64d6bf9722892eb8fee6fa0106fa14cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Photo © Norwegian People's Aid, October 2011

Cluster Munition Monitor 2012 Chapters: 1. Ban policy incl. prohibitions 2. Contamination and clearance 3. Casualties and victim assistance 4. Funding support

Convention on Cluster Munitions Photo © Landmine Survivors Initiatives, August 2012 A total of 111 states have joined the convention of which 75 are States Parties (72 ratified, 3 acceded)

Signatories still to ratify Angola Australia Benin Bolivia Canada Central African Republic Chad Colombia DR Congo Republic of Congo Cyprus Djibouti Gambia Guinea Haiti Iceland Indonesia Iraq Jamaica Kenya Liberia Liechtenstein Madagascar Namibia Nauru Nigeria Palau Paraguay Peru Philippines Rwanda Sao Tome e Principe Somalia South Africa Tanzania Uganda

Key meetings since August 2011 • Sept. 2011: Second Meeting of States Parties in Lebanon • Nov. 2011: Convention on Conventional Weapons review conference in Geneva • Apr. 2012: Intersessional meetings in Geneva • May 2012: Regional meetings in Croatia and Ghana • Sep. 2012: Third Meeting of States Parties in Norway

Cluster munition use Photo © Aris Roussinos/HRW, May 2012 Cluster munitions have been used by at least 19 government armed forces during conflict in 36 countries and four disputed territories since the end of World War II

Recent use of cluster munitions Since the Convention on Cluster Munitions entered into force on 1 August 2010 there has been: • No recorded use by States Parties or signatories. • Confirmed instances of new use by non-signatories Libya and Thailand in the first half of 2011. • Credible, but as yet unconfirmed reports of new use in non-signatories Sudan and Syria in the first half of 2012.

Production of cluster munitions Photo © Weapon Zero, August 2012 A total of 34 states have developed or produced more than 200 types of cluster munitions

Cluster munition producers Brazil Israel* Russia* China North Korea Singapore Egypt South Korea Slovakia Greece Pakistan Turkey India Poland United States* Iran Romania * None of the 17 producers are confirmed to have used cluster munitions, except for Israel, Russia, and the US

Former producers Argentina* France South Africa Australia Germany Spain Belgium Iraq Sweden Bi. H Italy Switzerland Chile Japan UK Croatia Netherlands The 16 former producers that have joined the convention and foresworn any future production incl. 13 States Parties and 3 signatories. * One non-signatory has ceased production.

Transfers of cluster munitions Brazil Chile* South Korea Spain* Egypt Russia France* Turkey Germany* United Kingdom* Israel United States Moldova* Yugoslavia Slovakia At least 15 countries have transferred over 50 types of cluster munitions to at least 60 countries. * 6 of these states have joined the convention and no longer export.

Stockpiling of cluster munitions Photo © Mark Hiznay/HRW, July 2012 91 countries have stockpiled millions of cluster munitions containing more than one billion submunitions, of which 73 currently stockpile

Stockpile destruction • A total of 19 States Parties have destroyed 744, 231 cluster munitions and 85. 8 million submunitions • Stockpile destruction completed by 13 States Parties and 4 signatories. • 18 States Parties are in process of destruction, incl. major stockpilers Germany, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Sweden, and the UK.

Stockpile destruction in 2011 In 2011, • 10 States Parties destroyed over 107, 000 munitions and 17. 6 million submunitions. • Hungary, Portugal, and Slovenia completed destruction. • Germany and the UK account for the majority of cluster munitions destroyed in the year.

Retention of cluster munitions • Most stockpilers are not retaining any cluster munitions and/or submunitions for training or research • 10 States Parties are retaining cluster munitions, of which Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, and Spain are each retaining more than 15, 000 submunitions • Others retaining are Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Sweden, Switzerland, and the UK.

Cluster munition contamination Photo © Mary Wareham/HRW, September 2011 At least 24 states/3 areas are currently contaminated by cluster munition remnants, incl. 10 States Parties and 3 signatories.

Contaminated states and areas Africa Americas Asia Europe-CIS Middle East. North Africa Chad DR Congo Chile Afghanistan Lao PDR Bi. H Croatia Iraq Lebanon Cambodia Vietnam Germany Montenegro Norway Libya Syria Western Sahara Mauritania South Sudan Azerbaijan Georgia (South Ossetia) Russia (Chechnya) Serbia Tajikistan Kosovo Nagorno-Karabakh Bold = States Parties and signatories Italics = Other areas

Clearance of cluster munitions In 2011, § At least 55 km 2 of contaminated land was cleared, resulting in destruction of 52, 845 unexploded submunitions § Bulk of the clearance was reported in State Party Lao PDR, the world’s most contaminated country § Clearance took place in 18 states and 2 areas incl. Croatia, Iraq, Lao PDR, Lebanon, and Norway as well as in non-signatories Cambodia, Libya, Serbia, South Sudan, and Vietnam

