7a49ecf727b80918b2470bc6c21c4e0b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Planning and Implementing CRM projects Semester Genap 2014/2015
Planning and Implementing CRM projects Semester Genap 2014/2015
 Learning Objectives v Understand major phases in a CRM implementation v Identify a number of tools and processes that can be applied in each phase of an implementation v Understand the importance of project management and change management throughout the implementation process
Learning Objectives v Understand major phases in a CRM implementation v Identify a number of tools and processes that can be applied in each phase of an implementation v Understand the importance of project management and change management throughout the implementation process
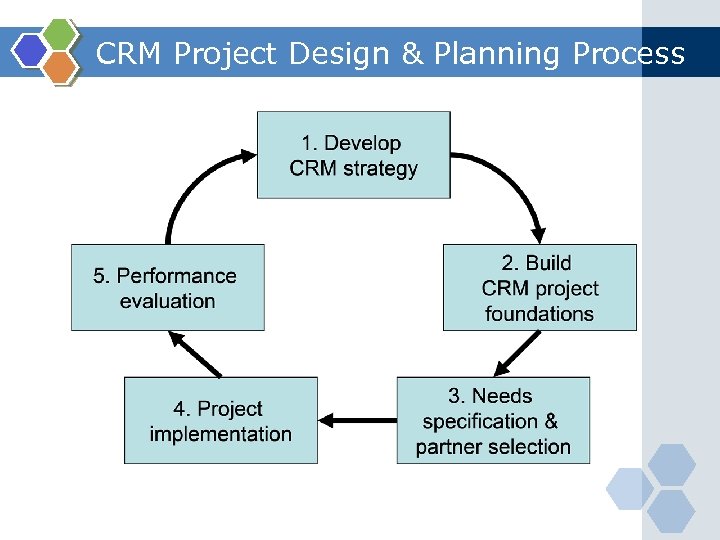 CRM Project Design & Planning Process
CRM Project Design & Planning Process
 Phase 1: Develop the CRM Strategy v CRM strategy: high level plan of action that aligns people, processes and technology to achieve customer-related goals v Sub-phases: § Situation analysis § Commence CRM education (Memulai) § Develop the CRM vision § Set priorities § Establish goals and objectives § Identify people, process and technology requirements § Develop the business case
Phase 1: Develop the CRM Strategy v CRM strategy: high level plan of action that aligns people, processes and technology to achieve customer-related goals v Sub-phases: § Situation analysis § Commence CRM education (Memulai) § Develop the CRM vision § Set priorities § Establish goals and objectives § Identify people, process and technology requirements § Develop the business case
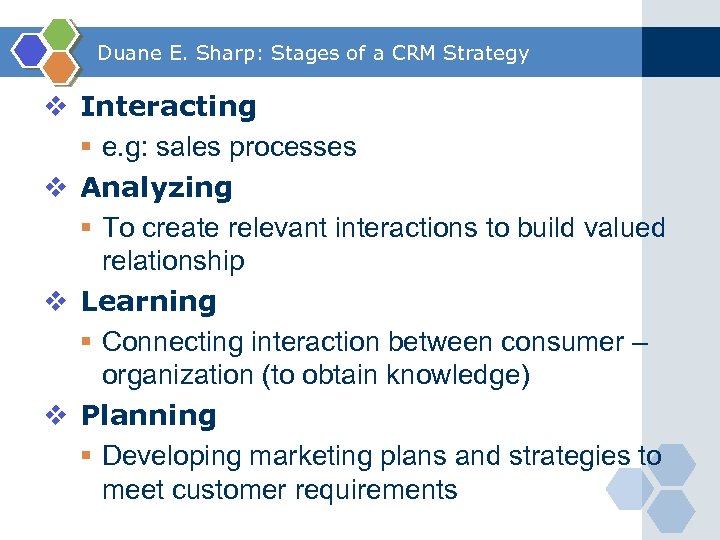 Duane E. Sharp: Stages of a CRM Strategy v Interacting § e. g: sales processes v Analyzing § To create relevant interactions to build valued relationship v Learning § Connecting interaction between consumer – organization (to obtain knowledge) v Planning § Developing marketing plans and strategies to meet customer requirements
Duane E. Sharp: Stages of a CRM Strategy v Interacting § e. g: sales processes v Analyzing § To create relevant interactions to build valued relationship v Learning § Connecting interaction between consumer – organization (to obtain knowledge) v Planning § Developing marketing plans and strategies to meet customer requirements
