e305138d91a49e53ee328005f49894b8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Phase 5. 3 Calibration Gary Shenk 3/31/2010 1
Calibration Method • Calibration method largely unchanged for several years – P 5. 1 – 8/2008 - first automated calibration – P 5. 2 – 6/2009 - better constraints on parameters and regional factors – P 5. 3 – 2/2010 - few small changes in reaction to new scenario builder data • Reviews – WQSC – Modeling Subcommittee – STAC review 2
Watershed Model Inputs • Phase 5. 1 – No Scenario Builder • Phase 5. 2 – Half-Built Scenario Builder with known issues • Phase 5. 3 – Final TMDL Scenario Builder 3

Fixed Issues with Scenario Builder for phase 5. 3 • Realistic uptake values • Realistic nutrient applications • Low variability between states for uptake and application • Manure spread logic improved • Scenarios now possible within Scenario Builder 4
Other P 5. 3 changes • Land Use – – Better characterization of ag land location – Better trend in urban land • Point Source – Addition of “non-significant” sources • Septic – Tied to land use modeling 5

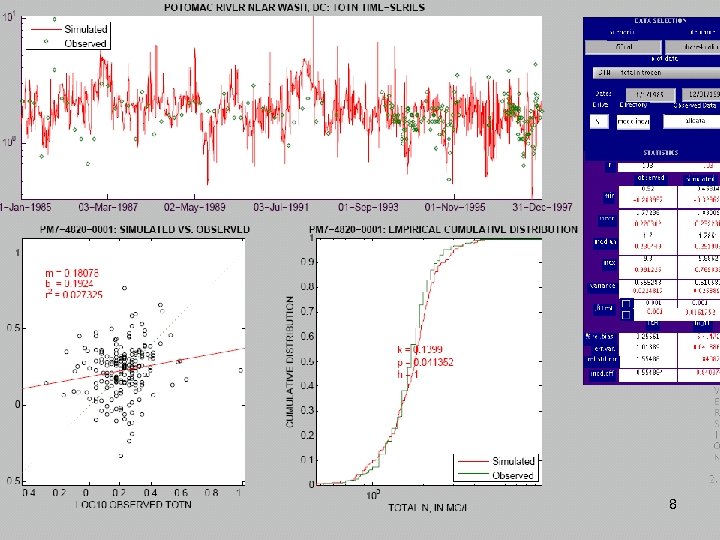
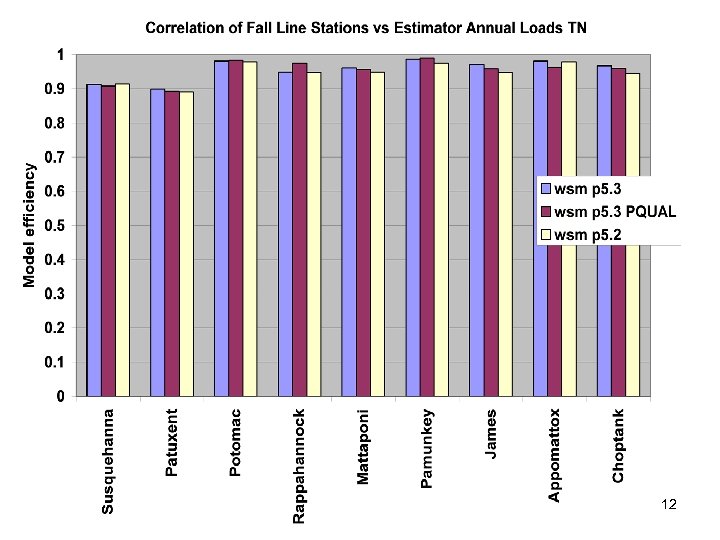
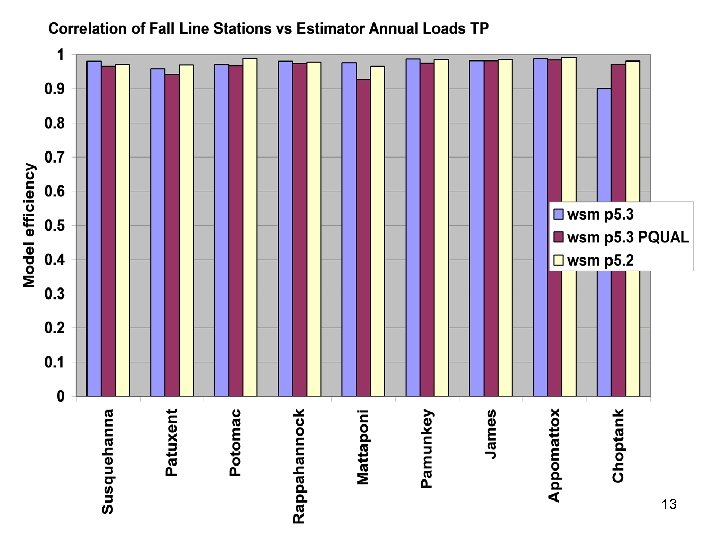
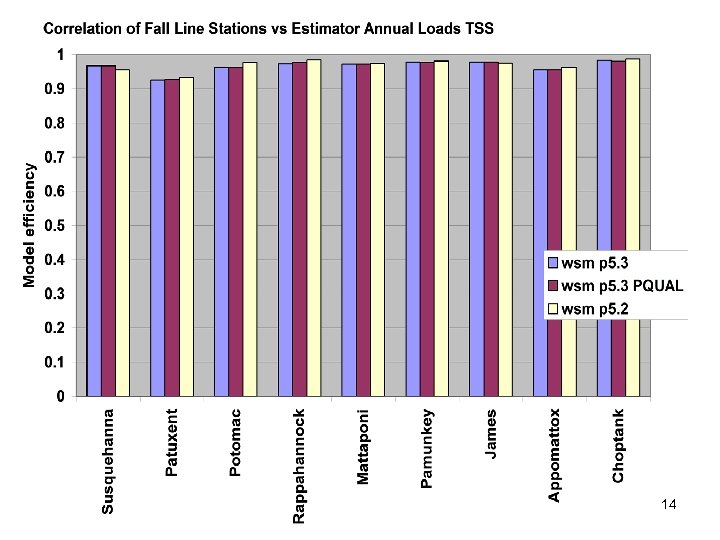
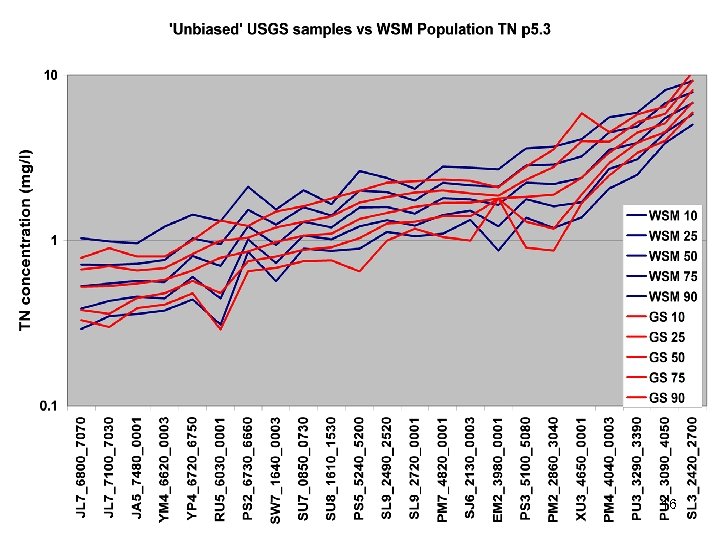
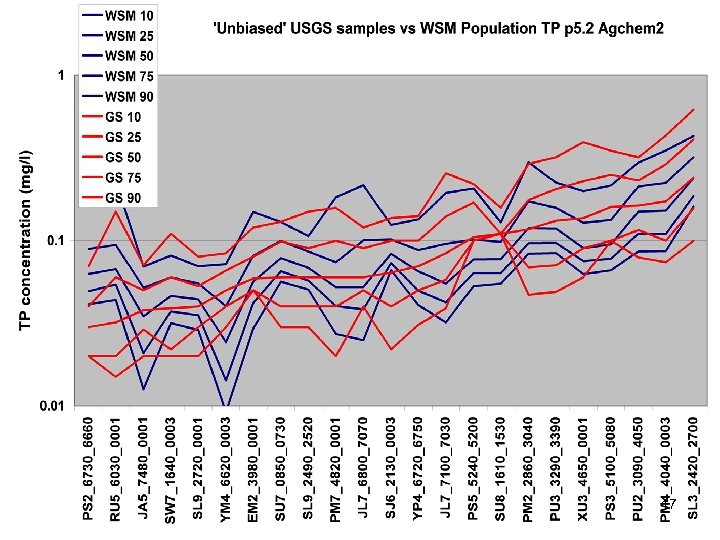
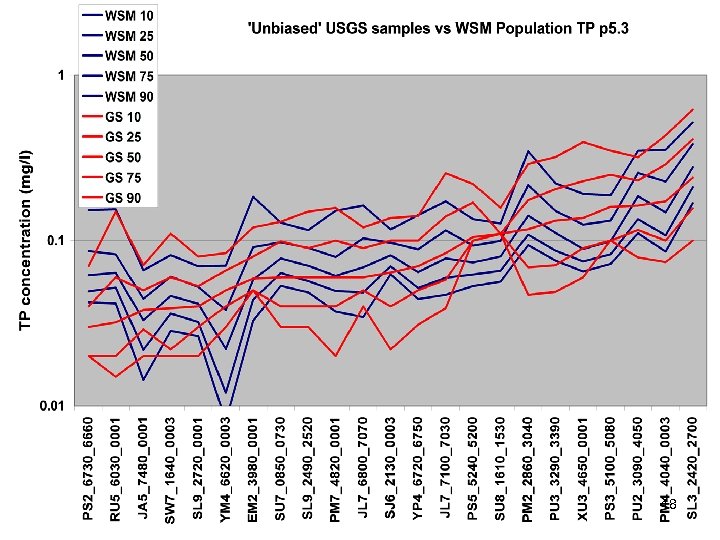
