432618429e7eb5f1b4a1d7f0570267a3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 Plant transformation methods Dr. Annamalai Muthusamy Manipal Life Sciences Centre Manipal University Manipal – 576 104 Karnataka, India amsamy 20@gmail. com
Plant transformation methods Dr. Annamalai Muthusamy Manipal Life Sciences Centre Manipal University Manipal – 576 104 Karnataka, India amsamy 20@gmail. com
 Why Plant Transformation Agricultural Production Different goods Plants & Animals
Why Plant Transformation Agricultural Production Different goods Plants & Animals
 Conventional & modern practice Improve the agricultural productivity
Conventional & modern practice Improve the agricultural productivity
 ICAR Union Minster of Agriculture - President Director – General & Secretary to GOI in DARE 8 Deputy Directors-General Crop Sci, Natural Resource Management, Animal Sci, Agricultural Edu, Agricultural Ext, Fisheries, Horticulture & Agricultural Eng. 33, 000 (7000 – Res & Management) in 28 SAUs
ICAR Union Minster of Agriculture - President Director – General & Secretary to GOI in DARE 8 Deputy Directors-General Crop Sci, Natural Resource Management, Animal Sci, Agricultural Edu, Agricultural Ext, Fisheries, Horticulture & Agricultural Eng. 33, 000 (7000 – Res & Management) in 28 SAUs
 Plant Agriculture
Plant Agriculture
 Sustain life on Earth Oxygen Food, Fiber & Shelter Habitats for animals Preserve soil Plants beautify
Sustain life on Earth Oxygen Food, Fiber & Shelter Habitats for animals Preserve soil Plants beautify
 Pulses – macronutrients & minerals, pulses also contain PSMs that are increasingly being recognized for their potential benefits for human health. Health potential of pulses - bioactivity of pulses Isoflavones, phytosterols, resistant starch, bioactive carbohydrates, alkaloids & saponins.
Pulses – macronutrients & minerals, pulses also contain PSMs that are increasingly being recognized for their potential benefits for human health. Health potential of pulses - bioactivity of pulses Isoflavones, phytosterols, resistant starch, bioactive carbohydrates, alkaloids & saponins.
