66b76ceb629358c1cbc8a12b572dde98.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
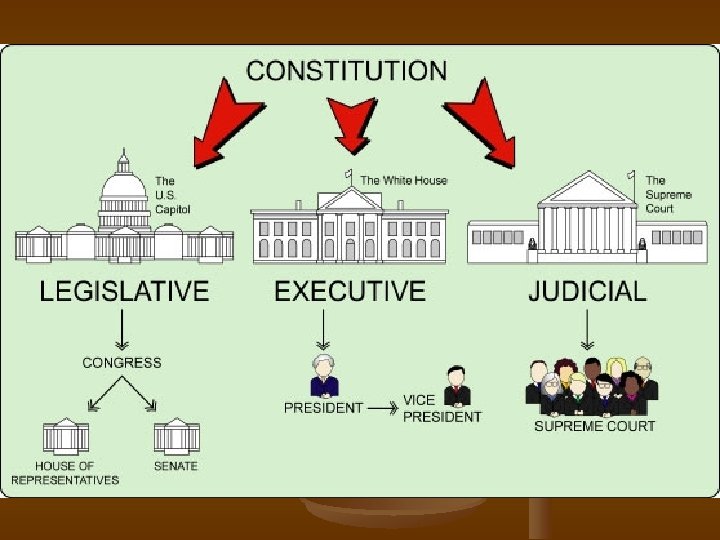
 Political & Economic Systems
Political & Economic Systems
 What is the meaning of the following Prefixes and Suffixes? ? ? Page 38 A in your spiral Prefixes: a) uni- and mono- one uni b) auto- self c) eco- house d) olig- few e) demo- people f) theo- God/religon n Suffixes: g) -cracy – power (democracy, theocracy, aristocracy, meritocracy) h) -nomy h)--nomy – law (Economy–system of rules governing i) archy n
What is the meaning of the following Prefixes and Suffixes? ? ? Page 38 A in your spiral Prefixes: a) uni- and mono- one uni b) auto- self c) eco- house d) olig- few e) demo- people f) theo- God/religon n Suffixes: g) -cracy – power (democracy, theocracy, aristocracy, meritocracy) h) -nomy h)--nomy – law (Economy–system of rules governing i) archy n
 Government Systems Levels of Government (Power) 1. Unitary System: gives all key powers to the national or central government. State, provincial or local governments have only limited powers and sovereignty. n Ex: United Kingdom and France
Government Systems Levels of Government (Power) 1. Unitary System: gives all key powers to the national or central government. State, provincial or local governments have only limited powers and sovereignty. n Ex: United Kingdom and France
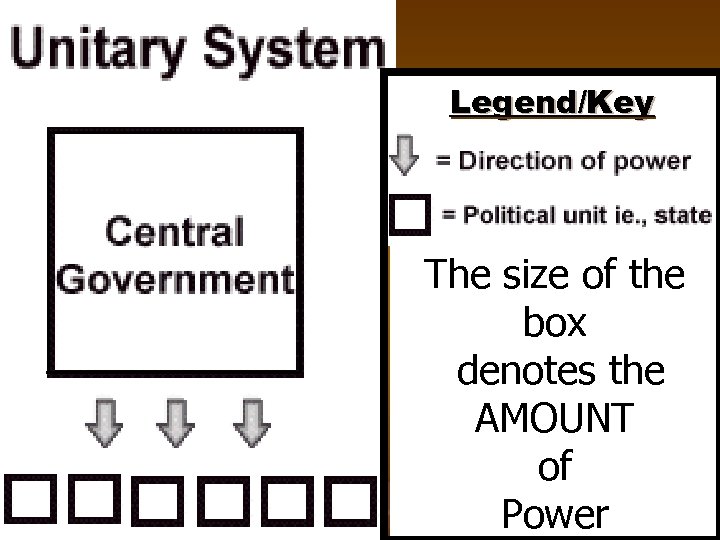 Legend/Key The size of the box denotes the AMOUNT of Power
Legend/Key The size of the box denotes the AMOUNT of Power
 If the Government is big enough to give you everything you want it is big enough to take away everything you have. ~Gerald R. Ford
If the Government is big enough to give you everything you want it is big enough to take away everything you have. ~Gerald R. Ford
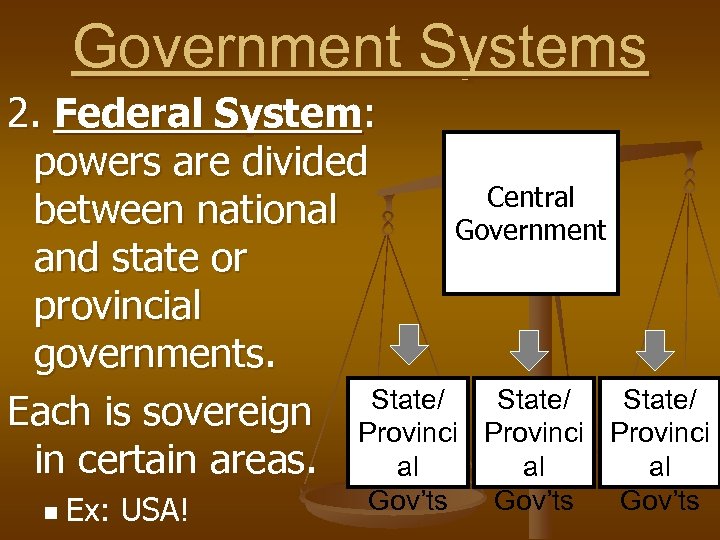 Government Systems 2. Federal System: powers are divided Central between national Government and state or provincial governments. State/ Each is sovereign Provinci in certain areas. al al al n Ex: USA! Gov’ts
Government Systems 2. Federal System: powers are divided Central between national Government and state or provincial governments. State/ Each is sovereign Provinci in certain areas. al al al n Ex: USA! Gov’ts


