8db8b231b44b6b5f473a3c3112d6c07c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Ping. ER: Methodology, Uses & Results Prepared by Les Cottrell, SLAC, for the Extending the Reach of Advanced Networking: Special International Workshop Arlington, VA. , April 22, 2004 www. slac. stanford. edu/grp/scs/net/talk 03/i 2 -method-apr 04. ppt Partially funded by DOE/MICS Field Work Proposal on Internet End-to-end Performance Monitoring (IEPM), also supported by IUPAP 1

Outline • • • What is Ping. ER World Internet performance trends Regions and Digital Divide Examples of use Challenges Summary of state of world Internet performance 2

Methodology • Use ubiquitous ping • Each 30 minutes from monitoring site to target : – 1 ping to prime caches – by default send 11 x 100 Byte pkts followed by 10 x 1000 Byte pkts • Low network impact good for developing world • Record loss & RTT, (+ reorders, duplicates) • Derive throughput, jitter, unreachability … 3
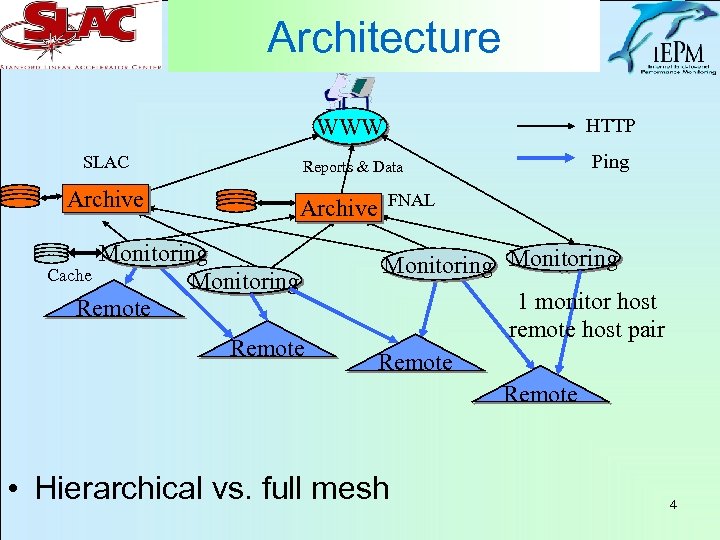
Architecture WWW Reports & Data SLAC Archive HTTP Ping Archive Monitoring Cache Monitoring Remote FNAL Monitoring 1 monitor host remote host pair Remote • Hierarchical vs. full mesh 4
Ping. ER Benefits • Aimed at: end-user (net-admin & sophisticated user), planners • Measures analyzes & reports round-trip times, losses, availability, throughput. . . – Uses ubiquitous ping, no special host, or software to install/configure at remote sites, no passwords or credentials needed – Low impact on network << 100 bits/s, important for many DD sites – Covers 100+ countries (> 90% of Internet connected population) • Provides quantitative historical (> 9 yrs) and near real-time information – Aggregate by regions, affiliations etc. – How bad is performance to various regions, rank countries? – Trends: who is catching up, falling behind, is progress being made? – Compare vs. economic, development indicators etc. • Use for trouble shooting setting expectations, identify needed upgrades, choosing a provider, presenting to policy makers, funding bodies Monitoring site vs. Remote 5 sites screen shot
