Lecture 2. Political economy.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 61
 Political economy Lecture 2. Commodity production. Commodity and Money
Political economy Lecture 2. Commodity production. Commodity and Money
 Questions 1. Commodity production: causes of origin and the mean features. 2. Simple commodity production and capitalist production: the unity and the differences. 3. Commodity and its factors: use-value and value. Exchange value. 4. The two-fold character of the labour embodied in commodities 5. The magnitude of commodity value. 6. The form of value and its historical development. 7. The appearance of money. The essence and functions of money 8. The law of value as the main law of commodity production. 9. The Fetishism of Commodities.
Questions 1. Commodity production: causes of origin and the mean features. 2. Simple commodity production and capitalist production: the unity and the differences. 3. Commodity and its factors: use-value and value. Exchange value. 4. The two-fold character of the labour embodied in commodities 5. The magnitude of commodity value. 6. The form of value and its historical development. 7. The appearance of money. The essence and functions of money 8. The law of value as the main law of commodity production. 9. The Fetishism of Commodities.
 Glossary of Terms • Natural economy – натуральное хозяйство • Division of labor – разделение труда • Commodity production – товарное производство • Simple commodity production – простое товарное производство • Capitalist commodity production – капиталистическое товарное производство
Glossary of Terms • Natural economy – натуральное хозяйство • Division of labor – разделение труда • Commodity production – товарное производство • Simple commodity production – простое товарное производство • Capitalist commodity production – капиталистическое товарное производство
 Glossary of Terms • • Commodity – товар Use-value – потребительская стоимость Value – стоимость Exchange value – меновая стоимость Concrete labor – конкретный труд Abstract labor – абстрактный труд Private labor – частный труд Social labor – общественный труд
Glossary of Terms • • Commodity – товар Use-value – потребительская стоимость Value – стоимость Exchange value – меновая стоимость Concrete labor – конкретный труд Abstract labor – абстрактный труд Private labor – частный труд Social labor – общественный труд
 Glossary of Terms • Magnitude of value – величина стоимости товара • Individual labor time – индивидуальное рабочее время • Socially necessary labor time – общественнонеобходимое рабочее время • Normal conditions of production – нормальные условия производства • Labour intensity – интенсивность труда
Glossary of Terms • Magnitude of value – величина стоимости товара • Individual labor time – индивидуальное рабочее время • Socially necessary labor time – общественнонеобходимое рабочее время • Normal conditions of production – нормальные условия производства • Labour intensity – интенсивность труда
 Glossary of Terms Labor productivity – производительность труда Simple labour – простой труд Compound labour – сложный труд Form of value – форма стоимости Relative form of value – относительная форма стоимости • Equivalent form of value – эквивалентная форма стоимости • • •
Glossary of Terms Labor productivity – производительность труда Simple labour – простой труд Compound labour – сложный труд Form of value – форма стоимости Relative form of value – относительная форма стоимости • Equivalent form of value – эквивалентная форма стоимости • • •
 Glossary of Terms Money – деньги Law of value – закон стоимости Measure of prices – масштаб цен Price – цена Inflation – инфляция Fetishism of commodities – товарный фетишизм • Fetishism of money – денежный фетишизм • • •
Glossary of Terms Money – деньги Law of value – закон стоимости Measure of prices – масштаб цен Price – цена Inflation – инфляция Fetishism of commodities – товарный фетишизм • Fetishism of money – денежный фетишизм • • •
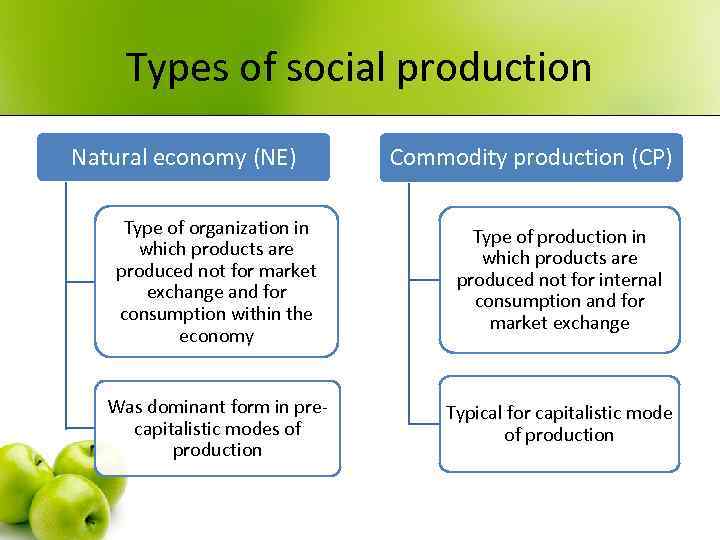 Types of social production Natural economy (NE) Commodity production (CP) Type of organization in which products are produced not for market exchange and for consumption within the economy Type of production in which products are produced not for internal consumption and for market exchange Was dominant form in precapitalistic modes of production Typical for capitalistic mode of production
