PlatformInvoke_engl.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Platform Invoke
Platform Invoke
 Platform Invoke (P/Invoke) a. NET feature for calling functions in unmanaged dynamic link libraries
Platform Invoke (P/Invoke) a. NET feature for calling functions in unmanaged dynamic link libraries
 To consume exported DLL functions Identifying Functions in DLLs Creating a Class to Hold DLL Functions Declare DLL functions within an existing class. Create an individual class for each DLL function, keeping functions isolated and easy to find. Create one class for a set of related DLL functions to form logical groupings and reduce overhead. Creating Prototypes in Managed Code Calling a DLL Function
To consume exported DLL functions Identifying Functions in DLLs Creating a Class to Hold DLL Functions Declare DLL functions within an existing class. Create an individual class for each DLL function, keeping functions isolated and easy to find. Create one class for a set of related DLL functions to form logical groupings and reduce overhead. Creating Prototypes in Managed Code Calling a DLL Function
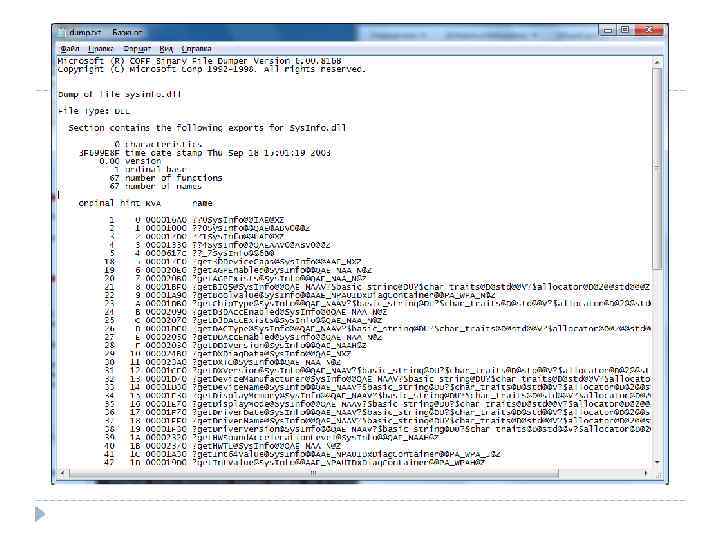
 Identifying Functions in DLLs The identity of a DLL function consists of the following elements: Function name or ordinal Name of the DLL file in which the implementation can be found Use for that: dumpbin /exports user 32. dll or link /dump /exports user 32. dll (Visual C++)
Identifying Functions in DLLs The identity of a DLL function consists of the following elements: Function name or ordinal Name of the DLL file in which the implementation can be found Use for that: dumpbin /exports user 32. dll or link /dump /exports user 32. dll (Visual C++)
 User 32. dll int WINAPI Message. Box( HWND h. Wnd, LPCTSTR lp. Text, LPCTSTR lp. Caption, UINT u. Type );
User 32. dll int WINAPI Message. Box( HWND h. Wnd, LPCTSTR lp. Text, LPCTSTR lp. Caption, UINT u. Type );
 Creating Prototypes in Managed Code (Creating P/Invoke Declarations ) Use namespace System. Runtime. Interop. Services using System. Runtime. Interop. Services; [Dll. Import(“DLL_name”, optional _attribute_list)] public static extern return_type function_name (parameter_list);
Creating Prototypes in Managed Code (Creating P/Invoke Declarations ) Use namespace System. Runtime. Interop. Services using System. Runtime. Interop. Services; [Dll. Import(“DLL_name”, optional _attribute_list)] public static extern return_type function_name (parameter_list);
 [Dll. Import("user 32. dll", Char. Set = Char. Set. Unicode)] public static extern int Message. Box(Int. Ptr h. Wnd, String text, String caption, uint type);
[Dll. Import("user 32. dll", Char. Set = Char. Set. Unicode)] public static extern int Message. Box(Int. Ptr h. Wnd, String text, String caption, uint type);
 Calling a DLL Function Locates implementing DLL Loads DLL Finds function address Fuzzy name matching algorithm Pushes arguments on stack Performs marshalling Enables pre-emptive garbage collection Transfers control to unmanaged code
