66bd89d50fbf0c41422a9ea2e3b2ddc7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Physical Security
Physical Security
 Types of Threats • Human Intrusion ◦ Attackers looking to perform some sort of damage or obtain useful information • “Natural” Disasters* ◦ ◦ Fire Flood Earthquake/Seismic Vibrations Power Outages/Fluctuations
Types of Threats • Human Intrusion ◦ Attackers looking to perform some sort of damage or obtain useful information • “Natural” Disasters* ◦ ◦ Fire Flood Earthquake/Seismic Vibrations Power Outages/Fluctuations
 Physical Protection from Human Attackers • One example why physical security should be taken very seriously ◦ The only tools you need to break into an unsecured PC: • A Phillips-head screwdriver • USB Thumbdrive or an external hard drive • Knoppix CD • Knoppix Floppy ◦ BIOS password can be bypassed. • Remove the machine’s hard drive and put it in another machine • Reset the BIOS password via jumpers on the motherboard • Simply remove the CMOS battery to reset ◦ Once accomplished, boot off CD or floppy (in this example, KNOPPIX), and copy.
Physical Protection from Human Attackers • One example why physical security should be taken very seriously ◦ The only tools you need to break into an unsecured PC: • A Phillips-head screwdriver • USB Thumbdrive or an external hard drive • Knoppix CD • Knoppix Floppy ◦ BIOS password can be bypassed. • Remove the machine’s hard drive and put it in another machine • Reset the BIOS password via jumpers on the motherboard • Simply remove the CMOS battery to reset ◦ Once accomplished, boot off CD or floppy (in this example, KNOPPIX), and copy.
 • Resetting admin passwords has never been easier ◦ Insert the Windows XP installation on a healthy installation ◦ Choose to repair the installation ◦ While “Setup is copying files”, simply press Shift+F 10 • This brings up a console in which the user has administrative rights and can, for example, reset the current administrator’s password.
• Resetting admin passwords has never been easier ◦ Insert the Windows XP installation on a healthy installation ◦ Choose to repair the installation ◦ While “Setup is copying files”, simply press Shift+F 10 • This brings up a console in which the user has administrative rights and can, for example, reset the current administrator’s password.
 Risk Assessment • Determine your primary threats and act accordingly • A very large company participating in the global market obviously has more at stake than John Q’s Computer Store. • While their susceptibility of attack is the same, the large company will house more profitable information and technology. • FBI statistics indicate that approximately 72% of all thefts, fraud, sabotage, and accidents are caused by a company’s own employees. • Only about 5% is done by external sources.
Risk Assessment • Determine your primary threats and act accordingly • A very large company participating in the global market obviously has more at stake than John Q’s Computer Store. • While their susceptibility of attack is the same, the large company will house more profitable information and technology. • FBI statistics indicate that approximately 72% of all thefts, fraud, sabotage, and accidents are caused by a company’s own employees. • Only about 5% is done by external sources.
 The “How-Tos” of Protection • Guarding the Outer Perimeter* ◦ Disguise • Out of sight, out of mind ◦ If disguising is not possible • • • High fences Barbed wire Round-the-clock security guard Security Cameras Motion Sensors The Serv. Path building, located in San Francisco, is a datacenter that houses “supernodes” for both AT&T and MCI.
The “How-Tos” of Protection • Guarding the Outer Perimeter* ◦ Disguise • Out of sight, out of mind ◦ If disguising is not possible • • • High fences Barbed wire Round-the-clock security guard Security Cameras Motion Sensors The Serv. Path building, located in San Francisco, is a datacenter that houses “supernodes” for both AT&T and MCI.
