23466f2eea5b037f113742d2da706525.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81
 PIA 2528 Intergovernmental Relationships
PIA 2528 Intergovernmental Relationships
 Some Oral Interview Questions: End of Semester 1. What major historical factors appear to have defined Governance, Local Government and Civil Society according to our "general reading. “ 2. What factors are unique and different for Africa, Middle East, Eastern Europe, Asia or Latin America? 3. To what extent is society and culture important at the "country" level? Be able to discuss at least one country in your region.
Some Oral Interview Questions: End of Semester 1. What major historical factors appear to have defined Governance, Local Government and Civil Society according to our "general reading. “ 2. What factors are unique and different for Africa, Middle East, Eastern Europe, Asia or Latin America? 3. To what extent is society and culture important at the "country" level? Be able to discuss at least one country in your region.
 Theme The Nature of Intergovernmental Relationships
Theme The Nature of Intergovernmental Relationships
 Overview: Historical Patterns of Relations ¡ ¡ ¡ AT ISSUE - Location of ultimate power and Responsibility Definition of Power: The authoritative allocation of values Balance: Leadership, Authority and Choice ¡ WORLD WIDE HUMOR- VIDEO ¡
Overview: Historical Patterns of Relations ¡ ¡ ¡ AT ISSUE - Location of ultimate power and Responsibility Definition of Power: The authoritative allocation of values Balance: Leadership, Authority and Choice ¡ WORLD WIDE HUMOR- VIDEO ¡
 Hierarchy and Authority: Feudal and Now?
Hierarchy and Authority: Feudal and Now?
 Symbolism, Power and Authority Leadership as Image
Symbolism, Power and Authority Leadership as Image
 German Liberalism 1848
German Liberalism 1848
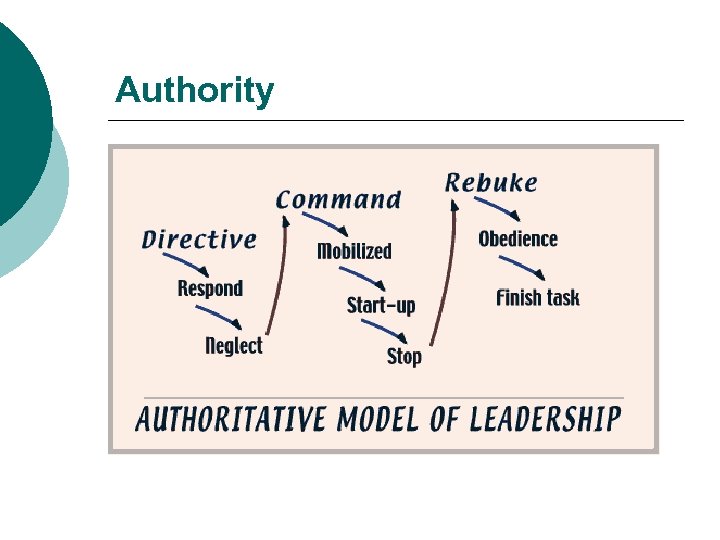 Authority
Authority
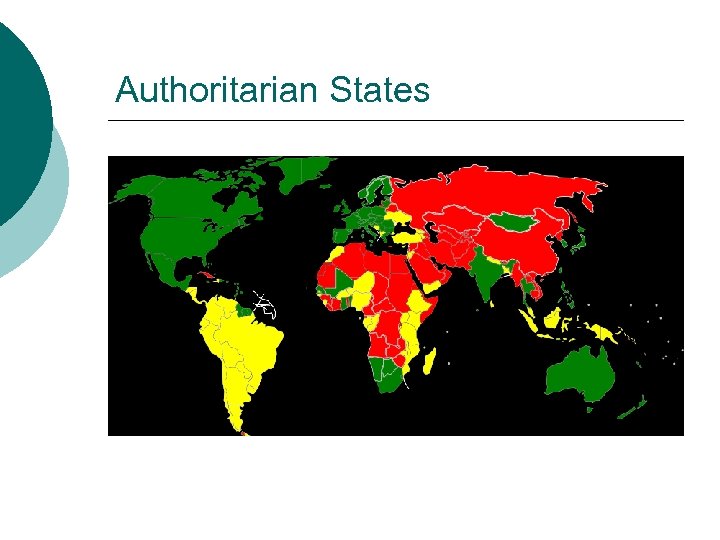 Authoritarian States
Authoritarian States
 TYPES OF INTER-GOVERNMENTAL AND INTERORGANIZATIONAL RELATIONS Confederation and loose confederal relationships
TYPES OF INTER-GOVERNMENTAL AND INTERORGANIZATIONAL RELATIONS Confederation and loose confederal relationships
 The Articles of Confederation, drafted in 1777 by the Continental Congress, served as the first Constitution of the United States.
The Articles of Confederation, drafted in 1777 by the Continental Congress, served as the first Constitution of the United States.
