eb3c541085d1146d73cad43d5e608e6f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 PKI Overview Tim Polk, NIST wpolk@nist. gov
PKI Overview Tim Polk, NIST wpolk@nist. gov
 Background u Secret key cryptography works, but key management is a nightmare u Public key cryptography uses two keys – one that is secret to the “owner” – one that is widely available u And all our problems were solved? – who’s key is this anyway? – who says so?
Background u Secret key cryptography works, but key management is a nightmare u Public key cryptography uses two keys – one that is secret to the “owner” – one that is widely available u And all our problems were solved? – who’s key is this anyway? – who says so?
 Public Key Infrastructure u Secure, reliable, and scalable method for distributing public keys for secrecy, correctness, and sender verification u “Binds” the owner to the public key using a digital certificate u Maintains and distributes status information for the life of that binding
Public Key Infrastructure u Secure, reliable, and scalable method for distributing public keys for secrecy, correctness, and sender verification u “Binds” the owner to the public key using a digital certificate u Maintains and distributes status information for the life of that binding
 Roles of PKI Components u CA is like the DMV and issues and revokes certificates u RA is the person that checks your identity u Client have and use certificates u Repository stores the certificate and status information so clients don’t have to
Roles of PKI Components u CA is like the DMV and issues and revokes certificates u RA is the person that checks your identity u Client have and use certificates u Repository stores the certificate and status information so clients don’t have to
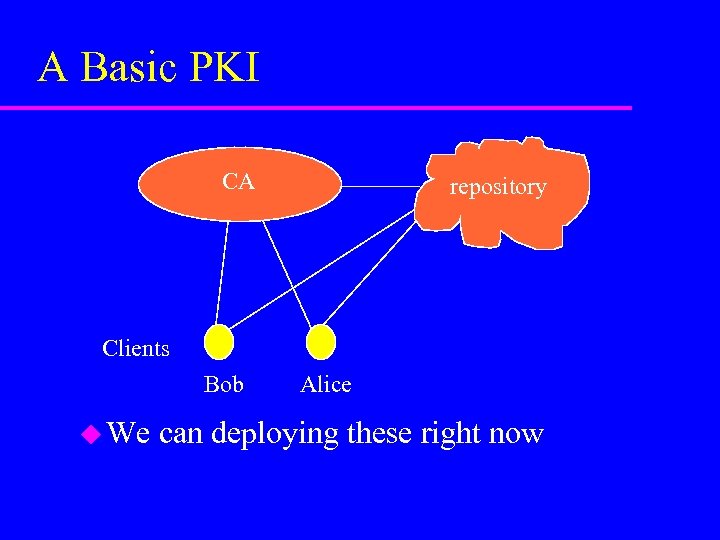 A Basic PKI CA repository Clients Bob u We Alice can deploying these right now
A Basic PKI CA repository Clients Bob u We Alice can deploying these right now
 Growing A PKI u bigger PKIs can be constructed by connecting CAs u they issue certificates to remote CAs, binding the remote CA to it’s public key u clients can construct “chains” of linked bindings
Growing A PKI u bigger PKIs can be constructed by connecting CAs u they issue certificates to remote CAs, binding the remote CA to it’s public key u clients can construct “chains” of linked bindings
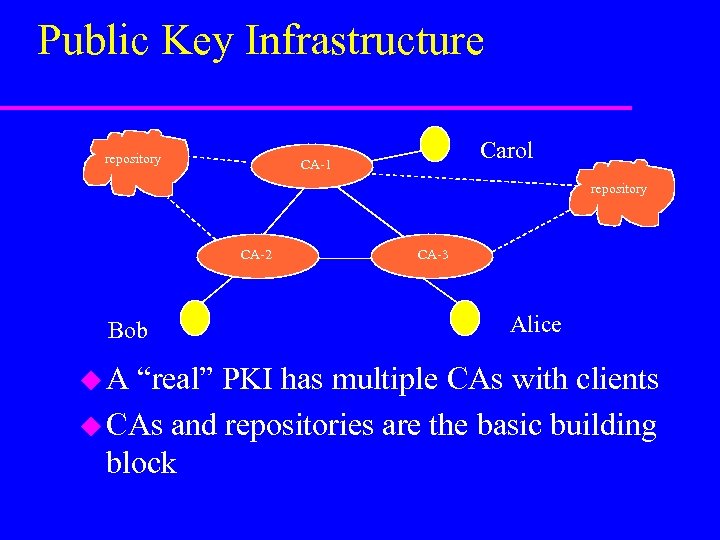 Public Key Infrastructure repository Carol CA-1 repository CA-2 Bob u. A CA-3 Alice “real” PKI has multiple CAs with clients u CAs and repositories are the basic building block