 • The Workstations ◦ Workstations should ALWAYS be logged off or locked out whenever unattended ◦ Screens positioned such that they cannot be seen through the windows • Hackers with telescopes to record keystrokes ◦ Workstations should be secured and physically locked while unattended ◦ Steel cable that runs through the computer case and attaches to an “anchor” to prevent the tower from being removed
• The Workstations ◦ Workstations should ALWAYS be logged off or locked out whenever unattended ◦ Screens positioned such that they cannot be seen through the windows • Hackers with telescopes to record keystrokes ◦ Workstations should be secured and physically locked while unattended ◦ Steel cable that runs through the computer case and attaches to an “anchor” to prevent the tower from being removed
 • Safeguarding the Computer Rooms • Keep the doors locked • Tuck networking cables out of sight • Keep networking cables inaccessible from outside room • Secure items in the room according to value • Intrusion detection systems • Ensure walls extend to the physical ceiling versus ceiling panels • Attackers can gain access to the room via scaling the wall • Access Control Methods • Biometrics • Key Card access w/ PIN #s • Security Guard presence at all times • Watchdogs if the assets merit • Security Cameras
• Safeguarding the Computer Rooms • Keep the doors locked • Tuck networking cables out of sight • Keep networking cables inaccessible from outside room • Secure items in the room according to value • Intrusion detection systems • Ensure walls extend to the physical ceiling versus ceiling panels • Attackers can gain access to the room via scaling the wall • Access Control Methods • Biometrics • Key Card access w/ PIN #s • Security Guard presence at all times • Watchdogs if the assets merit • Security Cameras
 • Control the flow of people in the building • Employee and visitor badges • Access restricitions to visitors and maintenance • Any unscheduled dropoffs or deliveries should be verified with vendors • You don’t want the wrong people getting in
• Control the flow of people in the building • Employee and visitor badges • Access restricitions to visitors and maintenance • Any unscheduled dropoffs or deliveries should be verified with vendors • You don’t want the wrong people getting in
 Physical Protection from “Natural” Disasters • Physical security is more than "guns, gates and guards" • Risk Assessment • Proper security solutions require a proper threat assessment • The likelihood of tsunami’s is very low in Phoenix
Physical Protection from “Natural” Disasters • Physical security is more than "guns, gates and guards" • Risk Assessment • Proper security solutions require a proper threat assessment • The likelihood of tsunami’s is very low in Phoenix
 Security Mechanisms • Fire* • Extinguishers • Carbon Dioxide • Harmful to Humans • Halon • Preferred Choice, but very expensive to refill • Binds with available oxygen molecules to starve the fire • Harmful to the ozone • Inergen • Safer and cleaner alternative to Halon • Allows a breathable atmosphere and starvation of the atmosphere without ozone harm
Security Mechanisms • Fire* • Extinguishers • Carbon Dioxide • Harmful to Humans • Halon • Preferred Choice, but very expensive to refill • Binds with available oxygen molecules to starve the fire • Harmful to the ozone • Inergen • Safer and cleaner alternative to Halon • Allows a breathable atmosphere and starvation of the atmosphere without ozone harm
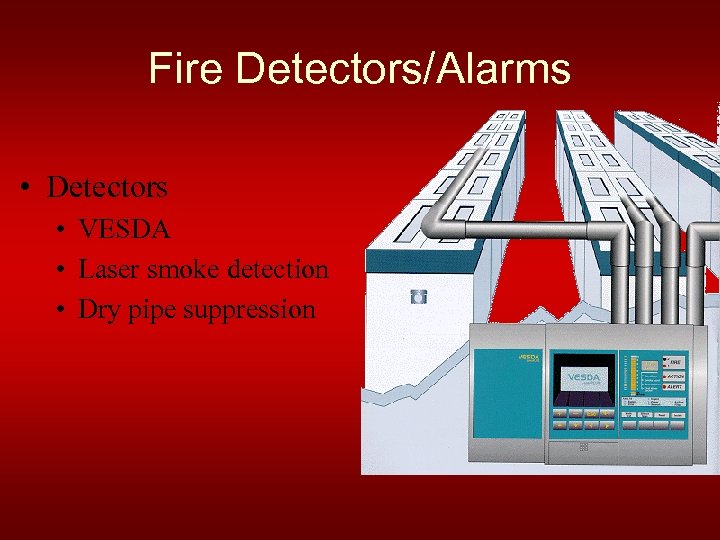 Fire Detectors/Alarms • Detectors • VESDA • Laser smoke detection • Dry pipe suppression
Fire Detectors/Alarms • Detectors • VESDA • Laser smoke detection • Dry pipe suppression