 Confederation Relationships Power lies with the sub-units ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ U. S. Articles of Confederation Canadian Federation European Union Southern African Development Council Economic Council of West African States ASEAN Mercusor
Confederation Relationships Power lies with the sub-units ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ U. S. Articles of Confederation Canadian Federation European Union Southern African Development Council Economic Council of West African States ASEAN Mercusor
 Federalism ¡ ¡ Concept: Can Transfer additional authority back to the sub-units but not take power away from the federated governments (Provinces, states) Principal: Divided Soveregnty
Federalism ¡ ¡ Concept: Can Transfer additional authority back to the sub-units but not take power away from the federated governments (Provinces, states) Principal: Divided Soveregnty
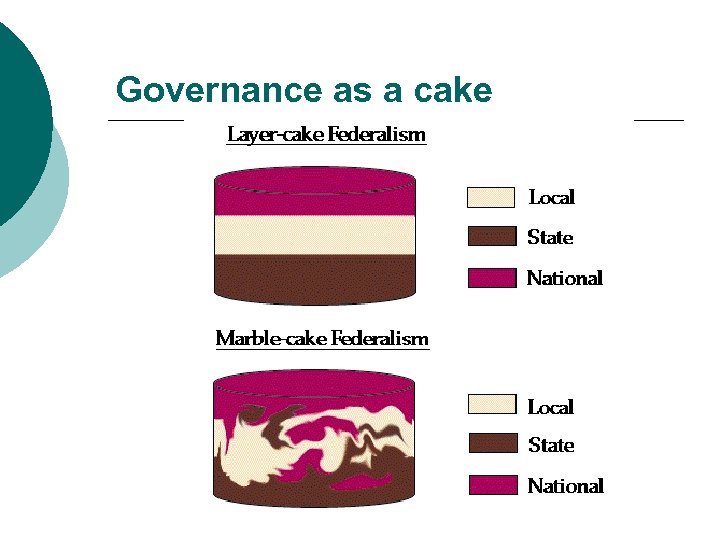 Governance as a cake
Governance as a cake
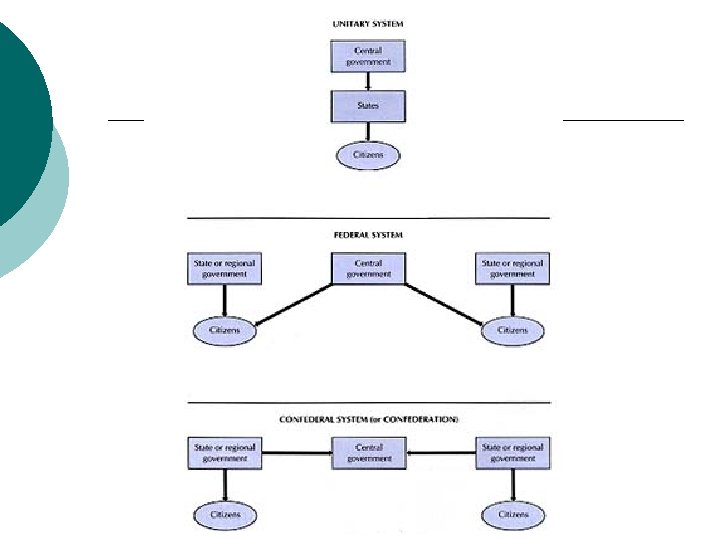
 Federal Systems In Federal Relationship • Some power lies with the National Unit • Some power lies with lower units • Layer Cake
Federal Systems In Federal Relationship • Some power lies with the National Unit • Some power lies with lower units • Layer Cake
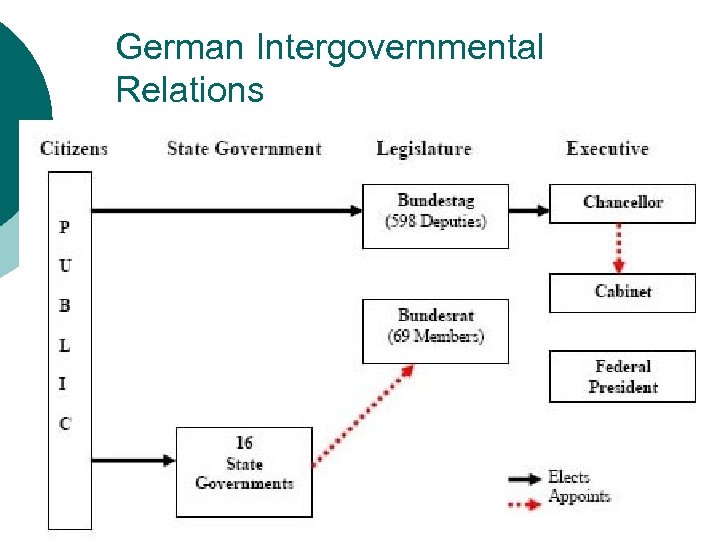 German Intergovernmental Relations
German Intergovernmental Relations
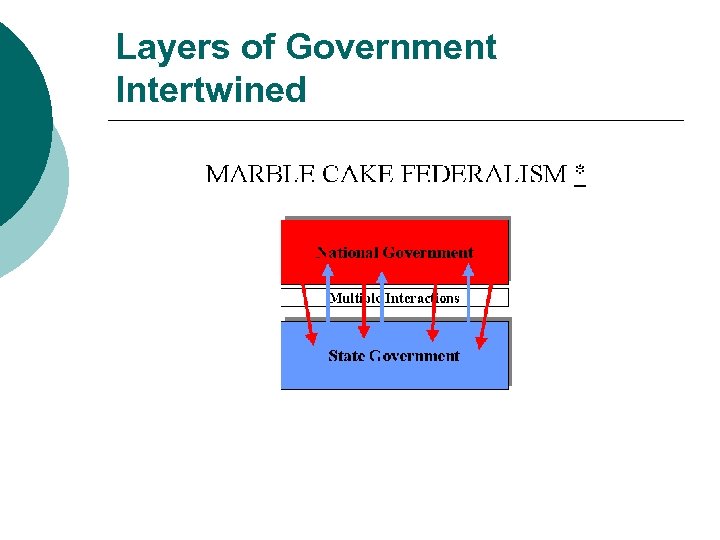 Layers of Government Intertwined
Layers of Government Intertwined

 Federal Powers ¡ ¡ Unique or Exclusive Powers. Federal and State Concurrent Powers- Federal and State Devolved Powers- State and Local Denied Authority
Federal Powers ¡ ¡ Unique or Exclusive Powers. Federal and State Concurrent Powers- Federal and State Devolved Powers- State and Local Denied Authority
 Federal Systems Key Distinction: 1. Lower units cannot break away from the National Unit 2. National Units cannot take power away from the lower units 3. Divided Sovereignty
Federal Systems Key Distinction: 1. Lower units cannot break away from the National Unit 2. National Units cannot take power away from the lower units 3. Divided Sovereignty
 Federalism: Examples: USA Canada Germany Nigeria India Russian Federation Austria Switzerland Malaysia
Federalism: Examples: USA Canada Germany Nigeria India Russian Federation Austria Switzerland Malaysia
 Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter
 Federal Relationships Taxation Indian States
Federal Relationships Taxation Indian States
 Unitary Systems and Sub-regional units 1. All power ultimately lies at the national level 2. What power the local level has, is given to it by the national level 3. The power that the national unit has given to the local level can also be taken away from it
Unitary Systems and Sub-regional units 1. All power ultimately lies at the national level 2. What power the local level has, is given to it by the national level 3. The power that the national unit has given to the local level can also be taken away from it
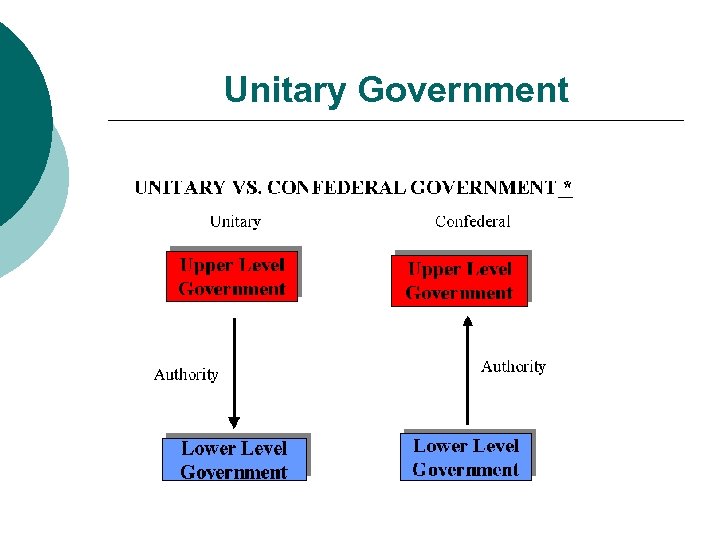 Unitary Government
Unitary Government
 Unitary Systems- Examples ¡ ¡ ¡ United Kingdom France Hungary Kenya Japan South Africa? (Unitary or Quasi. Federal) Bolivia China? Palestine? Indonesia Sweden
Unitary Systems- Examples ¡ ¡ ¡ United Kingdom France Hungary Kenya Japan South Africa? (Unitary or Quasi. Federal) Bolivia China? Palestine? Indonesia Sweden
 Indonesia
Indonesia
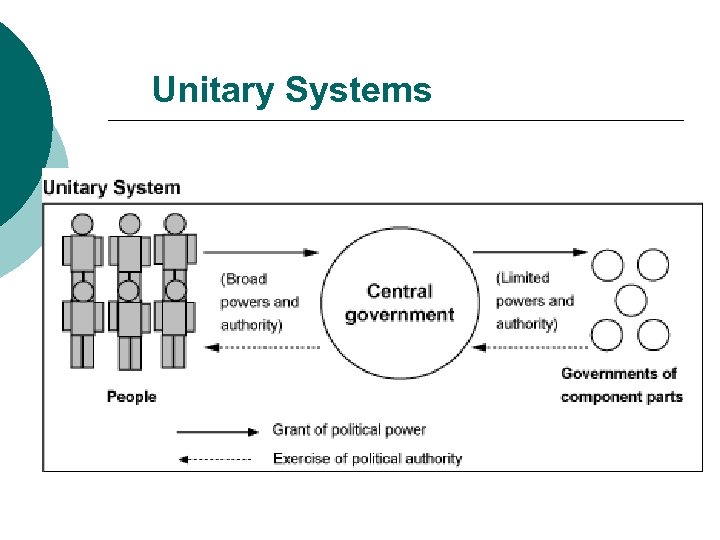 Unitary Systems
Unitary Systems
 Subsidiarity: European Union Term ¡ Subsidiarity is the idea that matters should be handled by the smallest (or, the lowest) competent government authority possible. ¡ It is presently best known as a fundamental principle of European Union Law. According to this principle, the EU may only act (i. e. make laws) where member states agree that action of individual countries (or local governments) is insufficient. ¡ Subsidiarity has become a principle of public sector reform in LDCs
Subsidiarity: European Union Term ¡ Subsidiarity is the idea that matters should be handled by the smallest (or, the lowest) competent government authority possible. ¡ It is presently best known as a fundamental principle of European Union Law. According to this principle, the EU may only act (i. e. make laws) where member states agree that action of individual countries (or local governments) is insufficient. ¡ Subsidiarity has become a principle of public sector reform in LDCs
 Term Avoids the Concept of Democracy ¡ South Africa
Term Avoids the Concept of Democracy ¡ South Africa