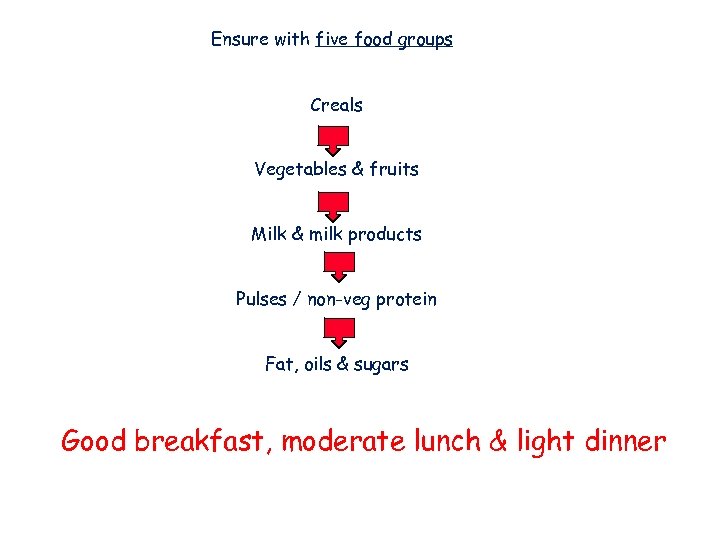 Ensure with five food groups Creals Vegetables & fruits Milk & milk products Pulses / non-veg protein Fat, oils & sugars Good breakfast, moderate lunch & light dinner
Ensure with five food groups Creals Vegetables & fruits Milk & milk products Pulses / non-veg protein Fat, oils & sugars Good breakfast, moderate lunch & light dinner
 Sufficient, nutritionally adequate & culturally acceptable food for an active, healthy life.
Sufficient, nutritionally adequate & culturally acceptable food for an active, healthy life.

 Conventional breeding Tissue culture Genetic engineering Plants
Conventional breeding Tissue culture Genetic engineering Plants
 Conventional breeding ♣ Selection Tissue culture ♣ Without in vitro selection ♣ With in vitro selection
Conventional breeding ♣ Selection Tissue culture ♣ Without in vitro selection ♣ With in vitro selection
 Plant Transformation • Plants are the easiest of higher organisms to transform • Both physical and biological methods exist for transformation • Until recently, only transgenic organisms in wide public release were plants
Plant Transformation • Plants are the easiest of higher organisms to transform • Both physical and biological methods exist for transformation • Until recently, only transgenic organisms in wide public release were plants

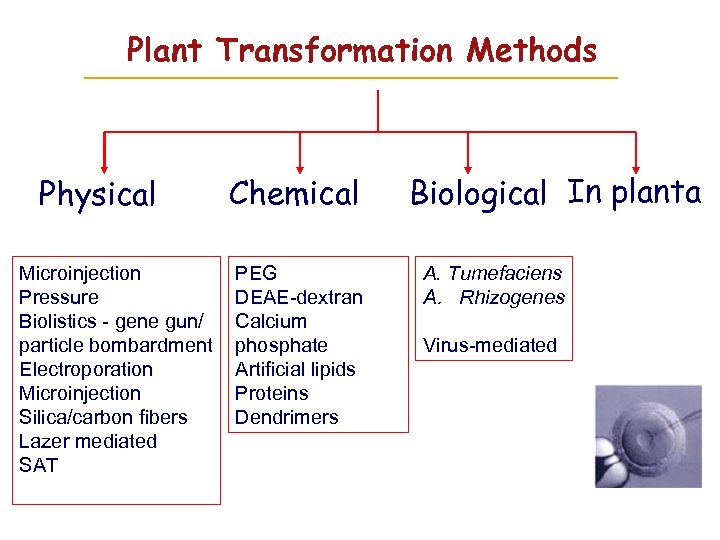 Plant Transformation Methods Physical Microinjection Pressure Biolistics - gene gun/ particle bombardment Electroporation Microinjection Silica/carbon fibers Lazer mediated SAT Chemical PEG DEAE-dextran Calcium phosphate Artificial lipids Proteins Dendrimers Biological In planta A. Tumefaciens A. Rhizogenes Virus-mediated
Plant Transformation Methods Physical Microinjection Pressure Biolistics - gene gun/ particle bombardment Electroporation Microinjection Silica/carbon fibers Lazer mediated SAT Chemical PEG DEAE-dextran Calcium phosphate Artificial lipids Proteins Dendrimers Biological In planta A. Tumefaciens A. Rhizogenes Virus-mediated
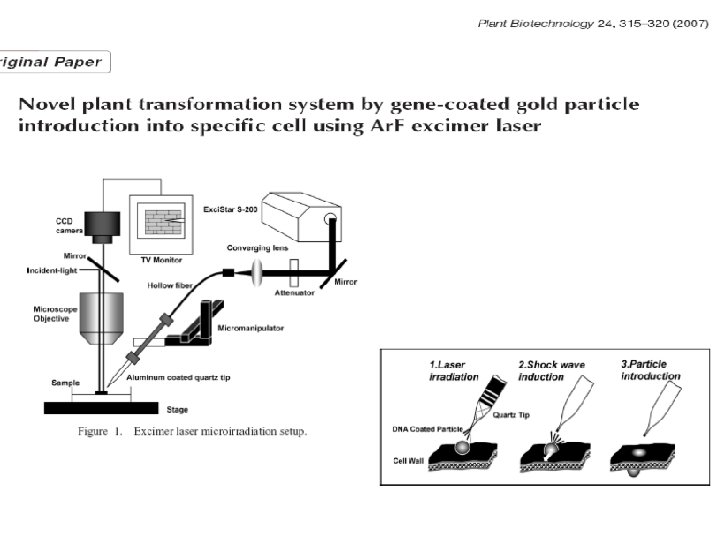
 Transformation • Plants - physical methods • • • Microinjection Electroporation Biolistics - gene gun Silica/carbon fibers Lazer mediated SAT
