6434ba01432306affbbc317149aa418d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Plasma Physics High Energy Density Physics Experiments with Intense Heavy Ion Beams at GSI D. Varentsov, A. Adonin, V. E. Fortov, V. K. Gryaznov, D. H. H. Hoffmann, M. Kulish, I. V. Lomonosov, V. Mintsev, P. Ni, D. Nikolaev, N. Shilkin, A. Shutov, N. A. Tahir, V. Ternovoi, S. Udrea Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforshung (GSI) – Darmstadt, Germany Institute for Problems in Chemical Physics (IPCP) RAS – Chernogolovka, Russia Technische Universität (TU) – Darmstadt, Germany Universität Frankfurt (UF) - Germany on behalf of the HEDge. HOB High Energy Density Matter Generated by Heavy Ion Beams collaboration Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics High Energy Density Physics Experiments with Intense Heavy Ion Beams at GSI D. Varentsov, A. Adonin, V. E. Fortov, V. K. Gryaznov, D. H. H. Hoffmann, M. Kulish, I. V. Lomonosov, V. Mintsev, P. Ni, D. Nikolaev, N. Shilkin, A. Shutov, N. A. Tahir, V. Ternovoi, S. Udrea Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforshung (GSI) – Darmstadt, Germany Institute for Problems in Chemical Physics (IPCP) RAS – Chernogolovka, Russia Technische Universität (TU) – Darmstadt, Germany Universität Frankfurt (UF) - Germany on behalf of the HEDge. HOB High Energy Density Matter Generated by Heavy Ion Beams collaboration Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Intense heavy ion beam is an excellent tool to generate large-volume HED samples Plasma Physics High Energy Density Matter (Warm Dense Matter) T ~ 2, 000 – 200, 000 K r ~ solid density P ~ kbar, Mbar Intense heavy ion beams large volume of sample (mm 3) fairly uniform physical conditions high entropy @ high densities efficient target diagnostics Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Intense heavy ion beam is an excellent tool to generate large-volume HED samples Plasma Physics High Energy Density Matter (Warm Dense Matter) T ~ 2, 000 – 200, 000 K r ~ solid density P ~ kbar, Mbar Intense heavy ion beams large volume of sample (mm 3) fairly uniform physical conditions high entropy @ high densities efficient target diagnostics Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
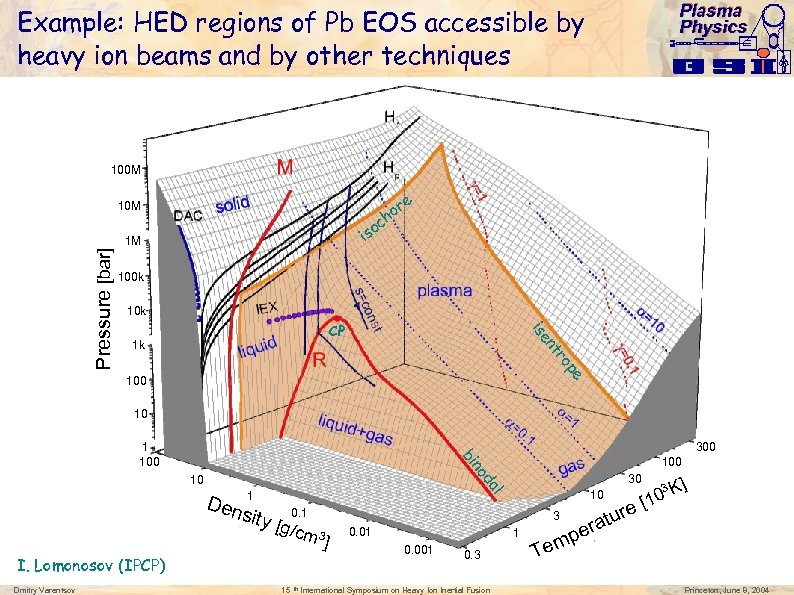 Plasma Physics Example: HED regions of Pb EOS accessible by heavy ion beams and by other techniques 100 M 10 M c iso 100 k 10 k CP nt 1 k ise pe ro Pressure [bar] 1 M e r ho 100 10 300 bi 1 100 no 1 sity 10 l Den 30 da 10 0. 1 [g/cm 3 ] I. Lomonosov (IPCP) Dmitry Varentsov 100 15 th 0. 01 1 0. 001 0. 3 International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion re ratu e 3 3 ] 0 K [1 p Tem Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics Example: HED regions of Pb EOS accessible by heavy ion beams and by other techniques 100 M 10 M c iso 100 k 10 k CP nt 1 k ise pe ro Pressure [bar] 1 M e r ho 100 10 300 bi 1 100 no 1 sity 10 l Den 30 da 10 0. 1 [g/cm 3 ] I. Lomonosov (IPCP) Dmitry Varentsov 100 15 th 0. 01 1 0. 001 0. 3 International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion re ratu e 3 3 ] 0 K [1 p Tem Princeton, June 8, 2004
