5860df5fe9b41d1daecdcebb9965eb87.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Polish pharmaceutical market in accession year Negotiations on accession to the European Union related to pharmaceutical sector 1999 – 2003 (case of Poland with some informations on other countries positions) Chapter 1 – Free Movement of Goods Chapter 5 – Company Law Cezary Sledziewski Polish Union of Employers in Pharmaceutical Industry Ankara, 2 nd June 2005
Polish pharmaceutical market in accession year Negotiations on accession to the European Union related to pharmaceutical sector 1999 – 2003 (case of Poland with some informations on other countries positions) Chapter 1 – Free Movement of Goods Chapter 5 – Company Law Cezary Sledziewski Polish Union of Employers in Pharmaceutical Industry Ankara, 2 nd June 2005
 Poland 2004 Market, Reimbursement and Pricing System n Law of 27 August 2004 on public health system n Law of 5 July 2001 on prices 2
Poland 2004 Market, Reimbursement and Pricing System n Law of 27 August 2004 on public health system n Law of 5 July 2001 on prices 2
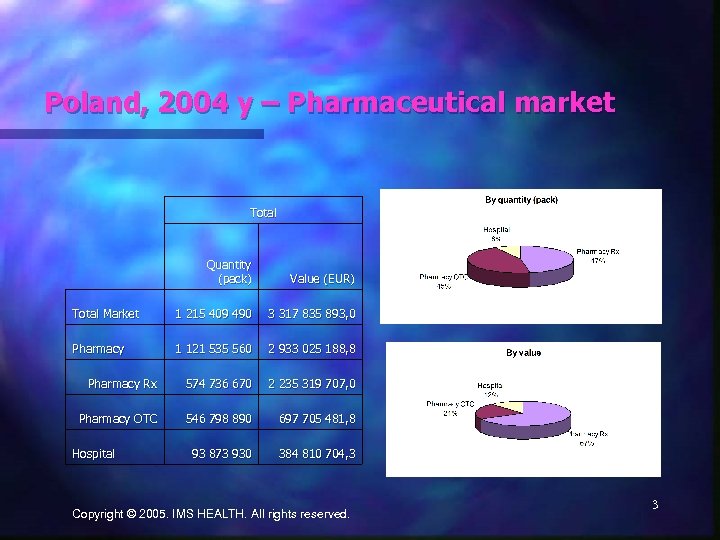 Poland, 2004 y – Pharmaceutical market Total Quantity (pack) Value (EUR) Total Market 1 215 409 490 3 317 835 893, 0 Pharmacy 1 121 535 560 2 933 025 188, 8 Pharmacy Rx 574 736 670 2 235 319 707, 0 Pharmacy OTC 546 798 890 697 705 481, 8 93 873 930 384 810 704, 3 Hospital Copyright © 2005. IMS HEALTH. All rights reserved. 3
Poland, 2004 y – Pharmaceutical market Total Quantity (pack) Value (EUR) Total Market 1 215 409 490 3 317 835 893, 0 Pharmacy 1 121 535 560 2 933 025 188, 8 Pharmacy Rx 574 736 670 2 235 319 707, 0 Pharmacy OTC 546 798 890 697 705 481, 8 93 873 930 384 810 704, 3 Hospital Copyright © 2005. IMS HEALTH. All rights reserved. 3
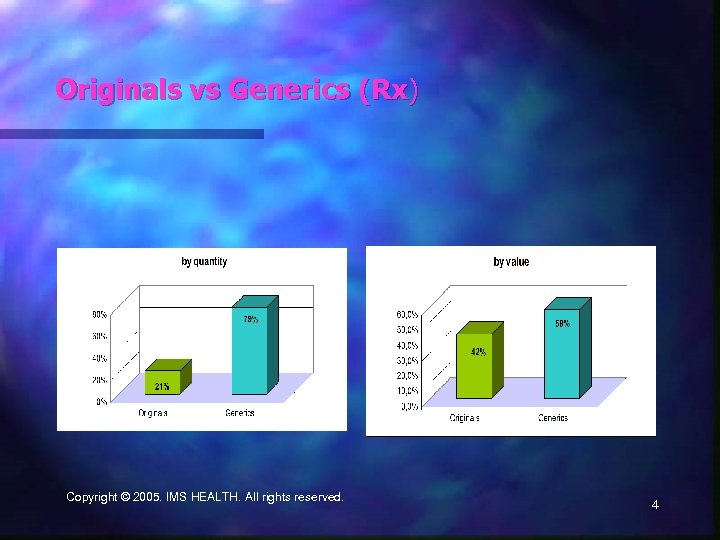 Originals vs Generics (Rx) Copyright © 2005. IMS HEALTH. All rights reserved. 4
Originals vs Generics (Rx) Copyright © 2005. IMS HEALTH. All rights reserved. 4
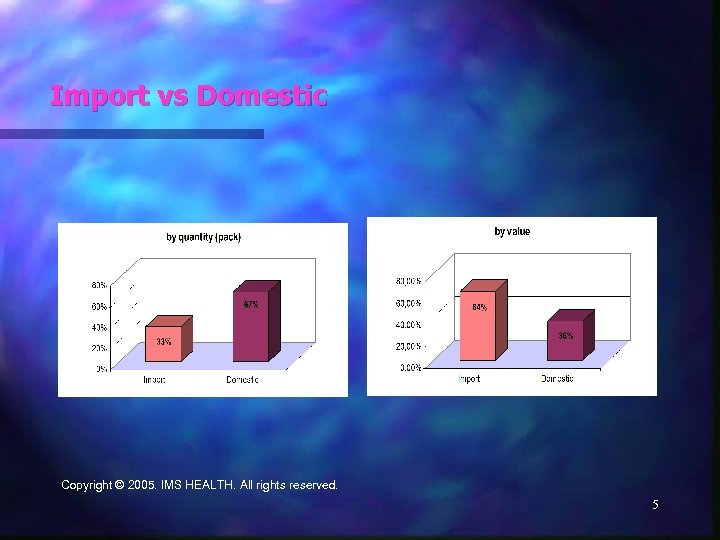 Import vs Domestic Copyright © 2005. IMS HEALTH. All rights reserved. 5
Import vs Domestic Copyright © 2005. IMS HEALTH. All rights reserved. 5
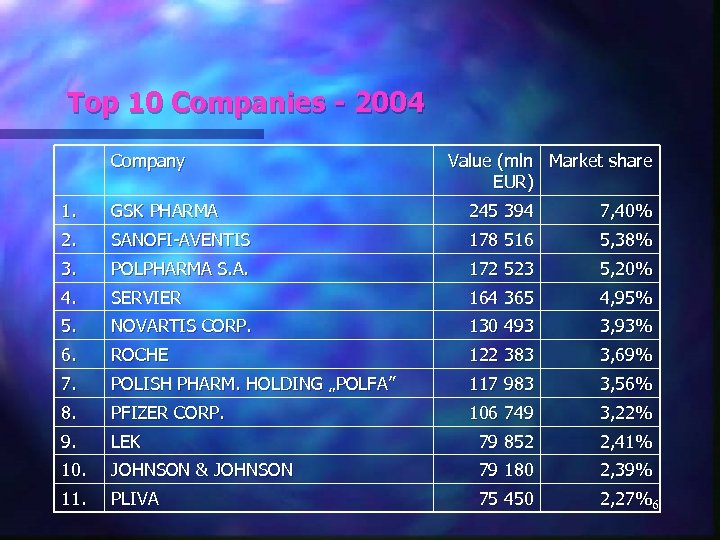 Top 10 Companies - 2004 Company Value (mln Market share EUR) 1. GSK PHARMA 245 394 7, 40% 2. SANOFI-AVENTIS 178 516 5, 38% 3. POLPHARMA S. A. 172 523 5, 20% 4. SERVIER 164 365 4, 95% 5. NOVARTIS CORP. 130 493 3, 93% 6. ROCHE 122 383 3, 69% 7. POLISH PHARM. HOLDING „POLFA” 117 983 3, 56% 8. PFIZER CORP. 106 749 3, 22% 9. LEK 79 852 2, 41% 10. JOHNSON & JOHNSON 79 180 2, 39% 11. PLIVA 75 450 2, 27%6
Top 10 Companies - 2004 Company Value (mln Market share EUR) 1. GSK PHARMA 245 394 7, 40% 2. SANOFI-AVENTIS 178 516 5, 38% 3. POLPHARMA S. A. 172 523 5, 20% 4. SERVIER 164 365 4, 95% 5. NOVARTIS CORP. 130 493 3, 93% 6. ROCHE 122 383 3, 69% 7. POLISH PHARM. HOLDING „POLFA” 117 983 3, 56% 8. PFIZER CORP. 106 749 3, 22% 9. LEK 79 852 2, 41% 10. JOHNSON & JOHNSON 79 180 2, 39% 11. PLIVA 75 450 2, 27%6
