b1881709db82c53b33b879b429843897.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68

Pharmacological GLI 2 Inhibition Prevents Myofibroblast Cell-cycle Progression and Reduces Kidney Fibrosis J Clin Invest. 2015; 125(8): 2935 -2951. Speaker: Chung-te Liu Supervisor: Professor Chun-ming Shih, Professor Fen-Yen Lin, Professor Po-hsun Huang

Introduction • Kidney fibrosis is the common final pathway for nearly all progressive kidney diseases. • However, there are currently no approved drugs available to treat kidney fibrosis.
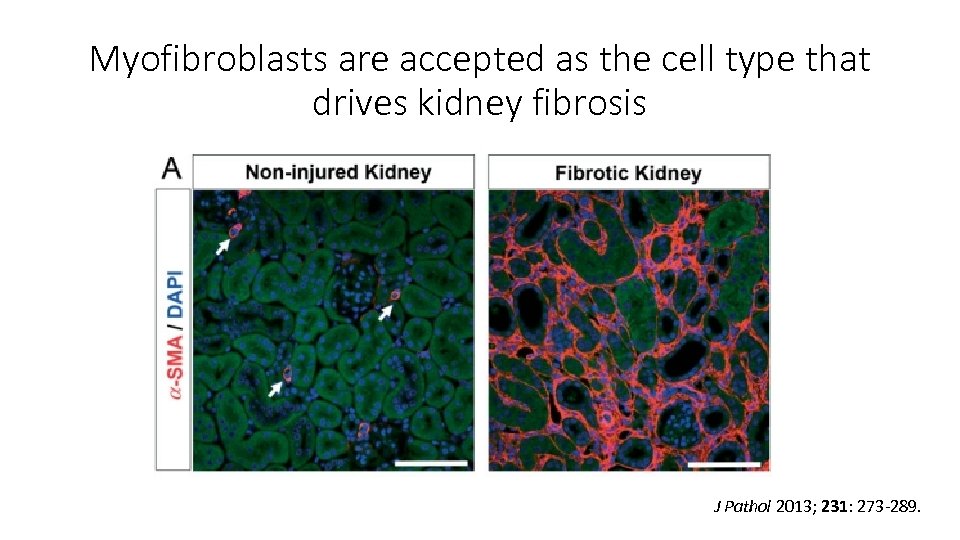
Myofibroblasts are accepted as the cell type that drives kidney fibrosis J Pathol 2013; 231: 273 -289.
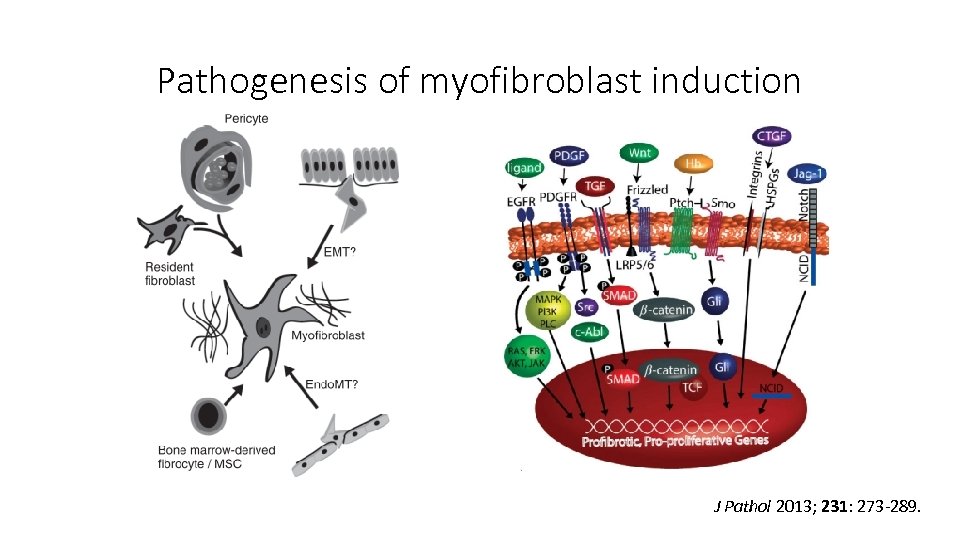
Pathogenesis of myofibroblast induction J Pathol 2013; 231: 273 -289.
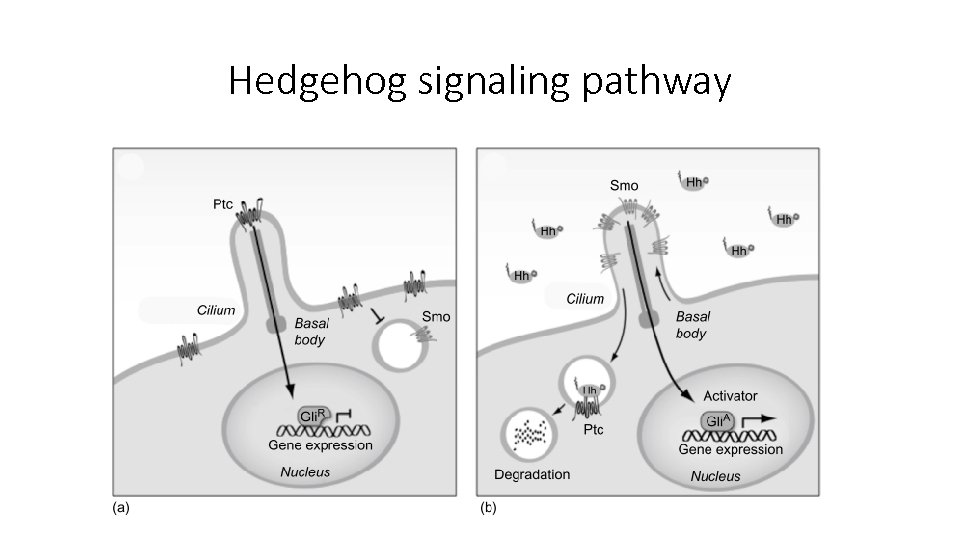
Hedgehog signaling pathway
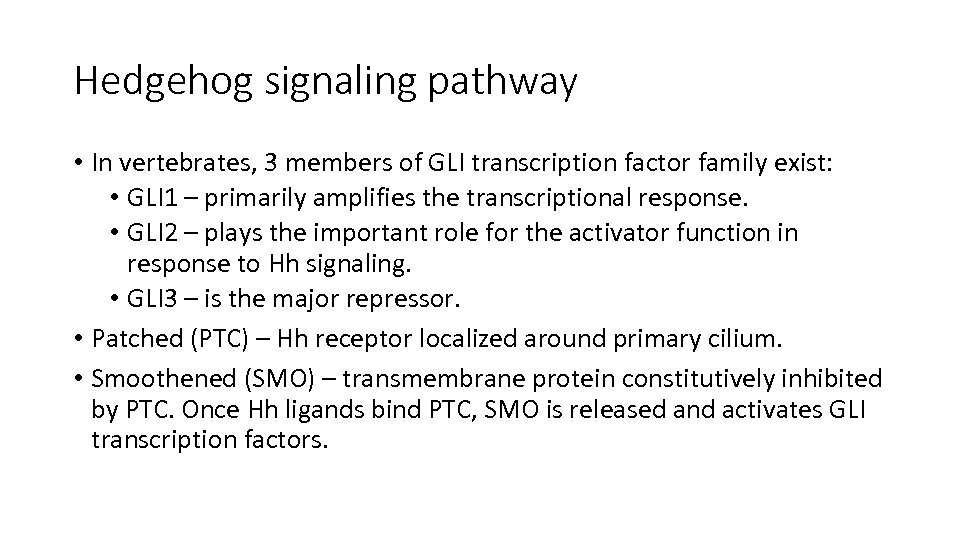
Hedgehog signaling pathway • In vertebrates, 3 members of GLI transcription factor family exist: • GLI 1 – primarily amplifies the transcriptional response. • GLI 2 – plays the important role for the activator function in response to Hh signaling. • GLI 3 – is the major repressor. • Patched (PTC) – Hh receptor localized around primary cilium. • Smoothened (SMO) – transmembrane protein constitutively inhibited by PTC. Once Hh ligands bind PTC, SMO is released and activates GLI transcription factors.
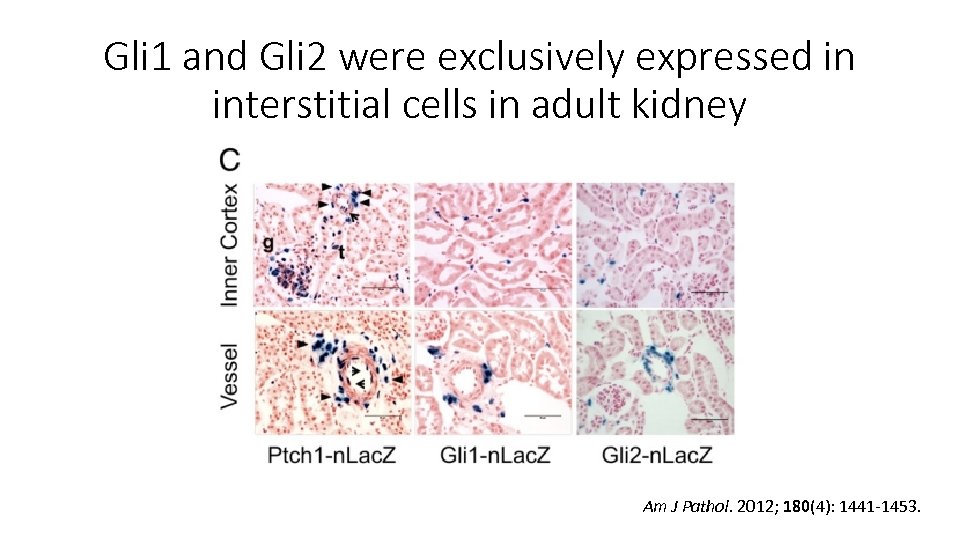
Gli 1 and Gli 2 were exclusively expressed in interstitial cells in adult kidney Am J Pathol. 2012; 180(4): 1441 -1453.
