3dad27e579f4aa80374cff327ca85c32.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Policy Driven Management for Distributed Systems Mi-Joung Choi mjchoi@postech. ac. kr DP&NM 1999. 4. 30 (1) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
Policy Driven Management Contents • Introduction – Definition, Architecture, Advantages • Policy Classification • Policy as Relationship Objects • Example Policy Objects – Access Rules, Domain Membership Policy, Security Administrator, Responsibility • Consideration Issues for policy • Conclusions • References 1999. 4. 30 (2) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.

Policy Driven Management Introduction (1) • Distributed System Management – monitoring the activity of a system – making management decision – performing control actions to modify the behavior of the system • Policy – a relationship between a domain of subjects (managers) and a domain of target managed objects – one aspect of information which influences the behavior of objects within the system • Policy Driven Management – perform management based on policy 1999. 4. 30 (3) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
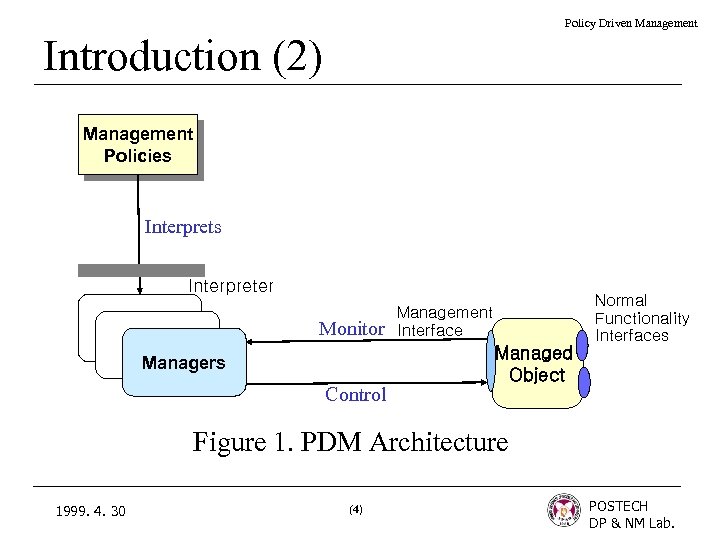
Policy Driven Management Introduction (2) Management Policies Interpreter Monitor Managers Control Normal Functionality Interfaces Management Interface Managed Object Figure 1. PDM Architecture 1999. 4. 30 (4) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
Policy Driven Management Introduction (3) • Advantages – facilitates the dynamic change of behavior of a distributed management system – permits the reuse of the managers in different environments 1999. 4. 30 (5) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
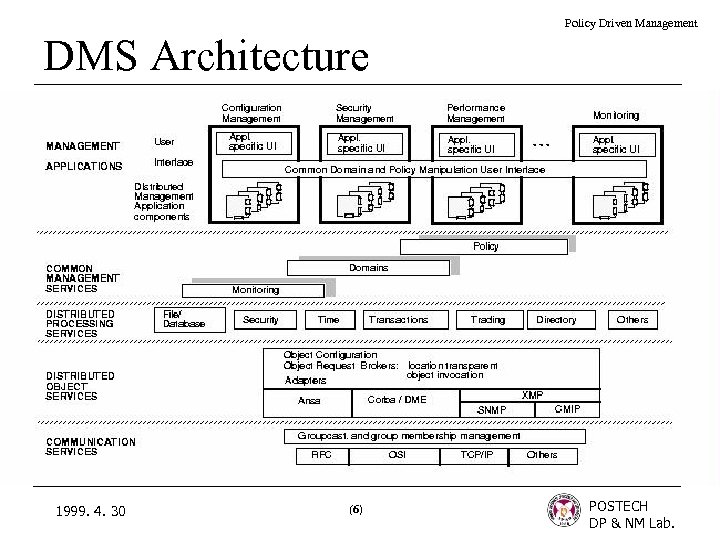
Policy Driven Management DMS Architecture 1999. 4. 30 (6) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.

