lecture 1. Political economy.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 44

Political economy Lecture 1. The subject and the methods of Political economy

Questions 1. Appearance of Political economy (PЕ) 2. Material production as a condition of society existence and development 3. The mode of production 4. Economic laws and their objective character 5. The subjects and functions of political economy 6. Methods of PE

Glossary of Terms • Material production – материальное производство • Labor-process – процесс труда • Subjects of labor – предметы труда • Means of labor – средства труда

Glossary of Terms • Means of production – средства производства • Productive forces – производительные силы • Productive relations – производственные отношения • Economic basis – экономический базис

Glossary of Terms • Superstructure – надстройка • Mode of production – способ производства • Economic term – экономическая категория • Economic law – экономический закон

Glossary of Terms • Abstract and concrete – абстрактное и конкретное • Historical and logical – историческое и логическое • Induction and deduction – индукция и дедукция • Analysis and synthesis – анализ и синтез
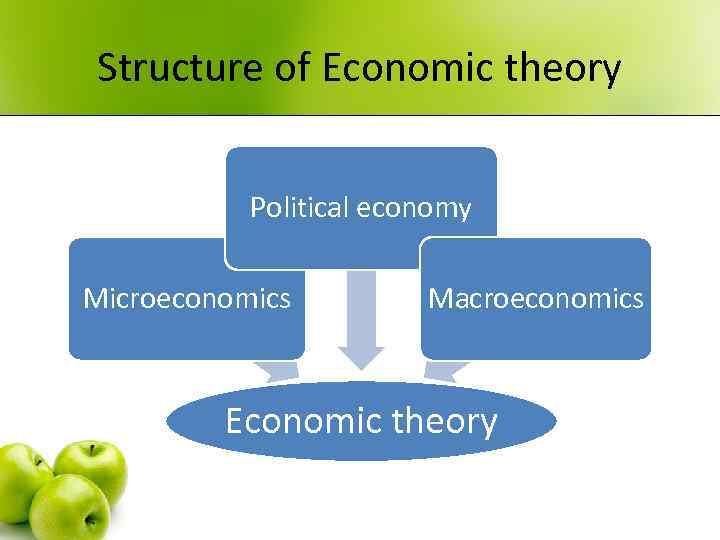
Structure of Economic theory Political economy Microeconomics Macroeconomics Economic theory
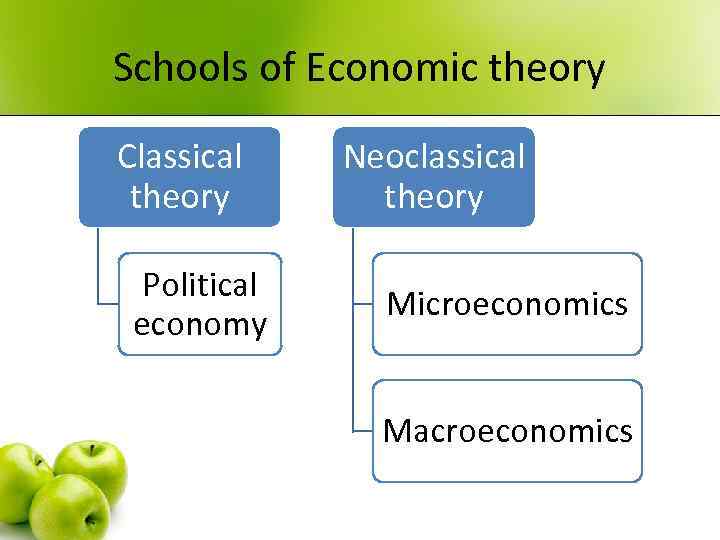
Schools of Economic theory Classical theory Political economy Neoclassical theory Microeconomics Macroeconomics

Evolution of economic terms • • • Term “economy” – from Greek: “οἶκος” – household; “nόμος” – rules. So – economy – science about householding. Term “economy” was introduced by Greek philosopher Aristotle.

Evolution of economic terms • Term “Political economy” was introduced by French economist Antoine de Montchretien in 1615 in his work “Treatise of political economy”. • “πόλις” from Greek – state • So – Political economy – science about state regulation of national economy

Evolution of economic terms • Тerm “Economics” was introduced in 1890 by Alfred Marshall in his work “Principles of economics”. • “Economics” – science that studies human behavior in the world of scarce resources and unlimited wants.