 What is necessary to apply for generics reimbursement status? n Marketing authorisation (also possible during validity of patent /SPC owing to „Bolar” exemption) n Brand name is allowed, however INN must be part of the product name n The generic Sm. PC should be identical to the originator to gain substitution or interchangeably status 7
What is necessary to apply for generics reimbursement status? n Marketing authorisation (also possible during validity of patent /SPC owing to „Bolar” exemption) n Brand name is allowed, however INN must be part of the product name n The generic Sm. PC should be identical to the originator to gain substitution or interchangeably status 7
 Positive lists by decision of Minister of Health (reimbursement lists should be revised twice a year) Essential drug lists n flat-rate (ca 0, 7 € per pack) n 2. Supplementary lists (partially reimbursed) n 30% patient co-payment n 50% patient co-payment n 3. Chronic diseases lists n free of charge n Flat-rate (ca 0, 7 € per pack) n 30% patient co-payment n 50% patient co-payment n 8
Positive lists by decision of Minister of Health (reimbursement lists should be revised twice a year) Essential drug lists n flat-rate (ca 0, 7 € per pack) n 2. Supplementary lists (partially reimbursed) n 30% patient co-payment n 50% patient co-payment n 3. Chronic diseases lists n free of charge n Flat-rate (ca 0, 7 € per pack) n 30% patient co-payment n 50% patient co-payment n 8
 Reference price system fixed on the lowest medicine price (understood as price limit paid by National Health Found) n The same active substance n Group of medicines having similar therapeutica mechanism. Criteria to qualify: n the same terapeutic indication, n similar efficacy n the same mechanism n the same adverse reaction n the same way administration n 9
Reference price system fixed on the lowest medicine price (understood as price limit paid by National Health Found) n The same active substance n Group of medicines having similar therapeutica mechanism. Criteria to qualify: n the same terapeutic indication, n similar efficacy n the same mechanism n the same adverse reaction n the same way administration n 9
 Condition set-up by Minister of Health 1. To stay on reimbursement list: - 2003 list – max 50% difference of the price, possible in relation to the reference price 2. To enter with new brand the reimbursement list – max 20% difference, possible in relation to the reference price (lowest generic price). 10
Condition set-up by Minister of Health 1. To stay on reimbursement list: - 2003 list – max 50% difference of the price, possible in relation to the reference price 2. To enter with new brand the reimbursement list – max 20% difference, possible in relation to the reference price (lowest generic price). 10
 Pricing system Prices of manufacturer are set up by Minister of Health on the basis of proposals submitted by companies taking into consideration the following elements: n Price level in other countries of similar GDP n Competitiveness of price n Cost of treatment n Effectiveness n Cost of production n Importance of drug on epidemiological diseases n Wholesaler margin fixed – 8, 91% n Pharmacy margin degressive n Price up to ca 0, 75€ – 40% 11 ca 20€ – 12 zł. n
