8f754a41cf7fe6c4d25712ac49ccac25.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Platform Product Management Case: Nokia Symbian Product Platforms Lea Lahti Nokia Technology Platforms/Symbian Product Platforms Head of Platform Business Development 1 © 2005 Nokia

Content • Part I: Introduction • Nokia Technology Platforms • Nokia SW Platforms • Nokia S 60 platform and Smart Phone market status • Part II: Nokia Symbian Product Platforms • SPP deliverables, value to Nokia business and purpose. • Part III: Platform product management key questions • Core platform vs product differentiation decision making. • Platform strategy vs platform architecture maturity. • Collaborative planning and product management with industry players. • Focus: long-term development vs profitable mature platform productization. 2 © 2005 Nokia

Part I Introduction 3 © 2005 Nokia

Nokia Technology Platforms in Nokia organization termimäärittely 4 © 2005 Nokia
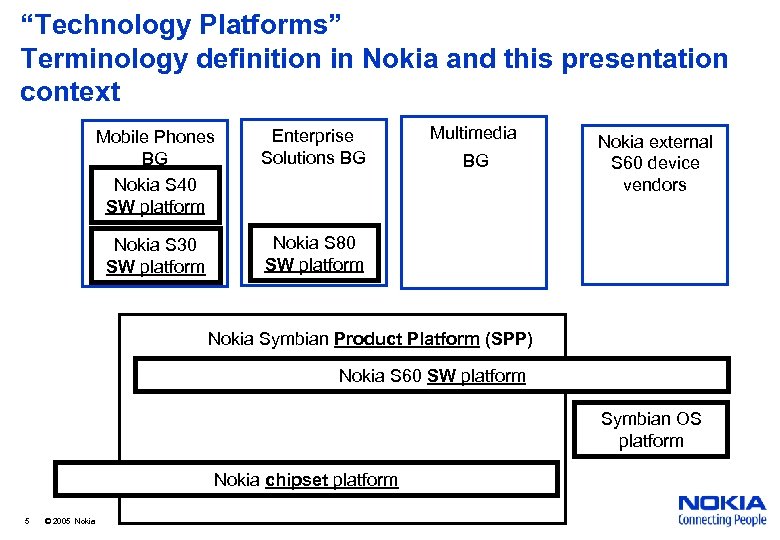
“Technology Platforms” Terminology definition in Nokia and this presentation context Mobile Phones BG Nokia S 40 SW platform Enterprise Solutions BG Nokia S 30 SW platform Multimedia Nokia S 80 SW platform BG Nokia external S 60 device vendors Nokia Symbian Product Platform (SPP) Nokia S 60 SW platform Symbian OS platform Nokia chipset platform 5 © 2005 Nokia
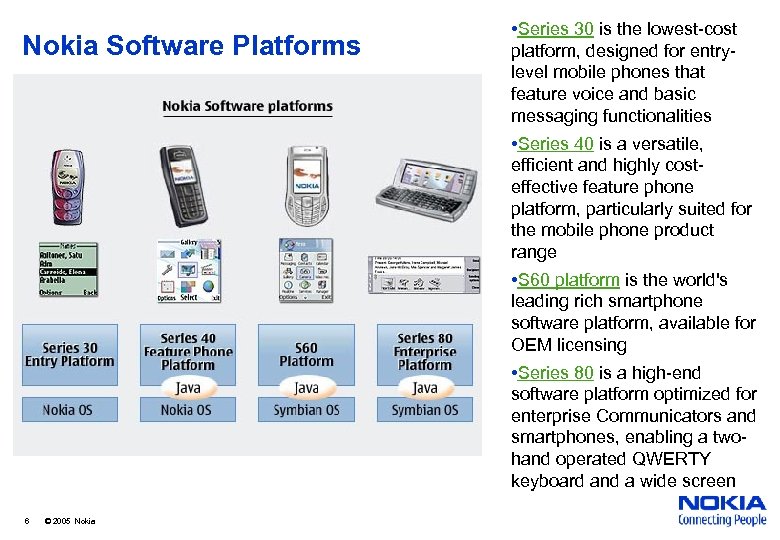
Nokia Software Platforms • Series 30 is the lowest-cost platform, designed for entrylevel mobile phones that feature voice and basic messaging functionalities • Series 40 is a versatile, efficient and highly costeffective feature phone platform, particularly suited for the mobile phone product range • S 60 platform is the world's leading rich smartphone software platform, available for OEM licensing • Series 80 is a high-end software platform optimized for enterprise Communicators and smartphones, enabling a twohand operated QWERTY keyboard and a wide screen 6 © 2005 Nokia
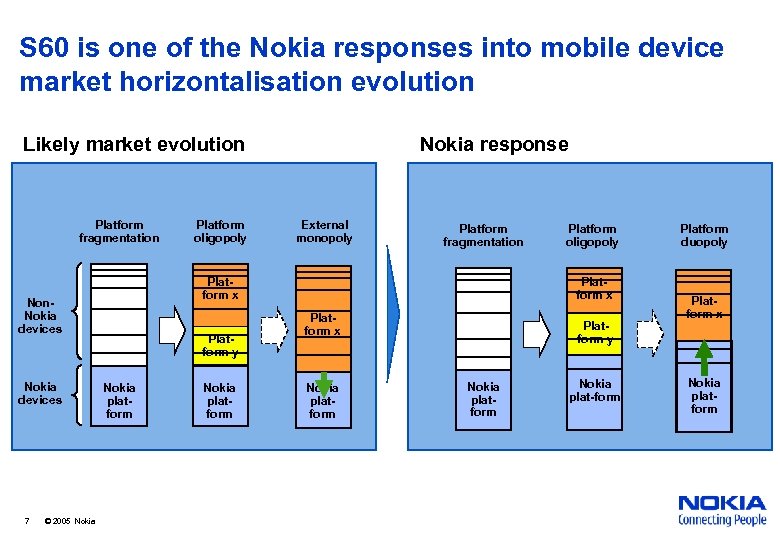
S 60 is one of the Nokia responses into mobile device market horizontalisation evolution Likely market evolution Platform fragmentation 7 © 2005 Nokia External monopoly Platform fragmentation Platform x Non. Nokia devices Platform oligopoly Nokia response Platform y Nokia platform Platform oligopoly Platform x Nokia platform Platform y Nokia platform Nokia plat-form Platform duopoly Platform x Nokia platform

