c34dd151e53e65399b763162f584e4c3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Policy and Coordination in Multilingual Internet Names Tan Tin Wee Vice Chairman Multilingual Internet Names Consortium (MINC)
Policy and Coordination in Multilingual Internet Names Tan Tin Wee Vice Chairman Multilingual Internet Names Consortium (MINC)
 Framework of Authority-I IANA US Govt Names Numbers Protocols Legal Govt Contract g. TLDs cc. TLDs SRI NSI Verisign Country NICs/ Mngrs APNIC ARIN RIPE IETF
Framework of Authority-I IANA US Govt Names Numbers Protocols Legal Govt Contract g. TLDs cc. TLDs SRI NSI Verisign Country NICs/ Mngrs APNIC ARIN RIPE IETF
 Framework of Authority-II US Govt Legal Govt Contract Stakeholders: Constituencies At Large etc GAC ICANN “Inc” Legal Contract DNSO ASO PSO Names Numbers Protocols g. TLDs cc. TLDs Verisign/NSI Registries Registrars IANA Country NICs/ Mngrs APNIC ARIN RIPE IETF
Framework of Authority-II US Govt Legal Govt Contract Stakeholders: Constituencies At Large etc GAC ICANN “Inc” Legal Contract DNSO ASO PSO Names Numbers Protocols g. TLDs cc. TLDs Verisign/NSI Registries Registrars IANA Country NICs/ Mngrs APNIC ARIN RIPE IETF

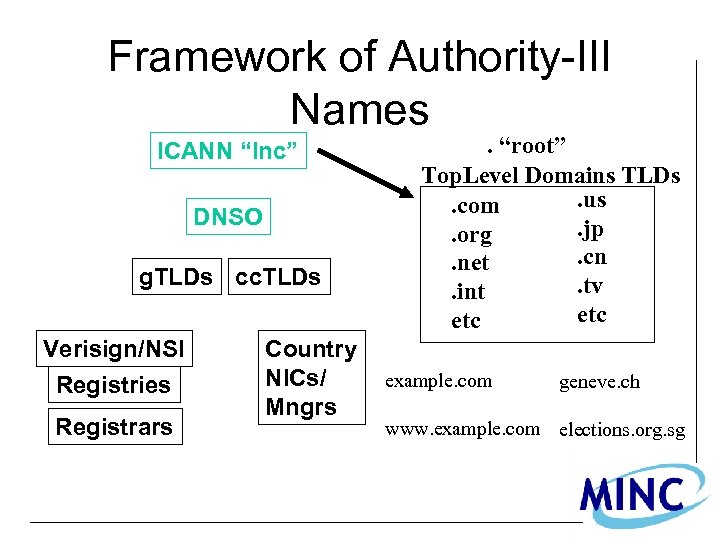 Framework of Authority-III Names ICANN “Inc” DNSO g. TLDs cc. TLDs Verisign/NSI Registries Registrars Country NICs/ Mngrs . “root” Top. Level Domains TLDs. us. com. jp. org. cn. net. tv. int etc example. com geneve. ch www. example. com elections. org. sg
Framework of Authority-III Names ICANN “Inc” DNSO g. TLDs cc. TLDs Verisign/NSI Registries Registrars Country NICs/ Mngrs . “root” Top. Level Domains TLDs. us. com. jp. org. cn. net. tv. int etc example. com geneve. ch www. example. com elections. org. sg
 Framework of Authority - IV • US Government Dept of Commerce • IANA original authority • ICANN is in charge of the “Root” inter alia • ICANN coordinates Insertion of TLDs in the Root • Delegates authority to g. TLDs and cc. TLDs
Framework of Authority - IV • US Government Dept of Commerce • IANA original authority • ICANN is in charge of the “Root” inter alia • ICANN coordinates Insertion of TLDs in the Root • Delegates authority to g. TLDs and cc. TLDs
 Justification for authority • US Government funded the original research, operation of IANA, Jon Postel – Precedence • Delegated Authority from USG • Universal Acceptance • Government Involvement through GAC • Contractual Agreements between authority and delegee – Commercial Contract law • Universal Representation from Stakeholders • Hierarchy of authority – ICANN – SOs – Stakeholders • Universal Suffrage of current Internet users?
Justification for authority • US Government funded the original research, operation of IANA, Jon Postel – Precedence • Delegated Authority from USG • Universal Acceptance • Government Involvement through GAC • Contractual Agreements between authority and delegee – Commercial Contract law • Universal Representation from Stakeholders • Hierarchy of authority – ICANN – SOs – Stakeholders • Universal Suffrage of current Internet users?
