lecture 4.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Physics of Semiconductor Devices Lecture 4. Generation and Recombination in Semiconductors A. V. Sogoyan
Physics of Semiconductor Devices Lecture 4. Generation and Recombination in Semiconductors A. V. Sogoyan
 Contents: • G&R mechanisms • Thermal equilibrium: principle of detailed balance • G&R rates outside thermal equilibrium
Contents: • G&R mechanisms • Thermal equilibrium: principle of detailed balance • G&R rates outside thermal equilibrium
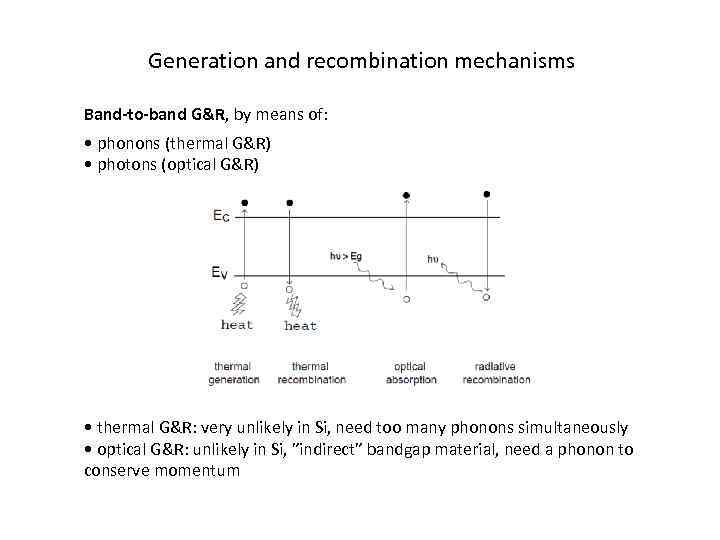 Generation and recombination mechanisms Band-to-band G&R, by means of: • phonons (thermal G&R) • photons (optical G&R) • thermal G&R: very unlikely in Si, need too many phonons simultaneously • optical G&R: unlikely in Si, ”indirect” bandgap material, need a phonon to conserve momentum
Generation and recombination mechanisms Band-to-band G&R, by means of: • phonons (thermal G&R) • photons (optical G&R) • thermal G&R: very unlikely in Si, need too many phonons simultaneously • optical G&R: unlikely in Si, ”indirect” bandgap material, need a phonon to conserve momentum
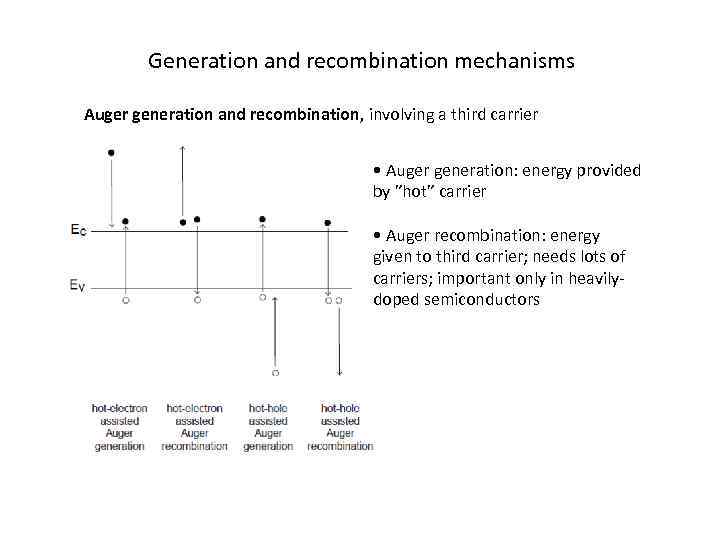 Generation and recombination mechanisms Auger generation and recombination, involving a third carrier • Auger generation: energy provided by ”hot” carrier • Auger recombination: energy given to third carrier; needs lots of carriers; important only in heavilydoped semiconductors
Generation and recombination mechanisms Auger generation and recombination, involving a third carrier • Auger generation: energy provided by ”hot” carrier • Auger recombination: energy given to third carrier; needs lots of carriers; important only in heavilydoped semiconductors