Pricing system Prices of manufacturer are set up by Minister of Health on the basis of proposals submitted by companies taking into consideration the following elements: n Price level in other countries of similar GDP n Competitiveness of price n Cost of treatment n Effectiveness n Cost of production n Importance of drug on epidemiological diseases n Wholesaler margin fixed – 8, 91% n Pharmacy margin degressive n Price up to ca 0, 75€ – 40% 11 ca 20€ – 12 zł. n
 Generic prescribing and substitution Generic prescribing – by brand name: • No restriction or incentive for doctors • Doctors are permitted to prevent generic substitution by marking prescription with „NZ” (do not substitute). Pharmacy substitution: 1. Product (brand name) on reimbursement list: Pharmacies should offer cheapest drug, provided prescription without doctor reservation (NZ). 2. Brand name not included into reimbursement lists. Pharmacy substitution is possible, but on the level of reference price (or lower). 12
Generic prescribing and substitution Generic prescribing – by brand name: • No restriction or incentive for doctors • Doctors are permitted to prevent generic substitution by marking prescription with „NZ” (do not substitute). Pharmacy substitution: 1. Product (brand name) on reimbursement list: Pharmacies should offer cheapest drug, provided prescription without doctor reservation (NZ). 2. Brand name not included into reimbursement lists. Pharmacy substitution is possible, but on the level of reference price (or lower). 12
 Chapter 1 – Free Movement of Goods § Up-date of MA of old dossiers § Application of Centralized Procedure and MRP § Data exclusivity application 13
Chapter 1 – Free Movement of Goods § Up-date of MA of old dossiers § Application of Centralized Procedure and MRP § Data exclusivity application 13
 Chapter 5 – Company Law (Industrial and Intellectural Property Rights) n Bolar Clause (testing and registration during patent validity) n Parallel trade n SPC – Supplementary Protection Certificate (Regulation 1768/92/EC) 14
Chapter 5 – Company Law (Industrial and Intellectural Property Rights) n Bolar Clause (testing and registration during patent validity) n Parallel trade n SPC – Supplementary Protection Certificate (Regulation 1768/92/EC) 14
 Update of documentation for existing products 5 Countries (Cz, Hu, LV, SK, EST) – date of accession n Transitional period for: harmonization of MA to acquis n communautaire: q Cyprus - 31 December 2005 q Lithuania and Malta – 31 December 2006 q Slovenia - 31 December 2007 q Poland - 31 December 2008 n Centralized Procedure (CP) & Mutual Recognition Procedure (MRP) to be adopted in Poland on the date of accession. 15
Update of documentation for existing products 5 Countries (Cz, Hu, LV, SK, EST) – date of accession n Transitional period for: harmonization of MA to acquis n communautaire: q Cyprus - 31 December 2005 q Lithuania and Malta – 31 December 2006 q Slovenia - 31 December 2007 q Poland - 31 December 2008 n Centralized Procedure (CP) & Mutual Recognition Procedure (MRP) to be adopted in Poland on the date of accession. 15