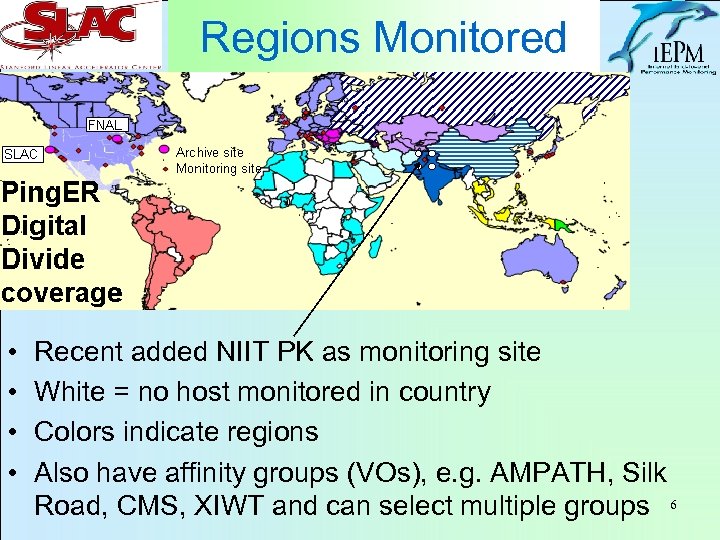
Regions Monitored • • Recent added NIIT PK as monitoring site White = no host monitored in country Colors indicate regions Also have affinity groups (VOs), e. g. AMPATH, Silk Road, CMS, XIWT and can select multiple groups 6
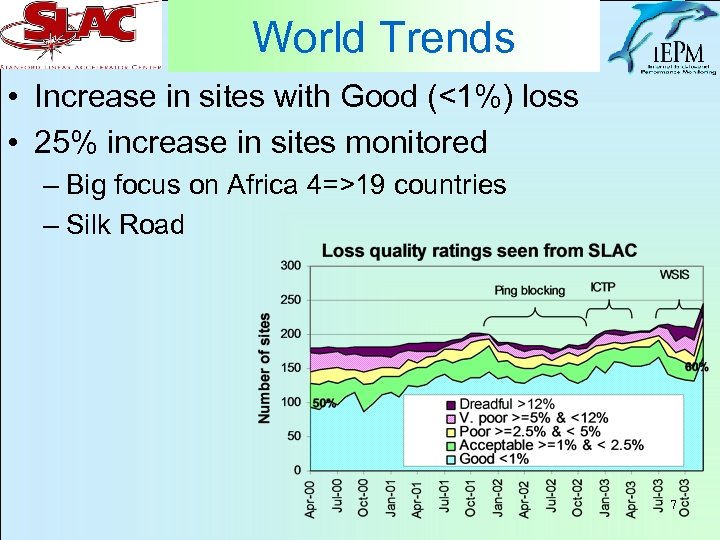
World Trends • Increase in sites with Good (<1%) loss • 25% increase in sites monitored – Big focus on Africa 4=>19 countries – Silk Road 7
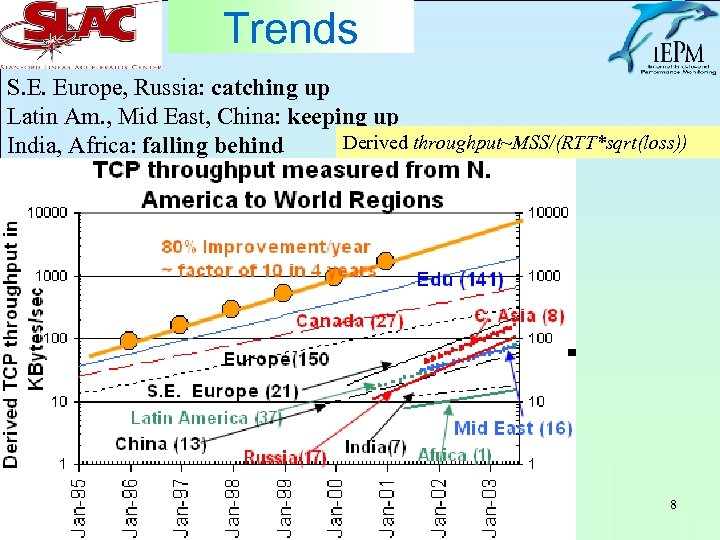
Trends S. E. Europe, Russia: catching up Latin Am. , Mid East, China: keeping up Derived throughput~MSS/(RTT*sqrt(loss)) India, Africa: falling behind 8
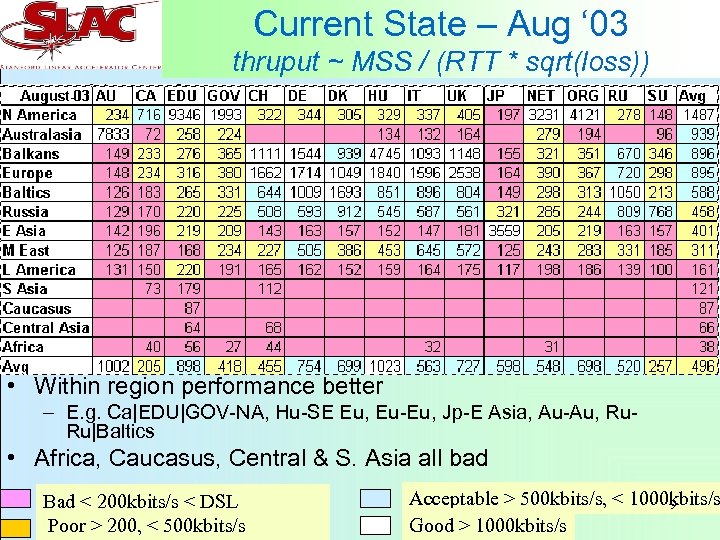
Current State – Aug ‘ 03 thruput ~ MSS / (RTT * sqrt(loss)) • Within region performance better – E. g. Ca|EDU|GOV-NA, Hu-SE Eu, Eu-Eu, Jp-E Asia, Au-Au, Ru. Ru|Baltics • Africa, Caucasus, Central & S. Asia all bad Bad < 200 kbits/s < DSL Poor > 200, < 500 kbits/s Acceptable > 500 kbits/s, < 1000 kbits/s 9 Good > 1000 kbits/s
Examples of Use • • Need for constant upgrades Upgrades Filtering Pakistan 10
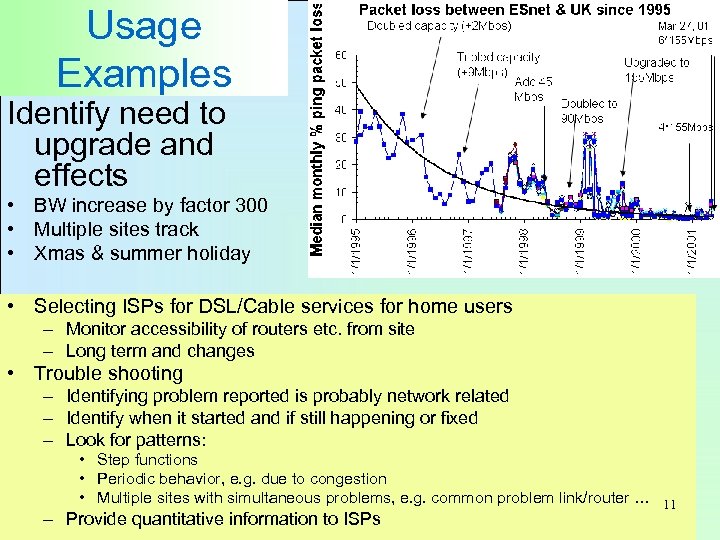
Usage Examples Identify need to upgrade and effects • BW increase by factor 300 • Multiple sites track • Xmas & summer holiday • Selecting ISPs for DSL/Cable services for home users – Monitor accessibility of routers etc. from site – Long term and changes • Trouble shooting – Identifying problem reported is probably network related – Identify when it started and if still happening or fixed – Look for patterns: • Step functions • Periodic behavior, e. g. due to congestion • Multiple sites with simultaneous problems, e. g. common problem link/router … 11 – Provide quantitative information to ISPs