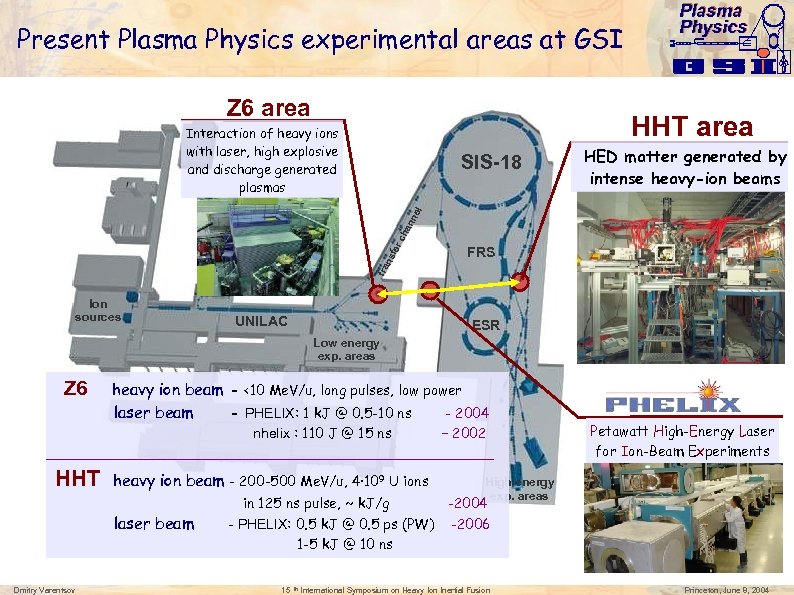 Present Plasma Physics experimental areas at GSI Z 6 area Plasma Physics HHT area Interaction of heavy ions with laser, high explosive and discharge generated plasmas HED matter generated by intense heavy-ion beams FRS tra ns fer ch an ne l SIS-18 Ion sources UNILAC ESR Low energy exp. areas Z 6 heavy ion beam - <10 Me. V/u, long pulses, low power laser beam - PHELIX: 1 k. J @ 0. 5 -10 ns - 2004 nhelix : 110 J @ 15 ns – 2002 __________________________ HHT heavy ion beam - 200 -500 Me. V/u, 4· 109 U ions laser beam Dmitry Varentsov in 125 ns pulse, ~ k. J/g - PHELIX: 0. 5 k. J @ 0. 5 ps (PW) 1 -5 k. J @ 10 ns 15 th Petawatt High-Energy Laser for Ion-Beam Experiments High energy exp. areas -2004 -2006 International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Present Plasma Physics experimental areas at GSI Z 6 area Plasma Physics HHT area Interaction of heavy ions with laser, high explosive and discharge generated plasmas HED matter generated by intense heavy-ion beams FRS tra ns fer ch an ne l SIS-18 Ion sources UNILAC ESR Low energy exp. areas Z 6 heavy ion beam - <10 Me. V/u, long pulses, low power laser beam - PHELIX: 1 k. J @ 0. 5 -10 ns - 2004 nhelix : 110 J @ 15 ns – 2002 __________________________ HHT heavy ion beam - 200 -500 Me. V/u, 4· 109 U ions laser beam Dmitry Varentsov in 125 ns pulse, ~ k. J/g - PHELIX: 0. 5 k. J @ 0. 5 ps (PW) 1 -5 k. J @ 10 ns 15 th Petawatt High-Energy Laser for Ion-Beam Experiments High energy exp. areas -2004 -2006 International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 SIS-100 will provide 3, 000 times the beam power and 600 times higher energy density in the target Plasma Physics SIS-100/300 SIS-18 HESR UNILAC PP Super FRS CR NESR Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
SIS-100 will provide 3, 000 times the beam power and 600 times higher energy density in the target Plasma Physics SIS-100/300 SIS-18 HESR UNILAC PP Super FRS CR NESR Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 The HEDge. HOB collaboration: HED states in matter generated by intense heavy ion beams Plasma Physics HEDge. HOB Collaboration High Energy Density Matter Generated by Heavy Ion Beams Studies on High-Energy-Density Matter with Intense Heavy Ion and Laser Beams at FAIR Physics program: fundamental properties of matter under extreme conditions (plasma physics, atomic physics, astrophysics, planetary sciences, material research) Equation-of-state of HED matter basic thermodynamic properties of matter in unexplored regions of the phase diagram Phase transitions and exotic states of matter metal-to-insulator or plasma phase transitions, hydrogen metallization problem, anomalies in non-ideal plasmas Transport and radiation properties of HED matter electrical and thermal conductivity, opacity, etc. Interaction of heavy ion and laser beams with HED matter anomalous temperature and density dependence of the stopping and charge-exchange cross sections in plasmas Quantum-mechanical effects in HED matter Inertial Fusion Energy research Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