Calling a DLL Function Locates implementing DLL Loads DLL Finds function address Fuzzy name matching algorithm Pushes arguments on stack Performs marshalling Enables pre-emptive garbage collection Transfers control to unmanaged code
 A Simple Example: Message. Box using System; using System. Runtime. Interop. Services; namespace Hello { class Hello { // Use Dll. Import to import the Win 32 Message. Box function [Dll. Import("user 32. dll", Char. Set = Char. Set. Unicode)] public static extern int Message. Box(Int. Ptr h. Wnd, String text, String caption, uint type); static void Main() { // Call the Message. Box function using platform invoke Message. Box(new Int. Ptr(0), "Hello World!", "Hello Dialog", 0); } } }
A Simple Example: Message. Box using System; using System. Runtime. Interop. Services; namespace Hello { class Hello { // Use Dll. Import to import the Win 32 Message. Box function [Dll. Import("user 32. dll", Char. Set = Char. Set. Unicode)] public static extern int Message. Box(Int. Ptr h. Wnd, String text, String caption, uint type); static void Main() { // Call the Message. Box function using platform invoke Message. Box(new Int. Ptr(0), "Hello World!", "Hello Dialog", 0); } } }
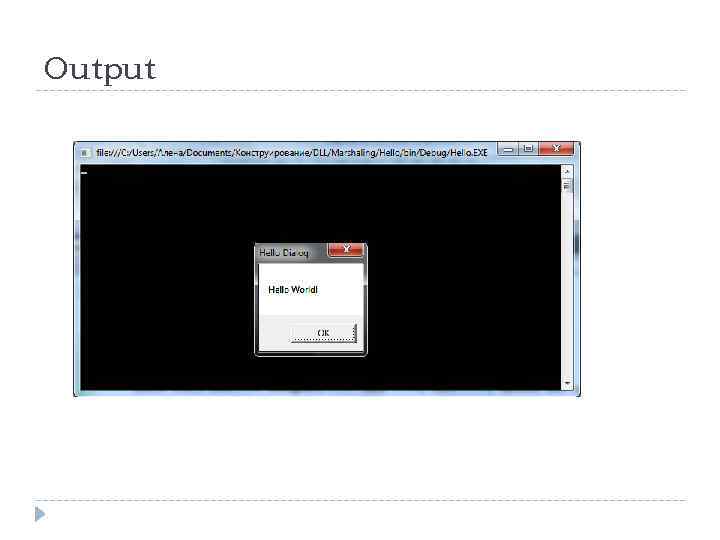 Output
Output
![The DLL Import Attribute [Dll. Import(“DLL_name”, optional _attribute_list)] public static extern return_type function_name (parameter_list); The DLL Import Attribute [Dll. Import(“DLL_name”, optional _attribute_list)] public static extern return_type function_name (parameter_list);](https://present5.com/presentation/67277600_52485834/image-12.jpg) The DLL Import Attribute [Dll. Import(“DLL_name”, optional _attribute_list)] public static extern return_type function_name (parameter_list);
The DLL Import Attribute [Dll. Import(“DLL_name”, optional _attribute_list)] public static extern return_type function_name (parameter_list);
 Optional Dll. Import. Attribute Properties Calling. Convention Indicates the calling convention of an entry point (Cdecl, Std. Call, Winapi) Char. Set Indicates how to marshal string parameters to the method and controls name mangling (Ansi, Unicode, Auto) Entry. Point Indicates the name or ordinal of the DLL entry point to be called bool Set. Last. Error Indicates whether the callee calls the Set. Last. Error Win 32 API function before returning from the attributed method
Optional Dll. Import. Attribute Properties Calling. Convention Indicates the calling convention of an entry point (Cdecl, Std. Call, Winapi) Char. Set Indicates how to marshal string parameters to the method and controls name mangling (Ansi, Unicode, Auto) Entry. Point Indicates the name or ordinal of the DLL entry point to be called bool Set. Last. Error Indicates whether the callee calls the Set. Last. Error Win 32 API function before returning from the attributed method
 Data Marshaling Marshalling is the process of transforming the memory representation of data to a data format suitable for storage or transmission.
Data Marshaling Marshalling is the process of transforming the memory representation of data to a data format suitable for storage or transmission.