Public Key Infrastructure repository Carol CA-1 repository CA-2 Bob u. A CA-3 Alice “real” PKI has multiple CAs with clients u CAs and repositories are the basic building block
 PKIs are simple. . . u as long as you have just one CA and one repository – theoretically, they are like lego blocks – in practice, they can be like a box of bicycle parts on Christmas Eve u the complexity is the result of – unstable standards – non-interoperable products and applications
PKIs are simple. . . u as long as you have just one CA and one repository – theoretically, they are like lego blocks – in practice, they can be like a box of bicycle parts on Christmas Eve u the complexity is the result of – unstable standards – non-interoperable products and applications
 Standardization Activities u IETF (PKIX WG) u ISO JTC 1/SC 6 directory work u ANSI X 9 F and ISO TC 68/SC 2/WG 8
Standardization Activities u IETF (PKIX WG) u ISO JTC 1/SC 6 directory work u ANSI X 9 F and ISO TC 68/SC 2/WG 8
 IETF Public Key Infrastructure Using X. 509 (PKIX) WG u Formed in 1995 u Five RFCs issued in ‘ 99, four more approved in the last month – certificate and CRL formats – PKI transaction formats and protocols – Certificate Policy Statements – certificate and certificate status retrieval mechanisms
IETF Public Key Infrastructure Using X. 509 (PKIX) WG u Formed in 1995 u Five RFCs issued in ‘ 99, four more approved in the last month – certificate and CRL formats – PKI transaction formats and protocols – Certificate Policy Statements – certificate and certificate status retrieval mechanisms
 Certificate and CRL Formats u Base profile is complete (RFC 2459) – based on X. 509, but adds semantics to Internetspecific fields and data u Supporting documents are (nearly) complete – KEA (RFC 2527) and ECDSA (I-D) – enhanced CRLs (I-D) – enhanced name semantics (I-D)
Certificate and CRL Formats u Base profile is complete (RFC 2459) – based on X. 509, but adds semantics to Internetspecific fields and data u Supporting documents are (nearly) complete – KEA (RFC 2527) and ECDSA (I-D) – enhanced CRLs (I-D) – enhanced name semantics (I-D)
 Transaction Formats and Protocols u Three major specifications – Certificate Request Message Format, or CRMF (RFC 2511) – Certificate Management Protocol, or CMP (RFC 2510) [references 2511] – Certificate Management Messages over CMS, or CMC (I-D) [references 2511] u Is there room for CMP and CMC?
Transaction Formats and Protocols u Three major specifications – Certificate Request Message Format, or CRMF (RFC 2511) – Certificate Management Protocol, or CMP (RFC 2510) [references 2511] – Certificate Management Messages over CMS, or CMC (I-D) [references 2511] u Is there room for CMP and CMC?