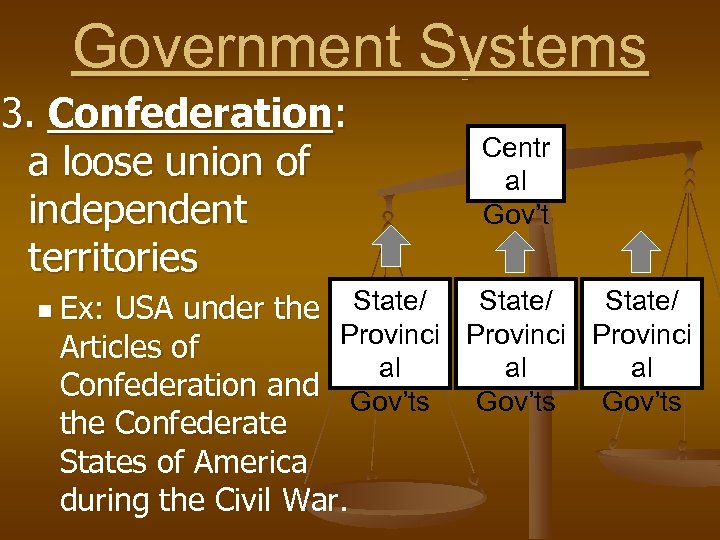 Government Systems 3. Confederation: a loose union of independent territories Centr al Gov’t State/ USA under the State/ Provinci Articles of al al al Confederation and Gov’ts the Confederate States of America during the Civil War. n Ex:
Government Systems 3. Confederation: a loose union of independent territories Centr al Gov’t State/ USA under the State/ Provinci Articles of al al al Confederation and Gov’ts the Confederate States of America during the Civil War. n Ex:
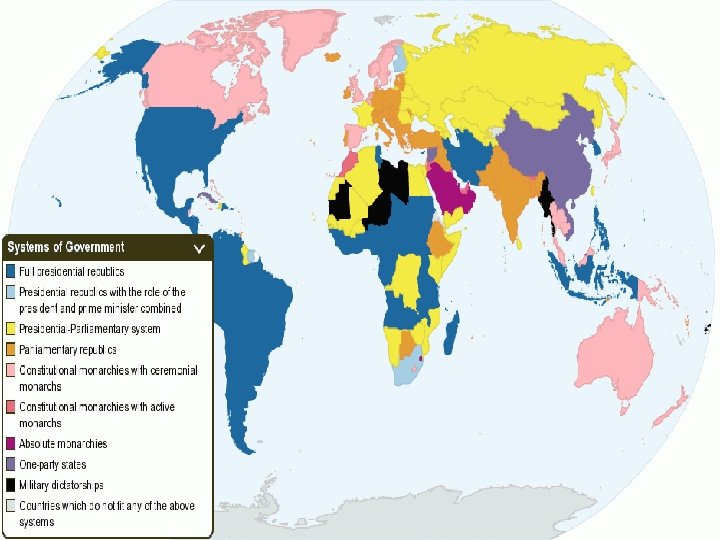
 Types of Authority 1. Autocracy — rule by one person n oldest n get and most common form of gov’t their position of power through inheritance (birth) or military power
Types of Authority 1. Autocracy — rule by one person n oldest n get and most common form of gov’t their position of power through inheritance (birth) or military power