 Data Exclusivity (1) 1. Situation in EU during negotiations: n n 6/10 year for national procedure/ MRP n 6 years (AT, DK, FI, SP, IRL, PT, EL) plus NO, IS n 10 years (BE, LU, FR, IT, DE, NL, SE, UK) 10 years for CP 16
Data Exclusivity (1) 1. Situation in EU during negotiations: n n 6/10 year for national procedure/ MRP n 6 years (AT, DK, FI, SP, IRL, PT, EL) plus NO, IS n 10 years (BE, LU, FR, IT, DE, NL, SE, UK) 10 years for CP 16
 Data Exclusivity (2) Introduction of Data Exclusivity in ACs 1997 Czech Republic 2000 Slovakia 2001 Estonia, Latvia, Slovenia 1 Jan 2003 (only for applications submited after 12. 04. 01) On accession 1 May 2004, hawever starting 2002 soft Data Exclusivity were introduced – 3 years calculating from first registration in the world (with no practical value). Hungary Poland 17
Data Exclusivity (2) Introduction of Data Exclusivity in ACs 1997 Czech Republic 2000 Slovakia 2001 Estonia, Latvia, Slovenia 1 Jan 2003 (only for applications submited after 12. 04. 01) On accession 1 May 2004, hawever starting 2002 soft Data Exclusivity were introduced – 3 years calculating from first registration in the world (with no practical value). Hungary Poland 17
 Data Exclusivity (3) Revision of legislation - 2004 n New rules n 8+2 (+1) for all procedures and all countries n 8 years data exclusivity but 10 years market exclusivity (filing after 8 years but marketing after 10 years) n Additional 1 year (+1) in case of new idication registered during first 8 years (significant clinical benefit in comparison with existing therapies)- no clear criteria 18
Data Exclusivity (3) Revision of legislation - 2004 n New rules n 8+2 (+1) for all procedures and all countries n 8 years data exclusivity but 10 years market exclusivity (filing after 8 years but marketing after 10 years) n Additional 1 year (+1) in case of new idication registered during first 8 years (significant clinical benefit in comparison with existing therapies)- no clear criteria 18
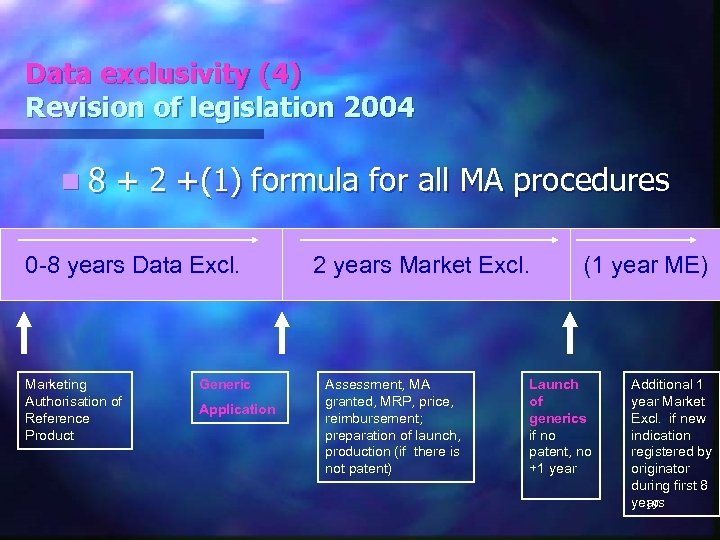 Data exclusivity (4) Revision of legislation 2004 n 8 + 2 +(1) formula for all MA procedures 0 -8 years Data Excl. Marketing Authorisation of Reference Product Generic Application 2 years Market Excl. Assessment, MA granted, MRP, price, reimbursement; preparation of launch, production (if there is not patent) (1 year ME) Launch of generics if no patent, no +1 year Additional 1 year Market Excl. if new indication registered by originator during first 8 years 19
Data exclusivity (4) Revision of legislation 2004 n 8 + 2 +(1) formula for all MA procedures 0 -8 years Data Excl. Marketing Authorisation of Reference Product Generic Application 2 years Market Excl. Assessment, MA granted, MRP, price, reimbursement; preparation of launch, production (if there is not patent) (1 year ME) Launch of generics if no patent, no +1 year Additional 1 year Market Excl. if new indication registered by originator during first 8 years 19
 Data Exclusivity (5) Acceding Countries position during legislation process n Extension of DE - change of the negotiation position (acquis communautaire) n “Milan Declaration” of 10 Health Ministers Petition of Observers to EP (94 Observers from 9 countries) n 20
