a5b08b67655ab5dee9012517e826c93f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
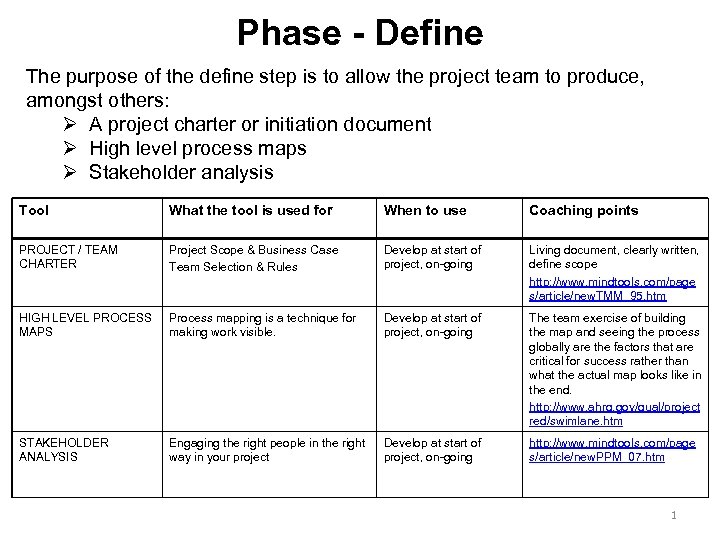 Phase - Define The purpose of the define step is to allow the project team to produce, amongst others: Ø A project charter or initiation document Ø High level process maps Ø Stakeholder analysis Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points PROJECT / TEAM CHARTER Project Scope & Business Case Team Selection & Rules Develop at start of project, on-going Living document, clearly written, define scope http: //www. mindtools. com/page s/article/new. TMM_95. htm HIGH LEVEL PROCESS MAPS Process mapping is a technique for making work visible. Develop at start of project, on-going The team exercise of building the map and seeing the process globally are the factors that are critical for success rather than what the actual map looks like in the end. http: //www. ahrq. gov/qual/project red/swimlane. htm STAKEHOLDER ANALYSIS Engaging the right people in the right way in your project Develop at start of project, on-going http: //www. mindtools. com/page s/article/new. PPM_07. htm 1
Phase - Define The purpose of the define step is to allow the project team to produce, amongst others: Ø A project charter or initiation document Ø High level process maps Ø Stakeholder analysis Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points PROJECT / TEAM CHARTER Project Scope & Business Case Team Selection & Rules Develop at start of project, on-going Living document, clearly written, define scope http: //www. mindtools. com/page s/article/new. TMM_95. htm HIGH LEVEL PROCESS MAPS Process mapping is a technique for making work visible. Develop at start of project, on-going The team exercise of building the map and seeing the process globally are the factors that are critical for success rather than what the actual map looks like in the end. http: //www. ahrq. gov/qual/project red/swimlane. htm STAKEHOLDER ANALYSIS Engaging the right people in the right way in your project Develop at start of project, on-going http: //www. mindtools. com/page s/article/new. PPM_07. htm 1
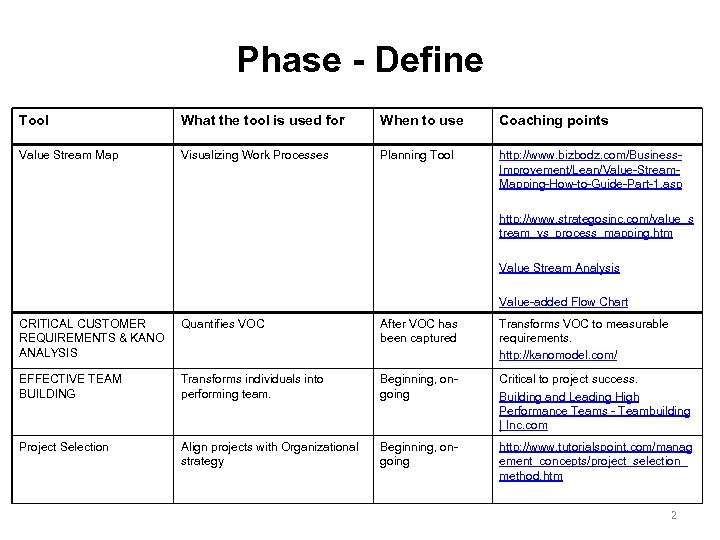 Phase - Define Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Value Stream Map Visualizing Work Processes Planning Tool http: //www. bizbodz. com/Business. Improvement/Lean/Value-Stream. Mapping-How-to-Guide-Part-1. asp http: //www. strategosinc. com/value_s tream_vs_process_mapping. htm Value Stream Analysis Value-added Flow Chart CRITICAL CUSTOMER REQUIREMENTS & KANO ANALYSIS Quantifies VOC After VOC has been captured Transforms VOC to measurable requirements. http: //kanomodel. com/ EFFECTIVE TEAM BUILDING Transforms individuals into performing team. Beginning, ongoing Critical to project success. Building and Leading High Performance Teams - Teambuilding | Inc. com Project Selection Align projects with Organizational strategy Beginning, ongoing http: //www. tutorialspoint. com/manag ement_concepts/project_selection_ method. htm 2
Phase - Define Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Value Stream Map Visualizing Work Processes Planning Tool http: //www. bizbodz. com/Business. Improvement/Lean/Value-Stream. Mapping-How-to-Guide-Part-1. asp http: //www. strategosinc. com/value_s tream_vs_process_mapping. htm Value Stream Analysis Value-added Flow Chart CRITICAL CUSTOMER REQUIREMENTS & KANO ANALYSIS Quantifies VOC After VOC has been captured Transforms VOC to measurable requirements. http: //kanomodel. com/ EFFECTIVE TEAM BUILDING Transforms individuals into performing team. Beginning, ongoing Critical to project success. Building and Leading High Performance Teams - Teambuilding | Inc. com Project Selection Align projects with Organizational strategy Beginning, ongoing http: //www. tutorialspoint. com/manag ement_concepts/project_selection_ method. htm 2
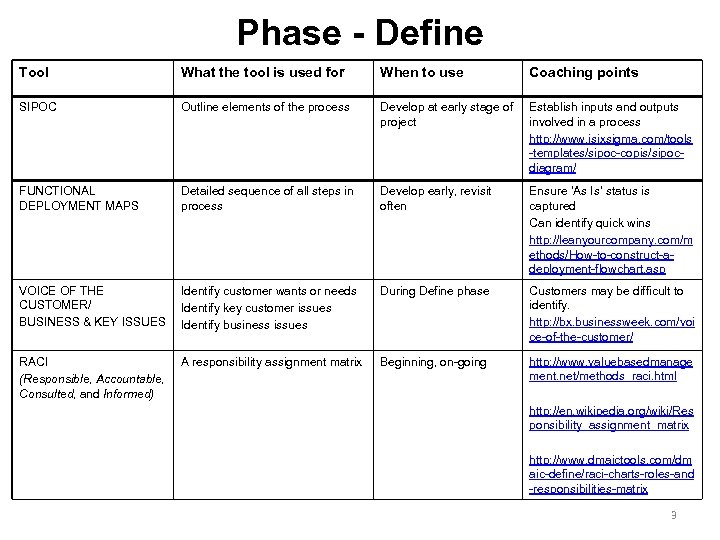 Phase - Define Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points SIPOC Outline elements of the process Develop at early stage of project Establish inputs and outputs involved in a process http: //www. isixsigma. com/tools -templates/sipoc-copis/sipocdiagram/ FUNCTIONAL DEPLOYMENT MAPS Detailed sequence of all steps in process Develop early, revisit often Ensure ‘As Is’ status is captured Can identify quick wins http: //leanyourcompany. com/m ethods/How-to-construct-adeployment-flowchart. asp VOICE OF THE CUSTOMER/ BUSINESS & KEY ISSUES Identify customer wants or needs Identify key customer issues Identify business issues During Define phase Customers may be difficult to identify. http: //bx. businessweek. com/voi ce-of-the-customer/ RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed) A responsibility assignment matrix Beginning, on-going http: //www. valuebasedmanage ment. net/methods_raci. html http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Res ponsibility_assignment_matrix http: //www. dmaictools. com/dm aic-define/raci-charts-roles-and -responsibilities-matrix 3
Phase - Define Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points SIPOC Outline elements of the process Develop at early stage of project Establish inputs and outputs involved in a process http: //www. isixsigma. com/tools -templates/sipoc-copis/sipocdiagram/ FUNCTIONAL DEPLOYMENT MAPS Detailed sequence of all steps in process Develop early, revisit often Ensure ‘As Is’ status is captured Can identify quick wins http: //leanyourcompany. com/m ethods/How-to-construct-adeployment-flowchart. asp VOICE OF THE CUSTOMER/ BUSINESS & KEY ISSUES Identify customer wants or needs Identify key customer issues Identify business issues During Define phase Customers may be difficult to identify. http: //bx. businessweek. com/voi ce-of-the-customer/ RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed) A responsibility assignment matrix Beginning, on-going http: //www. valuebasedmanage ment. net/methods_raci. html http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Res ponsibility_assignment_matrix http: //www. dmaictools. com/dm aic-define/raci-charts-roles-and -responsibilities-matrix 3
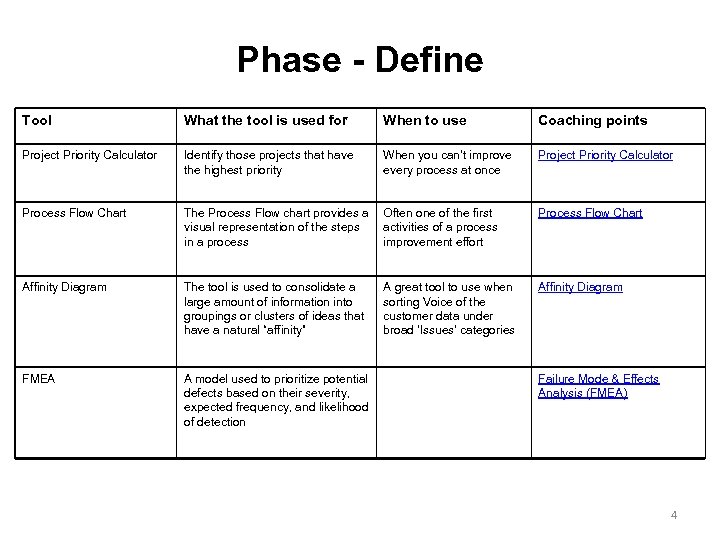 Phase - Define Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Project Priority Calculator Identify those projects that have the highest priority When you can’t improve every process at once Project Priority Calculator Process Flow Chart The Process Flow chart provides a visual representation of the steps in a process Often one of the first activities of a process improvement effort Process Flow Chart Affinity Diagram The tool is used to consolidate a large amount of information into groupings or clusters of ideas that have a natural “affinity” A great tool to use when sorting Voice of the customer data under broad 'Issues' categories Affinity Diagram FMEA A model used to prioritize potential defects based on their severity, expected frequency, and likelihood of detection Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA) 4
Phase - Define Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Project Priority Calculator Identify those projects that have the highest priority When you can’t improve every process at once Project Priority Calculator Process Flow Chart The Process Flow chart provides a visual representation of the steps in a process Often one of the first activities of a process improvement effort Process Flow Chart Affinity Diagram The tool is used to consolidate a large amount of information into groupings or clusters of ideas that have a natural “affinity” A great tool to use when sorting Voice of the customer data under broad 'Issues' categories Affinity Diagram FMEA A model used to prioritize potential defects based on their severity, expected frequency, and likelihood of detection Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA) 4
 Phase - Measure is the heart of what makes Lean Six Sigma work: Ø Evaluate the existing measurement system ü Improving it is necessary ü Developing a measurement system if you don’t already have one Ø Observe the process Ø Gather Data Ø Map the process in more depth Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Input/Process/Output Indicators Identify what to measure and the relationship between measurements. At beginning of Measure phase http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ IPO_Model Data Collection Plan To gather reliable and statistically valid data At beginning of Measure phase http: //www. isixsigma. com/t ools-templates/samplingdata/building-sound-datacollection-plan/ Measurement Plan Defines sample size, frequency, additional data to collect and how we use the data. Before measurement http: //www. qihub. scot. nhs. uk/knowledgecentre/qualityimprovement-tools/datacollection-plan-form. aspx 5