 Types of Autocracies a) Totalitarian Dictatorship — one person controls everything n government does not report to the people; has complete power
Types of Autocracies a) Totalitarian Dictatorship — one person controls everything n government does not report to the people; has complete power

 Types of Autocracies b) Monarchy — king or queen has power through inheritance n 2 Types of Monarchies n Absolute Monarchy — unlimited power to rule n very rare today n Ex: Saudi Arabia
Types of Autocracies b) Monarchy — king or queen has power through inheritance n 2 Types of Monarchies n Absolute Monarchy — unlimited power to rule n very rare today n Ex: Saudi Arabia

 n 2 Types of Monarchies 2) Constitutional Monarchy — share powers with elected legislators - sometimes it is just ceremonial Ex: United Kingdom, Japan, Thailand, Jordan
n 2 Types of Monarchies 2) Constitutional Monarchy — share powers with elected legislators - sometimes it is just ceremonial Ex: United Kingdom, Japan, Thailand, Jordan
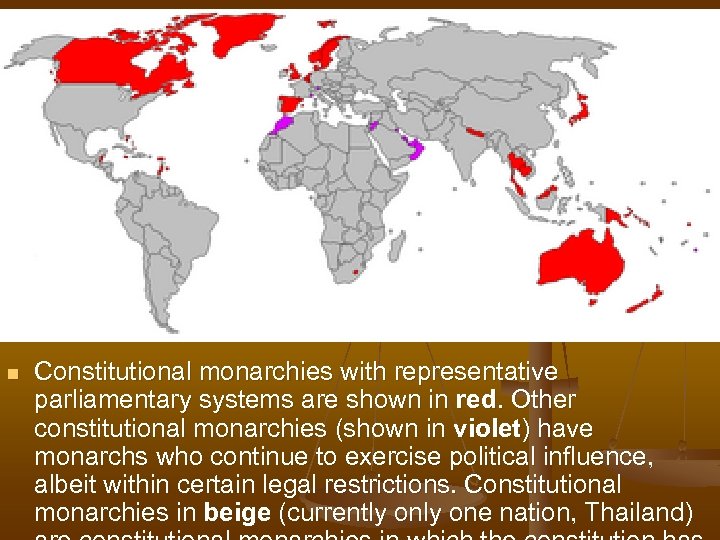 n Constitutional monarchies with representative parliamentary systems are shown in red. Other constitutional monarchies (shown in violet) have monarchs who continue to exercise political influence, albeit within certain legal restrictions. Constitutional monarchies in beige (currently one nation, Thailand)
n Constitutional monarchies with representative parliamentary systems are shown in red. Other constitutional monarchies (shown in violet) have monarchs who continue to exercise political influence, albeit within certain legal restrictions. Constitutional monarchies in beige (currently one nation, Thailand)
 Types of Authority 2. Oligarchy — rule by a few people n source of power is religion, wealth, military power, social position n Communist governments: run by leaders o Communist Party and armed forces n n Appear to be controlled by the people of the country, but are not in reality Legislatures only adopt policies of ruling party
Types of Authority 2. Oligarchy — rule by a few people n source of power is religion, wealth, military power, social position n Communist governments: run by leaders o Communist Party and armed forces n n Appear to be controlled by the people of the country, but are not in reality Legislatures only adopt policies of ruling party

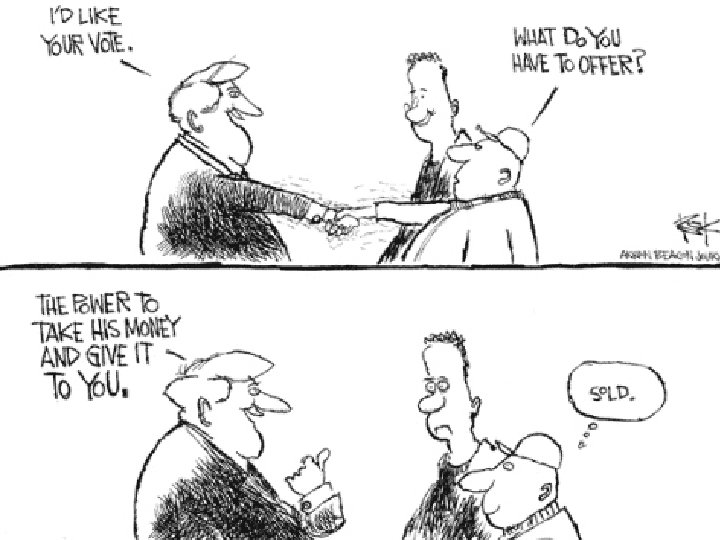
 Types of Authority 3. Democracy — rule by many people - consent of citizens n 2 Types of Democracy n a) Direct Democracy — citizens decide on issues directly n none exists in any country at a national level
Types of Authority 3. Democracy — rule by many people - consent of citizens n 2 Types of Democracy n a) Direct Democracy — citizens decide on issues directly n none exists in any country at a national level


