied. Yikes!! The House eventually votes for Jefferson as President • 12 th Amendment- separate elections for President and VP
 • Federalist party fades away and from 1816 -1824 we have the Era of Good Feeling • Also, white male suffrage begins to expand after 1815 • 1824 - most electors are chosen by popular vote. JQ Adams beats Jackson in the House of Reps despite losing the popular vote. Jackson calls it a ______
• Federalist party fades away and from 1816 -1824 we have the Era of Good Feeling • Also, white male suffrage begins to expand after 1815 • 1824 - most electors are chosen by popular vote. JQ Adams beats Jackson in the House of Reps despite losing the popular vote. Jackson calls it a ______
 2 nd Party System • Jackson’s group calls themselves Democrats. In 1828 Jackson is the first Democratic candidate. Relaxed voting requirements leads to a 300% inc. in voting. • Candidates for president are now nominated by national conventions where parties adopt a party platform. • Anti-Masonic party- 1 st 3 rd party in US History • National Republicans morph into the Whig party in 1834. They’ll be killed by the slavery issue by 1856
2 nd Party System • Jackson’s group calls themselves Democrats. In 1828 Jackson is the first Democratic candidate. Relaxed voting requirements leads to a 300% inc. in voting. • Candidates for president are now nominated by national conventions where parties adopt a party platform. • Anti-Masonic party- 1 st 3 rd party in US History • National Republicans morph into the Whig party in 1834. They’ll be killed by the slavery issue by 1856
 Current Party System • The Republican party is founded in 1854. 1856 first candidate is John Fremont. • 1860 - is considered a “critical election” because it was marked by a change in voter loyalties that will persist for several elections. • From 1880 -1920, no Republican wins a southern state. This “solid south” persists until the Democrats become associated with civil rights in the 1950 -60 s.
Current Party System • The Republican party is founded in 1854. 1856 first candidate is John Fremont. • 1860 - is considered a “critical election” because it was marked by a change in voter loyalties that will persist for several elections. • From 1880 -1920, no Republican wins a southern state. This “solid south” persists until the Democrats become associated with civil rights in the 1950 -60 s.
 Eras of party dominance • Critical Election- sharp change in patterns of party loyalty • Ex- 1932, 1980/1994 • This results in an electoral realignment
Eras of party dominance • Critical Election- sharp change in patterns of party loyalty • Ex- 1932, 1980/1994 • This results in an electoral realignment
 1860 -1894 • Reps win 8/10 presidential elections with the strategy of ______ • Control of Congress was 9 -9 sessions
1860 -1894 • Reps win 8/10 presidential elections with the strategy of ______ • Control of Congress was 9 -9 sessions
 1896 -1930 • 1896 - a critical election. When Dems nominate William Jennings Bryan, they are seen as “radical” and damage their brand. • The link between the GOP and business is forged and persists to this day. • With the exception of Wilson’s 2 terms, the GOP controls the White House and Congress continuously until the Great Depression. • Any arguments?
1896 -1930 • 1896 - a critical election. When Dems nominate William Jennings Bryan, they are seen as “radical” and damage their brand. • The link between the GOP and business is forged and persists to this day. • With the exception of Wilson’s 2 terms, the GOP controls the White House and Congress continuously until the Great Depression. • Any arguments?
 1932 -1968 • FDR is able to win 4 terms as the “Roosevelt Coalition” becomes the Democratic “safety net”. This is made up of labor, southerners and ethnic voters as well as urban residents. • Dems win presidency 7 of 9 times between 1932 -198. Only Eisenhower (a national hero like WASHINGTON) can break the Democratic hold • The Dems also hold both houses of Congress in most years from 1932 -1994.
1932 -1968 • FDR is able to win 4 terms as the “Roosevelt Coalition” becomes the Democratic “safety net”. This is made up of labor, southerners and ethnic voters as well as urban residents. • Dems win presidency 7 of 9 times between 1932 -198. Only Eisenhower (a national hero like WASHINGTON) can break the Democratic hold • The Dems also hold both houses of Congress in most years from 1932 -1994.
 Conservative Realignment • When did it occur? • Fist noticed in 1964 with Barry Goldwater • 1968 - Nixon wins with his “Southern Strategy” and appeal to the “Silent Majority”. Although Congress still stays Dem. • This is in direct response to the “permissiveness” and “radical” nature of the 1960 s. Particularly Civil Rights in the South and Student protests on college campuses. Also in response to decisions of the Warren Court.
Conservative Realignment • When did it occur? • Fist noticed in 1964 with Barry Goldwater • 1968 - Nixon wins with his “Southern Strategy” and appeal to the “Silent Majority”. Although Congress still stays Dem. • This is in direct response to the “permissiveness” and “radical” nature of the 1960 s. Particularly Civil Rights in the South and Student protests on college campuses. Also in response to decisions of the Warren Court.