Transformation • Plants - physical methods • • • Microinjection Electroporation Biolistics - gene gun Silica/carbon fibers Lazer mediated SAT
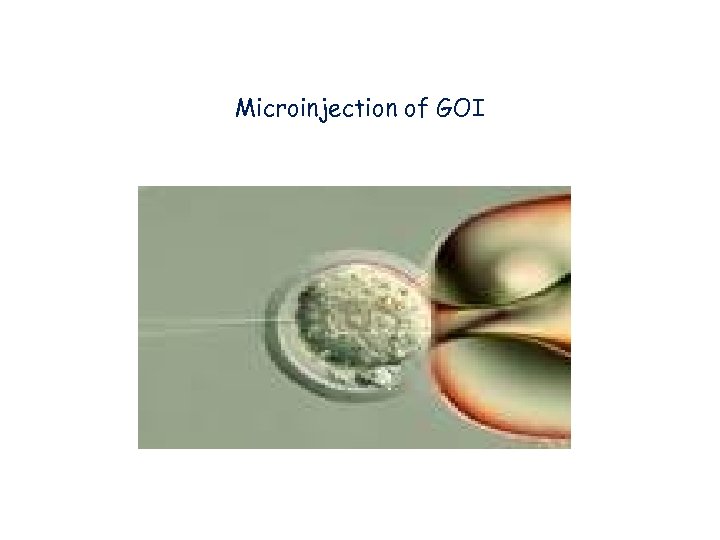 Microinjection of GOI
Microinjection of GOI
 This electroporator is for low-current applications such as those using small electrodes
This electroporator is for low-current applications such as those using small electrodes
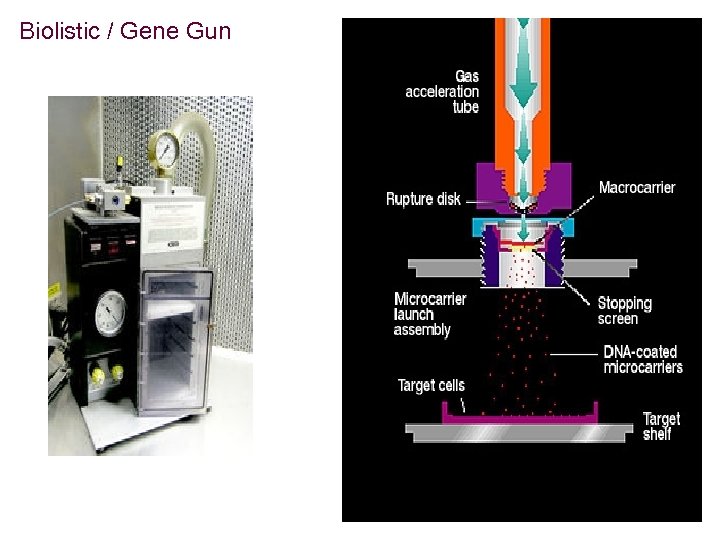 Biolistic / Gene Gun
Biolistic / Gene Gun
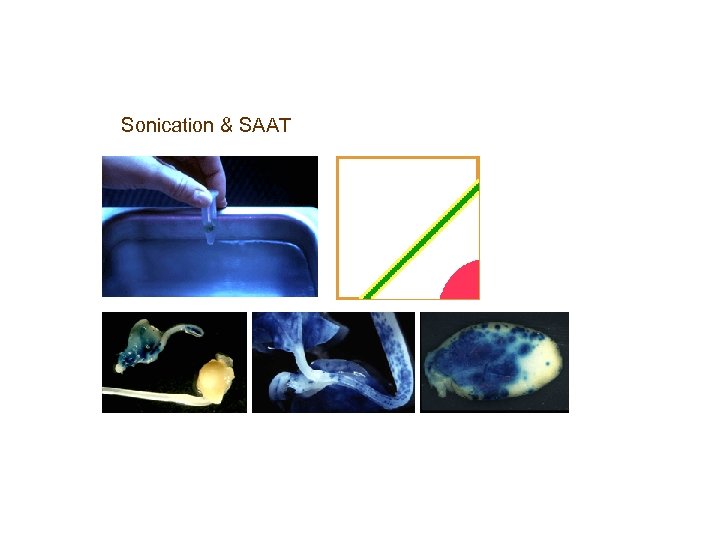 Sonication & SAAT
Sonication & SAAT
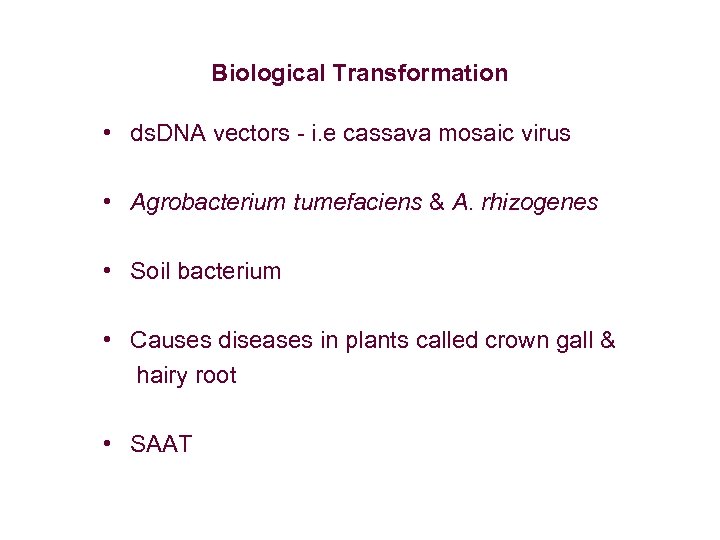 Biological Transformation • ds. DNA vectors - i. e cassava mosaic virus • Agrobacterium tumefaciens & A. rhizogenes • Soil bacterium • Causes diseases in plants called crown gall & hairy root • SAAT
Biological Transformation • ds. DNA vectors - i. e cassava mosaic virus • Agrobacterium tumefaciens & A. rhizogenes • Soil bacterium • Causes diseases in plants called crown gall & hairy root • SAAT
 Biological Transformation ♣ Agrobacterium tumefaciens & ♣ Agrobacterium rhizogenes
Biological Transformation ♣ Agrobacterium tumefaciens & ♣ Agrobacterium rhizogenes
 Possible plant compounds, that initiate Agrobacterium to infect plant cells. Acetosyringone, ferulic acid, gallic acid, Hydroxybenzoic acid, pyrogallic acid, vanillin etc. In monocot – not efficient Transformation frequencey – very less
Possible plant compounds, that initiate Agrobacterium to infect plant cells. Acetosyringone, ferulic acid, gallic acid, Hydroxybenzoic acid, pyrogallic acid, vanillin etc. In monocot – not efficient Transformation frequencey – very less
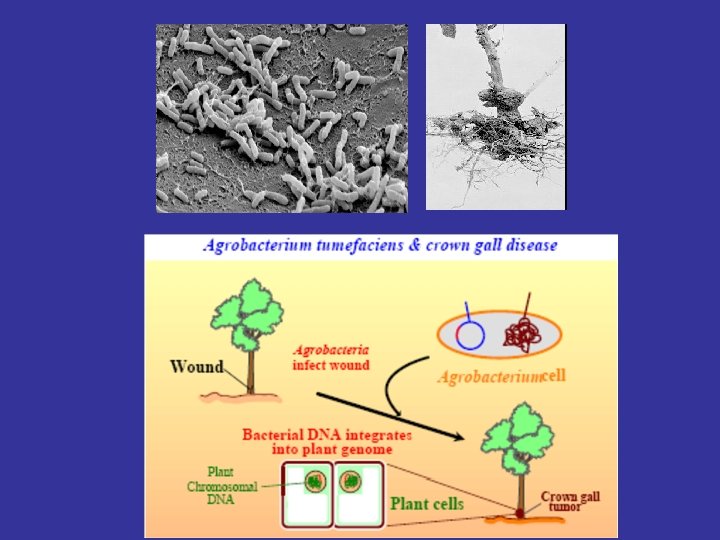
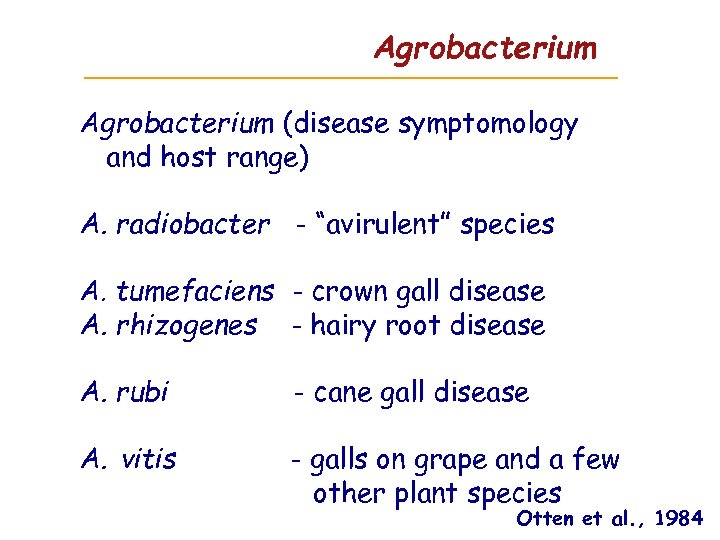 Agrobacterium (disease symptomology and host range) A. radiobacter - “avirulent” species A. tumefaciens - crown gall disease A. rhizogenes - hairy root disease A. rubi - cane gall disease A. vitis - galls on grape and a few other plant species Otten et al. , 1984
Agrobacterium (disease symptomology and host range) A. radiobacter - “avirulent” species A. tumefaciens - crown gall disease A. rhizogenes - hairy root disease A. rubi - cane gall disease A. vitis - galls on grape and a few other plant species Otten et al. , 1984