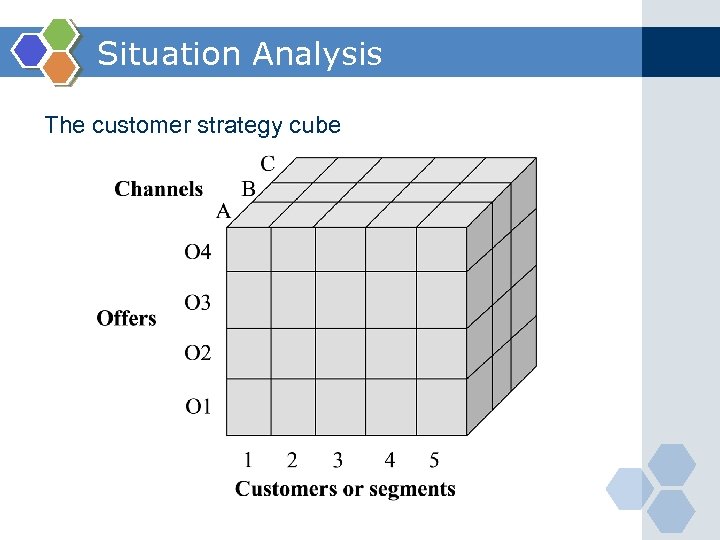 Situation Analysis The customer strategy cube
Situation Analysis The customer strategy cube
 What is a CRM Vision? v A CRM vision is a high-level statement of how CRM will change a business as it relates to customers
What is a CRM Vision? v A CRM vision is a high-level statement of how CRM will change a business as it relates to customers
 CRM Vision Statements (Example) Salesforce. com: v We will work with our members in a trust-based relationship to represent their interests, and to satisfy their needs for high value, security, and peace of mind in motoring, travel, and home. v Nurturing relationships one cup at a time. Deliver a customer experience that consistently develops enthusiastically satisfied customers in every market in which we do business. v Build and maintain long-term relationships with valuable customers by creating personalized experiences across all touch-points and by anticipating customer needs and providing customized offers. v Nothing is more important than making every user successful.
CRM Vision Statements (Example) Salesforce. com: v We will work with our members in a trust-based relationship to represent their interests, and to satisfy their needs for high value, security, and peace of mind in motoring, travel, and home. v Nurturing relationships one cup at a time. Deliver a customer experience that consistently develops enthusiastically satisfied customers in every market in which we do business. v Build and maintain long-term relationships with valuable customers by creating personalized experiences across all touch-points and by anticipating customer needs and providing customized offers. v Nothing is more important than making every user successful.
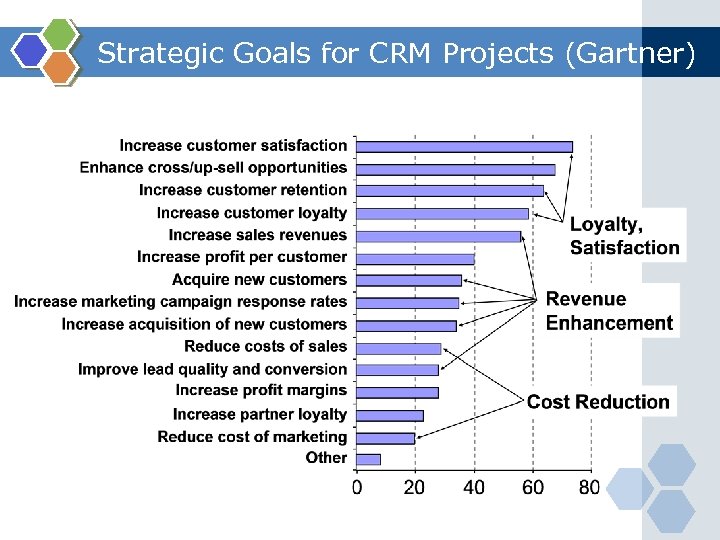 Strategic Goals for CRM Projects (Gartner)
Strategic Goals for CRM Projects (Gartner)
 Business Case: Revenues v CRM implementations can generate additional revenues in a number of ways: § § § § Conversion of more leads More cross-selling and up-selling More accurate product pricing Higher levels of customer satisfaction and retention Higher levels of word-of-mouth influence More leads and/or sales from marketing campaigns More sales from more effective selling processes
