4a8d78ffcf51d4d5b4b4407e5f17c1ca.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
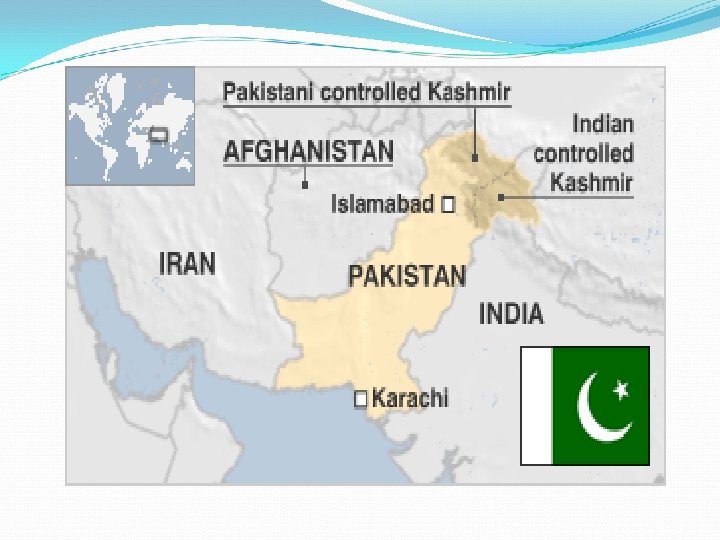
 Polio e Pakistan Dott. L. E. Pacifici MD Ph. D Responsabile CRI Cooperazione Sanitaria Internazionale
Polio e Pakistan Dott. L. E. Pacifici MD Ph. D Responsabile CRI Cooperazione Sanitaria Internazionale
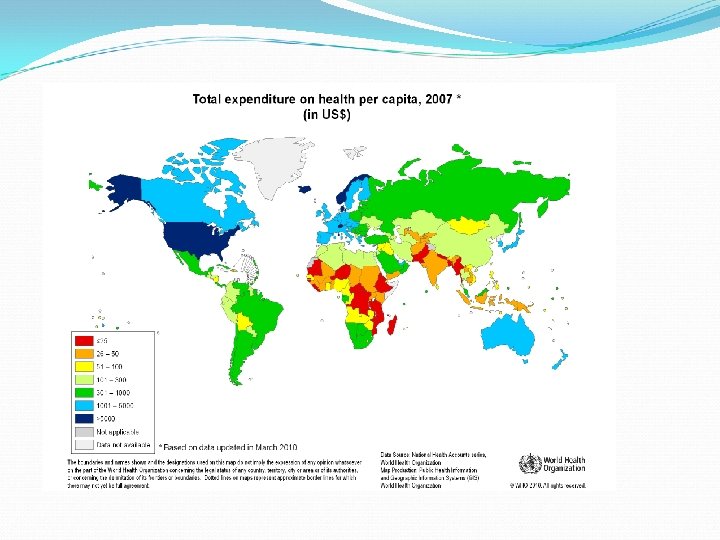
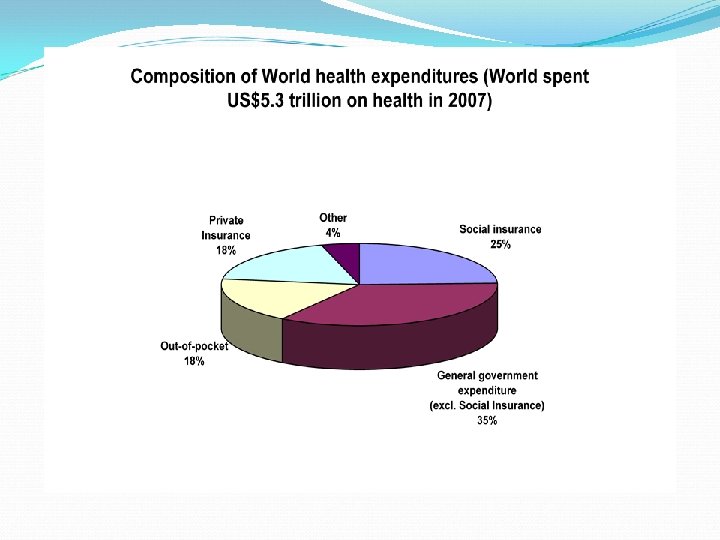
 Poor maternal and child health profile: • High maternal mortality ratio (276/100, 000 live births), low antenatal care coverage (61%), frequent complications of pregnancy and child birth. • High under five, infant and neonatal mortality (94, 78 and 54/1000 live births resp. ). • Malnutrition is an underlying cause in more than 50% with one-fifth of newborns with low birth weight and 38% of under-five children are underweight, aggravated by low exclusive breast feeding rate for under 6 months (37% of children) (1) and low vaccination coverage 47% Double burden of disease: • Pakistan is one of the 4 remaining countries with endemic polio and the sixth highest with burden of TB The burden of disease (Bo. D) is heavily dominated bycommunicable diseases, reproductive health problems and malnutrition which together account for about 50% of the total. • Added to this is the burden of non-communicable disease (cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancers, injuries and neuro-psychiatric disorders). This double burden of disease is a major challenge in the health sector of Pakistan. • Pakistan is the second country (after India) in South East Asia that is progressing towards a concentrated HIV/AIDS epidemic stage amongst groups like Injecting Drug Users (IDU’s) and Male Sex Workers (MSWs)(1). Poor access to water and sanitation: Almost half of the population in Pakistan, especially • in Rural areas has no access to safe drinking water while 22 percent households do not have any toilet facility. Emergencies: Pakistan has suffered several disasters in the past 6 years, from the earthquake in 2005 to the devastating and massive floods in 2010, this has affected the MDGs achievement setting back the health and development in Pakistan. • Other health determinants: Illiteracy, unemployment, gender inequality, social exclusion, rapid urbanization, environmental degradation, natural disasters • http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
Poor maternal and child health profile: • High maternal mortality ratio (276/100, 000 live births), low antenatal care coverage (61%), frequent complications of pregnancy and child birth. • High under five, infant and neonatal mortality (94, 78 and 54/1000 live births resp. ). • Malnutrition is an underlying cause in more than 50% with one-fifth of newborns with low birth weight and 38% of under-five children are underweight, aggravated by low exclusive breast feeding rate for under 6 months (37% of children) (1) and low vaccination coverage 47% Double burden of disease: • Pakistan is one of the 4 remaining countries with endemic polio and the sixth highest with burden of TB The burden of disease (Bo. D) is heavily dominated bycommunicable diseases, reproductive health problems and malnutrition which together account for about 50% of the total. • Added to this is the burden of non-communicable disease (cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancers, injuries and neuro-psychiatric disorders). This double burden of disease is a major challenge in the health sector of Pakistan. • Pakistan is the second country (after India) in South East Asia that is progressing towards a concentrated HIV/AIDS epidemic stage amongst groups like Injecting Drug Users (IDU’s) and Male Sex Workers (MSWs)(1). Poor access to water and sanitation: Almost half of the population in Pakistan, especially • in Rural areas has no access to safe drinking water while 22 percent households do not have any toilet facility. Emergencies: Pakistan has suffered several disasters in the past 6 years, from the earthquake in 2005 to the devastating and massive floods in 2010, this has affected the MDGs achievement setting back the health and development in Pakistan. • Other health determinants: Illiteracy, unemployment, gender inequality, social exclusion, rapid urbanization, environmental degradation, natural disasters • http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
