ch-2a 97-2003.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 Philosophies of Quality Gurus Topic-2 a
Philosophies of Quality Gurus Topic-2 a
 What is a quality guru? A guru, by definition, is a good person, a wise person and a teacher. v v. A quality guru should be all of these, plus have a concept and approach to quality within business that has made a major and lasting impact.
What is a quality guru? A guru, by definition, is a good person, a wise person and a teacher. v v. A quality guru should be all of these, plus have a concept and approach to quality within business that has made a major and lasting impact.
 There have been three groups of gurus since the 1940’s: Early 1950’s Americans who took the messages of quality to Japan Late 1950’s Japanese who developed new concepts in response to the Americans 1970’s-1980’s Western gurus who followed the Japanese industrial success
There have been three groups of gurus since the 1940’s: Early 1950’s Americans who took the messages of quality to Japan Late 1950’s Japanese who developed new concepts in response to the Americans 1970’s-1980’s Western gurus who followed the Japanese industrial success
 The Americans who went to Japan: W Edwards Deming Dr Joseph M Juran Armand V Feigenbaum The Japanese: Dr Kaoru Ishikawa Dr Genichi Taguchi Shigeo Shingo Western Gurus: Philip B Crosby Tom Peters
The Americans who went to Japan: W Edwards Deming Dr Joseph M Juran Armand V Feigenbaum The Japanese: Dr Kaoru Ishikawa Dr Genichi Taguchi Shigeo Shingo Western Gurus: Philip B Crosby Tom Peters
 Deming’s Theory 1. Create constancy of purpose 2. Adopt new philosophy 3. Cease dependence on inspection 4. End awarding business on price 5. Continuously improve the production and service 6. Institute training on the job 7. Institute leadership 8. Drive out fear so that everyone may work effectively for the company 9. Breakdown barriers between departments 10. Eliminate slogans and exhortations 11. Eliminate numerical goals and quota including management by objective 12. Remove barriers that rob people of their right to pride of workmanship 13. Institute vigorous program of education and self improvement 14. Put everybody in the company to work to accomplish the transformation
Deming’s Theory 1. Create constancy of purpose 2. Adopt new philosophy 3. Cease dependence on inspection 4. End awarding business on price 5. Continuously improve the production and service 6. Institute training on the job 7. Institute leadership 8. Drive out fear so that everyone may work effectively for the company 9. Breakdown barriers between departments 10. Eliminate slogans and exhortations 11. Eliminate numerical goals and quota including management by objective 12. Remove barriers that rob people of their right to pride of workmanship 13. Institute vigorous program of education and self improvement 14. Put everybody in the company to work to accomplish the transformation
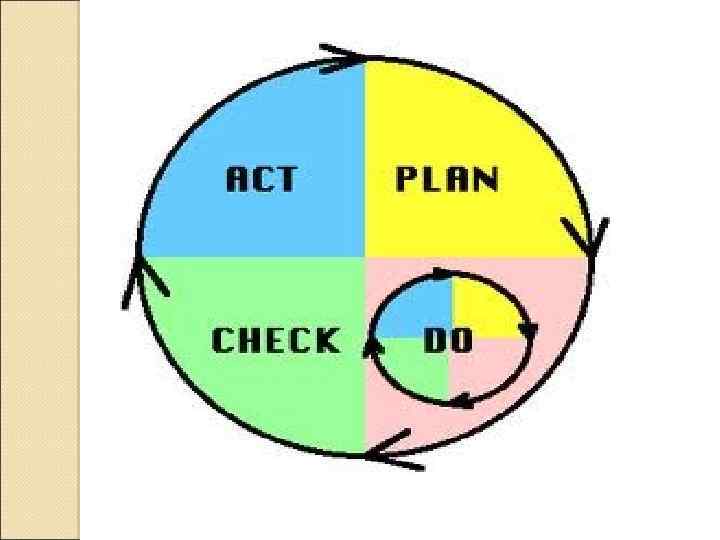
 Philip Crosby's theory 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Management Commitment The quality improvement team Measurement The cost of quality Quality awareness Corrective actions Zero defects planning Employee education Zero defects day Goal setting Error-cause removal Recognition Quality councils Do it all over again
Philip Crosby's theory 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Management Commitment The quality improvement team Measurement The cost of quality Quality awareness Corrective actions Zero defects planning Employee education Zero defects day Goal setting Error-cause removal Recognition Quality councils Do it all over again
 Juran’s Theory 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Build awareness of need and opportunity for improvement. Set goals for improvement. Organize to reach the goals (Establish a quality council, identify problems, select projects, appoint teams, designate facilitators) Provide training Carry out projects to solve problems Report progress Give recognition Communicate results Keep score Maintain momentum by making annual improvement part of the regular systems and processes of the company
Juran’s Theory 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Build awareness of need and opportunity for improvement. Set goals for improvement. Organize to reach the goals (Establish a quality council, identify problems, select projects, appoint teams, designate facilitators) Provide training Carry out projects to solve problems Report progress Give recognition Communicate results Keep score Maintain momentum by making annual improvement part of the regular systems and processes of the company
 Claus Moller’s Theory 1. Set personal quality goals 2. Establish own personal quality account 3. Check how satisfied others are with your efforts 4. Regard the next link as valued customer 5. Avoid errors 6. Perform tasks more effectively 7. Utilize resources well 8. Be committed 9. Learn to finish what you start 10. Control your stress 11. Be ethical 12. Demand quality Stop believing in management theories, start believing in common sense!
Claus Moller’s Theory 1. Set personal quality goals 2. Establish own personal quality account 3. Check how satisfied others are with your efforts 4. Regard the next link as valued customer 5. Avoid errors 6. Perform tasks more effectively 7. Utilize resources well 8. Be committed 9. Learn to finish what you start 10. Control your stress 11. Be ethical 12. Demand quality Stop believing in management theories, start believing in common sense!
 Common Message from Gurus There are no shortcuts to quality No quick fixes- it takes time to establish quality Improvement requires full commitment and support from top Extensive training needed Participation of all employees is a must
Common Message from Gurus There are no shortcuts to quality No quick fixes- it takes time to establish quality Improvement requires full commitment and support from top Extensive training needed Participation of all employees is a must
 Ten Principles of Quality Management 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Vision Based Customer focused Prevention oriented Scientifically approached Process given more importance than end results Data based analysis Continuous improvement strategies Cost conscious attempt Documentation for traceability Reward/Recognition assured
Ten Principles of Quality Management 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Vision Based Customer focused Prevention oriented Scientifically approached Process given more importance than end results Data based analysis Continuous improvement strategies Cost conscious attempt Documentation for traceability Reward/Recognition assured


