87789c3b75c7a18cd6d43c65cc6e1d2a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

PIONIER – fiber based NREN from an idea to the fact Artur Binczewski, Michał Przybylski, Maciej Stroiński artur | michalp | stroins@man. poznan. pl TERENA workshop on NREN-controlled fibers Copenhagen, 24 th October 2003

PIONIER - idea The idea of PIONIER emerged in 1999, based on newly announced e. Europe programme Goals: – to provide research infrastructures fulfilling the demands of modern science, education, services and applications – to develop and test new generation of applications for information society – to enable international collaboration, especially in the area of new software and services for information society PIONIER has been presented in 1999 and accepted in 2000 by KBN (State Committee for Scientific Research)

Phase I – network planning Market survey: • national providers unable to fulfill the requirements of science (lack of bandwidth, low reach, high prices) • inability to provide dark fibers Target: to find suitable solution for science • • 2000 - first DWDM over dark fiber testbed in Poland (done as PIONIER experiment), demonstration of pilot, lambda based applications 2001 – second DWDM testbed and MPLS test, Results: decision to build own fiber network, DWDM selected as the transport technology in PIONIER Problem: no dark fiber offers from telecoms Solution: PSNC will build fibers for academic community (ndependent investor or together with telcos)

Phase II – fibers deployment Financial limitations: – science cannot build fibers alone, need to cooperate with industry Solution: – some fibers were to be built with telco participation - green field deployments • 2001 – Telbank, Szeptel (1434 km) • 2002 – Telbank, (<1214) – main investor in other relations (2002, coop. with regional power grids) (reszta z 1214 km) Financial participation proportional to the fiber share in the whole cable (usually 16 fibers are owned by PIONIER, rest belongs to telcos)
Phase II – fibers deployment cont. Investment protection: – SMF (Standard Mode Fiber, G. 652, general purpose – regional and national; used currently for 10 GE transmission) – NZDSF (Non-zero Dispersion Shifted Fiber, G. 655, future long range multi-lambda 40 Gbit/s transmission for direct HPC connection) – average span length 60 km for national backbone (allows for different class of equipment to be used) – new interesting areas emerged – customer owned pipes (for future applications) Problems – local loop construction is sometimes difficult (urban area average 6 months waiting time for permissions)

Phase II – fibers deployment, 3 Q 2003.

Phase II½ – 10 GE transmission Late 2002: – the need to reduce operational costs. – availability of some fiber links scheduled at mid 2003 – needs from VLBI and CERN for high bandwidth links Decision to buy 10 GE transmission equipment for intermediate stage – tender announced. This solution shall exist until target 40 Gbit/s DWDM system is installed. Then the equipment will be moved to regional networks
Phase II½ – 10 GE transmission Tender conditions: – complete 10 GE transmission equipment had to be delivered, installed and trial-tested. – router for VLAN routing and international connectivity Tender results: – no appropriate 10 GE switch interface/line amplifier found – transport on simplified DWDM from ADVA / INRANGE – Black Diamond 10 GE switches used as core equipment – A 7770 for international connectivity and VLAN routing

Phase II½ – 10 GE transmission
![Technical details – link specification Line Poznan – Zielona Góra From To Distance [km] Technical details – link specification Line Poznan – Zielona Góra From To Distance [km]](https://present5.com/presentation/87789c3b75c7a18cd6d43c65cc6e1d2a/image-10.jpg)
Technical details – link specification Line Poznan – Zielona Góra From To Distance [km] Attenuation [d. B] Fiber type Poznan-TB ? 10 Corning G. 652 Poznan-TB Grodzisk 56. 67 13. 2 Corning G. 652 Grodzisk Wolsztyn 25. 75 6. 23 Corning G. 652 Wolsztyn Sulechów 42. 03 8. 97 Corning G. 652 Sulechów Zielona Gora TB 23. 64 5. 1 Corning G. 652 Zielona Gora TB Zielona Gora ? (4) 10 (2. 1) Corning G. 652