 Opportunities Health, education and poverty alleviation are government priorities. • The new National Health Policy (still draft stage) addresses all the key public health issues. • Devolution, its importance and implications in the current federal and provincial governments • The Polio Emergency plan launched and monitored by the President to ensure the eradication before the end of year • Prime minister’s initiative for prevention and control of Hepatitis • Resource mobilization and response to the floods which affected 78 districts of Pakistan, used to improve the health of the people in these areas • Use the humanitarian response, especially the early recovery period and resources to improve the health for future preparedness as well as sustainable development and hence improve health indicators http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
Opportunities Health, education and poverty alleviation are government priorities. • The new National Health Policy (still draft stage) addresses all the key public health issues. • Devolution, its importance and implications in the current federal and provincial governments • The Polio Emergency plan launched and monitored by the President to ensure the eradication before the end of year • Prime minister’s initiative for prevention and control of Hepatitis • Resource mobilization and response to the floods which affected 78 districts of Pakistan, used to improve the health of the people in these areas • Use the humanitarian response, especially the early recovery period and resources to improve the health for future preparedness as well as sustainable development and hence improve health indicators http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
 Challenges Low health expenditures and low public investment in the health sector; low focus on prevention; main expenditures for salaries and Inequity in allocation of resources • Low utilization rates in public system and inadequate institutional frameworks for outsourcing of services • Heavy reliance on private sector and insufficient regulation and certification systems. • Health referral pyramid not respected • Insufficient health district mapping and planning, Inadequately planned human resources for health • Transfer of critical responsibilities from federal to provincial level due to the devolution process (18 th Constitutional Amendment) • Recent and abrupt changes in the key decision makers within the Federal Ministry of Health. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
Challenges Low health expenditures and low public investment in the health sector; low focus on prevention; main expenditures for salaries and Inequity in allocation of resources • Low utilization rates in public system and inadequate institutional frameworks for outsourcing of services • Heavy reliance on private sector and insufficient regulation and certification systems. • Health referral pyramid not respected • Insufficient health district mapping and planning, Inadequately planned human resources for health • Transfer of critical responsibilities from federal to provincial level due to the devolution process (18 th Constitutional Amendment) • Recent and abrupt changes in the key decision makers within the Federal Ministry of Health. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