Types of social production Natural economy (NE) Commodity production (CP) Type of organization in which products are produced not for market exchange and for consumption within the economy Type of production in which products are produced not for internal consumption and for market exchange Was dominant form in precapitalistic modes of production Typical for capitalistic mode of production
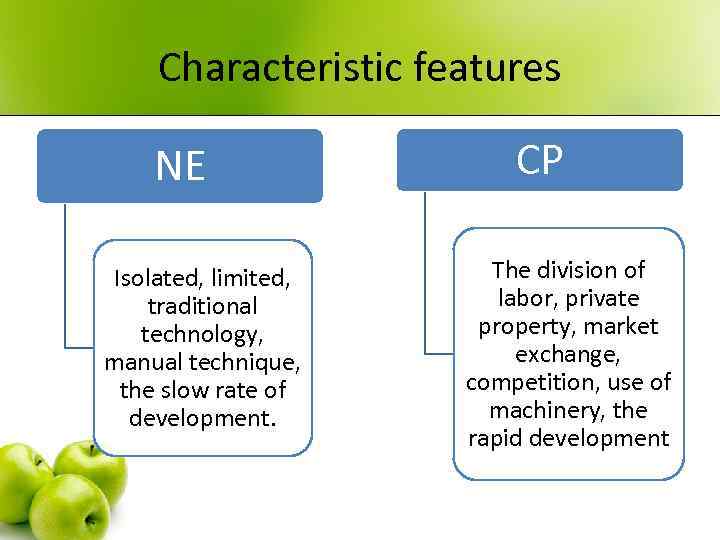 Characteristic features NE Isolated, limited, traditional technology, manual technique, the slow rate of development. CP The division of labor, private property, market exchange, competition, use of machinery, the rapid development
Characteristic features NE Isolated, limited, traditional technology, manual technique, the slow rate of development. CP The division of labor, private property, market exchange, competition, use of machinery, the rapid development
 Commodity production • The system of social production where products are produced by separate singular manufacturers, specializing on particular product, so to meet the needs of society exchange of products is necessary – as a result products become commodities on the market
Commodity production • The system of social production where products are produced by separate singular manufacturers, specializing on particular product, so to meet the needs of society exchange of products is necessary – as a result products become commodities on the market
 Preconditions of CP • The main precondition of CP is social division of labor (SDL) • SDL – separation of certain activity types • There are division of labor within society and within the enterprise
Preconditions of CP • The main precondition of CP is social division of labor (SDL) • SDL – separation of certain activity types • There are division of labor within society and within the enterprise
 SDL in historical process • History knows 3 largest division of labor: • 1. Separation of ranching and farming • 2. Separation of crafts from agriculture and ranching • 3. Separation of trade in a particular activity.
SDL in historical process • History knows 3 largest division of labor: • 1. Separation of ranching and farming • 2. Separation of crafts from agriculture and ranching • 3. Separation of trade in a particular activity.
 The role of SDL • • • Historically, CRP helped to: increase of labor productivity; appearance of regular exchange; emergence of private property; division of society into classes.
The role of SDL • • • Historically, CRP helped to: increase of labor productivity; appearance of regular exchange; emergence of private property; division of society into classes.
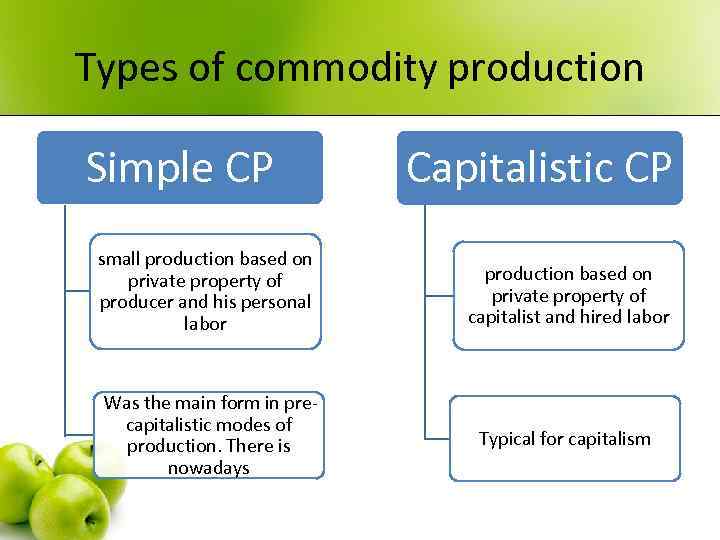 Types of commodity production Simple CP Capitalistic CP small production based on private property of producer and his personal labor production based on private property of capitalist and hired labor Was the main form in precapitalistic modes of production. There is nowadays Typical for capitalism
Types of commodity production Simple CP Capitalistic CP small production based on private property of producer and his personal labor production based on private property of capitalist and hired labor Was the main form in precapitalistic modes of production. There is nowadays Typical for capitalism
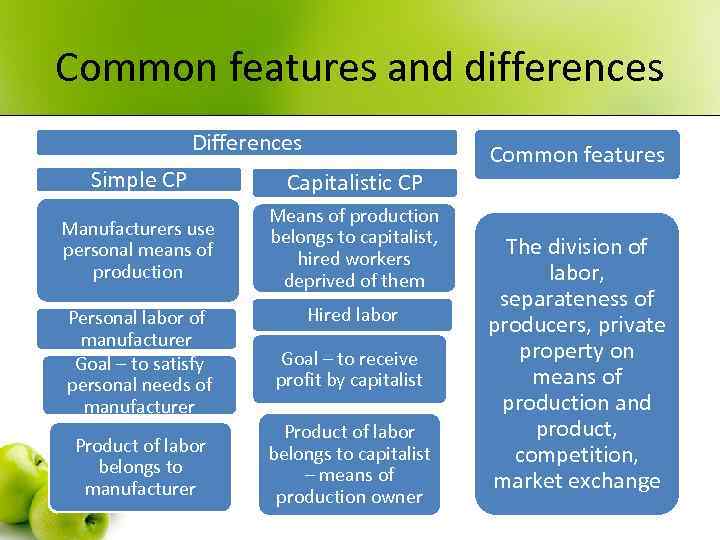 Common features and differences Differences Simple CP Capitalistic CP Manufacturers use personal means of production Means of production belongs to capitalist, hired workers deprived of them Hired labor Personal labor of manufacturer Goal – to satisfy personal needs of manufacturer Goal – to receive profit by capitalist Product of labor belongs to manufacturer Product of labor belongs to capitalist – means of production owner Common features The division of labor, separateness of producers, private property on means of production and product, competition, market exchange
Common features and differences Differences Simple CP Capitalistic CP Manufacturers use personal means of production Means of production belongs to capitalist, hired workers deprived of them Hired labor Personal labor of manufacturer Goal – to satisfy personal needs of manufacturer Goal – to receive profit by capitalist Product of labor belongs to manufacturer Product of labor belongs to capitalist – means of production owner Common features The division of labor, separateness of producers, private property on means of production and product, competition, market exchange
 Commodity and its properties Commodity – product of labor produced for market exchange Use-value Possibility of commodity to satisfy human needs. Exchange value a quantitative proportion in which use-value of one sort is exchanged for another sort.
