c6373ff61b18281f1e22a644a582cf6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 93
 Philippines FDA Circular No. 2014 -011 José A. Albert President & CEO GS 1 Philippines 1
Philippines FDA Circular No. 2014 -011 José A. Albert President & CEO GS 1 Philippines 1
 Philippines Introduction © 2011 GS 1
Philippines Introduction © 2011 GS 1
 FDA Circular No. 2014 -011 Philippines • The use of Global Data Standard • Scope: All products and establishment requiring FDA Registration • Global Product Identification & Global Establishment Identification • Date for full compliance: June 30, 2015 © 2011 GS 1 3
FDA Circular No. 2014 -011 Philippines • The use of Global Data Standard • Scope: All products and establishment requiring FDA Registration • Global Product Identification & Global Establishment Identification • Date for full compliance: June 30, 2015 © 2011 GS 1 3
 Philippines Guidelines Application Requirements 1. Each application for authorization of an establishment must indicate in the application form the unique establishment identification number. 2. Each application for authorization of a product must indicate in the application form the Global Trade Item Number. 3. No documents are required to be provided in support of the identification number as part of the authorization process. 4. The Agency can verify the identification numbers provided through a network that can synchronize global data. 5. Failure to provide a verifiable Global Trade Item Number by itself is sufficient ground for denial of application. © 2011 GS 1 4
Philippines Guidelines Application Requirements 1. Each application for authorization of an establishment must indicate in the application form the unique establishment identification number. 2. Each application for authorization of a product must indicate in the application form the Global Trade Item Number. 3. No documents are required to be provided in support of the identification number as part of the authorization process. 4. The Agency can verify the identification numbers provided through a network that can synchronize global data. 5. Failure to provide a verifiable Global Trade Item Number by itself is sufficient ground for denial of application. © 2011 GS 1 4
 Philippines Global Data Standard • Unique global product identification code and data structure • Identification code expressed in a machine readable manner (Barcode or RFID Tag) so as to enable automatic data capture or AIDC (Automatic Identification and Data Capture) techniques • Identification of each package level of a product • Key to unlock information about the product such as where the raw materials came from, who the suppliers were, and where the product was manufactured • Example: GS 1 GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) © 2011 GS 1
Philippines Global Data Standard • Unique global product identification code and data structure • Identification code expressed in a machine readable manner (Barcode or RFID Tag) so as to enable automatic data capture or AIDC (Automatic Identification and Data Capture) techniques • Identification of each package level of a product • Key to unlock information about the product such as where the raw materials came from, who the suppliers were, and where the product was manufactured • Example: GS 1 GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) © 2011 GS 1
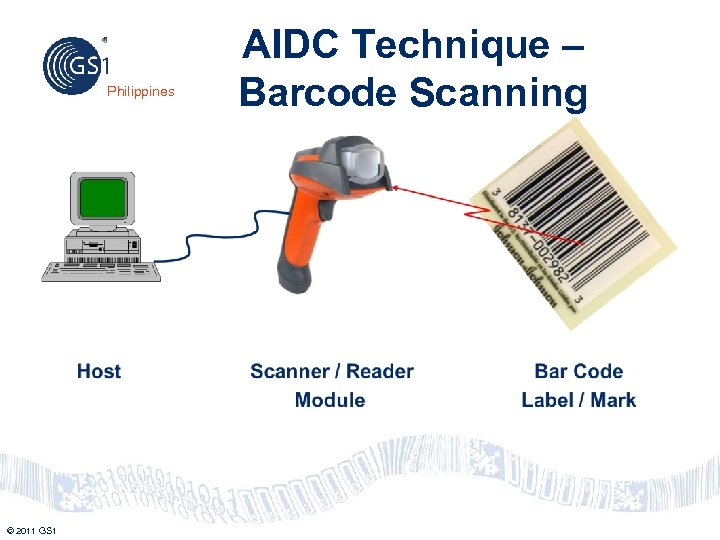 Philippines © 2011 GS 1 AIDC Technique – Barcode Scanning
Philippines © 2011 GS 1 AIDC Technique – Barcode Scanning
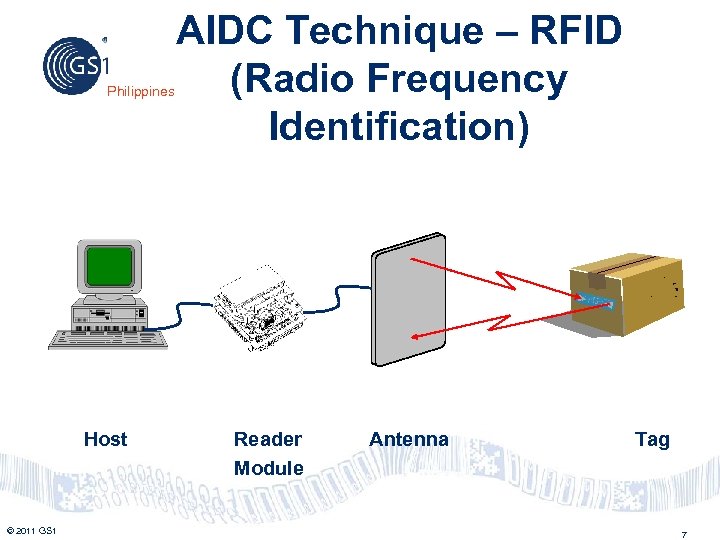 Philippines Host © 2011 GS 1 AIDC Technique – RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Reader Module Antenna Tag 7
Philippines Host © 2011 GS 1 AIDC Technique – RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Reader Module Antenna Tag 7
 Global Product Data Standard Philippines • Proposed framework for implementation of industry wide global product data standards to • Improve efficiency in cross border procedures • To increase supply chain visibility in trade • Initial improvement through capacity building/pilot projects • End goal the broad adoption of global product data standards throughout the supply chain in APEC member economies • Supports the APEC supply chain improvement goal to lower supply chain cost in APEC by 10% by 2015 © 2011 GS 1 8
Global Product Data Standard Philippines • Proposed framework for implementation of industry wide global product data standards to • Improve efficiency in cross border procedures • To increase supply chain visibility in trade • Initial improvement through capacity building/pilot projects • End goal the broad adoption of global product data standards throughout the supply chain in APEC member economies • Supports the APEC supply chain improvement goal to lower supply chain cost in APEC by 10% by 2015 © 2011 GS 1 8
 APEC Statements Qingdao, China, May 2014 Philippines • We reaffirm the positive contribution global data standards can make to enhancing supply chain efficiency and we welcome recent initiatives to share information and experiences on global data standards. We support further efforts to advance cooperation in this area. - APEC Ministers Responsible for Trade • APEC members promote the use and benefits of global data standards for cross-border control and supply chain management - Committee on Trade and Investment • APEC member economies are moving ahead with a joint multi -year initiative to improve the integrity of medical product manufacturing and security of distribution chains across borders to combat fraud in the world’s largest consumer market. - APEC Life Sciences Innovation Forum © 2011 GS 1
APEC Statements Qingdao, China, May 2014 Philippines • We reaffirm the positive contribution global data standards can make to enhancing supply chain efficiency and we welcome recent initiatives to share information and experiences on global data standards. We support further efforts to advance cooperation in this area. - APEC Ministers Responsible for Trade • APEC members promote the use and benefits of global data standards for cross-border control and supply chain management - Committee on Trade and Investment • APEC member economies are moving ahead with a joint multi -year initiative to improve the integrity of medical product manufacturing and security of distribution chains across borders to combat fraud in the world’s largest consumer market. - APEC Life Sciences Innovation Forum © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines • • • Advantages of Global Standard Data Automation Supply Chain (end-to-end) Visibility Assists with product traceability Facilitates Product Recall Enables to trace the Chain of Ownership of a Product • Facilitates identification of products entering the jurisdiction of a country © 2011 GS 1
Philippines • • • Advantages of Global Standard Data Automation Supply Chain (end-to-end) Visibility Assists with product traceability Facilitates Product Recall Enables to trace the Chain of Ownership of a Product • Facilitates identification of products entering the jurisdiction of a country © 2011 GS 1
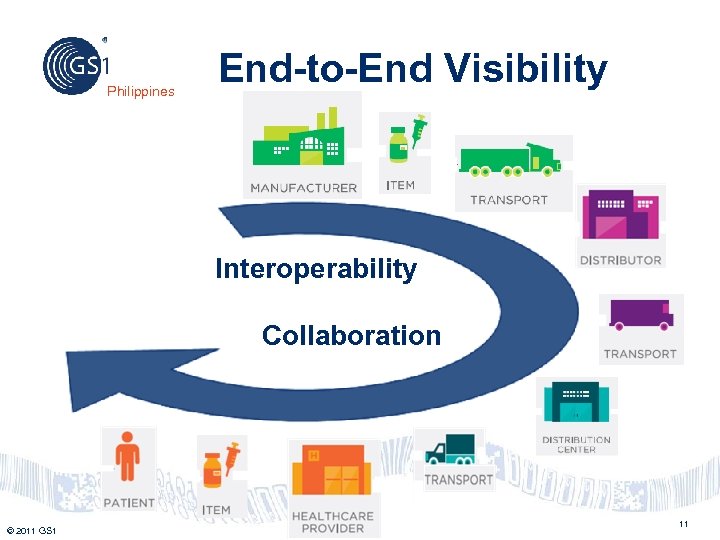 Philippines End-to-End Visibility Interoperability Collaboration © 2011 GS 1 11
Philippines End-to-End Visibility Interoperability Collaboration © 2011 GS 1 11
 Philippines Traceability • The ability to trace the history, application, or location of that which is under consideration (ISO 9001: 2000) • The ability to chronologically interrelate uniquely identifiable entities in a way that is verifiable • An end-to-end supply chain process where different companies collaborate to optimize the interfaces determined by its different directions, areas and subprocesses • The ability to track forward the movement through specified stage(s) of the extended supply chain and trace backward the history, application or location of that which is under consideration © 2011 GS 1
Philippines Traceability • The ability to trace the history, application, or location of that which is under consideration (ISO 9001: 2000) • The ability to chronologically interrelate uniquely identifiable entities in a way that is verifiable • An end-to-end supply chain process where different companies collaborate to optimize the interfaces determined by its different directions, areas and subprocesses • The ability to track forward the movement through specified stage(s) of the extended supply chain and trace backward the history, application or location of that which is under consideration © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines Recall/ Withdrawal • Withdrawal: “any measure aimed at preventing the distribution, display and offer of a product dangerous to the consumer (2001/95/EC)". • Recall: " any measure aimed at achieving the return of a dangerous product that has already been supplied or made available to consumers by the producer or distributor (2001/95/EC)". • Difference: Withdrawal happens when products are not available at the Point of Sales while Recall happens when products are available at the Point of Sales © 2011 GS 1 13