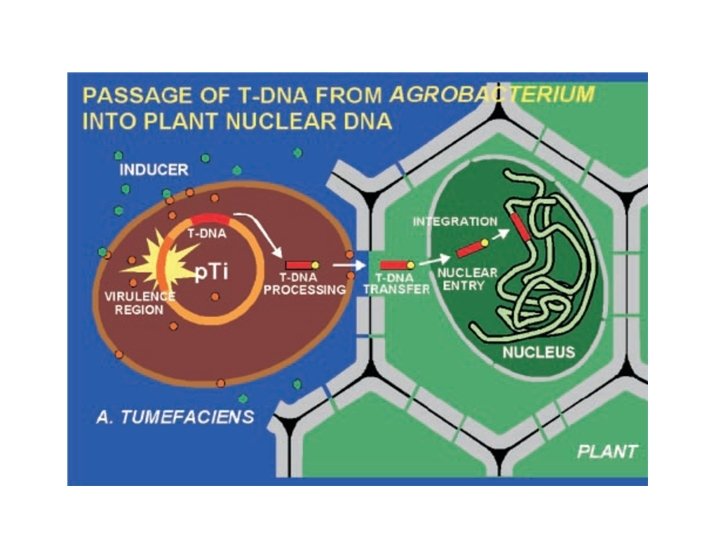
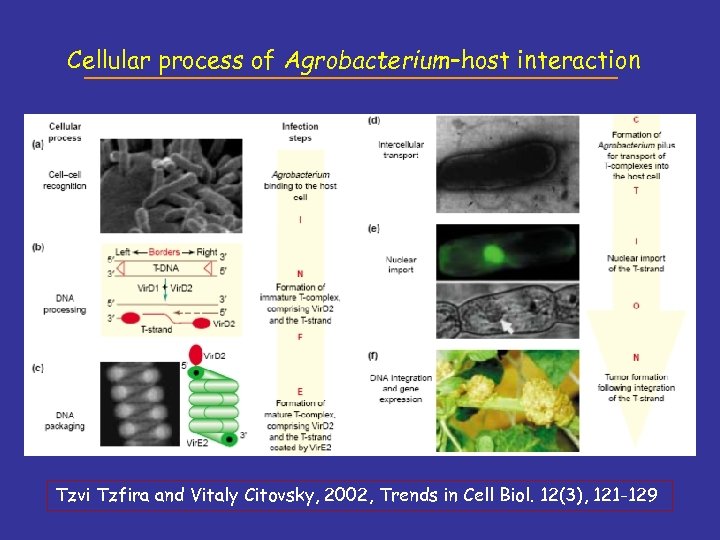 Cellular process of Agrobacterium–host interaction Tzvi Tzfira and Vitaly Citovsky, 2002, Trends in Cell Biol. 12(3), 121 -129
Cellular process of Agrobacterium–host interaction Tzvi Tzfira and Vitaly Citovsky, 2002, Trends in Cell Biol. 12(3), 121 -129
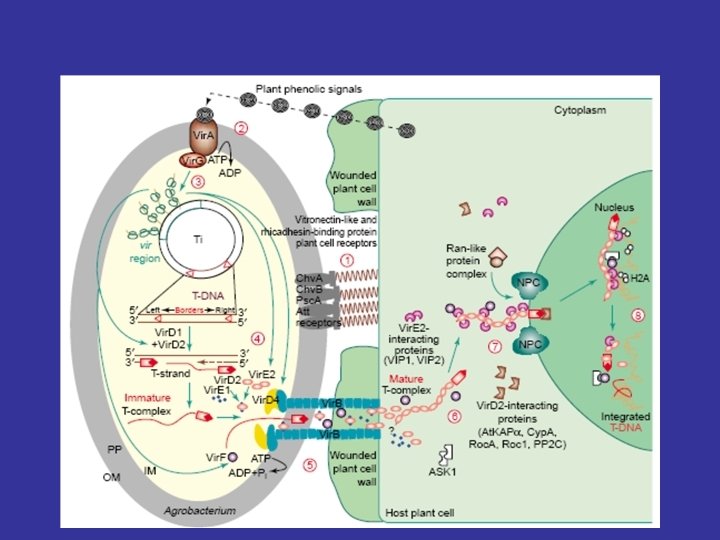
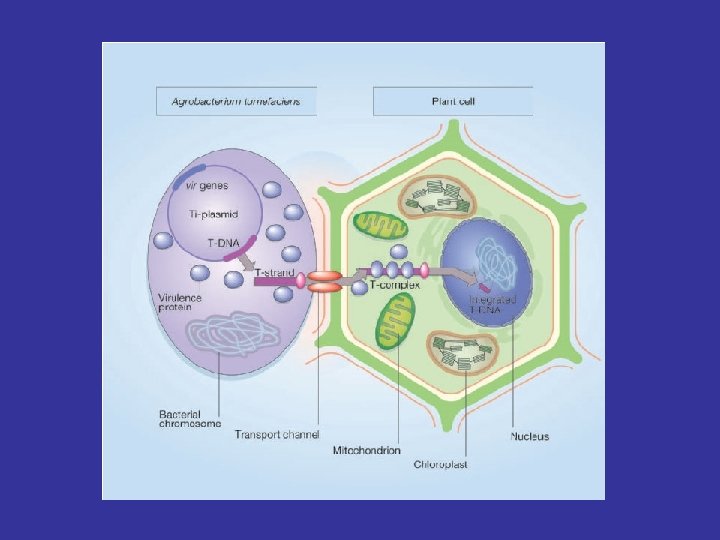

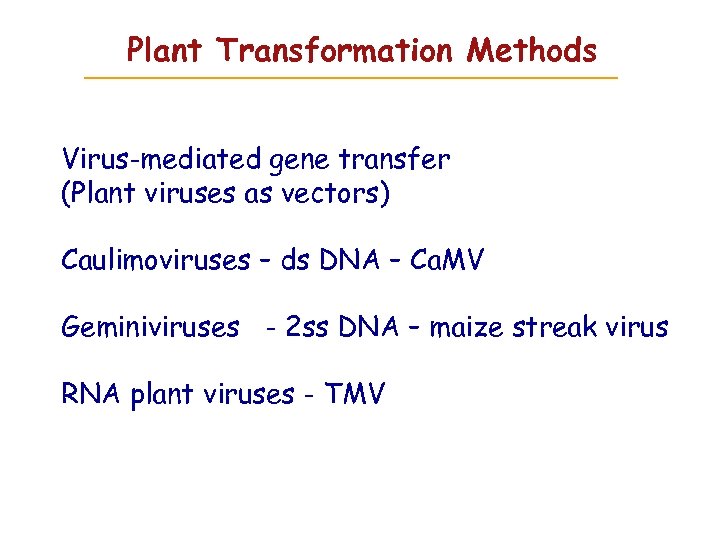 Plant Transformation Methods Virus-mediated gene transfer (Plant viruses as vectors) Caulimoviruses – ds DNA – Ca. MV Geminiviruses - 2 ss DNA – maize streak virus RNA plant viruses - TMV
Plant Transformation Methods Virus-mediated gene transfer (Plant viruses as vectors) Caulimoviruses – ds DNA – Ca. MV Geminiviruses - 2 ss DNA – maize streak virus RNA plant viruses - TMV
 In Planta Transformation ♣ ♣ ♣ Meristem transformation Floral dip method Pollen transformation
In Planta Transformation ♣ ♣ ♣ Meristem transformation Floral dip method Pollen transformation
 Chloroplast transformation - Horizontal gene transfer
Chloroplast transformation - Horizontal gene transfer
 Selectable Markers • A gene encoding an enzyme • Antibiotic resistance • Herbicide resistance • Positive selection genes – genes that allow use of some necessary media component.
Selectable Markers • A gene encoding an enzyme • Antibiotic resistance • Herbicide resistance • Positive selection genes – genes that allow use of some necessary media component.
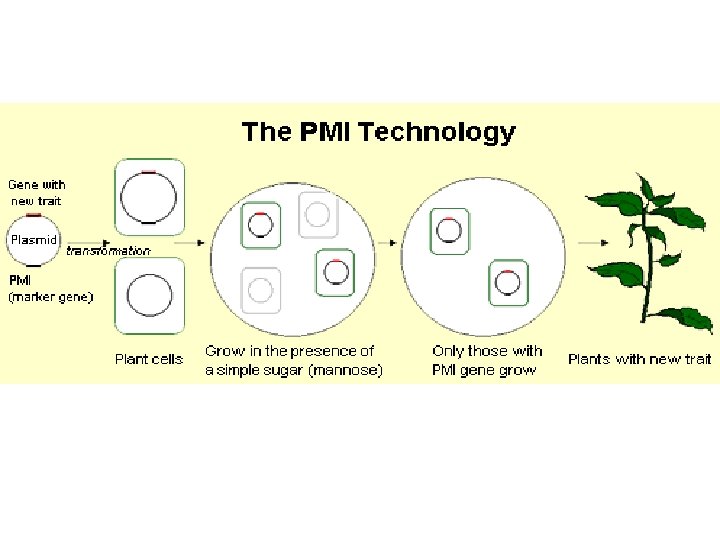
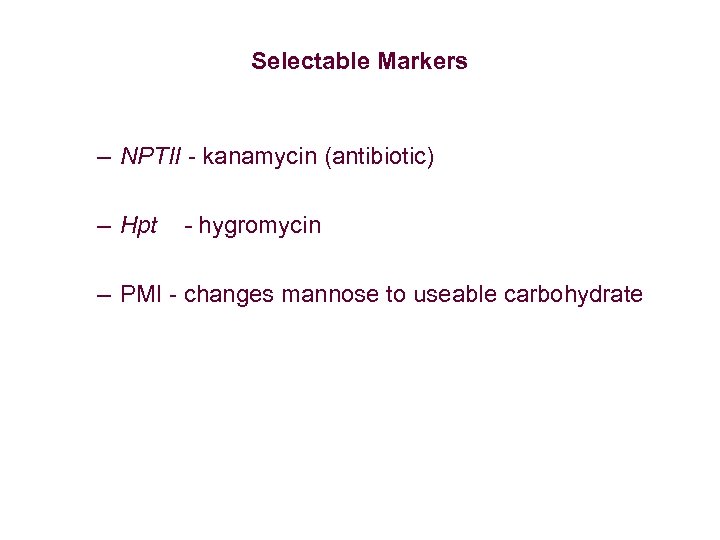 Selectable Markers – NPTII - kanamycin (antibiotic) – Hpt - hygromycin – PMI - changes mannose to useable carbohydrate
Selectable Markers – NPTII - kanamycin (antibiotic) – Hpt - hygromycin – PMI - changes mannose to useable carbohydrate
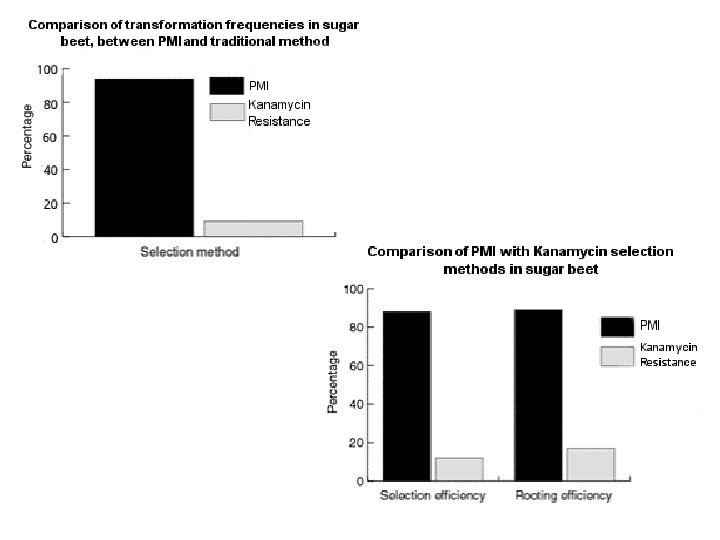
 Novel Selection Genes • Luciferase - gene from fireflies – substrate • Green Fluorescent Protein - from jellyfish - under lights and filter the transgenic plants - GFP • GUS - glucuronidase gene will convert added substrate to blue color.