Commodity and its properties Commodity – product of labor produced for market exchange Use-value Possibility of commodity to satisfy human needs. Exchange value a quantitative proportion in which use-value of one sort is exchanged for another sort.
 Value of commodity Exchange value - a form of the value manifestation in the act of exchange Value of commodity - is social labor embodied in commodity Labor – a measure of commodity value
Value of commodity Exchange value - a form of the value manifestation in the act of exchange Value of commodity - is social labor embodied in commodity Labor – a measure of commodity value
 Unity and contradiction of value and use value • Any commodity is result of labor but not any result of labor is commodity. • Only useful thing can has a value but not every use-value has value. • For example: • Bread produced by serf for feudal – is product of labor, but is not a commodity. • Land is useful thing but has not value
Unity and contradiction of value and use value • Any commodity is result of labor but not any result of labor is commodity. • Only useful thing can has a value but not every use-value has value. • For example: • Bread produced by serf for feudal – is product of labor, but is not a commodity. • Land is useful thing but has not value
 Solution of the contradiction Any commodity is unity of value and use-value This unity manifests itself only on the market in the process of commodity exchange So, value has historical character
Solution of the contradiction Any commodity is unity of value and use-value This unity manifests itself only on the market in the process of commodity exchange So, value has historical character
 Abstract and concrete labor • Properties of commodity are caused by twofold character of labor: on the one hand any labor is concrete, on the other hand - the abstract.
Abstract and concrete labor • Properties of commodity are caused by twofold character of labor: on the one hand any labor is concrete, on the other hand - the abstract.
 Concrete labor • - is heterogeneous and incomparable labor in special useful form which creates particular use-values. • Variety of use-values is determined by different types of concrete labor, which vary by technologies of production, means, subjects and results of labor. • For example, the labor of a goldsmith, builder, blacksmith, driver, teacher, etc.
Concrete labor • - is heterogeneous and incomparable labor in special useful form which creates particular use-values. • Variety of use-values is determined by different types of concrete labor, which vary by technologies of production, means, subjects and results of labor. • For example, the labor of a goldsmith, builder, blacksmith, driver, teacher, etc.
 Abstract labor • - is homogeneous and comparable labor as human energy spending independently from its concrete form. • For example, spending of physical, nervous and mental energy. • Abstract labor creates value of commodities because of its homogeneous character. • So, value is abstract labor embodied in commodities.
Abstract labor • - is homogeneous and comparable labor as human energy spending independently from its concrete form. • For example, spending of physical, nervous and mental energy. • Abstract labor creates value of commodities because of its homogeneous character. • So, value is abstract labor embodied in commodities.
 Private labor • In commodity production concrete labor appears as private affair of manufacturer who organize the production process at own risk. • So concrete labor manifests itself as a private labor of producer.
Private labor • In commodity production concrete labor appears as private affair of manufacturer who organize the production process at own risk. • So concrete labor manifests itself as a private labor of producer.
 Social labor • However, each manufacturer produces commodities not for himself but for others. Because of CDL separate manufacturers need commodities of other producers. • So, labor of separate manufacturer in society can’t be his own private deal. It is a part of social labor therefore has social character.
Social labor • However, each manufacturer produces commodities not for himself but for others. Because of CDL separate manufacturers need commodities of other producers. • So, labor of separate manufacturer in society can’t be his own private deal. It is a part of social labor therefore has social character.