Policy Driven Management Policy Classification (1) • Authorization policies – define what an manager is permitted or not permitted to do – the operations they are permitted to perform on managed objects – considered target based • Obligation Policies – define what a manager must or must not do – guide the decision making process – considered subject based 1999. 4. 30 (7) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
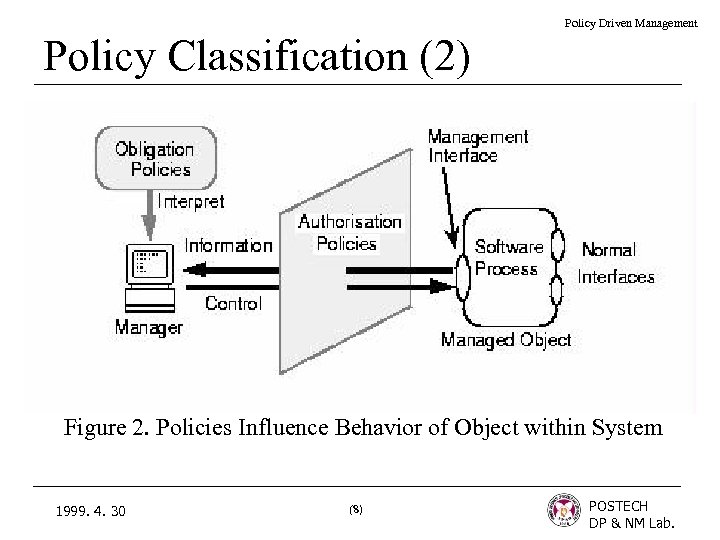
Policy Driven Management Policy Classification (2) Figure 2. Policies Influence Behavior of Object within System 1999. 4. 30 (8) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
Policy Driven Management Policy Classification (3) • Positive Policy : permitting or must • Negative Policy : prohibiting or must not • Activity Based : the simplest policies • State Based : include a predicate based on object state (ex) - John is permitted to read file F 1(authorization & positive & activity based) – John is prohibited to read personnel records where employment grade > 10 (authorization & negative & state based) – Manager must perform reset on links with error count > 50 (obligation & positive & state based) – The standby manager must not perform any control actions (obligation & negative & activity based) 1999. 4. 30 (9) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
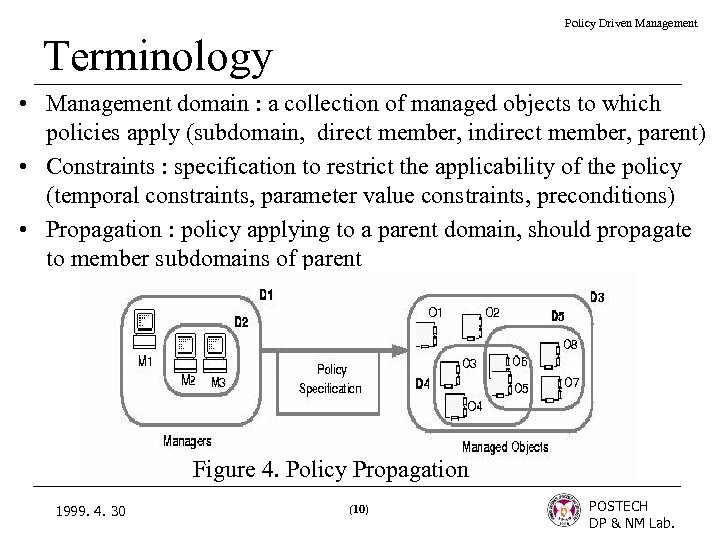
Policy Driven Management Terminology • Management domain : a collection of managed objects to which policies apply (subdomain, direct member, indirect member, parent) • Constraints : specification to restrict the applicability of the policy (temporal constraints, parameter value constraints, preconditions) • Propagation : policy applying to a parent domain, should propagate to member subdomains of parent Figure 4. Policy Propagation 1999. 4. 30 (10) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
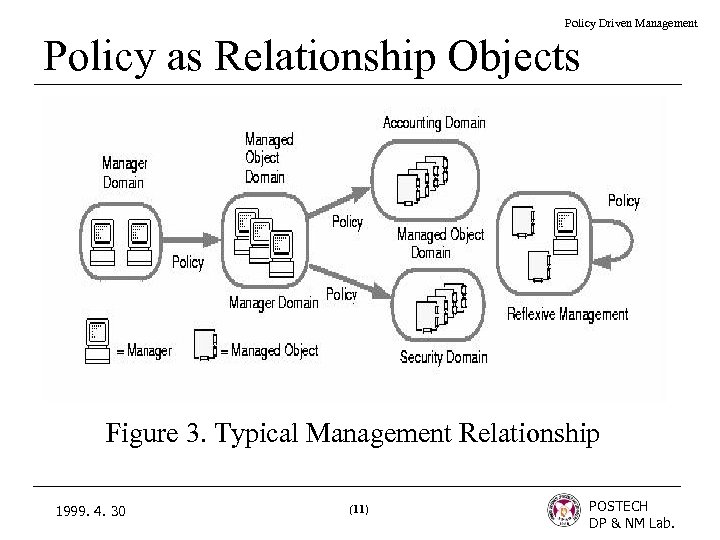
Policy Driven Management Policy as Relationship Objects Figure 3. Typical Management Relationship 1999. 4. 30 (11) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
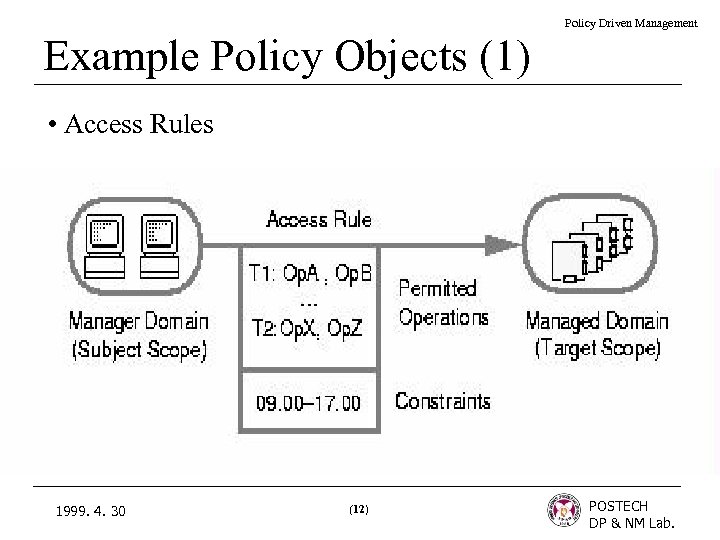
Policy Driven Management Example Policy Objects (1) • Access Rules 1999. 4. 30 (12) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.