 Default Marshaling For every. NET Framework type there is a default unmanaged type, which the common language runtime will use to marshal data across a managed to unmanaged function call.
Default Marshaling For every. NET Framework type there is a default unmanaged type, which the common language runtime will use to marshal data across a managed to unmanaged function call.
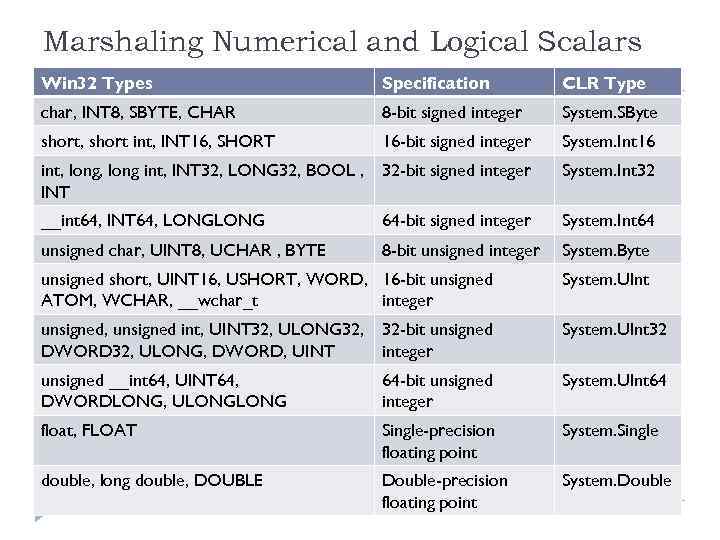 Marshaling Numerical and Logical Scalars Win 32 Types Specification CLR Type char, INT 8, SBYTE, CHAR 8 -bit signed integer System. SByte short, short int, INT 16, SHORT 16 -bit signed integer System. Int 16 int, long int, INT 32, LONG 32, BOOL , INT 32 -bit signed integer System. Int 32 __int 64, INT 64, LONG 64 -bit signed integer System. Int 64 unsigned char, UINT 8, UCHAR , BYTE 8 -bit unsigned integer System. Byte unsigned short, UINT 16, USHORT, WORD, 16 -bit unsigned ATOM, WCHAR, __wchar_t integer System. UInt unsigned, unsigned int, UINT 32, ULONG 32, 32 -bit unsigned DWORD 32, ULONG, DWORD, UINT integer System. UInt 32 unsigned __int 64, UINT 64, DWORDLONG, ULONG 64 -bit unsigned integer System. UInt 64 float, FLOAT Single-precision floating point System. Single double, long double, DOUBLE Double-precision floating point System. Double
Marshaling Numerical and Logical Scalars Win 32 Types Specification CLR Type char, INT 8, SBYTE, CHAR 8 -bit signed integer System. SByte short, short int, INT 16, SHORT 16 -bit signed integer System. Int 16 int, long int, INT 32, LONG 32, BOOL , INT 32 -bit signed integer System. Int 32 __int 64, INT 64, LONG 64 -bit signed integer System. Int 64 unsigned char, UINT 8, UCHAR , BYTE 8 -bit unsigned integer System. Byte unsigned short, UINT 16, USHORT, WORD, 16 -bit unsigned ATOM, WCHAR, __wchar_t integer System. UInt unsigned, unsigned int, UINT 32, ULONG 32, 32 -bit unsigned DWORD 32, ULONG, DWORD, UINT integer System. UInt 32 unsigned __int 64, UINT 64, DWORDLONG, ULONG 64 -bit unsigned integer System. UInt 64 float, FLOAT Single-precision floating point System. Single double, long double, DOUBLE Double-precision floating point System. Double
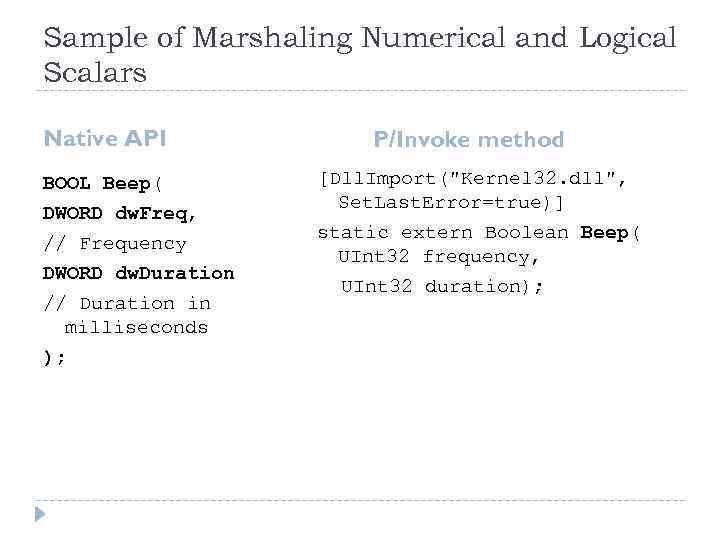 Sample of Marshaling Numerical and Logical Scalars Native API BOOL Beep( DWORD dw. Freq, // Frequency DWORD dw. Duration // Duration in milliseconds ); P/Invoke method [Dll. Import("Kernel 32. dll", Set. Last. Error=true)] static extern Boolean Beep( UInt 32 frequency, UInt 32 duration);
Sample of Marshaling Numerical and Logical Scalars Native API BOOL Beep( DWORD dw. Freq, // Frequency DWORD dw. Duration // Duration in milliseconds ); P/Invoke method [Dll. Import("Kernel 32. dll", Set. Last. Error=true)] static extern Boolean Beep( UInt 32 frequency, UInt 32 duration);
 Custom Marshaling Marshal. As attribute Indicates how to marshal the data between managed and unmanaged code. This attribute is optional, as each data type has a default marshaling behavior. This attribute is only necessary when a given type can be marshaled to multiple types void My. Method([Marshal. As(LPStr)] String s);
