5d63501d599f164319fdce684825b1cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
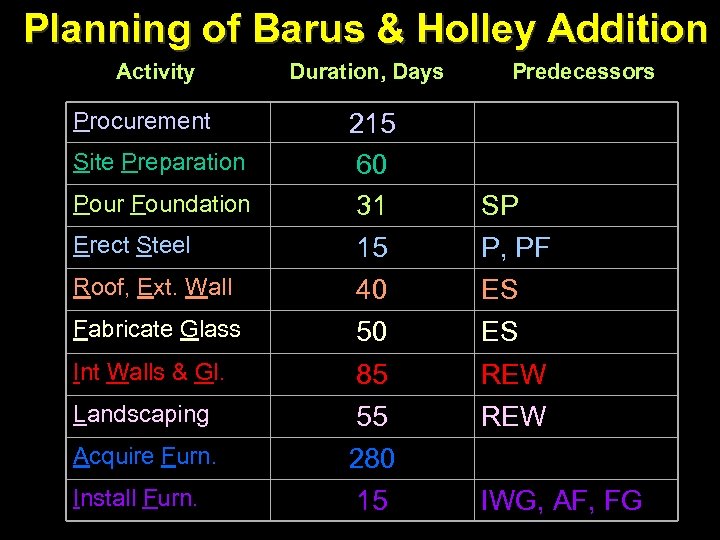
Planning of Barus & Holley Addition Activity Procurement Site Preparation Pour Foundation Erect Steel Roof, Ext. Wall Fabricate Glass Int Walls & Gl. Landscaping Acquire Furn. Install Furn. Duration, Days 215 60 31 15 40 50 85 55 280 15 Predecessors SP P, PF ES ES REW IWG, AF, FG
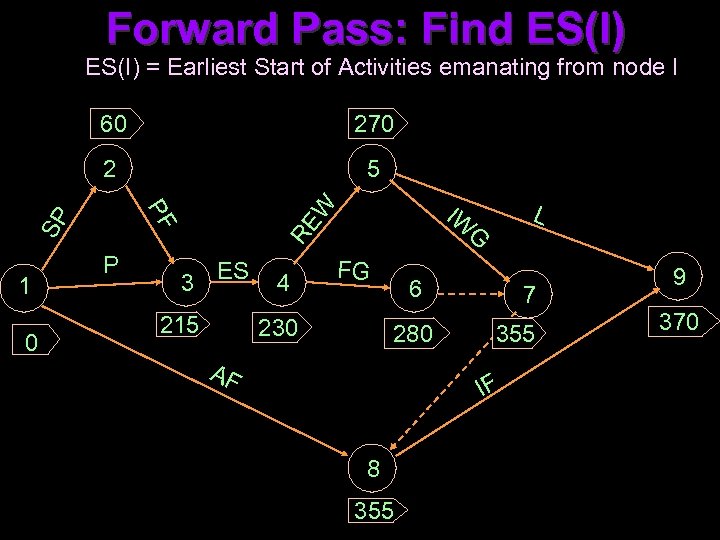
Forward Pass: Find ES(I) = Earliest Start of Activities emanating from node I 60 270 2 5 0 RE W SP PF 1 P IW 3 ES 215 4 L G FG 230 6 280 AF 7 355 IF 8 355 9 370
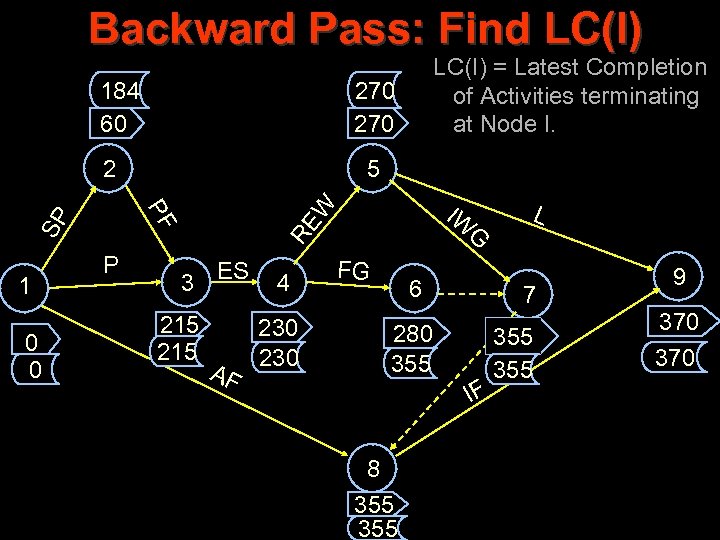
Backward Pass: Find LC(I) 184 60 270 SP PF 1 0 0 5 IW RE W 2 P LC(I) = Latest Completion of Activities terminating at Node I. 3 ES 215 AF 4 G FG 230 6 7 280 355 IF 8 355 L 355 9 370
