19a97974550138144f18d56ab28d799b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
PKI Robin Burke ECT 582

Outline ¢ ¢ Discussion Review l The need for PKI l hierarchical PKI l networked PKI l bridging Certificate policies l rationale l examples l X. 509 implementation

Review ¢ Private key cryptography l ¢ Public key cryptography l ¢ shared secrets proving identity Public key certificates l trusting a certificate

Certificate trust ¢ Bob has a certificate signed by T l ¢ saying that k is Alice's public key What does Bob need to convince him to trust T? l l Proof that the signature on the certificate was made by T Proof that T is not a front for Eve, or Proof that T is a trustworthy organization Proof that T's standard of proof for Alice's identity is appropriate

Hand-waving ¢ ¢ The CA's public key is "well-known" Why doesn't this work? l l l ¢ Too many CAs Different public keys for different purposes How are keys published? New assumption l l Every user has their own certificate Every user has a relationship with some CA

Certification paths ¢ Basic idea l l ¢ root CA non-root CAs Really we mean l l root certificate non-root certificates • signed by root or • some other CA ¢ Certification path l A path through hierarchy to a root CA

Path validation ¢ Certificate path is not included with the certificate l ¢ Path validation requires a directory l ¢ ¢ just the signature of the issuing CA where each link of the path can be retrieved Path validation is not just putting all the links together Inefficient path validation is the enemy of PKI

Path validation issues ¢ ¢ ¢ Verifying the digital signature and checking basic constraints Checking that the subject of every certificate is the issuer of the next certificate Checking the validity periods Checking that each certificate has not been revoked Checking the required certificate policies Checking name constraints

New problem How to organize multiple certification authorities? ¢ How to manage public keys/certificates on a large scale? ¢ Not just a technical problem ¢ legal changes l business practice changes l

Public key infrastructure A system of public key encryption using digital certificates from Certificate Authorities and other registration authorities that verify and authenticate the validity of each party involved in an electronic transaction. - FOLDOC

Hierarchical PKI ¢ ¢ Simplest case All certification paths start from the root CA Everyone absolutely trusts the top CA l uses it as root CA Advantages l Good scalability l Easy to find certification path • Unique certificate path for any end entity CA restrictions established by root Disadvantage: l ¢ l For commercial world, hard to identify a top CA l A single point of failure
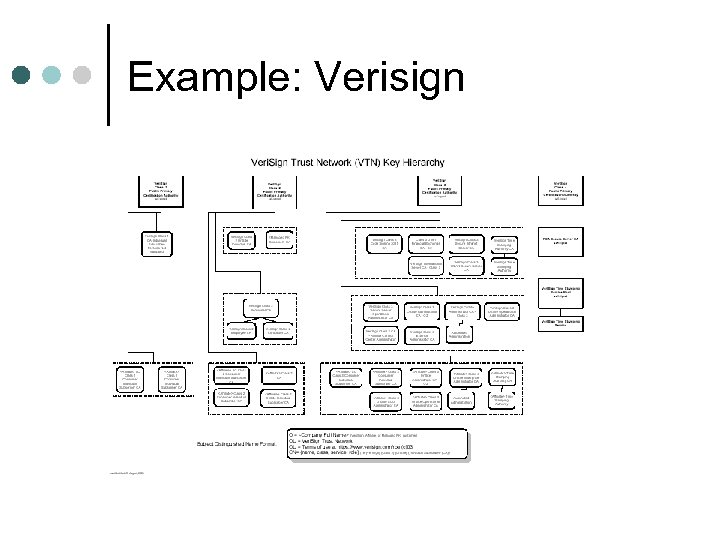
Example: Verisign
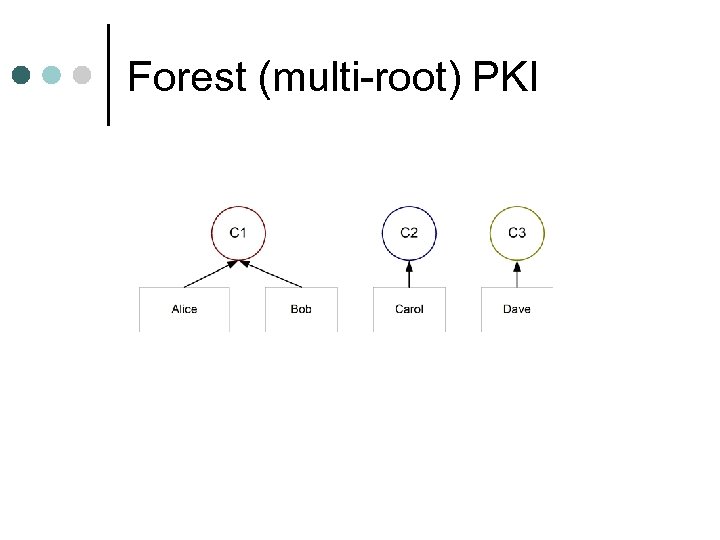
Forest (multi-root) PKI