Custom Marshaling Marshal. As attribute Indicates how to marshal the data between managed and unmanaged code. This attribute is optional, as each data type has a default marshaling behavior. This attribute is only necessary when a given type can be marshaled to multiple types void My. Method([Marshal. As(LPStr)] String s);
 The Marshal. As attribute can be placed on • method parameters, • method return values, • fields of structs and classes.
The Marshal. As attribute can be placed on • method parameters, • method return values, • fields of structs and classes.
 The Marshal. As attribute on method return values. . . [Dll. Import("msvcrt. dll")] [return : Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. I 4)] public static extern int puts (. . .
The Marshal. As attribute on method return values. . . [Dll. Import("msvcrt. dll")] [return : Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. I 4)] public static extern int puts (. . .
 Parameters that are Pointers BOOL File. Encryption. Status( LPCTSTR lp. File. Name, // file name LPDWORD lp. Status // encryption status ); [Dll. Import("Advapi 32. dll", Char. Set=Char. Set. Auto)] static extern Boolean File. Encryption. Status( String filename, out UInt 32 status);
Parameters that are Pointers BOOL File. Encryption. Status( LPCTSTR lp. File. Name, // file name LPDWORD lp. Status // encryption status ); [Dll. Import("Advapi 32. dll", Char. Set=Char. Set. Auto)] static extern Boolean File. Encryption. Status( String filename, out UInt 32 status);
![Out and Ref and Their Associated Attributes C# Keyword Attribute (none specified) [In. Attribute] Out and Ref and Their Associated Attributes C# Keyword Attribute (none specified) [In. Attribute]](https://present5.com/presentation/67277600_52485834/image-22.jpg) Out and Ref and Their Associated Attributes C# Keyword Attribute (none specified) [In. Attribute] out [Out. Attribute] ref [In. Attribute], [Out. Attribute] [In. Attribute] tells the CLR to marshal data from the caller to the callee at the beginning of the call [Out. Attribute] tells the CLR to marshal back from the callee to the caller upon return. Both the caller and the callee can be either unmanaged or managed code
Out and Ref and Their Associated Attributes C# Keyword Attribute (none specified) [In. Attribute] out [Out. Attribute] ref [In. Attribute], [Out. Attribute] [In. Attribute] tells the CLR to marshal data from the caller to the callee at the beginning of the call [Out. Attribute] tells the CLR to marshal back from the callee to the caller upon return. Both the caller and the callee can be either unmanaged or managed code
 MARSHALLIB_API void __stdcall Func_In_Attribute(char *arg) { printf("Inside Func_In_Attribute: arg = %sn", arg); strcpy(arg, "New"); } MARSHALLIB_API void __stdcall Func_Out_Attribute(char *arg) { printf("Inside Func_Out_Attribute: arg = %sn", arg); strcpy(arg, "New"); } MARSHALLIB_API void __stdcall Func_In. Out_Attribute(char *arg) { printf("Inside Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = %sn", arg); strcpy(arg, "New"); }