 Types of Authority n b) Representative Democracy — the citizens elect representatives to make and enforce laws. n Republics — voters elect all major officials n not all democracies are republics n Ex: United Kingdom
Types of Authority n b) Representative Democracy — the citizens elect representatives to make and enforce laws. n Republics — voters elect all major officials n not all democracies are republics n Ex: United Kingdom

 country whose government has changed from an autocracy to a democracy. Then suggest ways that people might address these challenges. Autocracy to Democracy Challenges Solutions · ·
country whose government has changed from an autocracy to a democracy. Then suggest ways that people might address these challenges. Autocracy to Democracy Challenges Solutions · ·
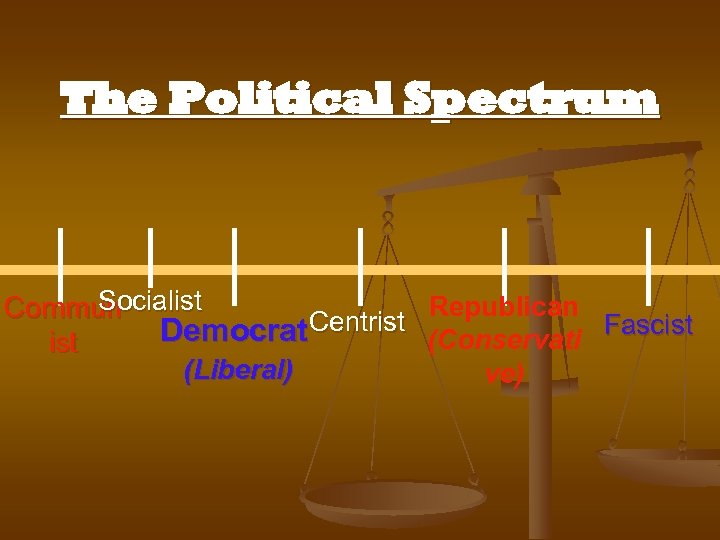 The Political Spectrum Socialist Republican Commun Democrat Centrist (Conservati Fascist (Liberal) ve)
The Political Spectrum Socialist Republican Commun Democrat Centrist (Conservati Fascist (Liberal) ve)
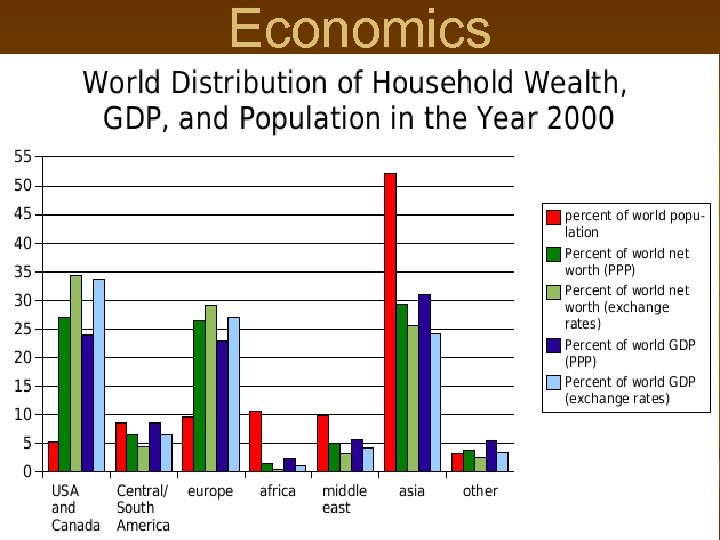 Economics
Economics
 Economic Systems 3 Basic Economic Questions that all economic systems must answer n 1. What and how many goods and services should be produced? n 2. How n 3. Who are they going to be produced? gets the goods and services that are produced?
Economic Systems 3 Basic Economic Questions that all economic systems must answer n 1. What and how many goods and services should be produced? n 2. How n 3. Who are they going to be produced? gets the goods and services that are produced?
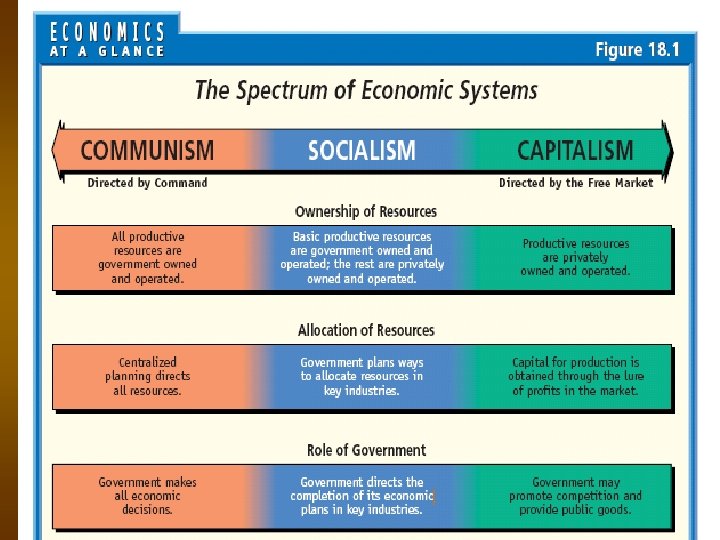

