33b0754eb0cc0a12b57d29dd244c2d3e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 PHYSICS 1 E 03 Dr. W. Okoń Office: ABB-236 e-mail: okon@physics. mcmaster. ca Office Hours: TBA Course web page (all sections) – Course Outline: http: //physwww. mcmaster. ca/PHYS 1 E 03 Course web page – I will be posting news and all lecture notes here: http: //physwww. mcmaster. ca/~okon/1 e 03. html
PHYSICS 1 E 03 Dr. W. Okoń Office: ABB-236 e-mail: okon@physics. mcmaster. ca Office Hours: TBA Course web page (all sections) – Course Outline: http: //physwww. mcmaster. ca/PHYS 1 E 03 Course web page – I will be posting news and all lecture notes here: http: //physwww. mcmaster. ca/~okon/1 e 03. html
 Components of the course -Lectures: three per week -Labs: approximately every second week, 4 labs in the term. 15% of the final grade. -Tutorials: approximately every second week, alternating with labs. 6% of the final grade. -CAPA assignments, every week. 4% of the final grade -Two term tests. Total 20% of the final grade. -Final exam, 3 hours. 50 -55% of the final grade. - Clicker participation 0 -5%
Components of the course -Lectures: three per week -Labs: approximately every second week, 4 labs in the term. 15% of the final grade. -Tutorials: approximately every second week, alternating with labs. 6% of the final grade. -CAPA assignments, every week. 4% of the final grade -Two term tests. Total 20% of the final grade. -Final exam, 3 hours. 50 -55% of the final grade. - Clicker participation 0 -5%
 Homework Using CAPA • There will be a CAPA assignment each week. Answers are entered into the computer The CAPA system tells you immediately whether the answer is correct, and allows you to try again. You can log on/off and keep working on an assignment as often as you like. • The CAPA assignments themselves are worth 4% of your grade; and the tutorial quizzes are based on the same problems. • You will get access to the CAPA assignments directly from Avenue. This is simpler than the procedure for other courses that use CAPA, but it means you have to get your Avenue login working (http: //avenue. mcmaster. ca/) • Read the CAPA help page before you start!
Homework Using CAPA • There will be a CAPA assignment each week. Answers are entered into the computer The CAPA system tells you immediately whether the answer is correct, and allows you to try again. You can log on/off and keep working on an assignment as often as you like. • The CAPA assignments themselves are worth 4% of your grade; and the tutorial quizzes are based on the same problems. • You will get access to the CAPA assignments directly from Avenue. This is simpler than the procedure for other courses that use CAPA, but it means you have to get your Avenue login working (http: //avenue. mcmaster. ca/) • Read the CAPA help page before you start!
 Homework Download and print the lecture notes in Power Point format from the my web page. Bring the notes for class and add your own notes to them during the lecture. Read the textbook, either just before or just after the lecture, and add to your notes as you read. We will prepare a list of suggested problems from the textbook (posted as a file, or at the end of lectures notes). You can download and print these. As we cover the material from the textbook you should also try to do the appropriate questions from this list.
Homework Download and print the lecture notes in Power Point format from the my web page. Bring the notes for class and add your own notes to them during the lecture. Read the textbook, either just before or just after the lecture, and add to your notes as you read. We will prepare a list of suggested problems from the textbook (posted as a file, or at the end of lectures notes). You can download and print these. As we cover the material from the textbook you should also try to do the appropriate questions from this list.