 The main contradiction of simple commodity production • As a result a deep contradiction between private and social labor appears. This is the main contradiction of SCP. • The contradiction is resolved in the process of market exchange. Only market exchange shows the necessity of private labor. If the product isn`t useful for society, the society never accept it as a part of social labor.
The main contradiction of simple commodity production • As a result a deep contradiction between private and social labor appears. This is the main contradiction of SCP. • The contradiction is resolved in the process of market exchange. Only market exchange shows the necessity of private labor. If the product isn`t useful for society, the society never accept it as a part of social labor.
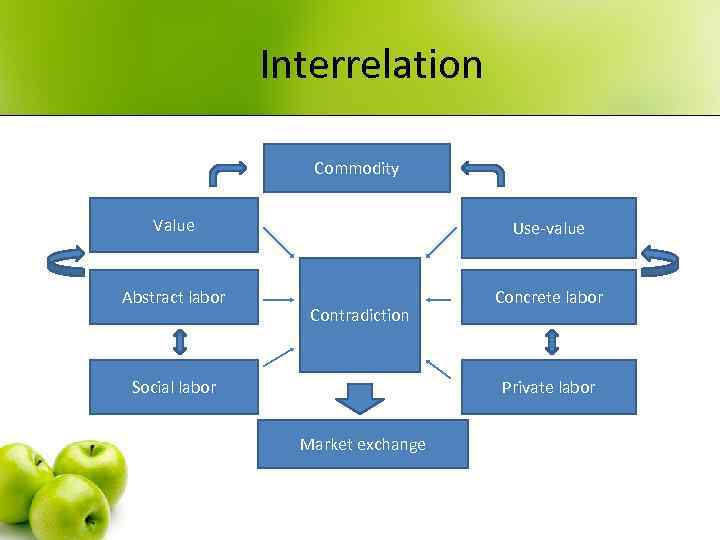 Interrelation Commodity Value Use-value Abstract labor Concrete labor Contradiction Social labor Private labor Market exchange
Interrelation Commodity Value Use-value Abstract labor Concrete labor Contradiction Social labor Private labor Market exchange
 Magnitude of commodity value • If commodity value is abstract labor embodied in it, how can we determine the magnitude of this labor? • Labor time is a measure of labor and value accordingly. • There are individual and socially necessary labor time
Magnitude of commodity value • If commodity value is abstract labor embodied in it, how can we determine the magnitude of this labor? • Labor time is a measure of labor and value accordingly. • There are individual and socially necessary labor time
 Individual labor time • - labor, which separate singular producer spent for unit of commodity production • But different producers spend different time for the same commodity’s production. • So, social value of commodity can’t be determined by individual labor time. It should be determined by socially necessary labor time (SNLT)
Individual labor time • - labor, which separate singular producer spent for unit of commodity production • But different producers spend different time for the same commodity’s production. • So, social value of commodity can’t be determined by individual labor time. It should be determined by socially necessary labor time (SNLT)
 Socially necessary labor time • - time necessary for commodity’s production in socially necessary conditions of production, average level of technology and means of production, qualification, skills, intensity and productivity of labor. • Socially necessary conditions of production – conditions in which the majority of certain commodities is produced
Socially necessary labor time • - time necessary for commodity’s production in socially necessary conditions of production, average level of technology and means of production, qualification, skills, intensity and productivity of labor. • Socially necessary conditions of production – conditions in which the majority of certain commodities is produced
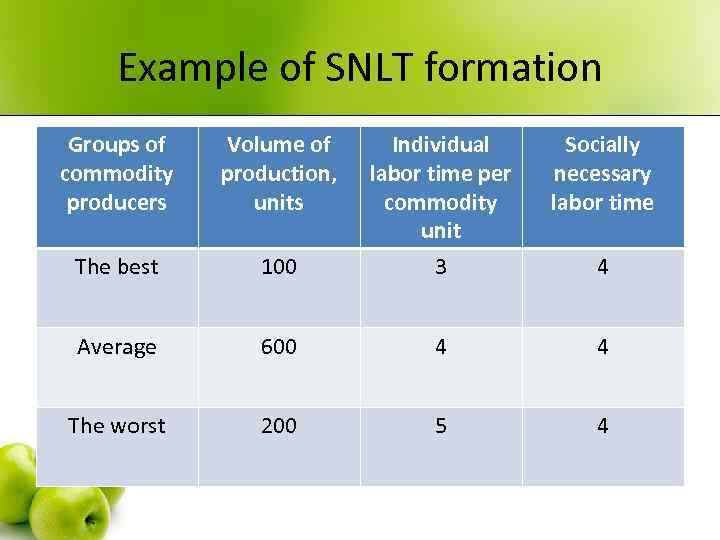 Example of SNLT formation Groups of commodity producers Volume of production, units Socially necessary labor time 100 Individual labor time per commodity unit 3 The best Average 600 4 4 The worst 200 5 4 4
Example of SNLT formation Groups of commodity producers Volume of production, units Socially necessary labor time 100 Individual labor time per commodity unit 3 The best Average 600 4 4 The worst 200 5 4 4