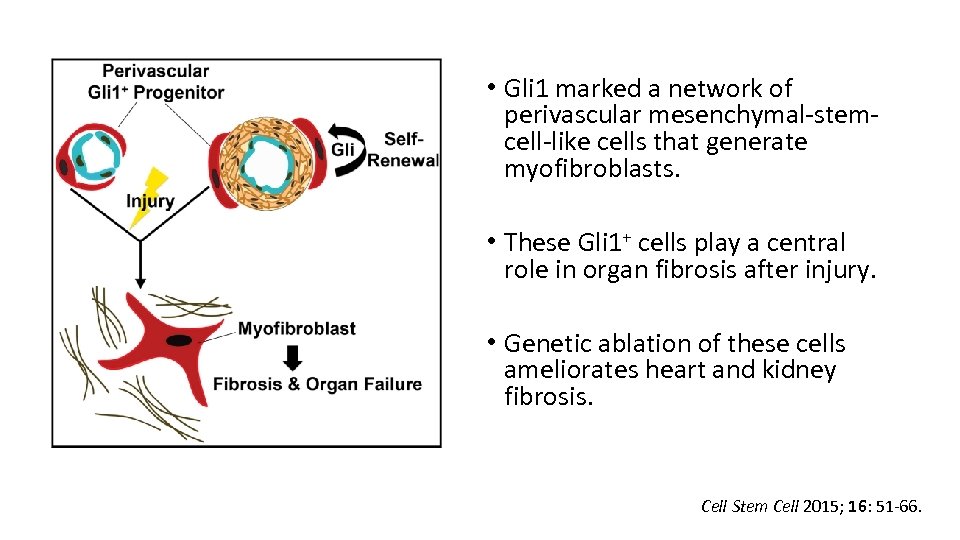
• Gli 1 marked a network of perivascular mesenchymal-stemcell-like cells that generate myofibroblasts. • These Gli 1+ cells play a central role in organ fibrosis after injury. • Genetic ablation of these cells ameliorates heart and kidney fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell 2015; 16: 51 -66.

Aim of the study • Given the specific expression of GLI 1 and GLI 2 in myofibroblast and their precursors and the possibility of activation of GLI proteins by known profibrotic pathways, this study investigate the role of GLI 1 and GLI 2 myofibroblast.
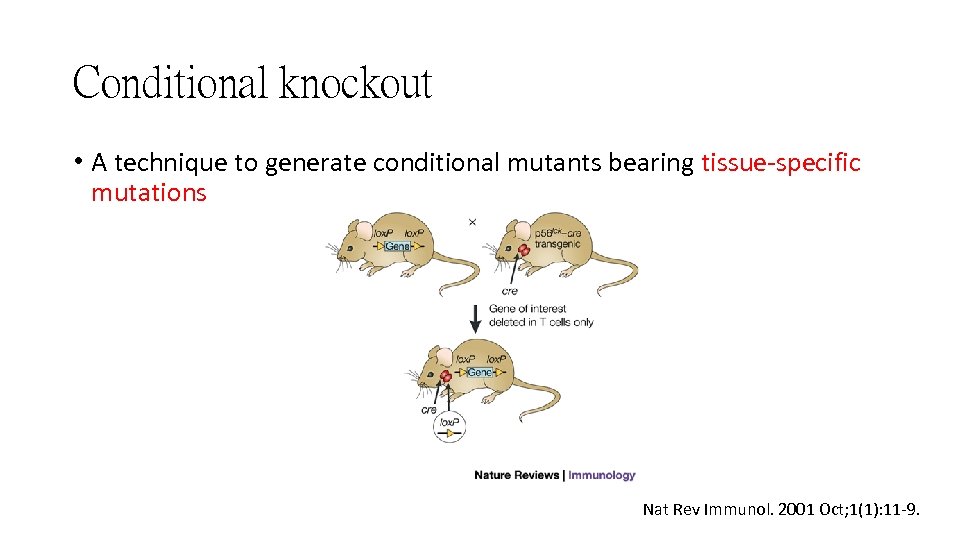
Conditional knockout • A technique to generate conditional mutants bearing tissue-specific mutations Nat Rev Immunol. 2001 Oct; 1(1): 11 -9.
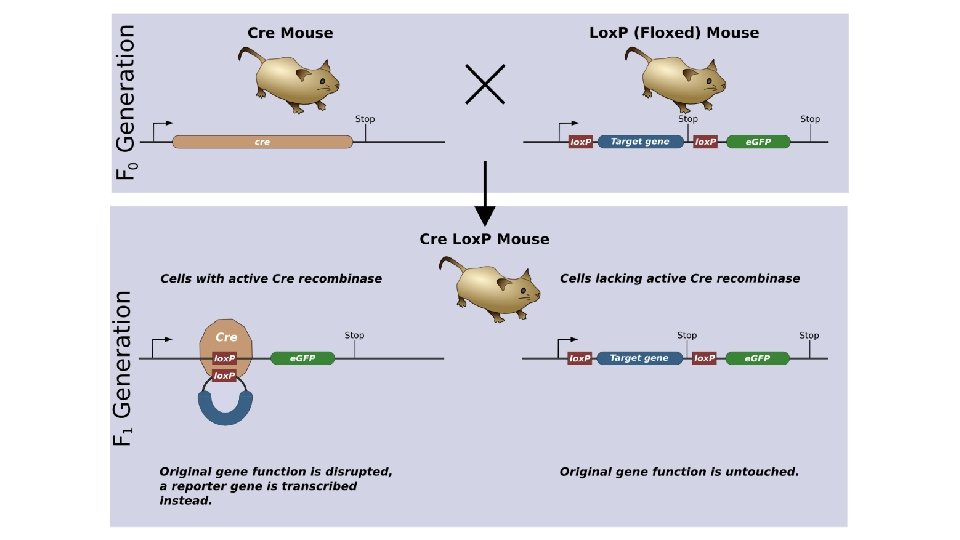
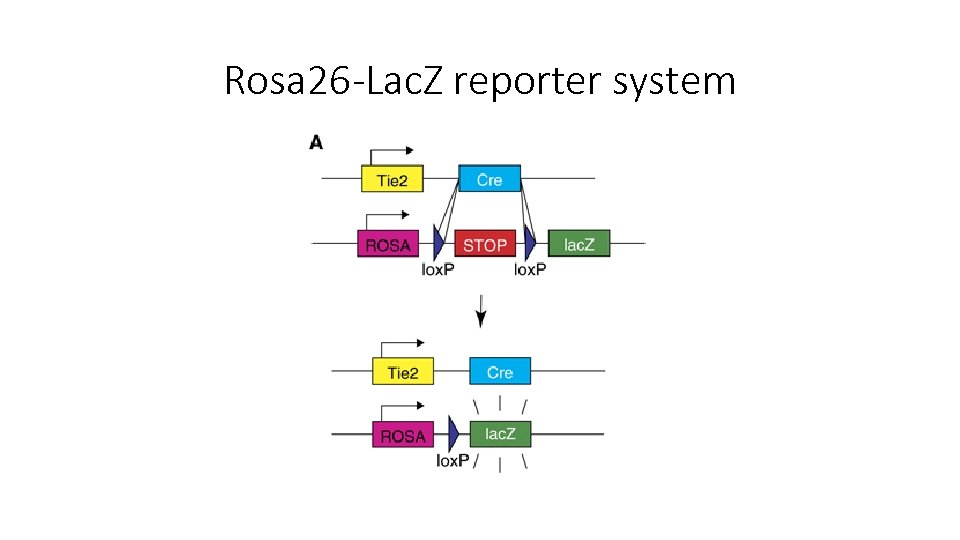
Rosa 26 -Lac. Z reporter system
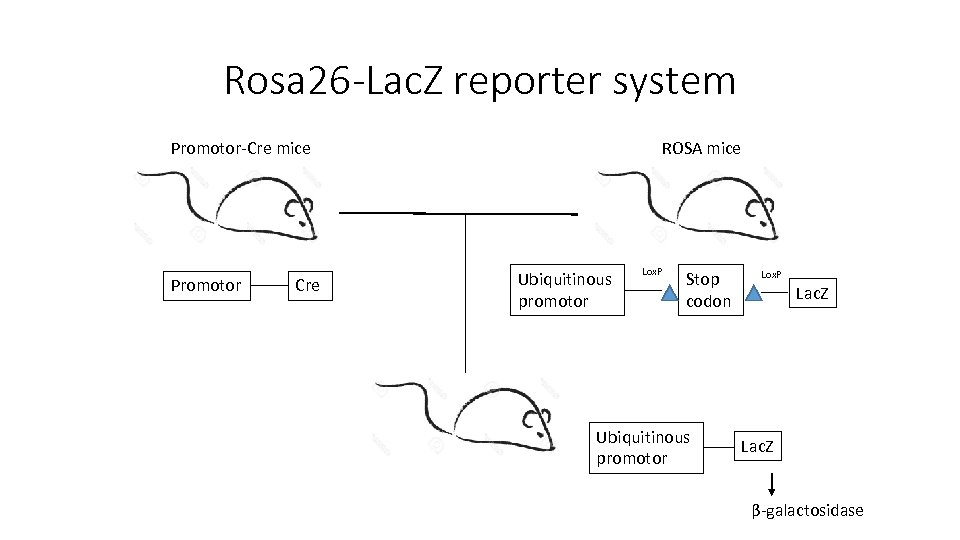
Rosa 26 -Lac. Z reporter system Promotor-Cre mice Promotor Cre ROSA mice Ubiquitinous promotor Lox. P Stop codon Ubiquitinous promotor Lox. P Lac. Z β-galactosidase
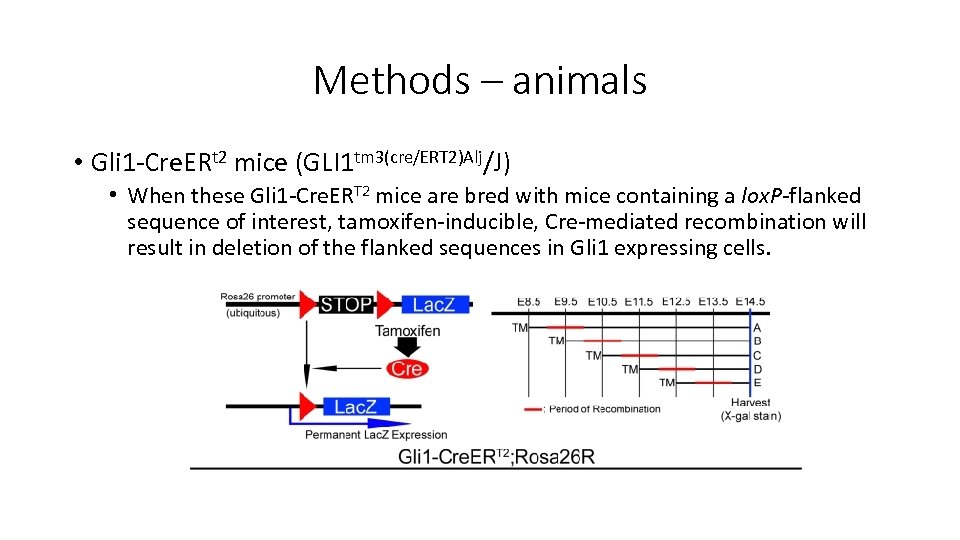
Methods – animals • Gli 1 -Cre. ERt 2 mice (GLI 1 tm 3(cre/ERT 2)Alj/J) • When these Gli 1 -Cre. ERT 2 mice are bred with mice containing a lox. P-flanked sequence of interest, tamoxifen-inducible, Cre-mediated recombination will result in deletion of the flanked sequences in Gli 1 expressing cells.

Methods – animals • Gli 3 T (Gt(ROSA)26 Sor tm 3(GLI 3)Amc /J) • These Rosa. Gli 3 TFlag c/c mice contain a floxed-neomycin resistance (neo) cassette and polyadenylation signal, c. DNA encoding a FLAG-tagged Gli 3 repressor gene, an internal ribosome entry site (IRES), and a Venus yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) under control of the ubiquitous Gt(ROSA)26 Sor locus.