Philippines Recall/ Withdrawal • Withdrawal: “any measure aimed at preventing the distribution, display and offer of a product dangerous to the consumer (2001/95/EC)". • Recall: " any measure aimed at achieving the return of a dangerous product that has already been supplied or made available to consumers by the producer or distributor (2001/95/EC)". • Difference: Withdrawal happens when products are not available at the Point of Sales while Recall happens when products are available at the Point of Sales © 2011 GS 1 13
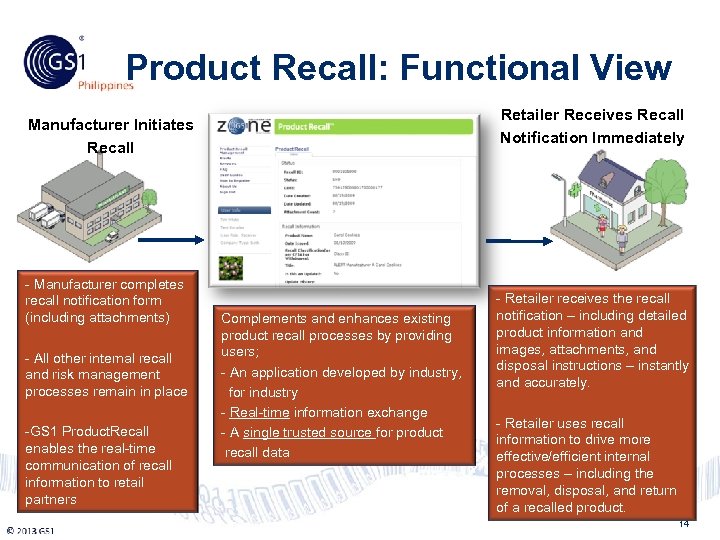 Product Recall: Functional View Philippines Retailer Receives Recall Notification Immediately Manufacturer Initiates Recall - Manufacturer completes recall notification form (including attachments) - All other internal recall and risk management processes remain in place -GS 1 Product. Recall enables the real-time communication of recall information to retail partners © 2011 GS 1 Complements and enhances existing product recall processes by providing users; - An application developed by industry, for industry - Real-time information exchange - A single trusted source for product recall data - Retailer receives the recall notification – including detailed product information and images, attachments, and disposal instructions – instantly and accurately. - Retailer uses recall information to drive more effective/efficient internal processes – including the removal, disposal, and return of a recalled product. 14
Product Recall: Functional View Philippines Retailer Receives Recall Notification Immediately Manufacturer Initiates Recall - Manufacturer completes recall notification form (including attachments) - All other internal recall and risk management processes remain in place -GS 1 Product. Recall enables the real-time communication of recall information to retail partners © 2011 GS 1 Complements and enhances existing product recall processes by providing users; - An application developed by industry, for industry - Real-time information exchange - A single trusted source for product recall data - Retailer receives the recall notification – including detailed product information and images, attachments, and disposal instructions – instantly and accurately. - Retailer uses recall information to drive more effective/efficient internal processes – including the removal, disposal, and return of a recalled product. 14
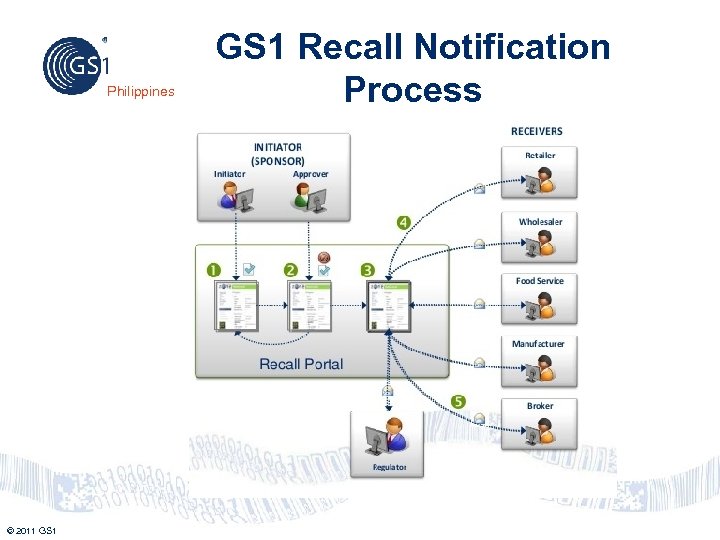 Philippines © 2011 GS 1 Recall Notification Process
Philippines © 2011 GS 1 Recall Notification Process
 Philippines Chain of Ownership (Pedigree) • The ability to trace the history of an individual item or product • A record, in electronic form, containing information regarding each transaction resulting in a change of ownership of a given product (drug), from sale by a manufacturer, through acquisition(s) and sale(s) by one or more wholesalers, manufacturers, or pharmacies, until final sale to a pharmacy or other person furnishing, administering or dispensing the drug. © 2011 GS 1 16
Philippines Chain of Ownership (Pedigree) • The ability to trace the history of an individual item or product • A record, in electronic form, containing information regarding each transaction resulting in a change of ownership of a given product (drug), from sale by a manufacturer, through acquisition(s) and sale(s) by one or more wholesalers, manufacturers, or pharmacies, until final sale to a pharmacy or other person furnishing, administering or dispensing the drug. © 2011 GS 1 16
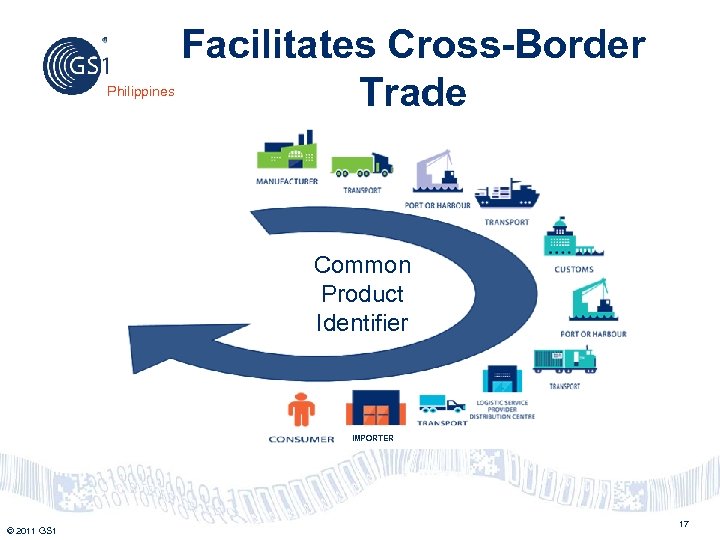 Philippines Facilitates Cross-Border Trade Common Product Identifier IMPORTER © 2011 GS 1 17
Philippines Facilitates Cross-Border Trade Common Product Identifier IMPORTER © 2011 GS 1 17
 Philippines GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) • A trade item is any item (product or service) upon which there is a need to retrieve pre-defined information and that may be priced, or ordered, or invoiced at any point in any supply chain. This includes individual items as well as all their different configurations in different types of packaging. • The Global Trade Item Number™ (GTIN™) is used for the unique identification of trade items worldwide. GTINs may be 8, 12, 13 or 14 -digits in length. Their data structures require up to 14 -digit fields, and all GTIN processing software should allow for 14 digits. © 2011 GS 1
Philippines GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) • A trade item is any item (product or service) upon which there is a need to retrieve pre-defined information and that may be priced, or ordered, or invoiced at any point in any supply chain. This includes individual items as well as all their different configurations in different types of packaging. • The Global Trade Item Number™ (GTIN™) is used for the unique identification of trade items worldwide. GTINs may be 8, 12, 13 or 14 -digits in length. Their data structures require up to 14 -digit fields, and all GTIN processing software should allow for 14 digits. © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines GS 1 and the Healthcare Sector © 2011 GS 1 19
Philippines GS 1 and the Healthcare Sector © 2011 GS 1 19
 Philippines Healthcare Timeline • 1995 – GS 1 expanded the use of the GS 1 Standards in the Healthcare Sector with the first Healthcare Collaboration Project • 2005 – Healthcare Sector came to GS 1 asking for help • 2005 – Healthcare becomes a GS 1 Focus Priority • 2005 – Healthcare User Group (HUG) Established • 2006 – 1 st HUG Conference • 2007 – 1 st GS 1 Healthcare Conference • 2009 – 1 st Publication of GS 1 Healthcare Reference Book • 2010 – GS 1 joins the Joint Initiative Council on Global Health Informatics • 2012 – Mc. Kinsey Healthcare Report © 2011 GS 1 20
Philippines Healthcare Timeline • 1995 – GS 1 expanded the use of the GS 1 Standards in the Healthcare Sector with the first Healthcare Collaboration Project • 2005 – Healthcare Sector came to GS 1 asking for help • 2005 – Healthcare becomes a GS 1 Focus Priority • 2005 – Healthcare User Group (HUG) Established • 2006 – 1 st HUG Conference • 2007 – 1 st GS 1 Healthcare Conference • 2009 – 1 st Publication of GS 1 Healthcare Reference Book • 2010 – GS 1 joins the Joint Initiative Council on Global Health Informatics • 2012 – Mc. Kinsey Healthcare Report © 2011 GS 1 20
 HUG Global Voting Members (Manufacturers) Philippines • • • © 2011 GS 1 Abbott Laboratories Astra. Zeneca Baxter Bayer B. Braun Bristol Myers Squibb Glaxo Smith Kline Johnson & Johnson Merck Novartis • Pfizer Inc. • Takeda Pharmaceuticals International GMBH • Alcon Laboratories • 3 M • Amgen • Cook • Covidien • Medtronic 21
HUG Global Voting Members (Manufacturers) Philippines • • • © 2011 GS 1 Abbott Laboratories Astra. Zeneca Baxter Bayer B. Braun Bristol Myers Squibb Glaxo Smith Kline Johnson & Johnson Merck Novartis • Pfizer Inc. • Takeda Pharmaceuticals International GMBH • Alcon Laboratories • 3 M • Amgen • Cook • Covidien • Medtronic 21
 Joint Initiative Council (JIC) on Global Health Informatics Philippines International European Organisation for Committee for Standardization Health Level 7 international International Health Terminology SDO Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise To enable common, timely informatics standards by addressing and resolving issues of gaps, overlaps and counterproductive standardization efforts GS 1 Supply and Demand Chain Standards Specialist © 2011 GS 1 22
Joint Initiative Council (JIC) on Global Health Informatics Philippines International European Organisation for Committee for Standardization Health Level 7 international International Health Terminology SDO Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise To enable common, timely informatics standards by addressing and resolving issues of gaps, overlaps and counterproductive standardization efforts GS 1 Supply and Demand Chain Standards Specialist © 2011 GS 1 22
 New Mc. Kinsey & Company Philippines Report New Mc. Kinsey report “Strength in unity: The promise of global standards in healthcare” Benefits of a Single Global Standards in healthcare Highlights the cost savings and patient safety benefits of adopting a single global supply chain standard in healthcare Available at: http: //www. gs 1. org/healthcare/mckinsey © 2011 GS 1
New Mc. Kinsey & Company Philippines Report New Mc. Kinsey report “Strength in unity: The promise of global standards in healthcare” Benefits of a Single Global Standards in healthcare Highlights the cost savings and patient safety benefits of adopting a single global supply chain standard in healthcare Available at: http: //www. gs 1. org/healthcare/mckinsey © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines Key Messages • Healthcare is at a crossroads • Global standards could help save thousands of lives and billions of dollars every year • Every part of the healthcare value chain could benefit • Multiple standards would diminish benefits • Senior leaders would have to collaborate © 2011 GS 1 24