Data Exclusivity (5) Acceding Countries position during legislation process n Extension of DE - change of the negotiation position (acquis communautaire) n “Milan Declaration” of 10 Health Ministers Petition of Observers to EP (94 Observers from 9 countries) n 20
 Data Exclusivity (6) Prospective Implementation of DE n New rules 8+2+(1) applicable only for reference products filed after date of transposition of new legislation (end of 2005) n significant delay of real impact of new DE expected in 2013 n Advantage: n For 6 -year all Acceding Countries and DE Countries (AT, DK, FI, SP, IRL, PT, EL) n Disadvantage: n For 10 -year DE Countries (BE, LU, FR, IT, DE, NL, SE, UK) 21
Data Exclusivity (6) Prospective Implementation of DE n New rules 8+2+(1) applicable only for reference products filed after date of transposition of new legislation (end of 2005) n significant delay of real impact of new DE expected in 2013 n Advantage: n For 6 -year all Acceding Countries and DE Countries (AT, DK, FI, SP, IRL, PT, EL) n Disadvantage: n For 10 -year DE Countries (BE, LU, FR, IT, DE, NL, SE, UK) 21
 Data Exclusivity (7) Prospective implementation of DE Article 1 a (new) (amending Directive) The periods of protection foreseen in Article 1, point 8, that modifies Article 10 (1), do not apply to reference medicinal products for which an application for authorisation has been submitted before the date of transposition referred to in Article 2 (1). n Article 88 a (new) (amending Regulation) The periods of protection foreseen in Articles 14 (11) and 39 (10) do not apply to reference medicinal products for which an application for authorisation has been submitted before the date referred to in Article 89 (2) n Request for transitional period: Poland, Hungary, Slovakia, Slovenia, Malta. 22
Data Exclusivity (7) Prospective implementation of DE Article 1 a (new) (amending Directive) The periods of protection foreseen in Article 1, point 8, that modifies Article 10 (1), do not apply to reference medicinal products for which an application for authorisation has been submitted before the date of transposition referred to in Article 2 (1). n Article 88 a (new) (amending Regulation) The periods of protection foreseen in Articles 14 (11) and 39 (10) do not apply to reference medicinal products for which an application for authorisation has been submitted before the date referred to in Article 89 (2) n Request for transitional period: Poland, Hungary, Slovakia, Slovenia, Malta. 22
 Chapter 5 Bolar clause introduced in Poland 2001 (earlier in Hungary) - Poland agreed to adapt regulation according to WTO rules and EU acquis after accesion. n Parallel trade – specific mechanizm introduced in AT to prevent re-export of patented medicinal products. Specific mechanism- scope of application – exhaustion of patent rights - Should apply to only to those products which could not benefit from product patent protection but still benefiting from patent in some EU States. n Supplementary Protection Certificate (SPC) n 23