Methods – animals • Gli 1 n. Lac. Z • This lac. Z reporter mutant mice harbor a β-galactosidase "knock-in" mutation that also abolishes endogenous Gli 1 gene function. • Gli 2 n. Lac. Z • Mice homozygous for this Gli 2 lzki allele harbor a β-galactosidase "knock-in" (lzki) mutation that also abolishes endogenous Gli 2 gene function. • Gli 2 floxed (GLI 2 tm 6 ALj /J) • C 57 Bl/6 J as wild type and background

Methods – animals • Gli 1 -KO mice • generated from homozygous Gli 1 -Cre. ER t 2 mice • by breeding heterozygous Gli 1 n. Lac. Z/+

Pharmacological inhibition of GLI • Darinaparsin (S-dimethylarsino-glutathione) • Arsenic trioxide (ATO) is used clinically to reat promyelocytic leukemia and was recently known to antagonize both GLI 1 and GLI 2. • Darinaparsin is a novel arsenic-based drug with favorable systemic toxicity profile and is currently undergoing clinical studies. • GANT 61 is a small-molecule inhibitor of GLI that had been shown to ameliorate renal fibrosis in mice.
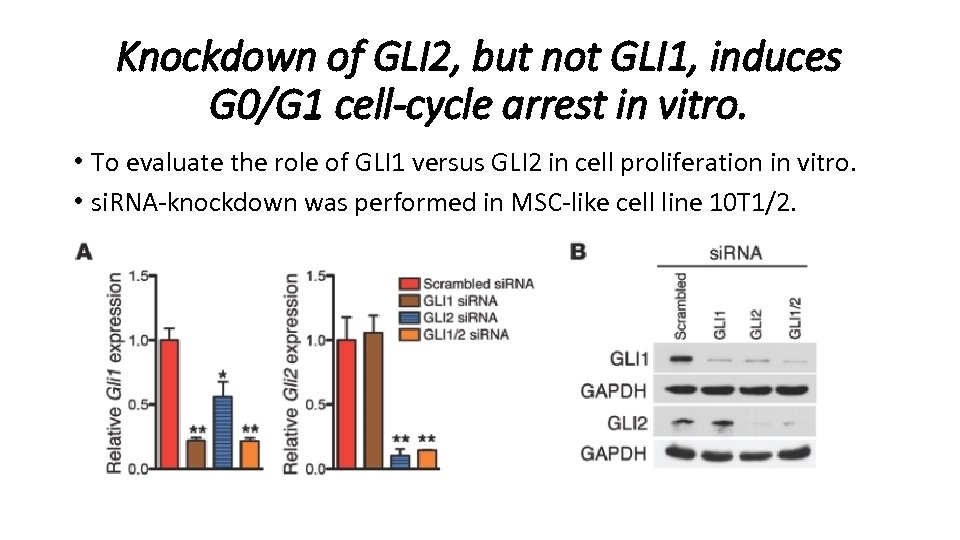
Knockdown of GLI 2, but not GLI 1, induces G 0/G 1 cell-cycle arrest in vitro. • To evaluate the role of GLI 1 versus GLI 2 in cell proliferation in vitro. • si. RNA-knockdown was performed in MSC-like cell line 10 T 1/2.
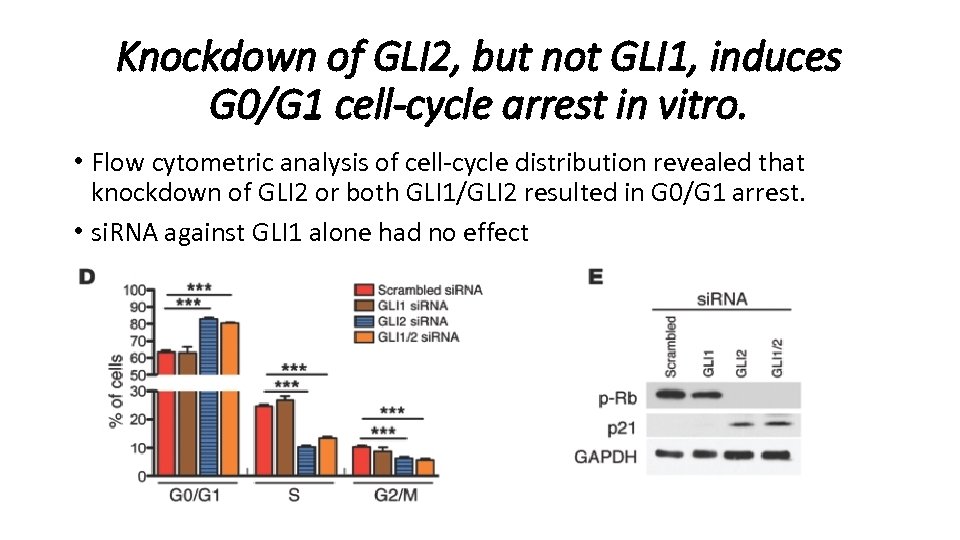
Knockdown of GLI 2, but not GLI 1, induces G 0/G 1 cell-cycle arrest in vitro. • Flow cytometric analysis of cell-cycle distribution revealed that knockdown of GLI 2 or both GLI 1/GLI 2 resulted in G 0/G 1 arrest. • si. RNA against GLI 1 alone had no effect

Overexpression of GLI 2 drives cell proliferation • Overexpression of GLI 2 was induced by delivery of retrovirus to rescue si. RNA knockdown of GLI 2.

Conditional KO of Gli 2 or overexpression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI 1+ cells reduces kidney fibrosis, but KO of GLI 1 has no effect. • Unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) expreriments in Gli 1 n. Lac. Z and Gli 2 n. Lac. Z mice costaining for α-SMA and β-gal confirmed that expression of GLI 1 and GLI 2 is restricted to myofibroblast. • Endogenous GLI 1 and GLI 2 protein were upregulated after kidney injury.