MARSHALLIB_API void __stdcall Func_In_Attribute(char *arg) { printf("Inside Func_In_Attribute: arg = %sn", arg); strcpy(arg, "New"); } MARSHALLIB_API void __stdcall Func_Out_Attribute(char *arg) { printf("Inside Func_Out_Attribute: arg = %sn", arg); strcpy(arg, "New"); } MARSHALLIB_API void __stdcall Func_In. Out_Attribute(char *arg) { printf("Inside Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = %sn", arg); strcpy(arg, "New"); }
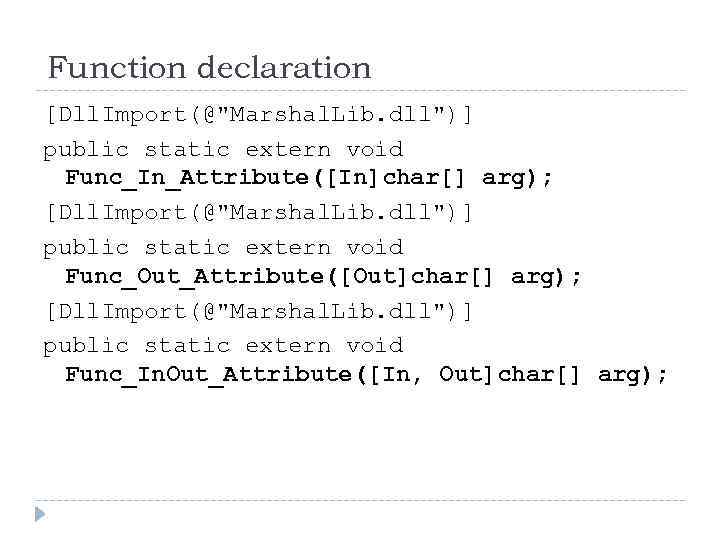 Function declaration [Dll. Import(@"Marshal. Lib. dll")] public static extern void Func_In_Attribute([In]char[] arg); [Dll. Import(@"Marshal. Lib. dll")] public static extern void Func_Out_Attribute([Out]char[] arg); [Dll. Import(@"Marshal. Lib. dll")] public static extern void Func_In. Out_Attribute([In, Out]char[] arg);
Function declaration [Dll. Import(@"Marshal. Lib. dll")] public static extern void Func_In_Attribute([In]char[] arg); [Dll. Import(@"Marshal. Lib. dll")] public static extern void Func_Out_Attribute([Out]char[] arg); [Dll. Import(@"Marshal. Lib. dll")] public static extern void Func_In. Out_Attribute([In, Out]char[] arg);
 Call function from unmanaged code with parameter old Before Func_In_Attribute: arg = Old Inside Func_In_Attribute: arg = Old After Func_In_Attribute: arg = Old Before Func_Out_Attribute: arg = Old Inside Func_Out_Attribute: arg = After Func_Out_Attribute: arg = New Before Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = Old Inside Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = Old After Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = New
Call function from unmanaged code with parameter old Before Func_In_Attribute: arg = Old Inside Func_In_Attribute: arg = Old After Func_In_Attribute: arg = Old Before Func_Out_Attribute: arg = Old Inside Func_Out_Attribute: arg = After Func_Out_Attribute: arg = New Before Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = Old Inside Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = Old After Func_In. Out_Attribute: arg = New
 PInvoke Interop Assistant Download http: //clrinterop. codeplex. com/releases/view/14120 The toolkit contains the following things: A command-line tool for managed-to-unmanaged signature conversion A command-line tool for unmanaged-to-managed signature conversion A GUI tool combining all the conversion functionality An XML database file containing Windows API signature data A help manual
PInvoke Interop Assistant Download http: //clrinterop. codeplex. com/releases/view/14120 The toolkit contains the following things: A command-line tool for managed-to-unmanaged signature conversion A command-line tool for unmanaged-to-managed signature conversion A GUI tool combining all the conversion functionality An XML database file containing Windows API signature data A help manual
 PInvoke Interop Assistant GUI
PInvoke Interop Assistant GUI
 Guidelines to wrap native methods Create an internal class named Native. Methods that wraps the platform invoke method calls. Create a public class to offer the native method functionality to. NET application.