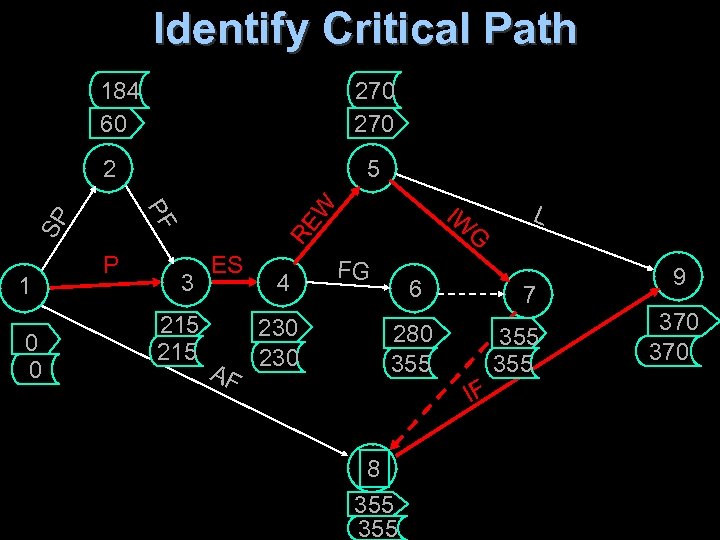
Identify Critical Path 184 60 270 SP PF 1 0 0 5 P IW RE W 2 3 215 ES AF 4 G FG 230 6 7 280 355 355 IF 8 355 L 9 370
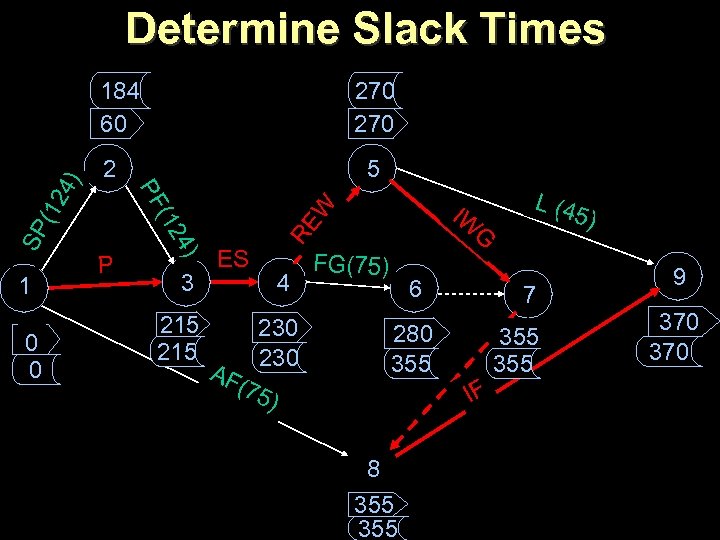
Determine Slack Times 2 3 215 ES AF IW RE W (12 SP P P 4) 0 0 5 (12 1 270 PF 4) 184 60 4 G FG(75) 230 6 355 IF ) 8 355 5) 7 280 355 (75 L (4 9 370

Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: The Campers Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Ray (i) Column Player: Carol (j) (1) (2) (3) (4) (1) 7 2 5 1 (2) 2 2 3 4 (3) 5 3 4 4 (4) 3 2 1 6
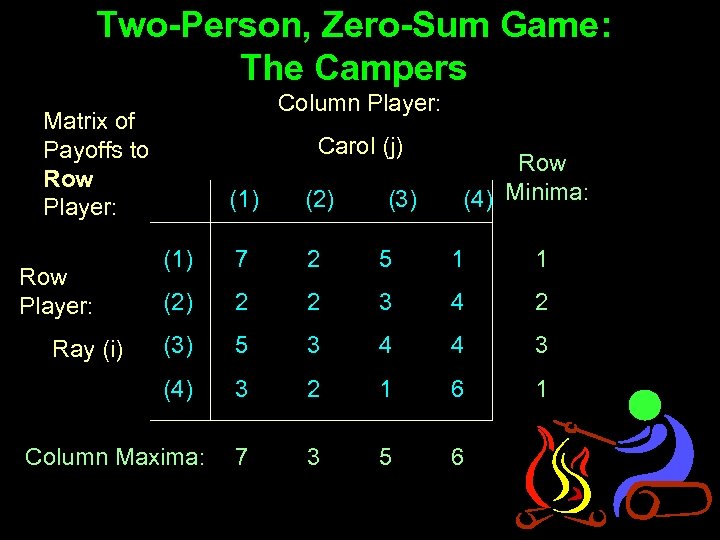
Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: The Campers Column Player: Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Carol (j) Ray (i) (1) (2) (1) 7 2 5 1 1 (2) 2 2 3 4 2 (3) 5 3 4 4 3 (4) Row Player: 3 2 1 6 1 7 3 5 6 Column Maxima: (3) Row (4) Minima:
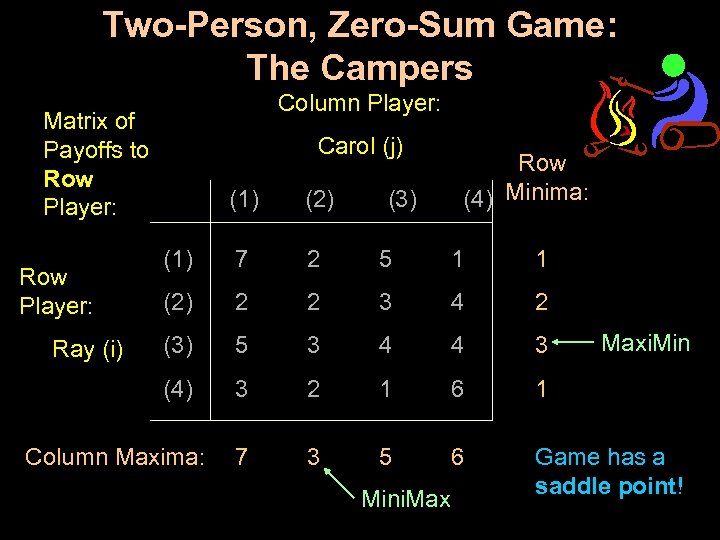
Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: The Campers Column Player: Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Carol (j) Ray (i) (1) (2) (1) 7 2 5 1 1 (2) 2 2 3 4 2 (3) 5 3 4 4 3 (4) Row Player: 3 2 1 6 1 7 3 5 6 Game has a saddle point! Column Maxima: (3) Row (4) Minima: Mini. Maxi. Min
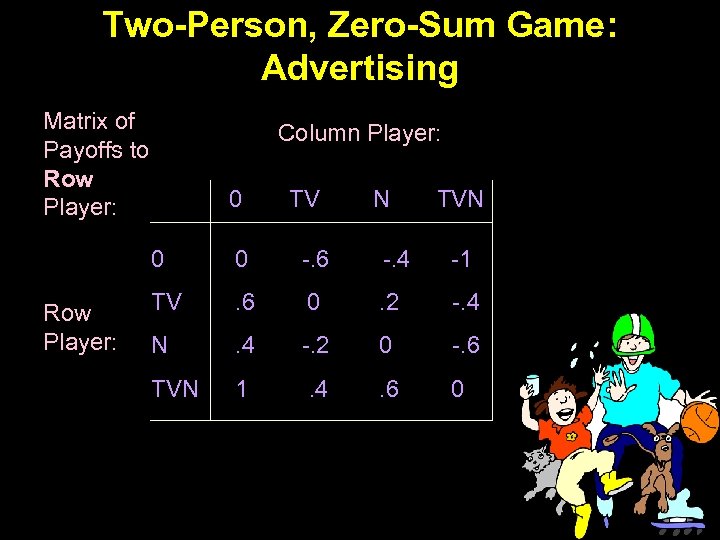
Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Advertising Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Column Player: 0 TV N TVN 0 Row Player: 0 -. 6 -. 4 -1 TV . 6 0 . 2 -. 4 N . 4 -. 2 0 -. 6 TVN 1 . 4 . 6 0
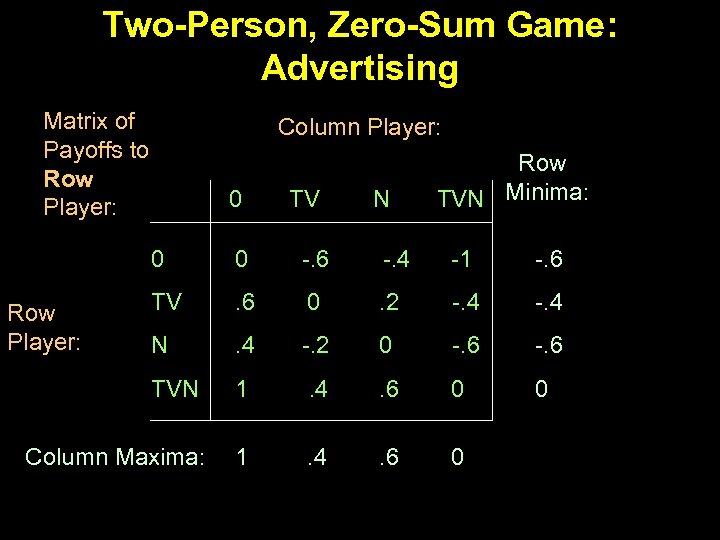
Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Advertising Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Column Player: 0 TV N Row TVN Minima: 0 0 -. 6 -. 4 -1 -. 6 TV . 6 0 . 2 -. 4 N . 4 -. 2 0 -. 6 TVN 1 . 4 . 6 0 0 Column Maxima: 1 . 4 . 6 0 Row Player:

Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Advertising Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Column Player: 0 TV N Row TVN Minima: 0 0 -. 6 -. 4 -1 -. 6 TV . 6 0 . 2 -. 4 N . 4 -. 2 0 -. 6 TVN 1 . 4 . 6 0 0 Column Maxima: 1 . 4 . 6 0 Row Player: Mini. Maxi. Min Game has a saddle point!

Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Advertising Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Column Player: 0 TV N Row TVN Minima: 0 TV 0 . 2 -. 4 N -. 2 0 -. 6 TVN . 4 . 6 0 0 Column Maxima: . 4 . 6 0 Row Player: Mini. Maxi. Min Game has a saddle point!

Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Advertising Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Column Player: 0 TV N Row TVN Minima: 0 Row Player: TV N 0 -. 6 TVN . 6 0 0 Column Maxima: . 6 0 Game has a saddle point! Mini. Maxi. Min

Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Advertising Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Column Player: 0 TV N Row TVN Minima: 0 Row Player: TV N TVN 0 0 Column Maxima: 0 Game has a saddle point! Mini. Maxi. Min
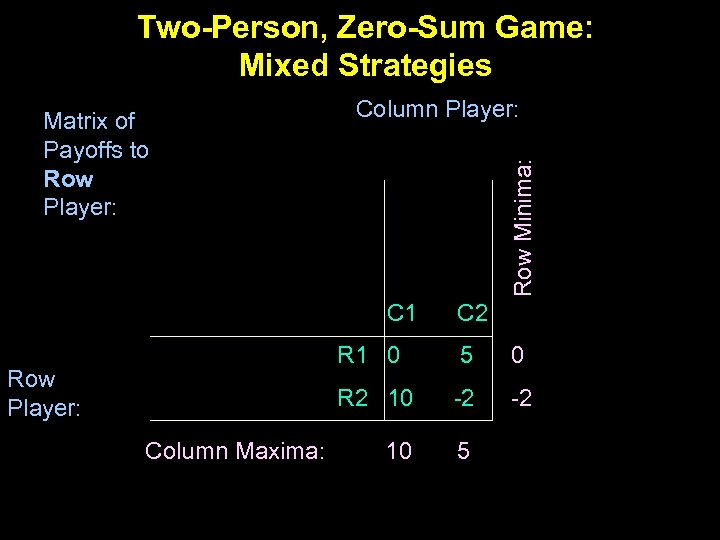
Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Mixed Strategies Column Player: Row Minima: Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: C 1 C 2 R 1 0 Column Maxima: 0 R 2 10 Row Player: 5 -2 -2 10 5
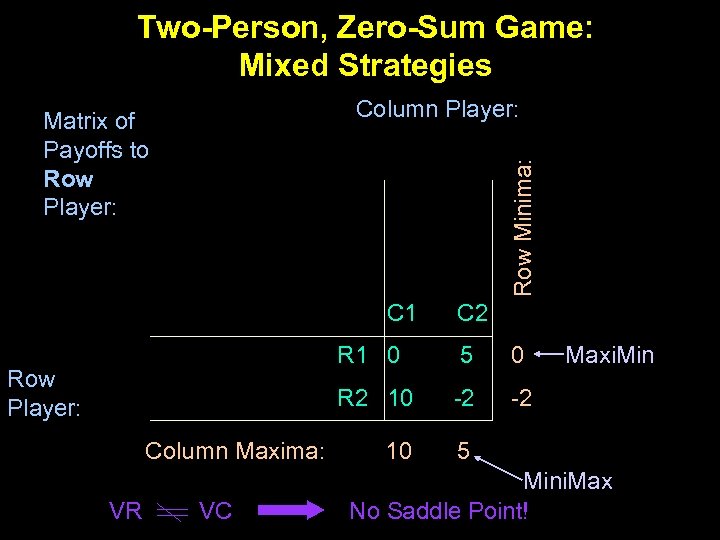
Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Mixed Strategies Column Player: Row Minima: Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: C 1 C 2 R 1 0 Column Maxima: VR VC 0 R 2 10 Row Player: 5 -2 -2 10 Maxi. Min 5 Mini. Max No Saddle Point!
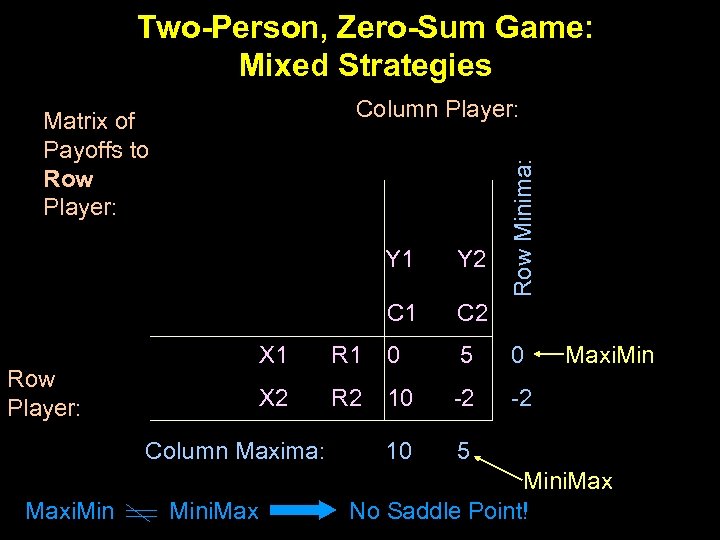
Two-Person, Zero-Sum Game: Mixed Strategies Y 1 C 2 X 1 R 1 0 5 0 X 2 Row Player: R 2 10 -2 10 Mini. Maxi. Min -2 5 Column Maxima: Maxi. Min Y 2 Row Minima: Column Player: Matrix of Payoffs to Row Player: Mini. Max No Saddle Point!