Business Case: Revenues v CRM implementations can generate additional revenues in a number of ways: § § § § Conversion of more leads More cross-selling and up-selling More accurate product pricing Higher levels of customer satisfaction and retention Higher levels of word-of-mouth influence More leads and/or sales from marketing campaigns More sales from more effective selling processes
 Phase 2: Build the CRM Project Foundations v Identify stakeholders v Establish governance structures v Identify change management needs v Identify project management needs v Identify critical success factors v Develop risk management plan
Phase 2: Build the CRM Project Foundations v Identify stakeholders v Establish governance structures v Identify change management needs v Identify project management needs v Identify critical success factors v Develop risk management plan
 Who are The Stakeholders in CRM Projects? v Stakeholders include any party that will be impacted by the adoption of CRM § § § § senior management users of any new system marketing staff sales people customer service agents channel partners customers IT specialists
Who are The Stakeholders in CRM Projects? v Stakeholders include any party that will be impacted by the adoption of CRM § § § § senior management users of any new system marketing staff sales people customer service agents channel partners customers IT specialists
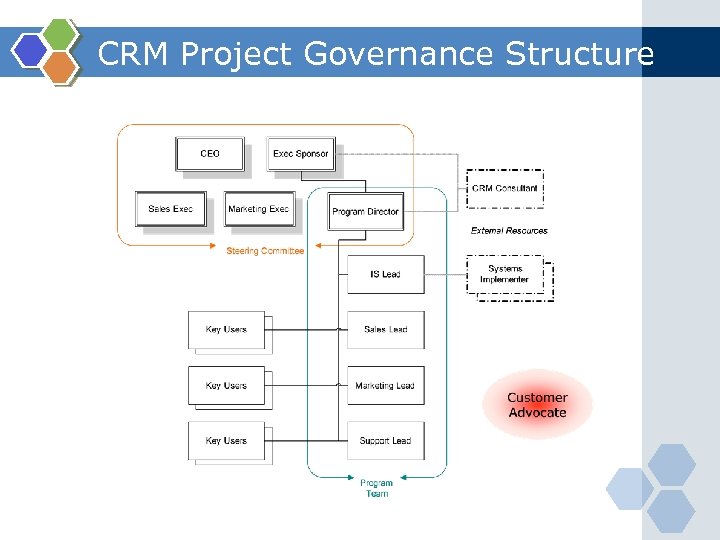 CRM Project Governance Structure
CRM Project Governance Structure
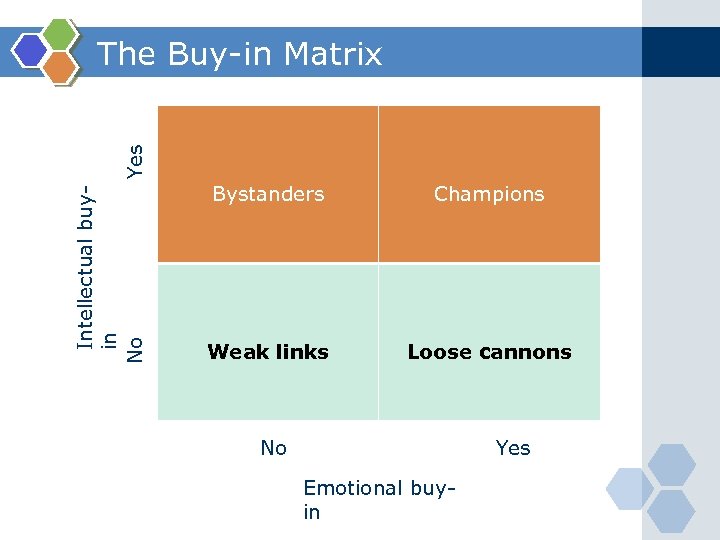 Intellectual buyin No Yes The Buy-in Matrix Bystanders Champions Weak links Loose cannons No Yes Emotional buyin
Intellectual buyin No Yes The Buy-in Matrix Bystanders Champions Weak links Loose cannons No Yes Emotional buyin
 Identify Project Management Needs v Role of CRM Program Director v Sets out steps of journey from situation analysis to achievement of CRM vision, goals and objectives v Tool kit: Gantt charts, Critical Path Analysis (CPA), Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) or network diagrams.