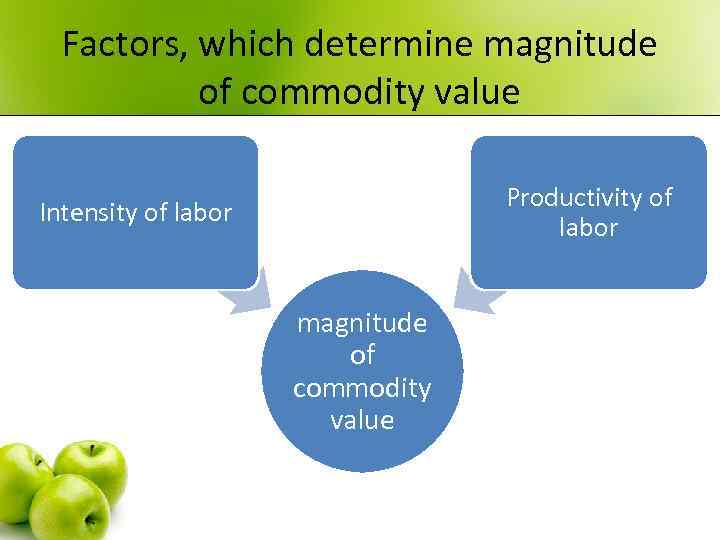 Factors, which determine magnitude of commodity value Productivity of labor Intensity of labor magnitude of commodity value
Factors, which determine magnitude of commodity value Productivity of labor Intensity of labor magnitude of commodity value
 Intensity of labor (IL) Productivity of labor (PL) • PL - number of units produced in particular period of time. Is an indicator of labor efficiency. • Factors affecting the PL • 1. Means of production quality. • 2. Labor organization. • 3. Qualification of workers. • 4. natural conditions of production • ІL – expenditures of labor power in particular period of time. Is an indicator of labor tension.
Intensity of labor (IL) Productivity of labor (PL) • PL - number of units produced in particular period of time. Is an indicator of labor efficiency. • Factors affecting the PL • 1. Means of production quality. • 2. Labor organization. • 3. Qualification of workers. • 4. natural conditions of production • ІL – expenditures of labor power in particular period of time. Is an indicator of labor tension.
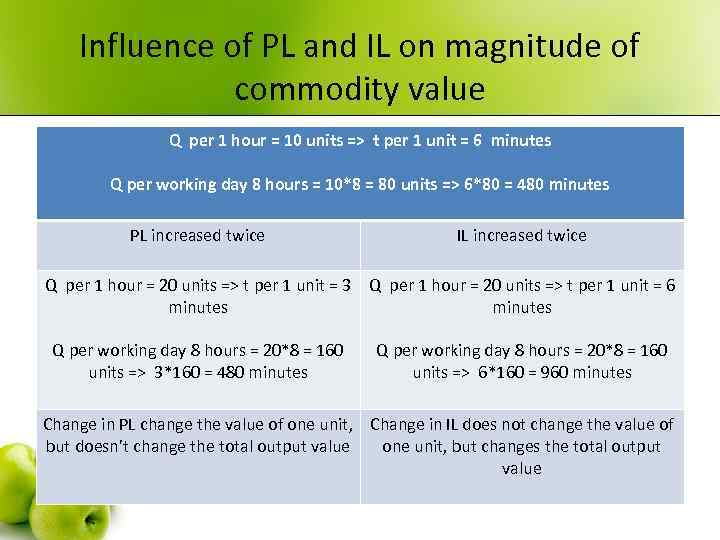 Influence of PL and IL on magnitude of commodity value Q per 1 hour = 10 units => t per 1 unit = 6 minutes Q per working day 8 hours = 10*8 = 80 units => 6*80 = 480 minutes PL increased twice IL increased twice Q per 1 hour = 20 units => t per 1 unit = 3 Q per 1 hour = 20 units => t per 1 unit = 6 minutes Q per working day 8 hours = 20*8 = 160 units => 3*160 = 480 minutes Q per working day 8 hours = 20*8 = 160 units => 6*160 = 960 minutes Change in PL change the value of one unit, Change in IL does not change the value of but doesn’t change the total output value one unit, but changes the total output value
Influence of PL and IL on magnitude of commodity value Q per 1 hour = 10 units => t per 1 unit = 6 minutes Q per working day 8 hours = 10*8 = 80 units => 6*80 = 480 minutes PL increased twice IL increased twice Q per 1 hour = 20 units => t per 1 unit = 3 Q per 1 hour = 20 units => t per 1 unit = 6 minutes Q per working day 8 hours = 20*8 = 160 units => 3*160 = 480 minutes Q per working day 8 hours = 20*8 = 160 units => 6*160 = 960 minutes Change in PL change the value of one unit, Change in IL does not change the value of but doesn’t change the total output value one unit, but changes the total output value
 Simple and compound labor • Simple labor – labor that does not require special training and education. • For example, the labor of cleaner, longshoreman, watchman, etc. ) • Compound labor – labor that require special training and education. • For example, labor economist, engineer, doctor, etc. ) • Compound labor – is multiplied simple labor
Simple and compound labor • Simple labor – labor that does not require special training and education. • For example, the labor of cleaner, longshoreman, watchman, etc. ) • Compound labor – labor that require special training and education. • For example, labor economist, engineer, doctor, etc. ) • Compound labor – is multiplied simple labor
 Evolution of value form • Value – is a social property of the product which manifests itself only in exchange process. • Relations of exchange have passed a long historical evolution from simple forms to more complex ones.