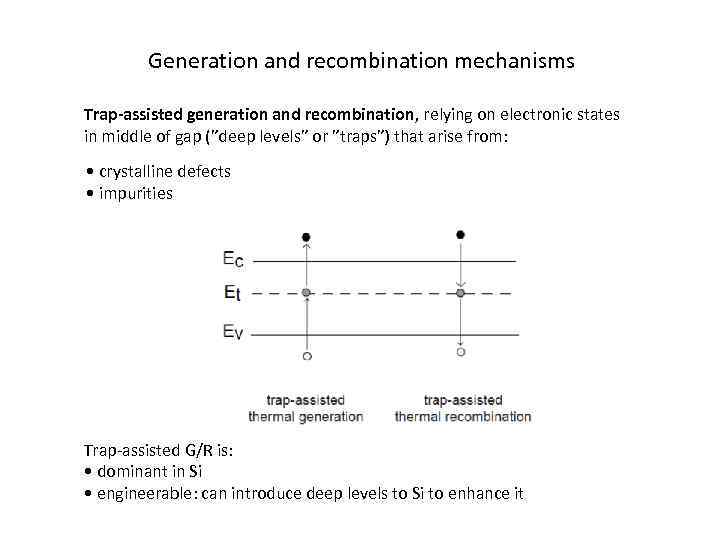 Generation and recombination mechanisms Trap-assisted generation and recombination, relying on electronic states in middle of gap (”deep levels” or ”traps”) that arise from: • crystalline defects • impurities Trap-assisted G/R is: • dominant in Si • engineerable: can introduce deep levels to Si to enhance it
Generation and recombination mechanisms Trap-assisted generation and recombination, relying on electronic states in middle of gap (”deep levels” or ”traps”) that arise from: • crystalline defects • impurities Trap-assisted G/R is: • dominant in Si • engineerable: can introduce deep levels to Si to enhance it
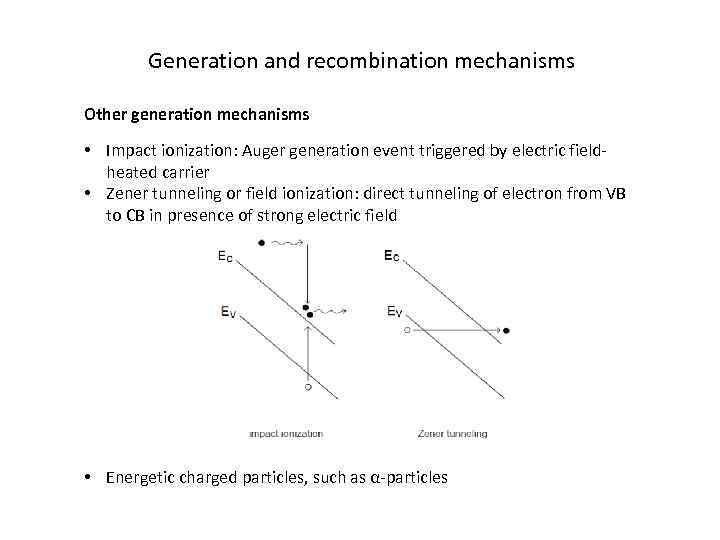 Generation and recombination mechanisms Other generation mechanisms • Impact ionization: Auger generation event triggered by electric fieldheated carrier • Zener tunneling or field ionization: direct tunneling of electron from VB to CB in presence of strong electric field • Energetic charged particles, such as α-particles
Generation and recombination mechanisms Other generation mechanisms • Impact ionization: Auger generation event triggered by electric fieldheated carrier • Zener tunneling or field ionization: direct tunneling of electron from VB to CB in presence of strong electric field • Energetic charged particles, such as α-particles
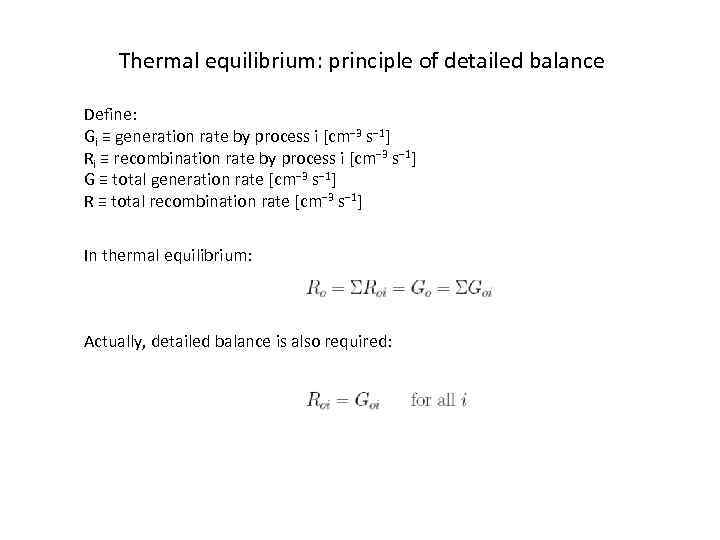 Thermal equilibrium: principle of detailed balance Define: Gi ≡ generation rate by process i [cm− 3 s− 1] Ri ≡ recombination rate by process i [cm− 3 s− 1] G ≡ total generation rate [cm− 3 s− 1] R ≡ total recombination rate [cm− 3 s− 1] In thermal equilibrium: Actually, detailed balance is also required:
Thermal equilibrium: principle of detailed balance Define: Gi ≡ generation rate by process i [cm− 3 s− 1] Ri ≡ recombination rate by process i [cm− 3 s− 1] G ≡ total generation rate [cm− 3 s− 1] R ≡ total recombination rate [cm− 3 s− 1] In thermal equilibrium: Actually, detailed balance is also required:
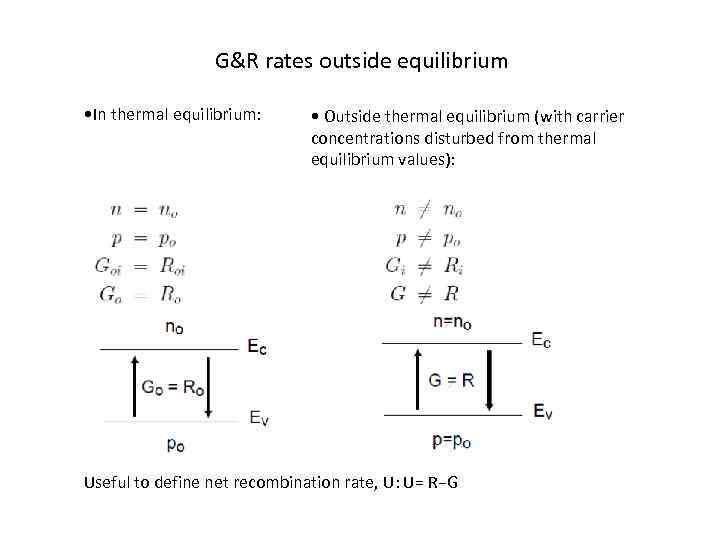 G&R rates outside equilibrium • In thermal equilibrium: • Outside thermal equilibrium (with carrier concentrations disturbed from thermal equilibrium values): Useful to define net recombination rate, U: U= R−G
G&R rates outside equilibrium • In thermal equilibrium: • Outside thermal equilibrium (with carrier concentrations disturbed from thermal equilibrium values): Useful to define net recombination rate, U: U= R−G
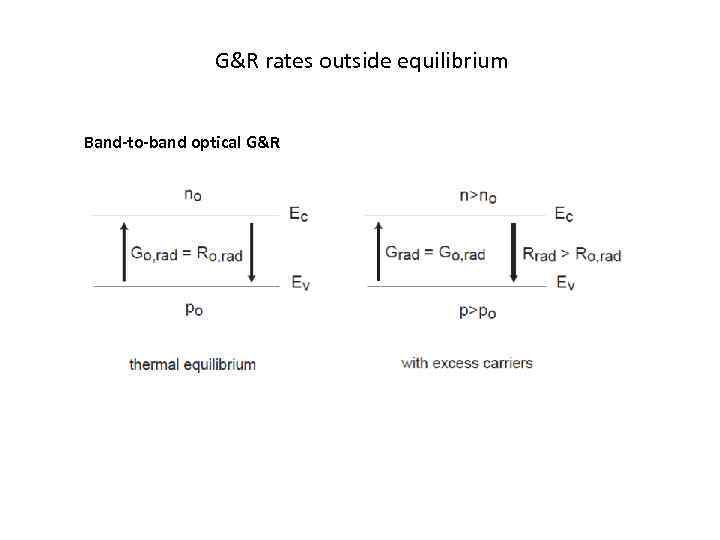 G&R rates outside equilibrium Band-to-band optical G&R
G&R rates outside equilibrium Band-to-band optical G&R
 G&R rates outside equilibrium In thermal equilibrium: A recombination process demands one electron and one hole ⇒ R depends of nopo: In TE, detailed balance implies:
G&R rates outside equilibrium In thermal equilibrium: A recombination process demands one electron and one hole ⇒ R depends of nopo: In TE, detailed balance implies:
 G&R rates outside equilibrium Outside TE generation rate remains unchanged since number of available bonds unchanged: optical recombination rate affected if electron and hole concentrations have changed: net recombination rate:
G&R rates outside equilibrium Outside TE generation rate remains unchanged since number of available bonds unchanged: optical recombination rate affected if electron and hole concentrations have changed: net recombination rate:
 G&R rates outside equilibrium Auger G&R In thermal equilibrium: • Involving hot electrons: The more electrons there are, the more likely it is to have hot ones capable of Auger generation: recombination event demands two electrons and one hole: In TE, detailed balance implies: • Involving hot holes: similar but substitute no for po and eeh by ehh above.