Identify Project Management Needs v Role of CRM Program Director v Sets out steps of journey from situation analysis to achievement of CRM vision, goals and objectives v Tool kit: Gantt charts, Critical Path Analysis (CPA), Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) or network diagrams.
 Critical Success Factors v CSF’s are attributes and variables that can significantly impact business outcomes
Critical Success Factors v CSF’s are attributes and variables that can significantly impact business outcomes
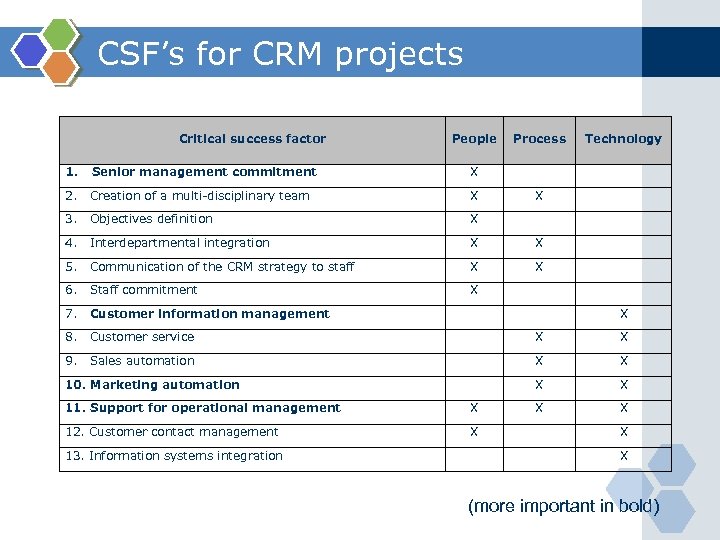 CSF’s for CRM projects Critical success factor People Process Technology 1. Senior management commitment X 2. Creation of a multi-disciplinary team X 3. Objectives definition X 4. Interdepartmental integration X X 5. Communication of the CRM strategy to staff X X 6. Staff commitment X 7. Customer information management 8. Customer service X X 9. Sales automation X X X X 10. Marketing automation 11. Support for operational management X 12. Customer contact management X 13. Information systems integration X X X (more important in bold)
CSF’s for CRM projects Critical success factor People Process Technology 1. Senior management commitment X 2. Creation of a multi-disciplinary team X 3. Objectives definition X 4. Interdepartmental integration X X 5. Communication of the CRM strategy to staff X X 6. Staff commitment X 7. Customer information management 8. Customer service X X 9. Sales automation X X X X 10. Marketing automation 11. Support for operational management X 12. Customer contact management X 13. Information systems integration X X X (more important in bold)
 Risk Management Plan v Gartner has identified a number of risks that threaten project success § management that has little customer understanding or involvement § rewards and incentives that are tied to old, non-customer objectives § organizational culture that is not customer-focussed § limited or no input from the customers § thinking that technology is the solution § lack of specifically designed, mutually reinforcing processes; § poor-quality customer data and information § little coordination between departmental initiatives and projects § creation of the CRM team happens last, and the team lacks business staff § no measures or monitoring of benefits and lack of testing
Risk Management Plan v Gartner has identified a number of risks that threaten project success § management that has little customer understanding or involvement § rewards and incentives that are tied to old, non-customer objectives § organizational culture that is not customer-focussed § limited or no input from the customers § thinking that technology is the solution § lack of specifically designed, mutually reinforcing processes; § poor-quality customer data and information § little coordination between departmental initiatives and projects § creation of the CRM team happens last, and the team lacks business staff § no measures or monitoring of benefits and lack of testing
 Phase 3: Need Specification & Partner Selection v Process engineering v Data review and gap analysis v Initial technology needs specification, and research alternative solutions v Write request for proposals (RFP) v Call for proposals v Revised technology needs identification v Assessment and partner selection
Phase 3: Need Specification & Partner Selection v Process engineering v Data review and gap analysis v Initial technology needs specification, and research alternative solutions v Write request for proposals (RFP) v Call for proposals v Revised technology needs identification v Assessment and partner selection