S 60 Device domain competition good – promotion of whole smart phone industry growth Device vendor news D 720 D 730 25 M X 700 X 800 N 90 N 70 N 91 X 2 8 © 2005 Nokia P 930

S 60 needs to create value for several mobile industry stakeholders Operators control the channel Main players: • Vodafone • France Telecom/Orange • Cingular • Do. Co. Mo • China Mobile • T-Mobile • Verizon • Sprint • CDMA operators 9 © 2005 Nokia Developers innovate 400+ Forum Nokia PRO member companies 2 million+ forum. nokia. com registered developers. End-users make the buy-decision

S 60 platform product content – 2005 definition • S 60 platform Application Suite - an extensive set of ready-made applications such as Telephony, Messaging, Browser, Calendar, Phonebook, Instant Messaging and Presence, etc. • S 60 platform Common TSY - the Telephony provider module for the S 60 platform. • S 60 platform Common UI components - a framework for creating S 60 platform style user interfaces for applications. The framework includes basic UI components such as menu, listbox, query dialog, etc. • Language variants - Files and instructions needed for localizing S 60 platform to support different languages. • UI content - Fonts, reference icons, reference UI themes, reference MMS templates, reference help texts and reference ringing tones needed for the S 60 platform UI. • OEM Adaptation Kit (OAK) - a software development environment with application programming interfaces to S 60 platform source code. Includes build tools, testing tools and documentation to help integrate the S 60 platform into vendor-specific terminal hardware and software, and to create new applications for the S 60 platform. • S 60 platform Development Kit (SDK) - a public SDK targeted at third party application developers who are implementing applications for S 60 platform products. • Documentation - Detailed documentation describing S 60 platform, including architecture documents, user interface specifications, design specifications, API specifications, etc. + Supporting services. Own and partners. Different cost model. 10 © 2005 Nokia