 Certificate and Certificate Status Retrieval u. A wealth of choices – LDAP V 2 schema – LDAP V 2 profile – FTP and HTTP – OCSP
Certificate and Certificate Status Retrieval u. A wealth of choices – LDAP V 2 schema – LDAP V 2 profile – FTP and HTTP – OCSP
 New PKIX Work u Timestamp service protocol u Data certification service protocol u Attribute certificates
New PKIX Work u Timestamp service protocol u Data certification service protocol u Attribute certificates
 ISO Directory Work u Three projects in the directory area were assigned to JTC 1/SC 6 – X. 509 » maintaining the public key certificate work » new work in attribute certificates – X. 500 directory work – ASN. 1 (X. 680? )
ISO Directory Work u Three projects in the directory area were assigned to JTC 1/SC 6 – X. 509 » maintaining the public key certificate work » new work in attribute certificates – X. 500 directory work – ASN. 1 (X. 680? )
 ANSI X 9 F u Provider of cryptographic standards u Developing certificate and certificate extension profiles for banking community – TC 68 documents 15782 -1 and 15782 -3 u Defining short certificates for bandwidth or storage impaired environments – smart cards, cell phones, etc. u Attribute certificate work (15782 -2)
ANSI X 9 F u Provider of cryptographic standards u Developing certificate and certificate extension profiles for banking community – TC 68 documents 15782 -1 and 15782 -3 u Defining short certificates for bandwidth or storage impaired environments – smart cards, cell phones, etc. u Attribute certificate work (15782 -2)
 Standardization Summary u ISO, IETF and ANSI are making good progress u Most of the work is complementary, or at least well-aligned u There are still too many choices in some areas (transaction and retrieval protocols) u Parallel attribute certificate projects may result in divergent standards
Standardization Summary u ISO, IETF and ANSI are making good progress u Most of the work is complementary, or at least well-aligned u There are still too many choices in some areas (transaction and retrieval protocols) u Parallel attribute certificate projects may result in divergent standards
 Interoperability Testing u The new frontier – PKI interoperability – PKI component interoperability u Issues: – are certificates and CRLs well-formed? – can components request/revoke certificates? – can clients build/validate paths?
Interoperability Testing u The new frontier – PKI interoperability – PKI component interoperability u Issues: – are certificates and CRLs well-formed? – can components request/revoke certificates? – can clients build/validate paths?
 NIST’s PKI Interoperability Testbed u Project Goals: – Creation of complex directory systems – Creation of heterogeneous PKIs – Determination of client functionality u Summary: – the state of the art is a homogeneous PKI with a very small number of CAs and exactly one directory
NIST’s PKI Interoperability Testbed u Project Goals: – Creation of complex directory systems – Creation of heterogeneous PKIs – Determination of client functionality u Summary: – the state of the art is a homogeneous PKI with a very small number of CAs and exactly one directory
 PKI Component Interoperability Testing u Three basic components – CAs: X. 509 certificate and CRL generation – Clients: X. 509 path validation – CAs, RAs, clients: transaction message formats and protocols u As protocols stabilize, interoperability testing is the logical next step
PKI Component Interoperability Testing u Three basic components – CAs: X. 509 certificate and CRL generation – Clients: X. 509 path validation – CAs, RAs, clients: transaction message formats and protocols u As protocols stabilize, interoperability testing is the logical next step
 Tools for Interoperability Testing u reference implementations – MISPC Reference Implementation from NIST (X. 509, CMP, and CRMF) – IBM (X. 509, CMP, and CRMF) u Conformance tests – NIST (CMP, CRMF)
Tools for Interoperability Testing u reference implementations – MISPC Reference Implementation from NIST (X. 509, CMP, and CRMF) – IBM (X. 509, CMP, and CRMF) u Conformance tests – NIST (CMP, CRMF)
 PKI deployment u Many pilots ongoing or planned – “many will play, few will win!” u Why? – directory infrastructure – application vacuum – unreasonable expectations
PKI deployment u Many pilots ongoing or planned – “many will play, few will win!” u Why? – directory infrastructure – application vacuum – unreasonable expectations
 Directories u Often the problem, instead of the solution! – X. 500 directories – LDAP directories u Alternative solutions – alternative retrieval protocols – all-inclusive packaging
Directories u Often the problem, instead of the solution! – X. 500 directories – LDAP directories u Alternative solutions – alternative retrieval protocols – all-inclusive packaging
 X. 500 u the global X. 500 directory is a myth – it would resolve most access problems – it would introduce new problems » DIT management – shadowing, replication and chaining » well specified » not well tested (different implementations don’t actually interoperate!)
X. 500 u the global X. 500 directory is a myth – it would resolve most access problems – it would introduce new problems » DIT management – shadowing, replication and chaining » well specified » not well tested (different implementations don’t actually interoperate!)