 PHYSICS 1 E 03 I. Electrostatics (4 weeks) II. DC Circuits (2 weeks, plus labs) III. Magnetism (3 weeks) IV. Waves (3 weeks) -includes electromagnetic waves
PHYSICS 1 E 03 I. Electrostatics (4 weeks) II. DC Circuits (2 weeks, plus labs) III. Magnetism (3 weeks) IV. Waves (3 weeks) -includes electromagnetic waves
 Introduction How do things interact? 1) Gravity - a force between masses - holds planets in orbit, etc. 2) Electromagnetism - a force between charges - responsible for all familiar forces (except gravity) – friction, normal, magnetic 3) Weak Nuclear Force - decay of particles 4) Strong Nuclear Force - holds nuclei together
Introduction How do things interact? 1) Gravity - a force between masses - holds planets in orbit, etc. 2) Electromagnetism - a force between charges - responsible for all familiar forces (except gravity) – friction, normal, magnetic 3) Weak Nuclear Force - decay of particles 4) Strong Nuclear Force - holds nuclei together
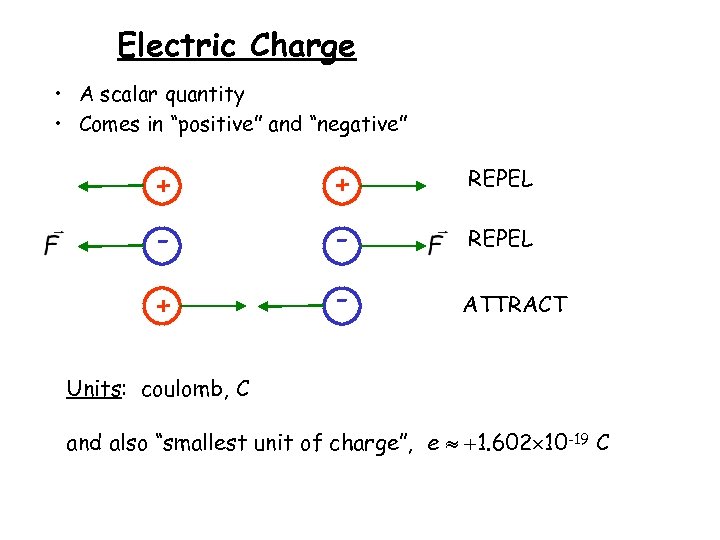 Electric Charge • A scalar quantity • Comes in “positive” and “negative” + + REPEL - - REPEL + - ATTRACT Units: coulomb, C and also “smallest unit of charge”, e 1. 602 10 -19 C
Electric Charge • A scalar quantity • Comes in “positive” and “negative” + + REPEL - - REPEL + - ATTRACT Units: coulomb, C and also “smallest unit of charge”, e 1. 602 10 -19 C
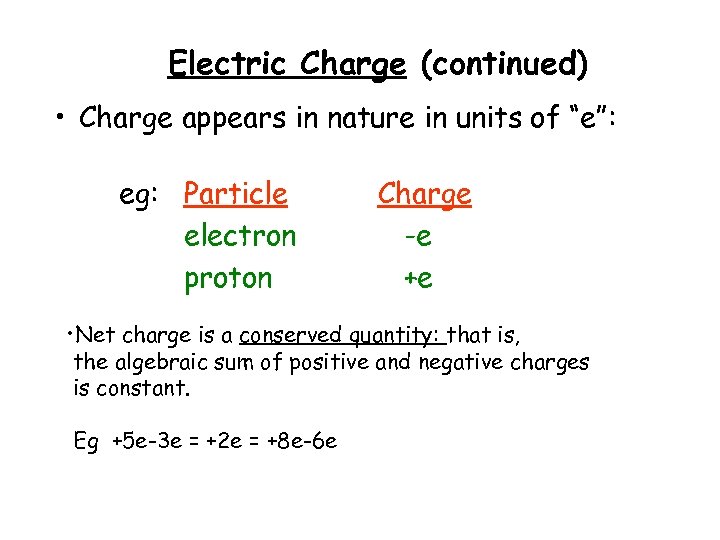 Electric Charge (continued) • Charge appears in nature in units of “e”: eg: Particle electron proton Charge -e +e • Net charge is a conserved quantity: that is, the algebraic sum of positive and negative charges is constant. Eg +5 e-3 e = +2 e = +8 e-6 e