Part II Nokia Symbian Product Platform mission 11 © 2005 Nokia

Scope of Nokia Symbian Product Platforms Unit • A Nokia Technology Platforms Unit with specific mission to support Nokia S 60 device businesses. • Responsibilities: • Development and management of Nokia S 60 adaptation SW asset. • Development of Nokia S 60 differentiation applications. • HW development in case of Nokia S 60 device chip-architecture. • Definition, verification, testing and delivery of total S 60 device configurations into Nokia Business Groups. • SPP products = deliverables: • S 60 differentiation applications. • Symbian Product Platform releases, consists of: • S 60 release (including Symbian OS release). • Modem/chipset. • Adaptation SW release. • All HW components: cameras, displays, antennas, accelerators, batteries. . • = Tested and functional Platform Reference set with agreed cost structure, which can be used as basis for BG product differentiation. • Note: Service level variation agreed product by product. 12 © 2005 Nokia
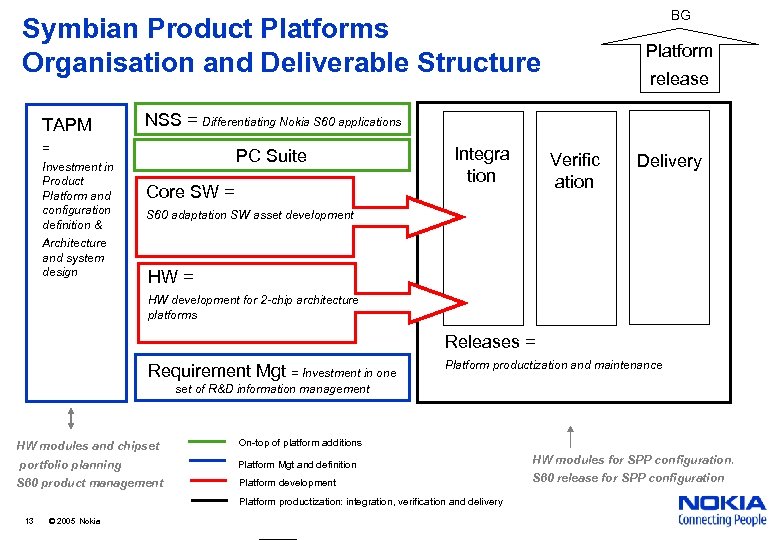
BG Symbian Product Platforms Organisation and Deliverable Structure TAPM Architecture and system design release NSS = Differentiating Nokia S 60 applications = Investment in Product Platform and configuration definition & Platform PC Suite Core SW = Integra tion Verific ation Delivery S 60 adaptation SW asset development HW = HW development for 2 -chip architecture platforms Releases = Requirement Mgt = Investment in one Platform productization and maintenance set of R&D information management HW modules and chipset portfolio planning S 60 product management On-top of platform additions Platform Mgt and definition HW modules for SPP configuration. Platform development S 60 release for SPP configuration Platform productization: integration, verification and delivery 13 © 2005 Nokia
Value of the Symbian Product Platform for Nokia device business • Cost efficiency (R&D resources and cost) by common platform development. • Adaptation SW asset. • Common platform part integration and testing. • Centralized scarce competencies. • Opportunity for learning and competence development. • BG Symbian development can focus on product differentiation. • Centralized Nokia S 60 platform promise: • Application developer and customer support. • Error corrections. • Operator specific variants without compromising core platform. • Centralized maintenance point of existing S 60 product platforms • Opportunity to create new S 60 products by productization of the old functional platform e. g. by new product mechanics. 14 © 2005 Nokia
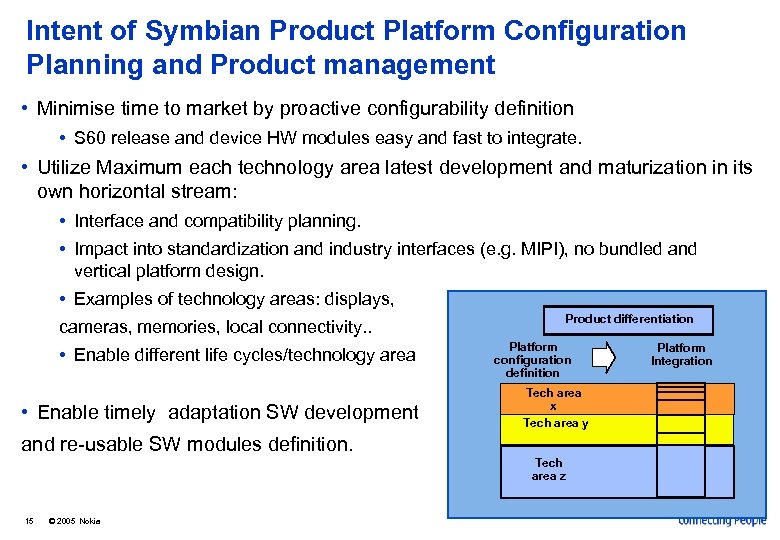
Intent of Symbian Product Platform Configuration Planning and Product management • Minimise time to market by proactive configurability definition • S 60 release and device HW modules easy and fast to integrate. • Utilize Maximum each technology area latest development and maturization in its own horizontal stream: • Interface and compatibility planning. • Impact into standardization and industry interfaces (e. g. MIPI), no bundled and vertical platform design. • Examples of technology areas: displays, cameras, memories, local connectivity. . • Enable different life cycles/technology area • Enable timely adaptation SW development Product differentiation Platform configuration definition Platform Integration Tech area x Tech area y and re-usable SW modules definition. Tech area z 15 © 2005 Nokia Tech area z