Phase - Measure is the heart of what makes Lean Six Sigma work: Ø Evaluate the existing measurement system ü Improving it is necessary ü Developing a measurement system if you don’t already have one Ø Observe the process Ø Gather Data Ø Map the process in more depth Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Input/Process/Output Indicators Identify what to measure and the relationship between measurements. At beginning of Measure phase http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ IPO_Model Data Collection Plan To gather reliable and statistically valid data At beginning of Measure phase http: //www. isixsigma. com/t ools-templates/samplingdata/building-sound-datacollection-plan/ Measurement Plan Defines sample size, frequency, additional data to collect and how we use the data. Before measurement http: //www. qihub. scot. nhs. uk/knowledgecentre/qualityimprovement-tools/datacollection-plan-form. aspx 5
 Phase - Measure Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Measurement System Analysis (MSA) Measurement System Analysis is to qualify a measurement system for use by quantifying its accuracy, precision, and stability To guide decisions Measurement System Analysis (MSA) Sampling Techniques Use to determine optimum sample size. When there is a large population of data. http: //www. experimentresources. com/statisticalsampling-techniques. html Measurement System Analysis (Gage R & R, MSE) To understand the sources of variation that can influence results. When you don’t understand the capability of the measurement system. http: //www. moresteam. co m/toolbox/measurementsystem-analysis. cfm Histogram Visual display of one variable showing data centre, spread, shape & outliers 1. Summarise 2. Understanding 3. Compare to spec http: //quarknet. fnal. gov/too lkits/ati/histograms. html http: //www. youtube. com/w atch? v=Ryx. Pp 22 x 9 PU 6
Phase - Measure Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Measurement System Analysis (MSA) Measurement System Analysis is to qualify a measurement system for use by quantifying its accuracy, precision, and stability To guide decisions Measurement System Analysis (MSA) Sampling Techniques Use to determine optimum sample size. When there is a large population of data. http: //www. experimentresources. com/statisticalsampling-techniques. html Measurement System Analysis (Gage R & R, MSE) To understand the sources of variation that can influence results. When you don’t understand the capability of the measurement system. http: //www. moresteam. co m/toolbox/measurementsystem-analysis. cfm Histogram Visual display of one variable showing data centre, spread, shape & outliers 1. Summarise 2. Understanding 3. Compare to spec http: //quarknet. fnal. gov/too lkits/ati/histograms. html http: //www. youtube. com/w atch? v=Ryx. Pp 22 x 9 PU 6
 Phase - Measure Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Control Charts Plots observations in time sequence against a mean and control limits. Monitor process to control & improve. Identify Special Causes. http: //asq. org/learn-aboutquality/data-collectionanalysistools/overview/controlchart. html http: //www. youtube. com/wa tch? v=zvp 8 qm. H 3 Eos Run Chart Plots observations in time sequence To identify trends, shifts or cycles over time. http: //www. shmula. com/runchart/3506/ http: //www. youtube. com/wa tch? v=K 8 q 6 HKr. UO 7 I Trend Chart 7
Phase - Measure Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Control Charts Plots observations in time sequence against a mean and control limits. Monitor process to control & improve. Identify Special Causes. http: //asq. org/learn-aboutquality/data-collectionanalysistools/overview/controlchart. html http: //www. youtube. com/wa tch? v=zvp 8 qm. H 3 Eos Run Chart Plots observations in time sequence To identify trends, shifts or cycles over time. http: //www. shmula. com/runchart/3506/ http: //www. youtube. com/wa tch? v=K 8 q 6 HKr. UO 7 I Trend Chart 7
 Phase - Analyze The purpose of the Analyze phase is to make sense of all the information and data collected: Ø Use data to confirm source of delays, waste, and poor quality Ø Biggest challenge is to “stick to the data” Ø Avoid using experience and opinions about the root cause of problems Ø Look for patterns in the data Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points 5 -Why Analysis used to move past symptoms and understand the true root cause of a problem. Related to the Cause & Effect (Fishbone) diagram, and can be used to complement the analysis necessary to complete a Cause & Effect diagram 5 -Why Analysis 8
Phase - Analyze The purpose of the Analyze phase is to make sense of all the information and data collected: Ø Use data to confirm source of delays, waste, and poor quality Ø Biggest challenge is to “stick to the data” Ø Avoid using experience and opinions about the root cause of problems Ø Look for patterns in the data Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points 5 -Why Analysis used to move past symptoms and understand the true root cause of a problem. Related to the Cause & Effect (Fishbone) diagram, and can be used to complement the analysis necessary to complete a Cause & Effect diagram 5 -Why Analysis 8
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for Design of Experiments The term experiment is defined as the systematic procedure carried out under controlled conditions in order to discover an unknown effect, to test or establish a hypothesis, or to illustrate a known effect. Cause and Effect Diagram (ishikawa) A tool for analyzing process dispersion. It is also referred to as the Ishikawa diagram, because Kaoru Ishikawa developed it, and the fishbone diagram, because the complete diagram resembles a fish skeleton. The diagram illustrates the main causes and subcauses leading to an effect (symptom). The cause-and-effect diagram is one of the seven tools of quality. Also called Fishbone diagram When to use Coaching points Design of Experiments Brainstorming of potential root causes of problems (idea generation) http: //www. mindtools. com /pages/article/new. TMC_0 3. htm Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram 9
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for Design of Experiments The term experiment is defined as the systematic procedure carried out under controlled conditions in order to discover an unknown effect, to test or establish a hypothesis, or to illustrate a known effect. Cause and Effect Diagram (ishikawa) A tool for analyzing process dispersion. It is also referred to as the Ishikawa diagram, because Kaoru Ishikawa developed it, and the fishbone diagram, because the complete diagram resembles a fish skeleton. The diagram illustrates the main causes and subcauses leading to an effect (symptom). The cause-and-effect diagram is one of the seven tools of quality. Also called Fishbone diagram When to use Coaching points Design of Experiments Brainstorming of potential root causes of problems (idea generation) http: //www. mindtools. com /pages/article/new. TMC_0 3. htm Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram 9
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Pareto Define specific problem to concentrate on its root cause analysis (identify vital few). A graphical tool for ranking causes from most significant to least significant. It is based on the Pareto principle, which was first defined by J. M. Juran in 1950. The principle, named after 19 thcentury economist Vilfredo Pareto, suggests that most effects come from relatively few causes; that is, 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes. The Pareto chart is one of the seven tools of quality. Identification of vital few causes of particular problem. http: //www. tutorialspoint. com/ management_concepts/paret o_chart_tool. htm After data collection from measurement phase http: //asq. org/learn-aboutquality/cause-analysistools/overview/pareto. html A tool which is used to prioritize potential causes by examining their relationship with the CTQs. The highest overall score should be addressed first because they will have the largest impact on the CTQs. C&E Matrix Pareto Chart (Manufacturing ex. ) Pareto Chart (Service ex. ) http: //www. processma. com/re source/cause_and_effect_ma trix. htm 10
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Pareto Define specific problem to concentrate on its root cause analysis (identify vital few). A graphical tool for ranking causes from most significant to least significant. It is based on the Pareto principle, which was first defined by J. M. Juran in 1950. The principle, named after 19 thcentury economist Vilfredo Pareto, suggests that most effects come from relatively few causes; that is, 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes. The Pareto chart is one of the seven tools of quality. Identification of vital few causes of particular problem. http: //www. tutorialspoint. com/ management_concepts/paret o_chart_tool. htm After data collection from measurement phase http: //asq. org/learn-aboutquality/cause-analysistools/overview/pareto. html A tool which is used to prioritize potential causes by examining their relationship with the CTQs. The highest overall score should be addressed first because they will have the largest impact on the CTQs. C&E Matrix Pareto Chart (Manufacturing ex. ) Pareto Chart (Service ex. ) http: //www. processma. com/re source/cause_and_effect_ma trix. htm 10