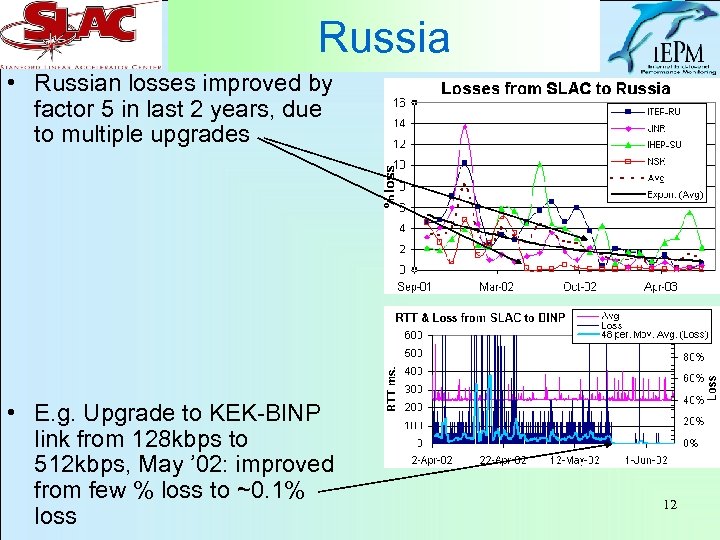
Russia • Russian losses improved by factor 5 in last 2 years, due to multiple upgrades • E. g. Upgrade to KEK-BINP link from 128 kbps to 512 kbps, May ’ 02: improved from few % loss to ~0. 1% loss 12
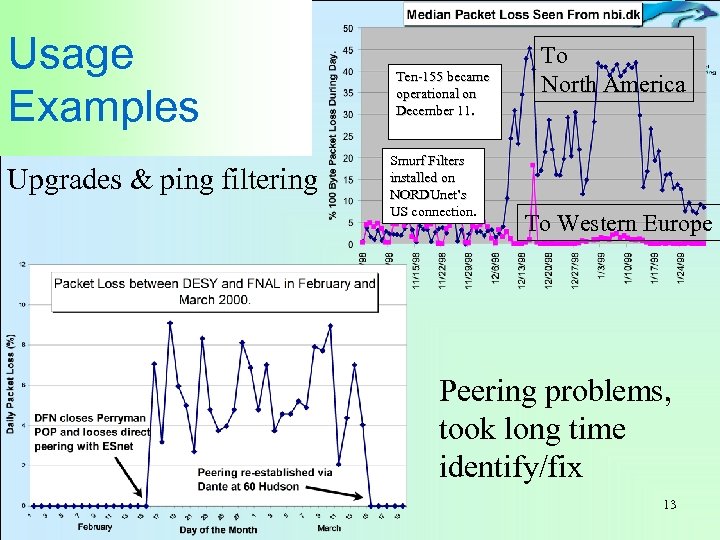
Usage Examples Upgrades & ping filtering Ten-155 became operational on December 11. Smurf Filters installed on NORDUnet’s US connection. To North America To Western Europe Peering problems, took long time identify/fix 13

Pakistan Conclusions • Big performance differences to sites, depend on ISP (at least 3 ISPs seen for Pakistan A&R sites) • To NIIT: – – Get about 300 Kbps, possibly 380 Kbps at best Verified bottleneck appeared to be in Pakistan Requested upgrade to 1 Mbps, and verified got it There is often congestion (packet loss & extended RTTs) during busy periods each weekday – Video will probably be sensitive to packet loss, so it may depend on the time of day – H. 323 (typically needs 384 Kbps + 64 Kbps), would appear to be marginal at best at any time. • No peering Pakistan between NIIT and NSC 14

Challenges • Effort: – Negligible for remote hosts – Monitoring host: < 1 day to install and configure, occasional updates to remote host tables and problem response – Archive host: 20% FTE, code stable, could do with upgrade, contact monitoring sites whose data is inaccessible – Analysis: your decision, usually for long term details download & use Excel – Trouble-shooting: • usually re-active, user reports, then look at Ping. ER data • have played with automating alerts, data will/is available via web services • Ping blocking – Complete block easy to ID, then contact site