Philippines Key Messages • Healthcare is at a crossroads • Global standards could help save thousands of lives and billions of dollars every year • Every part of the healthcare value chain could benefit • Multiple standards would diminish benefits • Senior leaders would have to collaborate © 2011 GS 1 24
 Barcoding in the Philippine Healthcare Sector Philippines • Pharmaceutical Products have been barcoded for the retail sector (Point-of-Sales) for the last 20 years • Dialogue between GS 1 Philippines and Hospitals currently on going • Two hospitals are currently engaged to pilot or implement barcoding to reduce error in medication – tracking pharmaceutical from manufacturer to patient © 2011 GS 1 25
Barcoding in the Philippine Healthcare Sector Philippines • Pharmaceutical Products have been barcoded for the retail sector (Point-of-Sales) for the last 20 years • Dialogue between GS 1 Philippines and Hospitals currently on going • Two hospitals are currently engaged to pilot or implement barcoding to reduce error in medication – tracking pharmaceutical from manufacturer to patient © 2011 GS 1 25
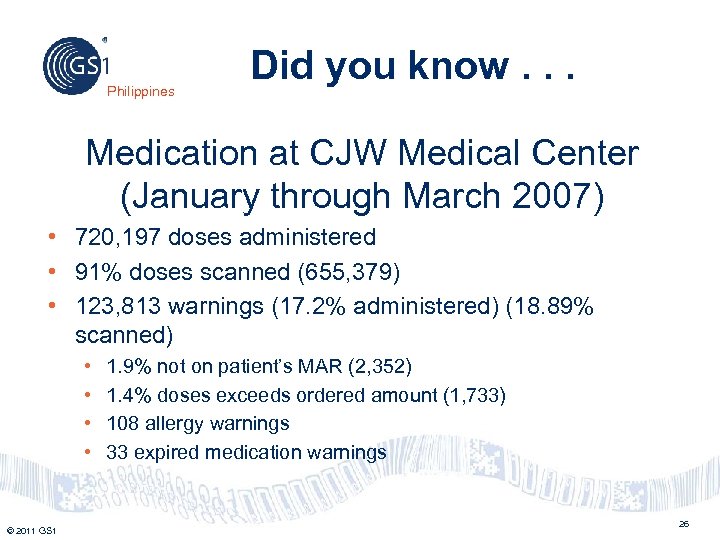 Philippines Did you know. . . Medication at CJW Medical Center (January through March 2007) • 720, 197 doses administered • 91% doses scanned (655, 379) • 123, 813 warnings (17. 2% administered) (18. 89% scanned) • • © 2011 GS 1 1. 9% not on patient’s MAR (2, 352) 1. 4% doses exceeds ordered amount (1, 733) 108 allergy warnings 33 expired medication warnings 26
Philippines Did you know. . . Medication at CJW Medical Center (January through March 2007) • 720, 197 doses administered • 91% doses scanned (655, 379) • 123, 813 warnings (17. 2% administered) (18. 89% scanned) • • © 2011 GS 1 1. 9% not on patient’s MAR (2, 352) 1. 4% doses exceeds ordered amount (1, 733) 108 allergy warnings 33 expired medication warnings 26
 Philippines GS 1 System and the Healthcare Sector © 2011 GS 1 27
Philippines GS 1 System and the Healthcare Sector © 2011 GS 1 27
 GS 1 System of Standards Philippines • The GS 1 System of Standards is designed to enable visibility to identify, capture and share information about products, between business partners and more - make it possible for companies to speak the same language, connect with other and move their business forward. Identify © 2011 GS 1 Capture Share 28
GS 1 System of Standards Philippines • The GS 1 System of Standards is designed to enable visibility to identify, capture and share information about products, between business partners and more - make it possible for companies to speak the same language, connect with other and move their business forward. Identify © 2011 GS 1 Capture Share 28
 Philippines IDENTIFY GS 1 Identification Keys Product Pack, Case, Pallet • Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) • Serialized Global Trade Item Number (SGTIN) • Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC) Companies Multiple Logistic Units • GS 1 Company Prefix • Global Location Number (GLN) • Electronic Product Code (EPC) Manager Number • Global Shipping Identification Number (GSIN) • Global Identification Number for Consignment (GINC) • Global Location Number (GLN) • Serialized Global Location Number (SGLN) • Global Individual Asset Identifier (GIAI) • Global Returnable Asset Identifier (GRAI) Location © 2011 GS 1 Assets Services • Global Service Relation Number (GSRN) • Global Document Type Identifier (GDTI) • Global Coupon Number (GCN) Product Attributes • Dates, e. g. Best before Date • Batch Number • Serial Number • Logistic Measures 29
Philippines IDENTIFY GS 1 Identification Keys Product Pack, Case, Pallet • Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) • Serialized Global Trade Item Number (SGTIN) • Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC) Companies Multiple Logistic Units • GS 1 Company Prefix • Global Location Number (GLN) • Electronic Product Code (EPC) Manager Number • Global Shipping Identification Number (GSIN) • Global Identification Number for Consignment (GINC) • Global Location Number (GLN) • Serialized Global Location Number (SGLN) • Global Individual Asset Identifier (GIAI) • Global Returnable Asset Identifier (GRAI) Location © 2011 GS 1 Assets Services • Global Service Relation Number (GSRN) • Global Document Type Identifier (GDTI) • Global Coupon Number (GCN) Product Attributes • Dates, e. g. Best before Date • Batch Number • Serial Number • Logistic Measures 29
 Philippines CAPTURE GS 1 Automatic Data Capture Tools © 2011 GS 1 30
Philippines CAPTURE GS 1 Automatic Data Capture Tools © 2011 GS 1 30
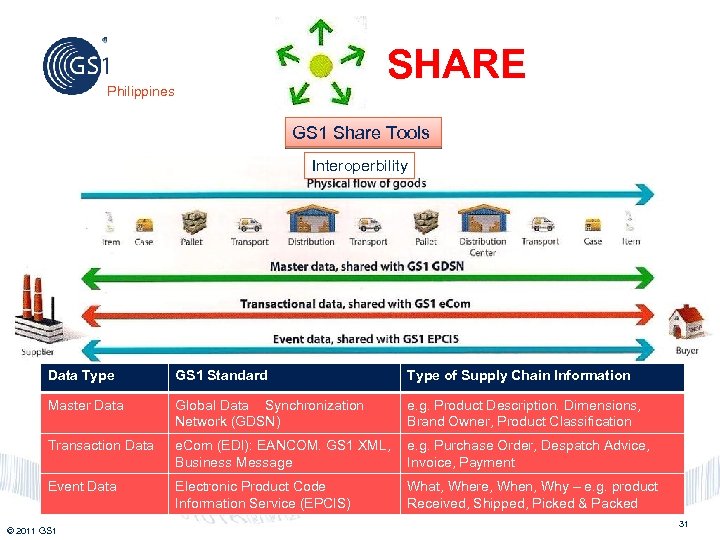 SHARE Philippines GS 1 Share Tools Interoperbility Physical Flow of Goods Data Type GS 1 Standard Type of Supply Chain Information Master Data Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) e. g. Product Description. Dimensions, Brand Owner, Product Classification Transaction Data e. Com (EDI): EANCOM. GS 1 XML, e. g. Purchase Order, Despatch Advice, Business Message Invoice, Payment Event Data Electronic Product Code Information Service (EPCIS) © 2011 GS 1 What, Where, When, Why – e. g. product Received, Shipped, Picked & Packed 31
SHARE Philippines GS 1 Share Tools Interoperbility Physical Flow of Goods Data Type GS 1 Standard Type of Supply Chain Information Master Data Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) e. g. Product Description. Dimensions, Brand Owner, Product Classification Transaction Data e. Com (EDI): EANCOM. GS 1 XML, e. g. Purchase Order, Despatch Advice, Business Message Invoice, Payment Event Data Electronic Product Code Information Service (EPCIS) © 2011 GS 1 What, Where, When, Why – e. g. product Received, Shipped, Picked & Packed 31
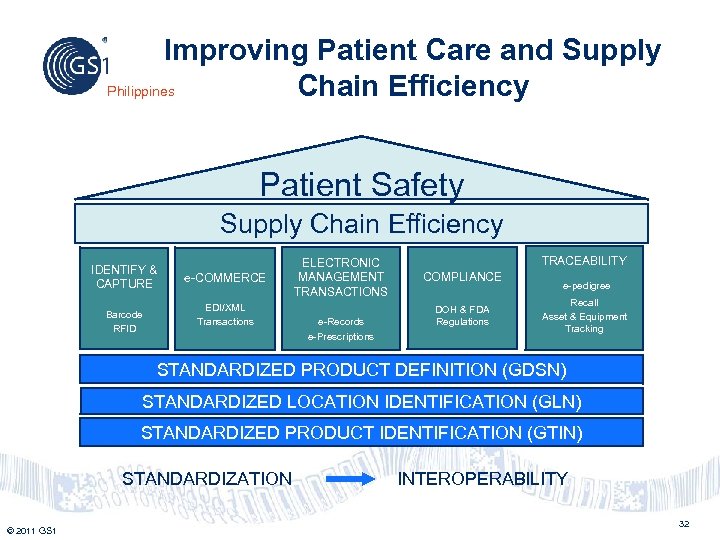 Improving Patient Care and Supply Philippines Chain Efficiency Patient Safety Supply Chain Efficiency IDENTIFY & CAPTURE Barcode RFID e-COMMERCE EDI/XML Transactions ELECTRONIC MANAGEMENT TRANSACTIONS e-Records e-Prescriptions TRACEABILITY COMPLIANCE DOH & FDA Regulations e-pedigree Recall Asset & Equipment Tracking STANDARDIZED PRODUCT DEFINITION (GDSN) STANDARDIZED LOCATION IDENTIFICATION (GLN) STANDARDIZED PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION (GTIN) STANDARDIZATION INTEROPERABILITY © 2011 GS 1 32
Improving Patient Care and Supply Philippines Chain Efficiency Patient Safety Supply Chain Efficiency IDENTIFY & CAPTURE Barcode RFID e-COMMERCE EDI/XML Transactions ELECTRONIC MANAGEMENT TRANSACTIONS e-Records e-Prescriptions TRACEABILITY COMPLIANCE DOH & FDA Regulations e-pedigree Recall Asset & Equipment Tracking STANDARDIZED PRODUCT DEFINITION (GDSN) STANDARDIZED LOCATION IDENTIFICATION (GLN) STANDARDIZED PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION (GTIN) STANDARDIZATION INTEROPERABILITY © 2011 GS 1 32
 Philippines Pallet Packaging levels Case / Shipper Secondary package Primary package Unit-ofuse Different packaging levels require different GTIN’s © 2011 GS 1
Philippines Pallet Packaging levels Case / Shipper Secondary package Primary package Unit-ofuse Different packaging levels require different GTIN’s © 2011 GS 1
 Case/Shipper and Pallet Philippines These packaging configurations that may be used either as trade units or logistic units. Case/Shipper may contain one or more trade items in their primary packaging or their secondary packaging. Pallets may contain one or more cases/shippers. Example: Case/Shipper Example: Pallet Note: Only fixed configuration pallets and shippers may be identified with a GTIN. © 2011 GS 1 34
Case/Shipper and Pallet Philippines These packaging configurations that may be used either as trade units or logistic units. Case/Shipper may contain one or more trade items in their primary packaging or their secondary packaging. Pallets may contain one or more cases/shippers. Example: Case/Shipper Example: Pallet Note: Only fixed configuration pallets and shippers may be identified with a GTIN. © 2011 GS 1 34
 Philippines Healthcare Secondary Package • A level of packaging marked with an AIDC carrier that may contain one or more primary packages or a group of primary packages containing a single item. © 2011 GS 1 35
Philippines Healthcare Secondary Package • A level of packaging marked with an AIDC carrier that may contain one or more primary packages or a group of primary packages containing a single item. © 2011 GS 1 35
 Philippines Healthcare Primary Package • Healthcare Primary Packaging trade items are pharmaceutical and medical products or their packages presented to support the Point-of. Care (direct consumption based on right product, dose, and route of administration. • If an item is a Regulated Healthcare Retail Consumer Trade Item and also a Non-Retail Trade Item then the bar code marking for Regulated Healthcare Retail Consumer Trade Items is required at a minimum. © 2011 GS 1