 Business Process Defined v A business process is set of activities performed by people and/or technology in order to achieve a desired outcome v Processes are ‘how things are done’ v Processes can be classified as § Vertical and horizontal § Front-office and back-office § Primary and secondary v CRM processes include all customer-facing (front-office) processes within sales, marketing and service functions
Business Process Defined v A business process is set of activities performed by people and/or technology in order to achieve a desired outcome v Processes are ‘how things are done’ v Processes can be classified as § Vertical and horizontal § Front-office and back-office § Primary and secondary v CRM processes include all customer-facing (front-office) processes within sales, marketing and service functions
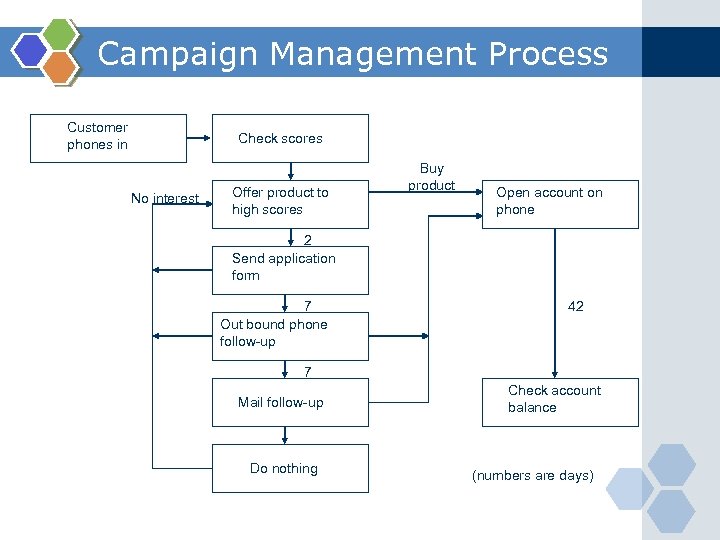 Campaign Management Process Customer phones in Check scores No interest Offer product to high scores Buy product Open account on phone 2 Send application form 7 Out bound phone follow-up 42 7 Mail follow-up Do nothing Check account balance (numbers are days)
Campaign Management Process Customer phones in Check scores No interest Offer product to high scores Buy product Open account on phone 2 Send application form 7 Out bound phone follow-up 42 7 Mail follow-up Do nothing Check account balance (numbers are days)
 Data Review and Gap Analysis v Customer-related data is used for strategic, operational, analytical and collaborative CRM purposes v Identify the information needed v Identify the information available v Identify the gap v Consider data quality issues
Data Review and Gap Analysis v Customer-related data is used for strategic, operational, analytical and collaborative CRM purposes v Identify the information needed v Identify the information available v Identify the gap v Consider data quality issues
 Initial Technology Needs …… …. . specification and research alternative solutions v Identify applications and functionality that meets business case requirements § Visit vendor websites § Join online communities and learn from members § Visit online CRM exhibitions § Read case studies § Join benchmarking group v Consider build, buy or rent decision § Consider total cost of ownership v Most users opt for an on-premise (installed) CRM system or a hosted (online) system
Initial Technology Needs …… …. . specification and research alternative solutions v Identify applications and functionality that meets business case requirements § Visit vendor websites § Join online communities and learn from members § Visit online CRM exhibitions § Read case studies § Join benchmarking group v Consider build, buy or rent decision § Consider total cost of ownership v Most users opt for an on-premise (installed) CRM system or a hosted (online) system
![Contents of Request For Proposal (RFP) [1] v Instructions to respondents v Company background Contents of Request For Proposal (RFP) [1] v Instructions to respondents v Company background](https://present5.com/presentation/7a49ecf727b80918b2470bc6c21c4e0b/image-25.jpg) Contents of Request For Proposal (RFP) [1] v Instructions to respondents v Company background v The CRM vision and strategy v Strategic, operational, analytical and collaborative CRM requirements v Process issues: § Customer interaction mapping § Process re-engineering