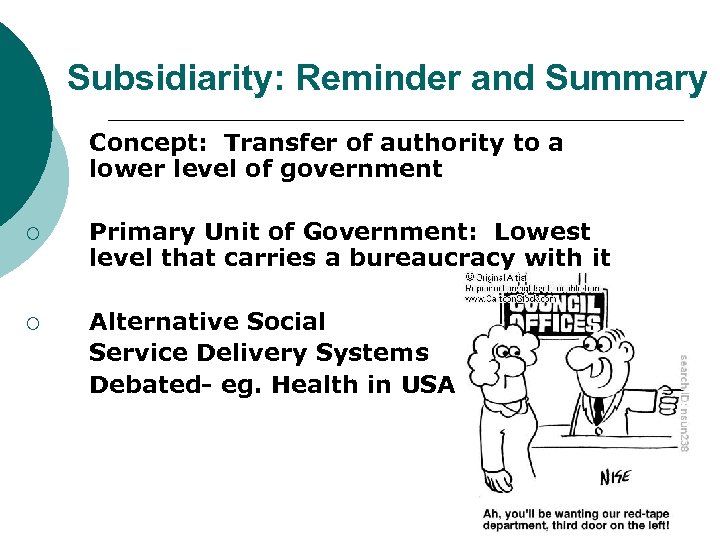 Subsidiarity: Reminder and Summary ¡ Concept: Transfer of authority to a lower level of government ¡ Primary Unit of Government: Lowest level that carries a bureaucracy with it ¡ Alternative Social Service Delivery Systems Debated- eg. Health in USA
Subsidiarity: Reminder and Summary ¡ Concept: Transfer of authority to a lower level of government ¡ Primary Unit of Government: Lowest level that carries a bureaucracy with it ¡ Alternative Social Service Delivery Systems Debated- eg. Health in USA
 Models of Subsidiarity: Review ¡ Devolution: Federal or Unitary (Political) ¡ Deconcentration (Administrative) ¡ Delegation (Special Unit- PAT) ¡ Privatization (Contracting Out) ¡ Program and Project Deconcentration: Principal Agency Issue)
Models of Subsidiarity: Review ¡ Devolution: Federal or Unitary (Political) ¡ Deconcentration (Administrative) ¡ Delegation (Special Unit- PAT) ¡ Privatization (Contracting Out) ¡ Program and Project Deconcentration: Principal Agency Issue)
 Local Governance South African Elections, May, 2011 VIDEO
Local Governance South African Elections, May, 2011 VIDEO
 Coffee Break ¡ Ten Minutes
Coffee Break ¡ Ten Minutes
 Intergovernmental Relationships Basic Assumptions and Local Governance
Intergovernmental Relationships Basic Assumptions and Local Governance
 Reiteration
Reiteration
 Devolution ¡ Transfer to a non-Federal political body e. g. Decision-Making Legal, Budget and personnel authority to district and town councils Key- power lies with lower level politicians
Devolution ¡ Transfer to a non-Federal political body e. g. Decision-Making Legal, Budget and personnel authority to district and town councils Key- power lies with lower level politicians
 Thomas P. (Tip) O’Neil, Speaker of the U. S. House of Representatives 1977 -1987
Thomas P. (Tip) O’Neil, Speaker of the U. S. House of Representatives 1977 -1987
 Street Level Issues- Costa Rica
Street Level Issues- Costa Rica
 Deconcentration: Transfer of authority to administrators at lower level within the administrative system
Deconcentration: Transfer of authority to administrators at lower level within the administrative system
 The Goal: Professionalism
The Goal: Professionalism
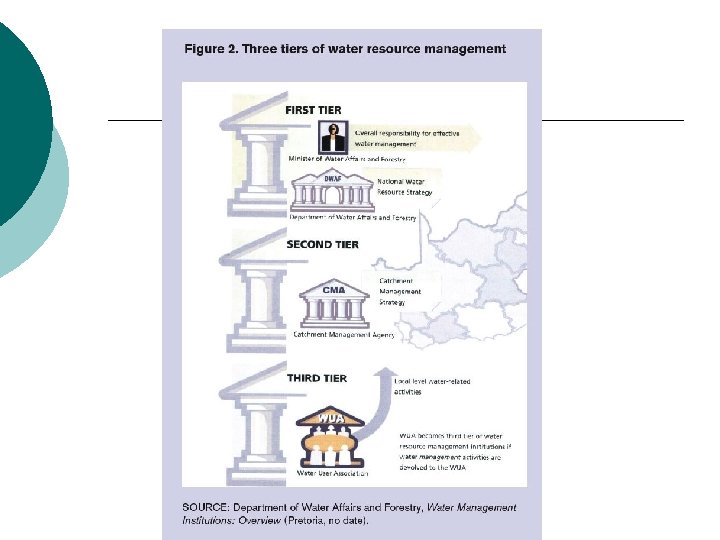
 Deconcentration: Review ¡ Functional vs. Prefectoral ¡ Prefectoral integrated ¡ Prefectoral unintegrated
