ba1bf5405c796c10f3a55878b16fe5d1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Poisonous Pastures By: John E. Woodmansee Extension Educator Agriculture/Natural Resources Purdue Extension – Grant County Reviewed by Glenn Nice, Extension weed scientist Purdue University


Introduction • Your veterinarian will be the person to check with for symptoms/treatments/cures • Some sources of information you find on this subject may contradict each other • We’ll discuss most common plants as referenced in Purdue Extension publication WS-9, “Indiana Plants Poisonous to Livestock and Pets” – supported by many references/research

Source: Purdue Extension publication WS-9, Indiana Plants Poisonous to Livestock and Pets • Available on-line at: http: //www. vet. purdue. edu/depts/addl/toxic/cover 1. htm

Introduction • In Indiana, poisonous plants far outnumber poisonings • Animals generally prefer other plants to poisonous plants – may only eat poisonous plants when nothing else is available • Poisonings most common in early spring, second most common in winter

You suspect a poisoning • Eliminate all other possibilities • Positively identify suspected plant • Match symptoms to those reported for plant

Prevention is the key! • No antidotes for many of the poisons in plants • Know the poisonous plants in your pasture and control or keep animals away with fencing • Supply good forage or feed • Avoid overgrazing

If an animal appears poisoned… • Avoid disturbing animal as much as possible • Contact your veterinarian • If practical or advised: move animal(s) to fresh pasture or give fresh feed/water

Animals react differently • Individual animals within a species may react differently • Different types of animals react differently (e. g. cattle may be killed, but swine fine)

Possible Symptoms • • • Birth defects Bleeding Blood clots in stools Blue coloration Breathing difficulties Death (sudden) Diarrhea Drooling Dullness, depression Excitedness, unusual behavior • • • Gangrene Heart or pulse problems Jaundice Nausea Prostration Rash, sunburn Staggering, incoordination Stomach upset, colic Throat irritations Trembles, convulsions

WS-9: Plants that cause physical injury (skin, eye, mouth, stomach, or hair-ball problems – mechanical injury to animals) • Foxtail barley • Common burdock

WS-9: House/Garden plants that poison • Aroids (Jack-in-the-pulpit, philodenron, etc. ) • Bulb-bearing plants (lily-of-the-valley, amaryllis, hyacinth, iris, daffodil, etc. ) • English ivy • Lupine, wild and cultivated (bluebonnet, Quakerbonnets) • Catnip • Christmas plant (poinsettia) • Rhubarb • Azalea, rhododendron • Castorbean • Common tansey

WS-9: Forage and crop plants that poison • Cultivated oats (nitrate poisoning) • Ergot (a fungus parasite on heads of grasses) • Tall fescue (varieties infected by Acremonium endophytic fungus – a “mold”) • Sweetclover, yellow and white • Tobacco • Alsike clover

WS-9: Woodland plants that poison • Jack-in-the-pulpit (Indian turnip) • Larkspur, dwarf and cultivated • Dutchman’s breeches, squirrelcorn (staggerweed, bleeding heart) • White snakeroot (white sanicle, richweed) • Brackenfern (brake fern) • Groundsel (butterweed, ragwort) • Green falsehellebore (white hellebore, Indian poke)

WS-9: Marsh and streambank plants that poison • Milkweeds • Spotted waterhemlock (waterhemlock, spotted cowbane) • Poison-hemlock • Field horsetail, scouringrush • Buttercups • Nettle, stinging and wood • Common cocklebur

WS-9: Plants of fields, roadsides, and open areas that poison • Redroot pigweed • Mustard family (wild mustard, pennycress, peppergrass, etc. ) • Hemp (marijuana) • Jimsonweed (thornapple) • Spurges (prostrate spurge, cypress spurge, etc. ) • Common St. Johnswort (klamath weed) • Star-of-Bethlehem (snowdrop, nap-at-noon) • Common Pokeweed (pokeberry, pokeroot, inkberry, poke) • Bouncingbet (soapwort) • Nightshades (eastern black nightshade, Carolina horsenettle, bull nettle, bitter nightshade, climbing bittersweet) • Johnsongrass