The HEDge. HOB collaboration: HED states in matter generated by intense heavy ion beams Plasma Physics HEDge. HOB Collaboration High Energy Density Matter Generated by Heavy Ion Beams Studies on High-Energy-Density Matter with Intense Heavy Ion and Laser Beams at FAIR Physics program: fundamental properties of matter under extreme conditions (plasma physics, atomic physics, astrophysics, planetary sciences, material research) Equation-of-state of HED matter basic thermodynamic properties of matter in unexplored regions of the phase diagram Phase transitions and exotic states of matter metal-to-insulator or plasma phase transitions, hydrogen metallization problem, anomalies in non-ideal plasmas Transport and radiation properties of HED matter electrical and thermal conductivity, opacity, etc. Interaction of heavy ion and laser beams with HED matter anomalous temperature and density dependence of the stopping and charge-exchange cross sections in plasmas Quantum-mechanical effects in HED matter Inertial Fusion Energy research Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Proposed HEDge. HOB experiments Plasma Physics HIHEX: Heavy Ion Heating and Expansion uniform quasi-isochoric heating of a large-volume dense target optional isentropic expansion in plane or cylindrical 1 D geometries numerous high-entropy HED states EOS, conductivity and radiation properties, non-ideal plasmas, critical point and warm dense matter regions for various materials LAPLAS: Laboratory Planetary Sciences hollow (ring-shaped) beam heats a heavy tamper shell cylindrical implosion and low-entropy compression of the sample Mbar pressures @ moderate temperatures interior of Jupiter and Saturn, hydrogen metallization Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Proposed HEDge. HOB experiments Plasma Physics HIHEX: Heavy Ion Heating and Expansion uniform quasi-isochoric heating of a large-volume dense target optional isentropic expansion in plane or cylindrical 1 D geometries numerous high-entropy HED states EOS, conductivity and radiation properties, non-ideal plasmas, critical point and warm dense matter regions for various materials LAPLAS: Laboratory Planetary Sciences hollow (ring-shaped) beam heats a heavy tamper shell cylindrical implosion and low-entropy compression of the sample Mbar pressures @ moderate temperatures interior of Jupiter and Saturn, hydrogen metallization Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Plasma Physics Target diagnostic instruments and methods for the HEDge. HOB experiments Diagnostics with petawatt laser ◊ ◊ ◊ X-ray backlighting laser-generated proton radiography Thomson scattering distribution of target density with high spatial and temporal resolution, target temperature, opacity Diagnostics by heavy ion beams ◊ ◊ energy loss and charge state dynamics radiography by heavy ions stopping properties, evolution of target density, etc. Spectroscopic methods ◊ ◊ fast multi-channel pyrometry emission spectroscopy time-resolved temperature, atomic states Laser interferometry ◊ ◊ displacement interferometry laser-Doppler (VISAR) pressure, mass and shock velocity Electrical conductivity measurements Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion S. Udrea, 12: 05 Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics Target diagnostic instruments and methods for the HEDge. HOB experiments Diagnostics with petawatt laser ◊ ◊ ◊ X-ray backlighting laser-generated proton radiography Thomson scattering distribution of target density with high spatial and temporal resolution, target temperature, opacity Diagnostics by heavy ion beams ◊ ◊ energy loss and charge state dynamics radiography by heavy ions stopping properties, evolution of target density, etc. Spectroscopic methods ◊ ◊ fast multi-channel pyrometry emission spectroscopy time-resolved temperature, atomic states Laser interferometry ◊ ◊ displacement interferometry laser-Doppler (VISAR) pressure, mass and shock velocity Electrical conductivity measurements Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion S. Udrea, 12: 05 Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Recent (December 2003) beamtime experiment on heavy-ion-beam generated HED matter at GSI Plasma Physics Goals of the experiment (12 -17. 12. 2003): commissioning of a fast multi-channel radiation pyrometer improvement of transport/focusing and diagnostics of full-intensity uranium beams experimental test of a new “plane-HIHEX” target design and several ideas on target diagnostics (eventually) new data on thermophysical properties of lead in HED states near the critical point Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Recent (December 2003) beamtime experiment on heavy-ion-beam generated HED matter at GSI Plasma Physics Goals of the experiment (12 -17. 12. 2003): commissioning of a fast multi-channel radiation pyrometer improvement of transport/focusing and diagnostics of full-intensity uranium beams experimental test of a new “plane-HIHEX” target design and several ideas on target diagnostics (eventually) new data on thermophysical properties of lead in HED states near the critical point Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
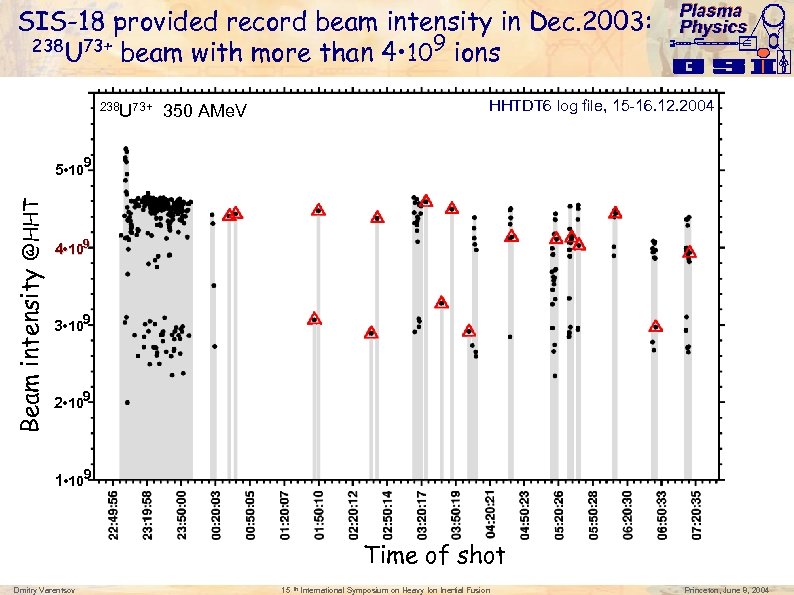 SIS-18 provided record beam intensity in Dec. 2003: 238 73+ U beam with more than 4 • 109 ions 238 U 73+ Plasma Physics HHTDT 6 log file, 15 -16. 12. 2004 350 AMe. V Beam intensity @HHT 5 • 109 4 • 109 3 • 109 2 • 109 1 • 109 Time of shot Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
SIS-18 provided record beam intensity in Dec. 2003: 238 73+ U beam with more than 4 • 109 ions 238 U 73+ Plasma Physics HHTDT 6 log file, 15 -16. 12. 2004 350 AMe. V Beam intensity @HHT 5 • 109 4 • 109 3 • 109 2 • 109 1 • 109 Time of shot Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
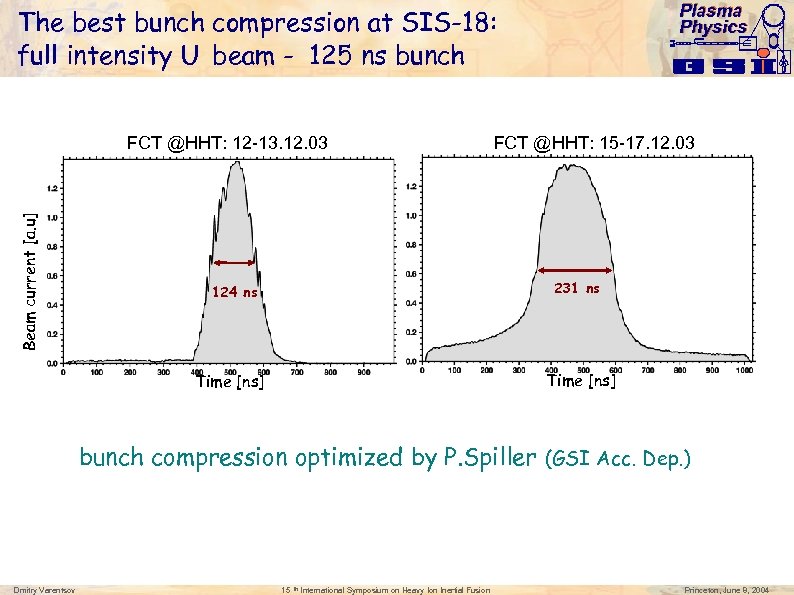 Plasma Physics The best bunch compression at SIS-18: full intensity U beam - 125 ns bunch Beam current [a. u] FCT @HHT: 12 -13. 12. 03 FCT @HHT: 15 -17. 12. 03 231 ns 124 ns Time [ns] bunch compression optimized by P. Spiller (GSI Acc. Dep. ) Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics The best bunch compression at SIS-18: full intensity U beam - 125 ns bunch Beam current [a. u] FCT @HHT: 12 -13. 12. 03 FCT @HHT: 15 -17. 12. 03 231 ns 124 ns Time [ns] bunch compression optimized by P. Spiller (GSI Acc. Dep. ) Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
