afa77d292c1348e2535663fb7d8f41d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 POLITICAL PARTIES Function, purpose, evolution Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
POLITICAL PARTIES Function, purpose, evolution Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 1 The Meaning of Party • Political Party • A “team of men [and women] seeking to control the governing apparatus by gaining office in a duly constituted election. ” • 3 parts of a political party • Party in the electorate • Party as an organization • Party in government To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 1 The Meaning of Party • Political Party • A “team of men [and women] seeking to control the governing apparatus by gaining office in a duly constituted election. ” • 3 parts of a political party • Party in the electorate • Party as an organization • Party in government To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 The Meaning of Party LO 8. 1 • Tasks of the Parties • • • Pick Candidates Run Campaigns Give Cues to Voters Articulate Policies Coordinate Policymaking To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
The Meaning of Party LO 8. 1 • Tasks of the Parties • • • Pick Candidates Run Campaigns Give Cues to Voters Articulate Policies Coordinate Policymaking To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
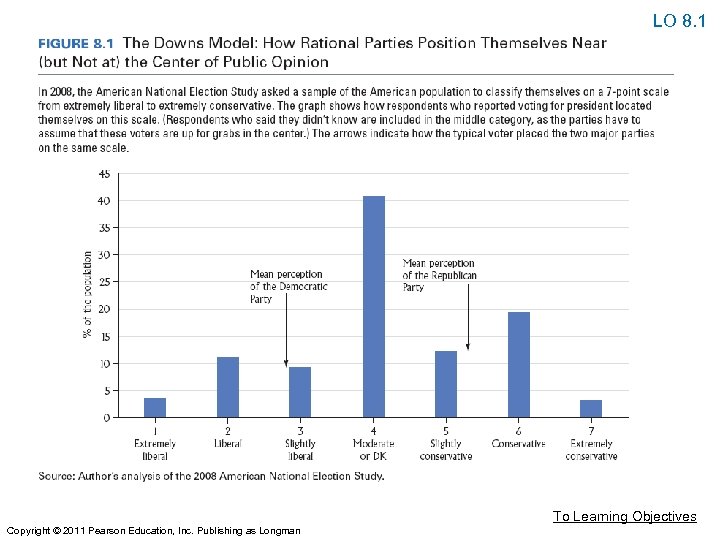
 LO 8. 1 The Meaning of Party • Parties, Voters, and Policy: The Downs Model • Rational-choice theory – People act in their own best interest, weighing the costs and benefits of possible alternatives. • Downs Model – (1) Voters want policies they favor adopted by government, and (2) parties want to win elected office. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 1 The Meaning of Party • Parties, Voters, and Policy: The Downs Model • Rational-choice theory – People act in their own best interest, weighing the costs and benefits of possible alternatives. • Downs Model – (1) Voters want policies they favor adopted by government, and (2) parties want to win elected office. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 1 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 1 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
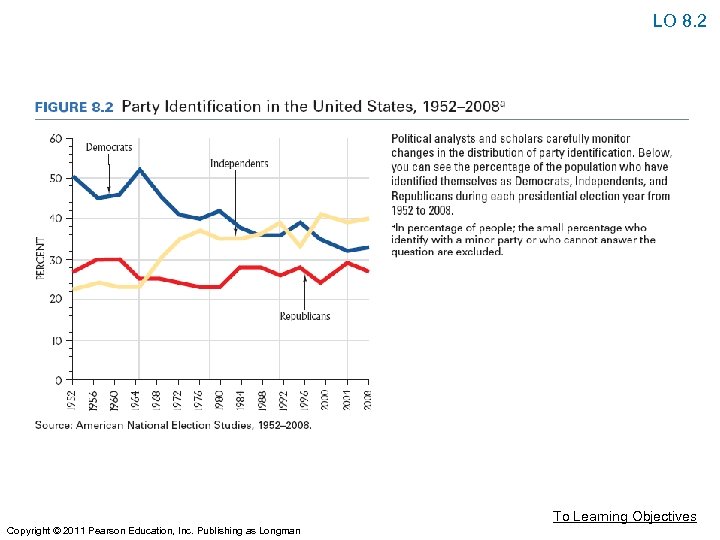
 The Party in the Electorate • Party Image • The voter’s perception of what the Republicans or Democrats stand for, such as conservatism or liberalism. • Party Identification • A citizen’s self-proclaimed preference for one party or the other. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
The Party in the Electorate • Party Image • The voter’s perception of what the Republicans or Democrats stand for, such as conservatism or liberalism. • Party Identification • A citizen’s self-proclaimed preference for one party or the other. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 2 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 2 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 2 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 2 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 2 The Party in the Electorate • Straight Tickets • Voting for all the same party for all offices in the election • Ticket Splitting • Voting with one party for one office and with another party for other offices. • It has become the norm in American voting behavior. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 2 The Party in the Electorate • Straight Tickets • Voting for all the same party for all offices in the election • Ticket Splitting • Voting with one party for one office and with another party for other offices. • It has become the norm in American voting behavior. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 The Party Organizations: From the Grass Roots to Washington LO 8. 3 • Local Parties • Party Machines – Political party organization that relies heavily on material inducements to win votes and to govern. • Tammany Hall- 1870 s New York City • Boss Tweed • Thomas Nast • Patronage – A job, promotion or contract given for political reasons rather than merit; used by party machines. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