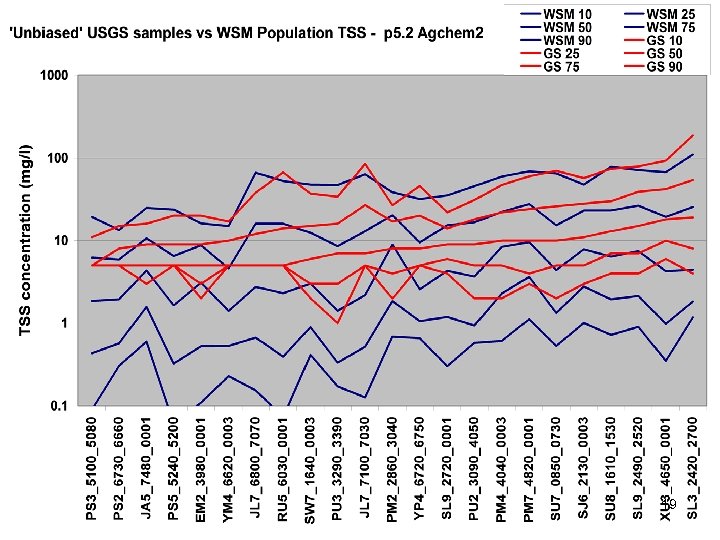
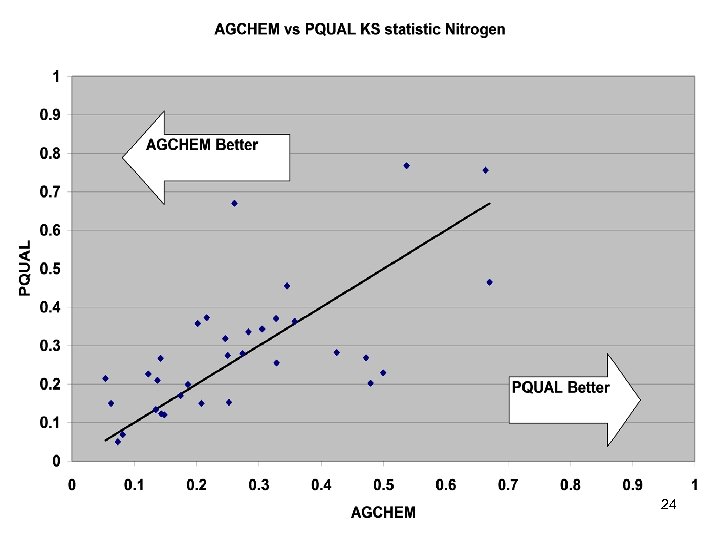
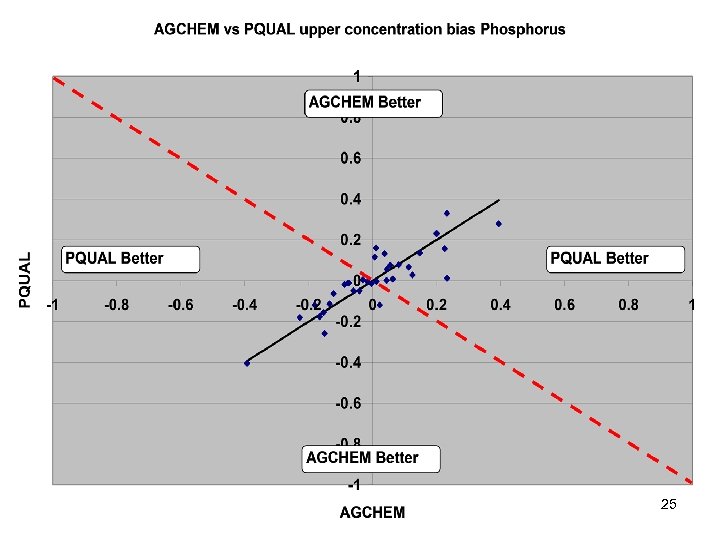
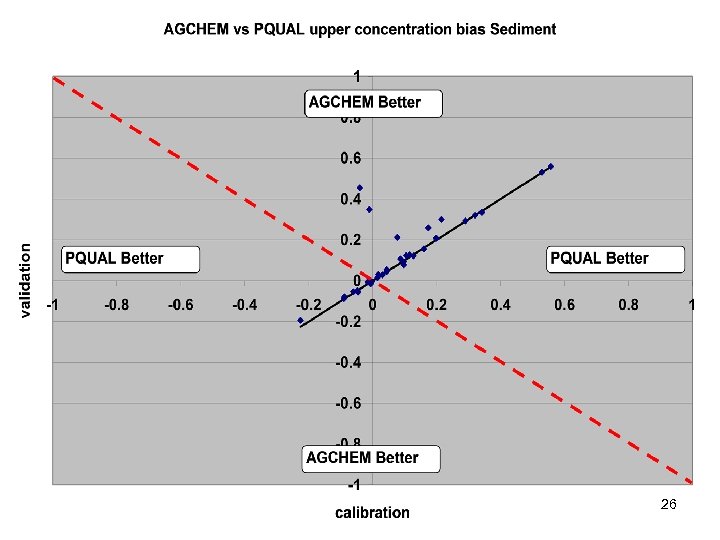
River Calibration Criteria • CFD only • Estimator Loads for Regional Factors • STAC thought this was good calibration strategy but not a representative way to present the results • Recommended that results communicated in the outputs of interest (loads) 6
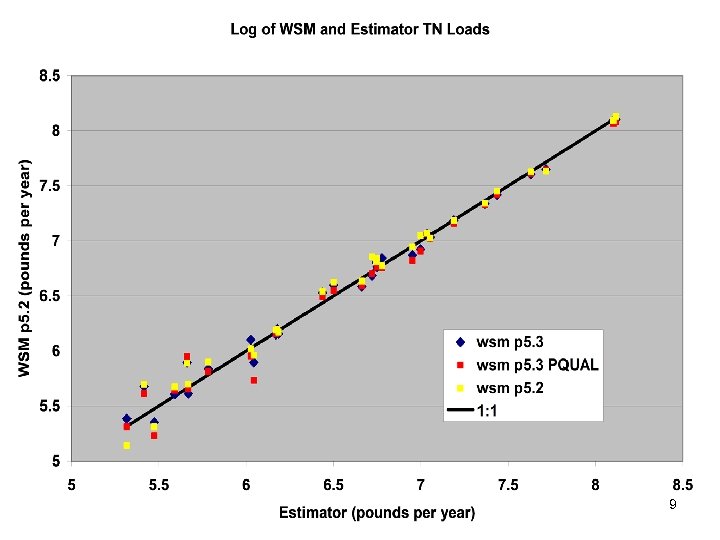
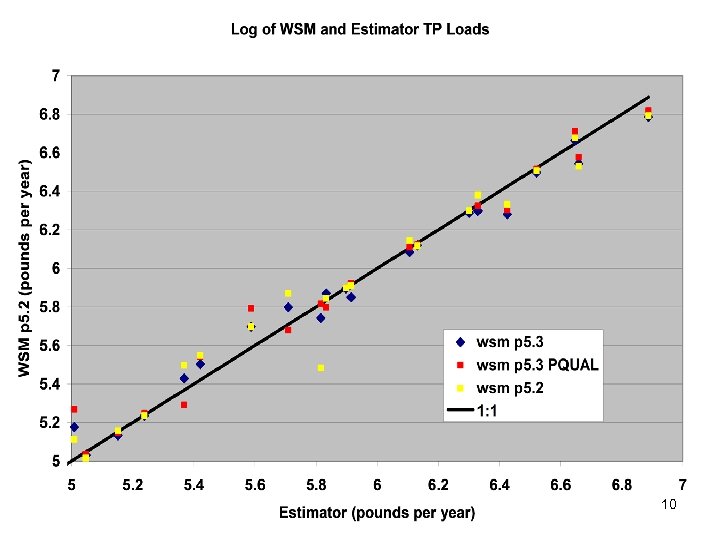
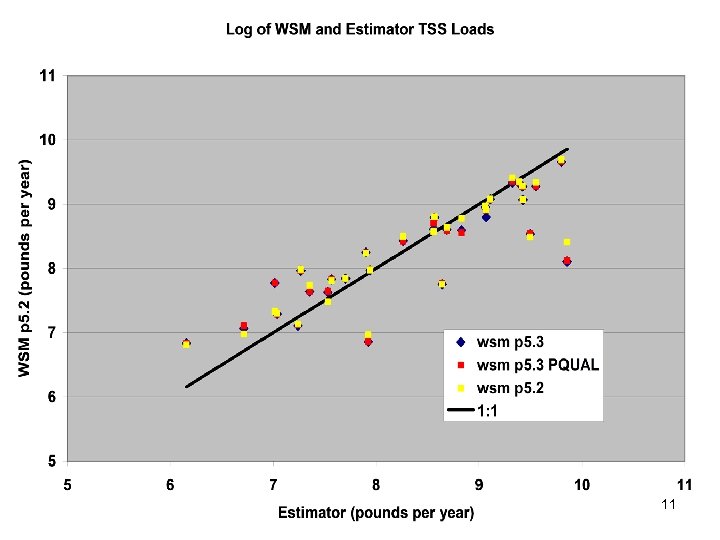
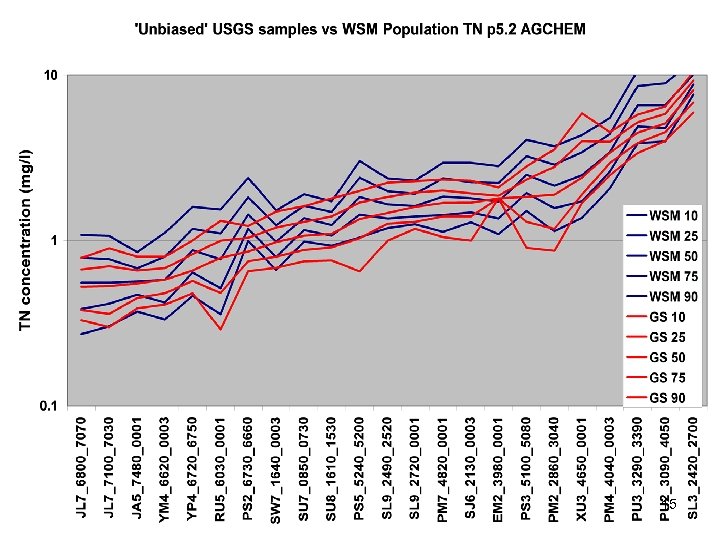
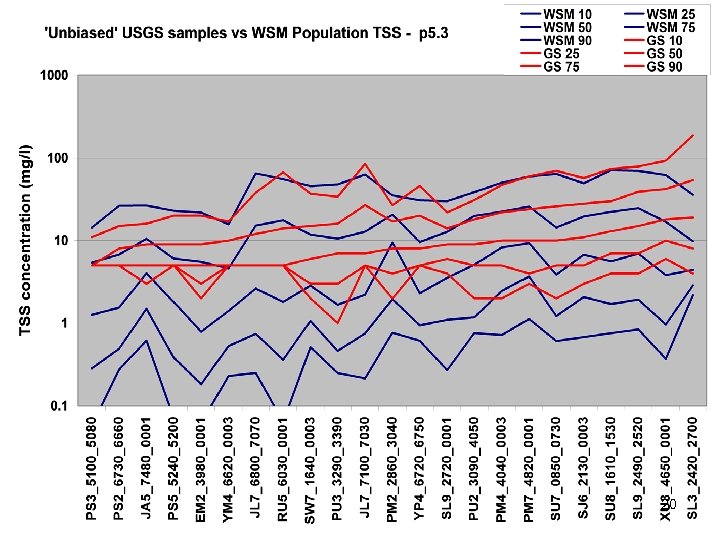
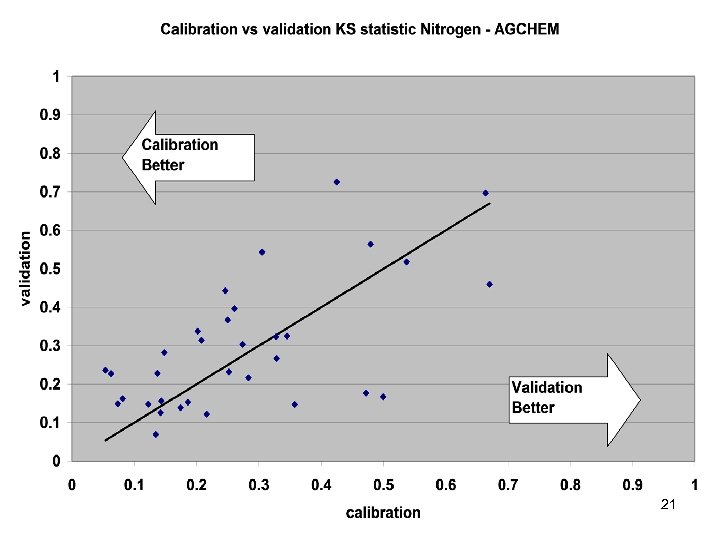