Novel Selection Genes • Luciferase - gene from fireflies – substrate • Green Fluorescent Protein - from jellyfish - under lights and filter the transgenic plants - GFP • GUS - glucuronidase gene will convert added substrate to blue color.
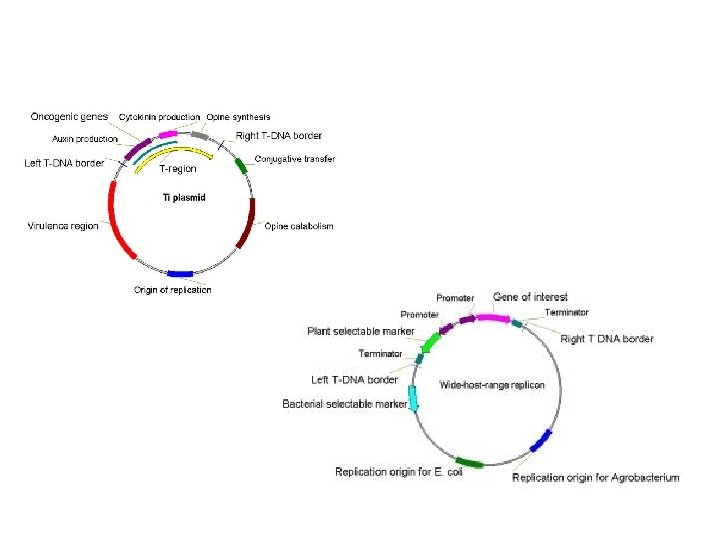
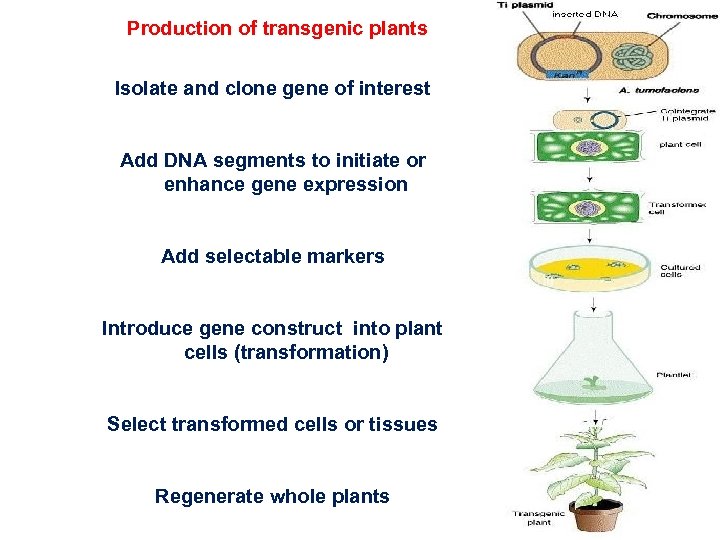 Production of transgenic plants Isolate and clone gene of interest Add DNA segments to initiate or enhance gene expression Add selectable markers Introduce gene construct into plant cells (transformation) Select transformed cells or tissues Regenerate whole plants
Production of transgenic plants Isolate and clone gene of interest Add DNA segments to initiate or enhance gene expression Add selectable markers Introduce gene construct into plant cells (transformation) Select transformed cells or tissues Regenerate whole plants
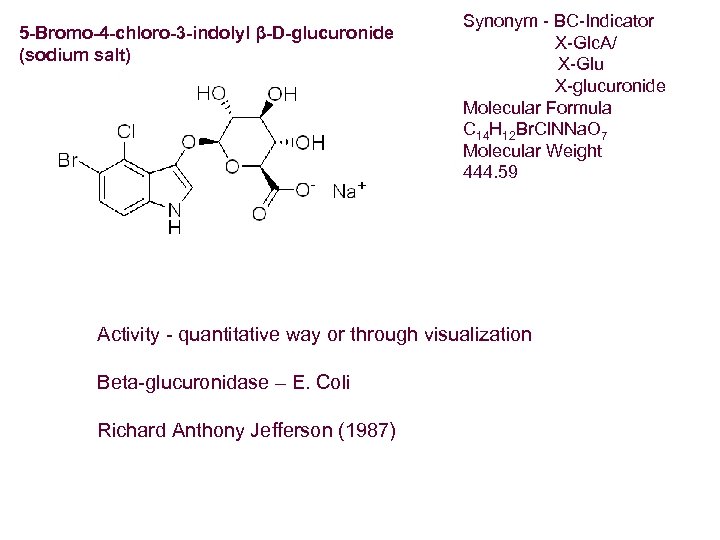 5 -Bromo-4 -chloro-3 -indolyl β-D-glucuronide (sodium salt) Synonym - BC-Indicator X-Glc. A/ X-Glu X-glucuronide Molecular Formula C 14 H 12 Br. Cl. NNa. O 7 Molecular Weight 444. 59 Activity - quantitative way or through visualization Beta-glucuronidase – E. Coli Richard Anthony Jefferson (1987)
5 -Bromo-4 -chloro-3 -indolyl β-D-glucuronide (sodium salt) Synonym - BC-Indicator X-Glc. A/ X-Glu X-glucuronide Molecular Formula C 14 H 12 Br. Cl. NNa. O 7 Molecular Weight 444. 59 Activity - quantitative way or through visualization Beta-glucuronidase – E. Coli Richard Anthony Jefferson (1987)
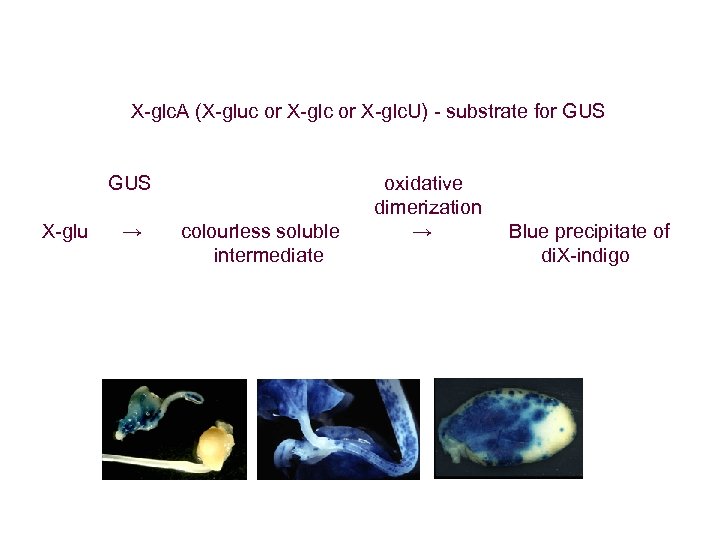 X-glc. A (X-gluc or X-glc. U) - substrate for GUS oxidative dimerization X-glu → colourless soluble → Blue precipitate of intermediate di. X-indigo
X-glc. A (X-gluc or X-glc. U) - substrate for GUS oxidative dimerization X-glu → colourless soluble → Blue precipitate of intermediate di. X-indigo
 Chloroplast transformation - Horizontal gene transfer
Chloroplast transformation - Horizontal gene transfer
 Selection & Regeneration • Cells which contain the selectable marker gene can grow • All plants that develop are transgenic • Plant transformation using physical or biological methods requires a tissue culture stage
Selection & Regeneration • Cells which contain the selectable marker gene can grow • All plants that develop are transgenic • Plant transformation using physical or biological methods requires a tissue culture stage
 In Planta Transformation • Meristem transformation – floral dip • Pollen transformation – electroporation
In Planta Transformation • Meristem transformation – floral dip • Pollen transformation – electroporation
 Analysis of T 0 plants Morphology Physiology Yield characters GUS expression Gene expression Confirmation with selectable marker, Screenable marker, Negative & Positive control
Analysis of T 0 plants Morphology Physiology Yield characters GUS expression Gene expression Confirmation with selectable marker, Screenable marker, Negative & Positive control
 Resistance & Stress tolerance in plants: Resistance: - able to break-down or - metabolize foreign molecules or - introduction a new enzyme to metabolize Tolerance: - able to grow -foreign molecules - either the target enzyme or - altered form of enzyme
Resistance & Stress tolerance in plants: Resistance: - able to break-down or - metabolize foreign molecules or - introduction a new enzyme to metabolize Tolerance: - able to grow -foreign molecules - either the target enzyme or - altered form of enzyme
 Golden rice contains increased levels of pro-vitamin A. Traditional rice is white (a). The prototype of golden rice was developed in 2000 and is a light yellow color (b). It contains 1. 6 mg/g of carotenoid. In 2005, new transgenic lines were developed that dramatically increased the amount of carotenoid synthesized, making the rice a deep golden color (c). This latest form contains 37 mg/g of carotenoid, of which 84% is b-carotene – trial