Formation of political economy’s subject • 18 -19 century – emergence and formation of political economy’s subject • Classics of Political economy: • Francois Quesnay • William Petty • Adam Smith • David Ricardo • Karl Marx

Material production and labor process • Material production – the main condition of society existence and development • Material production is based on labor-process. • Labor – is conscious and purposeful human activity directed on changing and adapting of nature elements to meet human needs

Particularities of human labor • Consciousness and purposefulness – the main moments of difference between human labor and animal`s activity • “The worst architect differs from the best bee because before to build cell of wax he built it in his head” К. Маркс, Ф. Єнгельс Соч. , т. 23, с. 189.
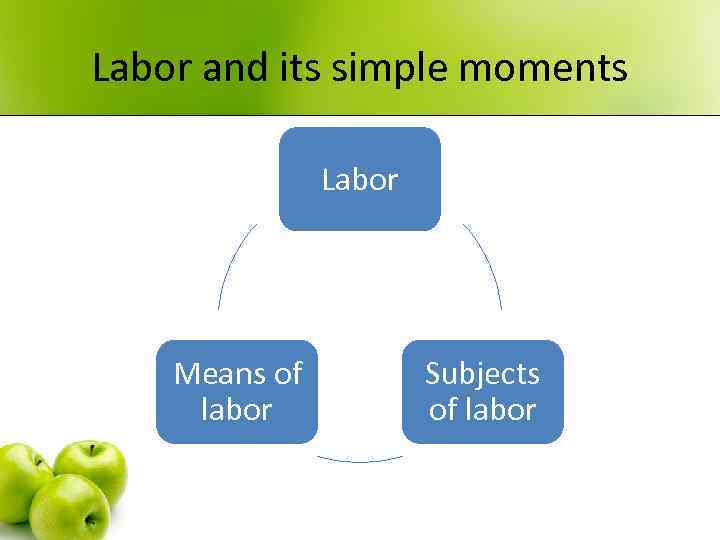
Labor and its simple moments Labor Means of labor Subjects of labor

Subjects of labor • - elements of nature the process of labor is directed on • The primary subjects of labor – subjects spontaneously provided by nature - mineral resources, flora and fauna • The secondary subjects of labor– subjects of labor, which have been filtered through previous labor – cloth, raw materials, semifinished products
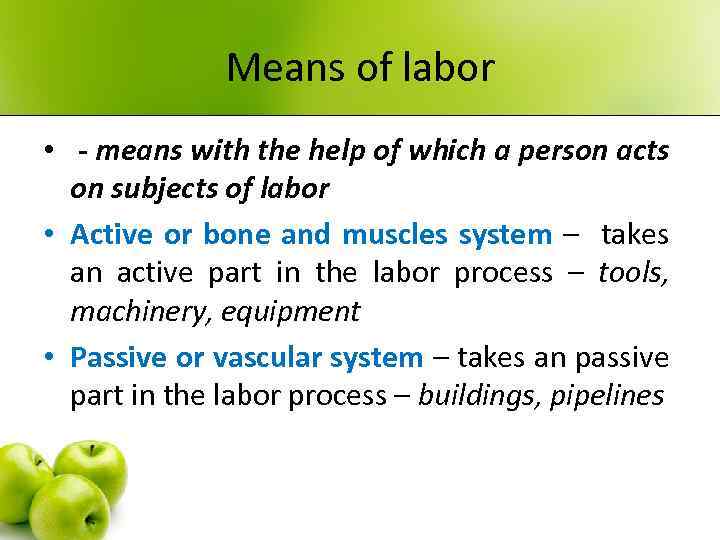
Means of labor • - means with the help of which a person acts on subjects of labor • Active or bone and muscles system – takes an active part in the labor process – tools, machinery, equipment • Passive or vascular system – takes an passive part in the labor process – buildings, pipelines
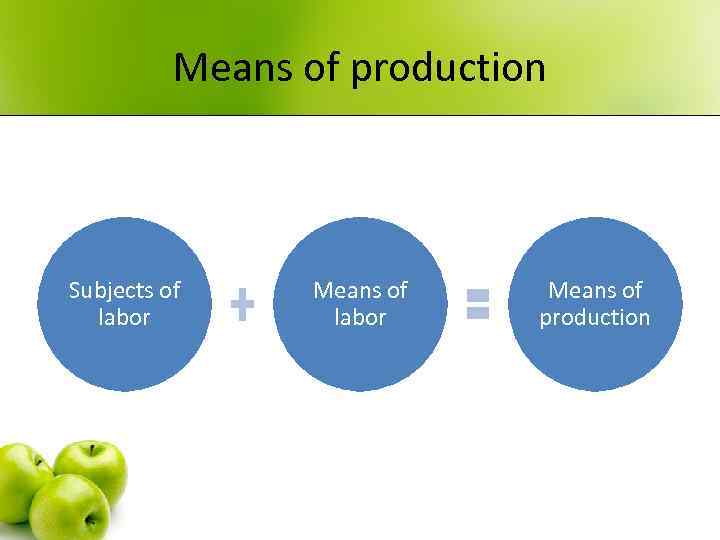
Means of production Subjects of labor Means of production