Part III Case: Nokia Symbian Product Platform Product Management key questions 16 © 2005 Nokia

Collaborative product management: what & when • Understand value and end-to-end maturity per functionality: Operators, developers and end-users. • Business group product plans and concepts. • S 60 strategy and S 60 product management. • Symbian OS releases product management. • Industry: standardization, IPR game, media and content format game players. • Technology suppliers. Operators control the channel Main players: • Vodafone • France Telecom/Orange • Cingular • Do. Co. Mo • China Mobile • T-Mobile • Verizon • Sprint • CDMA operators 17 © 2005 Nokia Developers innovate 400+ Forum Nokia PRO member companies 2 million+ forum. nokia. com registered developers. End-users make the buy-decision

Optimal focus on different lifecycle phases for maximum business benefits • Platform lifecycle management – Platform lifecycle phases: • Development and introduction. • Variation. • Maintenance. • R&D mindset drives focus easily into new platform development after first productization. • Variation and maintenance R&D is most profitable R&D. • Continuous resource balancing issues: • Maintenance and variation phase resource usage vs. new platform development. • Maintenance phase outsourcing? • Maintenance asset in BG. • Joint risk management with BGs: no business of top of development phase platform before certain maturity step. • Funnel and stage-gate model to manage short vs long-term R&D investment balance: several longterm development options under definition, conscious and timely decisions about new adaptation asset development and integration phase R&D investment. 18 © 2005 Nokia
Platform vs product differentiator - decisions • Continuous functionality level decisions: into platform or not. • Decision making factors: • Re-usability. • Several products. • Several operators. • Several platform releases. • BG capability to implement. • Scarce competence. • Architecture complexity. • Value for business • Importance for several Nokia businesses. • Value for Nokia technology or standardization strategy • Cross-platform functionality. • Platform or Nokia device portfolio Consistency • Feature which needs to be common cross-Nokia portfolio. 19 © 2005 Nokia
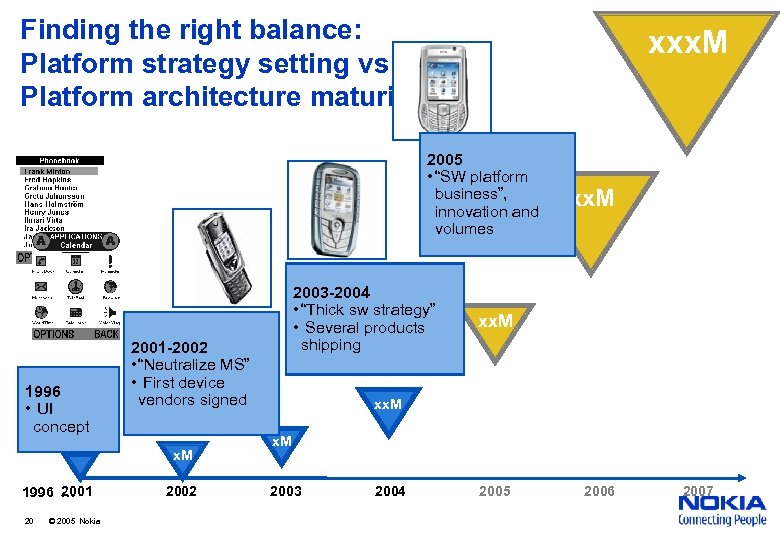
Finding the right balance: Platform strategy setting vs Platform architecture maturity xxx. M 2005 • “SW platform business”, innovation and volumes 1996 • UI concept 2001 -2002 • “Neutralize MS” • First device vendors signed x. M 2001 1996 … 20 © 2005 Nokia 2003 -2004 • “Thick sw strategy” • Several products shipping 2002 xx. M 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007

Portfolio aspect in platform product management • Dependencies between releases • Negative opportunity costs. -> Document and manage architecture and dependencies. • Scarce resources • Focus on most profitable work. -> Business case management for releases. • Wide range of S 60 devices to be built on top the platform, need of different S 60 product platform tiers • Guarantee enough focus for each tier: • High performance multimedia and communicator platforms. • Size and mass applications driven platforms. • Cost driven platforms to drive S 60 into lower price points and volumes. • -> Visibility into R&D investment and business contribution per tier. • S 60 product platform consistency to keep developer and compatibility promise throughout S 60 devices • -> Agree and guarantee minimum level application performance • -> consistency of APIs. 21 © 2005 Nokia
8f754a41cf7fe6c4d25712ac49ccac25.ppt