Golden rice contains increased levels of pro-vitamin A. Traditional rice is white (a). The prototype of golden rice was developed in 2000 and is a light yellow color (b). It contains 1. 6 mg/g of carotenoid. In 2005, new transgenic lines were developed that dramatically increased the amount of carotenoid synthesized, making the rice a deep golden color (c). This latest form contains 37 mg/g of carotenoid, of which 84% is b-carotene – trial
 Miraculin - taste-modifying protein – miracle fruit, the red berries of Richadella dulcifica - shrub native to West Africa Active principle - protein miraculin - not sweet Unusual property - turn a sour taste into a sweet taste Sour foods - lemons, limes & grapefruit, taste sweet when tasted together with this protein
Miraculin - taste-modifying protein – miracle fruit, the red berries of Richadella dulcifica - shrub native to West Africa Active principle - protein miraculin - not sweet Unusual property - turn a sour taste into a sweet taste Sour foods - lemons, limes & grapefruit, taste sweet when tasted together with this protein
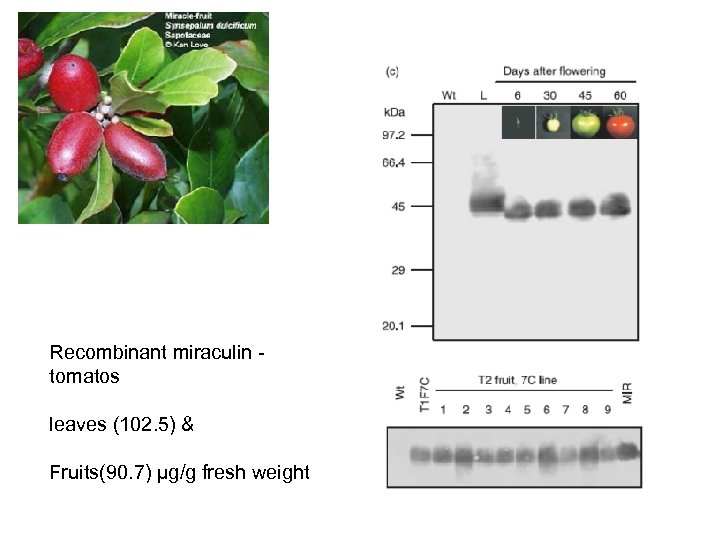 Recombinant miraculin - tomatos leaves (102. 5) & Fruits(90. 7) μg/g fresh weight
Recombinant miraculin - tomatos leaves (102. 5) & Fruits(90. 7) μg/g fresh weight
 Medical hypothesis, 2006 Tomatoes comes in many varieties, colors and shapes Transgenic tomatoes - expressing different malarial antigens
Medical hypothesis, 2006 Tomatoes comes in many varieties, colors and shapes Transgenic tomatoes - expressing different malarial antigens
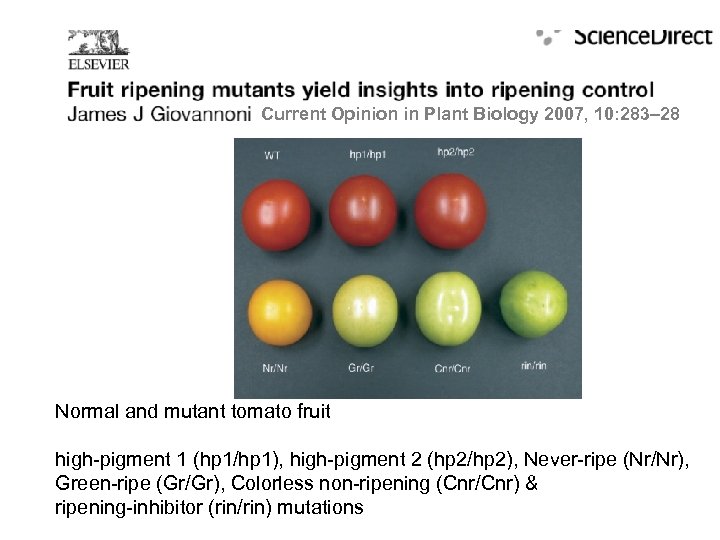 Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2007, 10: 283– 28 Normal and mutant tomato fruit high-pigment 1 (hp 1/hp 1), high-pigment 2 (hp 2/hp 2), Never-ripe (Nr/Nr), Green-ripe (Gr/Gr), Colorless non-ripening (Cnr/Cnr) & ripening-inhibitor (rin/rin) mutations
Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2007, 10: 283– 28 Normal and mutant tomato fruit high-pigment 1 (hp 1/hp 1), high-pigment 2 (hp 2/hp 2), Never-ripe (Nr/Nr), Green-ripe (Gr/Gr), Colorless non-ripening (Cnr/Cnr) & ripening-inhibitor (rin/rin) mutations
 Delivery of a corn-based edible vaccine Transgenic corn kernels (a) Corn snack (b) or Embryo or germ cells (c)
Delivery of a corn-based edible vaccine Transgenic corn kernels (a) Corn snack (b) or Embryo or germ cells (c)
 Tearless Onion Dr Eady Crop & Food Research in New Zealand his collaborators in Japan As onions are sliced, cells are broken, alliinases - break down aa sulphoxides - generate sulphenic acids - unstable - rearrange into a volatile gas - syn-propanethial-Soxide – diffuses by air - reaches the eye - reacts with the water to form a diluted solution of sulphuric acid - Tear glands produce tears to dilute and flush out the irritant
Tearless Onion Dr Eady Crop & Food Research in New Zealand his collaborators in Japan As onions are sliced, cells are broken, alliinases - break down aa sulphoxides - generate sulphenic acids - unstable - rearrange into a volatile gas - syn-propanethial-Soxide – diffuses by air - reaches the eye - reacts with the water to form a diluted solution of sulphuric acid - Tear glands produce tears to dilute and flush out the irritant
 http: //www. dailymail. co. uk/news/article-514799/The-orange-purple-greencauliflowers-scientists-claim-healthier-you. html
http: //www. dailymail. co. uk/news/article-514799/The-orange-purple-greencauliflowers-scientists-claim-healthier-you. html
 Purple tomatoes high in anthocyanins http: //news. bbc. co. uk/2/hi/health/7688310. stm High anthocyanin purple tomato and red wild-type tomato