Philippines Healthcare Primary Package • Healthcare Primary Packaging trade items are pharmaceutical and medical products or their packages presented to support the Point-of. Care (direct consumption based on right product, dose, and route of administration. • If an item is a Regulated Healthcare Retail Consumer Trade Item and also a Non-Retail Trade Item then the bar code marking for Regulated Healthcare Retail Consumer Trade Items is required at a minimum. © 2011 GS 1
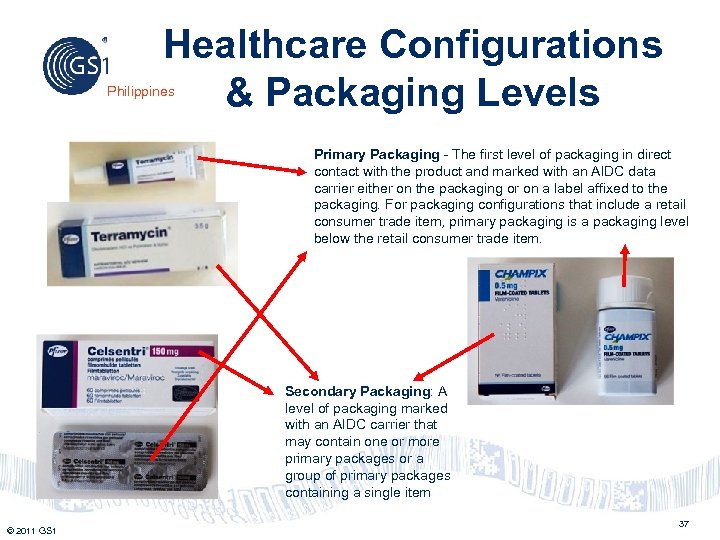 Healthcare Configurations & Packaging Levels Philippines Primary Packaging - The first level of packaging in direct contact with the product and marked with an AIDC data carrier either on the packaging or on a label affixed to the packaging. For packaging configurations that include a retail consumer trade item, primary packaging is a packaging level below the retail consumer trade item. Secondary Packaging: A level of packaging marked with an AIDC carrier that may contain one or more primary packages or a group of primary packages containing a single item © 2011 GS 1 37
Healthcare Configurations & Packaging Levels Philippines Primary Packaging - The first level of packaging in direct contact with the product and marked with an AIDC data carrier either on the packaging or on a label affixed to the packaging. For packaging configurations that include a retail consumer trade item, primary packaging is a packaging level below the retail consumer trade item. Secondary Packaging: A level of packaging marked with an AIDC carrier that may contain one or more primary packages or a group of primary packages containing a single item © 2011 GS 1 37
 Philippines Definitions • Single unit = Single item of medicine/Medical device without any package, for example the single tablet in a blister or bottle, the syringe as such. © 2011 GS 1 • Single unit package (GS 1 primary package) is the one that contains one discrete pharmaceutical dosage form. i. e. a tablet, a certain volume of a liquid or that is the immediate package for a medical device like a syringe 38
Philippines Definitions • Single unit = Single item of medicine/Medical device without any package, for example the single tablet in a blister or bottle, the syringe as such. © 2011 GS 1 • Single unit package (GS 1 primary package) is the one that contains one discrete pharmaceutical dosage form. i. e. a tablet, a certain volume of a liquid or that is the immediate package for a medical device like a syringe 38
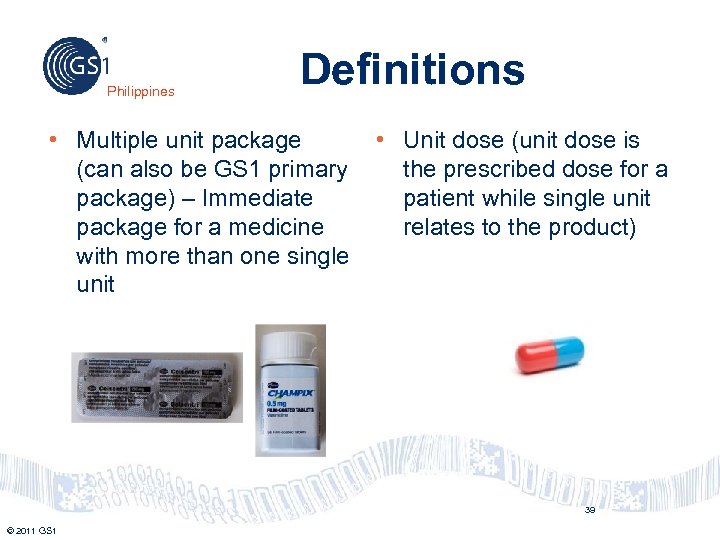 Philippines Definitions • Multiple unit package • Unit dose (unit dose is (can also be GS 1 primary the prescribed dose for a package) – Immediate patient while single unit package for a medicine relates to the product) with more than one single unit 39 © 2011 GS 1
Philippines Definitions • Multiple unit package • Unit dose (unit dose is (can also be GS 1 primary the prescribed dose for a package) – Immediate patient while single unit package for a medicine relates to the product) with more than one single unit 39 © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines Product Identification • A GTIN is the generic identification of the different configurations in different types of packaging of a specific product • A GTIN can be narrowed down by adding specific attributes • Expiry Date (AI 17) • Lot/Batch Number (AI 10) • Serial Number (AI 21) • A GTIN + Serial Number (AI 21) identifies a unique individual product © 2011 GS 1 40
Philippines Product Identification • A GTIN is the generic identification of the different configurations in different types of packaging of a specific product • A GTIN can be narrowed down by adding specific attributes • Expiry Date (AI 17) • Lot/Batch Number (AI 10) • Serial Number (AI 21) • A GTIN + Serial Number (AI 21) identifies a unique individual product © 2011 GS 1 40
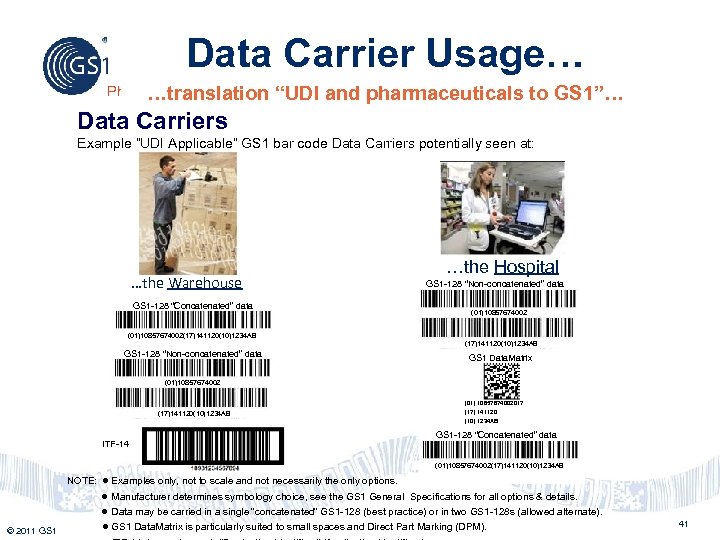 Data Carrier Usage… Philippines …translation “UDI and pharmaceuticals to GS 1”… Data Carriers Example “UDI Applicable” GS 1 bar code Data Carriers potentially seen at: …the Warehouse GS 1 -128 “Concatenated” data …the Hospital GS 1 -128 “Non-concatenated” data (01)10857674002(17)141120(10)1234 AB GS 1 -128 “Non-concatenated” data GS 1 Data. Matrix (01)10857674002 (17)141120(10)1234 AB ITF-14 (01) 10857674002017 (17) 141120 (10) 1234 AB GS 1 -128 “Concatenated” data (01)10857674002(17)141120(10)1234 AB NOTE: Examples only, not to scale and not necessarily the only options. Manufacturer determines symbology choice, see the GS 1 General Specifications for all options & details. Data may be carried in a single “concatenated” GS 1 -128 (best practice) or in two GS 1 -128 s (allowed alternate). © 2011 GS 1 GS 1 Data. Matrix is particularly suited to small spaces and Direct Part Marking (DPM). 41
Data Carrier Usage… Philippines …translation “UDI and pharmaceuticals to GS 1”… Data Carriers Example “UDI Applicable” GS 1 bar code Data Carriers potentially seen at: …the Warehouse GS 1 -128 “Concatenated” data …the Hospital GS 1 -128 “Non-concatenated” data (01)10857674002(17)141120(10)1234 AB GS 1 -128 “Non-concatenated” data GS 1 Data. Matrix (01)10857674002 (17)141120(10)1234 AB ITF-14 (01) 10857674002017 (17) 141120 (10) 1234 AB GS 1 -128 “Concatenated” data (01)10857674002(17)141120(10)1234 AB NOTE: Examples only, not to scale and not necessarily the only options. Manufacturer determines symbology choice, see the GS 1 General Specifications for all options & details. Data may be carried in a single “concatenated” GS 1 -128 (best practice) or in two GS 1 -128 s (allowed alternate). © 2011 GS 1 GS 1 Data. Matrix is particularly suited to small spaces and Direct Part Marking (DPM). 41
 Data Carrier Usage… Philippines …translation “UDI and pharmaceuticals to GS 1”… Data Carriers Example “UDI Applicable” GS 1 bar code Data Carriers potentially seen at: …the Point of Care …the Retail POS EAN 13 GS 1 -128 “Concatenated” data UPC-A (01)10857674002(17)141120(10)1234 AB GS 1 Data. Matrix ITF-14 (01) 10857674002017 (17) 141120 (10) 1234 AB NOTE: Examples only, not to scale and not necessarily the only options. Manufacturer determines symbology choice, see the GS 1 General Specifications for all options & details. UPC-A, EAN-13 and ITF-14 do not encode “Production Identifiers” (Application Identifiers) Data may be carried in a single “concatenated” GS 1 -128 (best practice) or in two GS 1 -128 s (allowed alternate). © 2011 GS 1 GS 1 Data. Matrix is particularly suited to small spaces and Direct Part Marking (DPM). 42
Data Carrier Usage… Philippines …translation “UDI and pharmaceuticals to GS 1”… Data Carriers Example “UDI Applicable” GS 1 bar code Data Carriers potentially seen at: …the Point of Care …the Retail POS EAN 13 GS 1 -128 “Concatenated” data UPC-A (01)10857674002(17)141120(10)1234 AB GS 1 Data. Matrix ITF-14 (01) 10857674002017 (17) 141120 (10) 1234 AB NOTE: Examples only, not to scale and not necessarily the only options. Manufacturer determines symbology choice, see the GS 1 General Specifications for all options & details. UPC-A, EAN-13 and ITF-14 do not encode “Production Identifiers” (Application Identifiers) Data may be carried in a single “concatenated” GS 1 -128 (best practice) or in two GS 1 -128 s (allowed alternate). © 2011 GS 1 GS 1 Data. Matrix is particularly suited to small spaces and Direct Part Marking (DPM). 42
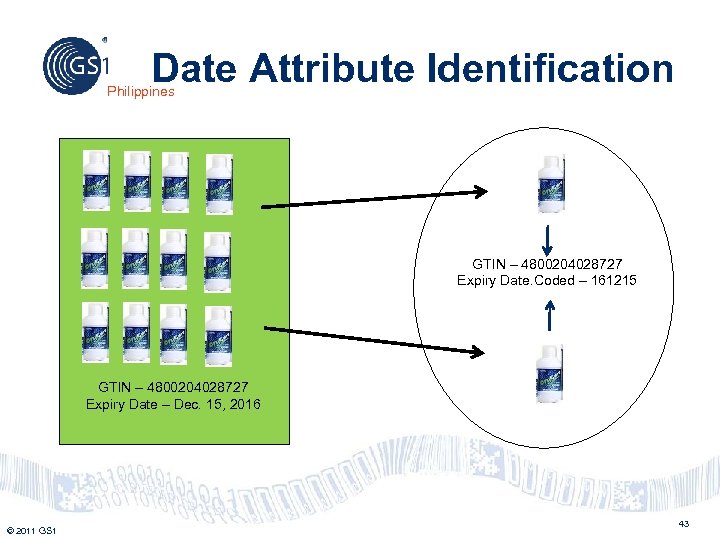 Date Attribute Identification Philippines GTIN – 4800204028727 Expiry Date. Coded – 161215 GTIN – 4800204028727 Expiry Date – Dec. 15, 2016 © 2011 GS 1 43
Date Attribute Identification Philippines GTIN – 4800204028727 Expiry Date. Coded – 161215 GTIN – 4800204028727 Expiry Date – Dec. 15, 2016 © 2011 GS 1 43
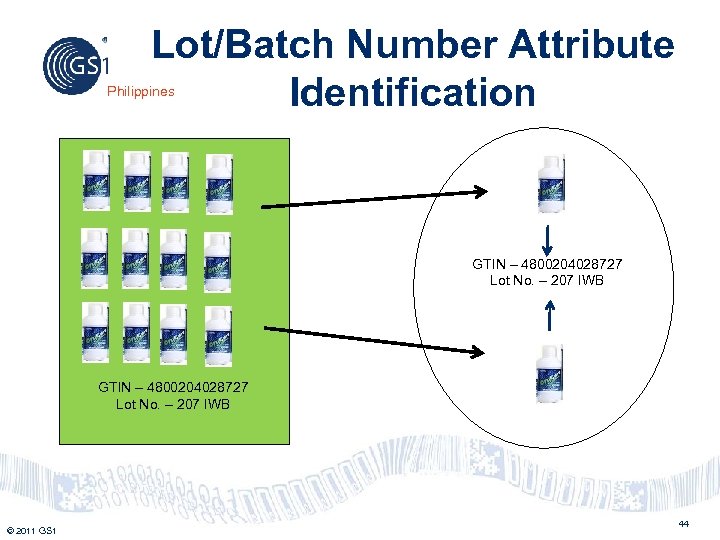 Lot/Batch Number Attribute Identification Philippines GTIN – 4800204028727 Lot No. – 207 IWB © 2011 GS 1 44
Lot/Batch Number Attribute Identification Philippines GTIN – 4800204028727 Lot No. – 207 IWB © 2011 GS 1 44
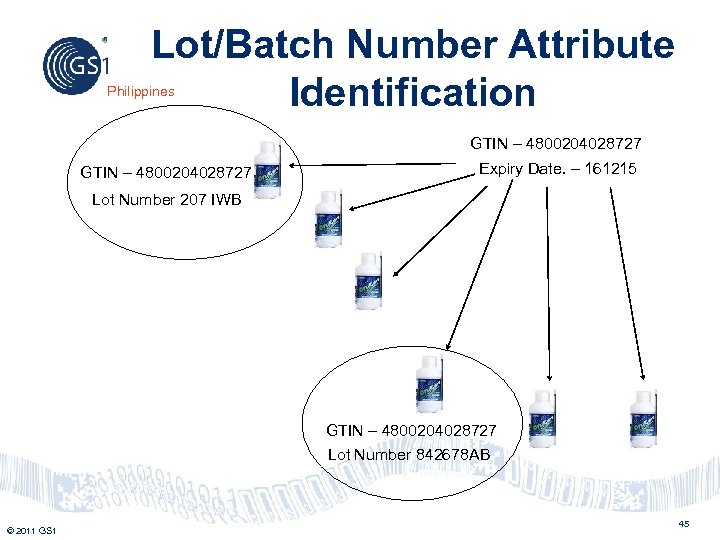 Lot/Batch Number Attribute Identification Philippines GTIN – 4800204028727 Expiry Date. – 161215 Lot Number 207 IWB GTIN – 4800204028727 Lot Number 842678 AB © 2011 GS 1 45
Lot/Batch Number Attribute Identification Philippines GTIN – 4800204028727 Expiry Date. – 161215 Lot Number 207 IWB GTIN – 4800204028727 Lot Number 842678 AB © 2011 GS 1 45
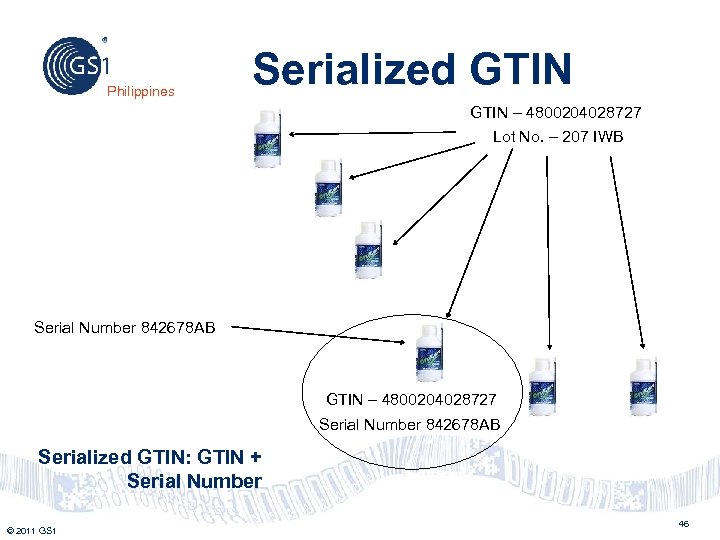 Philippines Serialized GTIN – 4800204028727 Lot No. – 207 IWB Serial Number 842678 AB GTIN – 4800204028727 Serial Number 842678 AB Serialized GTIN: GTIN + Serial Number © 2011 GS 1 46
Philippines Serialized GTIN – 4800204028727 Lot No. – 207 IWB Serial Number 842678 AB GTIN – 4800204028727 Serial Number 842678 AB Serialized GTIN: GTIN + Serial Number © 2011 GS 1 46
 Philippines Use of Different Attributes • Lot/Batch Number – Recall/Withdrawal • Serial Number – Chain of Ownership © 2011 GS 1 47
Philippines Use of Different Attributes • Lot/Batch Number – Recall/Withdrawal • Serial Number – Chain of Ownership © 2011 GS 1 47
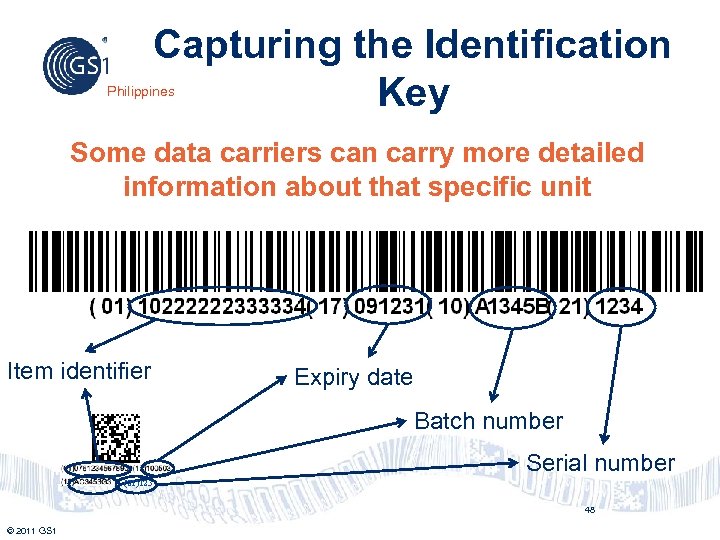 Capturing the Identification Key Philippines Some data carriers can carry more detailed information about that specific unit Item identifier Expiry date Batch number Serial number (21)123 48 © 2011 GS 1