Deconcentration: Review ¡ Functional vs. Prefectoral ¡ Prefectoral integrated ¡ Prefectoral unintegrated
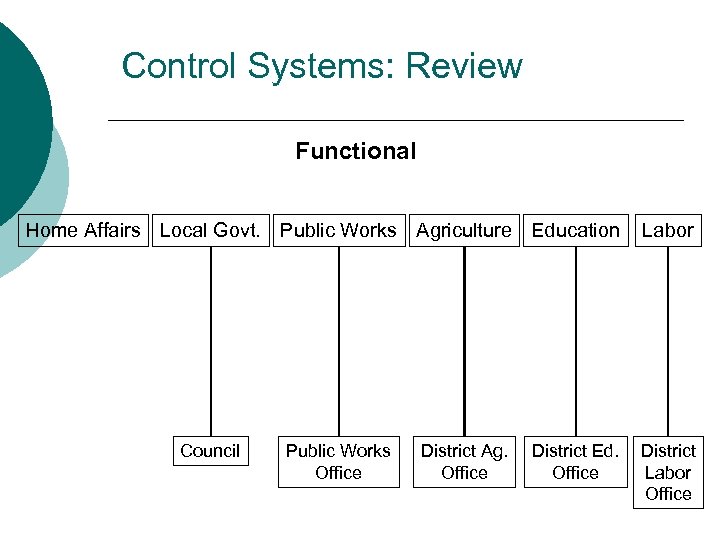 Control Systems: Review Functional Home Affairs Local Govt. Public Works Agriculture Education Council Public Works Office District Ag. Office District Ed. Office Labor District Labor Office
Control Systems: Review Functional Home Affairs Local Govt. Public Works Agriculture Education Council Public Works Office District Ag. Office District Ed. Office Labor District Labor Office
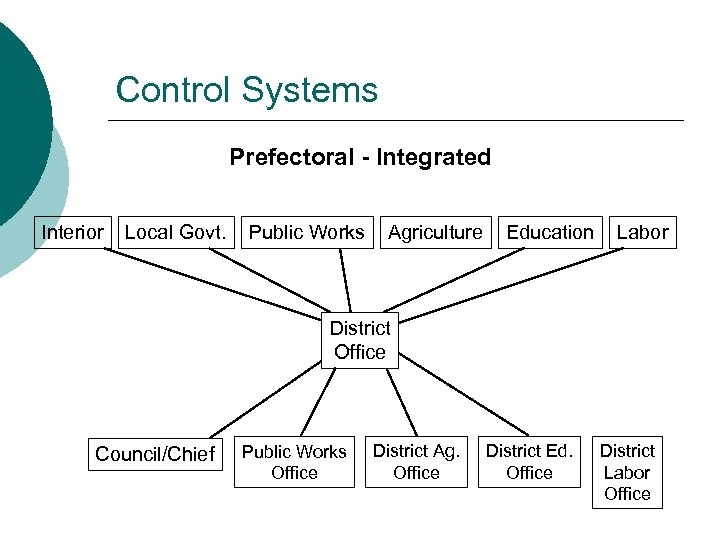 Control Systems Prefectoral - Integrated Interior Local Govt. Public Works Agriculture Education Labor District Office Council/Chief Public Works Office District Ag. Office District Ed. Office District Labor Office
Control Systems Prefectoral - Integrated Interior Local Govt. Public Works Agriculture Education Labor District Office Council/Chief Public Works Office District Ag. Office District Ed. Office District Labor Office
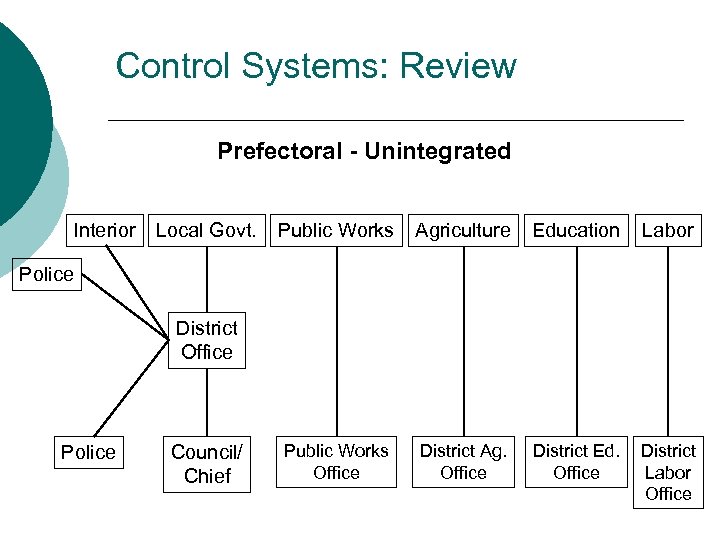 Control Systems: Review Prefectoral - Unintegrated Interior Local Govt. Public Works Agriculture Education Labor Public Works Office District Ag. Office District Ed. Office District Labor Office Police District Office Police Council/ Chief
Control Systems: Review Prefectoral - Unintegrated Interior Local Govt. Public Works Agriculture Education Labor Public Works Office District Ag. Office District Ed. Office District Labor Office Police District Office Police Council/ Chief
 The Critical View
The Critical View
 Delegation ¡ ¡ Transfer of authority to a statutory body such as Public Corporations or parastatals (UK) Eg. AMTRAK
Delegation ¡ ¡ Transfer of authority to a statutory body such as Public Corporations or parastatals (UK) Eg. AMTRAK
 Delegation ¡ ¡ ¡ Transfer Function Outside of line Departments Use of Board Commercialization vs. Privatization
Delegation ¡ ¡ ¡ Transfer Function Outside of line Departments Use of Board Commercialization vs. Privatization
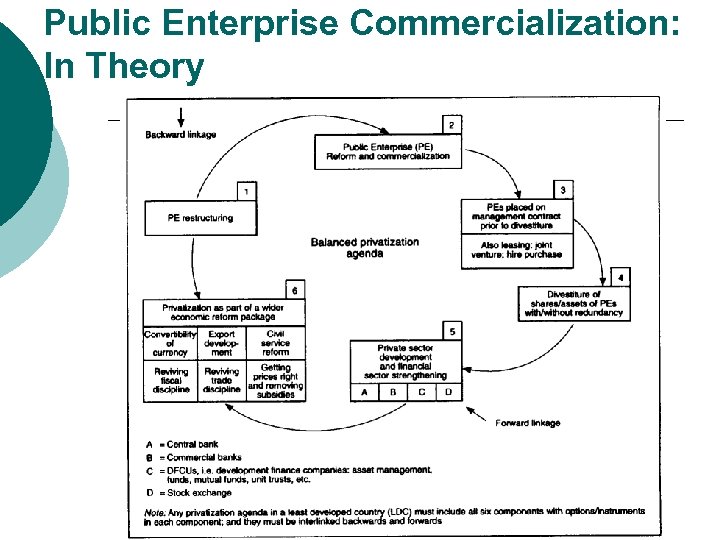 Public Enterprise Commercialization: In Theory
Public Enterprise Commercialization: In Theory
 Delegation
Delegation
 Privatization ¡ Transfer function out of government sector to the For Profit or Non-Profit Sector
Privatization ¡ Transfer function out of government sector to the For Profit or Non-Profit Sector