 Election of 1980 • Reagan trounces Carter 51% to 41% and 489 -49 in the electoral college although Congress did not change • However, Reagan’s ideology has been dominant in the GOP since then and is seen in virtually every 2012 GOP candidate and in the national debates on budget etc. .
Election of 1980 • Reagan trounces Carter 51% to 41% and 489 -49 in the electoral college although Congress did not change • However, Reagan’s ideology has been dominant in the GOP since then and is seen in virtually every 2012 GOP candidate and in the national debates on budget etc. .
 Control of the States • • • 23 Republican-controlled governments 11 Democratic-controlled governments 5 Democratic Governor/Republican-controlled Legislature 3 Republican Governor/Democratic-controlled Legislature 1 Independent Governor/Democratic-controlled Legislature 2 Republican Governor/Split Legislature 4 Democratic Governor/Split Legislature 1 Republican Governor/Non-partisan Legislature (Nebraska) 50 Total
Control of the States • • • 23 Republican-controlled governments 11 Democratic-controlled governments 5 Democratic Governor/Republican-controlled Legislature 3 Republican Governor/Democratic-controlled Legislature 1 Independent Governor/Democratic-controlled Legislature 2 Republican Governor/Split Legislature 4 Democratic Governor/Split Legislature 1 Republican Governor/Non-partisan Legislature (Nebraska) 50 Total
 Judicial Appointments
Judicial Appointments
 Minor Parties • 1) Bolter parties- factions off the 2 main parties. This happened 6 times since the Civil War. In 1912 (TR) and 1968 (George Wallace), they significantly impacted elections. • 2) Farmer-Labor Parties- 1892 - “People’s Party” AKA Populist Party was the 1 st third party to win electoral votes. • “Progressive Party” in 1924 nominated La. Follette who won 16. 6% and Wisconsin • Any chance for such a party today?
Minor Parties • 1) Bolter parties- factions off the 2 main parties. This happened 6 times since the Civil War. In 1912 (TR) and 1968 (George Wallace), they significantly impacted elections. • 2) Farmer-Labor Parties- 1892 - “People’s Party” AKA Populist Party was the 1 st third party to win electoral votes. • “Progressive Party” in 1924 nominated La. Follette who won 16. 6% and Wisconsin • Any chance for such a party today?
 Minor Parties • 3) Ideological Protest- these parties reject the political mainstream and offer radical proposals. A) Socialist Party- won 6% in 1912 B) Green Party- won 2. 7% in 2000 and helped George W. Bush to win C) Libertarian Party- since 1972 (Ron Paul is pretty close!!)
Minor Parties • 3) Ideological Protest- these parties reject the political mainstream and offer radical proposals. A) Socialist Party- won 6% in 1912 B) Green Party- won 2. 7% in 2000 and helped George W. Bush to win C) Libertarian Party- since 1972 (Ron Paul is pretty close!!)
 Minor Parties • 4) Single-Issue parties • Anti-Masonic, Free-Soil, Prohibition, and to some extent the American Party. Right to Life and Conservative parties are local, not national. • Generally, 3 rd parties do not fare well electorally, but they are very effective at raising issues
Minor Parties • 4) Single-Issue parties • Anti-Masonic, Free-Soil, Prohibition, and to some extent the American Party. Right to Life and Conservative parties are local, not national. • Generally, 3 rd parties do not fare well electorally, but they are very effective at raising issues
 • Do you think the Tea Party and/or Occupy movements have the potential to be 3 rd parties?
• Do you think the Tea Party and/or Occupy movements have the potential to be 3 rd parties?
 Why have we only had 2 parties? • 1) Electoral System- We are governed by “majority representation” which means we have single winners chosen by a simple plurality. This is also known as a “Winner takes all” system. • Many other nations (Israel and Denmark) follow a “proportional representation” system. • Also, to be elected President, a candidate needs a majority of electoral votes. So, they compete in every state and form alliances (Big Business and poor southern whites for example in the Republican Party)
Why have we only had 2 parties? • 1) Electoral System- We are governed by “majority representation” which means we have single winners chosen by a simple plurality. This is also known as a “Winner takes all” system. • Many other nations (Israel and Denmark) follow a “proportional representation” system. • Also, to be elected President, a candidate needs a majority of electoral votes. So, they compete in every state and form alliances (Big Business and poor southern whites for example in the Republican Party)
 • 2) Political Socialization- We have always been a 2 party system and since you initially are socialized at home, you are generally exposed to the 2 main parties.