 WHO's strategic agenda in Pakistan has been developed after an exhaustive situation analysis of the health sector and through an intensive process of consultation with federal, provincial and district levels of the Mo. H/Do. H, with donors and UN agencies. The strategic directions aim to support the Government in providing adequate health coverage to all people, the ongoing devolution process and the commitment to achievement of the MDGs. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
WHO's strategic agenda in Pakistan has been developed after an exhaustive situation analysis of the health sector and through an intensive process of consultation with federal, provincial and district levels of the Mo. H/Do. H, with donors and UN agencies. The strategic directions aim to support the Government in providing adequate health coverage to all people, the ongoing devolution process and the commitment to achievement of the MDGs. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
 • Communicable disease control. Disease surveillance and Early warning system establishment for the detection and timely control of communicablediseases including Polio, tuberculosis, malaria, HIV/AIDS, leishmaniasis, hepatitis, AWD, ARI, Malaria, Dengue fever, CCHF among other diseases of public health importance. Support the Mo. H in improving immunization • Women and children's health. Supporting the MNCH program at national and provincial level through technical assistance, training and placement of skilled personnel, promoting safe motherhood and pregnancy, family planning, prevention and control of sexually transmitted infections, reducing neonatal, peri-natal mortality. Prevention and Control of sexual and gender based violence. Improving child and Adolescent health through technical assistance, capacity building, dealing with underlying causes such as water, sanitation, malnutrition and education/awareness. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
• Communicable disease control. Disease surveillance and Early warning system establishment for the detection and timely control of communicablediseases including Polio, tuberculosis, malaria, HIV/AIDS, leishmaniasis, hepatitis, AWD, ARI, Malaria, Dengue fever, CCHF among other diseases of public health importance. Support the Mo. H in improving immunization • Women and children's health. Supporting the MNCH program at national and provincial level through technical assistance, training and placement of skilled personnel, promoting safe motherhood and pregnancy, family planning, prevention and control of sexually transmitted infections, reducing neonatal, peri-natal mortality. Prevention and Control of sexual and gender based violence. Improving child and Adolescent health through technical assistance, capacity building, dealing with underlying causes such as water, sanitation, malnutrition and education/awareness. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccsbrief_pak_en. pdf
 Key players Health is a provincial matter, the federal government has the overall responsibility of providing leadership and direction to stakeholders. The policies are formalized at federal level and implemented by provinces. The private sector provides a major chunk of curative care whereas the government provides a major share of preventive care, mainly through its vertical programmes. The devolution process has resulted in district government becoming a key player in provision of both preventive and curative health services. In the context of the health sector, the distribution of authority (and responsibility) between the district Nazim, the district coordination officer and the executive district officer for health (especially the latter two) has yet to be clearly delineated. Civil society organizations and philanthropy play a role in service delivery at micro level. Lately, some NGOs have been involved in policy formation as well. Donors and international development agencies have also been important stakeholders in the health sector in Pakistan, especially in recent years. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccs_pak_en. pdf
