Political and Economic Geography Lech Haydukiewicz lechhaydukiewicz@gmail. com

























political_and_economic_geography.pptx
- Размер: 4.0 Мб
- Автор:
- Количество слайдов: 34
Описание презентации Political and Economic Geography Lech Haydukiewicz lechhaydukiewicz@gmail. com по слайдам
 Political and Economic Geography Lech Haydukiewicz lechhaydukiewicz@gmail. com
Political and Economic Geography Lech Haydukiewicz lechhaydukiewicz@gmail. com
 What issues does the course cover? • Political map of the world and its changes (beginnings of world economy, the age of imperialism, decolonisation) • The field of political geography — the concepts of state — a world-systems approach to political geography (the spatial structure of world economy, the concepts of core and periphery, the dynamics of the world economy)
What issues does the course cover? • Political map of the world and its changes (beginnings of world economy, the age of imperialism, decolonisation) • The field of political geography — the concepts of state — a world-systems approach to political geography (the spatial structure of world economy, the concepts of core and periphery, the dynamics of the world economy)
 • Processes of integration and disintegration of countries • Socio-economic issues — (human geography: population growth, migration, sex, nationality, languages, literacy, health, income) — land use, global and regional food supply — mining, manufacturing and services — international trade patterns
• Processes of integration and disintegration of countries • Socio-economic issues — (human geography: population growth, migration, sex, nationality, languages, literacy, health, income) — land use, global and regional food supply — mining, manufacturing and services — international trade patterns
 • The course is to give the most important issues on political and economic geography. • • A student has the knowledge about the main international organizations, their geographical distribution and their international value. • • A student has the knowledge from the sphere of historical and political geography which refers to the main changes on the political map of Europe form the 18 th century and the Rest of Word • • A student has the knowledge about the main geographical background and the distribution of demographical, social and economic phenomena. • • A student is able to analyze the changes on the political map of the Word and the global and region al demographical changes. • • Student is able to recognize the cultural differentiation of particular regions of the Word. • • Student understands the need of permanent learning and improving its knowledge and skills to improve the quality of recognition and analysis the problems of modern Word.
• The course is to give the most important issues on political and economic geography. • • A student has the knowledge about the main international organizations, their geographical distribution and their international value. • • A student has the knowledge from the sphere of historical and political geography which refers to the main changes on the political map of Europe form the 18 th century and the Rest of Word • • A student has the knowledge about the main geographical background and the distribution of demographical, social and economic phenomena. • • A student is able to analyze the changes on the political map of the Word and the global and region al demographical changes. • • Student is able to recognize the cultural differentiation of particular regions of the Word. • • Student understands the need of permanent learning and improving its knowledge and skills to improve the quality of recognition and analysis the problems of modern Word.
