 PLASMAS • A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas of charged and neutral particles which exhibits collective behavior. • A fundamental characteristic of plasmas is its ability to shield out electric potential that are applied to it (Debye shielding) F. F. Chen, Introduction to Plasma Physics R. O. Dendy, Plasma Dynamics, 1990 C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
PLASMAS • A plasma is a quasi-neutral gas of charged and neutral particles which exhibits collective behavior. • A fundamental characteristic of plasmas is its ability to shield out electric potential that are applied to it (Debye shielding) F. F. Chen, Introduction to Plasma Physics R. O. Dendy, Plasma Dynamics, 1990 C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
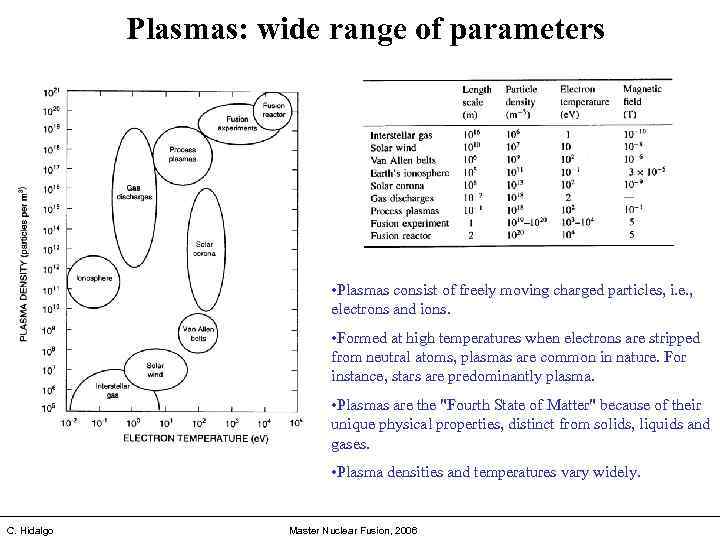 Plasmas: wide range of parameters • Plasmas consist of freely moving charged particles, i. e. , electrons and ions. • Formed at high temperatures when electrons are stripped from neutral atoms, plasmas are common in nature. For instance, stars are predominantly plasma. • Plasmas are the "Fourth State of Matter" because of their unique physical properties, distinct from solids, liquids and gases. • Plasma densities and temperatures vary widely. C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
Plasmas: wide range of parameters • Plasmas consist of freely moving charged particles, i. e. , electrons and ions. • Formed at high temperatures when electrons are stripped from neutral atoms, plasmas are common in nature. For instance, stars are predominantly plasma. • Plasmas are the "Fourth State of Matter" because of their unique physical properties, distinct from solids, liquids and gases. • Plasma densities and temperatures vary widely. C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
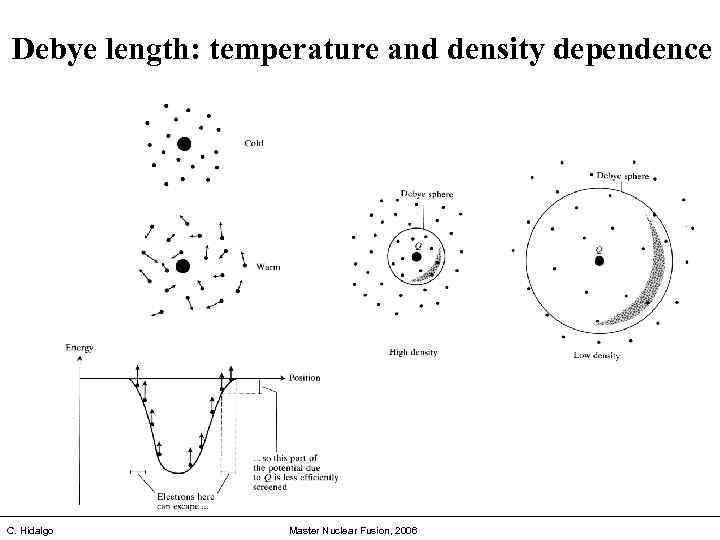 Debye length: temperature and density dependence C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
Debye length: temperature and density dependence C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
 Quasi-neutrality: Debye length: Balance between, thermal particle energy and electrostatic energy We can find a self-consistent solution for the electrostatic potencial f, which arises from a test charge Q and the response of the plasma to the presence of Q. Using Boltzmann´s equation, we can describe how the potencial f that is produced by Q tends to drive away the ions and attract the electrons. Assume the ions are in uniform density (ni = n 0) and there is a small perturbation in the electron density ne or potential F. Since electrons are in Boltzmann distribution, the electron density ne becomes When the potential energy of the electron is smaller than thermal energy (k. Te), we can use the following approximation: It follows that, for example, the Debye length takes the value of 7 x 10 -5 m for a plasma of 1 ke. V with n = 1019 m-3 C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
Quasi-neutrality: Debye length: Balance between, thermal particle energy and electrostatic energy We can find a self-consistent solution for the electrostatic potencial f, which arises from a test charge Q and the response of the plasma to the presence of Q. Using Boltzmann´s equation, we can describe how the potencial f that is produced by Q tends to drive away the ions and attract the electrons. Assume the ions are in uniform density (ni = n 0) and there is a small perturbation in the electron density ne or potential F. Since electrons are in Boltzmann distribution, the electron density ne becomes When the potential energy of the electron is smaller than thermal energy (k. Te), we can use the following approximation: It follows that, for example, the Debye length takes the value of 7 x 10 -5 m for a plasma of 1 ke. V with n = 1019 m-3 C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
 Plasma Parameter When the plasma size is a and a >>l. D is satisfied, then the plasma is considered quasi-neutral. If a < l. D, then individual particle is not shielded electrostatically and this state is no longer plasma but an assembly of independent charged particles. The number of electrons included in the sphere of radius l. D is called plasma parameter and is given by, The ratio of electron thermal energy (k. Te) and Coulomb energy between electrons, Ecoulomb =e 2/4 pe 0 d (d ≈ n-1/3 ), is given by When the plasma parameter is >> 1 means that the Coulomb energy is smaller than thermal energy. C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006
Plasma Parameter When the plasma size is a and a >>l. D is satisfied, then the plasma is considered quasi-neutral. If a < l. D, then individual particle is not shielded electrostatically and this state is no longer plasma but an assembly of independent charged particles. The number of electrons included in the sphere of radius l. D is called plasma parameter and is given by, The ratio of electron thermal energy (k. Te) and Coulomb energy between electrons, Ecoulomb =e 2/4 pe 0 d (d ≈ n-1/3 ), is given by When the plasma parameter is >> 1 means that the Coulomb energy is smaller than thermal energy. C. Hidalgo Master Nuclear Fusion, 2006