How to manage? ¢ Combine hierarchical CA relationship, or l peer-to-peer l ¢ Multiple trust points

Hierarchical combination Back to hierarchical PKI ¢ Either ¢ Add a new master root l Select one existing root as master l
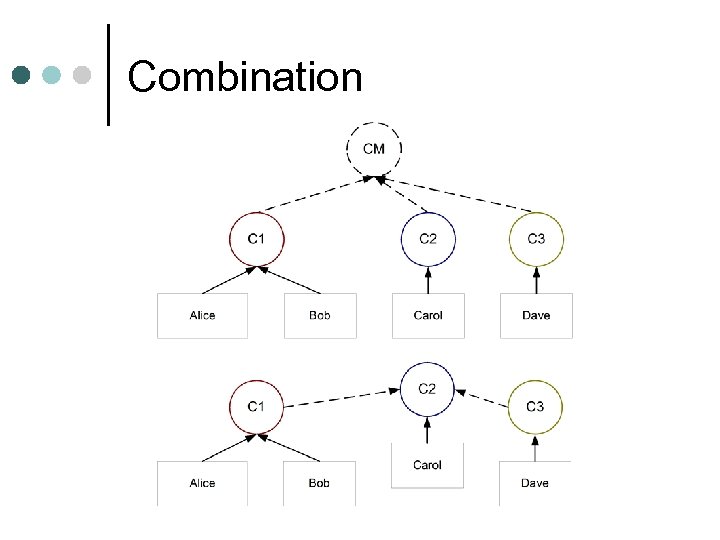
Combination

Problem ¢ Back to hierarchy
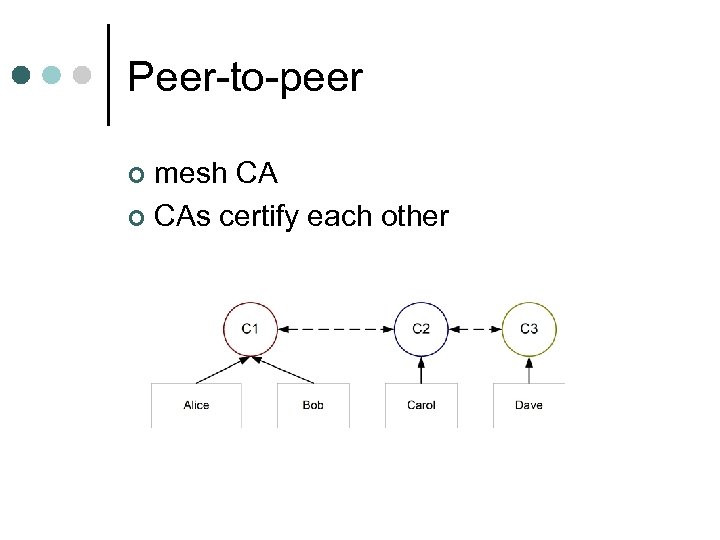
Peer-to-peer mesh CA ¢ CAs certify each other ¢

Advantages ¢ Easy to establish l ¢ Users don't have to change their trust relationships Resilient Compromise of one CA can't destroy network l Other CA's revoke certificates l

Disadvantages ¢ Certification paths difficult to compute possible loops, dead-ends l could be as long as the number of CAs in mesh l ¢ No controlling CA l restrictions hard to establish / enforce