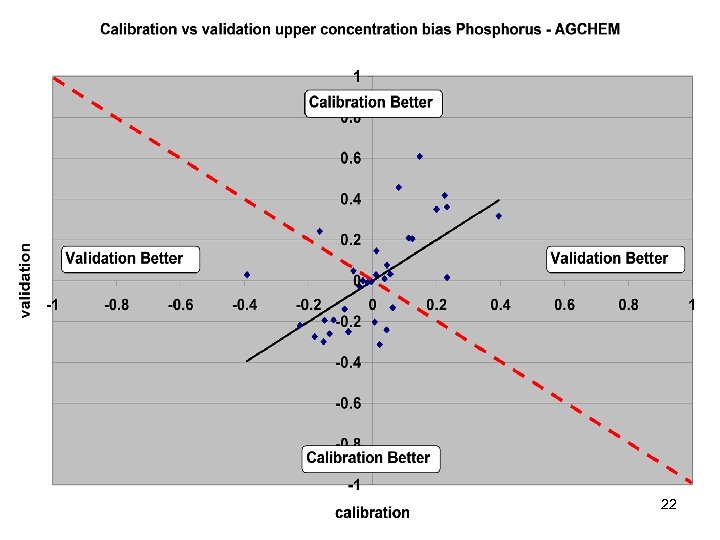
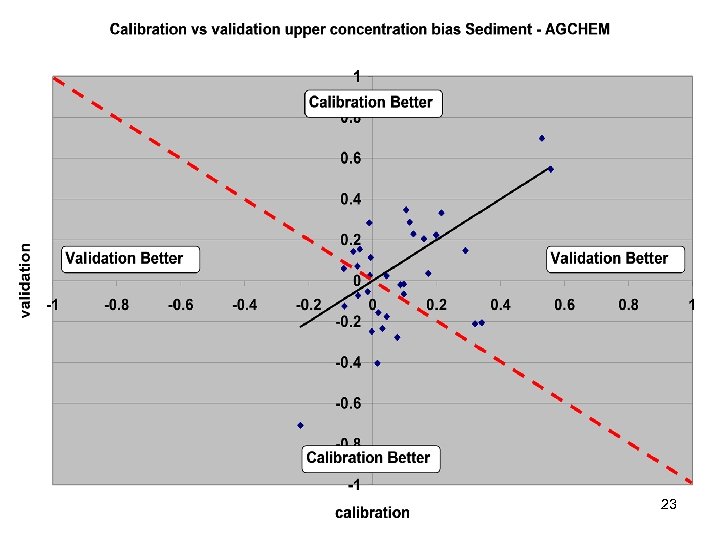
Comparisons • Statistics – Phase 5 and Estimator • Total Loads over space • Loads at a point over time – Phase 5 and USGS unbiased Samples – Phase 5 and Validation • Calibration Plots – Phase 4 and Phase 5 – Phase 5 all station • Compare Loads to Previous Models ftp: //ftp. chesapeakebay. net/modeling/phase 5/calibration_pdfs/p 53_2010_02/ 7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26

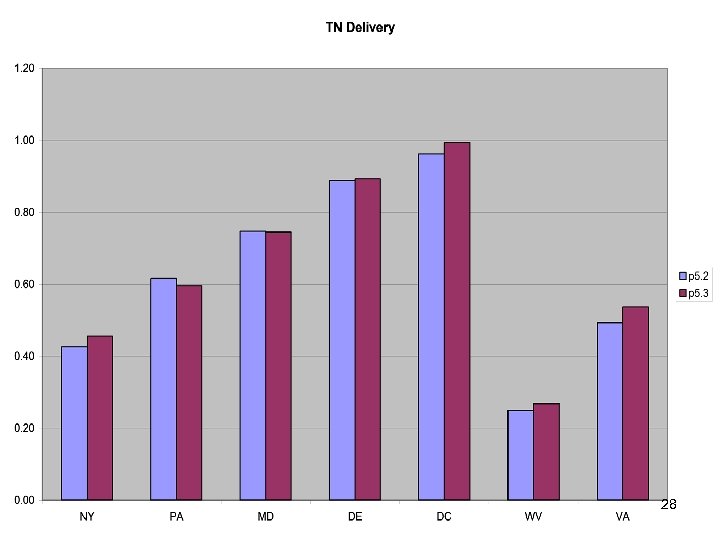
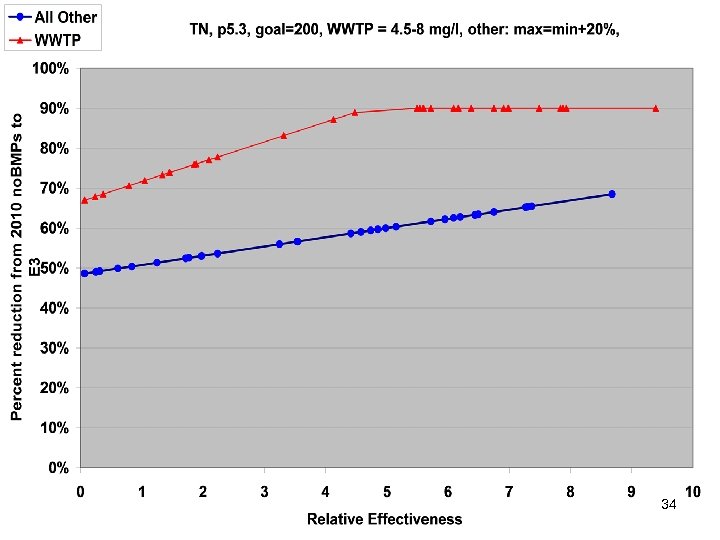
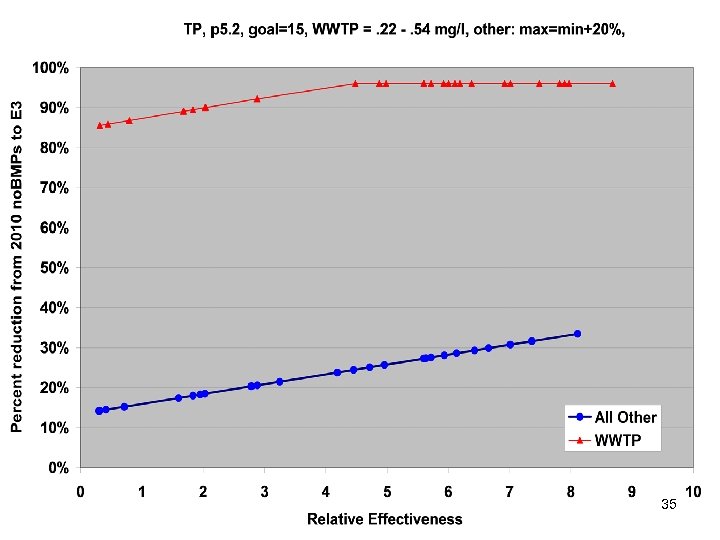
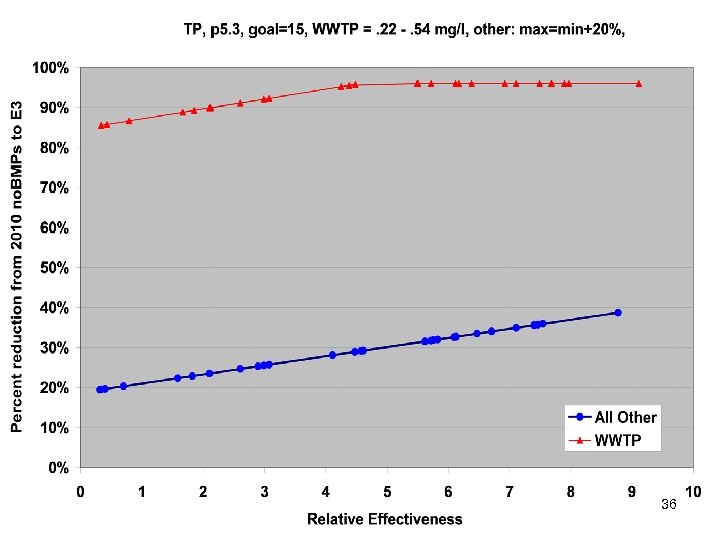