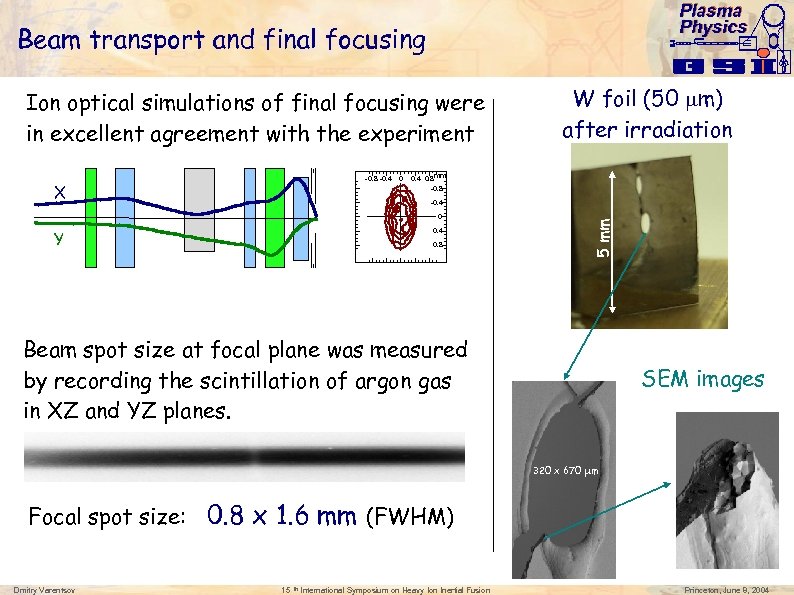 Plasma Physics Beam transport and final focusing Ion optical simulations of final focusing were in excellent agreement with the experiment -0. 8 -0. 4 X 0 W foil (50 m) after irradiation 0. 4 0. 8 mm -0. 8 -0. 4 5 mm 0 0. 4 Y 0. 8 Beam spot size at focal plane was measured by recording the scintillation of argon gas in XZ and YZ planes. SEM images 320 x 670 m Focal spot size: 0. 8 x 1. 6 mm (FWHM) Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics Beam transport and final focusing Ion optical simulations of final focusing were in excellent agreement with the experiment -0. 8 -0. 4 X 0 W foil (50 m) after irradiation 0. 4 0. 8 mm -0. 8 -0. 4 5 mm 0 0. 4 Y 0. 8 Beam spot size at focal plane was measured by recording the scintillation of argon gas in XZ and YZ planes. SEM images 320 x 670 m Focal spot size: 0. 8 x 1. 6 mm (FWHM) Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
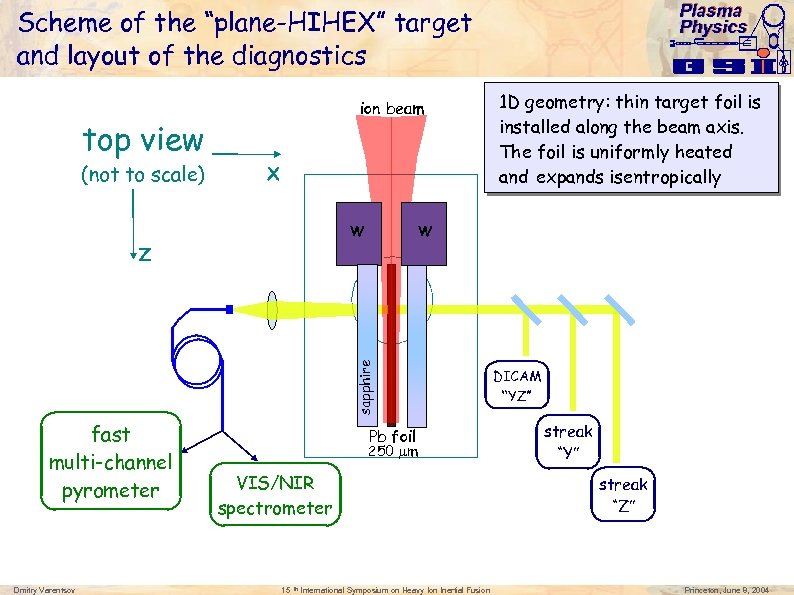 Plasma Physics Scheme of the “plane-HIHEX” target and layout of the diagnostics ion beam top view (not to scale) X 1 D geometry: thin target foil is installed along the beam axis. t The foil is uniformly heated and expands isentropically W W sapphire Z fast multi-channel pyrometer Dmitry Varentsov Pb foil 250 m VIS/NIR spectrometer 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion DICAM “YZ” streak “Y” streak “Z” Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics Scheme of the “plane-HIHEX” target and layout of the diagnostics ion beam top view (not to scale) X 1 D geometry: thin target foil is installed along the beam axis. t The foil is uniformly heated and expands isentropically W W sapphire Z fast multi-channel pyrometer Dmitry Varentsov Pb foil 250 m VIS/NIR spectrometer 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion DICAM “YZ” streak “Y” streak “Z” Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Experimental setup at the HHT cave Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Plasma Physics Princeton, June 8, 2004
Experimental setup at the HHT cave Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Plasma Physics Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Photos of targets and target chamber Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Plasma Physics Princeton, June 8, 2004
Photos of targets and target chamber Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Plasma Physics Princeton, June 8, 2004
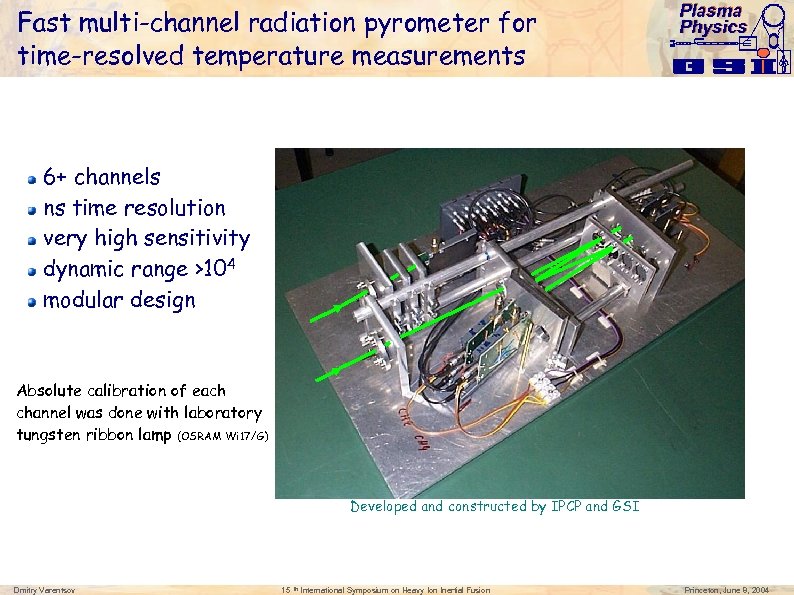 Fast multi-channel radiation pyrometer for time-resolved temperature measurements Plasma Physics 6+ channels ns time resolution very high sensitivity dynamic range >104 modular design Absolute calibration of each channel was done with laboratory tungsten ribbon lamp (OSRAM Wi 17/G) Developed and constructed by IPCP and GSI Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Fast multi-channel radiation pyrometer for time-resolved temperature measurements Plasma Physics 6+ channels ns time resolution very high sensitivity dynamic range >104 modular design Absolute calibration of each channel was done with laboratory tungsten ribbon lamp (OSRAM Wi 17/G) Developed and constructed by IPCP and GSI Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