WS-9: Trees and shrubs that poison • • • Ohio buckeye Black walnut Wild black cherry Red oak Black locust Yew, English and Japanese

WS-9: Most common toxic plants in Indiana • • • Alsike clover Bitter nightshade Black nightshade Common cocklebur Dutchman’s breeches Dwarf larkspur Groundsel Johnsongrass Poison-hemlock • Redroot pigweed • Field horsenettle, Scouringrush • Spotted waterhemlock • Sweetclover • White snakeroot • Wild black cherry • Yew Source: WS-9. All line drawings and pictures to follow are from WS-9 unless noted.

Alsike Clover Animals affected: dogs, sheep, cattle, poultry, caged birds

Bitter nightshade (also called bittersweet nightshade, climbing nightshade) Animals affected: Calves, goats, sheep, swine, poultry, rarely horses and cows Line drawing: USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database Bottom photo credit: George F. Russell @ USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database
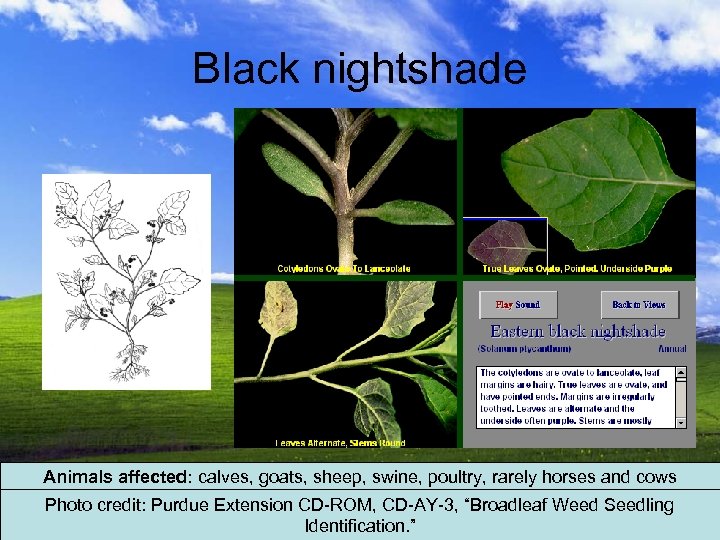
Black nightshade Animals affected: calves, goats, sheep, swine, poultry, rarely horses and cows Photo credit: Purdue Extension CD-ROM, CD-AY-3, “Broadleaf Weed Seedling Identification. ”
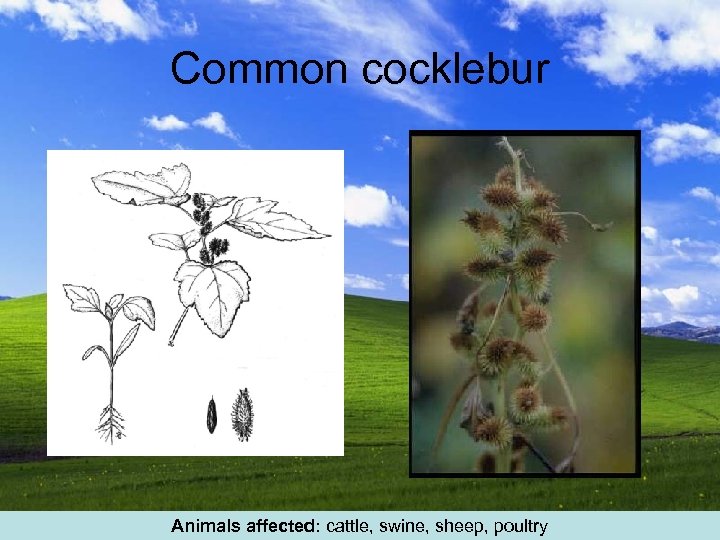