Chapter 5 Bolar clause introduced in Poland 2001 (earlier in Hungary) - Poland agreed to adapt regulation according to WTO rules and EU acquis after accesion. n Parallel trade – specific mechanizm introduced in AT to prevent re-export of patented medicinal products. Specific mechanism- scope of application – exhaustion of patent rights - Should apply to only to those products which could not benefit from product patent protection but still benefiting from patent in some EU States. n Supplementary Protection Certificate (SPC) n 23
 SPC in Accession Treaty n Common conditions of transition regulation: n valid basic patent, n link to the moment of first Marketing Authorisation (MA) in particular country, except PL, HU, n no territory mentioned PL, HU, n retrospective application- in most cases connected with different time for filing – latest 6 months after Accession. 24
SPC in Accession Treaty n Common conditions of transition regulation: n valid basic patent, n link to the moment of first Marketing Authorisation (MA) in particular country, except PL, HU, n no territory mentioned PL, HU, n retrospective application- in most cases connected with different time for filing – latest 6 months after Accession. 24
 SPC (AT cont. ) „Any medicinal product protected by a valid basic patent and for which the first authorisation to place it on the market as a medicinal product was obtained* after 1 January 2000 may be granted a certificate in Poland, provided that the application for a certificate is lodged within six months starting no later than the date of accession; ” *Remark: first wording „was obtained in Poland after January 2000” 25
SPC (AT cont. ) „Any medicinal product protected by a valid basic patent and for which the first authorisation to place it on the market as a medicinal product was obtained* after 1 January 2000 may be granted a certificate in Poland, provided that the application for a certificate is lodged within six months starting no later than the date of accession; ” *Remark: first wording „was obtained in Poland after January 2000” 25
 Retrospective implementation of SPC n Products with the first MA granted: q q q prior to date of Accession: Cyprus, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Slovenia. Czech Rep - after 10 th of November 1999 Slovakia - after 1 st of January 2000 in Slovakia Hungary – after 1 st of January 2000 Poland - after 1 st of January 2000 26
Retrospective implementation of SPC n Products with the first MA granted: q q q prior to date of Accession: Cyprus, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Slovenia. Czech Rep - after 10 th of November 1999 Slovakia - after 1 st of January 2000 in Slovakia Hungary – after 1 st of January 2000 Poland - after 1 st of January 2000 26
 Final remarks: n Have benefited from EGA - knowledge & exchange informations in the frame of EGA Accession Committee, n Be precise in wording your preliminary agreement. 27
Final remarks: n Have benefited from EGA - knowledge & exchange informations in the frame of EGA Accession Committee, n Be precise in wording your preliminary agreement. 27