Capturing the Identification Key Philippines Some data carriers can carry more detailed information about that specific unit Item identifier Expiry date Batch number Serial number (21)123 48 © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines Global Establishment Identification • A establishment is any entity (physical location or legal entity) within the supply chain • Global Location Number (GLN) is the GS 1 identification key used to identify physical locations or legal entities where there is a need to retrieve pre-defined information to improve the efficiency of communication within the supply chain © 2011 GS 1 49
Philippines Global Establishment Identification • A establishment is any entity (physical location or legal entity) within the supply chain • Global Location Number (GLN) is the GS 1 identification key used to identify physical locations or legal entities where there is a need to retrieve pre-defined information to improve the efficiency of communication within the supply chain © 2011 GS 1 49
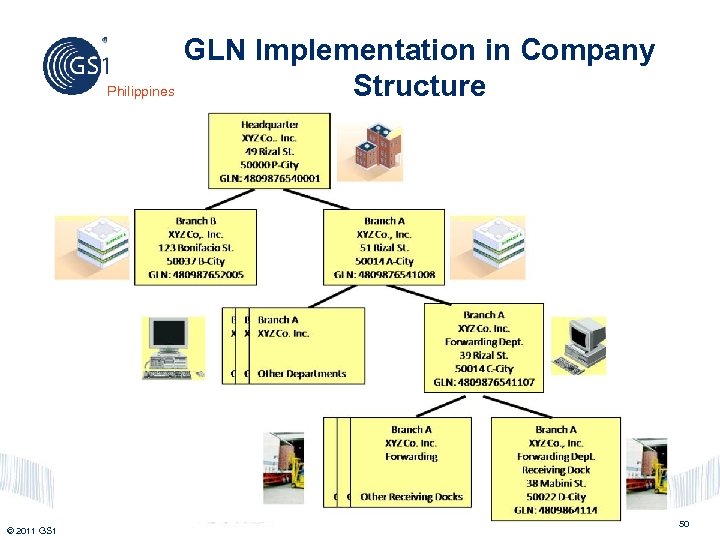 GLN Implementation in Company Philippines Structure © 2011 GS 1 50
GLN Implementation in Company Philippines Structure © 2011 GS 1 50
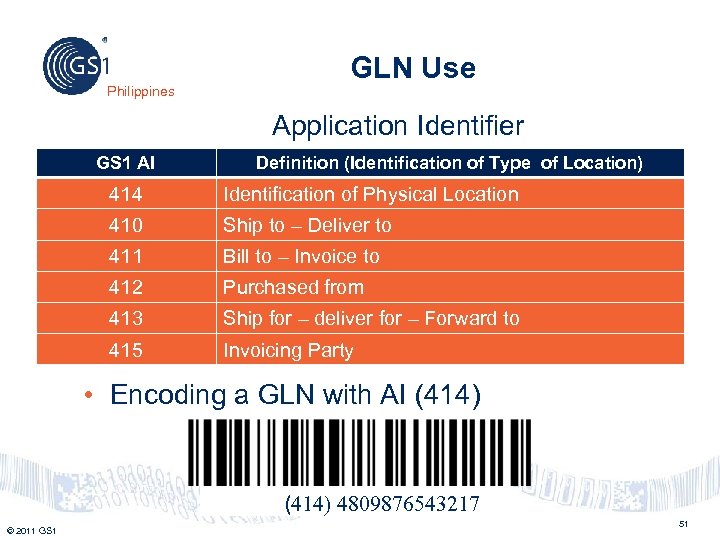 Philippines GLN Use Application Identifier GS 1 AI Definition (Identification of Type of Location) 414 Identification of Physical Location 410 Ship to – Deliver to 411 Bill to – Invoice to 412 Purchased from 413 Ship for – deliver for – Forward to 415 Invoicing Party • Encoding a GLN with AI (414) 4809876543217 © 2011 GS 1 51
Philippines GLN Use Application Identifier GS 1 AI Definition (Identification of Type of Location) 414 Identification of Physical Location 410 Ship to – Deliver to 411 Bill to – Invoice to 412 Purchased from 413 Ship for – deliver for – Forward to 415 Invoicing Party • Encoding a GLN with AI (414) 4809876543217 © 2011 GS 1 51
 Philippines A model for Global Standards Harmonization in Healthcare UDI (Unique Device Identification) © 2011 GS 1
Philippines A model for Global Standards Harmonization in Healthcare UDI (Unique Device Identification) © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines Global Harmonization • The world is flat • World trade has made the free flow of goods • Goods have to be tracked and trace most particlarly where consumer (patient) safety is concerned • The regulators from across the world realized the need for a common set of rules that would make this possible • The first area chosen was Unique Device Identification (UDI) © 2011 GS 1 53
Philippines Global Harmonization • The world is flat • World trade has made the free flow of goods • Goods have to be tracked and trace most particlarly where consumer (patient) safety is concerned • The regulators from across the world realized the need for a common set of rules that would make this possible • The first area chosen was Unique Device Identification (UDI) © 2011 GS 1 53
 Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Global Harmonization Task Force (GHTF) waws conceived in 1992 in order to obtain greater uniformity between national medical device regulatory systems for the purpose of enhancing patient safety and increase access to safe, effective an clinically benefinial technologies A partnership between regulators and te regulated for the purpose to encourage convergence in regulatory practices related to ensuring the safety, effectuveness/performance and quality of medical devives. Promote technological innovation and facilating international trade. This was primarily accomplished through publication and dissemination of harmonized guidance documents on basic regulatory practices. In February 2011, nternational Medical Device Regulators from around the world conceived of a forum to discuss future directions in medicall device regulatory harmonization A voluntary group was came together to build on the strong foundational work of the Global Harmonization Task Force on Medical Device (GHTF), and to accelarate international medical device regulatory harmonization and convergence 54
Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Global Harmonization Task Force (GHTF) waws conceived in 1992 in order to obtain greater uniformity between national medical device regulatory systems for the purpose of enhancing patient safety and increase access to safe, effective an clinically benefinial technologies A partnership between regulators and te regulated for the purpose to encourage convergence in regulatory practices related to ensuring the safety, effectuveness/performance and quality of medical devives. Promote technological innovation and facilating international trade. This was primarily accomplished through publication and dissemination of harmonized guidance documents on basic regulatory practices. In February 2011, nternational Medical Device Regulators from around the world conceived of a forum to discuss future directions in medicall device regulatory harmonization A voluntary group was came together to build on the strong foundational work of the Global Harmonization Task Force on Medical Device (GHTF), and to accelarate international medical device regulatory harmonization and convergence 54
 Philippines Composition of IMDRF Members Observer • • World Health Organization (WHO) © 2011 GS 1 Australia Brazil Canada European Union Japan United States Pending Membership • China • Russia • Affiliate Organization • Asian Harmonization Working Party (AHWP) • APEC LSIF Regulatory Harmonization Steering Committee
Philippines Composition of IMDRF Members Observer • • World Health Organization (WHO) © 2011 GS 1 Australia Brazil Canada European Union Japan United States Pending Membership • China • Russia • Affiliate Organization • Asian Harmonization Working Party (AHWP) • APEC LSIF Regulatory Harmonization Steering Committee
 Philippines UDI: Scope All products placed on the market that fall within the definition of a medical device in both the GHTF and IMDRF documents http: //www. gs 1. org/sites/default/files/do cs/healthcare/ghtf-sg 1 -n 071 -2012 definition-of-terms-120516. pdf © 2011 GS 1 56
Philippines UDI: Scope All products placed on the market that fall within the definition of a medical device in both the GHTF and IMDRF documents http: //www. gs 1. org/sites/default/files/do cs/healthcare/ghtf-sg 1 -n 071 -2012 definition-of-terms-120516. pdf © 2011 GS 1 56
 Philippines UDI: Purpose A common, worldwide system for product identification to eliminate differences between jurisdictions and offer significant benefits to manufacturers, users and/or patients, and Regulatory Authorities. © 2011 GS 1 57
Philippines UDI: Purpose A common, worldwide system for product identification to eliminate differences between jurisdictions and offer significant benefits to manufacturers, users and/or patients, and Regulatory Authorities. © 2011 GS 1 57
 Benefits for Patient Safety Philippines • Improved recall procedure and adverse event reporting • Documentation of product/patient relationship – in electronic health records (EHR) and registries • Visibility of inventory – availability of devices • Reduction of medical errors • Supply chain security/anti-counterfeiting © 2011 GS 1
Benefits for Patient Safety Philippines • Improved recall procedure and adverse event reporting • Documentation of product/patient relationship – in electronic health records (EHR) and registries • Visibility of inventory – availability of devices • Reduction of medical errors • Supply chain security/anti-counterfeiting © 2011 GS 1
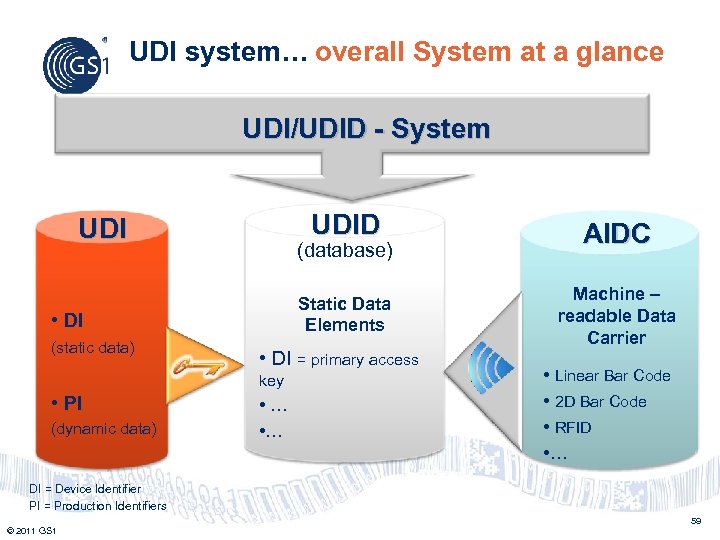 UDI system… overall System at a glance UDI/UDID - System UDID • DI = primary access key • PI (dynamic data) Machine – readable Data Carrier (database) • DI (static data) AIDC Static Data Elements UDI • … • Linear Bar Code • 2 D Bar Code • RFID • … DI = Device Identifier PI = Production Identifiers 59 © 2011 GS 1
UDI system… overall System at a glance UDI/UDID - System UDID • DI = primary access key • PI (dynamic data) Machine – readable Data Carrier (database) • DI (static data) AIDC Static Data Elements UDI • … • Linear Bar Code • 2 D Bar Code • RFID • … DI = Device Identifier PI = Production Identifiers 59 © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines UDI number • Develop UDI number based on ISO 15459 : US FDA will accredit issuing agencies (e. g. GS 1, HIBCC, ICCBBA) • Created and maintained by the manufacturer • Device Identifier (DI) Static : manufacturer, make, model, catalogue number • Production Identifier (PI) Dynamic : serial number, lot number, expiration/manufacturing date • Phase out national numbering system (NDC/NHRIC) © 2011 GS 1 60
Philippines UDI number • Develop UDI number based on ISO 15459 : US FDA will accredit issuing agencies (e. g. GS 1, HIBCC, ICCBBA) • Created and maintained by the manufacturer • Device Identifier (DI) Static : manufacturer, make, model, catalogue number • Production Identifier (PI) Dynamic : serial number, lot number, expiration/manufacturing date • Phase out national numbering system (NDC/NHRIC) © 2011 GS 1 60