Contents of Request For Proposal (RFP) [1] v Instructions to respondents v Company background v The CRM vision and strategy v Strategic, operational, analytical and collaborative CRM requirements v Process issues: § Customer interaction mapping § Process re-engineering
![Contents of RFP [2] v Technology issues: § Delivery model – Saa. S, on-premise, Contents of RFP [2] v Technology issues: § Delivery model – Saa. S, on-premise,](https://present5.com/presentation/7a49ecf727b80918b2470bc6c21c4e0b/image-26.jpg) Contents of RFP [2] v Technology issues: § Delivery model – Saa. S, on-premise, blended § Functionality required – sales, marketing and service § Management reports required § Hardware requirements § Architectural issues § Systems integration issues § Customization issues § Upgrades and service requirements
Contents of RFP [2] v Technology issues: § Delivery model – Saa. S, on-premise, blended § Functionality required – sales, marketing and service § Management reports required § Hardware requirements § Architectural issues § Systems integration issues § Customization issues § Upgrades and service requirements
![Contents of RFP [3] v People issues: § Project management services § Change management Contents of RFP [3] v People issues: § Project management services § Change management](https://present5.com/presentation/7a49ecf727b80918b2470bc6c21c4e0b/image-27.jpg) Contents of RFP [3] v People issues: § Project management services § Change management services § Management and staff training v Costing issues – TCO targets v Implementation issues – pilot, training, support, roll-out, time-line v Contractual issues v Criteria for assessing proposals v Time-line for responding to proposals
Contents of RFP [3] v People issues: § Project management services § Change management services § Management and staff training v Costing issues – TCO targets v Implementation issues – pilot, training, support, roll-out, time-line v Contractual issues v Criteria for assessing proposals v Time-line for responding to proposals
 Phase 4: Project Implementation v Refine project plan v Identify technology customisation needs v Prototype design, test, modify and roll out
Phase 4: Project Implementation v Refine project plan v Identify technology customisation needs v Prototype design, test, modify and roll out
 CRM Deployment Options v On premise § installed on your company’s own servers v 3 rd party hosted § Installed and accessed from another party’s servers via internet § ASP (Application Service Provider) model or the Software-as-a-Service (Saa. S) model v On-premise hosted § The software is on your site but managed by other party
CRM Deployment Options v On premise § installed on your company’s own servers v 3 rd party hosted § Installed and accessed from another party’s servers via internet § ASP (Application Service Provider) model or the Software-as-a-Service (Saa. S) model v On-premise hosted § The software is on your site but managed by other party
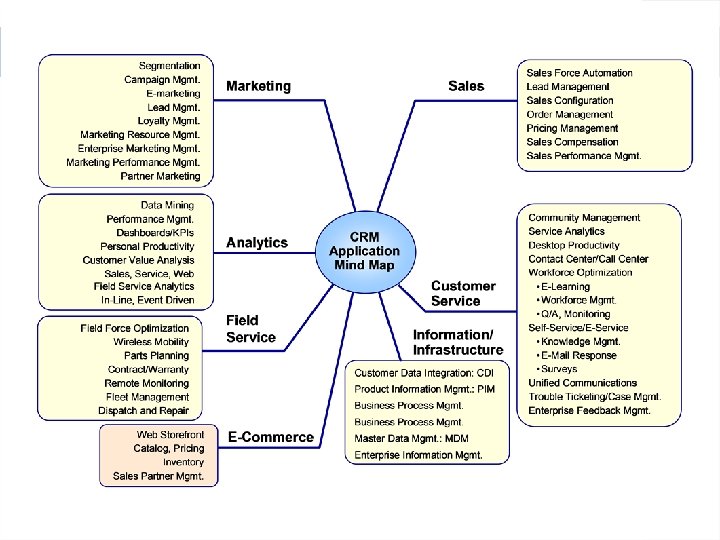
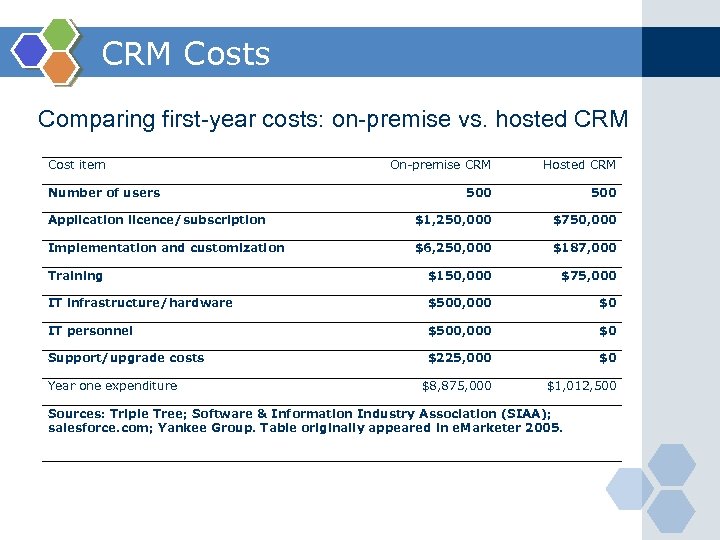 CRM Costs Comparing first-year costs: on-premise vs. hosted CRM Cost item On-premise CRM Hosted CRM 500 Application licence/subscription $1, 250, 000 $750, 000 Implementation and customization $6, 250, 000 $187, 000 Training $150, 000 $75, 000 IT infrastructure/hardware $500, 000 $0 IT personnel $500, 000 $0 Support/upgrade costs $225, 000 $0 $8, 875, 000 $1, 012, 500 Number of users Year one expenditure Sources: Triple Tree; Software & Information Industry Association (SIAA); salesforce. com; Yankee Group. Table originally appeared in e. Marketer 2005.