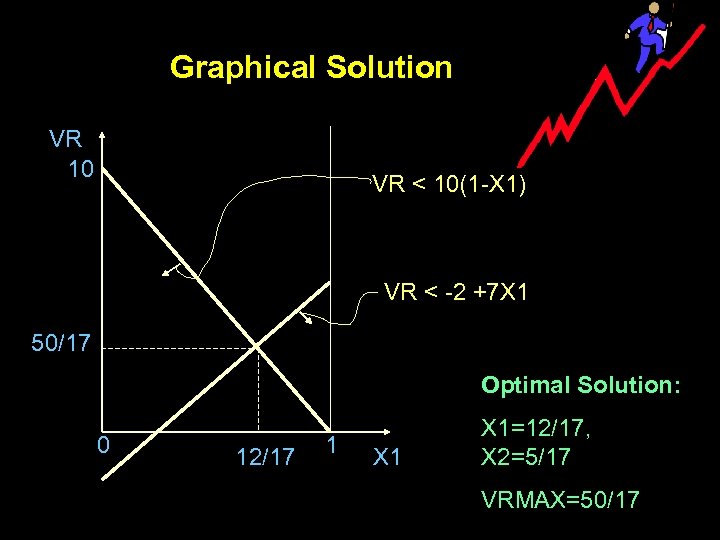
Graphical Solution VR 10 VR < 10(1 -X 1) VR < -2 +7 X 1 50/17 Optimal Solution: 0 12/17 1 X 1=12/17, X 2=5/17 VRMAX=50/17
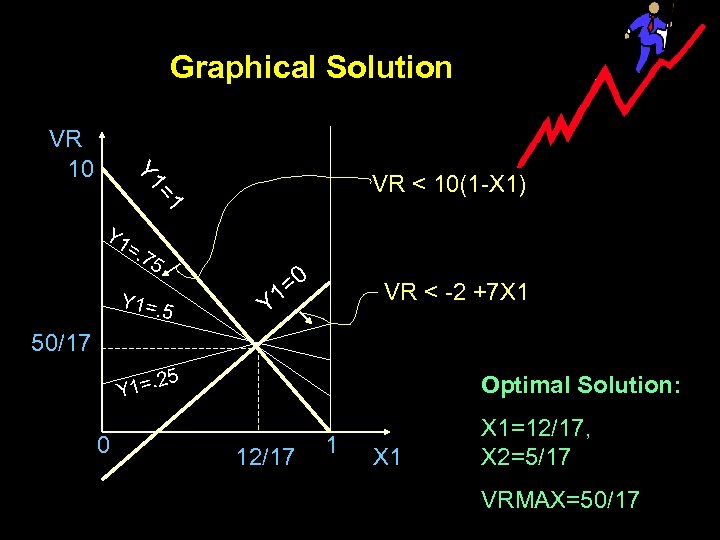
Graphical Solution = Y 1 VR 10 VR < 10(1 -X 1) 1 Y 1 =. 7 5 Y 1=. 5 Y =0 1 VR < -2 +7 X 1 50/17 5 2 Y 1=. 0 Optimal Solution: 12/17 1 X 1=12/17, X 2=5/17 VRMAX=50/17

Two-Person, Zero-Sum Games: Summary • Represent outcomes as payoffs to row player • Evaluate row minima and column maxima • If maximin=minimax, players adopt pure strategy corresponding to saddle point; choices are in stable equilibrium -- secrecy not required • If maximin minimax, use linear programming to find optimal mixed strategy; secrecy essential • Number of options to consider can be reduced by using iterative dominance procedure

The Minimax Theorem “Every finite, two-person, zero-sum game has a rational solution in the form of a pure or mixed strategy. ” John Von Neumann, 1926
5d63501d599f164319fdce684825b1cf.ppt