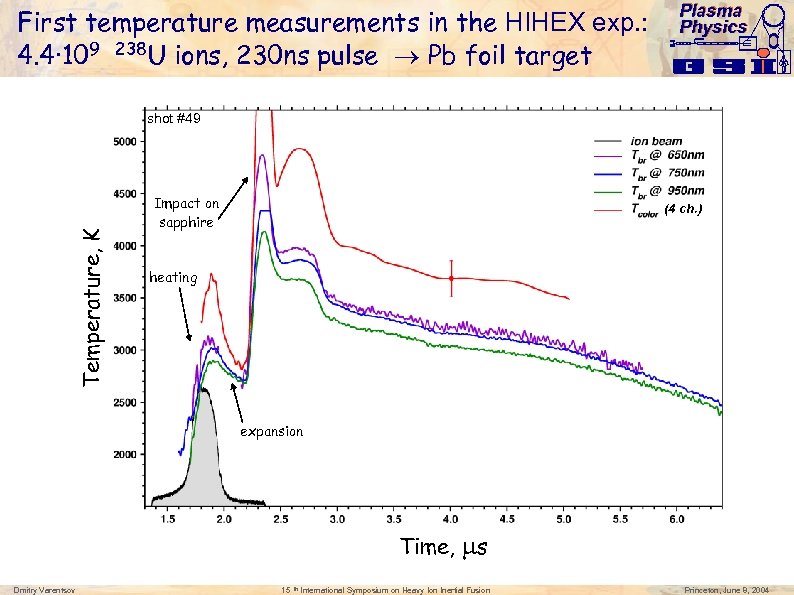 First temperature measurements in the HIHEX exp. : 4. 4· 109 238 U ions, 230 ns pulse Pb foil target Plasma Physics Temperature, K shot #49 Impact on sapphire (4 ch. ) heating expansion Time, s Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
First temperature measurements in the HIHEX exp. : 4. 4· 109 238 U ions, 230 ns pulse Pb foil target Plasma Physics Temperature, K shot #49 Impact on sapphire (4 ch. ) heating expansion Time, s Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Plasma Physics Outlook Three new beamtime experiments are scheduled at HHT for the rest of 2004. Developments for the experiment this year: high-rigidity upgrade of the beamline (18 Tm) improved light collection and data acquisition modules for the pyrometer better beam-target alignment and target precision displacement interferometer (pressure diagnostics) backlighting in VIS improved ion-beam diagnostics & spectroscopy different target materials (Pb, Cu, Fe, Al, Sn) + large work on preparing the HEDge. HOB experiments! Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics Outlook Three new beamtime experiments are scheduled at HHT for the rest of 2004. Developments for the experiment this year: high-rigidity upgrade of the beamline (18 Tm) improved light collection and data acquisition modules for the pyrometer better beam-target alignment and target precision displacement interferometer (pressure diagnostics) backlighting in VIS improved ion-beam diagnostics & spectroscopy different target materials (Pb, Cu, Fe, Al, Sn) + large work on preparing the HEDge. HOB experiments! Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 The HEDge. HOB collaborators Plasma Physics V. M. Adamyan, A. Adonin, J. Alcober Auban, I. V. Aleksandrova, E. M. Apfelbaum, P. Audebert, M. M. Basko, D. Batani, J. F. Benage, S. Borneis, R. Bock, A. Blazevic, E. Brambrink, D. Callahan, A. Caruso, C. Constantin, O. D. Cortazar, T. Cowan, R. Davidson, C. Deutsch, E. Dewald, S. Dudin, V. P. Efremov, A. Ya. Faenov, A. Fertman, V. Fisher, C. Fortmann, V. E. Fortov, A. Friedman, J. -C. Gauthier, M. Geissel, D. O. Gericke, S. H. Glenzer, A. A. Golubev, N. Grandjouan, G. Grubert, V. K. Gryaznov, D. Habs, M. Hegelich, D. H. H. Hoffmann, I. Iosilevski, J. Jacoby, K. Jungwirth, H. Juranek, V. Kain, M. Kalal, Yu. G. Kalinin, G. I. Kanel, K. V. Khishchenko, A. Kietzmann, Ch. J. Kim, V. V. Kim, A. S. Kingsep, H. J. Kong, E. Koresheva, S. Kuhlbrodt, T. Kuehl, P. R. Levashov, R. Li, Ch. Lim, L. S. Lisitsa, G. Logan, I. V. Lomonosov, J. J. Lopez-Cela, Q. H. Lou, A. I. Magunov, A. V. Matveichev, G. Maynard, T. Mehlhorn, V. V. Milyavskii, V. B. Mintsev, I. V. Morozov, M. S. Murillo, N. Nettelmann, R. Neumann, P. Ni, C. Niemann, D. N. Nikolaev, G. E. Norman, M. Ogawa, B. Omar, I. E. Osipov, A. V. Ostrik, T. A. Pikuz, A. R. Piriz, R. F. Portugues, V. I. Postnov, S. V. Razorenov, R. Redmer, H. Reinholz, D. Riley, G. Roepke, F. B. Rosmey, O. Rosmej, M. Roth, I. Roudskoy, H. Ruhl, J. C. Sanchez-Duque, R. Sauerbrey, G. Schaumann, M. Schlanges, G. Schurtz, V. Schwarz, B. Yu. Sharkov, N. Shilkin, A. V. Shutov, I. Yu. Skobelev, R. Schmidt, V. P. Smirnov, R. Stamm, A. Starobinets, H. Suk, V. G. Sultanov, M. Tabak, N. A. Tahir, A. Tauschwitz, M. Temporal, V. Ya. Ternovoi, V. Tiele, V. Tikhonchuk, I. M. Tkachenko