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Checksheet A simple data-recording device. The check sheet is customdesigned by the user, which allows him or her to readily interpret the results. The check sheet is one of the seven tools of quality. Check sheets are often confused with data sheets and checklists (see individual entries). To gather or collect data. http: //www. shmula. com/c heck-sheets/3932/ Cost/Benefit Analysis A multitude of methods used to determine the financial impacts of the project to the company. In the evaluation and selection of solutions. http: //management. about. com/cs/money/a/Cost. Ben efit. htm 11
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Checksheet A simple data-recording device. The check sheet is customdesigned by the user, which allows him or her to readily interpret the results. The check sheet is one of the seven tools of quality. Check sheets are often confused with data sheets and checklists (see individual entries). To gather or collect data. http: //www. shmula. com/c heck-sheets/3932/ Cost/Benefit Analysis A multitude of methods used to determine the financial impacts of the project to the company. In the evaluation and selection of solutions. http: //management. about. com/cs/money/a/Cost. Ben efit. htm 11
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Design of Experiments A branch of applied statistics dealing with planning, conducting, analyzing, and interpreting controlled tests to evaluate the factors that control the value of a parameter or group of parameters: To identify factors and their appropriate settings. http: //www. tutorialspoint. co m/management_concepts/ design_of_experiment. htm Histogram A graphic summary of variation in a set of data. The pictorial nature of the histogram lets people see patterns that are difficult to see in a simple table of numbers. The histogram is one of the seven tools of quality. When a picture is needed to graphically depict variation in data. http: //quarknet. fnal. gov/tool kits/ati/histograms. html Generate creative solutions to a problem To break out of stale, established patterns of thinking Brainstorming http: //www. youtube. com/w atch? v=Ryx. Pp 22 x 9 PU http: //www. mindtools. com/ brainstm. html 12
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Design of Experiments A branch of applied statistics dealing with planning, conducting, analyzing, and interpreting controlled tests to evaluate the factors that control the value of a parameter or group of parameters: To identify factors and their appropriate settings. http: //www. tutorialspoint. co m/management_concepts/ design_of_experiment. htm Histogram A graphic summary of variation in a set of data. The pictorial nature of the histogram lets people see patterns that are difficult to see in a simple table of numbers. The histogram is one of the seven tools of quality. When a picture is needed to graphically depict variation in data. http: //quarknet. fnal. gov/tool kits/ati/histograms. html Generate creative solutions to a problem To break out of stale, established patterns of thinking Brainstorming http: //www. youtube. com/w atch? v=Ryx. Pp 22 x 9 PU http: //www. mindtools. com/ brainstm. html 12
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Hypothesis Tests (t-test, ANOVA, Chi Square) A procedure whereby one of two mutually exclusive and exhaustive statements about a population parameter is concluded. Information form a sample is used to infer something about a population from which the sample was drawn. To determine whether true statistical differences exist in two or more sets of data. http: //stattrek. com/hypothe sis-test/hypothesistesting. aspx Non-value-Added Analysis Steps in the production and delivery of a product or service that are considered nonessential to meeting customer's needs and requirements (I. e. , steps the customer would not ne willing to pay for). When mapping process. http: //www. moresteam. co m/toolbox/value-addedflow-chart. cfm 13
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Hypothesis Tests (t-test, ANOVA, Chi Square) A procedure whereby one of two mutually exclusive and exhaustive statements about a population parameter is concluded. Information form a sample is used to infer something about a population from which the sample was drawn. To determine whether true statistical differences exist in two or more sets of data. http: //stattrek. com/hypothe sis-test/hypothesistesting. aspx Non-value-Added Analysis Steps in the production and delivery of a product or service that are considered nonessential to meeting customer's needs and requirements (I. e. , steps the customer would not ne willing to pay for). When mapping process. http: //www. moresteam. co m/toolbox/value-addedflow-chart. cfm 13
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Process Map A graphical representation of the steps in a process. Flowcharts are drawn to better understand processes. The flowchart is one of the seven tools of quality. At beginning of project to learn about the process. http: //www. processma. co m/resource/process_map ping. htm Spaghetti Diagram A graphical tool used to depict the physical flow of work or material in a process. http: //www. processma. co m/resource/spaghetti_dia gram. htm 14
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Process Map A graphical representation of the steps in a process. Flowcharts are drawn to better understand processes. The flowchart is one of the seven tools of quality. At beginning of project to learn about the process. http: //www. processma. co m/resource/process_map ping. htm Spaghetti Diagram A graphical tool used to depict the physical flow of work or material in a process. http: //www. processma. co m/resource/spaghetti_dia gram. htm 14
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Regression or Regression Analysis A statistical technique for determining the best mathematical expression describing the functional relationship between one response and one or more independent variables. Use after key factors identified to create model for process performance. http: //office. microsoft. com/e n-us/excel-help/perform-aregression-analysis. HA 001111963. aspx Basic Quality Tools When you want to know the rrelation between variables Regression Analysis http: //www. tutorialspoint. co m/management_concepts/d esign_of_experiment. htm 15
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Regression or Regression Analysis A statistical technique for determining the best mathematical expression describing the functional relationship between one response and one or more independent variables. Use after key factors identified to create model for process performance. http: //office. microsoft. com/e n-us/excel-help/perform-aregression-analysis. HA 001111963. aspx Basic Quality Tools When you want to know the rrelation between variables Regression Analysis http: //www. tutorialspoint. co m/management_concepts/d esign_of_experiment. htm 15
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Scatter Diagram A graphical technique to analyze To show relationships the relationship between two or more variables. Two sets of data are variables. plotted on a graph, with the y axis being used for the variable to be predicted and the x axis being used for the variable to make the prediction. The graph will show possible relationships (although two variables might appear to be related, they might not be-those who know most about the variables must make that evaluation). The scatter diagram is one of the seven tools of quality. Coaching points http: //web 2. concordia. ca/Qual ity/tools/25 scatter. pdf http: //academic. brooklyn. cuny. edu/economic/friedman/scatte rdiagramexcel. htm 16
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Scatter Diagram A graphical technique to analyze To show relationships the relationship between two or more variables. Two sets of data are variables. plotted on a graph, with the y axis being used for the variable to be predicted and the x axis being used for the variable to make the prediction. The graph will show possible relationships (although two variables might appear to be related, they might not be-those who know most about the variables must make that evaluation). The scatter diagram is one of the seven tools of quality. Coaching points http: //web 2. concordia. ca/Qual ity/tools/25 scatter. pdf http: //academic. brooklyn. cuny. edu/economic/friedman/scatte rdiagramexcel. htm 16
 Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Stratification A process characteristic used to divide data into subgroups to look for changes in process performance that might indicate the factor is a key driver of process performance. When existing data shows no patterns or key factors. http: //asq. org/learn-aboutquality/data-collectionanalysistools/overview/stratificatio n. html Scatter Plot or Correlation Diagram Scatter plots show much one variable is affected by another. The relationship between two variables is called their correlation. http: //mste. illinois. edu/cou rses/ci 330 ms/youtsey/sca tterinfo. html Statistical Process Control (SPC) The fundamental of business iimprovement revolves around studying and improving underlying processes. http: //www. processma. co m/resource/statistical_thin king. htm Statistical Thinking Statistical Process Control (SPC) Six Sigma Conversion Table Converts Defects Per Million Opportunities to a Sigma Level Six Sigma Conversion Table 17
Phase - Analyze Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Stratification A process characteristic used to divide data into subgroups to look for changes in process performance that might indicate the factor is a key driver of process performance. When existing data shows no patterns or key factors. http: //asq. org/learn-aboutquality/data-collectionanalysistools/overview/stratificatio n. html Scatter Plot or Correlation Diagram Scatter plots show much one variable is affected by another. The relationship between two variables is called their correlation. http: //mste. illinois. edu/cou rses/ci 330 ms/youtsey/sca tterinfo. html Statistical Process Control (SPC) The fundamental of business iimprovement revolves around studying and improving underlying processes. http: //www. processma. co m/resource/statistical_thin king. htm Statistical Thinking Statistical Process Control (SPC) Six Sigma Conversion Table Converts Defects Per Million Opportunities to a Sigma Level Six Sigma Conversion Table 17
 Phase - Improve The purpose of Improve: is to make recommendations for changes in a process that will eliminate the defects, waste, costs, etc… Ø Linked to the customer Ø Use creativity Ø Review existing “best practices” Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Osbom’s Brainstorming Idea Generation When existing data shows no patterns or key factors. http: //www. skymark. com/r esources/leaders/osborne. asp 18
Phase - Improve The purpose of Improve: is to make recommendations for changes in a process that will eliminate the defects, waste, costs, etc… Ø Linked to the customer Ø Use creativity Ø Review existing “best practices” Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Osbom’s Brainstorming Idea Generation When existing data shows no patterns or key factors. http: //www. skymark. com/r esources/leaders/osborne. asp 18
 Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Affinity Diagram Idea Generation. Use when you have lots of ideas, team paralysis Solution Mapping includes an initial white boarding session and top-level assessment to help clients formalize the purpose, requirements and uncover any hidden implementation barriers to the desired performance and development solution Idea Generation. Coaching points http: //www. processma. com/res ource/affinity_diagram. htm http: //www. google. com/searc h? q=solution+mapping&hl=e n&prmd=imvns&tbm=isch&t bo=u&source=univ&sa=X&ei =M 6 t 9 UNC 4 EMLHq. QGa 84 C YCQ&sqi=2&ved=0 CB 0 Qs. A Q&biw=1441&bih=656 Lateral Thinking 19
Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Affinity Diagram Idea Generation. Use when you have lots of ideas, team paralysis Solution Mapping includes an initial white boarding session and top-level assessment to help clients formalize the purpose, requirements and uncover any hidden implementation barriers to the desired performance and development solution Idea Generation. Coaching points http: //www. processma. com/res ource/affinity_diagram. htm http: //www. google. com/searc h? q=solution+mapping&hl=e n&prmd=imvns&tbm=isch&t bo=u&source=univ&sa=X&ei =M 6 t 9 UNC 4 EMLHq. QGa 84 C YCQ&sqi=2&ved=0 CB 0 Qs. A Q&biw=1441&bih=656 Lateral Thinking 19
 Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Mind Mapping Mind mapping is a creative and logical means of note-taking and note-making that literally "maps out" your ideas. Note-taking. http: //www. mindmapping. co m/ Six Thinking Hats Technique It is used to look at decisions from a number of important perspectives. When you need to move outside your habitual thinking style, http: //www. mindtools. com/pa ges/article/new. TED_07. htm Lateral Thinking Is solving problems through an indirect and creative approach, using reasoning that is not immediately obvious and involving ideas that may not be obtainable by using only traditional step-by-step logic Method for problem solving http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/L ateral_thinking 20
Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Mind Mapping Mind mapping is a creative and logical means of note-taking and note-making that literally "maps out" your ideas. Note-taking. http: //www. mindmapping. co m/ Six Thinking Hats Technique It is used to look at decisions from a number of important perspectives. When you need to move outside your habitual thinking style, http: //www. mindtools. com/pa ges/article/new. TED_07. htm Lateral Thinking Is solving problems through an indirect and creative approach, using reasoning that is not immediately obvious and involving ideas that may not be obtainable by using only traditional step-by-step logic Method for problem solving http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/L ateral_thinking 20
 Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points 5 S 5 S is the abbreviated reference to five Japanese words that govern workplace organization and housekeeping. The five words are: Seiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu, and Shitsuke Goes hand-in-hand with good safety practices, and is equally applicable to manufacturing and service settings 5 S Tool A 3 Reports are one-page reports used for documenting the necessary information needed for progress reporting and decisionmaking When you want to condense the information to a single page and visually communicate to the reader using graphs, charts, and succinct bullet points. A 3 Report Brainstorming is intended to encourage fresh thinking and "crazy" ideas. When you need fresh thinking and "crazy" ideas. Brainstorming Corrective Action Matrix The Corrective Action Matrix is used by problem-solving teams to keep track of who is doing what - by when To ensure action gets implemented and someone is responsible to make it happen. Corrective Action Matrix 21
Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points 5 S 5 S is the abbreviated reference to five Japanese words that govern workplace organization and housekeeping. The five words are: Seiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu, and Shitsuke Goes hand-in-hand with good safety practices, and is equally applicable to manufacturing and service settings 5 S Tool A 3 Reports are one-page reports used for documenting the necessary information needed for progress reporting and decisionmaking When you want to condense the information to a single page and visually communicate to the reader using graphs, charts, and succinct bullet points. A 3 Report Brainstorming is intended to encourage fresh thinking and "crazy" ideas. When you need fresh thinking and "crazy" ideas. Brainstorming Corrective Action Matrix The Corrective Action Matrix is used by problem-solving teams to keep track of who is doing what - by when To ensure action gets implemented and someone is responsible to make it happen. Corrective Action Matrix 21
 Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Error proofing Error-proofing refers to the implementation of fail-safe mechanisms to prevent a process from producing defects. This activity is also know by the Japanese term poka-yoke, from poka (inadvertent errors) and yokeru (to avoid) - pronounced POH-kuh YOH-kay. When it is not acceptable to make even a very small number of defects Error-Proofing Kaizen is the Japanese word for Continuous Improvement a series of ongoing incremental improvements by teams focusing on eliminating all forms of waste from the operation - typically with little capital Kaizen is a philosophy, not just a process, and it is a crucial component of the Lean Enterprise. Many companies have institutionalized the practice of Kaizen by shop floor teams, and have achieved significant performance advancement through the accumulation of incremental advancements over time. Kaizen Also referred to as Poka-yoke Kaizen 22
Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Error proofing Error-proofing refers to the implementation of fail-safe mechanisms to prevent a process from producing defects. This activity is also know by the Japanese term poka-yoke, from poka (inadvertent errors) and yokeru (to avoid) - pronounced POH-kuh YOH-kay. When it is not acceptable to make even a very small number of defects Error-Proofing Kaizen is the Japanese word for Continuous Improvement a series of ongoing incremental improvements by teams focusing on eliminating all forms of waste from the operation - typically with little capital Kaizen is a philosophy, not just a process, and it is a crucial component of the Lean Enterprise. Many companies have institutionalized the practice of Kaizen by shop floor teams, and have achieved significant performance advancement through the accumulation of incremental advancements over time. Kaizen Also referred to as Poka-yoke Kaizen 22
 Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points One Piece Flow Reduced lot sizes go hand-inhand with quick set-ups. The smaller the lot size, the better the flow through the process. Ideally the lot size is reduced to one. To link processes into cells, eliminating double-handling, and reducing inventory and the space it requires One Piece Flow Pull Scheduling is generally synonymous with Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management - a system of production scheduling that pulls product through the value-stream in a continuous flow rather than pushing it through in batches To eliminate overproduction, and hence in-process inventory - seen a manifestation of waste Pull Scheduling SMED (quick changeover) As lean production is dependent upon small lot sizes, small lot sizes are dependent upon quick changeovers. If set-ups or changeovers are lengthy, it is mathematically impossible to run small lots of parts with low inventory because large inprocess inventories must be maintained to feed production during changeovers. Quick Changeover (SMED) 23
Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points One Piece Flow Reduced lot sizes go hand-inhand with quick set-ups. The smaller the lot size, the better the flow through the process. Ideally the lot size is reduced to one. To link processes into cells, eliminating double-handling, and reducing inventory and the space it requires One Piece Flow Pull Scheduling is generally synonymous with Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management - a system of production scheduling that pulls product through the value-stream in a continuous flow rather than pushing it through in batches To eliminate overproduction, and hence in-process inventory - seen a manifestation of waste Pull Scheduling SMED (quick changeover) As lean production is dependent upon small lot sizes, small lot sizes are dependent upon quick changeovers. If set-ups or changeovers are lengthy, it is mathematically impossible to run small lots of parts with low inventory because large inprocess inventories must be maintained to feed production during changeovers. Quick Changeover (SMED) 23
 Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points System Diagrams System Dynamics is the study of the behavior of complex systems - seeking to understand the web of relationships between activities and to identify the linkage between cause and effect. Use system diagrams when you want to visually express the dynamic forces acting upon the components of a process and the interactions between those forces. System Diagrams TPM was developed in the 1970's as a method of involving machine operators in the preventive maintenance of their machines - a reaction to increasing specialization and centralization of the maintenance function that had created division-of-labor barriers between operators and the maintenance of their machines and equipment When you want to tap the knowledge and skill of the people who work with the equipment on a daily basis, and gives operators a stake in the performance of the equipment Total Productive Maintenance 24
Phase - Improve Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points System Diagrams System Dynamics is the study of the behavior of complex systems - seeking to understand the web of relationships between activities and to identify the linkage between cause and effect. Use system diagrams when you want to visually express the dynamic forces acting upon the components of a process and the interactions between those forces. System Diagrams TPM was developed in the 1970's as a method of involving machine operators in the preventive maintenance of their machines - a reaction to increasing specialization and centralization of the maintenance function that had created division-of-labor barriers between operators and the maintenance of their machines and equipment When you want to tap the knowledge and skill of the people who work with the equipment on a daily basis, and gives operators a stake in the performance of the equipment Total Productive Maintenance 24
 Phase - Improve Tool Idea Generation Action Plan It helps us turn our dreams into a reality. An action plan is a way to make sure your vision is made concrete http: //ctb. ku. edu/en/tablec ontents/sub_section_main _1089. aspx Cost/Benefit Analysis A cost benefit analysis is done to determine how well, or how poorly, a planned action will turn out. http: //management. about. co m/cs/money/a/Cost. Benefit. h tm Gaant Chart A type of a bar chart that is used for illustrating project schedules. Solution Evaluation Criteria Some idea of the value or merit of a solution to a problem When to use Gantt charts can be used in any projects that involve effort, resources, milestones, and deliveries. Coaching points http: //www. tutorialspoint. c om/management_concept s/gantt_chart_tool. htm http: //www. virtualsalt. com/ creative. htm 25
Phase - Improve Tool Idea Generation Action Plan It helps us turn our dreams into a reality. An action plan is a way to make sure your vision is made concrete http: //ctb. ku. edu/en/tablec ontents/sub_section_main _1089. aspx Cost/Benefit Analysis A cost benefit analysis is done to determine how well, or how poorly, a planned action will turn out. http: //management. about. co m/cs/money/a/Cost. Benefit. h tm Gaant Chart A type of a bar chart that is used for illustrating project schedules. Solution Evaluation Criteria Some idea of the value or merit of a solution to a problem When to use Gantt charts can be used in any projects that involve effort, resources, milestones, and deliveries. Coaching points http: //www. tutorialspoint. c om/management_concept s/gantt_chart_tool. htm http: //www. virtualsalt. com/ creative. htm 25
 Phase - Improve Tool Idea Generation Pairwise Ranking Matrix To determine the main preferences, priorities, needs, constraints or problems of a person or a group on a certain subject. http: //www. fao. org/Participati on/ft_more. jsp? ID=3022 Force Field Analysis is a decisionmaking technique. It helps you make a decision by analyzing the forces for and against a change, and it helps you communicate the reasoning behind your decision. http: //www. mindtools. com/pa ges/article/new. TED_06. htm Story Board A Storyboard provides a quick, visual summary of a team’s work. http: //business 901. com/blog 1/lean-six-sigma-storyboard/ When to use Coaching points 26
Phase - Improve Tool Idea Generation Pairwise Ranking Matrix To determine the main preferences, priorities, needs, constraints or problems of a person or a group on a certain subject. http: //www. fao. org/Participati on/ft_more. jsp? ID=3022 Force Field Analysis is a decisionmaking technique. It helps you make a decision by analyzing the forces for and against a change, and it helps you communicate the reasoning behind your decision. http: //www. mindtools. com/pa ges/article/new. TED_06. htm Story Board A Storyboard provides a quick, visual summary of a team’s work. http: //business 901. com/blog 1/lean-six-sigma-storyboard/ When to use Coaching points 26
 Phase - Control The purpose of Control: is to make sure that any gains will last. Ø Document the new, improved procedures Ø Train everyone involved Ø Set up procedures for tracking key “vital signs” Ø Hand-off ongoing management to the Process Owner Ø Complete Project documentation Ø Put measures in place to prevent “back sliding” Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Check Process The CHECK Process was created to give Supervisors and other shop floor personnel a simple tool to evaluate process conformance. Before gathering data and conducting in-depth research to determine the root cause of process instability, it is important to verify that the operation is being performed according to specifications and standards CHECK Process 27
Phase - Control The purpose of Control: is to make sure that any gains will last. Ø Document the new, improved procedures Ø Train everyone involved Ø Set up procedures for tracking key “vital signs” Ø Hand-off ongoing management to the Process Owner Ø Complete Project documentation Ø Put measures in place to prevent “back sliding” Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Check Process The CHECK Process was created to give Supervisors and other shop floor personnel a simple tool to evaluate process conformance. Before gathering data and conducting in-depth research to determine the root cause of process instability, it is important to verify that the operation is being performed according to specifications and standards CHECK Process 27
 Phase – Control Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Control Chart indicates whether the process is currently under control (i. e. , is stable, with variation only coming from sources common to the process), . Use to predict future performance Control chart Control Plan The control plan is the centralized document to keep track of the status of all significant process characteristics. Standardized Work The systematic determination and documentation of work element sequence and process for each operation. SPC Primary tool to improve product quality by reducing process variation. Control Plan When you want to achieve a balanced work flow, cycle time equal to Takt time, and high quality, . . work must be standardized at all operations for optimum efficiency and consistency Standardized Work Statistical Process Control (SPC) 28
Phase – Control Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Control Chart indicates whether the process is currently under control (i. e. , is stable, with variation only coming from sources common to the process), . Use to predict future performance Control chart Control Plan The control plan is the centralized document to keep track of the status of all significant process characteristics. Standardized Work The systematic determination and documentation of work element sequence and process for each operation. SPC Primary tool to improve product quality by reducing process variation. Control Plan When you want to achieve a balanced work flow, cycle time equal to Takt time, and high quality, . . work must be standardized at all operations for optimum efficiency and consistency Standardized Work Statistical Process Control (SPC) 28
 Phase – Control 5. 1 Pilot Plan Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Pilot Preliminary work as a test or trial Pilot experiments are frequently carried out before large-scale implementation http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Pil ot_experiment Objective & Key Topics To develop and execute a pilot Before starting a pilot http: //teaching. uncc. edu/articl es-books/best-practicearticles/goalsobjectives/writing-objectivesusing-blooms-taxonomy Training plan To make people aware Before starting pilot http: //www. google. com/searc h? q=training+plan&hl=en&pr md=imvns&tbm=isch&tbo=u& source=univ&sa=X&ei=CNLUIDHI 4 biig. Krso. DQ&ved= 0 CCg. Qs. AQ&biw=1366&bih= 622 Success Criteria Defining effectiveness of pilot Before and during pilot http: //office. microsoft. com/enus/project-help/define-yourproject-goals-and-successcriteria-HA 001211137. aspx 29
Phase – Control 5. 1 Pilot Plan Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Pilot Preliminary work as a test or trial Pilot experiments are frequently carried out before large-scale implementation http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Pil ot_experiment Objective & Key Topics To develop and execute a pilot Before starting a pilot http: //teaching. uncc. edu/articl es-books/best-practicearticles/goalsobjectives/writing-objectivesusing-blooms-taxonomy Training plan To make people aware Before starting pilot http: //www. google. com/searc h? q=training+plan&hl=en&pr md=imvns&tbm=isch&tbo=u& source=univ&sa=X&ei=CNLUIDHI 4 biig. Krso. DQ&ved= 0 CCg. Qs. AQ&biw=1366&bih= 622 Success Criteria Defining effectiveness of pilot Before and during pilot http: //office. microsoft. com/enus/project-help/define-yourproject-goals-and-successcriteria-HA 001211137. aspx 29
 Phase – Control 5. 1 Pilot Plan Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Proof of Concept Plan First Version Before starting pilot Example: http: //www. archives. gov/recor ds-mgmt/policy/pilotguidance. html Gantt Chart Aids to planning Before and during pilot http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Ga ntt_chart http: //www. youtube. com/watc h? v=s. A 67 g 6 za. KOE http: //office. microsoft. com/enus/excel-help/create-a-ganttchart-in-excel. HA 001034605. aspx Pilot Tips Aids to planning Before and during pilot http: //www. pilotproject. com/tip s. aspx 30
Phase – Control 5. 1 Pilot Plan Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Proof of Concept Plan First Version Before starting pilot Example: http: //www. archives. gov/recor ds-mgmt/policy/pilotguidance. html Gantt Chart Aids to planning Before and during pilot http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Ga ntt_chart http: //www. youtube. com/watc h? v=s. A 67 g 6 za. KOE http: //office. microsoft. com/enus/excel-help/create-a-ganttchart-in-excel. HA 001034605. aspx Pilot Tips Aids to planning Before and during pilot http: //www. pilotproject. com/tip s. aspx 30
 Phase – Control 5. 2 Plan & Implement Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Potential problem analysis To address potential barriers to solution implementation After executing pilot plan in control Apply Brainstorming techniques Risk assessment matrix To consider the ways in which the objectives for process may be at risk After executing pilot plan in control http: //www. cip. msu. edu/Co m. Fac. RAM-Howto. Use. pdf http: //www. lbjsc. txstate. edu /caso/soc/manage/forms/co ntent. Paragraph/014/docum ent/Risk. Assessment. Matrix. pdf Controls assessment matrix Identify activity designed to protect from the identified high priority risks After risk assessment in control http: //www. iwise 2. com/cont rols-assessment-matrix Communication Plan To communicate change After pilot plan in control Critical for buy in http: //www. hieran. com/com et/howto. html Implementation Planning To precisely define the implementation of a solution. Success relies on quality and thoroughness of implementation plan After communication plan in control http: //webaim. org/articles/i mplementation/plan 31
Phase – Control 5. 2 Plan & Implement Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Potential problem analysis To address potential barriers to solution implementation After executing pilot plan in control Apply Brainstorming techniques Risk assessment matrix To consider the ways in which the objectives for process may be at risk After executing pilot plan in control http: //www. cip. msu. edu/Co m. Fac. RAM-Howto. Use. pdf http: //www. lbjsc. txstate. edu /caso/soc/manage/forms/co ntent. Paragraph/014/docum ent/Risk. Assessment. Matrix. pdf Controls assessment matrix Identify activity designed to protect from the identified high priority risks After risk assessment in control http: //www. iwise 2. com/cont rols-assessment-matrix Communication Plan To communicate change After pilot plan in control Critical for buy in http: //www. hieran. com/com et/howto. html Implementation Planning To precisely define the implementation of a solution. Success relies on quality and thoroughness of implementation plan After communication plan in control http: //webaim. org/articles/i mplementation/plan 31
 Phase – Control 5. 3 Process Integration Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Standardization To identify project expansion opportunities for your solutions Once your best solutions have been identified. Replicate for same process but in different area. Standardize for different but similar processes. http: //www. lean. org/workshops/W orkshop. Description. cfm? Worksho p. Id=20 After you have identified replication opportunities http: //books. google. com/books? id =Crqm 2 Am. ECD 0 C&pg=PA 76&lpg =PA 76&dq=replication+as+lean+t ool&source=bl&ots=46 p. Y 2 YWzv. L &sig=T 48 CDFzt 4 Joye. TZKpbl 2 VH 2 Vu. XI&hl=en&sa=X&ei=s 9 m. LUJ 3 BM 9 DWig. K 4 v. YFI&ved=0 CEAQ 6 A Ew. BQ#v=onepage&q=replication %20 as%20 lean%20 tool&f=false Replication Identifying what you need to consider if you want to replicate http: //www. trainingwithinindustry. n et/SW. html 32
Phase – Control 5. 3 Process Integration Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Standardization To identify project expansion opportunities for your solutions Once your best solutions have been identified. Replicate for same process but in different area. Standardize for different but similar processes. http: //www. lean. org/workshops/W orkshop. Description. cfm? Worksho p. Id=20 After you have identified replication opportunities http: //books. google. com/books? id =Crqm 2 Am. ECD 0 C&pg=PA 76&lpg =PA 76&dq=replication+as+lean+t ool&source=bl&ots=46 p. Y 2 YWzv. L &sig=T 48 CDFzt 4 Joye. TZKpbl 2 VH 2 Vu. XI&hl=en&sa=X&ei=s 9 m. LUJ 3 BM 9 DWig. K 4 v. YFI&ved=0 CEAQ 6 A Ew. BQ#v=onepage&q=replication %20 as%20 lean%20 tool&f=false Replication Identifying what you need to consider if you want to replicate http: //www. trainingwithinindustry. n et/SW. html 32
 Phase – Control 5. 3 Process Integration Tool What the tool is used for Coaching points Before setting your deployment schedule Cost Benefit Analysis When to use http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Cost% E 2%80%93 benefit_analysis http: //management. about. com/cs/ money/a/Cost. Benefit. htm http: //www. dummies. com/howto/content/performing-acostbenefit-analysis. html Process Control Systems Critical tool for making improvement continuous, that is after you have gone As part of the detailed implementation plan http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Proces s_control http: //www. engineeringtoolbox. co m/process-control-systemst_32. html 33
Phase – Control 5. 3 Process Integration Tool What the tool is used for Coaching points Before setting your deployment schedule Cost Benefit Analysis When to use http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Cost% E 2%80%93 benefit_analysis http: //management. about. com/cs/ money/a/Cost. Benefit. htm http: //www. dummies. com/howto/content/performing-acostbenefit-analysis. html Process Control Systems Critical tool for making improvement continuous, that is after you have gone As part of the detailed implementation plan http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Proces s_control http: //www. engineeringtoolbox. co m/process-control-systemst_32. html 33
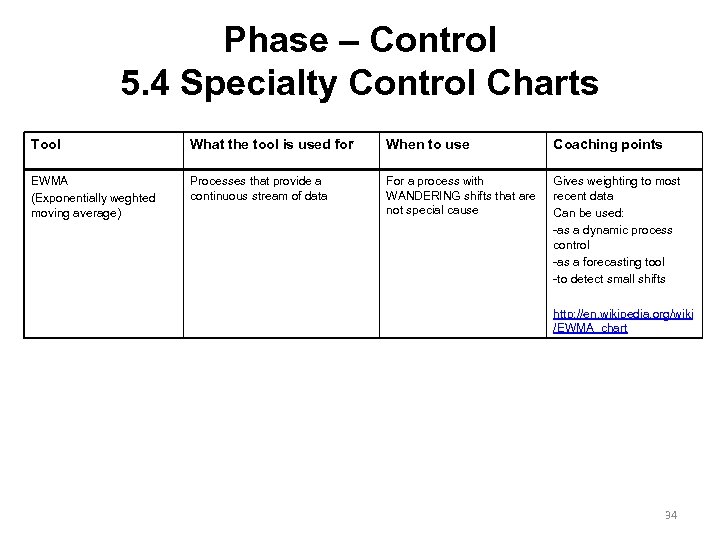 Phase – Control 5. 4 Specialty Control Charts Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points EWMA (Exponentially weghted moving average) Processes that provide a continuous stream of data For a process with WANDERING shifts that are not special cause Gives weighting to most recent data Can be used: -as a dynamic process control -as a forecasting tool -to detect small shifts http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /EWMA_chart 34
Phase – Control 5. 4 Specialty Control Charts Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points EWMA (Exponentially weghted moving average) Processes that provide a continuous stream of data For a process with WANDERING shifts that are not special cause Gives weighting to most recent data Can be used: -as a dynamic process control -as a forecasting tool -to detect small shifts http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /EWMA_chart 34
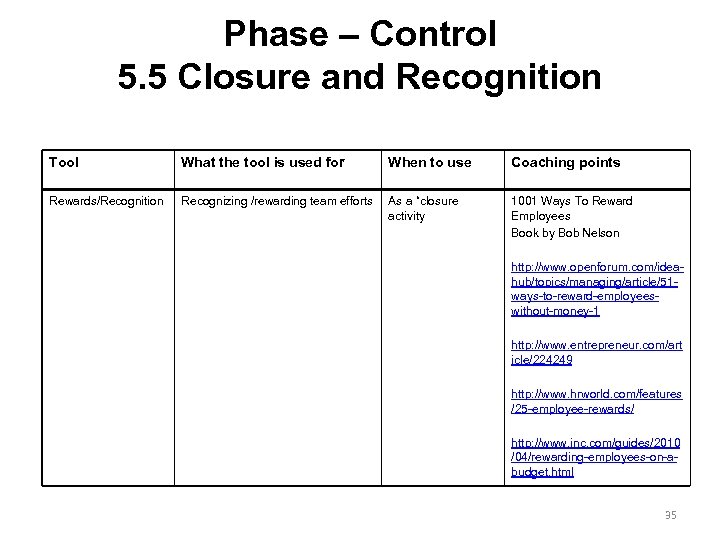 Phase – Control 5. 5 Closure and Recognition Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Rewards/Recognition Recognizing /rewarding team efforts As a “closure activity 1001 Ways To Reward Employees Book by Bob Nelson http: //www. openforum. com/ideahub/topics/managing/article/51 ways-to-reward-employeeswithout-money-1 http: //www. entrepreneur. com/art icle/224249 http: //www. hrworld. com/features /25 -employee-rewards/ http: //www. inc. com/guides/2010 /04/rewarding-employees-on-abudget. html 35
Phase – Control 5. 5 Closure and Recognition Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Rewards/Recognition Recognizing /rewarding team efforts As a “closure activity 1001 Ways To Reward Employees Book by Bob Nelson http: //www. openforum. com/ideahub/topics/managing/article/51 ways-to-reward-employeeswithout-money-1 http: //www. entrepreneur. com/art icle/224249 http: //www. hrworld. com/features /25 -employee-rewards/ http: //www. inc. com/guides/2010 /04/rewarding-employees-on-abudget. html 35
 Statistical Tools 36
Statistical Tools 36
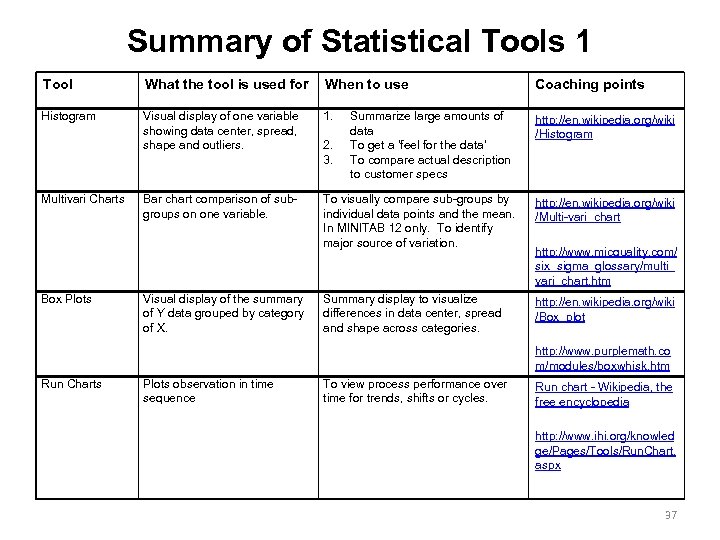 Summary of Statistical Tools 1 Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Histogram Visual display of one variable showing data center, spread, shape and outliers. 1. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /Histogram Bar chart comparison of subgroups on one variable. To visually compare sub-groups by individual data points and the mean. In MINITAB 12 only. To identify major source of variation. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /Multi-vari_chart Summary display to visualize differences in data center, spread and shape across categories. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /Box_plot Multivari Charts Box Plots Visual display of the summary of Y data grouped by category of X. 2. 3. Summarize large amounts of data To get a ‘feel for the data’ To compare actual description to customer specs http: //www. micquality. com/ six_sigma_glossary/multi_ vari_chart. htm http: //www. purplemath. co m/modules/boxwhisk. htm Run Charts Plots observation in time sequence To view process performance over time for trends, shifts or cycles. Run chart - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http: //www. ihi. org/knowled ge/Pages/Tools/Run. Chart. aspx 37
Summary of Statistical Tools 1 Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Histogram Visual display of one variable showing data center, spread, shape and outliers. 1. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /Histogram Bar chart comparison of subgroups on one variable. To visually compare sub-groups by individual data points and the mean. In MINITAB 12 only. To identify major source of variation. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /Multi-vari_chart Summary display to visualize differences in data center, spread and shape across categories. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki /Box_plot Multivari Charts Box Plots Visual display of the summary of Y data grouped by category of X. 2. 3. Summarize large amounts of data To get a ‘feel for the data’ To compare actual description to customer specs http: //www. micquality. com/ six_sigma_glossary/multi_ vari_chart. htm http: //www. purplemath. co m/modules/boxwhisk. htm Run Charts Plots observation in time sequence To view process performance over time for trends, shifts or cycles. Run chart - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http: //www. ihi. org/knowled ge/Pages/Tools/Run. Chart. aspx 37
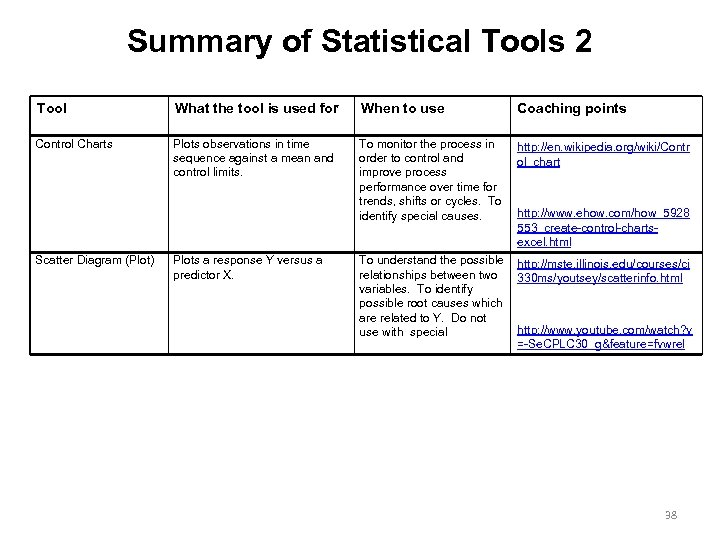 Summary of Statistical Tools 2 Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Control Charts Plots observations in time sequence against a mean and control limits. To monitor the process in order to control and improve process performance over time for trends, shifts or cycles. To identify special causes. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Contr ol_chart To understand the possible relationships between two variables. To identify possible root causes which are related to Y. Do not use with special http: //mste. illinois. edu/courses/ci 330 ms/youtsey/scatterinfo. html Scatter Diagram (Plot) Plots a response Y versus a predictor X. http: //www. ehow. com/how_5928 553_create-control-chartsexcel. html http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v =-Se. CPLC 30_g&feature=fvwrel 38
Summary of Statistical Tools 2 Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Control Charts Plots observations in time sequence against a mean and control limits. To monitor the process in order to control and improve process performance over time for trends, shifts or cycles. To identify special causes. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Contr ol_chart To understand the possible relationships between two variables. To identify possible root causes which are related to Y. Do not use with special http: //mste. illinois. edu/courses/ci 330 ms/youtsey/scatterinfo. html Scatter Diagram (Plot) Plots a response Y versus a predictor X. http: //www. ehow. com/how_5928 553_create-control-chartsexcel. html http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v =-Se. CPLC 30_g&feature=fvwrel 38