Evolution of value form • Value – is a social property of the product which manifests itself only in exchange process. • Relations of exchange have passed a long historical evolution from simple forms to more complex ones.
 Value form – form of value manifestation in the process of exchange • • 1. Elementary or accidental form 2. Total or expanded form 3. General form 4. Money form
Value form – form of value manifestation in the process of exchange • • 1. Elementary or accidental form 2. Total or expanded form 3. General form 4. Money form
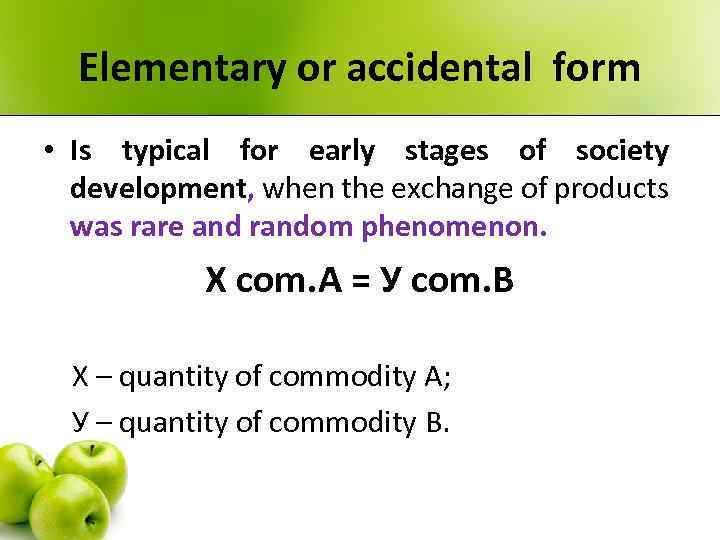 Elementary or accidental form • Is typical for early stages of society development, when the exchange of products was rare and random phenomenon. Х com. А = У com. В Х – quantity of commodity А; У – quantity of commodity В.
Elementary or accidental form • Is typical for early stages of society development, when the exchange of products was rare and random phenomenon. Х com. А = У com. В Х – quantity of commodity А; У – quantity of commodity В.
 Elementary or accidental form Х com. А = У com. В • Commodity А – is in relative value form, it tries to express its value through use-value of commodity B. • Commodity В – is in equivalent form, It expresses through its use-value a value of commodity A.
Elementary or accidental form Х com. А = У com. В • Commodity А – is in relative value form, it tries to express its value through use-value of commodity B. • Commodity В – is in equivalent form, It expresses through its use-value a value of commodity A.
 Total or expanded form • With the first SDL a big number of products is involved in the exchange process, as a result exchange becomes a regular phenomenon. Total value form appears. А – com. in relative form У com. В Х com. А = Z com. С В, С, D – commodities in М com. D equivalent form
Total or expanded form • With the first SDL a big number of products is involved in the exchange process, as a result exchange becomes a regular phenomenon. Total value form appears. А – com. in relative form У com. В Х com. А = Z com. С В, С, D – commodities in М com. D equivalent form
 Total or expanded form • Disadvantages of total form: • 1. It was a big number of commodity in equivalent form so value of each product had not received the completed expression; • 2. Value of each commodity hadn’t universal expression; • 3. The direct exchange of one commodity for another occurred in close borders.
Total or expanded form • Disadvantages of total form: • 1. It was a big number of commodity in equivalent form so value of each product had not received the completed expression; • 2. Value of each commodity hadn’t universal expression; • 3. The direct exchange of one commodity for another occurred in close borders.
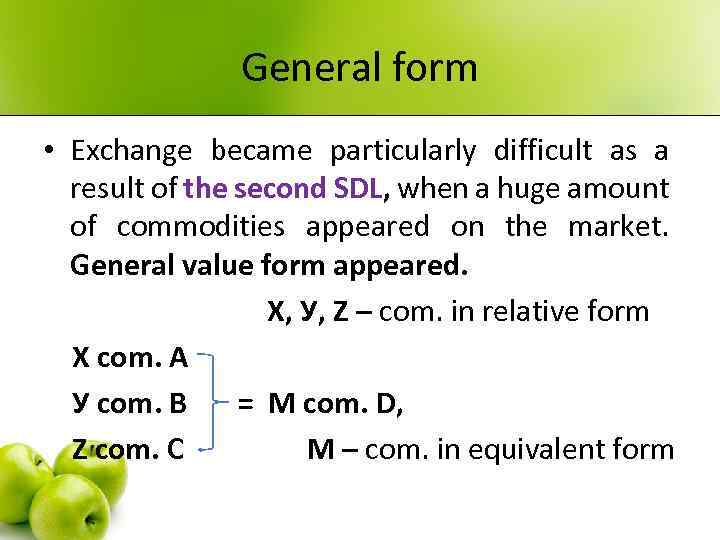 General form • Exchange became particularly difficult as a result of the second SDL, when a huge amount of commodities appeared on the market. General value form appeared. Х, У, Z – com. in relative form Х com. А У com. В = М com. D, Z com. С М – com. in equivalent form
General form • Exchange became particularly difficult as a result of the second SDL, when a huge amount of commodities appeared on the market. General value form appeared. Х, У, Z – com. in relative form Х com. А У com. В = М com. D, Z com. С М – com. in equivalent form
 Disadvantages of general form 1 The role of universal equivalent in different markets and at different times was performed by various products - furs, cattle, shells. 2 Products usually were hard divisible and hard transportable, uncomfortable in exchange, heterogeneous.