 Multilingual Name Space - I • New Name Spaces extended from ASCII • New Technology Originated from Asia Pacific 1998 • Testbed pioneered in Asia 1998/1999 • New Standards with Strong Asian Input in IETF processes 1999 • New Complexities of Languages and Scripts
Multilingual Name Space - I • New Name Spaces extended from ASCII • New Technology Originated from Asia Pacific 1998 • Testbed pioneered in Asia 1998/1999 • New Standards with Strong Asian Input in IETF processes 1999 • New Complexities of Languages and Scripts
 Multilingual Name Space - II • New Scenarios of TLDs – language TLDs? cc. TLDs and g. TLDs in other scripts? • New Names – IDNs and Keywords • New User communities of non-English speaking users • New authority/expertise framework nascent – MINC-INFITT-AINC-CDNC-JDNA-etc 20002001 • New Companies – I-DNS. net (1999) Neteka, Netpia, Realnames, Nativenames etc
Multilingual Name Space - II • New Scenarios of TLDs – language TLDs? cc. TLDs and g. TLDs in other scripts? • New Names – IDNs and Keywords • New User communities of non-English speaking users • New authority/expertise framework nascent – MINC-INFITT-AINC-CDNC-JDNA-etc 20002001 • New Companies – I-DNS. net (1999) Neteka, Netpia, Realnames, Nativenames etc
 ICANN ++ response • IETF Internationalized Domain Name IDN Working Group end 1999/ 2000 • IDN Committee 2001 • Names Council/DNSO IDN WG 2001 • Since 1998 to date.
ICANN ++ response • IETF Internationalized Domain Name IDN Working Group end 1999/ 2000 • IDN Committee 2001 • Names Council/DNSO IDN WG 2001 • Since 1998 to date.
 Different Premises may necessitate Review of Authority Framework • Is any change required of existing framework of authority? • Can existing framework be extended to include the new multilingual namespace? • Can the existing stakeholder base be extended to the new multilingual stakeholders? • Can the g. TLD/cc. TLD ICANN authority structure work for the new multilingual multiscript IDN namespaces?
Different Premises may necessitate Review of Authority Framework • Is any change required of existing framework of authority? • Can existing framework be extended to include the new multilingual namespace? • Can the existing stakeholder base be extended to the new multilingual stakeholders? • Can the g. TLD/cc. TLD ICANN authority structure work for the new multilingual multiscript IDN namespaces?
 Authority Matrix in IDN Language Script Country/ Economy Example 1 1 M 1 Hebrew, Greek Japanese 1 1 M M 1 1 0 Russian, Mongolian Ascii, Han, Arabic Tamil 1 M M Korean
Authority Matrix in IDN Language Script Country/ Economy Example 1 1 M 1 Hebrew, Greek Japanese 1 1 M M 1 1 0 Russian, Mongolian Ascii, Han, Arabic Tamil 1 M M Korean
 Matrix of Language-Script-Country I • Many. Languages-One. Script-Many. Countries – - Latin script-ASCII; - Arabic/Farsi/Urdu/Jawi-Arabic->20 countries; -Chinese/Japanese/Korean-Han. China/Japan/Koreas/Taiwan/HK/Macau/Singapore etc. • One. Language-One. Script-One. Country – Ancient Icelandic-Iceland; Hebrew-Israel Greek-Greece • One. Language-Many. Scripts-One. Country – Japanese-Hiragana/Katakana/Kanji-Japan
Matrix of Language-Script-Country I • Many. Languages-One. Script-Many. Countries – - Latin script-ASCII; - Arabic/Farsi/Urdu/Jawi-Arabic->20 countries; -Chinese/Japanese/Korean-Han. China/Japan/Koreas/Taiwan/HK/Macau/Singapore etc. • One. Language-One. Script-One. Country – Ancient Icelandic-Iceland; Hebrew-Israel Greek-Greece • One. Language-Many. Scripts-One. Country – Japanese-Hiragana/Katakana/Kanji-Japan
 Matrix of Language-Script-Country II • One. Language-One. Script-Many. Fonts-No. Country – - Tamil-Tamil. Nadu State+>12 countries with Tamil minorities; - American Indian languages; - Indian Languages such as Gujerati, Marathi, etc. • One. Language-One. Script-Several. Countries – - Mongolian-Mongolia/China; - Russian-Cyrillic-Russia/post. Soviet. Union states • One. Language-Several. Scripts-Several. Countries – - Korean-Hanguel/Hanja-North. Korea/South. Korea • Other combinations
Matrix of Language-Script-Country II • One. Language-One. Script-Many. Fonts-No. Country – - Tamil-Tamil. Nadu State+>12 countries with Tamil minorities; - American Indian languages; - Indian Languages such as Gujerati, Marathi, etc. • One. Language-One. Script-Several. Countries – - Mongolian-Mongolia/China; - Russian-Cyrillic-Russia/post. Soviet. Union states • One. Language-Several. Scripts-Several. Countries – - Korean-Hanguel/Hanja-North. Korea/South. Korea • Other combinations