TMDL Allocations Based on • • No Action E 3 Riverine Delivery Factors Estuarine Delivery Factors 27
28
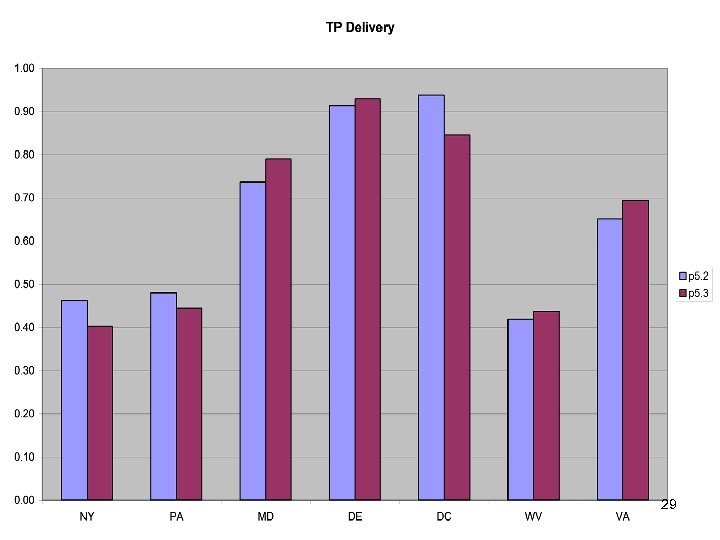
29

First Look at Draft Scenarios 30
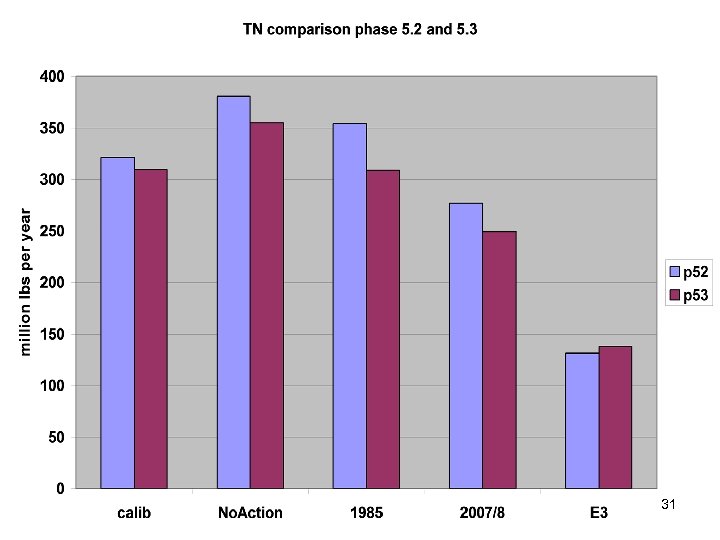
31
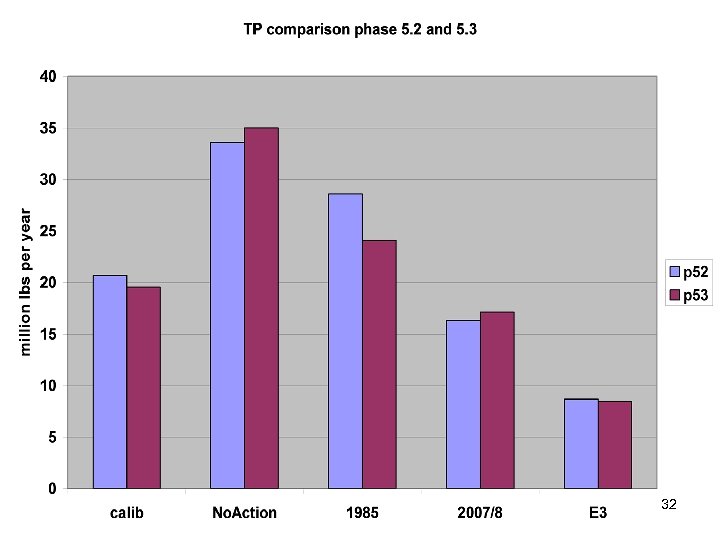
32
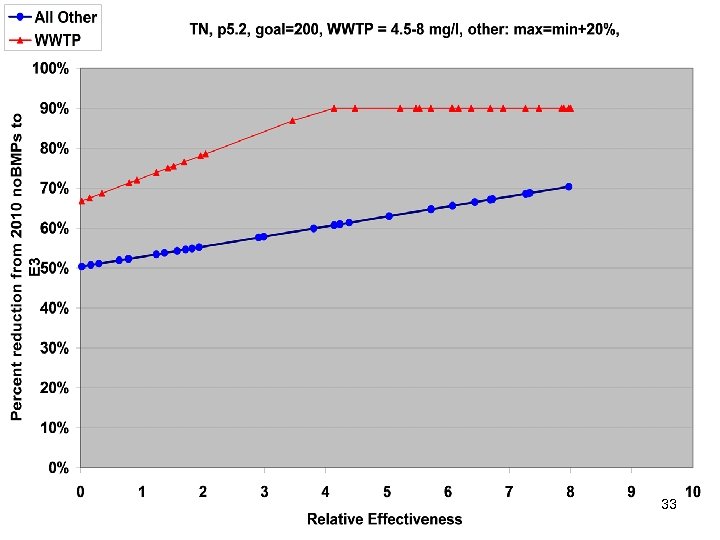
33
34
35
36
37
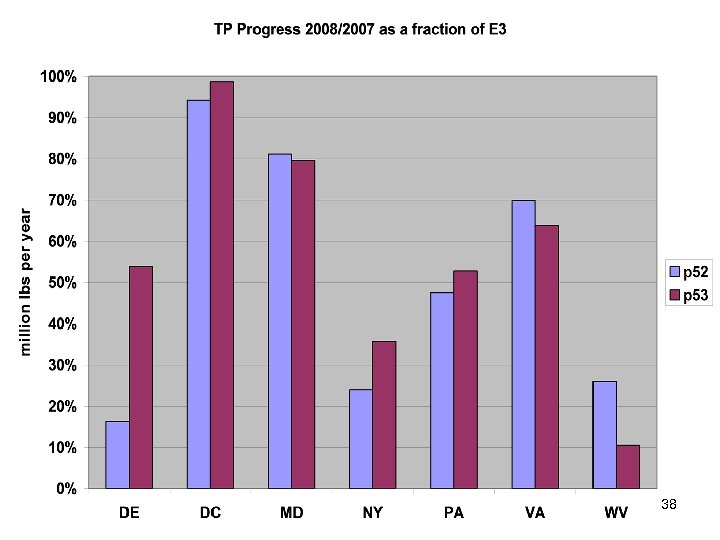
38
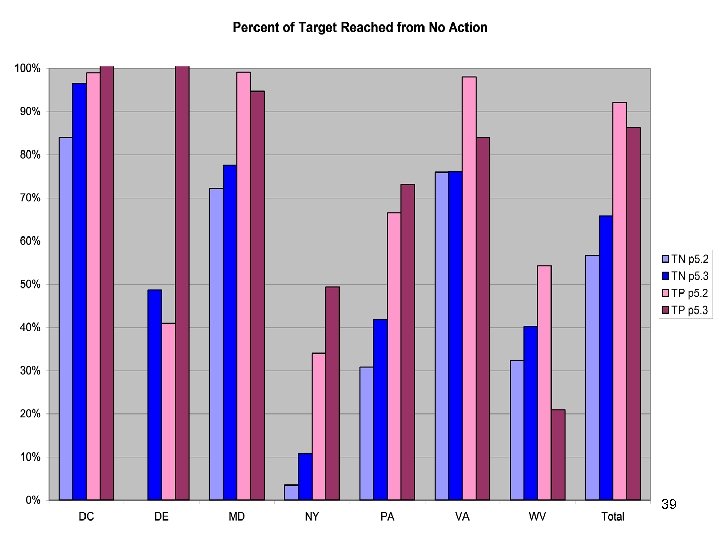
39

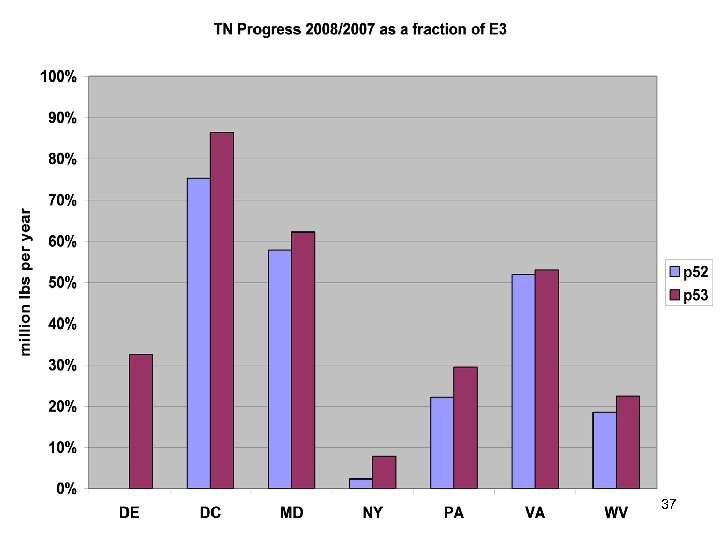
Additional Analyses before WQGIT • Investigate changes in progress for NY, DE, and WV • Verify that WWTP is correct • 2007 shows no progress for ESVA • Source contributions • . . . 40