The Party Organizations: From the Grass Roots to Washington LO 8. 3 • Local Parties • Party Machines – Political party organization that relies heavily on material inducements to win votes and to govern. • Tammany Hall- 1870 s New York City • Boss Tweed • Thomas Nast • Patronage – A job, promotion or contract given for political reasons rather than merit; used by party machines. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Political Machines • Informal political group designed to gain and keep power • Strongest in the cities • Mainly Democrats • Members of the machine become wealthy through illegal means or dishonorable means • Party bosses run the political machine such as George Washington Plunkett Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Political Machines • Informal political group designed to gain and keep power • Strongest in the cities • Mainly Democrats • Members of the machine become wealthy through illegal means or dishonorable means • Party bosses run the political machine such as George Washington Plunkett Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 3 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 3 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 The Party Organizations: From the Grass Roots to Washington LO 8. 3 • The 50 State Party Systems • Closed primaries – People who have registered with the party can vote for party’s candidates. • Open primaries – Voters decide on Election Day to vote in the Democrat or Republican primary. • Blanket primaries – A list of candidates from all parties. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
The Party Organizations: From the Grass Roots to Washington LO 8. 3 • The 50 State Party Systems • Closed primaries – People who have registered with the party can vote for party’s candidates. • Open primaries – Voters decide on Election Day to vote in the Democrat or Republican primary. • Blanket primaries – A list of candidates from all parties. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 The Party Organizations: From the Grass Roots to Washington LO 8. 3 • National Party Organizations • National Convention – Meeting of party delegates every four years to choose a presidential ticket and the party’s platform. • National Committee – Keep party operating between conventions. • National Chairperson – Day-to-day activities of the party. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
The Party Organizations: From the Grass Roots to Washington LO 8. 3 • National Party Organizations • National Convention – Meeting of party delegates every four years to choose a presidential ticket and the party’s platform. • National Committee – Keep party operating between conventions. • National Chairperson – Day-to-day activities of the party. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 The Party in Government: Promises and Policy LO 8. 4: Evaluate how well political parties generally do in carrying out their promises. • Party in Government • Elected officials who call themselves members of the party. • Coalition • Individuals and groups that support the political party. • Promises and Policies • Parties translate their platform promises into public policy. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