 “Russian Privatization and Silence of the Lambs”
“Russian Privatization and Silence of the Lambs”
 Principles of Privatization ¡ Key Conditionality. Privatization of the economy within a context of administrative Reform ¡ Linked to Contracting Out
Principles of Privatization ¡ Key Conditionality. Privatization of the economy within a context of administrative Reform ¡ Linked to Contracting Out
 The View from the 1080 s Redux
The View from the 1080 s Redux
 Principles of Privatization a. divestiture (full sale) b. contracting out c. liquidation d. sell off public private partnership shares
Principles of Privatization a. divestiture (full sale) b. contracting out c. liquidation d. sell off public private partnership shares
 Waste Removal
Waste Removal
 Principles of Privatization Goal: Small government and return to the recurrent budgeting process and balanced budget principles of “Neo-Orthodox Economists”
Principles of Privatization Goal: Small government and return to the recurrent budgeting process and balanced budget principles of “Neo-Orthodox Economists”
 The Image: Electrical Privatization in Brazil
The Image: Electrical Privatization in Brazil
 Programs and Projects ¡ Program and Project Deconcentration: (Principal Agency Issue) ¡ Assymetric ¡ Prone Relationships to Patron-Clientalism
Programs and Projects ¡ Program and Project Deconcentration: (Principal Agency Issue) ¡ Assymetric ¡ Prone Relationships to Patron-Clientalism
 President Chester A. Arthur and Patronage (1881 -1885)
President Chester A. Arthur and Patronage (1881 -1885)
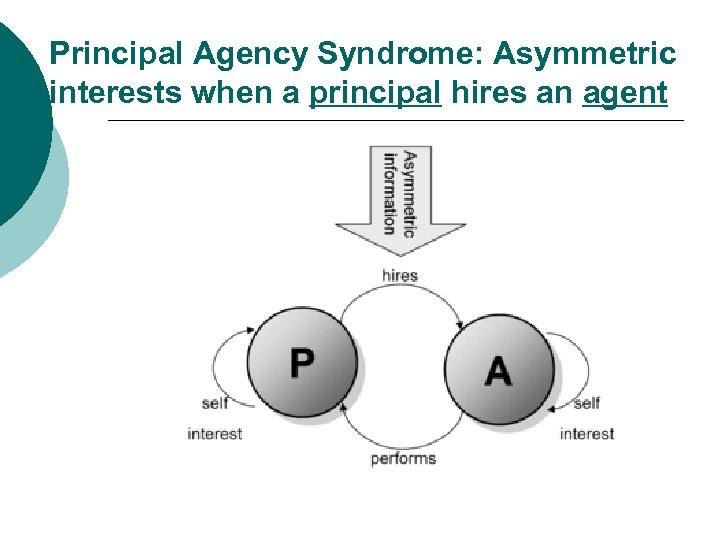 Principal Agency Syndrome: Asymmetric interests when a principal hires an agent
Principal Agency Syndrome: Asymmetric interests when a principal hires an agent
 Program and Project Decentralization: 1. Sectoral - By regular line or agency within a Ministry l l E. g. Focused activity - seed production (Green Revolution) Agricultural experiments
Program and Project Decentralization: 1. Sectoral - By regular line or agency within a Ministry l l E. g. Focused activity - seed production (Green Revolution) Agricultural experiments
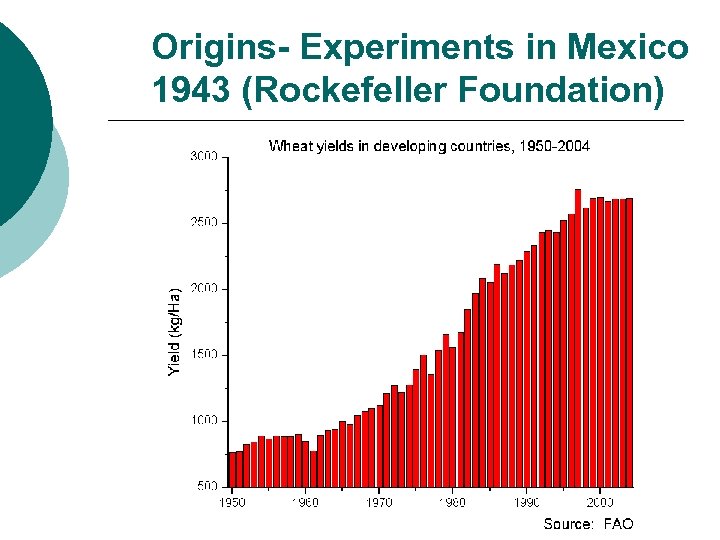 Origins- Experiments in Mexico 1943 (Rockefeller Foundation)
Origins- Experiments in Mexico 1943 (Rockefeller Foundation)
 Indian Department of Agriculture