Electric Charge (continued) • Charge appears in nature in units of “e”: eg: Particle electron proton Charge -e +e • Net charge is a conserved quantity: that is, the algebraic sum of positive and negative charges is constant. Eg +5 e-3 e = +2 e = +8 e-6 e
 Insulators: charges do NOT move eg: glass, rubber, paper - can be charged by rubbing, but charges do not move Conductors: (some) charges move freely eg: metals, some liquids Semiconductors: electrical properties between insulators and conductors eg: silicon, germanium
Insulators: charges do NOT move eg: glass, rubber, paper - can be charged by rubbing, but charges do not move Conductors: (some) charges move freely eg: metals, some liquids Semiconductors: electrical properties between insulators and conductors eg: silicon, germanium
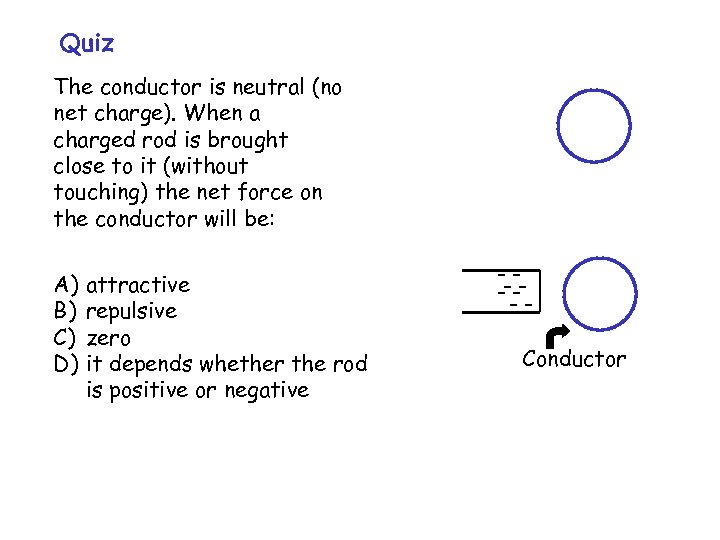 Quiz The conductor is neutral (no net charge). When a charged rod is brought close to it (without touching) the net force on the conductor will be: A) B) C) D) attractive repulsive zero it depends whether the rod is positive or negative -----Conductor
Quiz The conductor is neutral (no net charge). When a charged rod is brought close to it (without touching) the net force on the conductor will be: A) B) C) D) attractive repulsive zero it depends whether the rod is positive or negative -----Conductor
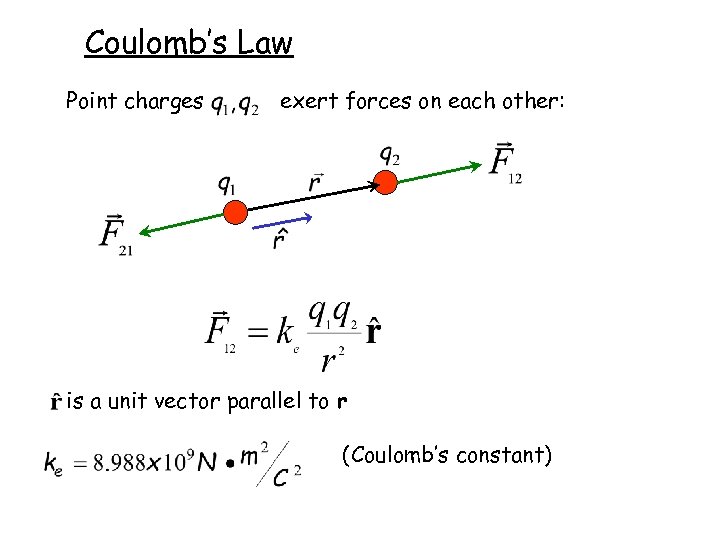 Coulomb’s Law Point charges exert forces on each other: is a unit vector parallel to r (Coulomb’s constant)
Coulomb’s Law Point charges exert forces on each other: is a unit vector parallel to r (Coulomb’s constant)
 Ex 1: Find the magnitude of the force between the charges +10 C and -5 C separated by 20 cm.
Ex 1: Find the magnitude of the force between the charges +10 C and -5 C separated by 20 cm.