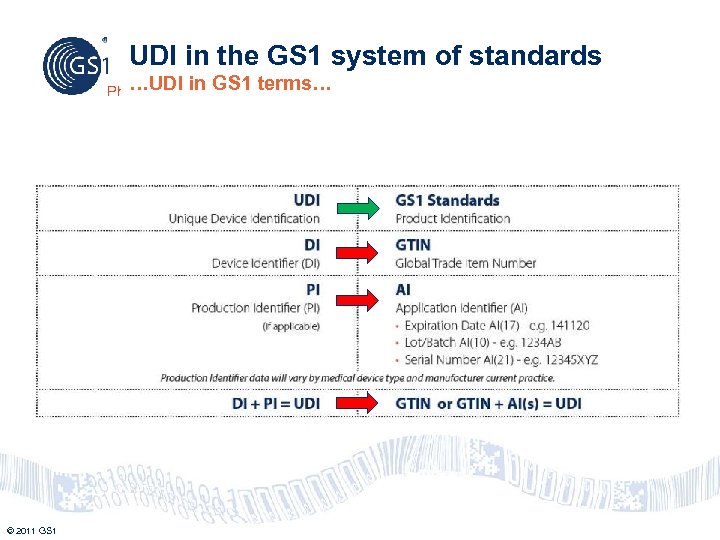 UDI in the GS 1 system of standards …UDI Philippines © 2011 GS 1 in GS 1 terms…
UDI in the GS 1 system of standards …UDI Philippines © 2011 GS 1 in GS 1 terms…
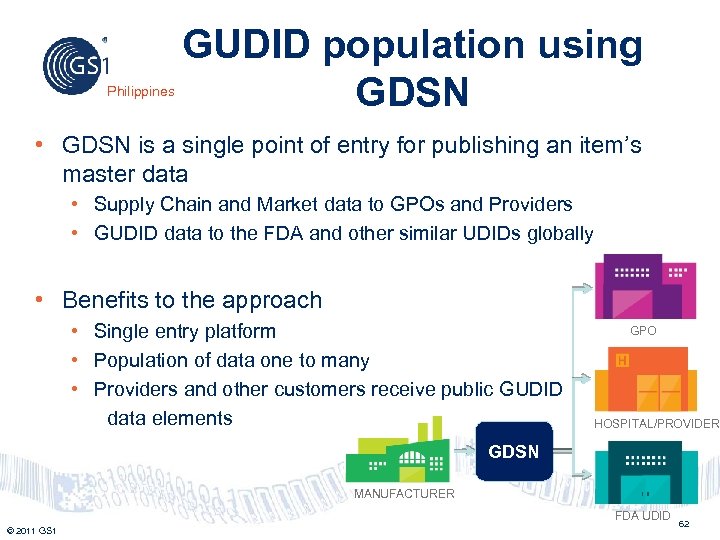 Philippines GUDID population using GDSN • GDSN is a single point of entry for publishing an item’s master data • Supply Chain and Market data to GPOs and Providers • GUDID data to the FDA and other similar UDIDs globally • Benefits to the approach • Single entry platform • Population of data one to many • Providers and other customers receive public GUDID data elements GPO HOSPITAL/PROVIDER GDSN MANUFACTURER FDA UDID © 2011 GS 1 62
Philippines GUDID population using GDSN • GDSN is a single point of entry for publishing an item’s master data • Supply Chain and Market data to GPOs and Providers • GUDID data to the FDA and other similar UDIDs globally • Benefits to the approach • Single entry platform • Population of data one to many • Providers and other customers receive public GUDID data elements GPO HOSPITAL/PROVIDER GDSN MANUFACTURER FDA UDID © 2011 GS 1 62
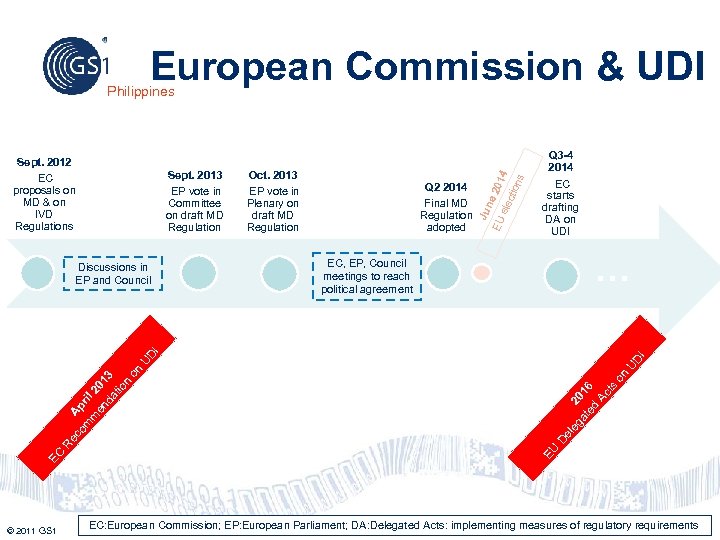 European Commission & UDI Philippines Sept. 2013 EP vote in Committee on draft MD Regulation Q 2 2014 Final MD Regulation adopted Q 3 -4 2014 EC starts drafting DA on UDI … EC, EP, Council meetings to reach political agreement © 2011 GS 1 U eg 20 at 1 ed 6 A ct s on el D EU EC R ec A om pr m il 2 en 01 da 3 tio n on U DI DI Discussions in EP and Council Oct. 2013 EP vote in Plenary on draft MD Regulation Jun EU e 201 ele 4 ctio ns Sept. 2012 EC proposals on MD & on IVD Regulations 63 EC: European Commission; EP: European Parliament; DA: Delegated Acts: implementing measures of regulatory requirements
European Commission & UDI Philippines Sept. 2013 EP vote in Committee on draft MD Regulation Q 2 2014 Final MD Regulation adopted Q 3 -4 2014 EC starts drafting DA on UDI … EC, EP, Council meetings to reach political agreement © 2011 GS 1 U eg 20 at 1 ed 6 A ct s on el D EU EC R ec A om pr m il 2 en 01 da 3 tio n on U DI DI Discussions in EP and Council Oct. 2013 EP vote in Plenary on draft MD Regulation Jun EU e 201 ele 4 ctio ns Sept. 2012 EC proposals on MD & on IVD Regulations 63 EC: European Commission; EP: European Parliament; DA: Delegated Acts: implementing measures of regulatory requirements
 Philippines Track and Trace Work Group APEC Roadmap for Global Medical Product Integrity and Supply Chain Security © 2011 GS 1 64
Philippines Track and Trace Work Group APEC Roadmap for Global Medical Product Integrity and Supply Chain Security © 2011 GS 1 64
 Global Medical Product Integrity and Philippines Supply Chain Security A 5 year project is sponsored by the APEC Committee on Trade and Investment (CTI). The proponent economy is the US and the cosponsoring economies are Canada, Korea, China, Taiwan, Singapore, Mexico, Thailand, Japan, Peru, Russia and Malaysia. The targeted audience is national regulatory authorities, industries regulated by national regulatory authorities, and other stakeholders concerned with quality, safety and efficacy of medical products moving in international commerce © 2011 GS 1 65
Global Medical Product Integrity and Philippines Supply Chain Security A 5 year project is sponsored by the APEC Committee on Trade and Investment (CTI). The proponent economy is the US and the cosponsoring economies are Canada, Korea, China, Taiwan, Singapore, Mexico, Thailand, Japan, Peru, Russia and Malaysia. The targeted audience is national regulatory authorities, industries regulated by national regulatory authorities, and other stakeholders concerned with quality, safety and efficacy of medical products moving in international commerce © 2011 GS 1 65
 Did you know. . . Philippines • In 2012, there was a 13% increase in the number of incidents of counterfeit drugs entering the Legitimate Supply Chain Pharmaceutical Security Institute (PSI) • A fake cancer drug was purchased by 19 hospitals and medical centers in the United States • The number of counterfeit drugs uncovered at EU borders in 2005 was 560, 598 and that it increased to 4, 081, 056 in 2007 • 34, 000 fake tablets sized on the continent borders in just 2 months – Gunter Verheugen VP European Commission (end 2009) © 2011 GS 1 66
Did you know. . . Philippines • In 2012, there was a 13% increase in the number of incidents of counterfeit drugs entering the Legitimate Supply Chain Pharmaceutical Security Institute (PSI) • A fake cancer drug was purchased by 19 hospitals and medical centers in the United States • The number of counterfeit drugs uncovered at EU borders in 2005 was 560, 598 and that it increased to 4, 081, 056 in 2007 • 34, 000 fake tablets sized on the continent borders in just 2 months – Gunter Verheugen VP European Commission (end 2009) © 2011 GS 1 66
 Philippines Track and Trace Work Group (TTWG) • Led by GS 1 • GS 1 is a neutral facilitator of the WG • Scope: pharmaceuticals © 2011 GS 1 67
Philippines Track and Trace Work Group (TTWG) • Led by GS 1 • GS 1 is a neutral facilitator of the WG • Scope: pharmaceuticals © 2011 GS 1 67
 Philippines Philippine Status • Philippines has been listed under APEC economies that decision making and/or not yet adopted requirements on pharmaceuticals traceability • The Philippines has endorsed and signified willingness to participate in the pilot (e-mail June 1, 2014 – Director. General Kenneth Hartigan-Go) © 2011 GS 1 68
Philippines Philippine Status • Philippines has been listed under APEC economies that decision making and/or not yet adopted requirements on pharmaceuticals traceability • The Philippines has endorsed and signified willingness to participate in the pilot (e-mail June 1, 2014 – Director. General Kenneth Hartigan-Go) © 2011 GS 1 68
 Philippines Requirements • Identify: refers to the data attributes assigned to a product • Capture: refers to the type of data carrier (bar code or RFID tag) that the identifier is held in • Share: refers to data that is capture and can be shared between parties within and outside of organisations across the supply chain. There are three types: • Master, Transactional and Event data NOTE: The Philippines has satisfied the Identify requirement with FDA Circular No. 2014 -011. Besides the Product ID, lot/batch number is required. © 2011 GS 1 69
Philippines Requirements • Identify: refers to the data attributes assigned to a product • Capture: refers to the type of data carrier (bar code or RFID tag) that the identifier is held in • Share: refers to data that is capture and can be shared between parties within and outside of organisations across the supply chain. There are three types: • Master, Transactional and Event data NOTE: The Philippines has satisfied the Identify requirement with FDA Circular No. 2014 -011. Besides the Product ID, lot/batch number is required. © 2011 GS 1 69
 Philippines Methods Agreed 1. identify countries of relevance of the primary analysis covering APEC economies and non-APEC economies with singular local situations 2. carry out a primary analysis of the situation in those countries covering regulatory requirements and industry practices 3. identify best practices based on the primary analysis 4. weight those best practices 5. develop recommendations and training material © 2011 GS 1 70
Philippines Methods Agreed 1. identify countries of relevance of the primary analysis covering APEC economies and non-APEC economies with singular local situations 2. carry out a primary analysis of the situation in those countries covering regulatory requirements and industry practices 3. identify best practices based on the primary analysis 4. weight those best practices 5. develop recommendations and training material © 2011 GS 1 70
 Philippines Purpose of Pilot • International adoption of electronic standards for serializing and tracking-and-tracing goods moving in international commerce not only will mitigate compliance costs for companies, but will also facilitate trade, efficiencies in the movement of goods, and better communication between responsible governmental authorities having jurisdiction over a set of goods. • In the case of the pharmaceutical sector, additional benefits can be reaped in the area of national drug safety, health care costs, and global public health. In this Proposal, the pharmaceutical sector is ready to participate in demonstrating the twin pillars of cost reduction and greater certainty of acceptance of products offered for import due to the enhanced security of the supply chain. © 2011 GS 1 71
Philippines Purpose of Pilot • International adoption of electronic standards for serializing and tracking-and-tracing goods moving in international commerce not only will mitigate compliance costs for companies, but will also facilitate trade, efficiencies in the movement of goods, and better communication between responsible governmental authorities having jurisdiction over a set of goods. • In the case of the pharmaceutical sector, additional benefits can be reaped in the area of national drug safety, health care costs, and global public health. In this Proposal, the pharmaceutical sector is ready to participate in demonstrating the twin pillars of cost reduction and greater certainty of acceptance of products offered for import due to the enhanced security of the supply chain. © 2011 GS 1 71