 Current Status - I • • IDN Technologies available Strong IDN demand is proven IDN Service providers already present IETF IDN standards imminent
Current Status - I • • IDN Technologies available Strong IDN demand is proven IDN Service providers already present IETF IDN standards imminent
 Current Status II • Even more new technologies forthcoming – Growth area • New Processes available – MINC, INFITT, AINC, JDNA, CDNC • New businesses and new opportunities and new services in keywords and above-DNS services
Current Status II • Even more new technologies forthcoming – Growth area • New Processes available – MINC, INFITT, AINC, JDNA, CDNC • New businesses and new opportunities and new services in keywords and above-DNS services
 Urgency • Multilingual masses shut of Internet because of linguistic limitation • IDN Technology/Service Vendors moving forward with proprietary software – fracturing internet • Alternative Root advocates getting stronger • Application-Dependent/ Vendor Specific Solutions – Keywords. Realnames/Verisign/Microsoft; AOL keywords; Netscape keywords • Country Authorities launching their own
Urgency • Multilingual masses shut of Internet because of linguistic limitation • IDN Technology/Service Vendors moving forward with proprietary software – fracturing internet • Alternative Root advocates getting stronger • Application-Dependent/ Vendor Specific Solutions – Keywords. Realnames/Verisign/Microsoft; AOL keywords; Netscape keywords • Country Authorities launching their own
 MINC • Multilingual Internet Names Consortium • Coordination of IDN and Keywords • Cooperation with relevant international organisations – ICANN, IETF, ISOC, ITU, WIPO, etc • Creation of and fostering of ties with new organisations – AINC, CDNC, JDNA, INFITT, etc • Formation in 2000
MINC • Multilingual Internet Names Consortium • Coordination of IDN and Keywords • Cooperation with relevant international organisations – ICANN, IETF, ISOC, ITU, WIPO, etc • Creation of and fostering of ties with new organisations – AINC, CDNC, JDNA, INFITT, etc • Formation in 2000
 MINC WGs and Other Associated Organisations • • • Chinese Domain Names Consortium – CDNC International Forum for IT in Tamil – INFITT Arabic Internet Names Consortium – AINC Japanese Domain Name Association – JDNA Urdu WG Russian WG Indian Lang WG Greek Langauge WG etc
MINC WGs and Other Associated Organisations • • • Chinese Domain Names Consortium – CDNC International Forum for IT in Tamil – INFITT Arabic Internet Names Consortium – AINC Japanese Domain Name Association – JDNA Urdu WG Russian WG Indian Lang WG Greek Langauge WG etc
 MINC Proactive Ongoing Plan • Work with all stakeholders and relevant organisations – ICANN, ISOC, ITU, WIPO etc • Set up Interoperability Testbed for Technology testing • Foster growth of new Stakeholder communities beyond AINC/INFITT/CDNC/JDNC etc for Self Determination process in their own languages • Formulation of workable authority structures • Formulation of Inter-language group coordination and dispute resolution • Creation of level playing field for all levels
MINC Proactive Ongoing Plan • Work with all stakeholders and relevant organisations – ICANN, ISOC, ITU, WIPO etc • Set up Interoperability Testbed for Technology testing • Foster growth of new Stakeholder communities beyond AINC/INFITT/CDNC/JDNC etc for Self Determination process in their own languages • Formulation of workable authority structures • Formulation of Inter-language group coordination and dispute resolution • Creation of level playing field for all levels
 Policy and Coordination • ICANN IDN Committee mid 2001 • ICANN Names Council IDN committee late 2001 • ITU-WIPO-MINC meeting on multilingual domain names – this conference late 2001. • MINC-AINC Mo. U and meeting • MINC-CDNC meeting • MINC official support of JDNC • MINC-INFITT Mo. U • MINC fostering Russian. WG, Indian. Lang. WG, Greek. WG, Hebrew. WG etc.
Policy and Coordination • ICANN IDN Committee mid 2001 • ICANN Names Council IDN committee late 2001 • ITU-WIPO-MINC meeting on multilingual domain names – this conference late 2001. • MINC-AINC Mo. U and meeting • MINC-CDNC meeting • MINC official support of JDNC • MINC-INFITT Mo. U • MINC fostering Russian. WG, Indian. Lang. WG, Greek. WG, Hebrew. WG etc.