Purple tomatoes high in anthocyanins http: //news. bbc. co. uk/2/hi/health/7688310. stm High anthocyanin purple tomato and red wild-type tomato
 Prof Cathie Martin from the John Innes Centre Anthocyanins offer protection against certain cancers, cardiovascular disease and age-related degenerative diseases. Anthocyanins also have anti-inflammatory activity, promote visual acuity and hinder obesity and diabetes. Tomatoes already contain high levels of the antioxidant lycopene. Highly processed tomatoes are the best source, or tomatoes cooked in a little oil, which helps to release the lycopene from cells. Flavonoids meanwhile are soluble in water, and foods containing both water soluble and fat-dissolved antioxidants are considered to offer the best protection against disease. In this study the scientists expressed two genes from snapdragon that induce the production of anthocyanins in snapdragon flowers. The genes were turned on in tomato fruit. Anthocyanins accumulated in tomatoes at higher levels than anything previously reported for metabolic engineering in both the peel and flesh of the fruit. The fruit are an intense purple colour. http: //www. seedquest. com/News/releases/2008/october/24091. htm
Prof Cathie Martin from the John Innes Centre Anthocyanins offer protection against certain cancers, cardiovascular disease and age-related degenerative diseases. Anthocyanins also have anti-inflammatory activity, promote visual acuity and hinder obesity and diabetes. Tomatoes already contain high levels of the antioxidant lycopene. Highly processed tomatoes are the best source, or tomatoes cooked in a little oil, which helps to release the lycopene from cells. Flavonoids meanwhile are soluble in water, and foods containing both water soluble and fat-dissolved antioxidants are considered to offer the best protection against disease. In this study the scientists expressed two genes from snapdragon that induce the production of anthocyanins in snapdragon flowers. The genes were turned on in tomato fruit. Anthocyanins accumulated in tomatoes at higher levels than anything previously reported for metabolic engineering in both the peel and flesh of the fruit. The fruit are an intense purple colour. http: //www. seedquest. com/News/releases/2008/october/24091. htm
 Biodegradation of explosives (TNT, RDX) Aresa – Danish biotech company - planting tg tabacco plant to detect - Permission from Serbian authorities - Enzymatic detection & destruction 19 strains of Rhodoccus – use RDX as N 2 source Cytochrome p 450 system - breakdown
Biodegradation of explosives (TNT, RDX) Aresa – Danish biotech company - planting tg tabacco plant to detect - Permission from Serbian authorities - Enzymatic detection & destruction 19 strains of Rhodoccus – use RDX as N 2 source Cytochrome p 450 system - breakdown
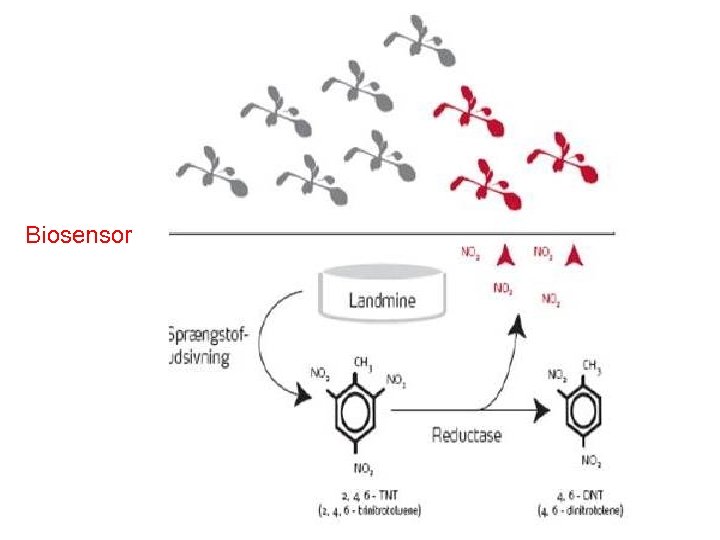 Biosensor
Biosensor

 World's First Blue Roses On Display In Japan - Danielle Demetriou, Daily Telegraph, October 31, 2008, See the rose at http: //www. telegraph. co. uk/news/worldnews/asia/japan/3 327043/Worlds-first-blue-roses-on-display-in-Japan. html Tokyo, Japan - World's first blue roses have been unveiled to the public for the first time at an international flower fair in Japan, following nearly two decades of scientific research. The blue-hued blooms are genetically modified and have been implanted with a gene that simulates the synthesis of blue pigment in pansies. Its scientists successfully pioneered implanting into the flowers the gene that produces Delphinidin, the primary The Blue Rose was plant pigment that produces a blue hue but is not found developed by naturally in roses. Suntory Flowers The world's first genetically modified blue roses were unveiled in the laboratory four years ago, although further research was required to make them safe to grow in nature.