Common cocklebur Animals affected: cattle, swine, sheep, poultry
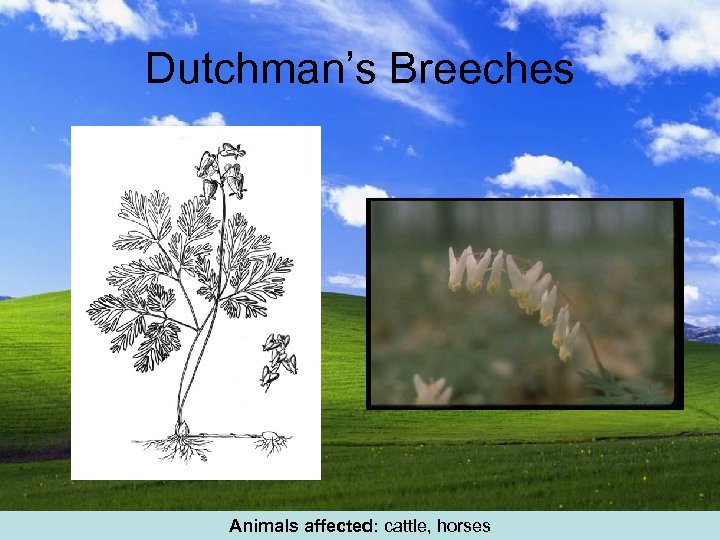
Dutchman’s Breeches Animals affected: cattle, horses
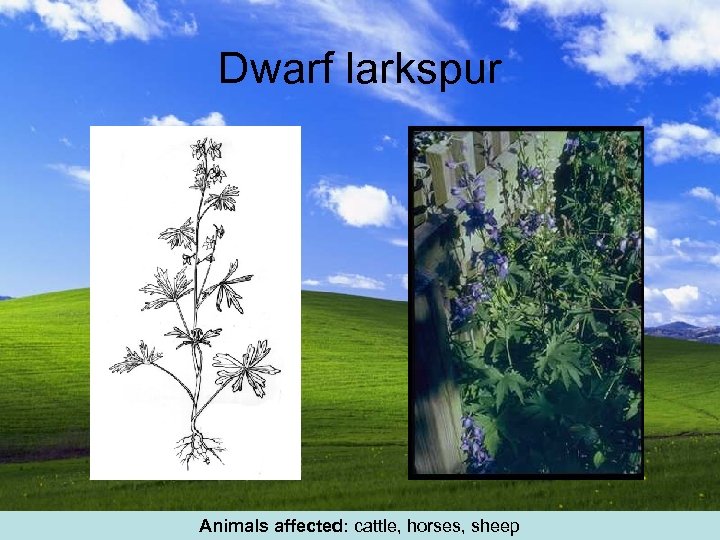
Dwarf larkspur Animals affected: cattle, horses, sheep
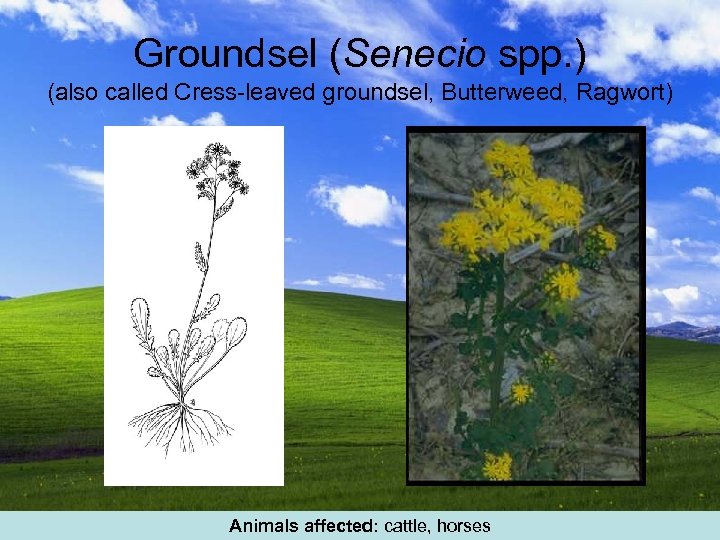
Groundsel (Senecio spp. ) (also called Cress-leaved groundsel, Butterweed, Ragwort) Animals affected: cattle, horses
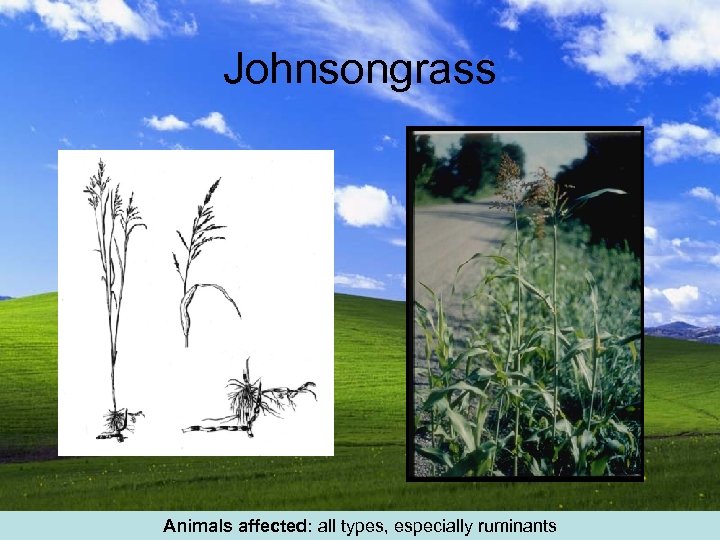
Johnsongrass Animals affected: all types, especially ruminants
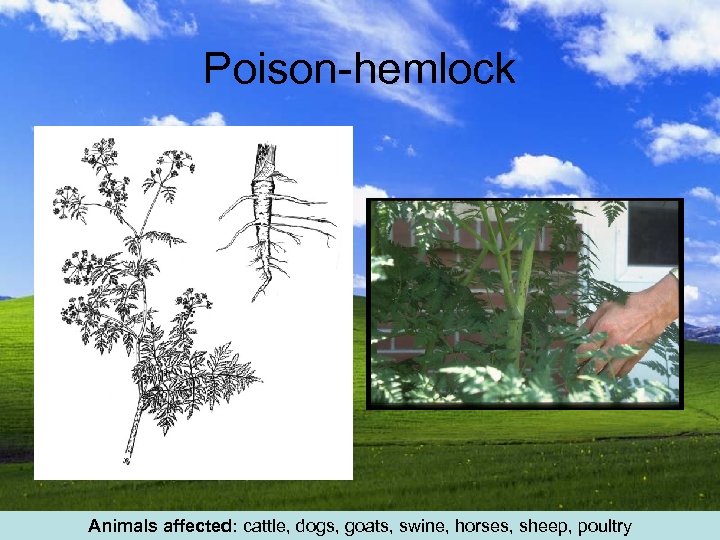
Poison-hemlock Animals affected: cattle, dogs, goats, swine, horses, sheep, poultry