 • Introduction to the course and to economic and political geography, 2 • Historical and political geography: the changes on political map of the World: reasons, processes and results. 8 • The classifications of countries. Some issues on borderlines. 4 • Demography: the population growth, migrations, age and sex ratio. 6 • Social and cultural diversity of modern World: ethnicity, language, religion. 4 • Economic Geography: Industry, agriculture, services, international organizations. 6 • • Student is obliged to attend the lectures and to pass the writing test on the political map of the Word (student must point 90% or more from the given countries). The absence in more than 3 lectures must result with an additional consultation. The below mentioned parts are obligatory to be admitted to the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test (student is obliged to have at least 65% of total score) • • Student is obliged to have between 65% and 69% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. 3, 0 • Student is obliged to have between 70% and 74% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. • Student is obliged to have between 75% and 79% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. • Student is obliged to have between 80% and 84% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. • Student is obliged to have 85% or more of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. 5,
• Introduction to the course and to economic and political geography, 2 • Historical and political geography: the changes on political map of the World: reasons, processes and results. 8 • The classifications of countries. Some issues on borderlines. 4 • Demography: the population growth, migrations, age and sex ratio. 6 • Social and cultural diversity of modern World: ethnicity, language, religion. 4 • Economic Geography: Industry, agriculture, services, international organizations. 6 • • Student is obliged to attend the lectures and to pass the writing test on the political map of the Word (student must point 90% or more from the given countries). The absence in more than 3 lectures must result with an additional consultation. The below mentioned parts are obligatory to be admitted to the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test (student is obliged to have at least 65% of total score) • • Student is obliged to have between 65% and 69% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. 3, 0 • Student is obliged to have between 70% and 74% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. • Student is obliged to have between 75% and 79% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. • Student is obliged to have between 80% and 84% of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. • Student is obliged to have 85% or more of total score of the final examination which is the writing multiple-choice and filling test. 5,