Gorski, C. Toepffer, C. Trautmann, K. Tsigutkin, V. Turtikov, S. Udrea, J. Ullschmied, A. V. Utkin, D. Varentsov, J. Vorberger, H. Wahl, K. Weyrich, P. Wiewior, J. G. Wouchuk, Yu. Zaporojets, M. V. Zhernokletov, J. Q. Zhu, G. Zwicknagel 138 scientists Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
The HEDge. HOB collaborators Plasma Physics V. M. Adamyan, A. Adonin, J. Alcober Auban, I. V. Aleksandrova, E. M. Apfelbaum, P. Audebert, M. M. Basko, D. Batani, J. F. Benage, S. Borneis, R. Bock, A. Blazevic, E. Brambrink, D. Callahan, A. Caruso, C. Constantin, O. D. Cortazar, T. Cowan, R. Davidson, C. Deutsch, E. Dewald, S. Dudin, V. P. Efremov, A. Ya. Faenov, A. Fertman, V. Fisher, C. Fortmann, V. E. Fortov, A. Friedman, J. -C. Gauthier, M. Geissel, D. O. Gericke, S. H. Glenzer, A. A. Golubev, N. Grandjouan, G. Grubert, V. K. Gryaznov, D. Habs, M. Hegelich, D. H. H. Hoffmann, I. Iosilevski, J. Jacoby, K. Jungwirth, H. Juranek, V. Kain, M. Kalal, Yu. G. Kalinin, G. I. Kanel, K. V. Khishchenko, A. Kietzmann, Ch. J. Kim, V. V. Kim, A. S. Kingsep, H. J. Kong, E. Koresheva, S. Kuhlbrodt, T. Kuehl, P. R. Levashov, R. Li, Ch. Lim, L. S. Lisitsa, G. Logan, I. V. Lomonosov, J. J. Lopez-Cela, Q. H. Lou, A. I. Magunov, A. V. Matveichev, G. Maynard, T. Mehlhorn, V. V. Milyavskii, V. B. Mintsev, I. V. Morozov, M. S. Murillo, N. Nettelmann, R. Neumann, P. Ni, C. Niemann, D. N. Nikolaev, G. E. Norman, M. Ogawa, B. Omar, I. E. Osipov, A. V. Ostrik, T. A. Pikuz, A. R. Piriz, R. F. Portugues, V. I. Postnov, S. V. Razorenov, R. Redmer, H. Reinholz, D. Riley, G. Roepke, F. B. Rosmey, O. Rosmej, M. Roth, I. Roudskoy, H. Ruhl, J. C. Sanchez-Duque, R. Sauerbrey, G. Schaumann, M. Schlanges, G. Schurtz, V. Schwarz, B. Yu. Sharkov, N. Shilkin, A. V. Shutov, I. Yu. Skobelev, R. Schmidt, V. P. Smirnov, R. Stamm, A. Starobinets, H. Suk, V. G. Sultanov, M. Tabak, N. A. Tahir, A. Tauschwitz, M. Temporal, V. Ya. Ternovoi, V. Tiele, V. Tikhonchuk, I. M. Tkachenko Gorski, C. Toepffer, C. Trautmann, K. Tsigutkin, V. Turtikov, S. Udrea, J. Ullschmied, A. V. Utkin, D. Varentsov, J. Vorberger, H. Wahl, K. Weyrich, P. Wiewior, J. G. Wouchuk, Yu. Zaporojets, M. V. Zhernokletov, J. Q. Zhu, G. Zwicknagel 138 scientists Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
 Plasma Physics The HEDge. HOB Collaboration Italy Germany Technische Universität Darmstadt Johann-Wolfgang-Goethe Universität Frankfurt Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI), Darmstadt Universität Rostock Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald Universität Erlangen Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) München Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena Russia Institute of Problems of Chemical Physcics (IPCP), Chernogolovka Institute of High Energy Density (IHED), Moscow Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Moscow Nuclear Fusion Institute, RRC "Kurchatov Institute", Moscow All-Russian Institute of Experimental Physics, Sarov MISDC of