Link specification 2 Tender specification • fiber optics parameters specification (span, attenuation. , att. estimation @ 0. 25 d. B/km, real att. approx. 0. 23 d. B/km) • node localisation (where, what voltage, rack space) • regeneration points (where, what voltage, access etc. ) • 10 GE switch-based transport technology required (no WAN/LAN specification), one standard for whole network • number & type of required interfaces in each node • functionality of 10 GE nodes • extra functionality (ATM transport)
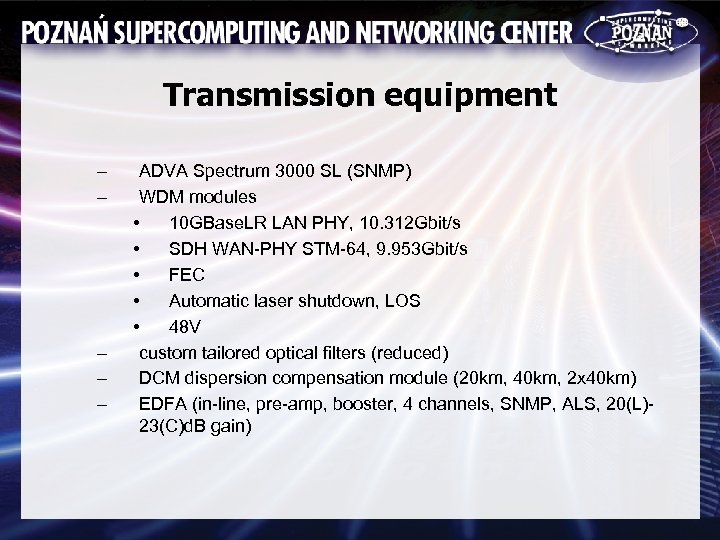
Transmission equipment – – – ADVA Spectrum 3000 SL (SNMP) WDM modules • 10 GBase. LR LAN PHY, 10. 312 Gbit/s • SDH WAN-PHY STM-64, 9. 953 Gbit/s • FEC • Automatic laser shutdown, LOS • 48 V custom tailored optical filters (reduced) DCM dispersion compensation module (20 km, 40 km, 2 x 40 km) EDFA (in-line, pre-amp, booster, 4 channels, SNMP, ALS, 20(L)23(C)d. B gain)
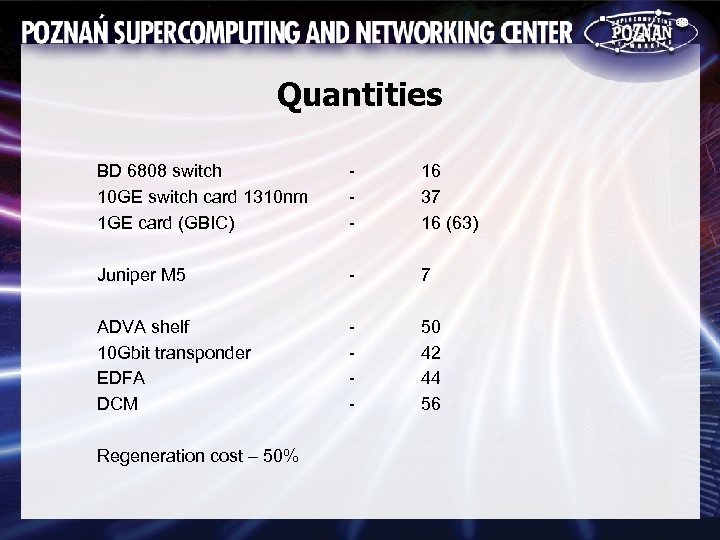
Quantities BD 6808 switch 10 GE switch card 1310 nm 1 GE card (GBIC) - 16 37 16 (63) Juniper M 5 - 7 ADVA shelf 10 Gbit transponder EDFA DCM - 50 42 44 56 Regeneration cost – 50%