![Literature • [1] James B. Rubinstein — The Cultural Landscape. An Introduction to Human Geography, Upper Literature • [1] James B. Rubinstein — The Cultural Landscape. An Introduction to Human Geography, Upper](http://present5.com/presentforday2/20161125/political_and_economic_geography.pptx_images/political_and_economic_geography.pptx_5.jpg) Literature • [1] James B. Rubinstein — The Cultural Landscape. An Introduction to Human Geography, Upper Saddle River NJ, 2010, Prentice Hall [partially] • [2] Historical Atlas of the World, • [3] Geographical Atlas of the World,
Literature • [1] James B. Rubinstein — The Cultural Landscape. An Introduction to Human Geography, Upper Saddle River NJ, 2010, Prentice Hall [partially] • [2] Historical Atlas of the World, • [3] Geographical Atlas of the World,
![Literature • [1] Colin Flint, Peter Taylor — Political Geography. World Economy, Nation-state and Locality, 2007, Literature • [1] Colin Flint, Peter Taylor — Political Geography. World Economy, Nation-state and Locality, 2007,](http://present5.com/presentforday2/20161125/political_and_economic_geography.pptx_images/political_and_economic_geography.pptx_6.jpg) Literature • [1] Colin Flint, Peter Taylor — Political Geography. World Economy, Nation-state and Locality, 2007, Pearson, Prentice Hall • [2] Frederick Stutz, Barney Warf — The World Economy, Resources, Location, Trade and Development, 2007, Pearson, Prentice Hall • [3] Kevin Cox — Political Geography: Territory, State and Society, 2002, Wiley-Blackwell
Literature • [1] Colin Flint, Peter Taylor — Political Geography. World Economy, Nation-state and Locality, 2007, Pearson, Prentice Hall • [2] Frederick Stutz, Barney Warf — The World Economy, Resources, Location, Trade and Development, 2007, Pearson, Prentice Hall • [3] Kevin Cox — Political Geography: Territory, State and Society, 2002, Wiley-Blackwell
 The Map
The Map
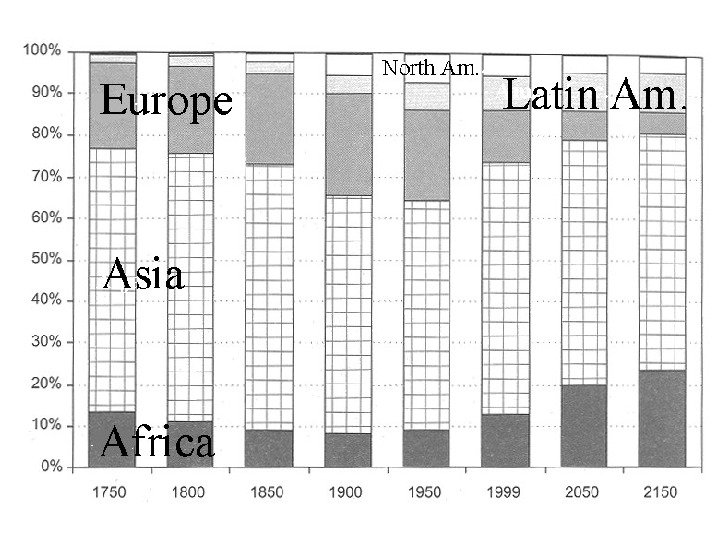
 Number of states 1914: 52 independent states Europe: 22 Asia: 8 – which ones? Africa: 2 – which ones? Americas:
Number of states 1914: 52 independent states Europe: 22 Asia: 8 – which ones? Africa: 2 – which ones? Americas:

 Number of states 1957: 84 independent states Europe: 32 Asia: 19 Africa: 9 Americas: 22 Oceania:
Number of states 1957: 84 independent states Europe: 32 Asia: 19 Africa: 9 Americas: 22 Oceania:

 Number of states 1975: 153 independent states Europe: 33 Asia: 39 Africa: 46 Americas: 28 Oceania:
Number of states 1975: 153 independent states Europe: 33 Asia: 39 Africa: 46 Americas: 28 Oceania:
 Number of states 2004: 196 independent states Europe: 43 – which new ones? Asia: 48 Africa: 53 Americas: 36 Oceania:
Number of states 2004: 196 independent states Europe: 43 – which new ones? Asia: 48 Africa: 53 Americas: 36 Oceania:


 Modern World
Modern World

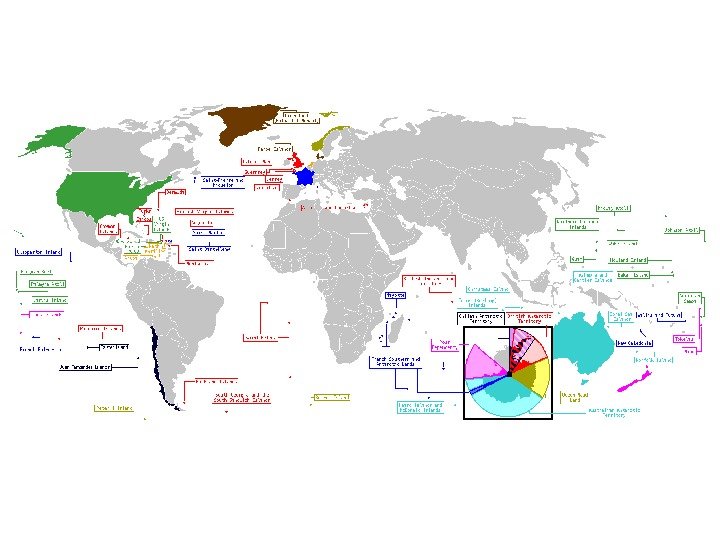