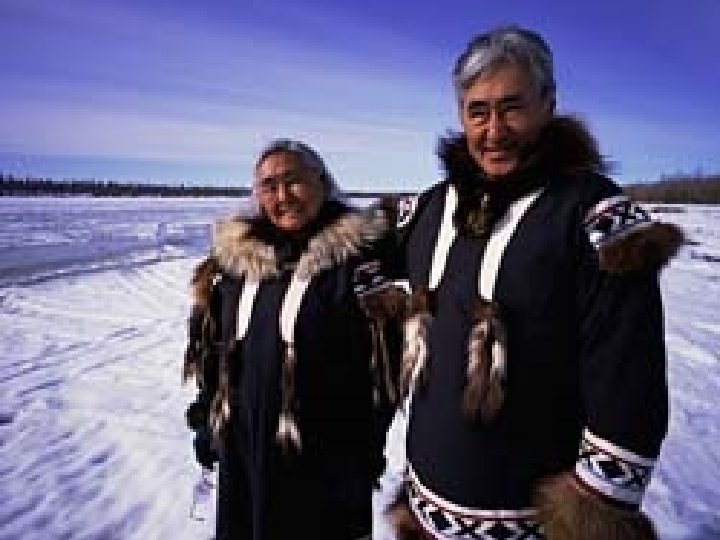
 3 Types of Economic Systems n They each make decisions differently 1. Traditional Economy — all decisions defined by customs, traditions (elders in the group) n not based on what one would like to have, but what is customary n Ex: Inuit of Canada — hunters shared with other families
3 Types of Economic Systems n They each make decisions differently 1. Traditional Economy — all decisions defined by customs, traditions (elders in the group) n not based on what one would like to have, but what is customary n Ex: Inuit of Canada — hunters shared with other families

 2. Market Economy — private groups and individuals make decisions about what to make or produce n based on free enterprise — idea that private individuals or groups have the right to own property or businesses and make a profit with little government interference n people decide what to buy or not to buy n people decide what they want to do to make a living & who they want to work for
2. Market Economy — private groups and individuals make decisions about what to make or produce n based on free enterprise — idea that private individuals or groups have the right to own property or businesses and make a profit with little government interference n people decide what to buy or not to buy n people decide what they want to do to make a living & who they want to work for