• 2) Political Socialization- We have always been a 2 party system and since you initially are socialized at home, you are generally exposed to the 2 main parties.
 Party Identification
Party Identification
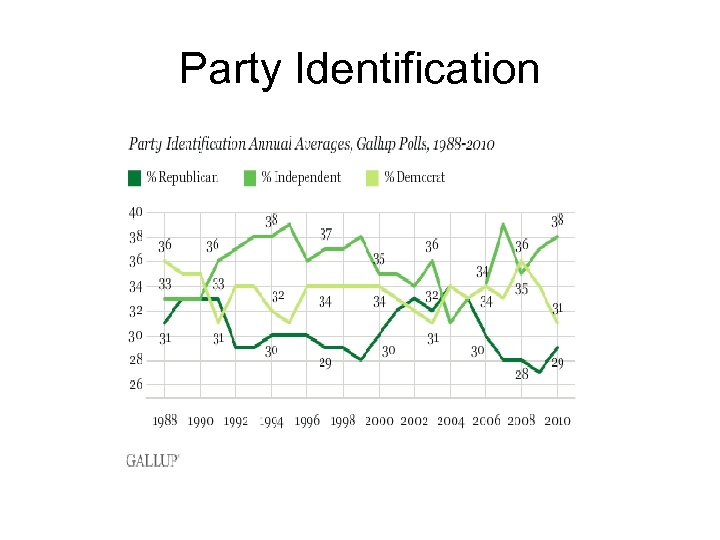
 3 main points • 1) Reps + Dems is greater than Independents • 2) The number of Dems is Greater than the number of Reps (exception being immediately after 9/11. Why? ) • 3) Dems have shrunk so that they are roughly equal with Reps and Inds.
3 main points • 1) Reps + Dems is greater than Independents • 2) The number of Dems is Greater than the number of Reps (exception being immediately after 9/11. Why? ) • 3) Dems have shrunk so that they are roughly equal with Reps and Inds.
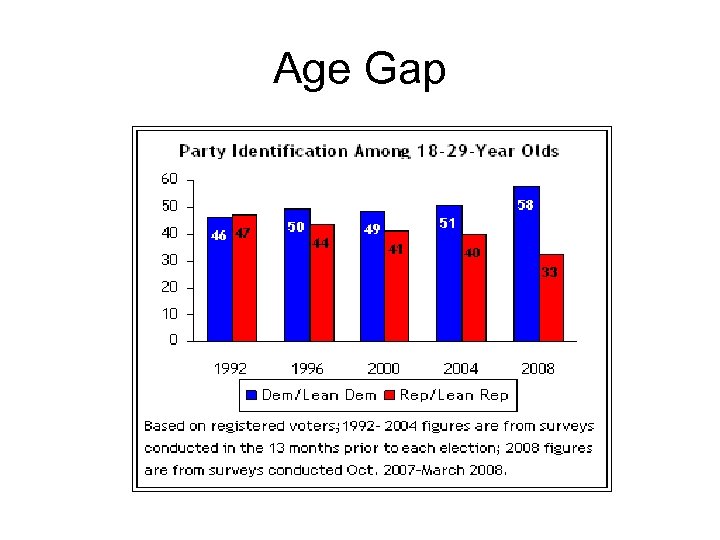
 Age Gap • The current generation of young voters, who came of age during the George W. Bush years, is leading the way in giving the Democrats a wide advantage in party identification, just as the previous generation of young people who grew up in the Reagan years -Generation X -- fueled the Republican surge of the mid-1990's. • In surveys conducted between October 2007 and March 2008, 58% of voters under age 30 identified or leaned toward the Democratic Party, compared with 33% who identified or leaned toward the GOP. The Democratic Party's current lead in party identification among young voters has more than doubled since the 2004 campaign, from 11 points to 25 points. • In fact, the Democrats' advantage among the young is now so broad -based that younger men as well as younger women favor the Democrats over the GOP -- making their age category the only one in the electorate in which men are significantly more inclined to selfidentify as Democrats rather than as Republicans
Age Gap • The current generation of young voters, who came of age during the George W. Bush years, is leading the way in giving the Democrats a wide advantage in party identification, just as the previous generation of young people who grew up in the Reagan years -Generation X -- fueled the Republican surge of the mid-1990's. • In surveys conducted between October 2007 and March 2008, 58% of voters under age 30 identified or leaned toward the Democratic Party, compared with 33% who identified or leaned toward the GOP. The Democratic Party's current lead in party identification among young voters has more than doubled since the 2004 campaign, from 11 points to 25 points. • In fact, the Democrats' advantage among the young is now so broad -based that younger men as well as younger women favor the Democrats over the GOP -- making their age category the only one in the electorate in which men are significantly more inclined to selfidentify as Democrats rather than as Republicans
 Age Gap
Age Gap
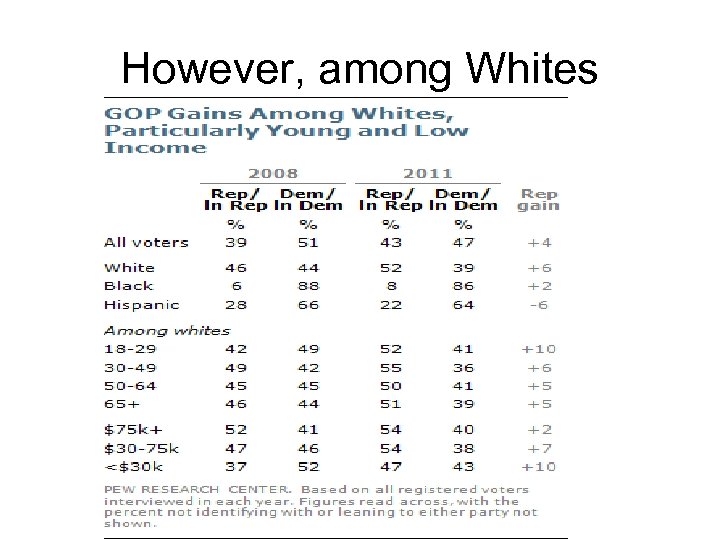 However, among Whites
However, among Whites
 National Party Organizations • • • 4 Components 1) National Convention 2) National Committee 3) Congressional Party Conferences 4) Congressional Campaign Committees-
National Party Organizations • • • 4 Components 1) National Convention 2) National Committee 3) Congressional Party Conferences 4) Congressional Campaign Committees-
 Changes in the 1970 s • After Vietnam, the Democratic Party began to be more inclusive. This included “affirmative action” rules for delegates. • At the 1972 convention, there were more women, blacks, latinos and young voters than ever before. ( although they nominated an unelectable candidate, George Mc. Govern) • By the 1980 s these groups were effectively socialized into the Democratic party.