Indian Department of Agriculture
 Program and Project Decentralization: 2. Deconcentration or Devolution of authority to central level special unit eg. Transport, water, health or education projects to subordinate administrative or structures (Education Service) PAT (Port Authority Transport) Buses
Program and Project Decentralization: 2. Deconcentration or Devolution of authority to central level special unit eg. Transport, water, health or education projects to subordinate administrative or structures (Education Service) PAT (Port Authority Transport) Buses
 Program and Project Decentralization: ¡ 3. Inter-Ministerial Committees or Units l Planning supervision l Overlapping memberships, e. g. Land Use Planning
Program and Project Decentralization: ¡ 3. Inter-Ministerial Committees or Units l Planning supervision l Overlapping memberships, e. g. Land Use Planning
 Inter-ministerial Cooperation in Botswana (and Expatriates)
Inter-ministerial Cooperation in Botswana (and Expatriates)
 Land Use Plan, Berlin Germany
Land Use Plan, Berlin Germany
 Program and Project Decentralization: 4. Creation of field level Special Project Units with semiautonomous status (Special designated geographical areas) Integrated Development Programs (Deliver Social and Economic Services)
Program and Project Decentralization: 4. Creation of field level Special Project Units with semiautonomous status (Special designated geographical areas) Integrated Development Programs (Deliver Social and Economic Services)
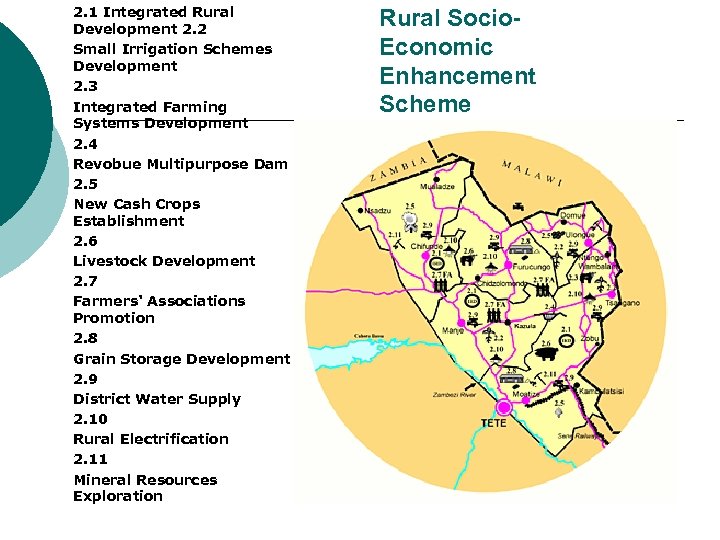 2. 1 Integrated Rural Development 2. 2 Small Irrigation Schemes Development 2. 3 Integrated Farming Systems Development 2. 4 Revobue Multipurpose Dam 2. 5 New Cash Crops Establishment 2. 6 Livestock Development 2. 7 Farmers' Associations Promotion 2. 8 Grain Storage Development 2. 9 District Water Supply 2. 10 Rural Electrification 2. 11 Mineral Resources Exploration Rural Socio. Economic Enhancement Scheme
2. 1 Integrated Rural Development 2. 2 Small Irrigation Schemes Development 2. 3 Integrated Farming Systems Development 2. 4 Revobue Multipurpose Dam 2. 5 New Cash Crops Establishment 2. 6 Livestock Development 2. 7 Farmers' Associations Promotion 2. 8 Grain Storage Development 2. 9 District Water Supply 2. 10 Rural Electrification 2. 11 Mineral Resources Exploration Rural Socio. Economic Enhancement Scheme