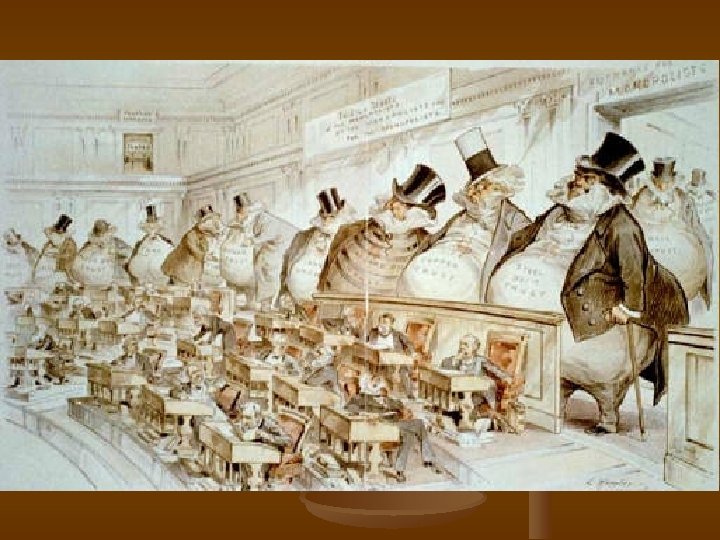
 Robber Barons or Industry? n Cornelius Vanderbilt – railroads n n Titans of John D. Rockefeller – oil Andrew Carnegie – steel n J. P. Morgan – banking/finance
Robber Barons or Industry? n Cornelius Vanderbilt – railroads n n Titans of John D. Rockefeller – oil Andrew Carnegie – steel n J. P. Morgan – banking/finance
 Market Economy n also n no called Capitalism pure market economy system exists n most are Mixed Economies — government supports and regulates free enterprise through decisions that affect the marketplace
Market Economy n also n no called Capitalism pure market economy system exists n most are Mixed Economies — government supports and regulates free enterprise through decisions that affect the marketplace


 3 Types of Economic Systems (con’t) 3. Command Economy — ownership and direction of land, labor, machinery, factories, and managers are by the government; all distribution of goods is by the government
3 Types of Economic Systems (con’t) 3. Command Economy — ownership and direction of land, labor, machinery, factories, and managers are by the government; all distribution of goods is by the government
 Old Soviet saying, “We’ll keep pretending to work if they’ll keep pretending to pay us. ”
Old Soviet saying, “We’ll keep pretending to work if they’ll keep pretending to pay us. ”

 2 types of Command Economies 1. Socialist — free enterprise mixed with government control n Government control of only certain industries with the following main goals: n equal distribution of wealth n society’s control, through the government of decisions about production n public ownership of land, factories, means of production
2 types of Command Economies 1. Socialist — free enterprise mixed with government control n Government control of only certain industries with the following main goals: n equal distribution of wealth n society’s control, through the government of decisions about production n public ownership of land, factories, means of production
 Protest rally Chicago 2009
Protest rally Chicago 2009

 Deaths due to Communism n USSR – about 8 -20 million people executed However, it is widely believed that if you take into account the deaths caused by the regime's "criminal neglect" and "ruthlessness" (starvation, disease, exposure and overwork) about 61 million people were killed during the almost 70 years of Communist rule in the USSR. June 1943 - mass graves dating from 1937– 38 opened up and hundreds of bodies exhumed for
Deaths due to Communism n USSR – about 8 -20 million people executed However, it is widely believed that if you take into account the deaths caused by the regime's "criminal neglect" and "ruthlessness" (starvation, disease, exposure and overwork) about 61 million people were killed during the almost 70 years of Communist rule in the USSR. June 1943 - mass graves dating from 1937– 38 opened up and hundreds of bodies exhumed for
 Deaths due to Communism n n Local and provincial Chinese archives indicate that the death toll was at least 45 million, and that "In most cases the party knew very well that it was starving its own people to death. ” In a secret meeting at Shanghai in 1959, Mao issued the order to procure one third of all grain from the countryside. He said: “When there is not enough to eat people starve to death. It is better to let half of the people die so that the other half can eat their fill. ”
Deaths due to Communism n n Local and provincial Chinese archives indicate that the death toll was at least 45 million, and that "In most cases the party knew very well that it was starving its own people to death. ” In a secret meeting at Shanghai in 1959, Mao issued the order to procure one third of all grain from the countryside. He said: “When there is not enough to eat people starve to death. It is better to let half of the people die so that the other half can eat their fill. ”

 2. Communist — very strict control of economy n The Communist Party makes all of the decisions about: n what to produce n how much to produce n how to distribute the goods and services most decline in the long-run n no competition to make products more innovative or better n China & Vietnam are now allowing some free enterprise to boost their economy n
2. Communist — very strict control of economy n The Communist Party makes all of the decisions about: n what to produce n how much to produce n how to distribute the goods and services most decline in the long-run n no competition to make products more innovative or better n China & Vietnam are now allowing some free enterprise to boost their economy n

 What kind of benefits do people receive in a market economy that they would NOT receive in a command economy?
What kind of benefits do people receive in a market economy that they would NOT receive in a command economy?

 Modern Slavery http: //www. freetheslaves. net/Page. aspx? pid=524
Modern Slavery http: //www. freetheslaves. net/Page. aspx? pid=524