Production as a social process • Labor process is always done by humans who act in society and with the help of society. • Only collectively human creativity can be developed. • In the process of historical development means of production were created and improved collectively • So, labor and production process have social character.
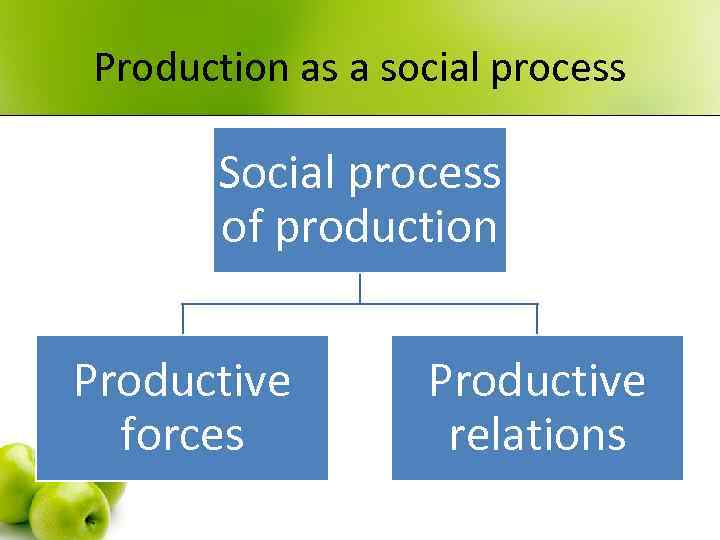
Production as a social process Social process of production Productive forces Productive relations
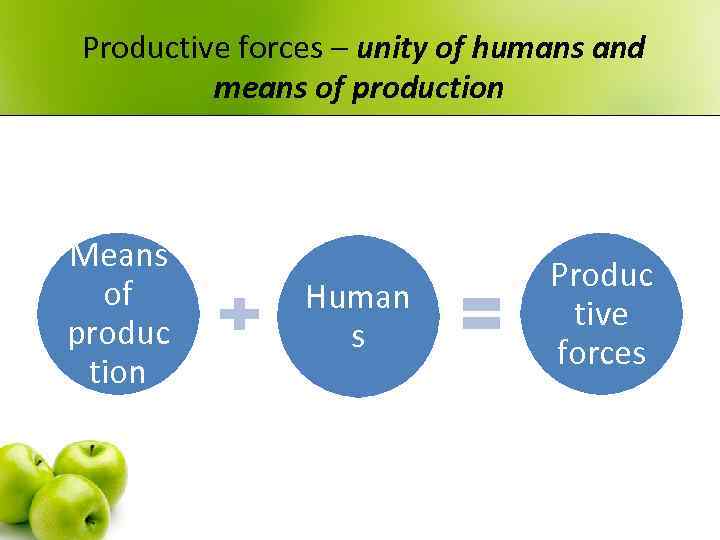
Productive forces – unity of humans and means of production Means of produc tion Human s Produc tive forces

Productive forces • The main and the most active link of social production. • Human is the main productive force. • The level of productive forces progress depends on social division of labor and means of production development. • Science – is the main productive force of modern society

Productive relations • - relations which arise between people in the process of social production, distribution, exchange and consumption of material commodities. • Production – relations, connected with humans and means of production allocation between types of economics activity • Distribution – process, in which the part of every participant is determined and incomes are distributed according to degree of their participation in the process of production. • Exchange - process of incomes exchange on commodities • Consumption – relations, connected with final consumption of material goods

