d6479e89aff20de6d2692177233287c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Phishing into the Future Starr Alexander Sugato Bose Annie Chanchaisri Philip Fort David Salley Allen Walker Thomas Witnauer

What is Phishing? Originates in the analogy that internet scammers use e-mail lures to fish for passwords and financial data from the sea of internet users.

What is Phishing? § Web page code is copied from a major site § Replica page, that appears to be part of the companies’ site, is set up § A fake e-mail is sent out with a link to this site § Sends financial data or password to scammer § Leaves user on a company web site

The History § A form of social engineering attack § Term was coined in 1996 by hackers § May have been used even earlier in “ 2600” (hacker newsletter)

The History Earliest citation: “It used to be that you could make a fake account on AOL so long as you had a credit card generator. However, AOL became smart. Now they verify every card with a bank after it is typed in. Does anyone know of a way to get an account other than phishing? ” - mk 590, “AOL for free? ”, alt. 2600, January 28, 1996.

The History Phishing is not a new concept § A type of scam that has been around for years § Predates computers § Called social engineering

Phishing Underlying concept of spoofing users into revealing sensitive information is not new § Password capturing via fake login prompts is a basic hacker trick for years § Hackers did it over the phone for years

Phone Phreaking § First form of hacking § Used a “blue box” that emitted tones that allowed a hacker to control phone switches § Made long distance calls billed to someone else’s account § Possibly the origin of the “PH” in phishing

Navigating the Frontier: Where Frauds Are 1. Online Investment Newsletters 2. Online Bulletin Boards 3. Email Spams
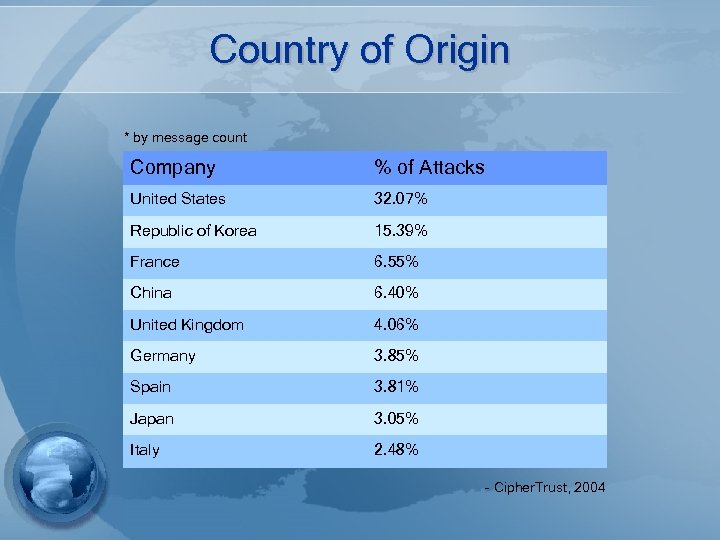
Country of Origin * by message count Company % of Attacks United States 32. 07% Republic of Korea 15. 39% France 6. 55% China 6. 40% United Kingdom 4. 06% Germany 3. 85% Spain 3. 81% Japan 3. 05% Italy 2. 48% - Cipher. Trust, 2004

Top 10 Tricks Used in Phishing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Mimic Reputable Companies Use Different Reply Address From the Claimed Sender Create a Plausible Premise Require a Quick Response Promise Security and/or Privacy Collect Information in the E-mail Link to Web Sites That Gather Information Fake a Secure Connection Process Submitted Information Immediately Buy Time to Access Accounts - Mail. Frontier, Inc. 2004

Other Forms of Hacking Slamming § Switching a customer from one long distance carrier to another without permission Web Cramming § A person or business accepts an offer for a free website, only to be charged a monthly fee on their phone bill Identity Theft § The use of personal authentication information (i. e. name, social security, etc. ) to commit fraud by opening credit card accounts, ordering checks, etc.

Consumer Confidence § 28% of consumers identified fraudulent e-mails as legitimate according to a study by Mail Frontier Inc. § 50% of consumers thought a legitimate Federal Trade Commission e-mail was fraudulent § 20% of consumers identified a legitimate Pay. Pal “payment received” e-mail as fraud § 31% fell for a fraudulent Pay. Pal e-mail that had been reported about widely.

Consumer Confidence § These statistics indicate the success rate of phishing to fool people § It is inhibiting the effectiveness of e-mail as a form of communication to the consumer § If consumers cannot correctly identify a legitimate e-mail, they may ignore all business related e-mails § Many fraudulent websites are hosted through international computers § 15% in Republic of Korea, 6% in China, and 6% in France § Criminals may be located in different location than the computer

Consumer Confidence § International locations make it more difficult to shut down due to time zone and language barriers § Average life span of fraudulent websites is 2. 25 days § Phishing is the fastest growing scam according to Barbara Span of First Data § Phishing has gone from no complaints a year ago to #4 of the list with the National Consumer League

Percentage of Corporate Phishing Victims Company % of Attacks Citibank 54. 16% Smith Barney 13. 48% Suntrust 10. 02% Pay. Pal 7. 57% Wells Fargo 5. 42% HSBC 5. 07% e. Bay 4. 15% USBank 0. 11% Citizens. Bank 0. 014% - Cipher. Trust, 2004

Software Solutions 1. Symantec § 2. The Online Fraud Management Solution SMS based security § SSL/TLS channel

Existing Federal Laws § No Existing Law solely devoted to Phishing. § Existing federal laws do criminalize phishing - but mainly after a consumer has already been defrauded. § Such laws include the laws against wire fraud, identity theft, credit card fraud, computer fraud, CAN SPAM Act, and a number of trade laws. § The Identity Theft Penalty Enhancement Act, (ITPEA) establishes a new crime of "aggravated identity theft“. Convictions for aggravated identity theft - including phishing -- would carry a mandatory two-year prison sentence.

The Anti-Phishing Act § Bill introduced to senate by Senator Patrick Leahy on July 9, 2004. § It targets the entire scam, all the way from sending the e-mail to creating fraudulent sites. § It averts free speech issues by exempting parodies and political speech (via email or on websites) from its reach. § It stipulates that the perpetrator must have the specific criminal purpose of committing a crime of fraud or identity theft.

Strengths of the Act § It criminalizes the bait - not just successful phishing. § It makes it illegal to knowingly send out spoofed email that links to sham websites, with the intention of committing a crime. § It criminalizes the operation of the sham websites that are the locus of the wrongdoing. § If the bill were to become law, then each and every element of the scam would become a felony subject to five years in prison and/or a fine up to $250, 000.

Tips to Protect Yourself from Phishing Scam 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Never Click on Hyperlinks within Emails Use Anti-Spam Filter Software Use Anti-Virus Software Use a Personal Firewall Keep Software Updated (Operating Systems & Browsers Always Look for “https” and “padlock” on site that request personal information 7. Keep Your Computer Clean From Spyware 8. Educate Yourself on Fraudulent Activity on the Internet 9. Check Your Credit Report Immediately, for Free 10. Seek Advice if you’re Unsure

What To Do If You Are A Victim § For financial concerns close accounts immediately and call your institution § For SSN concerns, again call your bank § Clear yourself of responsibility § Check your credit report § Contact FTC

Mail. Frontier Phishing IQ Test II http: //survey. mailfrontier. com/survey/quiztest. html

Questions? ? ?
d6479e89aff20de6d2692177233287c6.ppt