 • Flood/Water • “Go to the high ground” • Locate sensitive equipment on the second story or above • Don’t allow water pipes to run through or around computer room • Earthquake/Seismic Vibrations • Airports, railroads, major thoroughfares, industrial tools, and road construction are common sources of vibration • Common solutions involve supporting the foundation of computers with springs, gel-filled mats, or rubber pads. • THE most effective solution: • Don’t position your data center near a source of seismic vibrations
• Flood/Water • “Go to the high ground” • Locate sensitive equipment on the second story or above • Don’t allow water pipes to run through or around computer room • Earthquake/Seismic Vibrations • Airports, railroads, major thoroughfares, industrial tools, and road construction are common sources of vibration • Common solutions involve supporting the foundation of computers with springs, gel-filled mats, or rubber pads. • THE most effective solution: • Don’t position your data center near a source of seismic vibrations
 • Power Outages/Fluctuations • UPS • Large solutions available to large power consumption • Generator • When UPS just isn’t enough • Extreme Temperature/Humidity • Control must be maintained over the environment • Larger computers run hotter and thus more susceptible to heat in the room • Humidity problems with moisture developing on the inside of the machine – Redundant HVAC unit (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) that can handle temperature and humidity control of the computer room, sheltered from the weather
• Power Outages/Fluctuations • UPS • Large solutions available to large power consumption • Generator • When UPS just isn’t enough • Extreme Temperature/Humidity • Control must be maintained over the environment • Larger computers run hotter and thus more susceptible to heat in the room • Humidity problems with moisture developing on the inside of the machine – Redundant HVAC unit (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) that can handle temperature and humidity control of the computer room, sheltered from the weather
 Bibliography • • • • http: //www. servepath. com/why/datacenter. htm http: //searchsecurity. techtarget. com/tip/1, 289483, sid 14_gci 993832, 00. html http: //www. servepath. com/why/datacenter. htm http: //www 2. fpm. wisc. edu/safety/gsp/Fire%20 Suppression%20 Systems. html http: //www. reliablefire. com/inergenfolder/inergen. html http: //www. reliablefire. com/vesdafolder/vesdalaserplus. html http: //www. sans. org/rr/whitepapers/physcial/ http: //www. servepath. com/why/datacenter. htm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Computer_security http: //security. uchicago. edu/docs/physicalsec. shtml http: //searchsecurity. techtarget. com/generic/0, 295582, sid 14_gci 1131341, 00. html? tra ck=top 10 oct http: //searchsecurity. techtarget. com/original. Content/0, 289142, sid 14_gci 1131405, 00. h tml? track=top 10 oct http: //www. cccure. org/Documents/HISM/675 -680. html https: //my. tennessee. edu/portal/page? _pageid=40, 38376&_dad=portal&_schema=P ORTAL http: //www. securityfocus. com/archive/101/383003
Bibliography • • • • http: //www. servepath. com/why/datacenter. htm http: //searchsecurity. techtarget. com/tip/1, 289483, sid 14_gci 993832, 00. html http: //www. servepath. com/why/datacenter. htm http: //www 2. fpm. wisc. edu/safety/gsp/Fire%20 Suppression%20 Systems. html http: //www. reliablefire. com/inergenfolder/inergen. html http: //www. reliablefire. com/vesdafolder/vesdalaserplus. html http: //www. sans. org/rr/whitepapers/physcial/ http: //www. servepath. com/why/datacenter. htm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Computer_security http: //security. uchicago. edu/docs/physicalsec. shtml http: //searchsecurity. techtarget. com/generic/0, 295582, sid 14_gci 1131341, 00. html? tra ck=top 10 oct http: //searchsecurity. techtarget. com/original. Content/0, 289142, sid 14_gci 1131405, 00. h tml? track=top 10 oct http: //www. cccure. org/Documents/HISM/675 -680. html https: //my. tennessee. edu/portal/page? _pageid=40, 38376&_dad=portal&_schema=P ORTAL http: //www. securityfocus. com/archive/101/383003
 Physical Security
Physical Security