Base and superstructure • Set of historically determined productive relations forms economic base of the society • Economic base of each historical epoch creates particular legal, political and social institutes called superstructure of the society • State takes the main position in superstructure
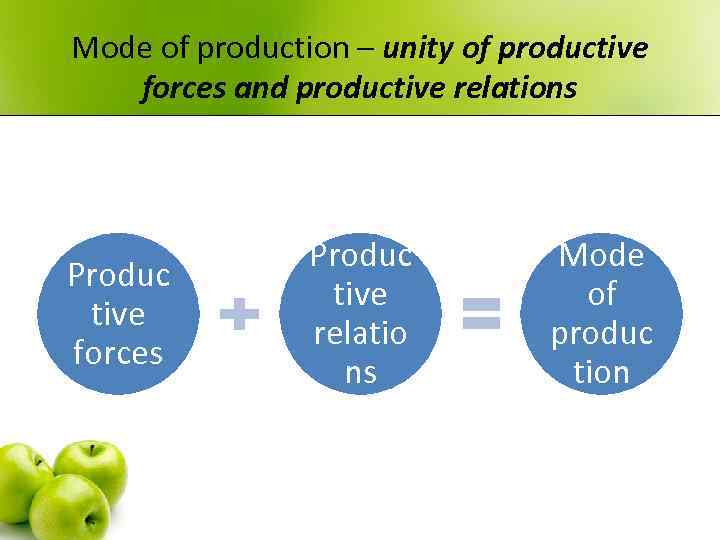
Mode of production – unity of productive forces and productive relations Produc tive forces Produc tive relatio ns Mode of produc tion
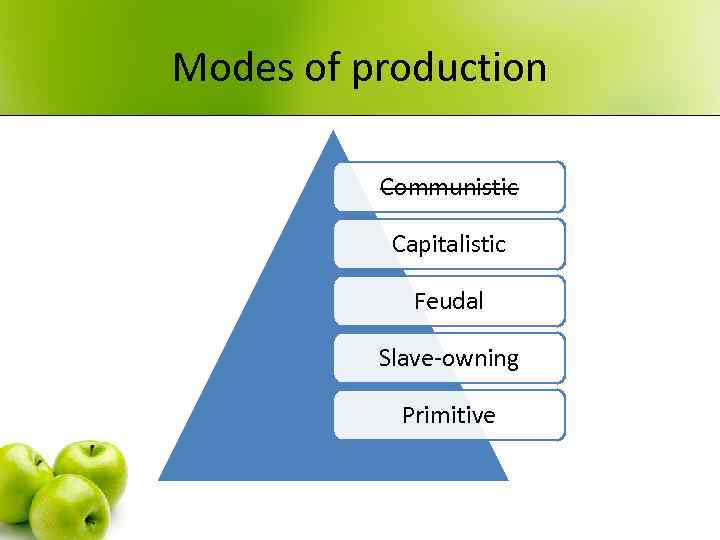
Modes of production Communistic Capitalistic Feudal Slave-owning Primitive
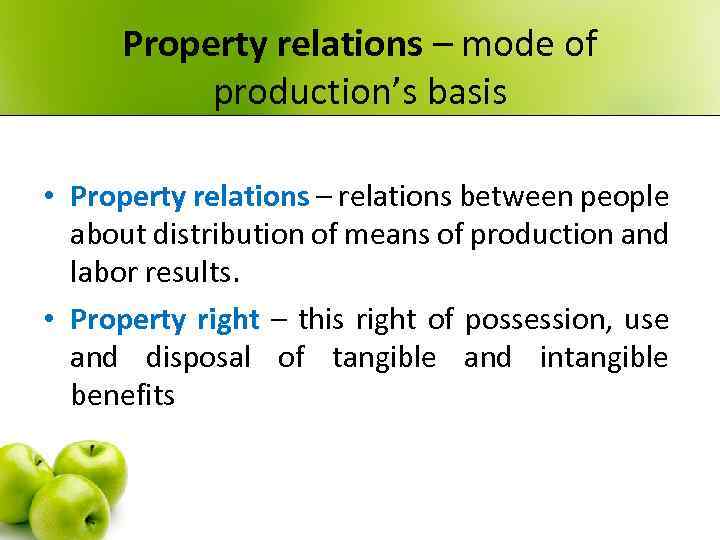
Property relations – mode of production’s basis • Property relations – relations between people about distribution of means of production and labor results. • Property right – this right of possession, use and disposal of tangible and intangible benefits