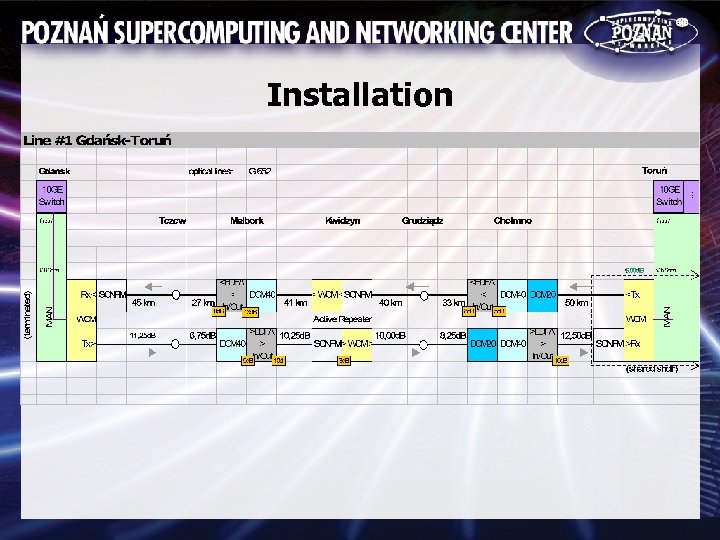
Installation
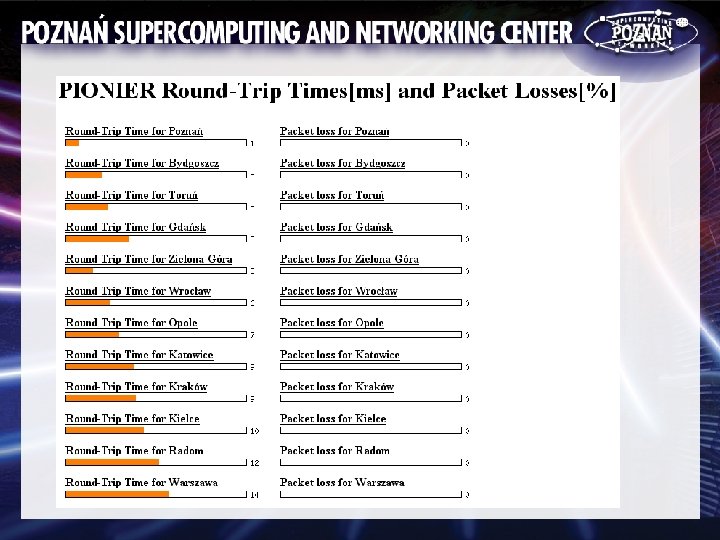
Problems • real line attenuation different (lower!) than planned (extra attenuators needed) • need to keep proper signal/noise ratio (NSR, carefull amp/WDM) operating point selection • last minute project changes (last mile length variation) • equipment relocation (changes during fiber works) • optimisation (changes wrt original project) • others not yet known (but will surely come up!)

Maintenance agreement with line operator, in case of major failure 24 hrs to restore connectivity. Failures may result from: a) improper installation b) material defects c) Force Majeure d) others (aging. . . ? ) They are repaired by the specialized company and are paid respectively by: a) installing company b) cable manufacturer c) PSNC d) PSNC. . ?

Why CEF? The economy behind Telco provided channels between 21 MANs, per year: • 622 Mb/s (real cost) : 4. 8 MEuro • 2. 5 Gb/s (estimated cost, no offers available) : 9. 6 MEuro • 10 Gb/s (estimated cost, no offers available) : 19. 2 MEuro Estimated PIONIER costs (based on actual costs for 2600 km) • cost of 5200 km of fibers + 10 GE transmission : 55. 0 MEuro • annual PIONIER maintenance costs : 2. 1 MEuro Return of Investment in 3 years! (calculations made for only 1 channel used) other advantages not included in calculation ; )

2003 1. To continue the development of remaining 2500 km of fibers (new funding of 5 MEuro received) 2. To start the deployment of regional networks

Questions?

Thank you! Michal Przybylski michalp@man. poznan. pl
87789c3b75c7a18cd6d43c65cc6e1d2a.ppt