Multiple trust points ¢ Don't join trust hierarchies l ¢ Who makes this decision? l ¢ Accept multiple trusted entities user / administrator How is it accomplished? direct trust relationship l cross-certification l
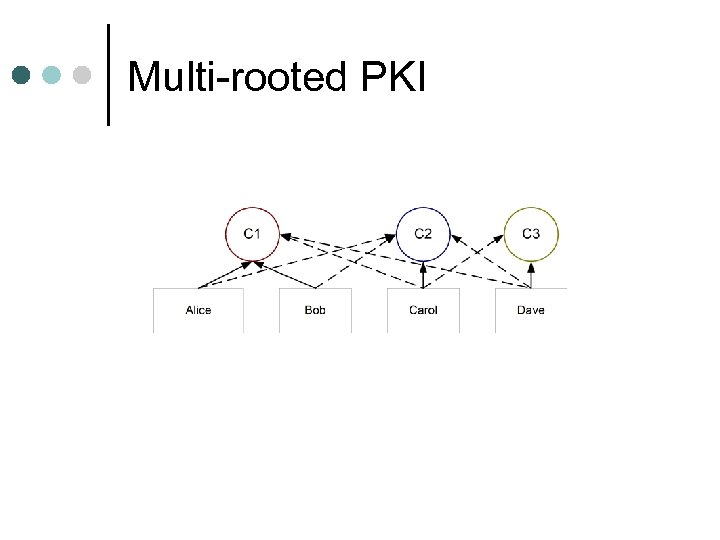
Multi-rooted PKI

User-controlled direct IE model ¢ Multiple root certificates available ¢ To add a new one ¢ l ¢ user must choose to trust or not Problem l can the user make adequate trust decisions?

User-controlled crosscertification Lotus Notes model ¢ User acts as a mini-CA ¢ l each trusted certificate signed by user Converts forest back to hierarchy ¢ Again, user has to make trust decisions ¢
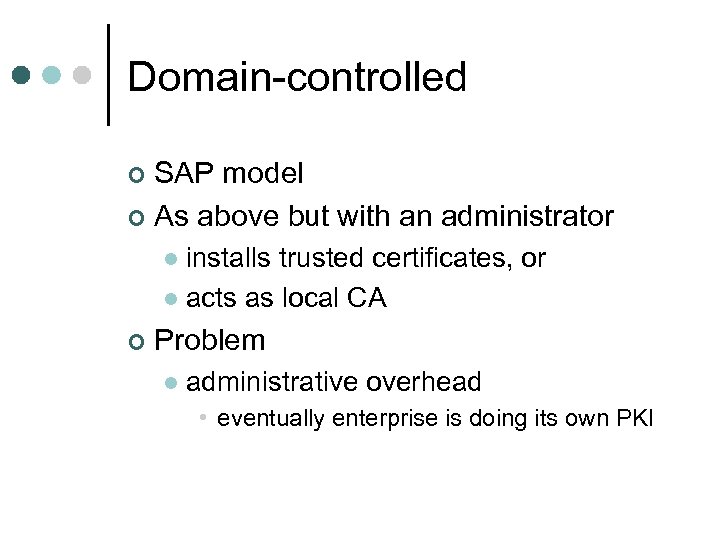
Domain-controlled SAP model ¢ As above but with an administrator ¢ installs trusted certificates, or l acts as local CA l ¢ Problem l administrative overhead • eventually enterprise is doing its own PKI

Multi-rooted ¢ Advantages Each CA forms a hierarchy l Easy to add new hierarchies l ¢ Disadvantages Not scalable l Too many trust decisions l

PGP ¢ ¢ ¢ Accepts X. 509 certificates Also, has alternative to CA l "web of trust" Model l local key ring l trust individuals as introducers l levels of trust • • l trusted untrusted case-by-case marginal multiple marginal introducers = 1 trusted

Advantages ¢ Simplicity l ¢ Every user his own CA Free l No contracts to sign Counter-cultural ¢ Multiple signers ¢ l independent confirmation of identity

Disadvantages Certification standards ¢ Counter-cultural ¢ End user responsibility ¢ Technical ¢ l Multiple signatures not part of X. 509

Bridge CA ¢ Establish a CA l ¢ just for the bridging function BCA establishes bi-directional trust with the root of each hierarchy l cross-signed certificates l
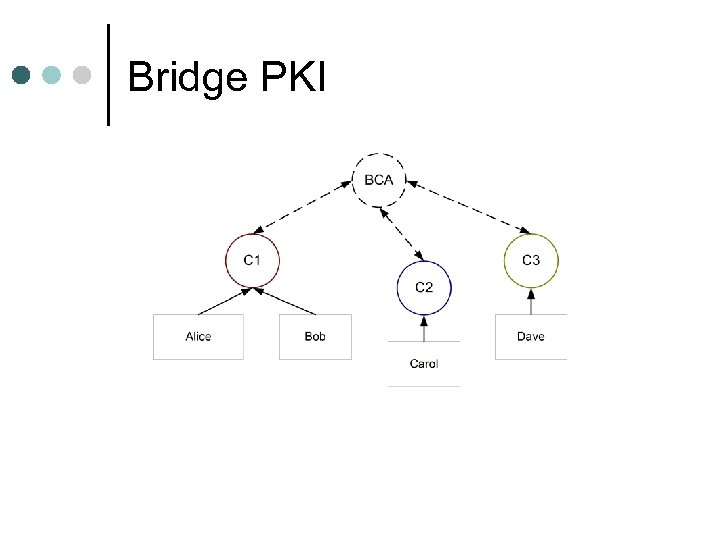
Bridge PKI