Cluster munition casualties Photo © Mary Wareham/HRW, September 2011 Cluster munition casualties have been recorded in at least 30 states and areas, including 16 States Parties and signatories
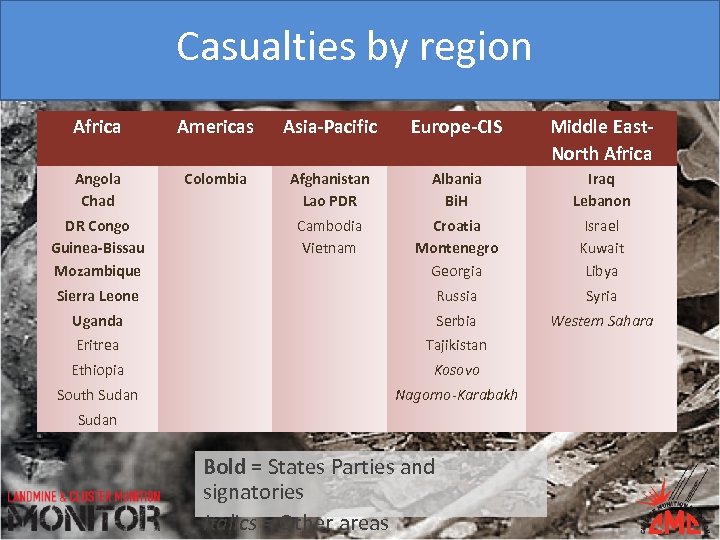
Casualties by region Africa Americas Asia-Pacific Europe-CIS Middle East. North Africa Angola Chad Colombia Afghanistan Lao PDR Albania Bi. H Iraq Lebanon Cambodia Vietnam Croatia Montenegro Georgia Israel Kuwait Libya Sierra Leone Russia Syria Uganda Serbia Western Sahara Eritrea Tajikistan Ethiopia Kosovo South Sudan Nagorno-Karabakh DR Congo Guinea-Bissau Mozambique Sudan Bold = States Parties and signatories Italics = Other areas

Cluster munition victim assistance § Afghanistan, Iraq, Lao PDR, Lebanon, Cambodia, and Vietnam are considered to be the “worst affected” countries with significant numbers of cluster munition victims. § More VA efforts were underway in all States Parties, but there were few significant or readily measurable improvements in accessibility of services. § Continued VA challenges incl. lack of funding, inadequate infrastructure, and conflict.

Cluster munitions funding support In 2011, • 21 states and the European Commission provided US$60 million in support of cluster munition-related activities • Almost 90% of total recorded international cluster munitionrelated funding went toward clearance of cluster munition remnants • Five donors—Australia, Germany, Norway, UK, and US— contributed more than $6 million each. This does not represent full extent of global support

National legislation • 18 States Parties have enacted national legislation to implement the convention, including 3 in 2011 (Cook Islands, Czech Republic, and Italy) and 3 in the first half of 2012 (Hungary, Sweden, and Switzerland). • 20+ States Parties and signatories are in the process of drafting, considering, or adopting national legislation incl. Australia and Canada

Transparency reporting • A total of 44 States Parties have submitted an initial transparency report as required by Article 7 of the convention – this represents three-quarters of States Parties • Less compliance on providing annual updated reports • 3 voluntary reports provided by signatories

Assistance with prohibited acts • At least 35 States Parties and signatories agree that the convention’s Article 21 provision on interoperability should not be read as allowing states to avoid their specific obligation under Article 1 to prohibit assistance with prohibited acts • States Parties Japan, the Netherlands, and the UK have indicated support for the contrary view

Transit and foreign stockpiling • At least 34 states have declared that transit and foreign stockpiling are prohibited by the Convention on Cluster Munitions • A number of states have indicated support for the opposite view, incl. States Parties Japan, the Netherlands, Portugal, and the UK

US transit and stockpiling • States Parties Norway and the UK have both confirmed that the US has removed its stockpiled cluster munitions from their respective territories • US diplomatic cables released by Wikileaks show that the US has stockpiled/may continue to stockpile cluster munitions in States Parties Afghanistan, Germany, Italy, Japan, and Spain, as well as in non-signatories Israel, Qatar, and perhaps Kuwait

Disinvestment • 6 states have enacted legislation explicitly prohibiting investment in cluster munitions, incl. Switzerland in 2012 • 23 States Parties and signatories have expressed their view that investment in cluster munitions production is a form of assistance that is prohibited by the convention

Thank you! See country profiles at: www. the-monitor. org monitor@icblcmc. org @banclusterbombs
64d6bf9722892eb8fee6fa0106fa14cf.ppt