Key players Health is a provincial matter, the federal government has the overall responsibility of providing leadership and direction to stakeholders. The policies are formalized at federal level and implemented by provinces. The private sector provides a major chunk of curative care whereas the government provides a major share of preventive care, mainly through its vertical programmes. The devolution process has resulted in district government becoming a key player in provision of both preventive and curative health services. In the context of the health sector, the distribution of authority (and responsibility) between the district Nazim, the district coordination officer and the executive district officer for health (especially the latter two) has yet to be clearly delineated. Civil society organizations and philanthropy play a role in service delivery at micro level. Lately, some NGOs have been involved in policy formation as well. Donors and international development agencies have also been important stakeholders in the health sector in Pakistan, especially in recent years. http: //www. who. int/countryfocus/cooperation_strategy/ccs_pak_en. pdf
 La poliomielite nel mondo La poliomelite colpisce soprattutto i bambini sotto i cinque anni di età e 1 infezione su 200 provoca una paralisi flaccida irreversibile (di solito delle gambe). Tra coloro che rimangono paralizzati, il 5 -10% muore a causa della paralisi dei muscoli respiratori. Fino a quando anche un solo bambino verrà infettato dal virus della poliomielite, tutti i bambini del mondo sono a rischio di contrarre la malattia. I poliovirus, infatti, sono facilmente importabili da un Paese a un altro e si diffondono rapidamente in popolazioni non immunizzate. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio/epid. asp
La poliomielite nel mondo La poliomelite colpisce soprattutto i bambini sotto i cinque anni di età e 1 infezione su 200 provoca una paralisi flaccida irreversibile (di solito delle gambe). Tra coloro che rimangono paralizzati, il 5 -10% muore a causa della paralisi dei muscoli respiratori. Fino a quando anche un solo bambino verrà infettato dal virus della poliomielite, tutti i bambini del mondo sono a rischio di contrarre la malattia. I poliovirus, infatti, sono facilmente importabili da un Paese a un altro e si diffondono rapidamente in popolazioni non immunizzate. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio/epid. asp
 Dagli anni settanta in poi, il programma di vaccinazione è stato esteso in tutto il mondo con l’obiettivo di controllare la diffusione della polio a livello globale. Oggi la polio è endemica solo in 4 Paesi: Afghanistan, India, Nigeria e Pakistan. L’Oms ha messo in campo numerose iniziative per combattere la malattia, con l’obiettivo di giungere alla sua completa eradicazione. Grazie alle campagne di vaccinazione di massa, il numero di casi di poliomielite negli ultimi anni si è drasticamente ridotto. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio/epid. asp
Dagli anni settanta in poi, il programma di vaccinazione è stato esteso in tutto il mondo con l’obiettivo di controllare la diffusione della polio a livello globale. Oggi la polio è endemica solo in 4 Paesi: Afghanistan, India, Nigeria e Pakistan. L’Oms ha messo in campo numerose iniziative per combattere la malattia, con l’obiettivo di giungere alla sua completa eradicazione. Grazie alle campagne di vaccinazione di massa, il numero di casi di poliomielite negli ultimi anni si è drasticamente ridotto. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio/epid. asp