Disadvantages of general form 1 The role of universal equivalent in different markets and at different times was performed by various products - furs, cattle, shells. 2 Products usually were hard divisible and hard transportable, uncomfortable in exchange, heterogeneous.
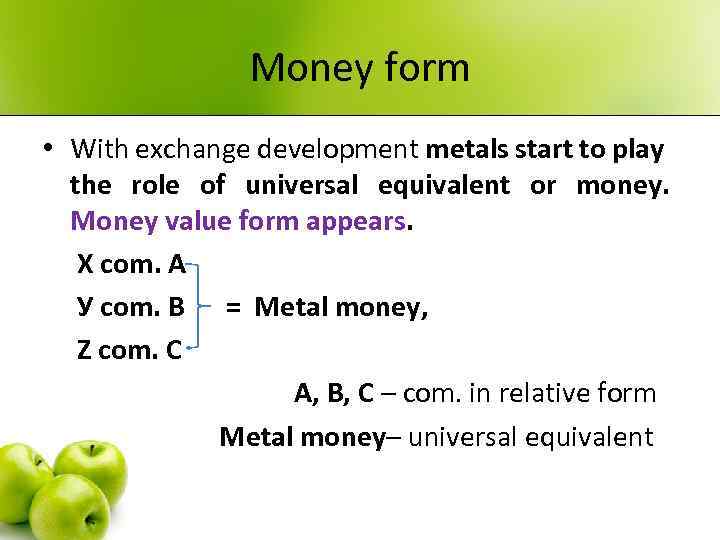 Money form • With exchange development metals start to play the role of universal equivalent or money. Money value form appears. Х com. А У com. В = Metal money, Z com. С А, В, С – com. in relative form Metal money– universal equivalent
Money form • With exchange development metals start to play the role of universal equivalent or money. Money value form appears. Х com. А У com. В = Metal money, Z com. С А, В, С – com. in relative form Metal money– universal equivalent
 Money form • Historically copper start to play the role of money first. Later precious metals – silver and gold – start to serve as money. • There are several reasons that explain why the role of money was fixed for gold: • 1 High cost of extraction; • 2 Homogeneity; • 3 Divisibility; • 4 Ease of exchange; • 5 Transportability.
Money form • Historically copper start to play the role of money first. Later precious metals – silver and gold – start to serve as money. • There are several reasons that explain why the role of money was fixed for gold: • 1 High cost of extraction; • 2 Homogeneity; • 3 Divisibility; • 4 Ease of exchange; • 5 Transportability.
 Money and its functions • Money – is particular commodity, which serves as universal equivalent. • Necessity of money is a result of internal commodity’s contradiction solution. • To understand the essence of money better we should study it’s functions.
Money and its functions • Money – is particular commodity, which serves as universal equivalent. • Necessity of money is a result of internal commodity’s contradiction solution. • To understand the essence of money better we should study it’s functions.
 Functions of money • • • 1. The measure of values 2. The medium of circulation 3. The mean of saving 4. The mean of payment 5. Universal money
Functions of money • • • 1. The measure of values 2. The medium of circulation 3. The mean of saving 4. The mean of payment 5. Universal money
 The measure of values • Money is a measure of commodity value. • Commodity value expressed in money is price of commodity. • This function of money is performed perfectly. Setting the price of the product the manufacturer may not have cash. It is enough to know that money exists and he can get it in exchange for commodities.
The measure of values • Money is a measure of commodity value. • Commodity value expressed in money is price of commodity. • This function of money is performed perfectly. Setting the price of the product the manufacturer may not have cash. It is enough to know that money exists and he can get it in exchange for commodities.
 Measure of prices • This function is associated with measure of prices. • Measure of prices – the mechanism by which the weight content of metal in money is determined.
Measure of prices • This function is associated with measure of prices. • Measure of prices – the mechanism by which the weight content of metal in money is determined.
 The medium of circulation • - the ability of money to be intermediary in the commodity exchange. • Performance of this function is done formula M-C-M. The act of purchase and sale is indissoluble in time and space. • Money perform this function transiently, so metal money in circulation can be replaced with credit and paper money (bills, banknotes, etc. ).
The medium of circulation • - the ability of money to be intermediary in the commodity exchange. • Performance of this function is done formula M-C-M. The act of purchase and sale is indissoluble in time and space. • Money perform this function transiently, so metal money in circulation can be replaced with credit and paper money (bills, banknotes, etc. ).
 The mean of saving • Carrying out this function money temporary withdraw from the process of circulation and accumulated in the form of treasure. • Accumulation can occur in two forms: in cash in the form of metal or paper money and cashless form - in the form of deposits in the bank. • With the help this function money transfer their purchasing power for the future.