to try and by-pass, can be frustrating for 3 rd world – Partial blocks trickier, compare with synack • Funding – “Unfortunately, network management research has historically been very underfunded, because it is difficult to get funding bodies to recognize this as legitimate networking research. ” Sally Floyd, IAB Concerns & Recommendations Regarding Internet Research & Evolution. – http: //www. ietf. org/internet-drafts/draft-iab-research-funding-00. txt 15

Summary • Performance from U. S. & Europe is improving all over • Performance to developed countries are orders of magnitude better than to developing countries • Poorer regions 5 -10 years behind • Poorest regions Africa, Caucasus, Central & S. Asia • Some regions are: – catching up (SE Europe, Russia), – keeping up (Latin America, Mid East, China), – falling further behind (e. g. India, Africa) 16

More Information • Ping. ER: – www-iepm. slac. stanford. edu/pinger/ • Mona. Lisa – monalisa. cacr. caltech. edu/ • GGF/NMWG – www-didc. lbl. gov/NMWG/ • ICFA/SCIC Network Monitoring report, Jan 03 – www. slac. stanford. edu/xorg/icfa-net-paper-dec 02 • Monitoring the Digital Divide, CHEP 03 paper – arxiv. org/ftp/physics/papers/0305016. pdf • Human Development Index – www. undp. org/hdr 2003/pdf/hdr 03_backmatter_2. pdf • Network Readiness Index – www. weforum. org/site/homepublic. nsf/Content/Initiatives+subhome 17

Extra Slides 18
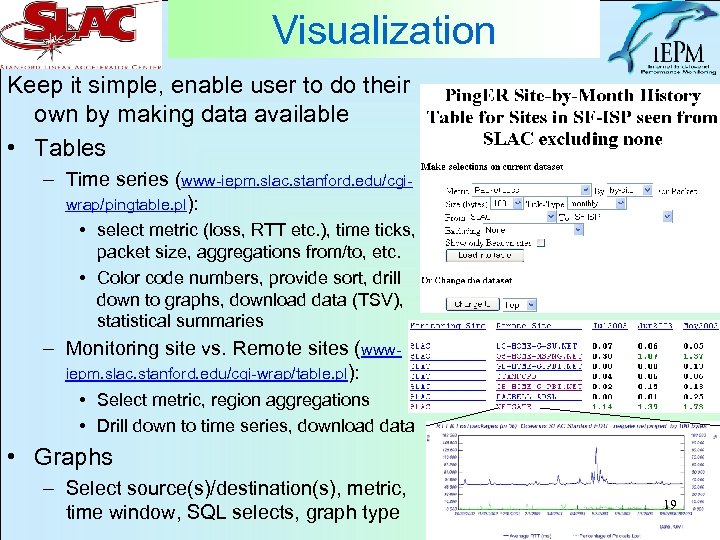
Visualization Keep it simple, enable user to do their own by making data available • Tables – Time series (www-iepm. slac. stanford. edu/cgiwrap/pingtable. pl): • select metric (loss, RTT etc. ), time ticks, packet size, aggregations from/to, etc. • Color code numbers, provide sort, drill down to graphs, download data (TSV), statistical summaries – Monitoring site vs. Remote sites (wwwiepm. slac. stanford. edu/cgi-wrap/table. pl): • Select metric, region aggregations • Drill down to time series, download data • Graphs – Select source(s)/destination(s), metric, time window, SQL selects, graph type 19