The Party in Government: Promises and Policy LO 8. 4: Evaluate how well political parties generally do in carrying out their promises. • Party in Government • Elected officials who call themselves members of the party. • Coalition • Individuals and groups that support the political party. • Promises and Policies • Parties translate their platform promises into public policy. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
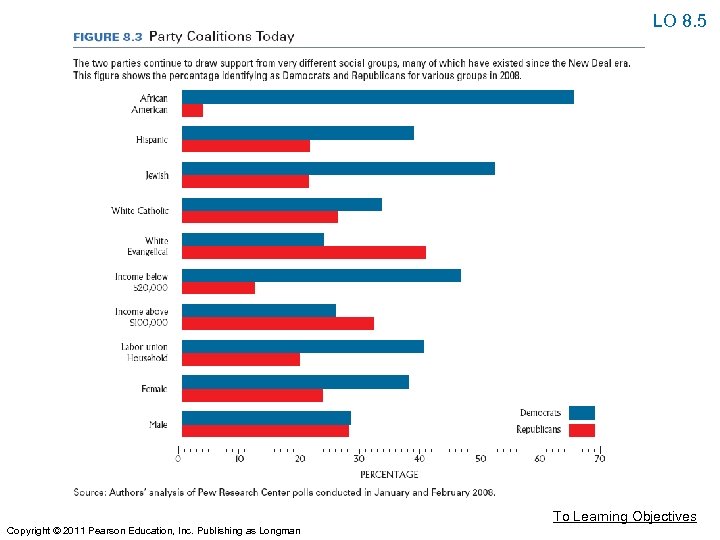
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5: Differentiate the various party eras in American history. • 1796– 1824: The First Party System • 1828– 1856: Jackson and the Democrats Versus the Whigs • 1860– 1928: The Two Republican Eras • 1932– 1964: The New Deal Coalition • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5: Differentiate the various party eras in American history. • 1796– 1824: The First Party System • 1828– 1856: Jackson and the Democrats Versus the Whigs • 1860– 1928: The Two Republican Eras • 1932– 1964: The New Deal Coalition • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • Party Eras • Periods in which a majority of votes cling to party in power. • Critical Election • Electoral “earthquake” where new issues and new coalitions emerge • Party Realignment • Displacement of majority party by the minority party, usually during a critical election. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • Party Eras • Periods in which a majority of votes cling to party in power. • Critical Election • Electoral “earthquake” where new issues and new coalitions emerge • Party Realignment • Displacement of majority party by the minority party, usually during a critical election. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1796– 1824: The First Party System • Federalist Party was the first political party and capitalists supported the Federalists. • Democratic-Republican Party derived its coalition from agrarian interests and dominated the era after the 1800 election. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1796– 1824: The First Party System • Federalist Party was the first political party and capitalists supported the Federalists. • Democratic-Republican Party derived its coalition from agrarian interests and dominated the era after the 1800 election. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1828– 1856: Jackson and the Democrats Versus the Whigs • Democrats coalition included Westerners, Southerners, new immigrants, and settled America. • Whigs coalition included Northern industrialists and Southern planters. • Democrats dominated this era. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1828– 1856: Jackson and the Democrats Versus the Whigs • Democrats coalition included Westerners, Southerners, new immigrants, and settled America. • Whigs coalition included Northern industrialists and Southern planters. • Democrats dominated this era. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1860– 1928: The Two Republican Eras • The main issue of the election of 1860 was slavery. • The main issue of the election of 1896 was the economy. • Republicans dominated both party eras by forming new coalitions and winning both elections. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1860– 1928: The Two Republican Eras • The main issue of the election of 1860 was slavery. • The main issue of the election of 1896 was the economy. • Republicans dominated both party eras by forming new coalitions and winning both elections. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 5 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 5 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1932– 1964: New Deal Coalition • A coalition forged by the Democrats, who dominated American politics from the 1930 s to the 1960 s. • Its basic elements were the urban working class, ethnic groups, Catholics and Jews, the poor, Southerners, African Americans, and intellectuals. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1932– 1964: New Deal Coalition • A coalition forged by the Democrats, who dominated American politics from the 1930 s to the 1960 s. • Its basic elements were the urban working class, ethnic groups, Catholics and Jews, the poor, Southerners, African Americans, and intellectuals. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 5 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 5 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government • 1987 Southern delegates – 77 of 116 House seats, and 6 of 22 Senate seats were from GOP. • 2009 Southern delegates – 70 of 131 House seats, and 15 of 22 Senate seats were from GOP. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government • 1987 Southern delegates – 77 of 116 House seats, and 6 of 22 Senate seats were from GOP. • 2009 Southern delegates – 70 of 131 House seats, and 15 of 22 Senate seats were from GOP. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government • Divided government – When one party controls the White House and the other party controls one or both houses of Congress. • Both houses of Congress and the presidency have been controlled by the same party for just 14 of the 44 years from 1969 to 2012. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government • Divided government – When one party controls the White House and the other party controls one or both houses of Congress. • Both houses of Congress and the presidency have been controlled by the same party for just 14 of the 44 years from 1969 to 2012. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government • Party dealignment – The gradual disengagement of people from the parties, as seen in part by shrinking party identification. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Party Eras in American History LO 8. 5 • 1968–Present: Southern Realignment and the Era of Divided Party Government • Party dealignment – The gradual disengagement of people from the parties, as seen in part by shrinking party identification. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
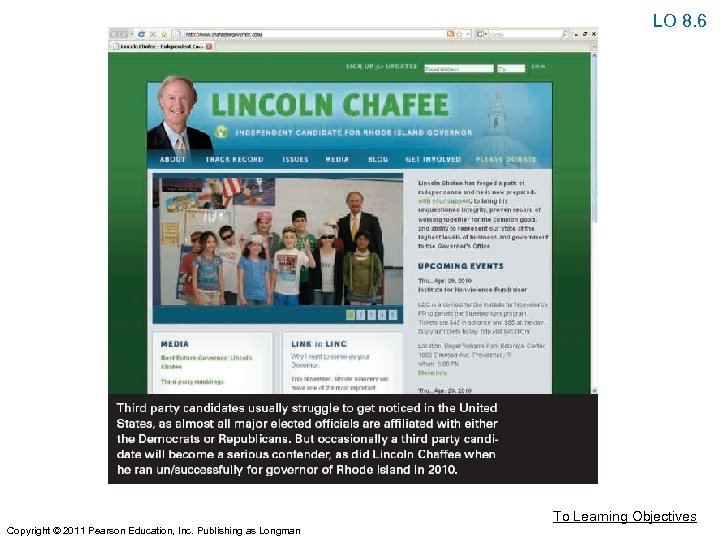
 Third Parties: Their Impact on American Politics LO 8. 6: Assess both the impact of third parties on American politics and their limitations. • Third Parties • Electoral contenders other than the two major parties. • Three Basic Varieties • Promote certain causes. • Splinter parties • Extension of popular individual with presidential aspirations. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Third Parties: Their Impact on American Politics LO 8. 6: Assess both the impact of third parties on American politics and their limitations. • Third Parties • Electoral contenders other than the two major parties. • Three Basic Varieties • Promote certain causes. • Splinter parties • Extension of popular individual with presidential aspirations. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 6 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 6 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 6 Third Parties: Their Impact on American Politics • Third Parties Are Important • Bring new groups into the electorate. • Serve as “safety valves” for popular discontent. • Put many social reforms on the political agenda. • Bring new issues to the campaign ignored by the major parties. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 6 Third Parties: Their Impact on American Politics • Third Parties Are Important • Bring new groups into the electorate. • Serve as “safety valves” for popular discontent. • Put many social reforms on the political agenda. • Bring new issues to the campaign ignored by the major parties. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Third Parties: Their Impact on American Politics LO 8. 6 • Two-Party Governance • Moderation of political conflict. • Contributes to political ambiguity. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Third Parties: Their Impact on American Politics LO 8. 6 • Two-Party Governance • Moderation of political conflict. • Contributes to political ambiguity. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