 What Policy/Coordination needed going forward? • Conservative Central-Control Approach • Revolutionary Liberal Free-Market Approach • Something in-between?
What Policy/Coordination needed going forward? • Conservative Central-Control Approach • Revolutionary Liberal Free-Market Approach • Something in-between?
 Conservative Central-Control Approach Unique Root With Single Authority ICANN DNSO g. TLDs Verisign/NSI others cc. SO? cc. TLDs Country NICs/Mngrs Registries Registrars ? SO? IDN-TLDs Country NICs/ Mngr ? ? Language TLDs ? ?
Conservative Central-Control Approach Unique Root With Single Authority ICANN DNSO g. TLDs Verisign/NSI others cc. SO? cc. TLDs Country NICs/Mngrs Registries Registrars ? SO? IDN-TLDs Country NICs/ Mngr ? ? Language TLDs ? ?
 Revolutionary Liberal Free-Market Approach Loose or No Coordination With colliding namespaces ICANN ? ? DNSO cc. SO? ? ? Non-Unique Root With Multiple Authorities g. TLDs cc. TLDs Other TLDs Verisign/NSI Country others NICs/Mngrs Registries Registrars ? ? …. ? ? ? IDN-TLDs Other i. TLDs Country NICs/ Mngr ? ? Language TLDs ? ?
Revolutionary Liberal Free-Market Approach Loose or No Coordination With colliding namespaces ICANN ? ? DNSO cc. SO? ? ? Non-Unique Root With Multiple Authorities g. TLDs cc. TLDs Other TLDs Verisign/NSI Country others NICs/Mngrs Registries Registrars ? ? …. ? ? ? IDN-TLDs Other i. TLDs Country NICs/ Mngr ? ? Language TLDs ? ?
 Something in Between? Unique Distributed Root With Coordinated Multi-Lateral Multiple Authorities Agreements /Coordination ICANN ? ? DNSO cc. SO? ? ? g. TLDs cc. TLDs Verisign/NSI Country others NICs/Mngrs ? ? …. ? ? ? IDN-TLDs Country NICs/ Mngr ? ? Registries Registrars Language TLDs ? ?
Something in Between? Unique Distributed Root With Coordinated Multi-Lateral Multiple Authorities Agreements /Coordination ICANN ? ? DNSO cc. SO? ? ? g. TLDs cc. TLDs Verisign/NSI Country others NICs/Mngrs ? ? …. ? ? ? IDN-TLDs Country NICs/ Mngr ? ? Registries Registrars Language TLDs ? ?
 Past Present Future of IDN • • • Technically Impossible, but 1998 i. DNS proxy Technically Unimplementable, but 1998 APNG Testbed No Commercial Interest, but 1998 I-DNS. net Inc No Demand, but 1999 Overwhelming response No Standard, but 1999 IETF IDN WG No Organisation, but 2000 MINC No Language Support, but 2000/1 CDNC, INFITT, AINC, JDNA No Authority, but ICANN IDN Committee, NC IDN WG No Fair, Equitable, Proactive, Responsive Authority Structure to address the complexity of languages
Past Present Future of IDN • • • Technically Impossible, but 1998 i. DNS proxy Technically Unimplementable, but 1998 APNG Testbed No Commercial Interest, but 1998 I-DNS. net Inc No Demand, but 1999 Overwhelming response No Standard, but 1999 IETF IDN WG No Organisation, but 2000 MINC No Language Support, but 2000/1 CDNC, INFITT, AINC, JDNA No Authority, but ICANN IDN Committee, NC IDN WG No Fair, Equitable, Proactive, Responsive Authority Structure to address the complexity of languages
 When can the non-English speaker start to use IDN? • • • Define standards Demythologise the unique root Devolve authority and responsibility Deploy Coordination process Delimit and Delegate new IDN TLDs More work, mostly political work needed.
When can the non-English speaker start to use IDN? • • • Define standards Demythologise the unique root Devolve authority and responsibility Deploy Coordination process Delimit and Delegate new IDN TLDs More work, mostly political work needed.
 Please provide feedback to: • • Tan Tin Wee tinwee@bic. nus. edu. sg MINC Website: www. minc. org MINC Email: sec@minc. org MINC Mailing Lists
Please provide feedback to: • • Tan Tin Wee tinwee@bic. nus. edu. sg MINC Website: www. minc. org MINC Email: sec@minc. org MINC Mailing Lists