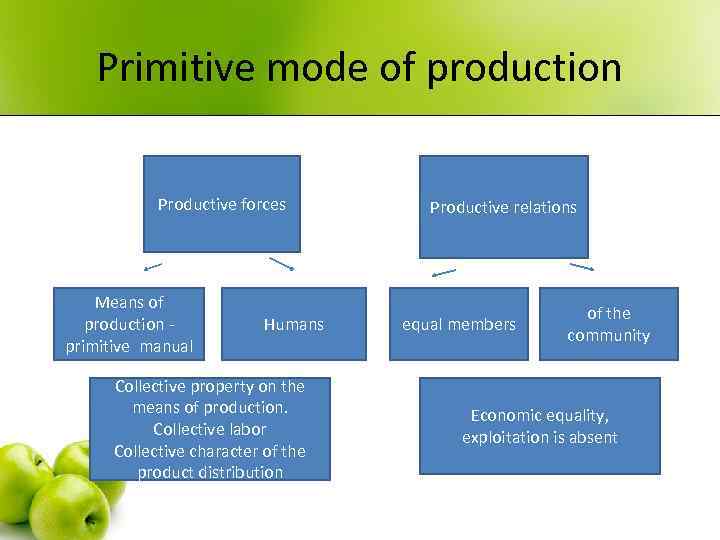
Primitive mode of production Productive forces Means of production - primitive manual Humans Collective property on the means of production. Collective labor Collective character of the product distribution Productive relations equal members of the community Economic equality, exploitation is absent
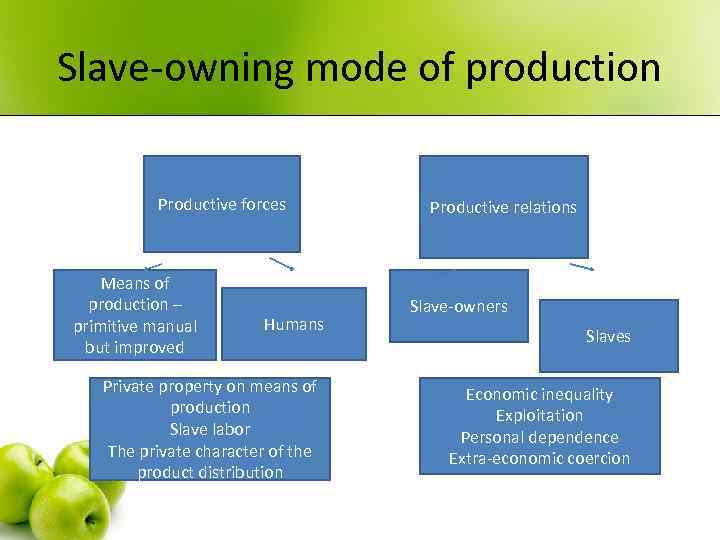
Slave-owning mode of production Productive forces Means of production – primitive manual but improved Humans Private property on means of production Slave labor The private character of the product distribution Productive relations Slave-owners Slaves Economic inequality Exploitation Personal dependence Extra-economic coercion
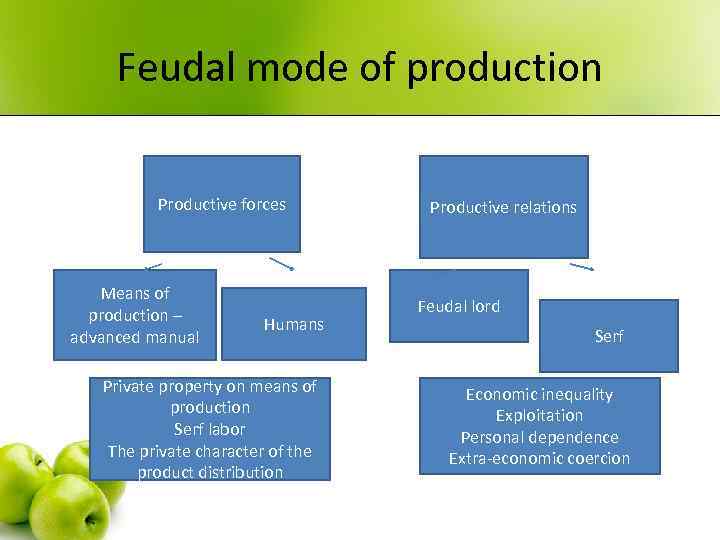
Feudal mode of production Productive forces Means of production – advanced manual Humans Private property on means of production Serf