Guidelines to wrap native methods Create an internal class named Native. Methods that wraps the platform invoke method calls. Create a public class to offer the native method functionality to. NET application.
 TASK Retrieve and output the type of the specified file. Input the file name by typing Use API WIN 32 function Get. File. Type
TASK Retrieve and output the type of the specified file. Input the file name by typing Use API WIN 32 function Get. File. Type
 DWORD WINAPI Get. File. Type( HANDLE h. File ); [Dll. Import("kernel 32. dll")] static extern File. Type Get. File. Type(Int. Ptr h. File); enum File. Type : uint { File. Type. Char = 0 x 0002, File. Type. Disk = 0 x 0001, File. Type. Pipe = 0 x 0003, File. Type. Remote = 0 x 8000, File. Type. Unknown = 0 x 0000, }
DWORD WINAPI Get. File. Type( HANDLE h. File ); [Dll. Import("kernel 32. dll")] static extern File. Type Get. File. Type(Int. Ptr h. File); enum File. Type : uint { File. Type. Char = 0 x 0002, File. Type. Disk = 0 x 0001, File. Type. Pipe = 0 x 0003, File. Type. Remote = 0 x 8000, File. Type. Unknown = 0 x 0000, }
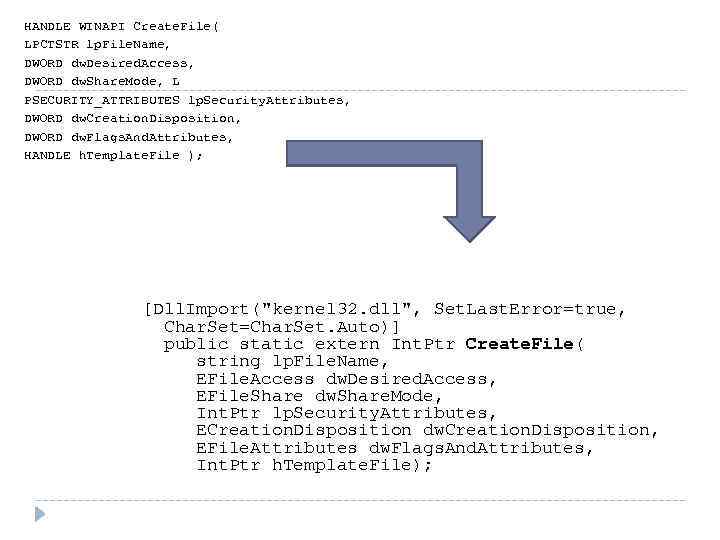 HANDLE WINAPI Create. File( LPCTSTR lp. File. Name, DWORD dw. Desired. Access, DWORD dw. Share. Mode, L PSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lp. Security. Attributes, DWORD dw. Creation. Disposition, DWORD dw. Flags. And. Attributes, HANDLE h. Template. File ); [Dll. Import("kernel 32. dll", Set. Last. Error=true, Char. Set=Char. Set. Auto)] public static extern Int. Ptr Create. File( string lp. File. Name, EFile. Access dw. Desired. Access, EFile. Share dw. Share. Mode, Int. Ptr lp. Security. Attributes, ECreation. Disposition dw. Creation. Disposition, EFile. Attributes dw. Flags. And. Attributes, Int. Ptr h. Template. File);
HANDLE WINAPI Create. File( LPCTSTR lp. File. Name, DWORD dw. Desired. Access, DWORD dw. Share. Mode, L PSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lp. Security. Attributes, DWORD dw. Creation. Disposition, DWORD dw. Flags. And. Attributes, HANDLE h. Template. File ); [Dll. Import("kernel 32. dll", Set. Last. Error=true, Char. Set=Char. Set. Auto)] public static extern Int. Ptr Create. File( string lp. File. Name, EFile. Access dw. Desired. Access, EFile. Share dw. Share. Mode, Int. Ptr lp. Security. Attributes, ECreation. Disposition dw. Creation. Disposition, EFile. Attributes dw. Flags. And. Attributes, Int. Ptr h. Template. File);