World's First Blue Roses On Display In Japan - Danielle Demetriou, Daily Telegraph, October 31, 2008, See the rose at http: //www. telegraph. co. uk/news/worldnews/asia/japan/3 327043/Worlds-first-blue-roses-on-display-in-Japan. html Tokyo, Japan - World's first blue roses have been unveiled to the public for the first time at an international flower fair in Japan, following nearly two decades of scientific research. The blue-hued blooms are genetically modified and have been implanted with a gene that simulates the synthesis of blue pigment in pansies. Its scientists successfully pioneered implanting into the flowers the gene that produces Delphinidin, the primary The Blue Rose was plant pigment that produces a blue hue but is not found developed by naturally in roses. Suntory Flowers The world's first genetically modified blue roses were unveiled in the laboratory four years ago, although further research was required to make them safe to grow in nature.
 Myco-diesel Bozeman, Mont. -- U. S. scientists say a FUNGUS in the Patagonian rainforest might be a new source of biofuels since it produces a number of diesel compounds from cellulose. "This is the only organism that has ever been shown to produce such an important combination of fuel substances, " said Montana State University Professor Gary Strobel, making it a better source of biofuels than anything used now. The fungus, Gliocladium roseum, produces various molecules made of hydrogen and carbon that are found in diesel, the researchers said. Because of that, the fuel it produces is called "myco-diesel. " "Gliocladium roseum lives inside the Ulmo tree in the Patagonian rainforest, " Strobel said. "We were trying to discover totally novel fungi in this tree by exposing its tissues to the volatile ANTIBIOTICS of the fungus Muscodor albus. Quite unexpectedly, G. roseum grew in the presence of these gases when almost all other fungi were killed. "It was also making volatile ANTIBIOTICS. Then we examined the gas composition of G. roseum, we were totally surprised to learn it was making a plethora of hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon derivatives, " Strobel said the discovery brings into question scientists' knowledge of the way fossil fuels are made. The discovery is reported in the journal Microbiology. The fungus grows inside the Ulmo tree in the temperate Patagonian rainforest of Chile and Argentina.
Myco-diesel Bozeman, Mont. -- U. S. scientists say a FUNGUS in the Patagonian rainforest might be a new source of biofuels since it produces a number of diesel compounds from cellulose. "This is the only organism that has ever been shown to produce such an important combination of fuel substances, " said Montana State University Professor Gary Strobel, making it a better source of biofuels than anything used now. The fungus, Gliocladium roseum, produces various molecules made of hydrogen and carbon that are found in diesel, the researchers said. Because of that, the fuel it produces is called "myco-diesel. " "Gliocladium roseum lives inside the Ulmo tree in the Patagonian rainforest, " Strobel said. "We were trying to discover totally novel fungi in this tree by exposing its tissues to the volatile ANTIBIOTICS of the fungus Muscodor albus. Quite unexpectedly, G. roseum grew in the presence of these gases when almost all other fungi were killed. "It was also making volatile ANTIBIOTICS. Then we examined the gas composition of G. roseum, we were totally surprised to learn it was making a plethora of hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon derivatives, " Strobel said the discovery brings into question scientists' knowledge of the way fossil fuels are made. The discovery is reported in the journal Microbiology. The fungus grows inside the Ulmo tree in the temperate Patagonian rainforest of Chile and Argentina.
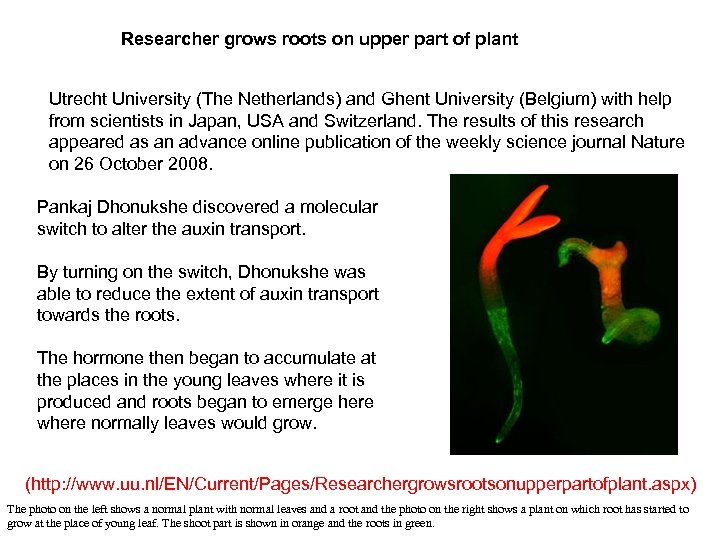 Researcher grows roots on upper part of plant Utrecht University (The Netherlands) and Ghent University (Belgium) with help from scientists in Japan, USA and Switzerland. The results of this research appeared as an advance online publication of the weekly science journal Nature on 26 October 2008. Pankaj Dhonukshe discovered a molecular switch to alter the auxin transport. By turning on the switch, Dhonukshe was able to reduce the extent of auxin transport towards the roots. The hormone then began to accumulate at the places in the young leaves where it is produced and roots began to emerge here where normally leaves would grow. (http: //www. uu. nl/EN/Current/Pages/Researchergrowsrootsonupperpartofplant. aspx) The photo on the left shows a normal plant with normal leaves and a root and the photo on the right shows a plant on which root has started to grow at the place of young leaf. The shoot part is shown in orange and the roots in green.
Researcher grows roots on upper part of plant Utrecht University (The Netherlands) and Ghent University (Belgium) with help from scientists in Japan, USA and Switzerland. The results of this research appeared as an advance online publication of the weekly science journal Nature on 26 October 2008. Pankaj Dhonukshe discovered a molecular switch to alter the auxin transport. By turning on the switch, Dhonukshe was able to reduce the extent of auxin transport towards the roots. The hormone then began to accumulate at the places in the young leaves where it is produced and roots began to emerge here where normally leaves would grow. (http: //www. uu. nl/EN/Current/Pages/Researchergrowsrootsonupperpartofplant. aspx) The photo on the left shows a normal plant with normal leaves and a root and the photo on the right shows a plant on which root has started to grow at the place of young leaf. The shoot part is shown in orange and the roots in green.
 n 1 st generation of tg plants n 2 nd generation of tg plants
n 1 st generation of tg plants n 2 nd generation of tg plants