labor The private character of the product distribution Productive relations Feudal lord Serf Economic inequality Exploitation Personal dependence Extra-economic coercion
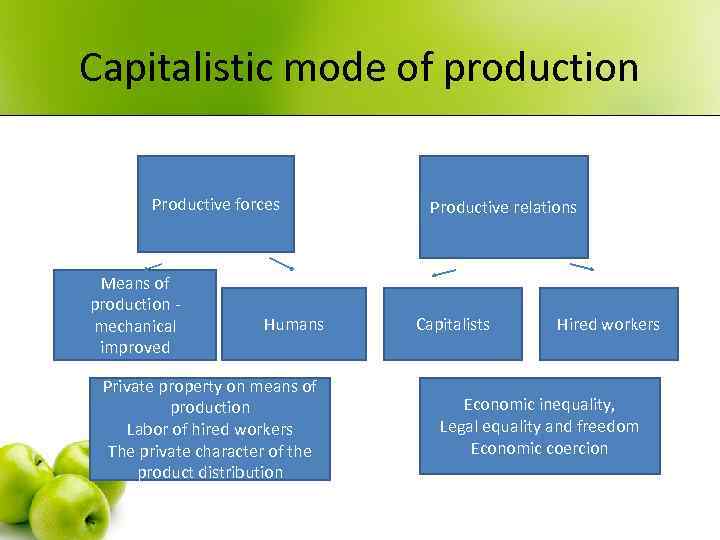
Capitalistic mode of production Productive forces Means of production - mechanical improved Humans Private property on means of production Labor of hired workers The private character of the product distribution Productive relations Capitalists Hired workers Economic inequality, Legal equality and freedom Economic coercion
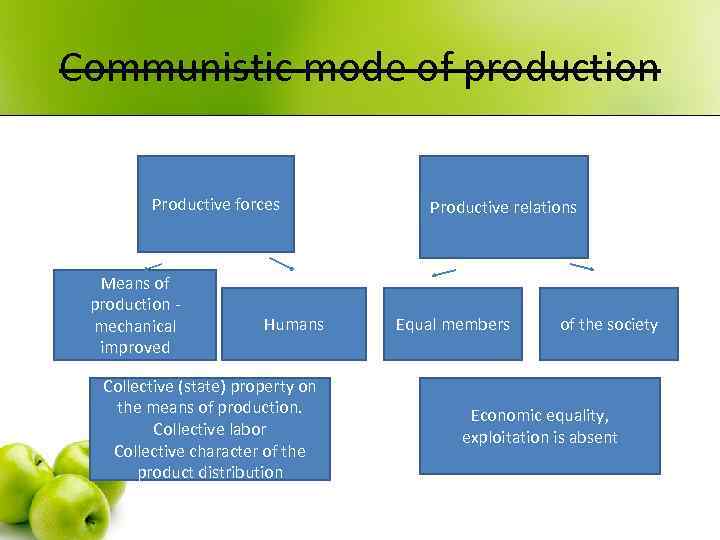
Communistic mode of production Productive forces Means of production - mechanical improved Humans Collective (state) property on the means of production. Collective labor Collective character of the product distribution Productive relations Equal members of the society Economic equality, exploitation is absent