 LDAP u LDAP is ubiquitous, but: – resolves localized access problems – relies on referrals to scale » performance bottleneck » poor client support – shadowing, replication and chaining » proprietary solutions, if they exist at all » may be addressed in LDAP V 3 extensions
LDAP u LDAP is ubiquitous, but: – resolves localized access problems – relies on referrals to scale » performance bottleneck » poor client support – shadowing, replication and chaining » proprietary solutions, if they exist at all » may be addressed in LDAP V 3 extensions
 Alternative Solutions u Why rely on directories at all? – FTP/HTTP/DNS retrieval » we’ve already got these servers, and they work! » requires a pointer in the certificate – all-inclusive packaging (S/MIME) » just include the certificate(s) and CRL(s) in each transaction and the client doesn’t have to search » not a complete solution because you can’t always predict the path for the receiving client
Alternative Solutions u Why rely on directories at all? – FTP/HTTP/DNS retrieval » we’ve already got these servers, and they work! » requires a pointer in the certificate – all-inclusive packaging (S/MIME) » just include the certificate(s) and CRL(s) in each transaction and the client doesn’t have to search » not a complete solution because you can’t always predict the path for the receiving client
 The Application Vacuum u PKI-aware products are limited – TLS and SSL (browsers), S/MIME u Why aren’t there more PKI-aware products? – chicken and egg problem (what PKI? ) – not a straightforward upgrade (e. g. , adding digital signatures to insecure applications) – no standard API (rewrite for every product)
The Application Vacuum u PKI-aware products are limited – TLS and SSL (browsers), S/MIME u Why aren’t there more PKI-aware products? – chicken and egg problem (what PKI? ) – not a straightforward upgrade (e. g. , adding digital signatures to insecure applications) – no standard API (rewrite for every product)
 Unreasonable Expectations u PKI is a not going to solve all your problems – first and foremost, PKI is a key management solution – overloading with additional semantics (e. g. , roles and complex policies) is beyond the state of the art
Unreasonable Expectations u PKI is a not going to solve all your problems – first and foremost, PKI is a key management solution – overloading with additional semantics (e. g. , roles and complex policies) is beyond the state of the art
 Piloting for Success u choose an existing application with: – a close-knit community of users – security in place (esp. access control), but – a known key management problem u use a single repository for all information u focus on the key management problem first u attempt to leverage certificates for access control second (if at all)
Piloting for Success u choose an existing application with: – a close-knit community of users – security in place (esp. access control), but – a known key management problem u use a single repository for all information u focus on the key management problem first u attempt to leverage certificates for access control second (if at all)
 Current Market Players u PKI product providers – rudimentary assurance – high assurance u Service providers – certificate issuers – status information providers u Community of Interest Groups – ANX, Federal Government, financial
Current Market Players u PKI product providers – rudimentary assurance – high assurance u Service providers – certificate issuers – status information providers u Community of Interest Groups – ANX, Federal Government, financial
 Community of Interest Groups Rule u they determine the winners and losers – communities of interest that use the PKI will determine the features and protocols – if no communities emerge to use PKI, it will all disappear u they are emerging (ANX, US government, SET, etc. ) and PKI will appear in more applications
Community of Interest Groups Rule u they determine the winners and losers – communities of interest that use the PKI will determine the features and protocols – if no communities emerge to use PKI, it will all disappear u they are emerging (ANX, US government, SET, etc. ) and PKI will appear in more applications
 Summary u The standards bodies have gotten their act together, but a few thorns remain u The state of the art PKI products – can support focused applications today – can’t support a global infrastructure today – aren’t interoperable, but will be “soon” u Application and directory solutions are lagging, but vendors will respond to communities of interest deploying PKIs
Summary u The standards bodies have gotten their act together, but a few thorns remain u The state of the art PKI products – can support focused applications today – can’t support a global infrastructure today – aren’t interoperable, but will be “soon” u Application and directory solutions are lagging, but vendors will respond to communities of interest deploying PKIs
 For More Information u http: //csrc. nist. gov/pki u wpolk@nist. gov
For More Information u http: //csrc. nist. gov/pki u wpolk@nist. gov