Policy Driven Management Example Policy Objects (2) • Domain Membership Policy : – specify membership of a domain by specifying an object selection predicate & creating & deleting (Ex) – A+ any {include X, create X} Dt when X. type=T (any subject is permitted to include or create objects of type T in target domain Dt) – A- any {remove, delete} Dt when Dt. membernum > 2 (any subject is prohibited to remove or delete domain Dt when the member number is more than 2) 1999. 4. 30 (13) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
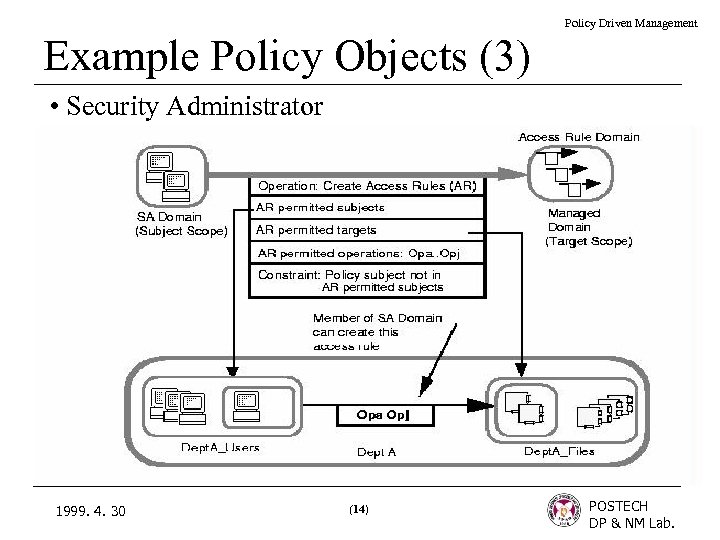
Policy Driven Management Example Policy Objects (3) • Security Administrator 1999. 4. 30 (14) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
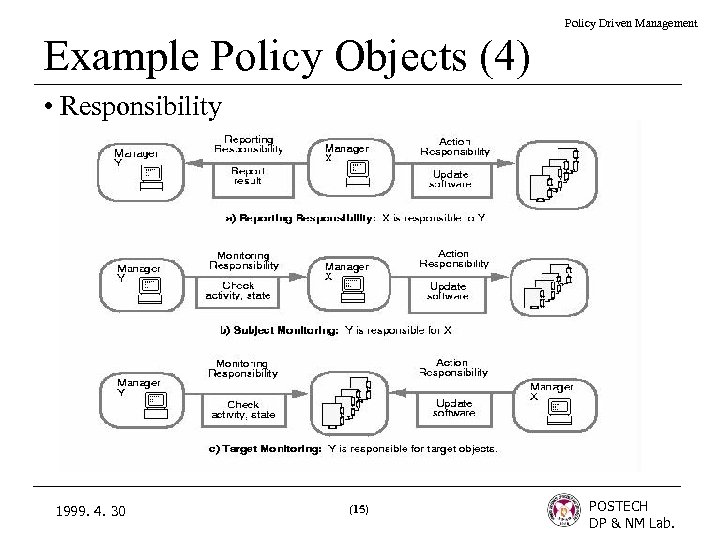
Policy Driven Management Example Policy Objects (4) • Responsibility 1999. 4. 30 (15) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.

Policy Driven Management Consideration Issues of Policy • Policy Implementation Issues : Policy Dissemination Function – transforms policies into a form suitable for interpretation – sends obligation policies to managers in subject domain – sends authorization policies to reference monitors associated with objects in the target domain Form : O+ | O- [on<event>] <subject> {actions} <target> [when <constraints>] • Policy Hierarchy – Policy Goals – Policy Rules – Policy Mechanism Information • Policy Analysis – Coverage – Missing Obligation/Authorization – Conflicts 1999. 4. 30 (16) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.

Policy Driven Management Conclusions • PDM provides the basis for dealing with automated & dynamic & reusable management • Policy specification language should produce a set of rules which can be interpreted by managers • Domains are used to specify the scope for applying the policy • Important Issues : policy analysis, conflict detection & resolution 1999. 4. 30 (17) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.

Policy Driven Management References • Morris Sloman, “Policy Driven Management for Distributed Systems, ” Journal of Network and Systems Management, Plenum Press. Vol. 2 No. 4, 1994. 1999. 4. 30 (18) POSTECH DP & NM Lab.
3dad27e579f4aa80374cff327ca85c32.ppt