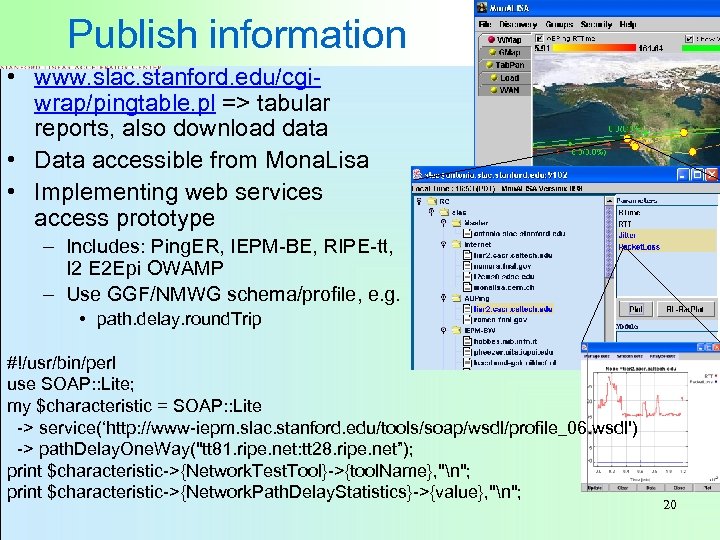
Publish information • www. slac. stanford. edu/cgiwrap/pingtable. pl => tabular reports, also download data • Data accessible from Mona. Lisa • Implementing web services access prototype – Includes: Ping. ER, IEPM-BE, RIPE-tt, I 2 E 2 Epi OWAMP – Use GGF/NMWG schema/profile, e. g. • path. delay. round. Trip #!/usr/bin/perl use SOAP: : Lite; my $characteristic = SOAP: : Lite -> service(‘http: //www-iepm. slac. stanford. edu/tools/soap/wsdl/profile_06. wsdl') -> path. Delay. One. Way("tt 81. ripe. net: tt 28. ripe. net”); print $characteristic->{Network. Test. Tool}->{tool. Name}, "n"; print $characteristic->{Network. Path. Delay. Statistics}->{value}, "n"; 20
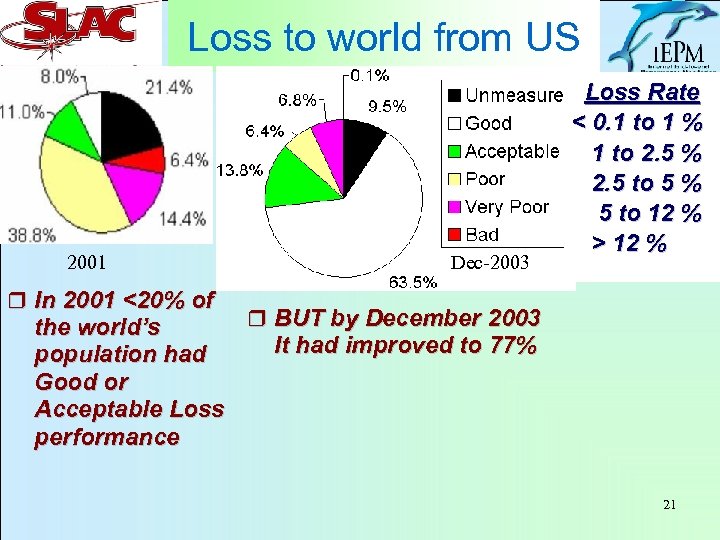
Loss to world from US 2001 Dec-2003 Loss Rate < 0. 1 to 1 % 1 to 2. 5 % 2. 5 to 5 % 5 to 12 % > 12 % r In 2001 <20% of r BUT by December 2003 the world’s It had improved to 77% population had Good or Acceptable Loss performance 21
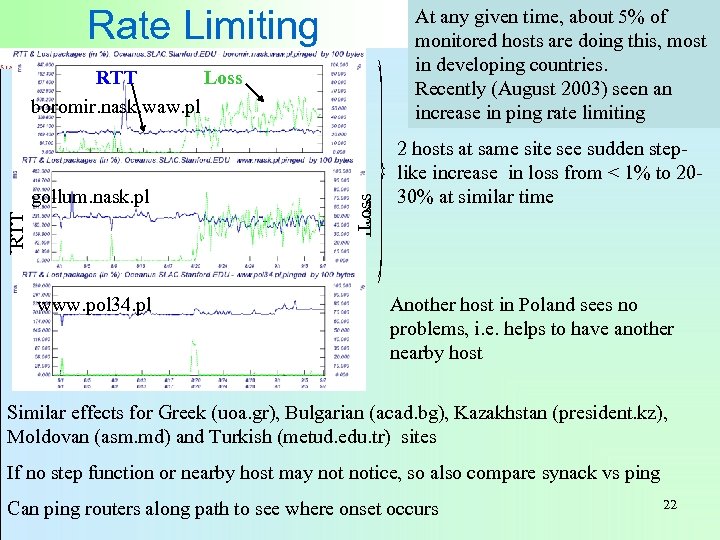
Rate Limiting At any given time, about 5% of monitored hosts are doing this, most in developing countries. Recently (August 2003) seen an increase in ping rate limiting gollum. nask. pl www. pol 34. pl Loss RTT RTT Loss boromir. nask. waw. pl 2 hosts at same site see sudden steplike increase in loss from < 1% to 2030% at similar time Another host in Poland sees no problems, i. e. helps to have another nearby host Similar effects for Greek (uoa. gr), Bulgarian (acad. bg), Kazakhstan (president. kz), Moldovan (asm. md) and Turkish (metud. edu. tr) sites If no step function or nearby host may notice, so also compare synack vs ping Can ping routers along path to see where onset occurs 22