 Philippines Anti-Counterfeit © 2011 GS 1 72
Philippines Anti-Counterfeit © 2011 GS 1 72
 Philippines ISO 16678: 2014 (1) SO 16678: 2014 describes framework for identification and authentication systems. It provides recommendations and best practice guidance that include: • consequences and guidance of • management and verification of identifiers, • physical expression of identifiers, and • participants' due diligence; • vetting of all participants within the system; • relationship between the unique identifier and possible authentication elements related to it; • questions that deal with the identification of the inspector and any authorized access to privileged information about the object; and • inspector access history (logs). © 2011 GS 1
Philippines ISO 16678: 2014 (1) SO 16678: 2014 describes framework for identification and authentication systems. It provides recommendations and best practice guidance that include: • consequences and guidance of • management and verification of identifiers, • physical expression of identifiers, and • participants' due diligence; • vetting of all participants within the system; • relationship between the unique identifier and possible authentication elements related to it; • questions that deal with the identification of the inspector and any authorized access to privileged information about the object; and • inspector access history (logs). © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines ISO 16678: 2014 (2) Accordingly, ISO 16678: 2014 establishes a framework and outlines functional units used to achieve trustworthiness and interoperability of such systems. It does not specify any specific technical solutions, but instead describes processes, functions, and functional units using a generic model to illustrate what solutions have in common. Object identification systems can incorporate other functions and features such as supply chain traceability, quality traceability, marketing activities, and others, but these aspects are out of scope of ISO 16678: 2014. © 2011 GS 1
Philippines ISO 16678: 2014 (2) Accordingly, ISO 16678: 2014 establishes a framework and outlines functional units used to achieve trustworthiness and interoperability of such systems. It does not specify any specific technical solutions, but instead describes processes, functions, and functional units using a generic model to illustrate what solutions have in common. Object identification systems can incorporate other functions and features such as supply chain traceability, quality traceability, marketing activities, and others, but these aspects are out of scope of ISO 16678: 2014. © 2011 GS 1
 Philippines Solution to Counterfeit Drugs • Supply Chain Visibility • Documenting each transaction of the product • Pedigree (Universal and Uniform or Electronic) – Chain of Ownership • Track and Trace • Harmonized Coding and Identification System for Drugs © 2011 GS 1 75
Philippines Solution to Counterfeit Drugs • Supply Chain Visibility • Documenting each transaction of the product • Pedigree (Universal and Uniform or Electronic) – Chain of Ownership • Track and Trace • Harmonized Coding and Identification System for Drugs © 2011 GS 1 75
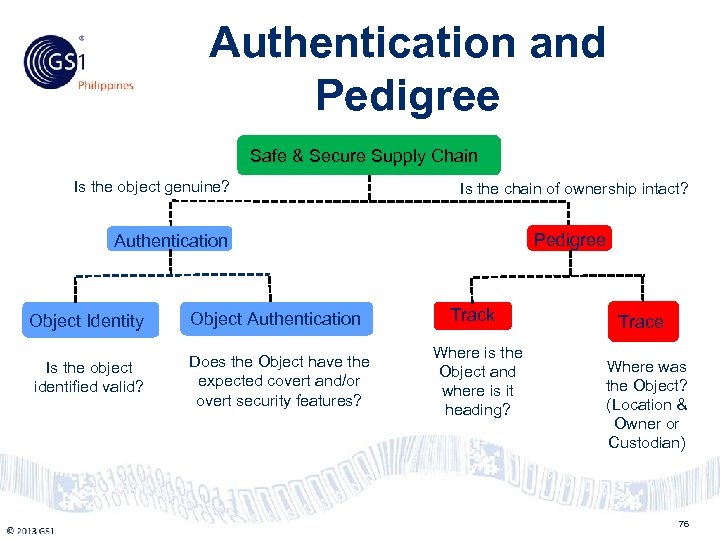 Philippines Authentication and Pedigree Safe & Secure Supply Chain Is the object genuine? Is the chain of ownership intact? Pedigree Authentication Object Identity Is the object identified valid? © 2011 GS 1 Object Authentication Does the Object have the expected covert and/or overt security features? Track Where is the Object and where is it heading? Trace Where was the Object? (Location & Owner or Custodian) 76
Philippines Authentication and Pedigree Safe & Secure Supply Chain Is the object genuine? Is the chain of ownership intact? Pedigree Authentication Object Identity Is the object identified valid? © 2011 GS 1 Object Authentication Does the Object have the expected covert and/or overt security features? Track Where is the Object and where is it heading? Trace Where was the Object? (Location & Owner or Custodian) 76
 Philippines Authentication Object Identity Object Authentication • Physical and visual inspection (e. g. specific material, unique construction features. stitching) • Integrity of the outer packaging • Presence of the brand insignia, label including a GS 1 barcode • Sensory Tools © 2011 GS 1 • Overt (open) • Covert (hidden) • Forensic (analytic) • Digital Tools • Object Serialization • Object Identification 77
Philippines Authentication Object Identity Object Authentication • Physical and visual inspection (e. g. specific material, unique construction features. stitching) • Integrity of the outer packaging • Presence of the brand insignia, label including a GS 1 barcode • Sensory Tools © 2011 GS 1 • Overt (open) • Covert (hidden) • Forensic (analytic) • Digital Tools • Object Serialization • Object Identification 77
 Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Chain of Ownership e-Pedigree A record, in electronic form, containing information regarding each transaction resulting in a change of ownership of a given drug, from sale by a manufacturer, through acquisition and sale by one or more wholesalers, manufacturers, or pharmacies, until final sale to a pharmacy or other person furnishing, administering A single pedigree shall include every change of ownership of a given drug from its initial manufacture through to its final transaction to a pharmacy or other person for furnishing, administering, or dispensing the drug A pedigree shall track each drug at the smallest package or immediate container distributed by the manufacturer, received and distributed by the wholesaler, and received by the pharmacy or another person furnishing, administering, or dispensing the drug Any return of a drug to a wholesaler or manufacturer shall be documented on the same pedigree as the transaction that resulted in the receipt of the drug by the party returning it. 78
Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Chain of Ownership e-Pedigree A record, in electronic form, containing information regarding each transaction resulting in a change of ownership of a given drug, from sale by a manufacturer, through acquisition and sale by one or more wholesalers, manufacturers, or pharmacies, until final sale to a pharmacy or other person furnishing, administering A single pedigree shall include every change of ownership of a given drug from its initial manufacture through to its final transaction to a pharmacy or other person for furnishing, administering, or dispensing the drug A pedigree shall track each drug at the smallest package or immediate container distributed by the manufacturer, received and distributed by the wholesaler, and received by the pharmacy or another person furnishing, administering, or dispensing the drug Any return of a drug to a wholesaler or manufacturer shall be documented on the same pedigree as the transaction that resulted in the receipt of the drug by the party returning it. 78
 Information in a Pedigree Record Philippines • The source of the dangerous drug, including the name, the federal manufacturer's registration number or a state license number as determined by the board, and principal address of the source • The trade or generic name of the drug, the quantity of the dangerous drug, its dosage form and strength, the date of the transaction, the sales invoice number, the container size, the number of containers, the expiration dates, the lot numbers, and serial number (if provided) • The business name, address, and the federal manufacturer's registration number of each owner of the drug, and the drug shipping information, including the name and address of each person certifying delivery or receipt of the dangerous drug • A certification under penalty of perjury from a responsible party of the source of the dangerous drug that the information contained in the pedigree is true and accurate © 2011 GS 1 79
Information in a Pedigree Record Philippines • The source of the dangerous drug, including the name, the federal manufacturer's registration number or a state license number as determined by the board, and principal address of the source • The trade or generic name of the drug, the quantity of the dangerous drug, its dosage form and strength, the date of the transaction, the sales invoice number, the container size, the number of containers, the expiration dates, the lot numbers, and serial number (if provided) • The business name, address, and the federal manufacturer's registration number of each owner of the drug, and the drug shipping information, including the name and address of each person certifying delivery or receipt of the dangerous drug • A certification under penalty of perjury from a responsible party of the source of the dangerous drug that the information contained in the pedigree is true and accurate © 2011 GS 1 79
 Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Anti-Counterfeit Measures Adopted Turkey Argentina Saudi State of California (superceded by Federal Law – Drug Supply Chain Security Act) 80
Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Anti-Counterfeit Measures Adopted Turkey Argentina Saudi State of California (superceded by Federal Law – Drug Supply Chain Security Act) 80
 Philippines Laws/Projects to be Implemented • • • EU – e. TACT Project EU – Falsified Drug USA – Drug Supply Chain Security Act South Korea – Drug Distribution Management Policy APEC – Global Medical Product Integrity and Supply Chain Security • ESM (A Medicine Verification for Europe) © 2011 GS 1 81
Philippines Laws/Projects to be Implemented • • • EU – e. TACT Project EU – Falsified Drug USA – Drug Supply Chain Security Act South Korea – Drug Distribution Management Policy APEC – Global Medical Product Integrity and Supply Chain Security • ESM (A Medicine Verification for Europe) © 2011 GS 1 81
 Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Common Features Tamper-free Packaging Track and Trace Unique Medicine Identification Verification Hub 82
Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Common Features Tamper-free Packaging Track and Trace Unique Medicine Identification Verification Hub 82
 Philippines Models of Verification Hubs © 2011 GS 1 83
Philippines Models of Verification Hubs © 2011 GS 1 83
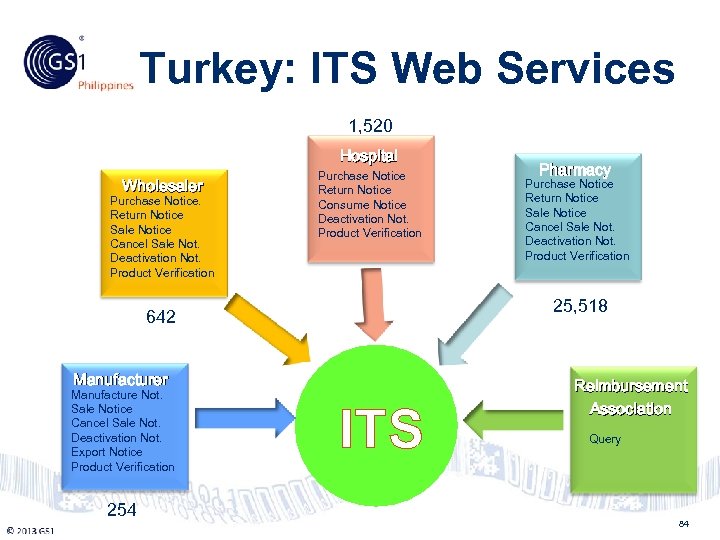 Turkey: ITS Web Services Philippines 1, 520 Hospital Wholesaler Purchase Notice. Return Notice Sale Notice Cancel Sale Not. Deactivation Not. Product Verification Purchase Notice Return Notice Consume Notice Deactivation Not. Product Verification 25, 518 642 Manufacturer Manufacture Not. Sale Notice Cancel Sale Not. Deactivation Not. Export Notice Product Verification 254 © 2011 GS 1 Pharmacy Purchase Notice Return Notice Sale Notice Cancel Sale Not. Deactivation Not. Product Verification ITS Reimbursement Association Query 84
Turkey: ITS Web Services Philippines 1, 520 Hospital Wholesaler Purchase Notice. Return Notice Sale Notice Cancel Sale Not. Deactivation Not. Product Verification Purchase Notice Return Notice Consume Notice Deactivation Not. Product Verification 25, 518 642 Manufacturer Manufacture Not. Sale Notice Cancel Sale Not. Deactivation Not. Export Notice Product Verification 254 © 2011 GS 1 Pharmacy Purchase Notice Return Notice Sale Notice Cancel Sale Not. Deactivation Not. Product Verification ITS Reimbursement Association Query 84
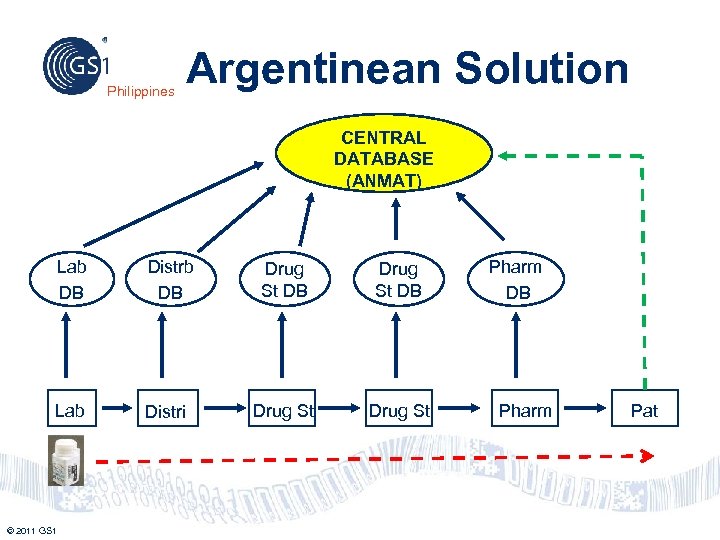 Philippines Argentinean Solution CENTRAL DATABASE (ANMAT) Lab DB Distrb DB Drug St DB Lab Distri Drug St © 2011 GS 1 Pharm DB Pharm Pat
Philippines Argentinean Solution CENTRAL DATABASE (ANMAT) Lab DB Distrb DB Drug St DB Lab Distri Drug St © 2011 GS 1 Pharm DB Pharm Pat
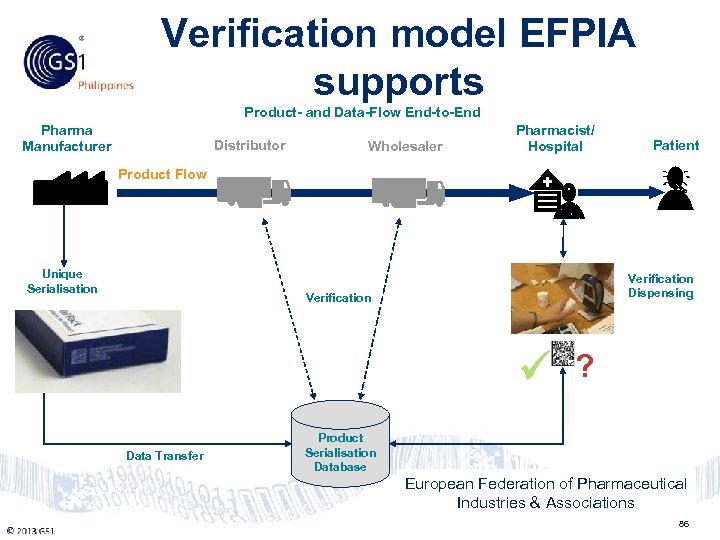 Verification model EFPIA supports Philippines Product- and Data-Flow End-to-End Pharma Manufacturer Distributor Wholesaler Pharmacist/ Hospital Patient Product Flow Unique Serialisation Verification Dispensing Verification ? Data Transfer Product Serialisation Database European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries & Associations © 2011 GS 1 86
Verification model EFPIA supports Philippines Product- and Data-Flow End-to-End Pharma Manufacturer Distributor Wholesaler Pharmacist/ Hospital Patient Product Flow Unique Serialisation Verification Dispensing Verification ? Data Transfer Product Serialisation Database European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries & Associations © 2011 GS 1 86
 Authentication Process for Viagra™ Philippines EPC data in matrix barcode. RFID Tags have been introduced in the most counterfeited product at Pfizer: Viagra™. © 2011 GS 1 87
Authentication Process for Viagra™ Philippines EPC data in matrix barcode. RFID Tags have been introduced in the most counterfeited product at Pfizer: Viagra™. © 2011 GS 1 87
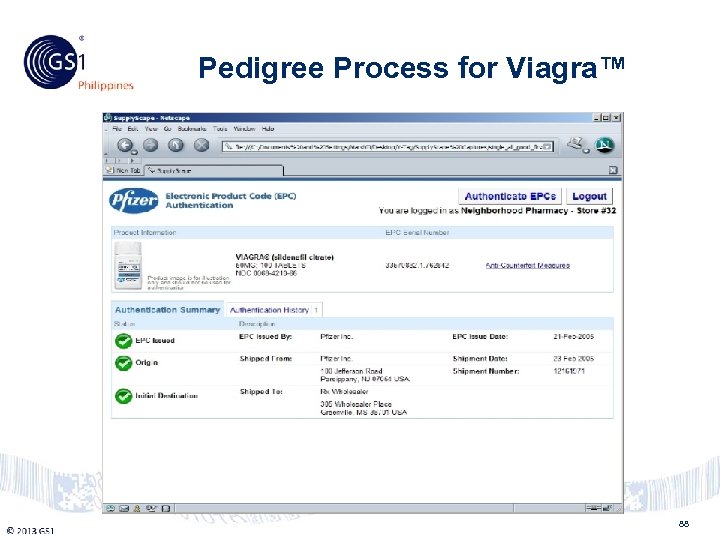 Philippines © 2011 GS 1 Pedigree Process for Viagra™ 88
Philippines © 2011 GS 1 Pedigree Process for Viagra™ 88
 Philippines U. S. Traceability: the Drug Supply Chain Security Act © 2011 GS 1 89
Philippines U. S. Traceability: the Drug Supply Chain Security Act © 2011 GS 1 89
 Philippines The Drug Supply Chain Security Act • Outlines critical steps to build an electronic, interoperable system to identify and trace certain prescription drugs as they are distributed in the United States. • Ten years after enactment, the system will facilitate the exchange of information at the individual package level about where a drug has been in the supply chain. The new system will: • enable verification of the legitimacy of the drug product identifier down to the package level; • enhance detection and notification of illegitimate products in the drug supply chain; and • facilitate more efficient recalls of drug products. © 2011 GS 1 90
Philippines The Drug Supply Chain Security Act • Outlines critical steps to build an electronic, interoperable system to identify and trace certain prescription drugs as they are distributed in the United States. • Ten years after enactment, the system will facilitate the exchange of information at the individual package level about where a drug has been in the supply chain. The new system will: • enable verification of the legitimacy of the drug product identifier down to the package level; • enhance detection and notification of illegitimate products in the drug supply chain; and • facilitate more efficient recalls of drug products. © 2011 GS 1 90
 Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Key Provisions Product identification: Manufacturers and repackagers to put a unique product identifier on certain prescription drug packages, for example, using a bar code that can be easily read electronically. Product tracing: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) in the drug supply chain to provide information about a drug and who handled it each time it is sold in the U. S. market. Product verification: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) to establish systems and processes to be able to verify the product identifier on certain prescription drug packages. Detection and response: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) to quarantine and promptly investigate a drug that has been identified as suspect, meaning that it may be counterfeit, unapproved, or potentially dangerous. 91
Philippines • • © 2011 GS 1 Key Provisions Product identification: Manufacturers and repackagers to put a unique product identifier on certain prescription drug packages, for example, using a bar code that can be easily read electronically. Product tracing: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) in the drug supply chain to provide information about a drug and who handled it each time it is sold in the U. S. market. Product verification: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) to establish systems and processes to be able to verify the product identifier on certain prescription drug packages. Detection and response: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) to quarantine and promptly investigate a drug that has been identified as suspect, meaning that it may be counterfeit, unapproved, or potentially dangerous. 91
 Philippines • • • © 2011 GS 1 Key Provisions (2) Notification: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) to establish systems and processes to notify FDA and other stakeholders if an illegitimate drug is found. Wholesaler licensing: Wholesale drug distributors to report their licensing status and contact information to FDA. This information will then be made available in a public database. Third-party logistics provider licensing: Third-party logistic providers, those who provide storage and logistical operations related to drug distribution, to obtain a state or federal license. 92
Philippines • • • © 2011 GS 1 Key Provisions (2) Notification: Manufacturers, wholesaler drug distributors, repackagers, and many dispensers (primarily pharmacies) to establish systems and processes to notify FDA and other stakeholders if an illegitimate drug is found. Wholesaler licensing: Wholesale drug distributors to report their licensing status and contact information to FDA. This information will then be made available in a public database. Third-party logistics provider licensing: Third-party logistic providers, those who provide storage and logistical operations related to drug distribution, to obtain a state or federal license. 92
 Contact Details Philippines GS 1 Philippines, Inc. #20 San Rafael St. , Bo. Kapitolyo, Pasig City PHILIPPINES T +63 2 637 08 97 to 98 W www. gs 1 ph. org
Contact Details Philippines GS 1 Philippines, Inc. #20 San Rafael St. , Bo. Kapitolyo, Pasig City PHILIPPINES T +63 2 637 08 97 to 98 W www. gs 1 ph. org