G&R rates outside equilibrium Auger G&R In thermal equilibrium: • Involving hot electrons: The more electrons there are, the more likely it is to have hot ones capable of Auger generation: recombination event demands two electrons and one hole: In TE, detailed balance implies: • Involving hot holes: similar but substitute no for po and eeh by ehh above.
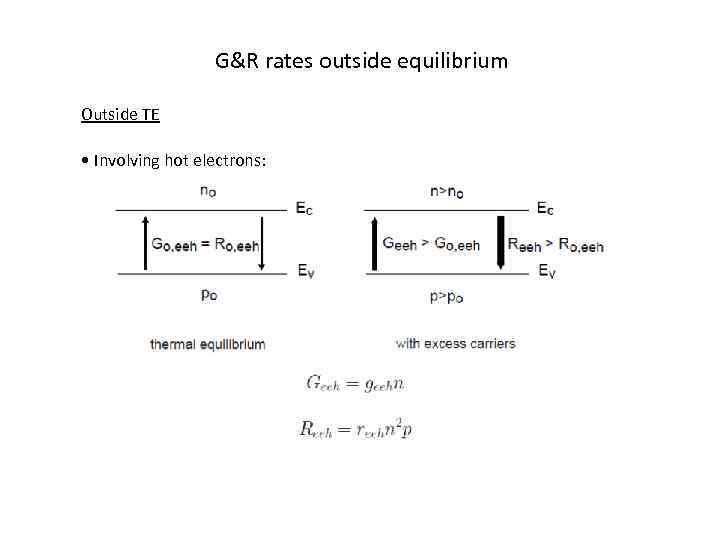 G&R rates outside equilibrium Outside TE • Involving hot electrons:
G&R rates outside equilibrium Outside TE • Involving hot electrons:
 G&R rates outside equilibrium If relationship between geeh and reeh unchanged from TE: • Involving hot holes, similarly: • Total Auger:
G&R rates outside equilibrium If relationship between geeh and reeh unchanged from TE: • Involving hot holes, similarly: • Total Auger:
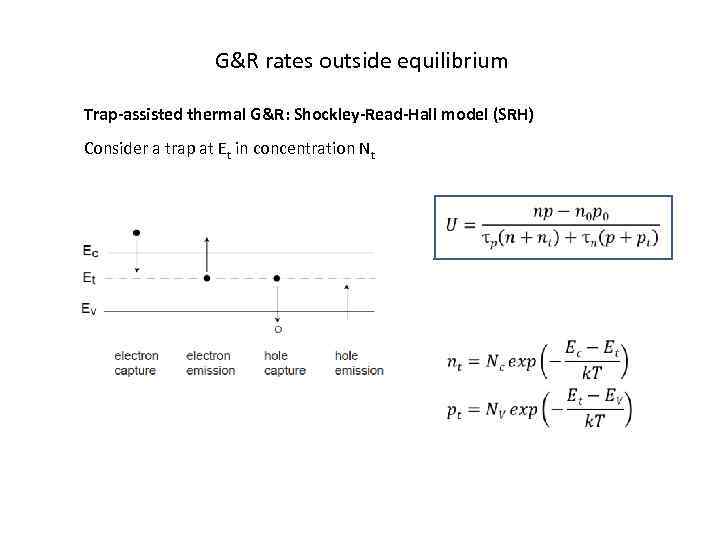 G&R rates outside equilibrium Trap-assisted thermal G&R: Shockley-Read-Hall model (SRH) Consider a trap at Et in concentration Nt
G&R rates outside equilibrium Trap-assisted thermal G&R: Shockley-Read-Hall model (SRH) Consider a trap at Et in concentration Nt
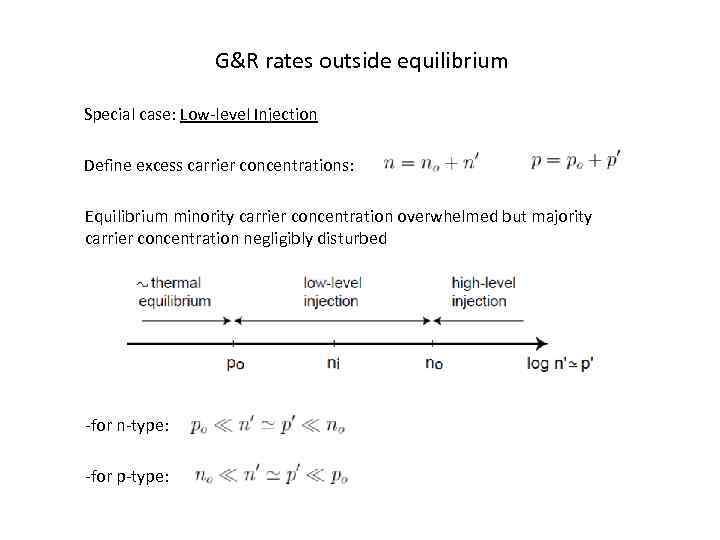 G&R rates outside equilibrium Special case: Low-level Injection Define excess carrier concentrations: Equilibrium minority carrier concentration overwhelmed but majority carrier concentration negligibly disturbed -for n-type: -for p-type:
G&R rates outside equilibrium Special case: Low-level Injection Define excess carrier concentrations: Equilibrium minority carrier concentration overwhelmed but majority carrier concentration negligibly disturbed -for n-type: -for p-type:
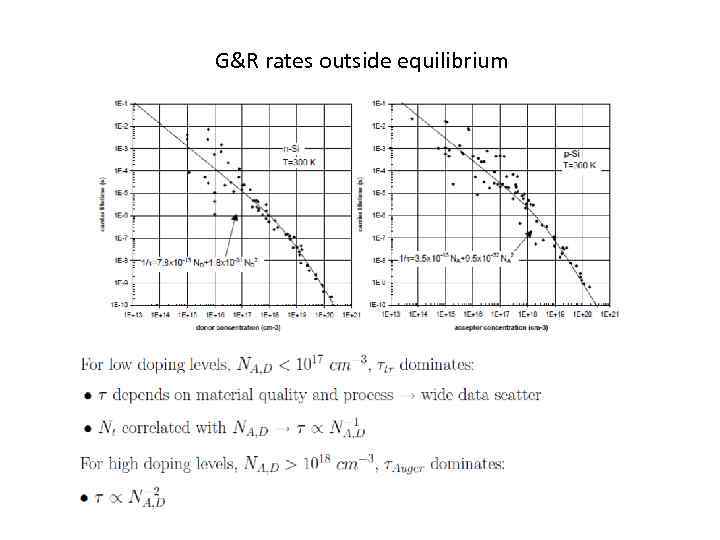
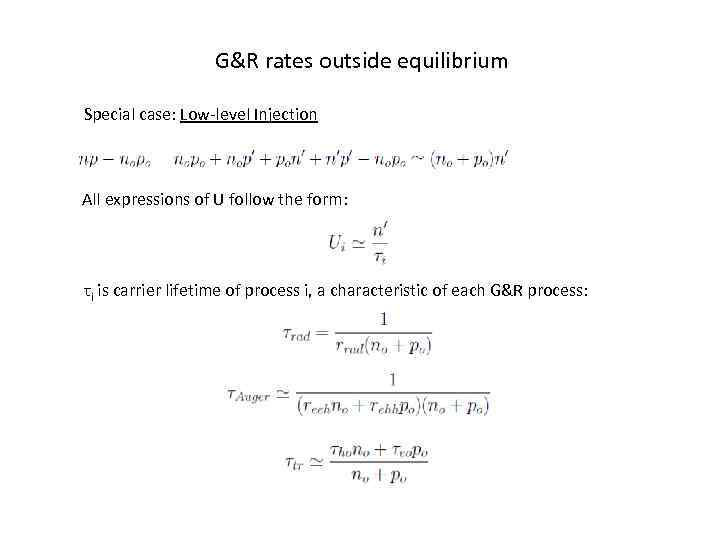 G&R rates outside equilibrium Special case: Low-level Injection All expressions of U follow the form: τi is carrier lifetime of process i, a characteristic of each G&R process:
G&R rates outside equilibrium Special case: Low-level Injection All expressions of U follow the form: τi is carrier lifetime of process i, a characteristic of each G&R process:
 G&R rates outside equilibrium Special case: Low-level Injection If all G&R processes are independent, combined process: τ is mean time between recombination event per excess carrier [s] or average time excess carrier will ”survive” before recombining
G&R rates outside equilibrium Special case: Low-level Injection If all G&R processes are independent, combined process: τ is mean time between recombination event per excess carrier [s] or average time excess carrier will ”survive” before recombining
 G&R rates outside equilibrium
G&R rates outside equilibrium