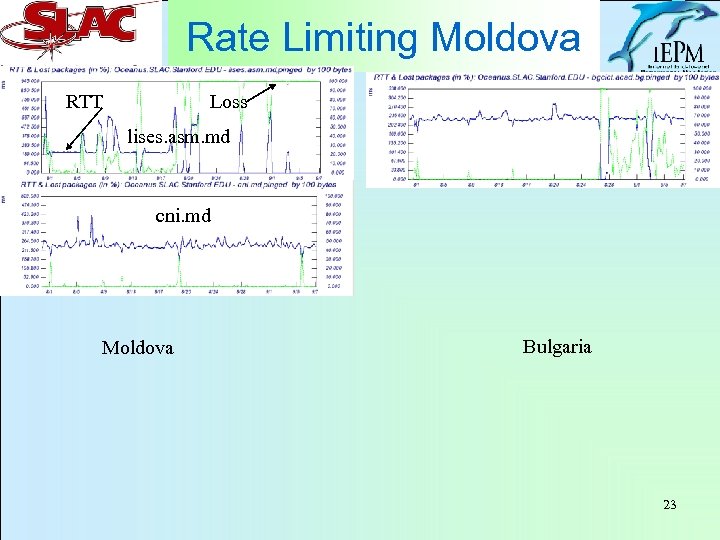
Rate Limiting Moldova RTT Loss lises. asm. md cni. md Moldova Bulgaria 23
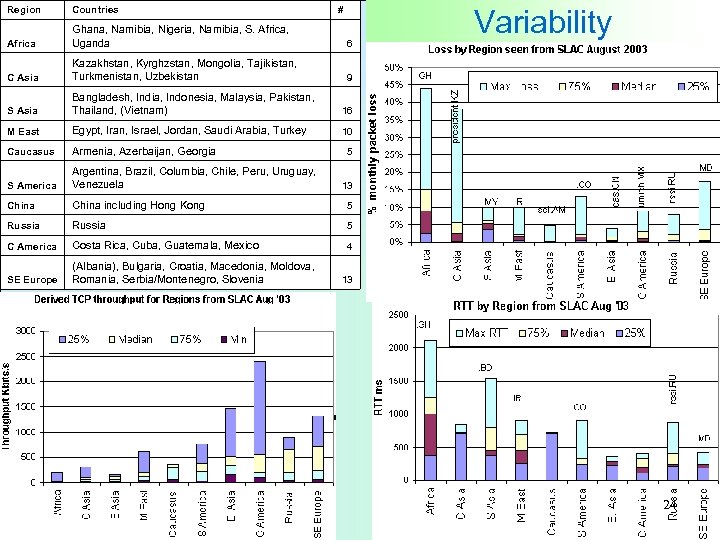
Region Countries # Africa Ghana, Namibia, Nigeria, Namibia, S. Africa, Uganda 6 C Asia Kazakhstan, Kyrghzstan, Mongolia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan 9 S Asia Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Pakistan, Thailand, (Vietnam) 16 M East Egypt, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Turkey 10 Caucasus Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia S America Argentina, Brazil, Columbia, Chile, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela China including Hong Kong 5 Russia 5 C America Costa Rica, Cuba, Guatemala, Mexico 4 SE Europe (Albania), Bulgaria, Croatia, Macedonia, Moldova, Romania, Serbia/Montenegro, Slovenia Variability 5 13 13 24

Africa • Hosts in: Ife-Ife/Nigeria, Accra/Ghana, Kampala/Uganda, Windhoek/Namibia, UCT/ZA, Johannesburg/ZA, Musselbay/ZA • Carriers: – GH uses UUNET/Satworks, NA uses UUNET/xantic, NG uses TELIANET/New. Skies, UG uses Level(3)/globalconnex – ZA varies from site to site: UUNET/ALTERNET, C&W Telecom S. Africa, CAIS telcom S. Africa • UG, NA, NG, GH use satellites (> 600 ms) • ZA uses landlines 25
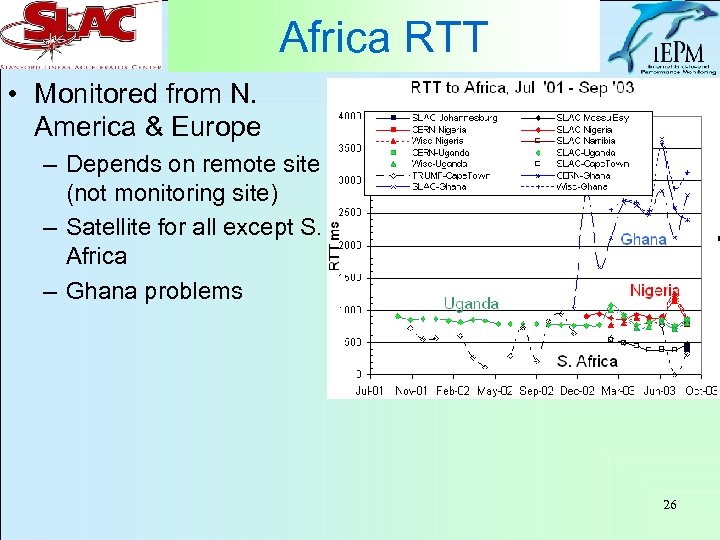
Africa RTT • Monitored from N. America & Europe – Depends on remote site (not monitoring site) – Satellite for all except S. Africa – Ghana problems 26
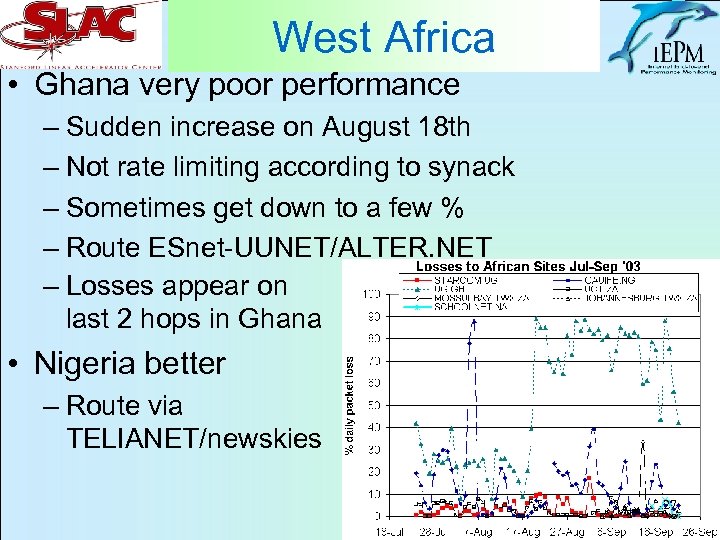
West Africa • Ghana very poor performance – Sudden increase on August 18 th – Not rate limiting according to synack – Sometimes get down to a few % – Route ESnet-UUNET/ALTER. NET – Losses appear on last 2 hops in Ghana • Nigeria better – Route via TELIANET/newskies 27