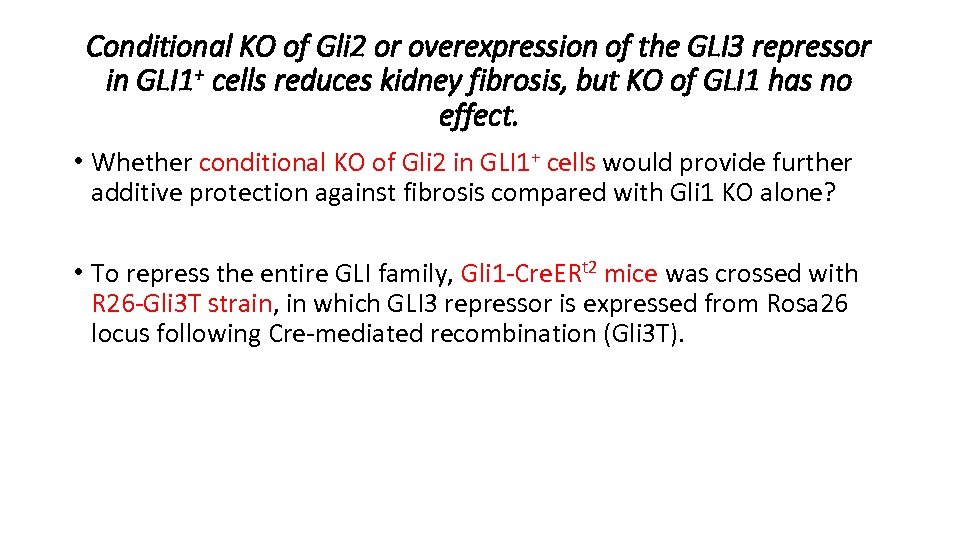
Conditional KO of Gli 2 or overexpression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI 1+ cells reduces kidney fibrosis, but KO of GLI 1 has no effect. • Whether conditional KO of Gli 2 in GLI 1+ cells would provide further additive protection against fibrosis compared with Gli 1 KO alone? • To repress the entire GLI family, Gli 1 -Cre. ERt 2 mice was crossed with R 26 -Gli 3 T strain, in which GLI 3 repressor is expressed from Rosa 26 locus following Cre-mediated recombination (Gli 3 T).
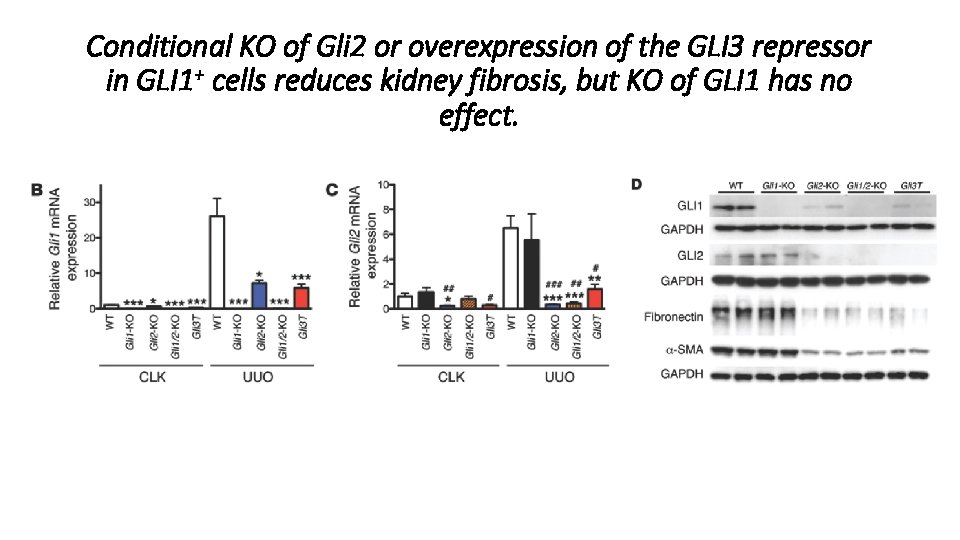
Conditional KO of Gli 2 or overexpression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI 1+ cells reduces kidney fibrosis, but KO of GLI 1 has no effect.
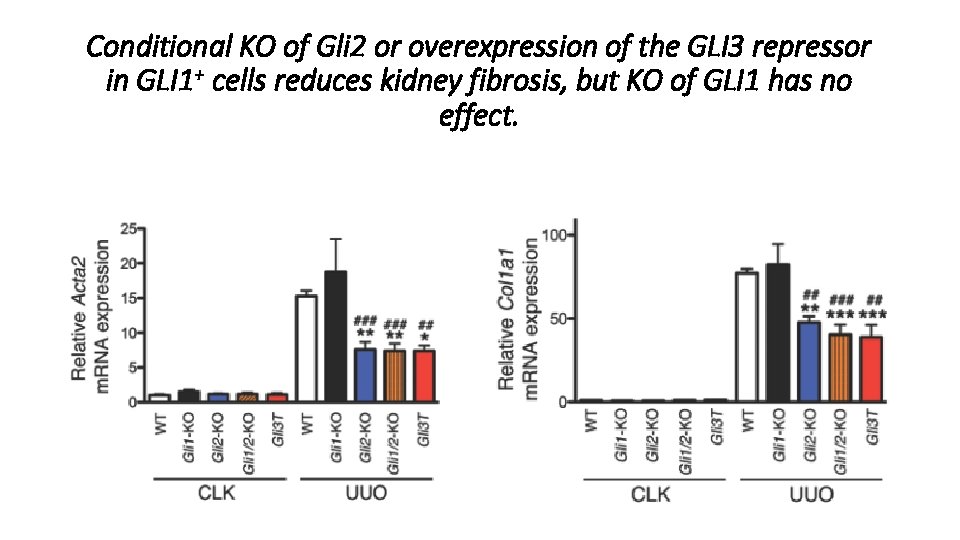
Conditional KO of Gli 2 or overexpression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI 1+ cells reduces kidney fibrosis, but KO of GLI 1 has no effect.
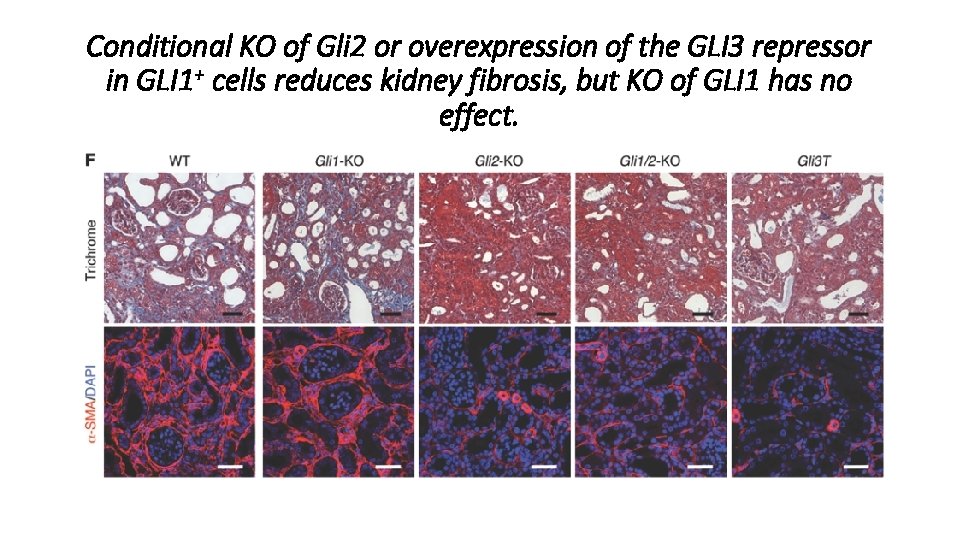
Conditional KO of Gli 2 or overexpression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI 1+ cells reduces kidney fibrosis, but KO of GLI 1 has no effect.
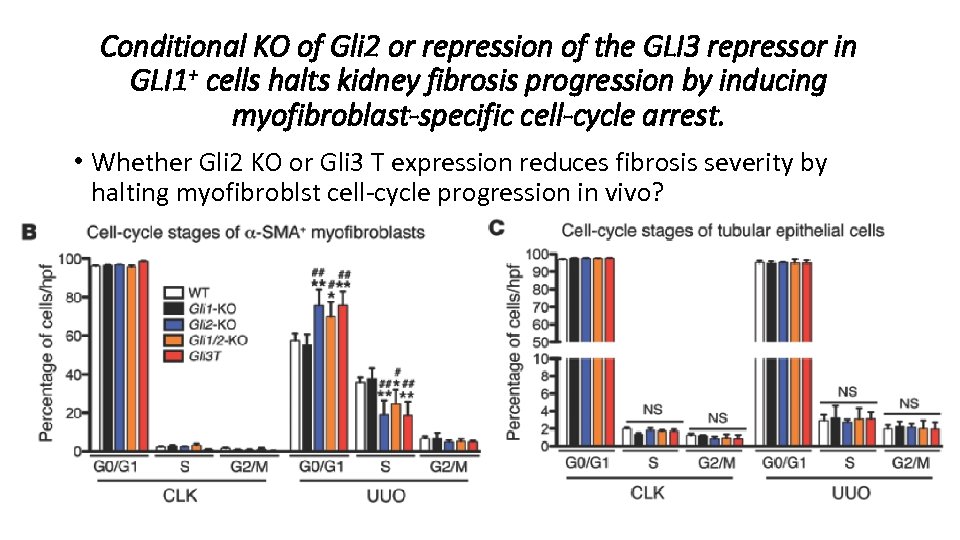
Conditional KO of Gli 2 or repression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI 1+ cells halts kidney fibrosis progression by inducing myofibroblast-specific cell-cycle arrest. • Whether Gli 2 KO or Gli 3 T expression reduces fibrosis severity by halting myofibroblst cell-cycle progression in vivo?