VNIIFTRI, Mendeleevo Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) Lebedev Physics Institute, Moscow France LPGP, Universite Paris Sud, Orsay Cedex LULI, Ecole Polytechnique, Cedex Universite de Provence, Marseille Universite de Bordeaux, Talence Cedex Spain Universidad de Castilla La Mancha, Ciudad Real Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Valencia Ukraine Odessa National University ENEA, Frascati University of Milano Czech Republic Institute of Plasma Physics, PALS Recearch Center, Prague Switzerland CERN, Geneva Israel Weizmann Institute of Sciences, Rehovot Ireland Queens University of Belfast USA Princeton University, Princeton Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LNBL), Berkeley Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Livermore Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), Los Alamos University of Nevada, Reno Japan Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo S. Korea KAIST, Daejon Center for Advanced Accelerators (KERI) Korea Atomic Energy Research Center (KAERI) China Institute for Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS, Shanghai 40 institutions, 14 countries Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004
Plasma Physics The HEDge. HOB Collaboration Italy Germany Technische Universität Darmstadt Johann-Wolfgang-Goethe Universität Frankfurt Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI), Darmstadt Universität Rostock Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald Universität Erlangen Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) München Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena Russia Institute of Problems of Chemical Physcics (IPCP), Chernogolovka Institute of High Energy Density (IHED), Moscow Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Moscow Nuclear Fusion Institute, RRC "Kurchatov Institute", Moscow All-Russian Institute of Experimental Physics, Sarov MISDC of VNIIFTRI, Mendeleevo Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (MIPT) Lebedev Physics Institute, Moscow France LPGP, Universite Paris Sud, Orsay Cedex LULI, Ecole Polytechnique, Cedex Universite de Provence, Marseille Universite de Bordeaux, Talence Cedex Spain Universidad de Castilla La Mancha, Ciudad Real Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Valencia Ukraine Odessa National University ENEA, Frascati University of Milano Czech Republic Institute of Plasma Physics, PALS Recearch Center, Prague Switzerland CERN, Geneva Israel Weizmann Institute of Sciences, Rehovot Ireland Queens University of Belfast USA Princeton University, Princeton Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LNBL), Berkeley Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Livermore Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), Los Alamos University of Nevada, Reno Japan Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo S. Korea KAIST, Daejon Center for Advanced Accelerators (KERI) Korea Atomic Energy Research Center (KAERI) China Institute for Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS, Shanghai 40 institutions, 14 countries Dmitry Varentsov 15 th International Symposium on Heavy Ion Inertial Fusion Princeton, June 8, 2004