 Il contagio avviene per via oro-fecale: attraverso l’ingestione di acqua o cibi contaminati tramite la saliva e le goccioline emesse con i colpi di tosse e gli starnuti da soggetti ammalati o portatori sani. Il poliovirus si moltiplica nella mucosa oro-faringea, nell’intestino e nei tessuti linfatici sottostanti e può diffondersi anche attraverso le feci, ben prima che i sintomi della malattia siano evidenti. L’uomo rappresenta l’unico serbatoio naturale del virus della poliomielite, che può colpire persone di tutte le età ma principalmente si manifesta nei bambini sotto i tre anni. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio/epid. asp
Il contagio avviene per via oro-fecale: attraverso l’ingestione di acqua o cibi contaminati tramite la saliva e le goccioline emesse con i colpi di tosse e gli starnuti da soggetti ammalati o portatori sani. Il poliovirus si moltiplica nella mucosa oro-faringea, nell’intestino e nei tessuti linfatici sottostanti e può diffondersi anche attraverso le feci, ben prima che i sintomi della malattia siano evidenti. L’uomo rappresenta l’unico serbatoio naturale del virus della poliomielite, che può colpire persone di tutte le età ma principalmente si manifesta nei bambini sotto i tre anni. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio/epid. asp
 Cure per la poliomielite ? NON ESISTONO ! Solo trattamenti sintomatici che possono solo in parte minimizzare gli effetti della malattia. L’unica strada per evitare potenziali conseguenze è la prevenzione tramite vaccinazione. Esistono due tipi di vaccini diversi: quello “inattivato” di Salk (IPV), da somministrare con iniezione intramuscolo, e quello “vivo attenuato” di Sabin (OPV), da somministrare per via orale. Il vaccino di Sabin, somministrato fino ad anni recenti anche in Italia, ha permesso di eradicare la poliomielite in Europa ed è raccomandato dall’Organizzazione mondiale della sanità nella sua campagna di eradicazione della malattia a livello mondiale. L’obiettivo dell’Oms è infatti quello di eliminare completamente la presenza della malattia, seguendo il successo ottenuto con il vaiolo nel 1980. In Italia, per decisione della Conferenza Stato Regioni nel 2002, dopo l’eradicazione completa della polio in Europa, l’unica forma di vaccino somministrato è quello inattivato. Presso il Ministero della salute viene mantenuta una scorta di vaccino orale attivo come misura precauzionale, in caso di emergenza e di importazione del virus. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio. asp
Cure per la poliomielite ? NON ESISTONO ! Solo trattamenti sintomatici che possono solo in parte minimizzare gli effetti della malattia. L’unica strada per evitare potenziali conseguenze è la prevenzione tramite vaccinazione. Esistono due tipi di vaccini diversi: quello “inattivato” di Salk (IPV), da somministrare con iniezione intramuscolo, e quello “vivo attenuato” di Sabin (OPV), da somministrare per via orale. Il vaccino di Sabin, somministrato fino ad anni recenti anche in Italia, ha permesso di eradicare la poliomielite in Europa ed è raccomandato dall’Organizzazione mondiale della sanità nella sua campagna di eradicazione della malattia a livello mondiale. L’obiettivo dell’Oms è infatti quello di eliminare completamente la presenza della malattia, seguendo il successo ottenuto con il vaiolo nel 1980. In Italia, per decisione della Conferenza Stato Regioni nel 2002, dopo l’eradicazione completa della polio in Europa, l’unica forma di vaccino somministrato è quello inattivato. Presso il Ministero della salute viene mantenuta una scorta di vaccino orale attivo come misura precauzionale, in caso di emergenza e di importazione del virus. http: //www. epicentro. iss. it/problemi/polio. asp
 http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/world-asia-20880948 Pakistan: Seven charity workers shot dead http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/world-asia 20785252 Pakistan polio campaign attacks 'horrific'
http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/world-asia-20880948 Pakistan: Seven charity workers shot dead http: //www. bbc. co. uk/news/world-asia 20785252 Pakistan polio campaign attacks 'horrific'