Interrelation between productive forces (PF) and productive relations (PR) • PF – the most active, dynamic part of production mode, PR – more conservative and inert component. • The conflict between them - is inevitable. • It is solved by evolutionary or revolutionary way.

Economic law • This is necessary, steady, causal relationship between economic processes and phenomena, when one phenomenon follows another. • Economic laws do not depend on the will and people want - so they are objective.

Economic laws and laws of Nature Laws of Nature Economic laws Eternal and immutable Historic character Operate in the nature Operate only in human society Objective character

Classification of economic laws • 1) General - operate in all modes of production (the law of increasing productivity, saving time law, accordance of productive relations to the nature of productive forces) • 2) Special - operate in several modes of production (the law of supply and demand) • 3) Specific - operate in a certain mode of production (the law of surplus value)

Subject of Political economy (PE) • In broad sense: • PE studies productive relations, which arise in the process of production, distribution, exchange and consumption in any mode of production • In a narrow sense: • PE studies productive relations of capitalism • PE examines the economic laws of capitalism

Functions of PE • Cognitive - is the scientific explanation of processes and phenomena of economic life, thus forming a scientific outlook and economic thinking. • Methodological - PE is a theoretical basis for other applied sciences such as business economics, finance and credit, government regulation of the economy and so on. • Practical - PE is theoretical basis for the economic policy development
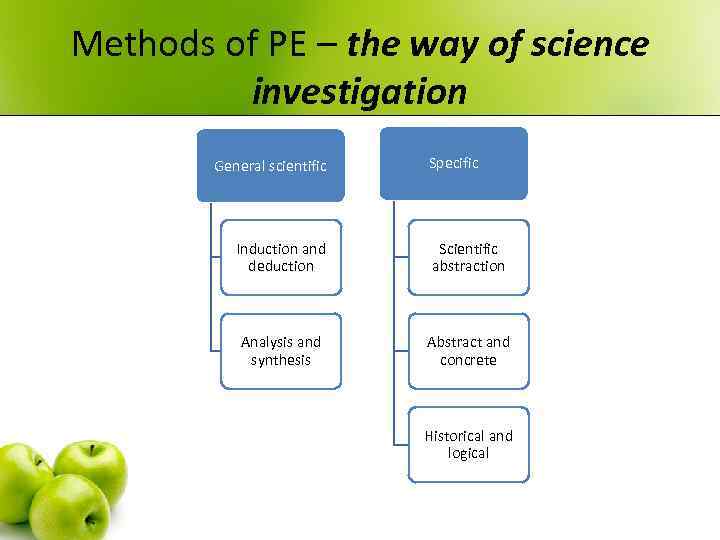
Methods of PE – the way of science investigation General scientific Specific Induction and deduction Scientific abstraction Analysis and synthesis Abstract and concrete Historical and logical
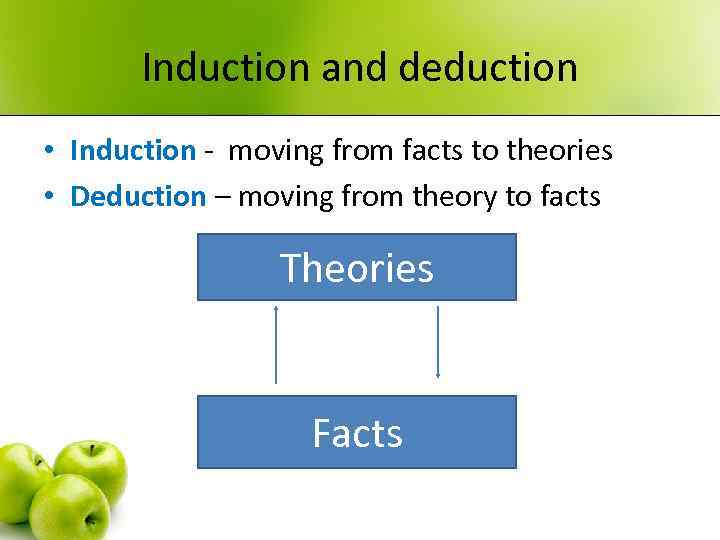
Induction and deduction • Induction - moving from facts to theories • Deduction – moving from theory to facts Theories Facts

Analysis and synthesis • Analysis - the process of mentally breaking down of the whole into its constituent parts and studying them separately. • Synthesis - the process of reconstituting a whole from its parts and obtaining a new knowledge about phenomenon.
Specific methods of PE • Scientific abstraction - the process of perfect theoretical model building. In this process only those facts and relationships are elected which are relevant to theory. These facts and relationships are the basis for real world model formation. • The result of scientific abstraction – scientific categories formation – labor, commodity, money, surplus-value, etc.

Specific methods of PE • Abstract and concrete - a method of ascension from the simplest economic relations to more complex ones. • To receive a concrete knowledge of any phenomena we have to add each new abstraction to previous ones. • So, a concrete is a combination of many abstractions. • The simplest abstraction of capitalism, determined by Marx, is “commodity”.

Specific methods of PE • Historical method studies events according to their historical appearance. • Logical approach studies events according to their logical connection. • Unity of historical and logical studies historical events according to their logical connection. If any event isn`t connected with general logic it is not included in investigation process.
lecture 1. Political economy.pptx