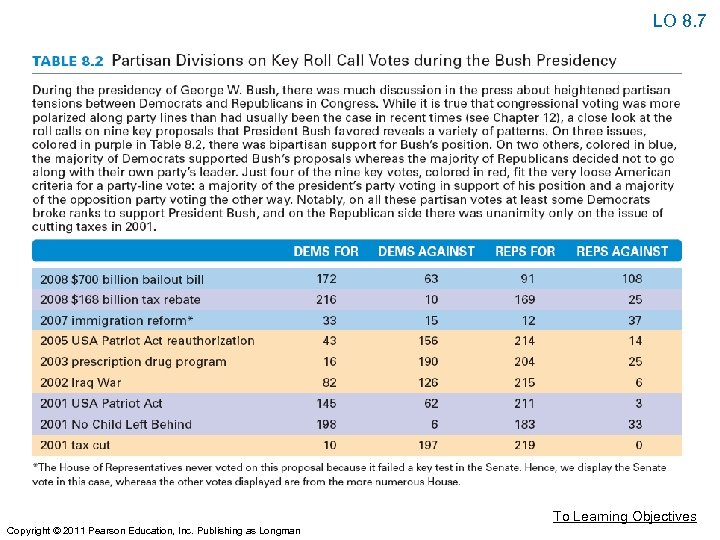
 Understanding Political Parties LO 8. 7 • Democracy and Responsible Party Government: How Should We Govern? • Responsible party model – A view about how parties should work. • Party should offer clear choices to the voters, who can then use those choices as cues to their own preferences of candidates. • Party in government should carry out their campaign promises. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Understanding Political Parties LO 8. 7 • Democracy and Responsible Party Government: How Should We Govern? • Responsible party model – A view about how parties should work. • Party should offer clear choices to the voters, who can then use those choices as cues to their own preferences of candidates. • Party in government should carry out their campaign promises. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 LO 8. 7 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
LO 8. 7 To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Understanding Political Parties LO 8. 7 • Democracy and Responsible Party Government: How Should We Govern? (cont. ) • Blue Dog Democrats – Fiscally conservative Democrats who are mostly from the South and rural parts of the United States, and are resistant to any domestic policy proposals that would enlarge the scope of government. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Understanding Political Parties LO 8. 7 • Democracy and Responsible Party Government: How Should We Govern? (cont. ) • Blue Dog Democrats – Fiscally conservative Democrats who are mostly from the South and rural parts of the United States, and are resistant to any domestic policy proposals that would enlarge the scope of government. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Understanding Political Parties LO 8. 7 • American Political Parties and the Scope of Government • Lack of uniformity keeps government small, but also makes cutting government programs difficult. • Individual politicians focus on getting more from government for their own constituents. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Understanding Political Parties LO 8. 7 • American Political Parties and the Scope of Government • Lack of uniformity keeps government small, but also makes cutting government programs difficult. • Individual politicians focus on getting more from government for their own constituents. To Learning Objectives Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Photo Credits • • • 224: AP Photo 225 T: Matt Brewer Hamilton 224 TC: Bettmann/Corbis 224 TB: Toles 2000, Washington Post. Reprinted with permission of Universal Press Syndicate 224 B: Neo Images/Photo. Edit 228: Matt Brewer Hamilton 232: Jean Claude Lejeune 230: Bettmaann/Corbis 234: Toles 2000, Washington Post. Reprinted with permission of Universal Press Syndicate 239: The Granger Collection 243: Neo Images/Photo. Edit 247: Robert Mankoff/The New Yorker Cartoon/www. cartoonbank. com Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
Photo Credits • • • 224: AP Photo 225 T: Matt Brewer Hamilton 224 TC: Bettmann/Corbis 224 TB: Toles 2000, Washington Post. Reprinted with permission of Universal Press Syndicate 224 B: Neo Images/Photo. Edit 228: Matt Brewer Hamilton 232: Jean Claude Lejeune 230: Bettmaann/Corbis 234: Toles 2000, Washington Post. Reprinted with permission of Universal Press Syndicate 239: The Granger Collection 243: Neo Images/Photo. Edit 247: Robert Mankoff/The New Yorker Cartoon/www. cartoonbank. com Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman