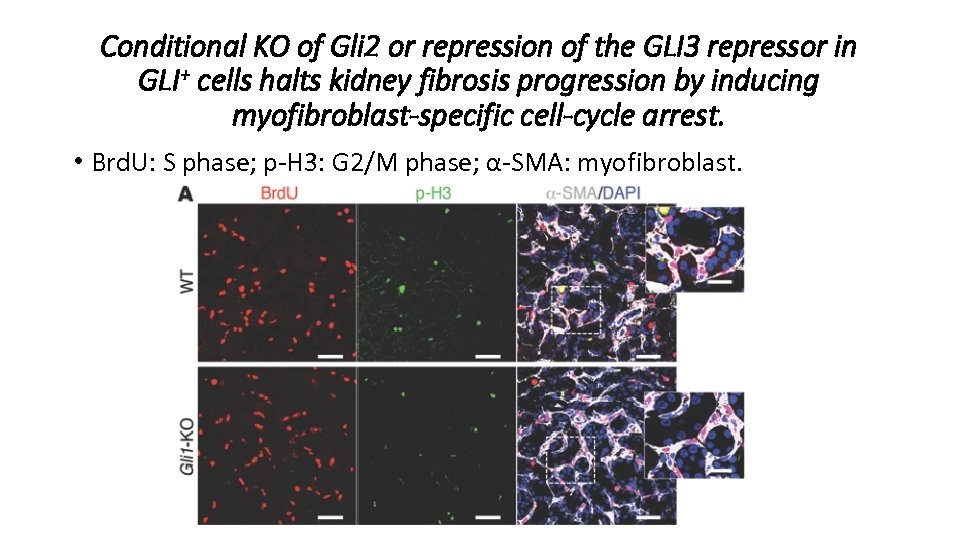
Conditional KO of Gli 2 or repression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI+ cells halts kidney fibrosis progression by inducing myofibroblast-specific cell-cycle arrest. • Brd. U: S phase; p-H 3: G 2/M phase; α-SMA: myofibroblast.
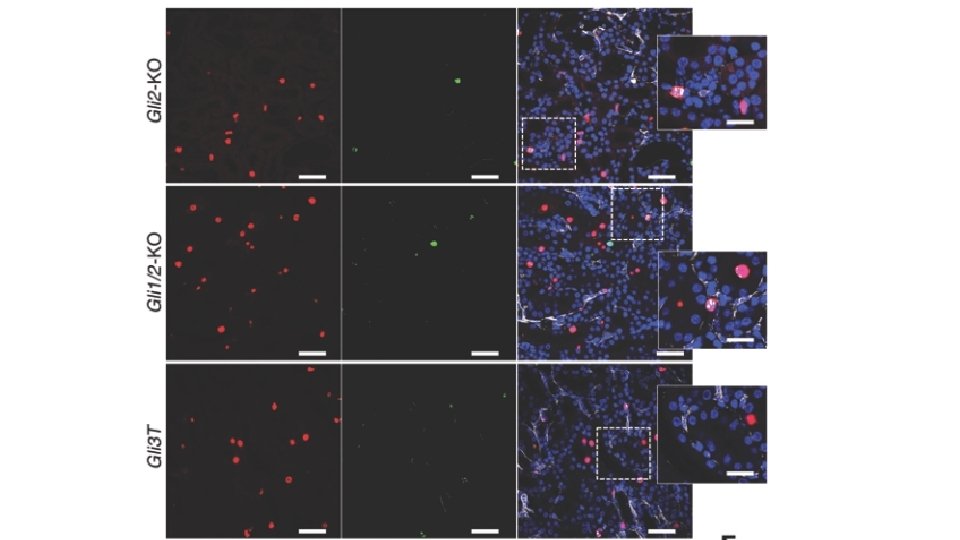
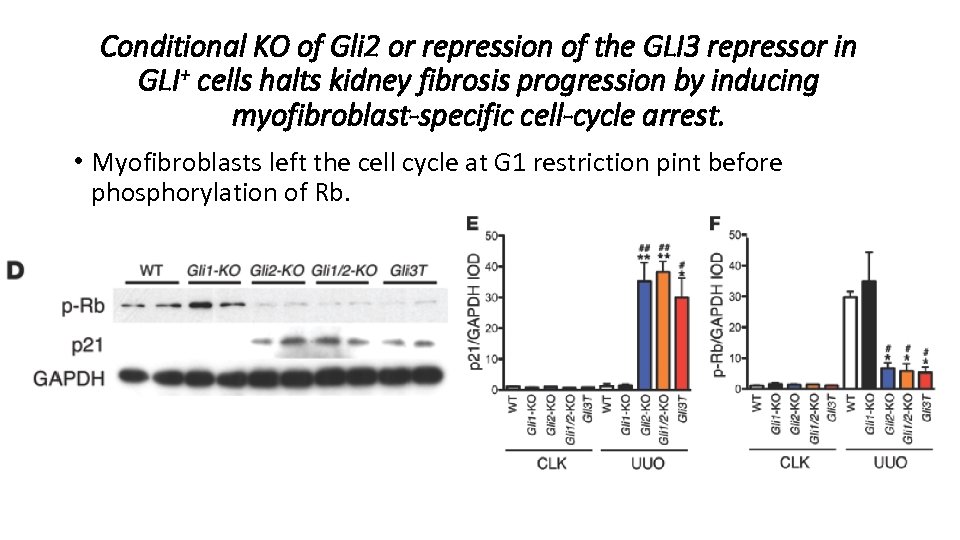
Conditional KO of Gli 2 or repression of the GLI 3 repressor in GLI+ cells halts kidney fibrosis progression by inducing myofibroblast-specific cell-cycle arrest. • Myofibroblasts left the cell cycle at G 1 restriction pint before phosphorylation of Rb.
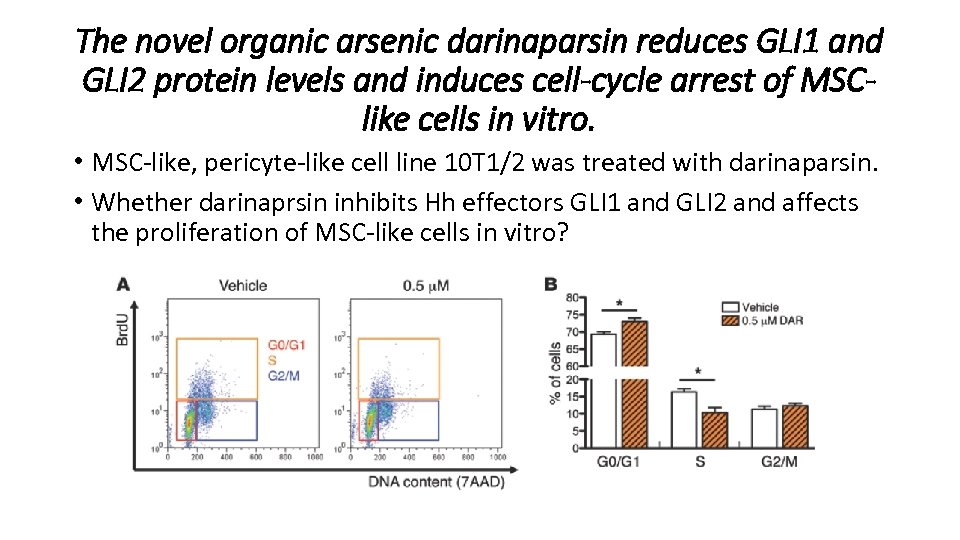
The novel organic arsenic darinaparsin reduces GLI 1 and GLI 2 protein levels and induces cell-cycle arrest of MSClike cells in vitro. • MSC-like, pericyte-like cell line 10 T 1/2 was treated with darinaparsin. • Whether darinaprsin inhibits Hh effectors GLI 1 and GLI 2 and affects the proliferation of MSC-like cells in vitro?
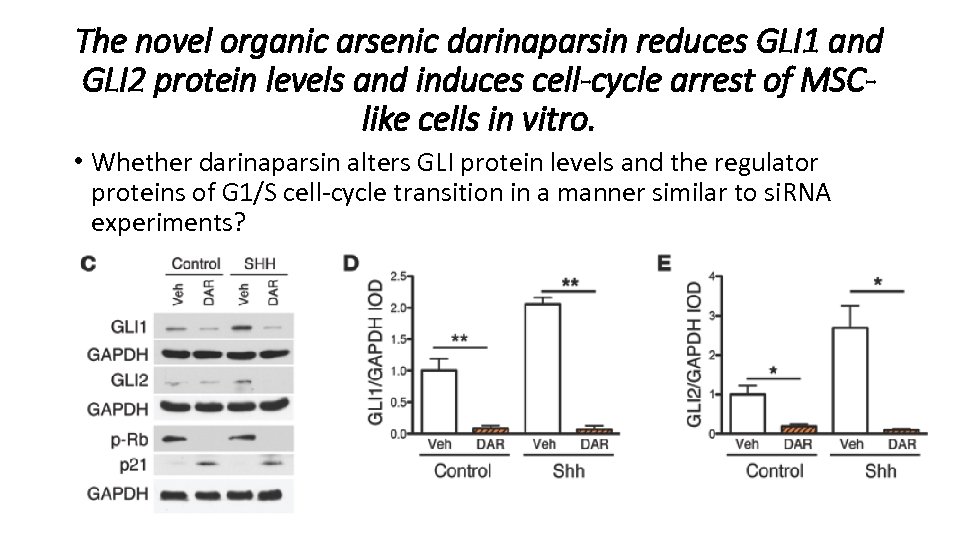
The novel organic arsenic darinaparsin reduces GLI 1 and GLI 2 protein levels and induces cell-cycle arrest of MSClike cells in vitro. • Whether darinaparsin alters GLI protein levels and the regulator proteins of G 1/S cell-cycle transition in a manner similar to si. RNA experiments?

The novel organic arsenic darinaparsin reduces GLI 1 and GLI 2 protein levels and induces cell-cycle arrest of MSClike cells in vitro. • Darinaparsin decreased Gli 1 m. RNA, but Gli 2 m. RNA levels remained unchanged, suggesting an effect of darinaparsin in GLI 2 protein stability.
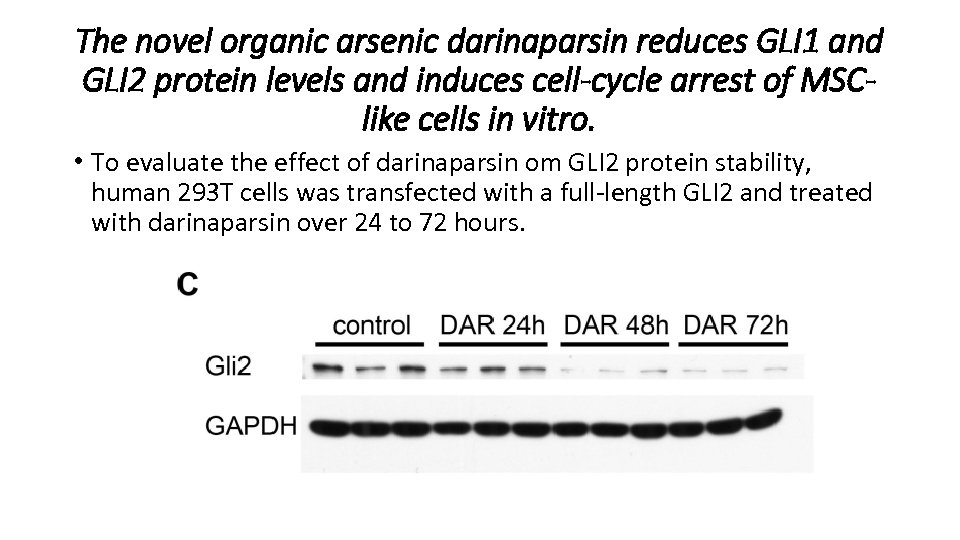
The novel organic arsenic darinaparsin reduces GLI 1 and GLI 2 protein levels and induces cell-cycle arrest of MSClike cells in vitro. • To evaluate the effect of darinaparsin om GLI 2 protein stability, human 293 T cells was transfected with a full-length GLI 2 and treated with darinaparsin over 24 to 72 hours.

Overexpression of GLI 2 rescue the cell-cycle inhibitory effect of darinaparsin. • Whether overexpression of GLI 2 was sufficient to rescue the inhibitory effect of darsinaparsin? • GLI 2 was overexpressed in 10 T 1/2 cells delivered retrovirally.

Co-IP suggests that darinaparsin might bind GLI 2 in vitro • Arsenic has been proposed to bind to thiol groups on cysteine residues in the GLI zinc finger domains. • Myc-tagged GLI 2 (p. CS 2 -MT GLI 2 FL) and myc-tagged e. GFP (p. EGFP-C 1 myc, as a control protein) were overexpressed in human 293 T cells. • The cells were treated with 0. 5μM darinaparsin or vehicle, and the cell lysate was incubated with glutathione-S-transferase (GST) agarose beads. • GST would bind the glutathione and pull down daripanarsin and proteins binding to it.
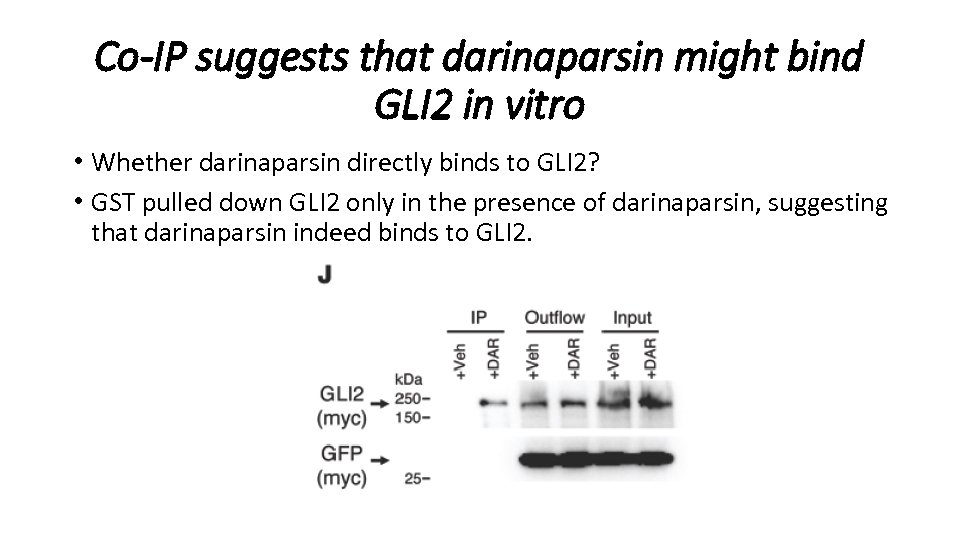
Co-IP suggests that darinaparsin might bind GLI 2 in vitro • Whether darinaparsin directly binds to GLI 2? • GST pulled down GLI 2 only in the presence of darinaparsin, suggesting that darinaparsin indeed binds to GLI 2.
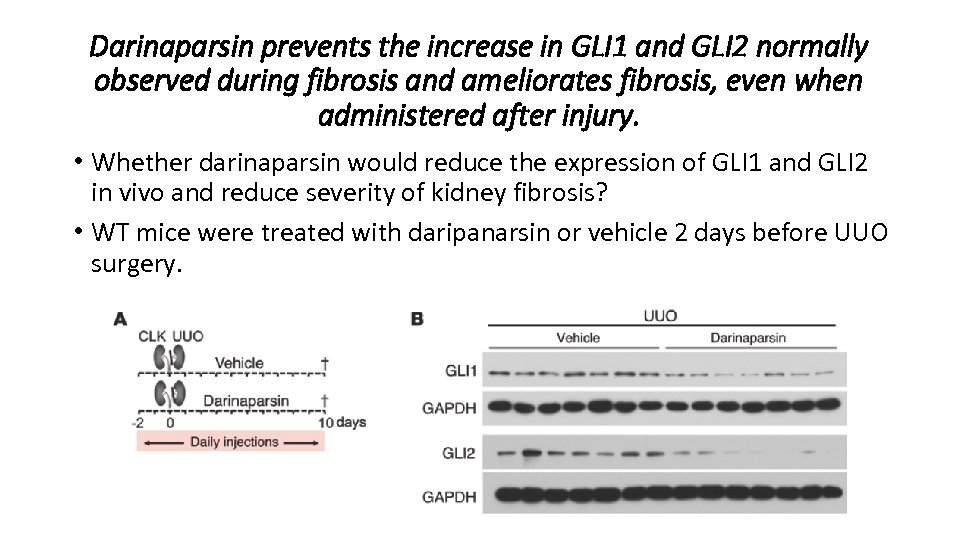
Darinaparsin prevents the increase in GLI 1 and GLI 2 normally observed during fibrosis and ameliorates fibrosis, even when administered after injury. • Whether darinaparsin would reduce the expression of GLI 1 and GLI 2 in vivo and reduce severity of kidney fibrosis? • WT mice were treated with daripanarsin or vehicle 2 days before UUO surgery.
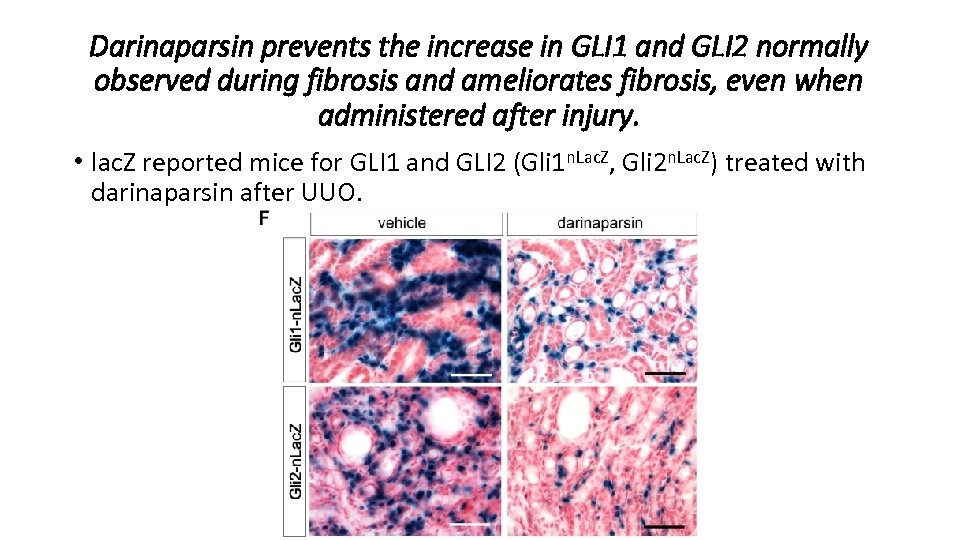
Darinaparsin prevents the increase in GLI 1 and GLI 2 normally observed during fibrosis and ameliorates fibrosis, even when administered after injury. • lac. Z reported mice for GLI 1 and GLI 2 (Gli 1 n. Lac. Z, Gli 2 n. Lac. Z) treated with darinaparsin after UUO.