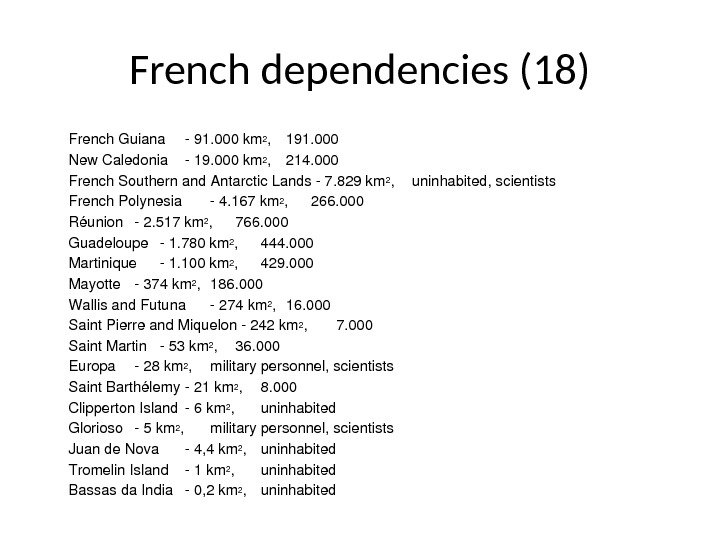
 French dependencies (18) French. Guiana 91. 000 km 2 , 191. 000 New. Caledonia 19. 000 km 2 , 214. 000 French. Southernand. Antarctic. Lands 7. 829 km 2 , uninhabited, scientists French. Polynesia 4. 167 km 2 , 266. 000 Réunion 2. 517 km 2 , 766. 000 Guadeloupe 1. 780 km 2 , 444. 000 Martinique 1. 100 km 2 , 429. 000 Mayotte 374 km 2 , 186. 000 Wallisand. Futuna 274 km 2 , 16. 000 Saint. Pierreand. Miquelon 242 km 2 , 7. 000 Saint. Martin 53 km 2 , 36. 000 Europa 28 km 2 , militarypersonnel, scientists Saint. Barth élemy 21 km 2 , 8. 000 Clipperton. Island 6 km 2 , uninhabited Glorioso 5 km 2 , militarypersonnel, scientists Juande. Nova 4, 4 km 2 , uninhabited Tromelin. Island 1 km 2 , uninhabited Bassasda. India 0, 2 km 2 , uninhabited
French dependencies (18) French. Guiana 91. 000 km 2 , 191. 000 New. Caledonia 19. 000 km 2 , 214. 000 French. Southernand. Antarctic. Lands 7. 829 km 2 , uninhabited, scientists French. Polynesia 4. 167 km 2 , 266. 000 Réunion 2. 517 km 2 , 766. 000 Guadeloupe 1. 780 km 2 , 444. 000 Martinique 1. 100 km 2 , 429. 000 Mayotte 374 km 2 , 186. 000 Wallisand. Futuna 274 km 2 , 16. 000 Saint. Pierreand. Miquelon 242 km 2 , 7. 000 Saint. Martin 53 km 2 , 36. 000 Europa 28 km 2 , militarypersonnel, scientists Saint. Barth élemy 21 km 2 , 8. 000 Clipperton. Island 6 km 2 , uninhabited Glorioso 5 km 2 , militarypersonnel, scientists Juande. Nova 4, 4 km 2 , uninhabited Tromelin. Island 1 km 2 , uninhabited Bassasda. India 0, 2 km 2 , uninhabited
 British Dependencies (16) Falkland. Islands 12. 173 km 2 , 3. 000 South. Georgiaandthe. South. Sandwich. Islands 3. 903 km 2 , uninhabited Cayman. Islands 626 km 2 , 43. 000 Man 572 km 2 , 75. 000 Turksand. Caicos. Islands 430 km 2 , 20. 000 Saint. Helena, Ascensionand. Tristanda. Cunha 410 km 2 , 7. 000 Akrotiriand. Dhekelia 254 km 2 , 8. 000 British. Virgin. Islands 153 km 2 , 22. 000 Jersey 116 km 2 , 90. 000 Anguilla 102 km 2 , 13. 000 Montserrat 102 km 2 , 9. 000 Guernsey 78 km 2 , 65. 000 British. Indian. Ocean. Territory 69 km 2 , 2. 000 andmilitarypersonnel Bermuda 53, 3 km 2 , 65. 000 Pitcairn. Islands 47 km 2 , 46 persons!!! Gibraltar 6, 5 km 2 , 28.
British Dependencies (16) Falkland. Islands 12. 173 km 2 , 3. 000 South. Georgiaandthe. South. Sandwich. Islands 3. 903 km 2 , uninhabited Cayman. Islands 626 km 2 , 43. 000 Man 572 km 2 , 75. 000 Turksand. Caicos. Islands 430 km 2 , 20. 000 Saint. Helena, Ascensionand. Tristanda. Cunha 410 km 2 , 7. 000 Akrotiriand. Dhekelia 254 km 2 , 8. 000 British. Virgin. Islands 153 km 2 , 22. 000 Jersey 116 km 2 , 90. 000 Anguilla 102 km 2 , 13. 000 Montserrat 102 km 2 , 9. 000 Guernsey 78 km 2 , 65. 000 British. Indian. Ocean. Territory 69 km 2 , 2. 000 andmilitarypersonnel Bermuda 53, 3 km 2 , 65. 000 Pitcairn. Islands 47 km 2 , 46 persons!!! Gibraltar 6, 5 km 2 , 28.