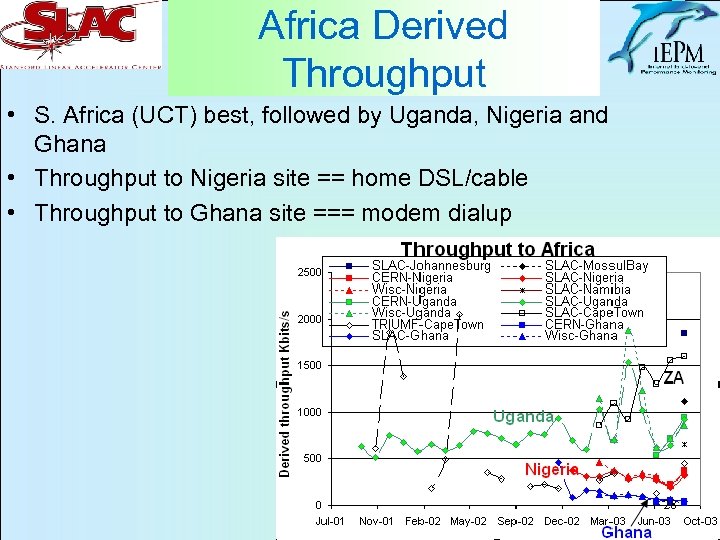
Africa Derived Throughput • S. Africa (UCT) best, followed by Uganda, Nigeria and Ghana • Throughput to Nigeria site == home DSL/cable • Throughput to Ghana site === modem dialup 28
29
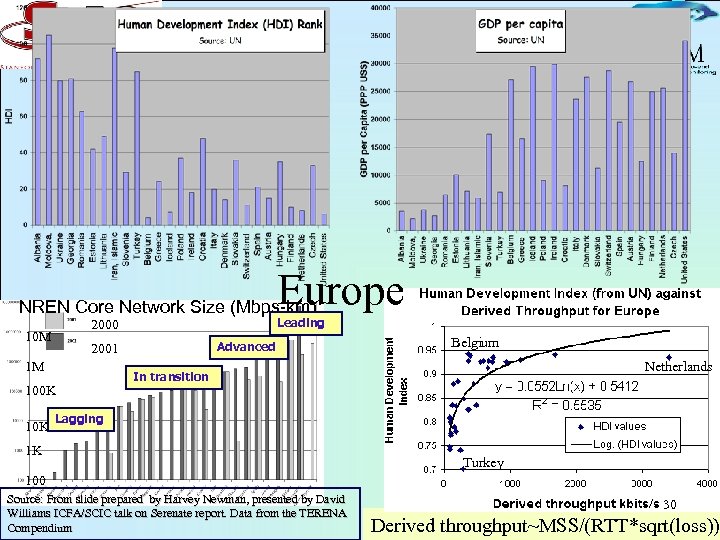
Europe NREN Core Network Size (Mbps-km) 10 M Advanced 2001 1 M 100 K 10 K Leading 2000 Belgium Netherlands In transition Lagging 1 K Turkey 100 Source: From slide prepared by Harvey Newman, presented by David Williams ICFA/SCIC talk on Serenate report. Data from the TERENA Compendium 30 Derived throughput~MSS/(RTT*sqrt(loss))
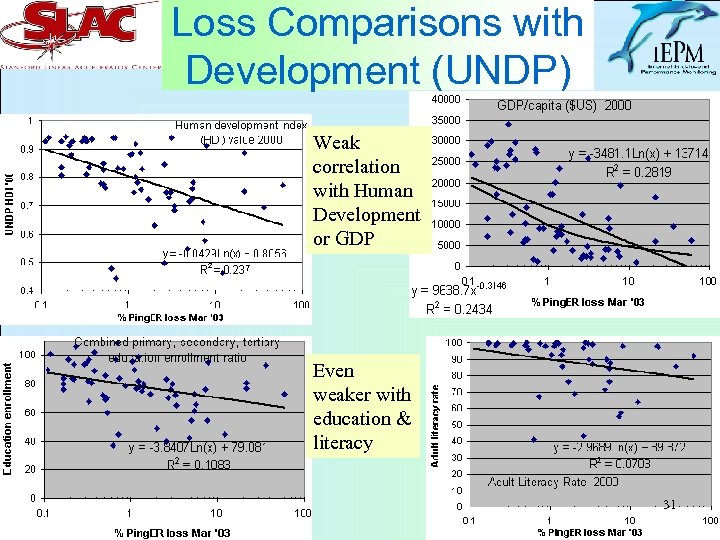
Loss Comparisons with Development (UNDP) Weak correlation with Human Development or GDP Even weaker with education & literacy 31
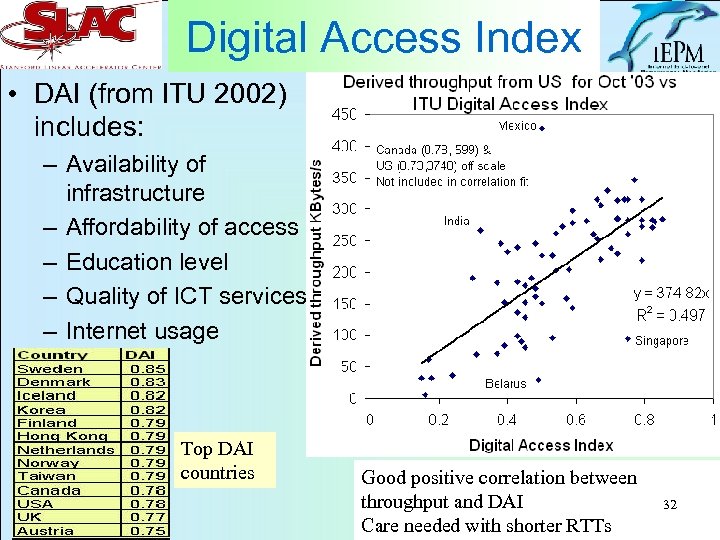
Digital Access Index • DAI (from ITU 2002) includes: – Availability of infrastructure – Affordability of access – Education level – Quality of ICT services – Internet usage Top DAI countries Good positive correlation between throughput and DAI Care needed with shorter RTTs 32
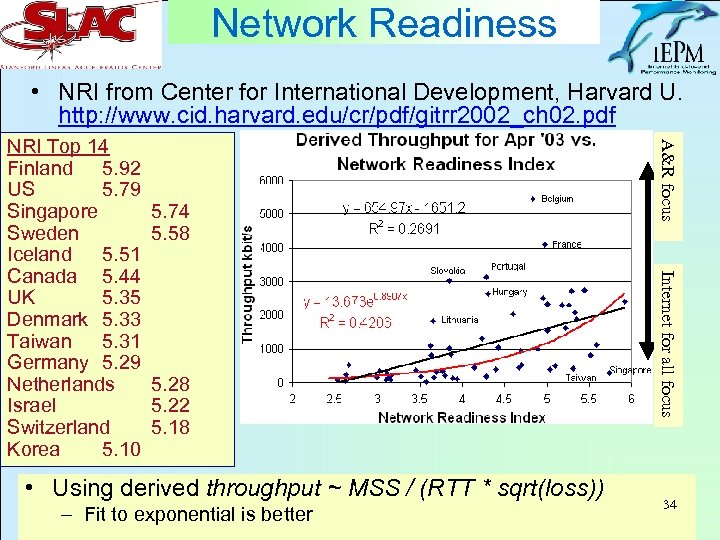
Network Readiness • NRI from Center for International Development, Harvard U. http: //www. cid. harvard. edu/cr/pdf/gitrr 2002_ch 02. pdf 5. 74 5. 58 • Using derived throughput ~ MSS / (RTT * sqrt(loss)) – Fit to exponential is better Internet for all focus 5. 28 5. 22 5. 18 A&R focus NRI Top 14 Finland 5. 92 US 5. 79 Singapore Sweden Iceland 5. 51 Canada 5. 44 UK 5. 35 Denmark 5. 33 Taiwan 5. 31 Germany 5. 29 Netherlands Israel Switzerland Korea 5. 10 34
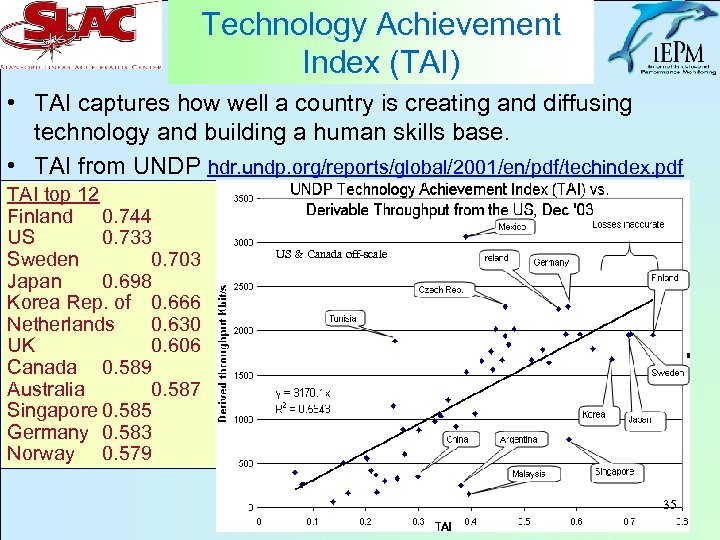