 Create an internal class named Native. Methods that wraps the platform invoke method calls. // Native. Methods. cs namespace PInvoke { internal static class Native. Methods { /// Return Type: DWORD->unsigned int ///h. File: HANDLE->void* [Dll. Import. Attribute("kernel 32. dll", Entry. Point="Get. File. Type")] public static extern uint Get. File. Type( [In. Attribute()] Safe. File. Handle h. File); [Dll. Import("Kernel 32. dll", Set. Last. Error = true, Char. Set = Char. Set. Auto)] public static extern Safe. File. Handle Create. File( string file. Name, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. U 4)] File. Access file. Access, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. U 4)] File. Share file. Share, Int. Ptr security. Attributes, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. U 4)] File. Mode creation. Disposition, int flags, Int. Ptr template);
Create an internal class named Native. Methods that wraps the platform invoke method calls. // Native. Methods. cs namespace PInvoke { internal static class Native. Methods { /// Return Type: DWORD->unsigned int ///h. File: HANDLE->void* [Dll. Import. Attribute("kernel 32. dll", Entry. Point="Get. File. Type")] public static extern uint Get. File. Type( [In. Attribute()] Safe. File. Handle h. File); [Dll. Import("Kernel 32. dll", Set. Last. Error = true, Char. Set = Char. Set. Auto)] public static extern Safe. File. Handle Create. File( string file. Name, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. U 4)] File. Access file. Access, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. U 4)] File. Share file. Share, Int. Ptr security. Attributes, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. U 4)] File. Mode creation. Disposition, int flags, Int. Ptr template);
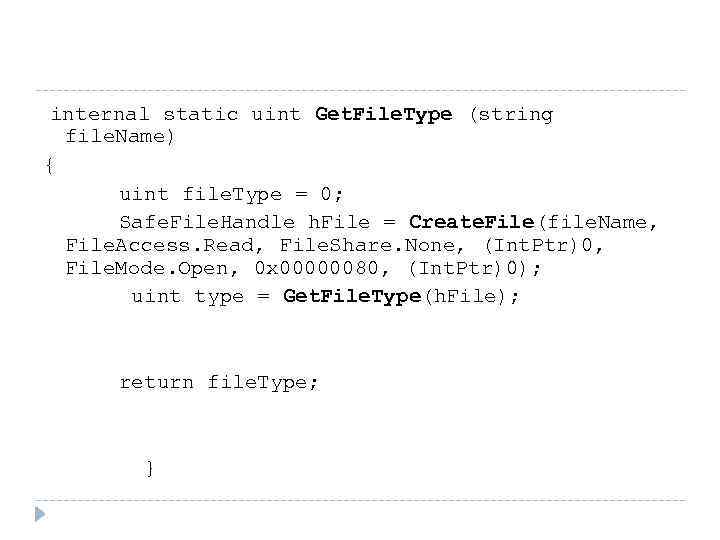 internal static uint Get. File. Type (string file. Name) { uint file. Type = 0; Safe. File. Handle h. File = Create. File(file. Name, File. Access. Read, File. Share. None, (Int. Ptr)0, File. Mode. Open, 0 x 00000080, (Int. Ptr)0); uint type = Get. File. Type(h. File); return file. Type; }
internal static uint Get. File. Type (string file. Name) { uint file. Type = 0; Safe. File. Handle h. File = Create. File(file. Name, File. Access. Read, File. Share. None, (Int. Ptr)0, File. Mode. Open, 0 x 00000080, (Int. Ptr)0); uint type = Get. File. Type(h. File); return file. Type; }
 Create a public class to offer the native method functionality to. NET application. class File. Utility { public static string Get. File. Type (string file. Name){ string file. Type = ""; uint type = Native. Methods. Get. File. Type(file. Name); switch (type){ case 0 x 0002: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Char. To. String(); break; case 0 x 0001: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Disk. To. String(); break; case 0 x 0003: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Pipe. To. String(); break; case 0 x 8000: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Remote. To. String(); break; case 0 x 0000: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Unknown. To. String(); break; } return file. Type;