 US Dependencies (13 + 2) Puerto. Rico 9. 104 km 2 , 3. 898. 000 Guam 549 km 2 , 199. 000 Northern. Mariana. Islands 477 km 2 , 78. 000 USVirgin. Islands 352 km 2 , 109. 000 American. Samoa 199 km 2 , 58. 000 Wake. Island 6, 5 km 2 , militarypersonnel Midway. Island 6, 2 km 2 , uninhabited Navassa. Island 5, 2 km 2 , uninhabited Jarvis. Island 4, 5 km 2 , uninhabited Johnston. Atoll 2, 8 km 2 , militarypersonnel Howland. Island 1, 6 km 2 , uninhabited Baker. Island 1, 4 km 2 , uninhabited Kingman. Reef 1 km 2 , uninhabited Bajo. Nuevo. Bankand. Serranilla. Bankareuninhabitedandcurrentlycontrolledby Colombia
US Dependencies (13 + 2) Puerto. Rico 9. 104 km 2 , 3. 898. 000 Guam 549 km 2 , 199. 000 Northern. Mariana. Islands 477 km 2 , 78. 000 USVirgin. Islands 352 km 2 , 109. 000 American. Samoa 199 km 2 , 58. 000 Wake. Island 6, 5 km 2 , militarypersonnel Midway. Island 6, 2 km 2 , uninhabited Navassa. Island 5, 2 km 2 , uninhabited Jarvis. Island 4, 5 km 2 , uninhabited Johnston. Atoll 2, 8 km 2 , militarypersonnel Howland. Island 1, 6 km 2 , uninhabited Baker. Island 1, 4 km 2 , uninhabited Kingman. Reef 1 km 2 , uninhabited Bajo. Nuevo. Bankand. Serranilla. Bankareuninhabitedandcurrentlycontrolledby Colombia
 Australian Dependencies (6) Heard. Islandand. Mc. Donald. Island 412 km 2 , uninhabited Christmas. Island 135 km 2 , 396 persons Norfolk 34, 6 km 2 , 2. 000 Cocos(Keeling)Islands 14 km 2 , 629 persons Ashmoreand. Cartier. Islands 5 km 2 , uninhabited Coral. Sea. Islands 3 km 2 , uninhabited
Australian Dependencies (6) Heard. Islandand. Mc. Donald. Island 412 km 2 , uninhabited Christmas. Island 135 km 2 , 396 persons Norfolk 34, 6 km 2 , 2. 000 Cocos(Keeling)Islands 14 km 2 , 629 persons Ashmoreand. Cartier. Islands 5 km 2 , uninhabited Coral. Sea. Islands 3 km 2 , uninhabited
 New Zealand Dependencies (3) Niue 260 km 2 , 2. 000 Cook. Islands 240 km 2 , 21. 200 Tokelau 10 km 2 , 1. 405 osób
New Zealand Dependencies (3) Niue 260 km 2 , 2. 000 Cook. Islands 240 km 2 , 21. 200 Tokelau 10 km 2 , 1. 405 osób
 Norwegian Dependencies (3) Svalbard(Spitsbergen) 62. 049 km 2 , 2. 756 Jan. Mayen 373 km 2 , uninhabited Bouvet. Island 58, 5 km 2 , uninhabited
Norwegian Dependencies (3) Svalbard(Spitsbergen) 62. 049 km 2 , 2. 756 Jan. Mayen 373 km 2 , uninhabited Bouvet. Island 58, 5 km 2 , uninhabited
 Danish Dependencies (2) • Greenland 2. 166. 086 km 2 , 56. 384 • Faroe. Islands 1. 399 km 2 , 46.