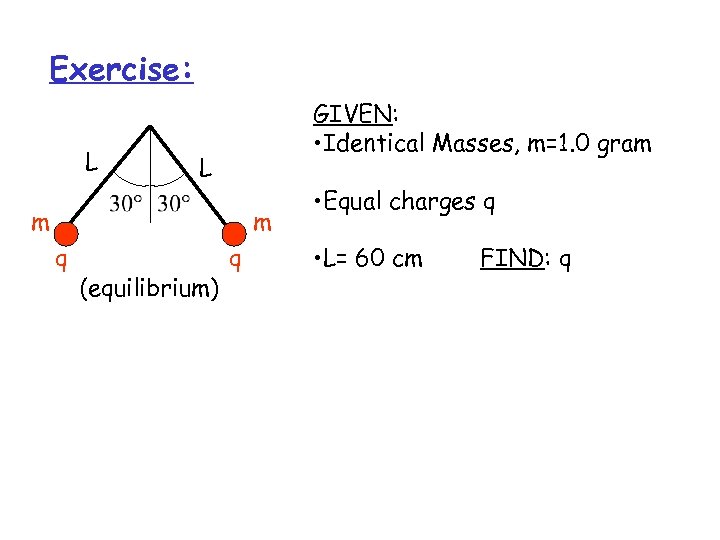 Exercise: L GIVEN: • Identical Masses, m=1. 0 gram L m m q (equilibrium) q • Equal charges q • L= 60 cm FIND: q
Exercise: L GIVEN: • Identical Masses, m=1. 0 gram L m m q (equilibrium) q • Equal charges q • L= 60 cm FIND: q
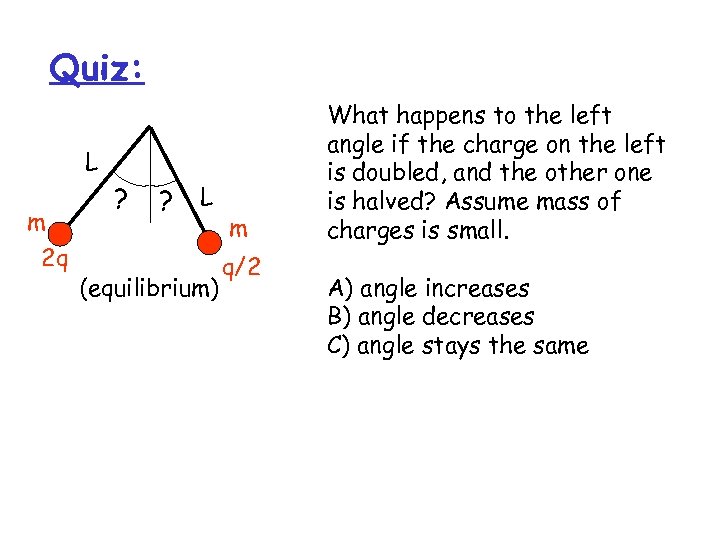 Quiz: L m 2 q ? ? L (equilibrium) m q/2 What happens to the left angle if the charge on the left is doubled, and the other one is halved? Assume mass of charges is small. A) angle increases B) angle decreases C) angle stays the same
Quiz: L m 2 q ? ? L (equilibrium) m q/2 What happens to the left angle if the charge on the left is doubled, and the other one is halved? Assume mass of charges is small. A) angle increases B) angle decreases C) angle stays the same
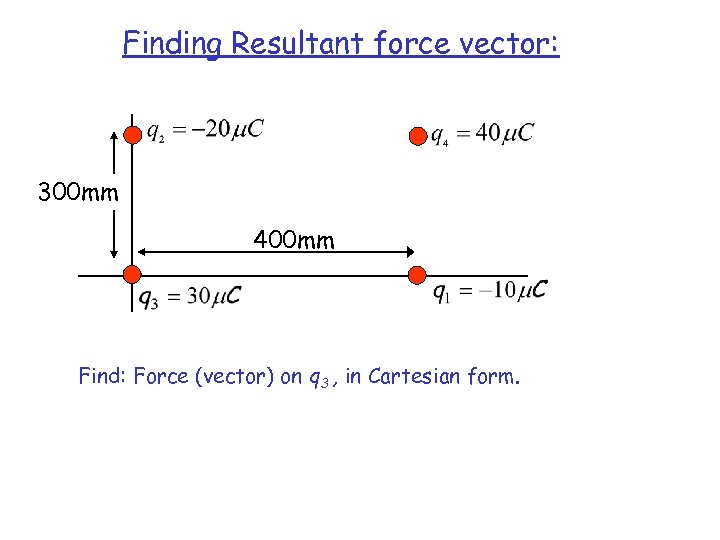 Finding Resultant force vector: 300 mm 400 mm Find: Force (vector) on q 3 , in Cartesian form.
Finding Resultant force vector: 300 mm 400 mm Find: Force (vector) on q 3 , in Cartesian form.
 solution
solution