Create a public class to offer the native method functionality to. NET application. class File. Utility { public static string Get. File. Type (string file. Name){ string file. Type = ""; uint type = Native. Methods. Get. File. Type(file. Name); switch (type){ case 0 x 0002: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Char. To. String(); break; case 0 x 0001: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Disk. To. String(); break; case 0 x 0003: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Pipe. To. String(); break; case 0 x 8000: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Remote. To. String(); break; case 0 x 0000: file. Type = Native. Methods. File. Type. Unknown. To. String(); break; } return file. Type;
![static void Main(string[] args) { Console. Write. Line (File. Utility. Get. File. Type( static void Main(string[] args) { Console. Write. Line (File. Utility. Get. File. Type(](https://present5.com/presentation/67277600_52485834/image-35.jpg) static void Main(string[] args) { Console. Write. Line (File. Utility. Get. File. Type("C: \Temp\install. log")); }
static void Main(string[] args) { Console. Write. Line (File. Utility. Get. File. Type("C: \Temp\install. log")); }

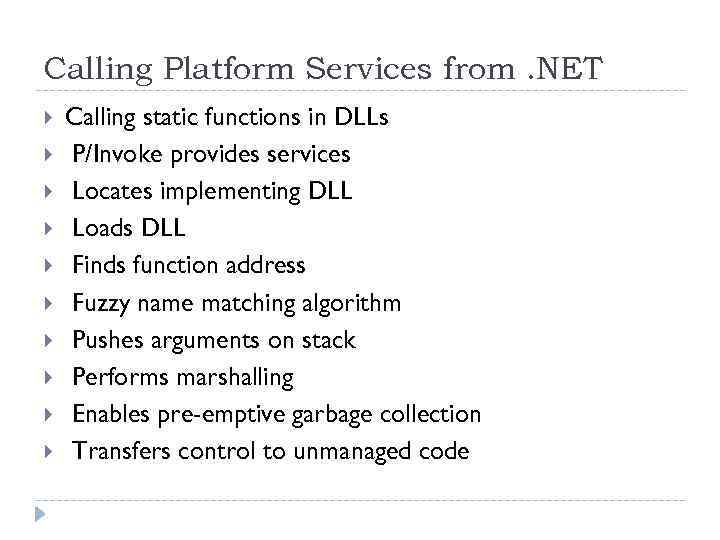 Calling Platform Services from. NET Calling static functions in DLLs P/Invoke provides services Locates implementing DLL Loads DLL Finds function address Fuzzy name matching algorithm Pushes arguments on stack Performs marshalling Enables pre-emptive garbage collection Transfers control to unmanaged code
Calling Platform Services from. NET Calling static functions in DLLs P/Invoke provides services Locates implementing DLL Loads DLL Finds function address Fuzzy name matching algorithm Pushes arguments on stack Performs marshalling Enables pre-emptive garbage collection Transfers control to unmanaged code
 Showcase for the Standard Marshaller Given a method in some DLL int Some. Func( int sel, void* buf, int size); Standard declaration may need special decoding [Dll. Import("some. dll")] static extern int Some. Func(int sel, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. LPArray)] byte[] buf, int size); May use taylored versions [Dll. Import("some. dll", Entry. Point="Some. Func")] static extern int Some. Func_String(int sel, String. Builder sb, int size); [Dll. Import("some. dll", Entry. Point="Some. Func")] static extern int Some. Func_Int(int sel, ref int i, int size);
Showcase for the Standard Marshaller Given a method in some DLL int Some. Func( int sel, void* buf, int size); Standard declaration may need special decoding [Dll. Import("some. dll")] static extern int Some. Func(int sel, [Marshal. As(Unmanaged. Type. LPArray)] byte[] buf, int size); May use taylored versions [Dll. Import("some. dll", Entry. Point="Some. Func")] static extern int Some. Func_String(int sel, String. Builder sb, int size); [Dll. Import("some. dll", Entry. Point="Some. Func")] static extern int Some. Func_Int(int sel, ref int i, int size);