Danish Dependencies (2) • Greenland 2. 166. 086 km 2 , 56. 384 • Faroe. Islands 1. 399 km 2 , 46.
 The Netherlands Dependencies (3) The. Nederlands. Antilles 960 km 2 , 218. 000 Aruba 193 km 2 , 71. 000 Followingthedissolutionofthenetherlands. Antillesin. October 2010, Bonaire, Sabaand. Sint. Eustatiusbecamelegallyintegratedwiththe Netherlands. Curaçaoand. Sint. Maartenbecameseparateddependencies
The Netherlands Dependencies (3) The. Nederlands. Antilles 960 km 2 , 218. 000 Aruba 193 km 2 , 71. 000 Followingthedissolutionofthenetherlands. Antillesin. October 2010, Bonaire, Sabaand. Sint. Eustatiusbecamelegallyintegratedwiththe Netherlands. Curaçaoand. Sint. Maartenbecameseparateddependencies
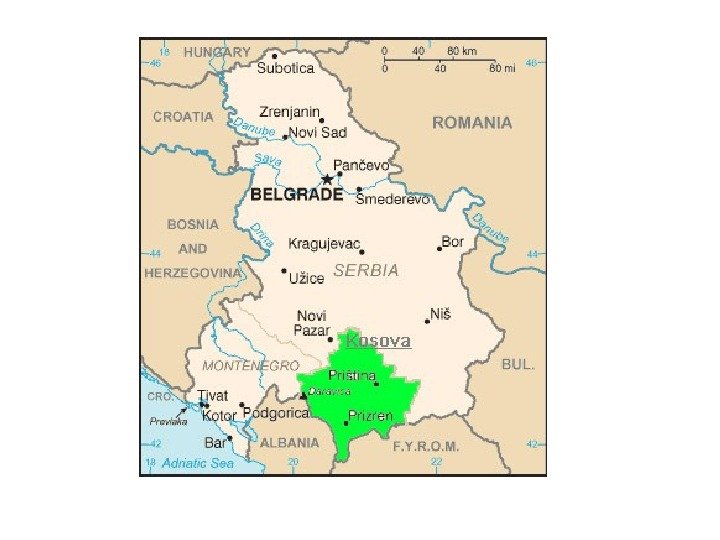
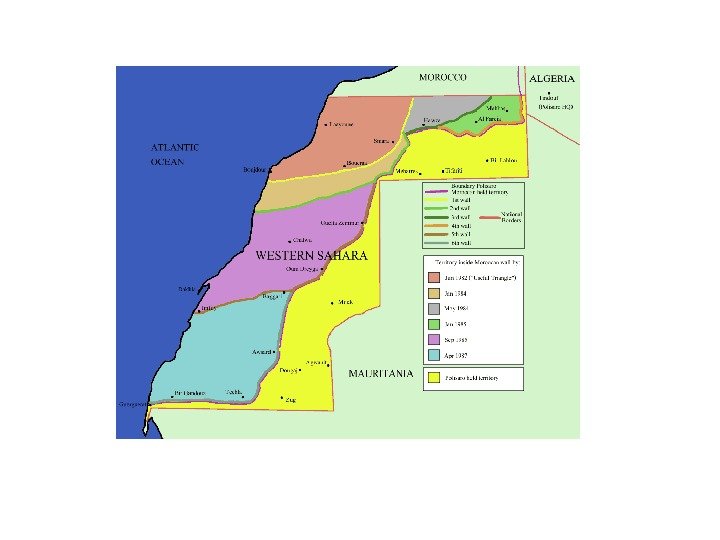
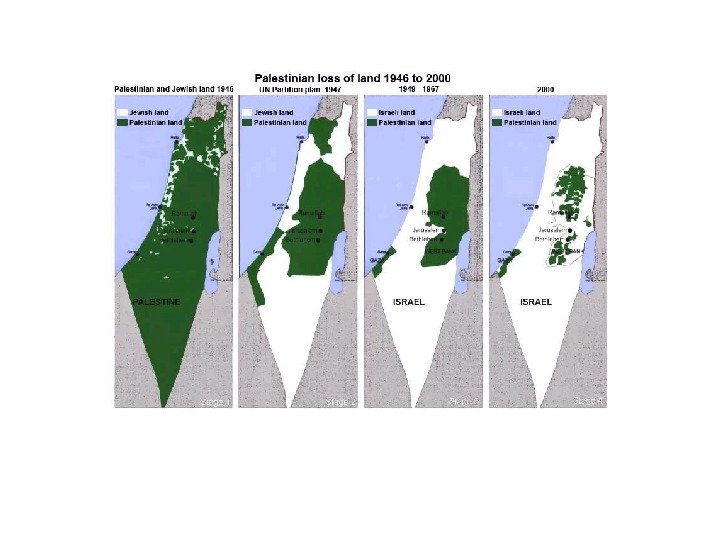
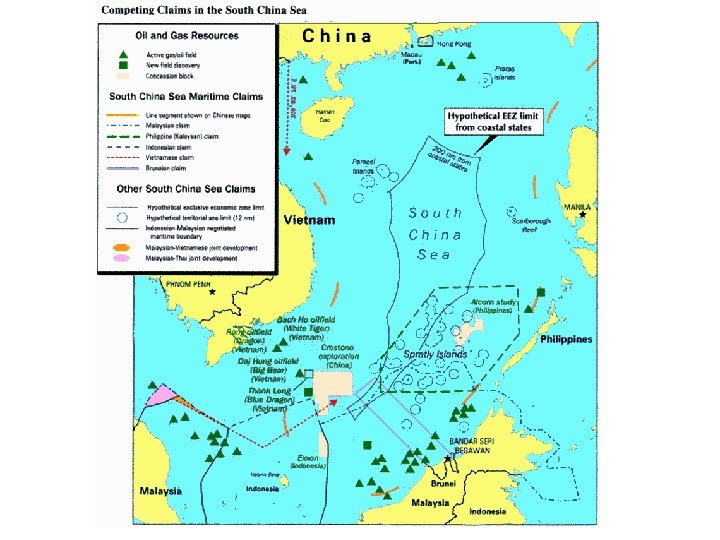
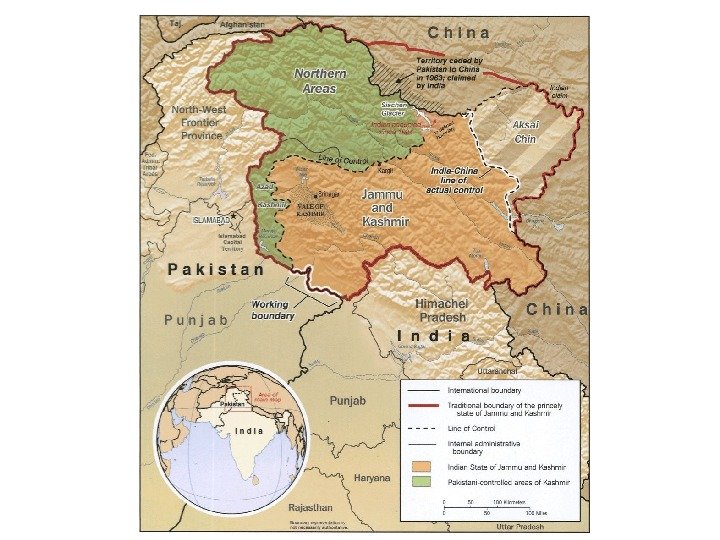
 Some of Disputed Territories Kosova Antarctis Western. Sahara Gaza. Stripandthe. West. Bank Paracel. Islands Spratly. Islands Kashmir
Some of Disputed Territories Kosova Antarctis Western. Sahara Gaza. Stripandthe. West. Bank Paracel. Islands Spratly. Islands Kashmir