Changes in the 1970 s • After Vietnam, the Democratic Party began to be more inclusive. This included “affirmative action” rules for delegates. • At the 1972 convention, there were more women, blacks, latinos and young voters than ever before. ( although they nominated an unelectable candidate, George Mc. Govern) • By the 1980 s these groups were effectively socialized into the Democratic party.
 Changes in the 1970’s • Republicans focused on organizational reforms as opposed to procedural reforms. They focused on fundraising, research and service roles. With the advent of various campaign financing laws, fundraising took on an outsize importance. Generally, Republicans do a better job at this. They typically use direct mail appeals.
Changes in the 1970’s • Republicans focused on organizational reforms as opposed to procedural reforms. They focused on fundraising, research and service roles. With the advent of various campaign financing laws, fundraising took on an outsize importance. Generally, Republicans do a better job at this. They typically use direct mail appeals.
 State and local party organizations • Party machines- ex- Tammany Hall, Cook County in Illinois (The Dayley Machine) and even the Nassau County Reps. were all powerful machines. They controlled elections as well as jobs and social services. • Nowadays state and local parties vary in strength but no one party has an advantage. Additionally money now flows from national party downward, not the other way around.
State and local party organizations • Party machines- ex- Tammany Hall, Cook County in Illinois (The Dayley Machine) and even the Nassau County Reps. were all powerful machines. They controlled elections as well as jobs and social services. • Nowadays state and local parties vary in strength but no one party has an advantage. Additionally money now flows from national party downward, not the other way around.
 Political party decentralization • Although national committees have more power, political parties are still very decentralized. • Ex- Clinton, Gephardt and trade legislation. • Also, there are many more Independent voters • Overall, Reps. Enjoy greater party loyalty from their members than do Democrats. (think of yesterday’s reading)
Political party decentralization • Although national committees have more power, political parties are still very decentralized. • Ex- Clinton, Gephardt and trade legislation. • Also, there are many more Independent voters • Overall, Reps. Enjoy greater party loyalty from their members than do Democrats. (think of yesterday’s reading)
 The model of responsible party government • 4 Principles • 1) parties should present clear and coherent programs to voters • 2) voters should choose candidates on the basis of party programs • 3) the winning party should carry out its programs once in office • 4) voters should hold the governing party responsible at the next election for its program
The model of responsible party government • 4 Principles • 1) parties should present clear and coherent programs to voters • 2) voters should choose candidates on the basis of party programs • 3) the winning party should carry out its programs once in office • 4) voters should hold the governing party responsible at the next election for its program