The mean of saving • Carrying out this function money temporary withdraw from the process of circulation and accumulated in the form of treasure. • Accumulation can occur in two forms: in cash in the form of metal or paper money and cashless form - in the form of deposits in the bank. • With the help this function money transfer their purchasing power for the future.
 The mean of payment • is modification of medium of circulation function. • The function appears with the development of credit relations and serves the sale of commodities with payment delay. • The act of purchase and sale is broken in time and space. • Money perform this function also in the payment of wages, dividends, interest, utilities, etc.
The mean of payment • is modification of medium of circulation function. • The function appears with the development of credit relations and serves the sale of commodities with payment delay. • The act of purchase and sale is broken in time and space. • Money perform this function also in the payment of wages, dividends, interest, utilities, etc.
 Universal money • Money perform this function going beyond the borders of national economy and serving the international trade. • Earlier this role was performed directly by gold and silver. Now this function performed by free convertible currencies - dollar, euro, yen.
Universal money • Money perform this function going beyond the borders of national economy and serving the international trade. • Earlier this role was performed directly by gold and silver. Now this function performed by free convertible currencies - dollar, euro, yen.
 The law of money circulation • establishes the number of money necessary for commodity exchange during particular period of time, mostly one year. • The number of money directly depends on sum of commodities prices, because money is used for commodity prices estimation. And is in inverse relationship with velocity of money circulation - a number of circles, which money makes in 1 year.
The law of money circulation • establishes the number of money necessary for commodity exchange during particular period of time, mostly one year. • The number of money directly depends on sum of commodities prices, because money is used for commodity prices estimation. And is in inverse relationship with velocity of money circulation - a number of circles, which money makes in 1 year.
 The law of money circulation М = P*Q / V М – quantity of money V - velocity of money circulation Р – prices of commodities Q - quantity of commodities
The law of money circulation М = P*Q / V М – quantity of money V - velocity of money circulation Р – prices of commodities Q - quantity of commodities
 The law of money circulation • With credit relations development formula of money circulation takes expanded look: М = ∑Cp - ∑CC + ∑MPN - ∑CL / V, • ∑Cp – sum of commodities prices; • ∑CC – sum of commodity prices sold in credit; • ∑MPN – sum of payments under mature promissory notes; • ∑CL – sum of clearing payments.
The law of money circulation • With credit relations development formula of money circulation takes expanded look: М = ∑Cp - ∑CC + ∑MPN - ∑CL / V, • ∑Cp – sum of commodities prices; • ∑CC – sum of commodity prices sold in credit; • ∑MPN – sum of payments under mature promissory notes; • ∑CL – sum of clearing payments.
 The Law of value (LV) - is the main law of commodity production, which sets that proportions of commodity exchange are established according equality of commodity values or socially necessary labor time.
The Law of value (LV) - is the main law of commodity production, which sets that proportions of commodity exchange are established according equality of commodity values or socially necessary labor time.
 Functions of LV • 1. Means of production and labor power allocation between industries and regions; • 2. Regulation of social productions and exchange proportions; • 3. Differentiation of producers
Functions of LV • 1. Means of production and labor power allocation between industries and regions; • 2. Regulation of social productions and exchange proportions; • 3. Differentiation of producers
 LV mechanism • LV regulates commodity production through price mechanism. In short period commodity prices can differ from commodity values according to changes in supply and demand. • Market price is equal to commodity value when market supply is equal to market demand. • If demand is higher than supply market price is higher than commodity value, so there is a possibility to production increase. • If demand is lower than supply market price is lower than commodity value, so volume of commodity production decreases.
LV mechanism • LV regulates commodity production through price mechanism. In short period commodity prices can differ from commodity values according to changes in supply and demand. • Market price is equal to commodity value when market supply is equal to market demand. • If demand is higher than supply market price is higher than commodity value, so there is a possibility to production increase. • If demand is lower than supply market price is lower than commodity value, so volume of commodity production decreases.
 LV mechanism • So, the LV is spontaneous regulator of the whole social production • In advanced capitalism LV operates through prices of production. On the monopoly stage - through monopoly prices.
LV mechanism • So, the LV is spontaneous regulator of the whole social production • In advanced capitalism LV operates through prices of production. On the monopoly stage - through monopoly prices.
 Commodity fetishism • - a domination of things over people. • Every manufacturer every day convinces that his fate depends on the behavior of commodities produced by himself. So, people do not prevail over the products of their labor, but products of labor in commodity form dominate over its creators.
Commodity fetishism • - a domination of things over people. • Every manufacturer every day convinces that his fate depends on the behavior of commodities produced by himself. So, people do not prevail over the products of their labor, but products of labor in commodity form dominate over its creators.
 Features of commodity fetishism • Personification of things - things from inanimate objects are transformed into independent actors with a special public power. • Reification of people - people became appendages of things acting their will. From the subjects of social relations they have transformed into passive acting will things.
Features of commodity fetishism • Personification of things - things from inanimate objects are transformed into independent actors with a special public power. • Reification of people - people became appendages of things acting their will. From the subjects of social relations they have transformed into passive acting will things.