 Program and Project Decentralization: Project Decent. l E. g. A Range management project; or l Integrated Rural Development - Most well known type of special project ¡ l Multitude of project activity in different sectors that may overlap or compliment.
Program and Project Decentralization: Project Decent. l E. g. A Range management project; or l Integrated Rural Development - Most well known type of special project ¡ l Multitude of project activity in different sectors that may overlap or compliment.
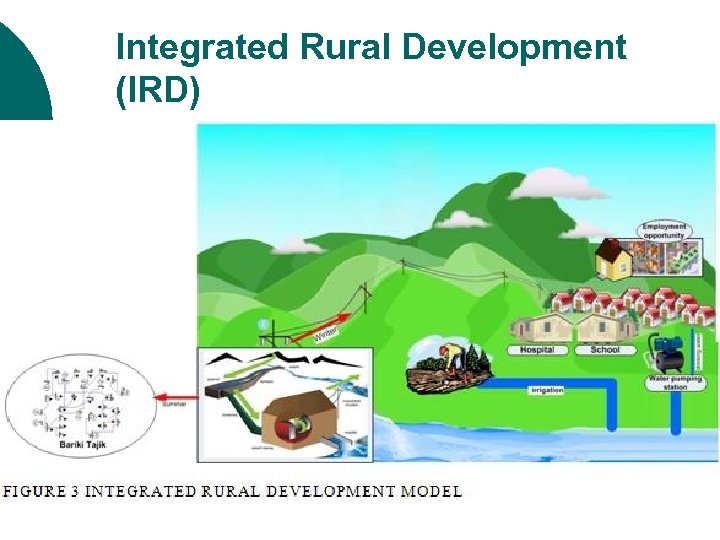 Integrated Rural Development (IRD)
Integrated Rural Development (IRD)
 DISCUSSION ISSUES AND CONCERNS Democracy: Writers and Themes
DISCUSSION ISSUES AND CONCERNS Democracy: Writers and Themes
 Discussion: What Have You Been Reading? Discussion One: What is unique about each part of the world as seen from our authors? Discussion Two: Limited Government- What is it? Discussion Three: Command Economy?
Discussion: What Have You Been Reading? Discussion One: What is unique about each part of the world as seen from our authors? Discussion Two: Limited Government- What is it? Discussion Three: Command Economy?
 VIDEO: Dictatorship Charlie Chaplin, “The Great Dictator” (1940)
VIDEO: Dictatorship Charlie Chaplin, “The Great Dictator” (1940)
 Case Studies: Stereotypes and The Institutional Legacy- Geographical Themes and Myths ¡ Africa: “Dark Continent, ” Slavery, race and Europe: ¡ Eastern Europe: Balkan Ghosts ¡ Asia: Villagization and Collectivism and the Asian Model ¡ Latin America: Iberian heritage (or US)Marxism, the U. S. and Ideology ¡ Middle East: Ottoman Legacy, Islam, Israel, vs. Europe
Case Studies: Stereotypes and The Institutional Legacy- Geographical Themes and Myths ¡ Africa: “Dark Continent, ” Slavery, race and Europe: ¡ Eastern Europe: Balkan Ghosts ¡ Asia: Villagization and Collectivism and the Asian Model ¡ Latin America: Iberian heritage (or US)Marxism, the U. S. and Ideology ¡ Middle East: Ottoman Legacy, Islam, Israel, vs. Europe
 Regional Discussions: What are you finding out? 1. Democracy 1. Governance 2. Local Government 3. Civil Society 4. Institutional State
Regional Discussions: What are you finding out? 1. Democracy 1. Governance 2. Local Government 3. Civil Society 4. Institutional State