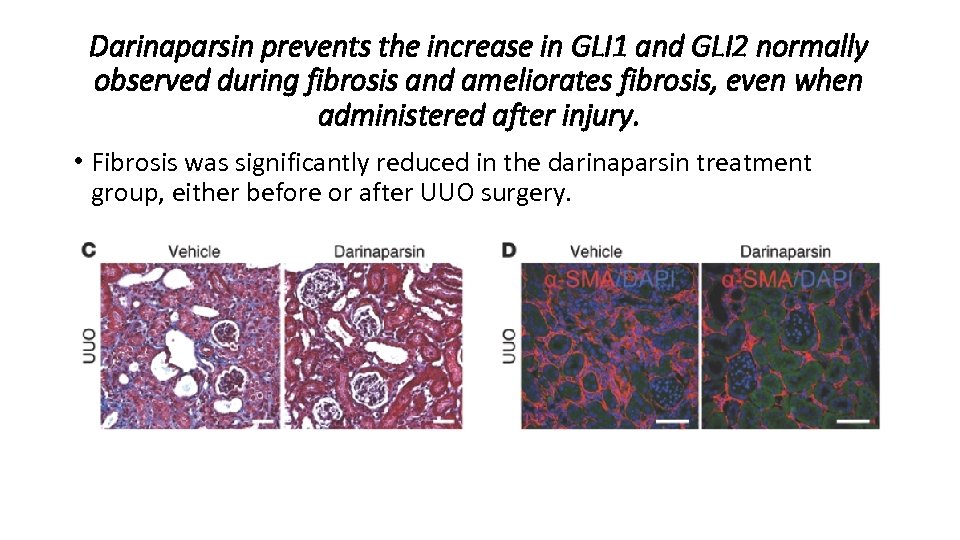
Darinaparsin prevents the increase in GLI 1 and GLI 2 normally observed during fibrosis and ameliorates fibrosis, even when administered after injury. • Fibrosis was significantly reduced in the darinaparsin treatment group, either before or after UUO surgery.
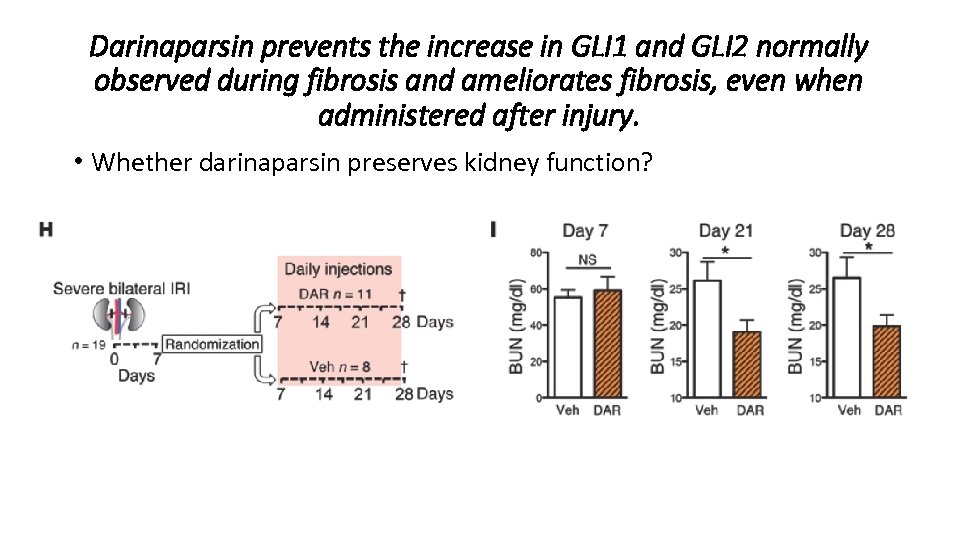
Darinaparsin prevents the increase in GLI 1 and GLI 2 normally observed during fibrosis and ameliorates fibrosis, even when administered after injury. • Whether darinaparsin preserves kidney function?
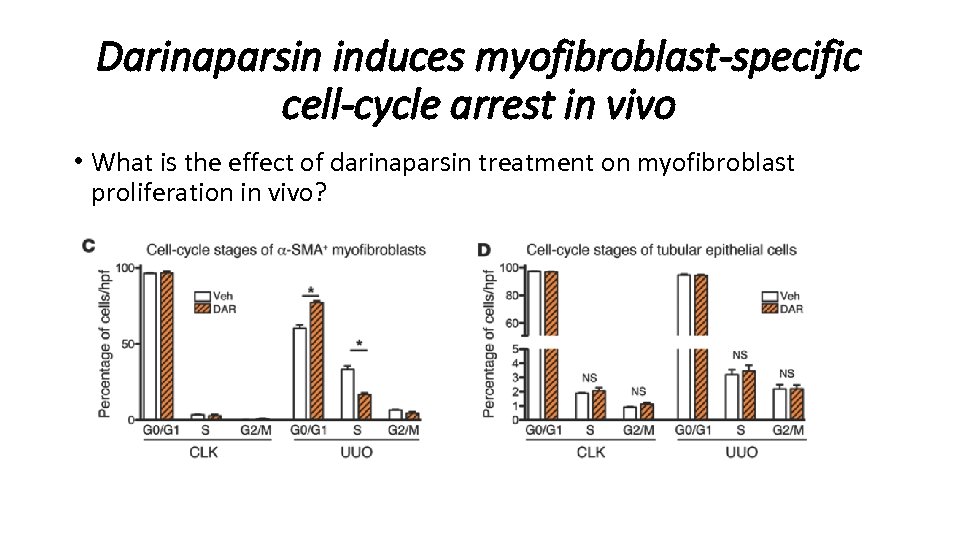
Darinaparsin induces myofibroblast-specific cell-cycle arrest in vivo • What is the effect of darinaparsin treatment on myofibroblast proliferation in vivo?
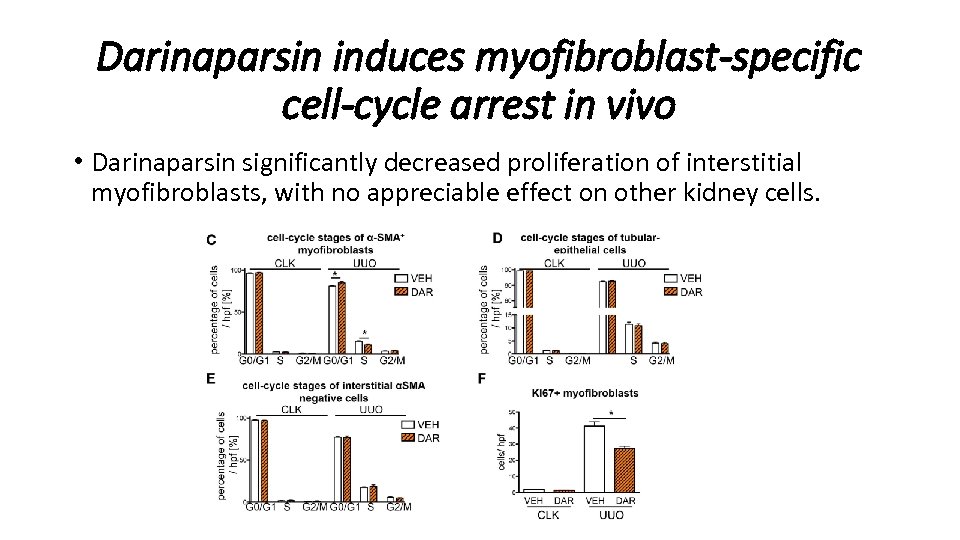
Darinaparsin induces myofibroblast-specific cell-cycle arrest in vivo • Darinaparsin significantly decreased proliferation of interstitial myofibroblasts, with no appreciable effect on other kidney cells.