Redroot pigweed Animals affected: cattle, goats, sheep, swine

Field Horsetail, Scouringrush Animals affected: horses, rarely cattle and sheep
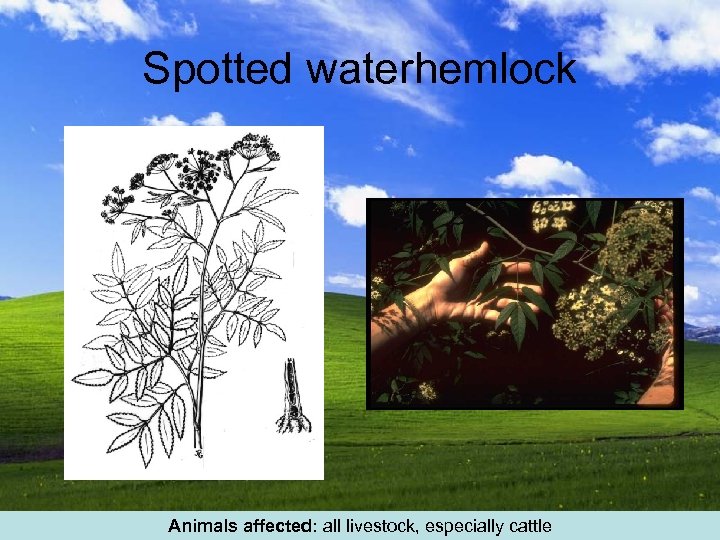
Spotted waterhemlock Animals affected: all livestock, especially cattle

Sweetclover Animals affected: cattle, horses, sheep, rabbits
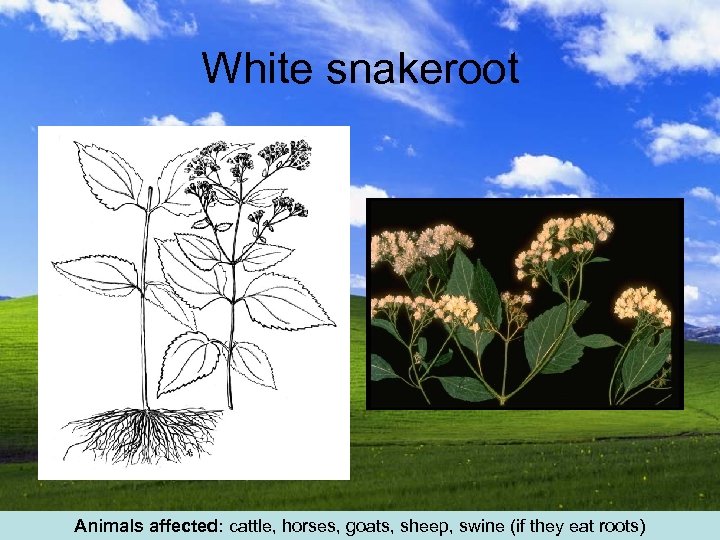
White snakeroot Animals affected: cattle, horses, goats, sheep, swine (if they eat roots)
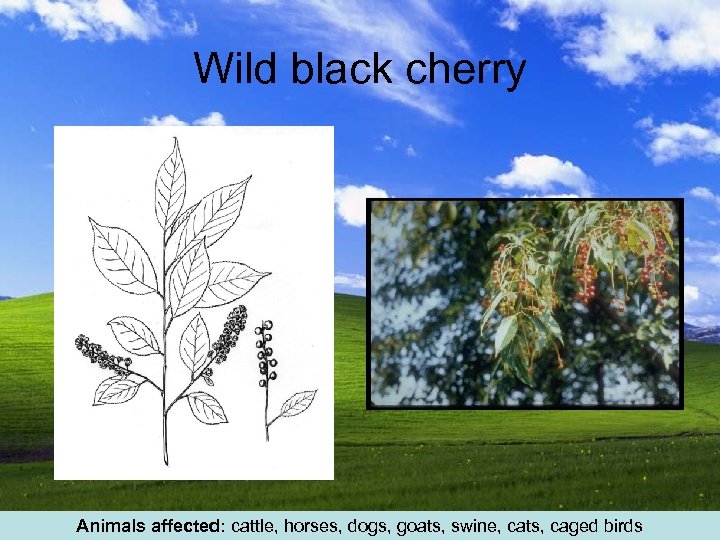
Wild black cherry Animals affected: cattle, horses, dogs, goats, swine, cats, caged birds

Yew (also called English or Japanese Yew, Taxus spp. ) Animals affected: all livestock (especially horses), dogs, caged birds
ba1bf5405c796c10f3a55878b16fe5d1.ppt