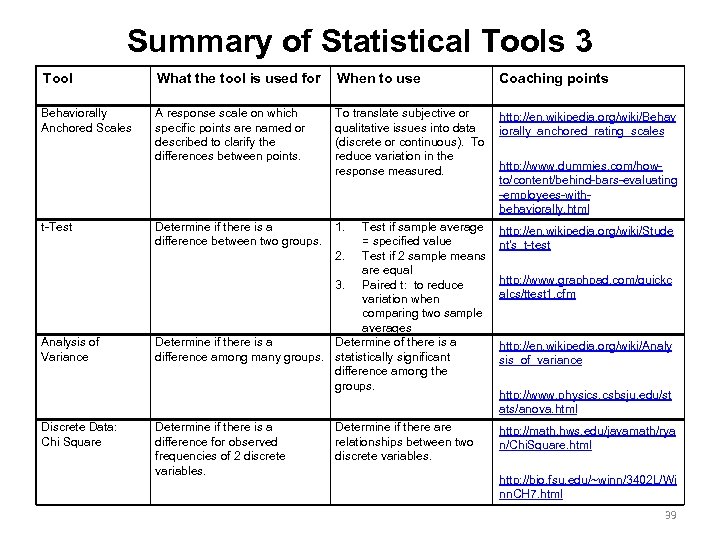 Summary of Statistical Tools 3 Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Behaviorally Anchored Scales A response scale on which specific points are named or described to clarify the differences between points. To translate subjective or qualitative issues into data (discrete or continuous). To reduce variation in the response measured. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Behav iorally_anchored_rating_scales Determine if there is a difference between two groups. 1. Test if sample average = specified value 2. Test if 2 sample means are equal 3. Paired t: to reduce variation when comparing two sample averages Determine if there is a Determine of there is a difference among many groups. statistically significant difference among the groups. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Stude nt's_t-test Determine if there is a difference for observed frequencies of 2 discrete variables. http: //math. hws. edu/javamath/rya n/Chi. Square. html t-Test Analysis of Variance Discrete Data: Chi Square Determine if there are relationships between two discrete variables. http: //www. dummies. com/howto/content/behind-bars-evaluating -employees-withbehaviorally. html http: //www. graphpad. com/quickc alcs/ttest 1. cfm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Analy sis_of_variance http: //www. physics. csbsju. edu/st ats/anova. html http: //bio. fsu. edu/~winn/3402 L/Wi nn. CH 7. html 39
Summary of Statistical Tools 3 Tool What the tool is used for When to use Coaching points Behaviorally Anchored Scales A response scale on which specific points are named or described to clarify the differences between points. To translate subjective or qualitative issues into data (discrete or continuous). To reduce variation in the response measured. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Behav iorally_anchored_rating_scales Determine if there is a difference between two groups. 1. Test if sample average = specified value 2. Test if 2 sample means are equal 3. Paired t: to reduce variation when comparing two sample averages Determine if there is a Determine of there is a difference among many groups. statistically significant difference among the groups. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Stude nt's_t-test Determine if there is a difference for observed frequencies of 2 discrete variables. http: //math. hws. edu/javamath/rya n/Chi. Square. html t-Test Analysis of Variance Discrete Data: Chi Square Determine if there are relationships between two discrete variables. http: //www. dummies. com/howto/content/behind-bars-evaluating -employees-withbehaviorally. html http: //www. graphpad. com/quickc alcs/ttest 1. cfm http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Analy sis_of_variance http: //www. physics. csbsju. edu/st ats/anova. html http: //bio. fsu. edu/~winn/3402 L/Wi nn. CH 7. html 39
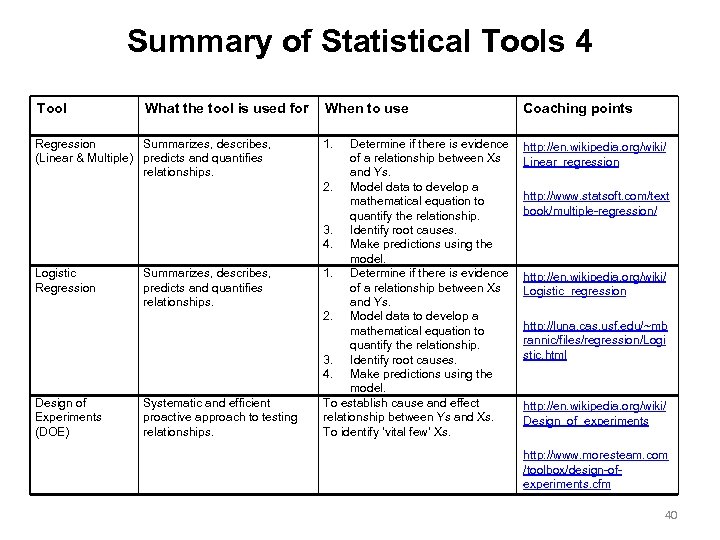 Summary of Statistical Tools 4 Tool What the tool is used for Regression Summarizes, describes, (Linear & Multiple) predicts and quantifies relationships. Logistic Regression Design of Experiments (DOE) Summarizes, describes, predicts and quantifies relationships. Systematic and efficient proactive approach to testing relationships. When to use Coaching points 1. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ Linear_regression Determine if there is evidence of a relationship between Xs and Ys. 2. Model data to develop a mathematical equation to quantify the relationship. 3. Identify root causes. 4. Make predictions using the model. 1. Determine if there is evidence of a relationship between Xs and Ys. 2. Model data to develop a mathematical equation to quantify the relationship. 3. Identify root causes. 4. Make predictions using the model. To establish cause and effect relationship between Ys and Xs. To identify ‘vital few’ Xs. http: //www. statsoft. com/text book/multiple-regression/ http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ Logistic_regression http: //luna. cas. usf. edu/~mb rannic/files/regression/Logi stic. html http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ Design_of_experiments http: //www. moresteam. com /toolbox/design-ofexperiments. cfm 40
Summary of Statistical Tools 4 Tool What the tool is used for Regression Summarizes, describes, (Linear & Multiple) predicts and quantifies relationships. Logistic Regression Design of Experiments (DOE) Summarizes, describes, predicts and quantifies relationships. Systematic and efficient proactive approach to testing relationships. When to use Coaching points 1. http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ Linear_regression Determine if there is evidence of a relationship between Xs and Ys. 2. Model data to develop a mathematical equation to quantify the relationship. 3. Identify root causes. 4. Make predictions using the model. 1. Determine if there is evidence of a relationship between Xs and Ys. 2. Model data to develop a mathematical equation to quantify the relationship. 3. Identify root causes. 4. Make predictions using the model. To establish cause and effect relationship between Ys and Xs. To identify ‘vital few’ Xs. http: //www. statsoft. com/text book/multiple-regression/ http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ Logistic_regression http: //luna. cas. usf. edu/~mb rannic/files/regression/Logi stic. html http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/ Design_of_experiments http: //www. moresteam. com /toolbox/design-ofexperiments. cfm 40
 7 Basic Tools • • The designation arose in postwar Japan, inspired by the seven famous weapons of Benkei. At that time, companies that had set about training their workforces in statistical quality control found that the complexity of the subject intimidated the vast majority of their workers and scaled back training to focus primarily on simpler methods which suffice for most quality-related issues. The Seven Basic Tools stand in contrast to more advanced statistical methods such as survey sampling, acceptance sampling, statistical hypothesis testing, design of experiments, multivariate analysis, and various methods developed in the field of operations research. The seven tools are: • Cause-and-effect (also known as the "fish-bone" or Ishikawa) diagram • Check sheet • Control chart • Histogram • Pareto chart • Scatter diagram • Stratification (alternately, flow chart or run chart) 41
7 Basic Tools • • The designation arose in postwar Japan, inspired by the seven famous weapons of Benkei. At that time, companies that had set about training their workforces in statistical quality control found that the complexity of the subject intimidated the vast majority of their workers and scaled back training to focus primarily on simpler methods which suffice for most quality-related issues. The Seven Basic Tools stand in contrast to more advanced statistical methods such as survey sampling, acceptance sampling, statistical hypothesis testing, design of experiments, multivariate analysis, and various methods developed in the field of operations research. The seven tools are: • Cause-and-effect (also known as the "fish-bone" or Ishikawa) diagram • Check sheet • Control chart • Histogram • Pareto chart • Scatter diagram • Stratification (alternately, flow chart or run chart) 41
 • • • • • • Resources http: //www. khanacademy. org/ Statistics Handbook http: //davidmlane. com/hyperstat/index. html http: //www. statsoft. com/textbook/elementary-concepts-in-statistics/? button=1 http: //onlinestatbook. com/version_1. html http: //lib. stat. cmu. edu/ http: //www. strategosinc. com/human_side. htm http: //ocw. mit. edu/index. htm (search Lean Six Sigma) http: //www. moresteam. com/toolbox/index. cfm http: //www. moresteam. com/resources/lean. cfm http: //www. itl. nist. gov/div 898/handbook/quantgal. htm http: //www. leansixsigmahpo. com/tools. html http: //www. skymark. com/resources/refhome. asp http: //www. strategosinc. com/value_stream_vs_process_mapping. htm http: //www. freeleansite. com/ http: //www. dmaictools. com/ http: //www. statpac. org/research-library/ http: //www. accountability. wa. gov/leadership/lean/default. asp http: //www. gembutsu. com/lean_faq. html http: //leanyourcompany. com/improve/What-are-the-seven-wastes. asp http: //www. micquality. com/six_sigma_glossary/process_improvement_tools. htm 42
• • • • • • Resources http: //www. khanacademy. org/ Statistics Handbook http: //davidmlane. com/hyperstat/index. html http: //www. statsoft. com/textbook/elementary-concepts-in-statistics/? button=1 http: //onlinestatbook. com/version_1. html http: //lib. stat. cmu. edu/ http: //www. strategosinc. com/human_side. htm http: //ocw. mit. edu/index. htm (search Lean Six Sigma) http: //www. moresteam. com/toolbox/index. cfm http: //www. moresteam. com/resources/lean. cfm http: //www. itl. nist. gov/div 898/handbook/quantgal. htm http: //www. leansixsigmahpo. com/tools. html http: //www. skymark. com/resources/refhome. asp http: //www. strategosinc. com/value_stream_vs_process_mapping. htm http: //www. freeleansite. com/ http: //www. dmaictools. com/ http: //www. statpac. org/research-library/ http: //www. accountability. wa. gov/leadership/lean/default. asp http: //www. gembutsu. com/lean_faq. html http: //leanyourcompany. com/improve/What-are-the-seven-wastes. asp http: //www. micquality. com/six_sigma_glossary/process_improvement_tools. htm 42