Summary • Calibration method has been stable for years. • Scenario Builder is now producing reasonable input data • Phase 5. 3 calibration similar to phase 5. 2 – Point source based changes in Potomac and Patuxent – Coastal Plain changes in unmonitored area • Delivery Factors similar 41

Scenario Builder: Role, Documentation and Planned Continued Enhancements Chris Brosch Chesapeake Bay Program Nonpoint Source Analyst University of Maryland/CBPO 42
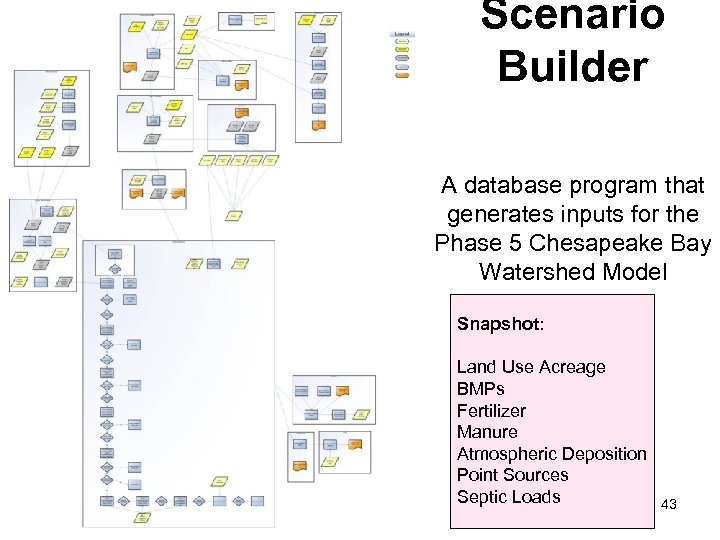
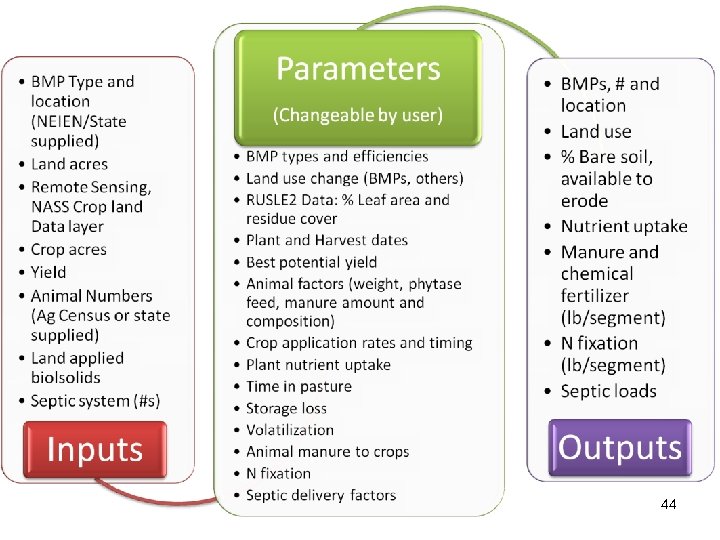
Scenario Builder A database program that generates inputs for the Phase 5 Chesapeake Bay Watershed Model Snapshot: Land Use Acreage BMPs Fertilizer Manure Atmospheric Deposition Point Sources Septic Loads 43