Advantages ¢ ¢ Doesn't matter what type of PKI are joining l hierarchies can join with meshes Doesn't establish a new hierarchy l with attendant political issues Bridge is not a single point of failure l if bridge is compromised, joining CAs revoke their certification l bridging must be restablished, but CAs still function independently Bridge adds only minimally to the certification path l p 1 + p 2 + 2 l hard to see how to do better

Disadvantages ¢ New entity (BCA) must be established l sufficiently trusted by root CAs

Example ¢ ¢ Federal Bridge Certification Authority Original plan l l ¢ Meanwhile l l ¢ hierarchical CA infighting about who would control the root federal agencies developed separate PKIs need to integrate Development of Bridge CA (2003) l now different agencies can communicate securely

Break

Trusted Third Party The CA is a trusted third party ¢ How do we come to trust the CA? ¢ l published practices • how the business operates l independent audit • fourth party verification of conformance l statement of liability • assumption of liability for nonperformance

CPS ¢ ¢ ¢ "Certification Practice Statement" Documentation of internal practices used in CA Many dimensions l l ¢ technical personnel insurance procedures Example on line

Certificate policy ¢ CPS usually sets forth different types of certificates l conditions under which those certificates will be issued l relevant certificate policy IDs l • X. 509 OID l pertinent extensions

Certificate Policies ¢ Requirements for various secure transactions l usually community-defined Different CAs may issue certificates in accordance with the policy ¢ Application software can recognize a key ¢ l appropriate for a particular task

Examples ¢ Procurement l l ¢ Inter-library loan l l ¢ Under $100 Under $5000, etc. General loan Reference/Periodical Music l l Low-quality download High-quality download

Components of policy key usage ¢ security level ¢

Key Usage signature ¢ non-repudiation ¢ key encipherment ¢ data encipherment ¢ key agreement ¢ certificate signing ¢ CRL signing ¢

Security level ¢ Two factors how secure the private key is l how thoroughly the identity of the holder is verified l

Levels of Assurance ¢ Test l ¢ Rudimentary l l ¢ l l basic level of assurance Risk low May be used to secure private information Medium l l ¢ lowest degree of assurance concerning identity of the individual. Data integrity only Risk low No for authentication, confidentiality Basic l ¢ interoperability testing between the FBCA and Principal CAs. Transactions having substantial monetary value or risk of fraud Access to private information where likelihood of malicious access is substantial High l l Consequence of failure are high, or risk is high High-value transactions -- FBCA

Documentation standards ¢ Test l ¢ Rudimentary l ¢ l l in-person appearance or data comparison against trusted DB or attestation of authorized agent Medium l l ¢ email address only Basic l ¢ None in-person appearance information shall be verified pre-existing relationship may suffice (employee documents) one Federal Gov't issue photo ID (passport/green card), or State photo ID (drivers license) plus one other form of ID High l same as Medium but in-person appearance required

Key protection standards ¢ Test, Rudimentary, Basic l ¢ Medium l ¢ software OK hardware preferred High hardware only l tamper-evident hardware preferred l

X. 509 Implementation ¢ A policy has a OID l ¢ Book example: {joint-iso-itu-t (2) country (16) us (840) organization (1) sharons (15678) policies (4) generaluse (2)} A policy is either critical or l not critical l

Examples ¢ Certificate profile l ¢ outline of certificate contents Certificate l Data format

Midterm ¢ 10/9 1. 5 hours l no following lecture l

Topics ¢ ¢ Chapters 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 10 Security and e-commerce l l ¢ Cryptography l l ¢ attacks mechanisms private key public key exchange digital signature PKI l l l key management X. 509 certificate distribution certification authority certification path PKI structures: hierarchy, mesh and bridge
19a97974550138144f18d56ab28d799b.ppt