Technology Achievement Index (TAI) • TAI captures how well a country is creating and diffusing technology and building a human skills base. • TAI from UNDP hdr. undp. org/reports/global/2001/en/pdf/techindex. pdf TAI top 12 Finland 0. 744 US 0. 733 Sweden 0. 703 Japan 0. 698 Korea Rep. of 0. 666 Netherlands 0. 630 UK 0. 606 Canada 0. 589 Australia 0. 587 Singapore 0. 585 Germany 0. 583 Norway 0. 579 US & Canada off-scale 35

Futures • Get >= 2 hosts/country • Better/quicker detection of rate limiting • Have 4 students at GATech rewriting parts of Ping. ER to improve (reduce effort required for) day to day management and improve portability • Submitting a proposal to IDRC for monitoring Africa and adding a measurement host in Nigeria • Need better automated tools to produce graphs like in this presentation. 36

Collaborations & Funding • 35+ monitoring sites in 13 countries – Plan to add ICTP Trieste if funded – Other projects used toolkit, e. g. XIWT, PPCNG/EDG, IAEA … • SLAC with help from FNAL • Digital Divide collaboration (MOU) with ICTP, Trieste – e. JDS – We are requesting an IDRC grant for e. JDS and Ping. ER • Need funding for coming year (Do. E funding ended): – Tasks: • (0. 5 FTE) ongoing maintain data collection, explain needs, reopen connections, open firewall blocks, find replacement hosts, make limited special analyses, prepare & make presentations, respond to questions • (+ 0. 5 FTE) extend the code for new environment (more countries, more data collections), fix known non-critical bugs, improve visualization, automate some of reports generated by hand today, find new country site contacts, add route histories and visualization, automate alarms, detect rate limiting earlier, update web site for better navigation, add more DD monitoring sites/countries, improve code portability, understand regions better • ICFA: show importance to policy makers, funding agencies, 37 identify sympathetic contacts at agencies, get support
8db8b231b44b6b5f473a3c3112d6c07c.ppt