44

Scenario Builder Planned Enhancements • Version 2. 2 a: System Maintenance and Documentation Release – System documentation updated • Version 2. 3: Septic and Atmospheric Deposition – Add these are two new sub-systems • Version 2. 4: BMP Descriptions and Other BMP Files – Accessory BMP files that the model needs to process BMP data from Scenario Builder. – Input the Phase 5. 3 watershed model outputs • Version 2. 5: Improve Animal Waste Management System BMPs and Dead Birds – Both are being addressed by BMPs now—will be addressed more accurately • Version 2. 6: Wastewater Sub System – Will automate input data generation over 3, 000 facilities • Version 3: NEIEN Exchange – Conversion of NEIEN BMP exchange data into Scenario Builder formats. • Version 4: Data Products – Developing reports or other data products that will stream-line the process for states, locals and other partners/stakeholders to request information • Version 5: User Interface – Evolution of version 2. 2 User Interface for running “what if” scenarios 45

Scenario List • We have – – – 1985 (1985 and allocation air) 2007 (2007 and allocation air) (not final) 2010 No Action 2010 E 3 with N-based NM (not final) VA EPIL (not final) • Next Up – – – 1985 No Action 1985 E 3 2010 E 3 with P-based NM 2008 Trib Strategy 2009 WQGIT 46
e305138d91a49e53ee328005f49894b8.ppt