CRM Costs Comparing first-year costs: on-premise vs. hosted CRM Cost item On-premise CRM Hosted CRM 500 Application licence/subscription $1, 250, 000 $750, 000 Implementation and customization $6, 250, 000 $187, 000 Training $150, 000 $75, 000 IT infrastructure/hardware $500, 000 $0 IT personnel $500, 000 $0 Support/upgrade costs $225, 000 $0 $8, 875, 000 $1, 012, 500 Number of users Year one expenditure Sources: Triple Tree; Software & Information Industry Association (SIAA); salesforce. com; Yankee Group. Table originally appeared in e. Marketer 2005.
 Phase 5: Performance Evaluation v Project outcomes § Was the project has been delivered on time and to budget? v Business outcomes § Have business goals and specific CRM objectives been achieved? § Consider time-frame for CRM objectives
Phase 5: Performance Evaluation v Project outcomes § Was the project has been delivered on time and to budget? v Business outcomes § Have business goals and specific CRM objectives been achieved? § Consider time-frame for CRM objectives
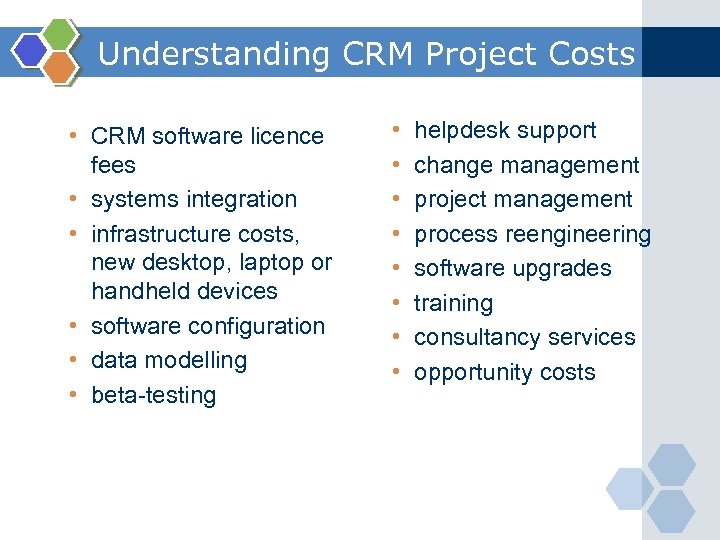 Understanding CRM Project Costs • CRM software licence fees • systems integration • infrastructure costs, new desktop, laptop or handheld devices • software configuration • data modelling • beta-testing • • helpdesk support change management project management process reengineering software upgrades training consultancy services opportunity costs
Understanding CRM Project Costs • CRM software licence fees • systems integration • infrastructure costs, new desktop, laptop or handheld devices • software configuration • data modelling • beta-testing • • helpdesk support change management project management process reengineering software upgrades training consultancy services opportunity costs
 References v Francis Buttle, Customer Relationship Management: Concepts and Technologies, 2 e, Elsevier Ltd. , 2009 v Baran, Galka and Strunk, Principles of Customer Relationship Management, South-Western, 2008
References v Francis Buttle, Customer Relationship Management: Concepts and Technologies, 2 e, Elsevier Ltd. , 2009 v Baran, Galka and Strunk, Principles of Customer Relationship Management, South-Western, 2008