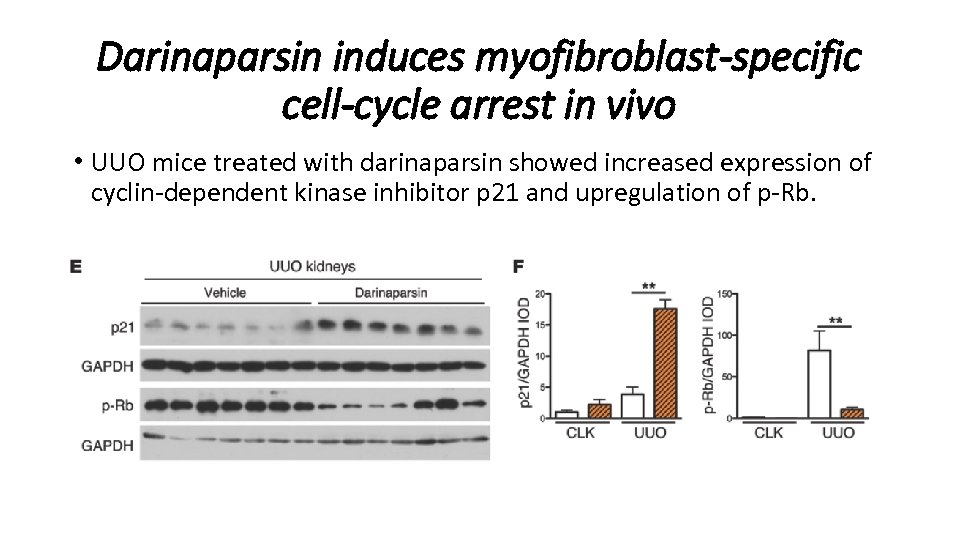
Darinaparsin induces myofibroblast-specific cell-cycle arrest in vivo • UUO mice treated with darinaparsin showed increased expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p 21 and upregulation of p-Rb.
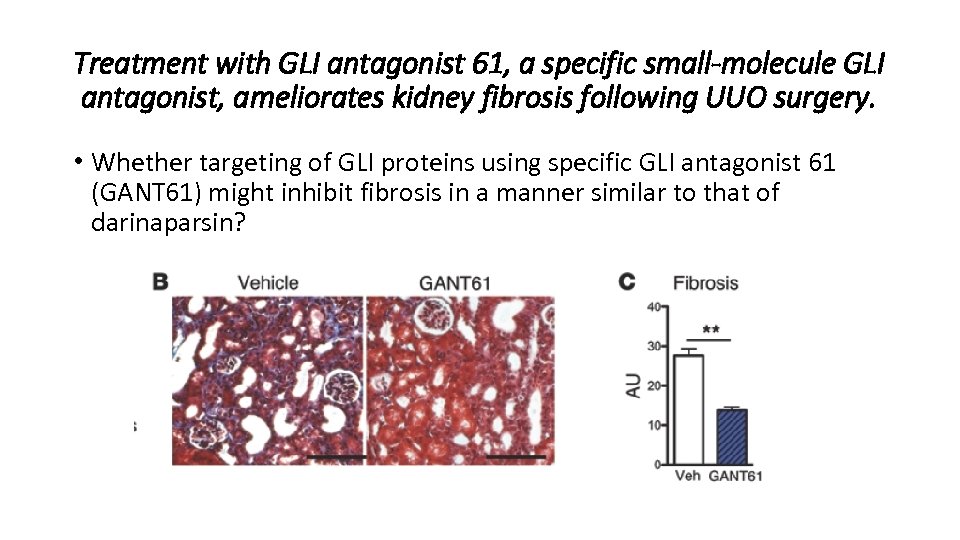
Treatment with GLI antagonist 61, a specific small-molecule GLI antagonist, ameliorates kidney fibrosis following UUO surgery. • Whether targeting of GLI proteins using specific GLI antagonist 61 (GANT 61) might inhibit fibrosis in a manner similar to that of darinaparsin?
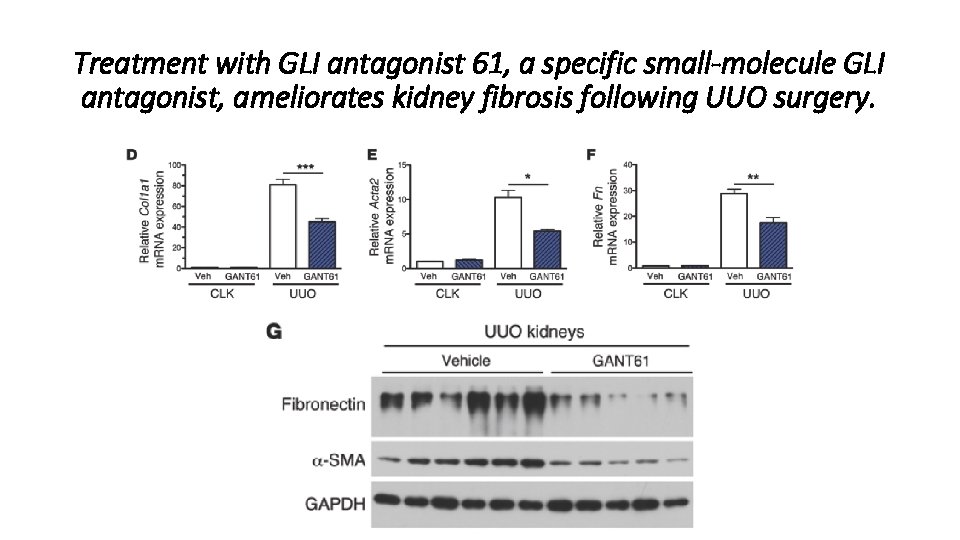
Treatment with GLI antagonist 61, a specific small-molecule GLI antagonist, ameliorates kidney fibrosis following UUO surgery.
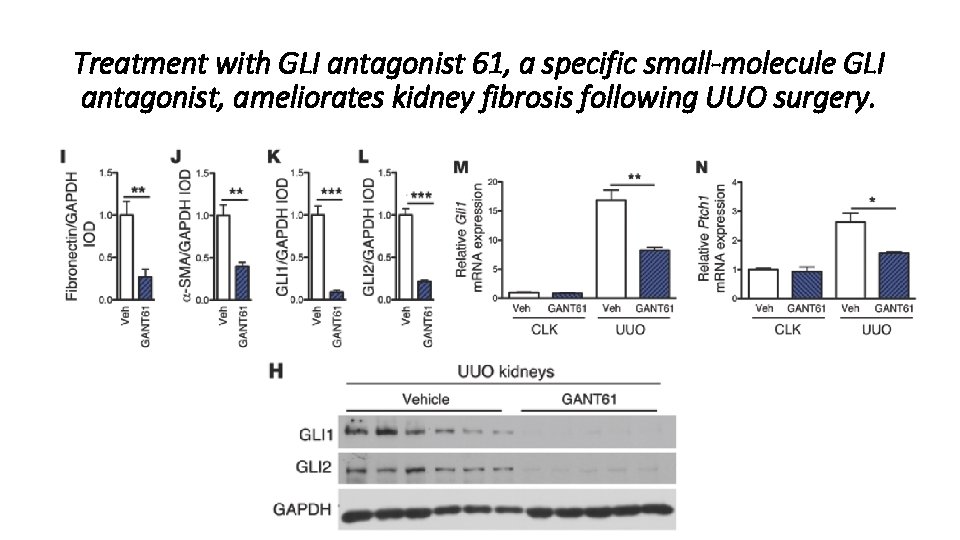
Treatment with GLI antagonist 61, a specific small-molecule GLI antagonist, ameliorates kidney fibrosis following UUO surgery.
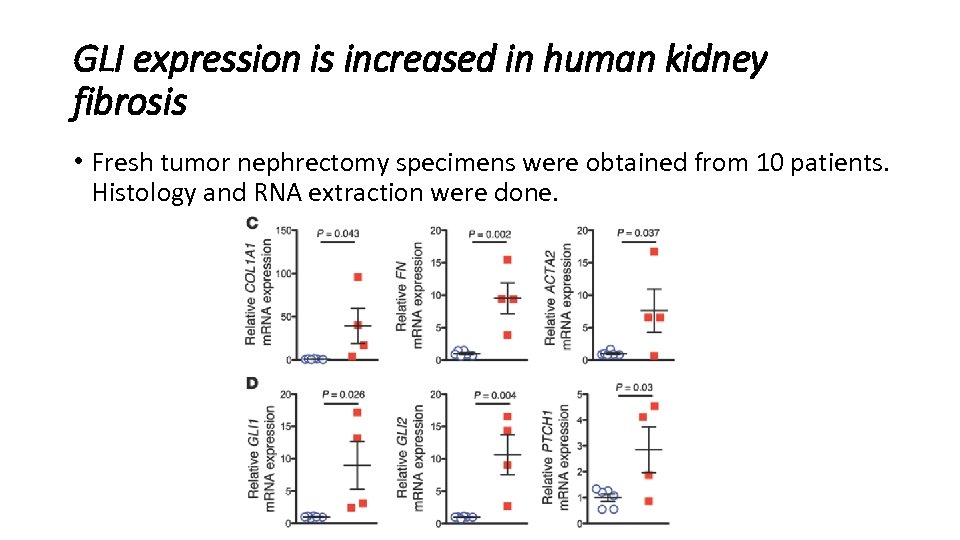
GLI expression is increased in human kidney fibrosis • Fresh tumor nephrectomy specimens were obtained from 10 patients. Histology and RNA extraction were done.
Conclusion • GLI 2 plays a critical functional role in regulating the proliferation of myofibroblasts in the pathogenesis of kidney fibrosis. • Conditional KO of GLI 2 or overexpression of GLI 3 repressor in GLI 1+ cells ameliorates kidney fibrosis by inducing myofibroblast-specific cell-cycle arrest. • GLI 2 inhibition via darinaparsin exhibited the same myofibroblastspecific cell-cycle arrest effect.

Role of FGF 21 in Arteriovenous Fistula Neointimal Hyperplasia
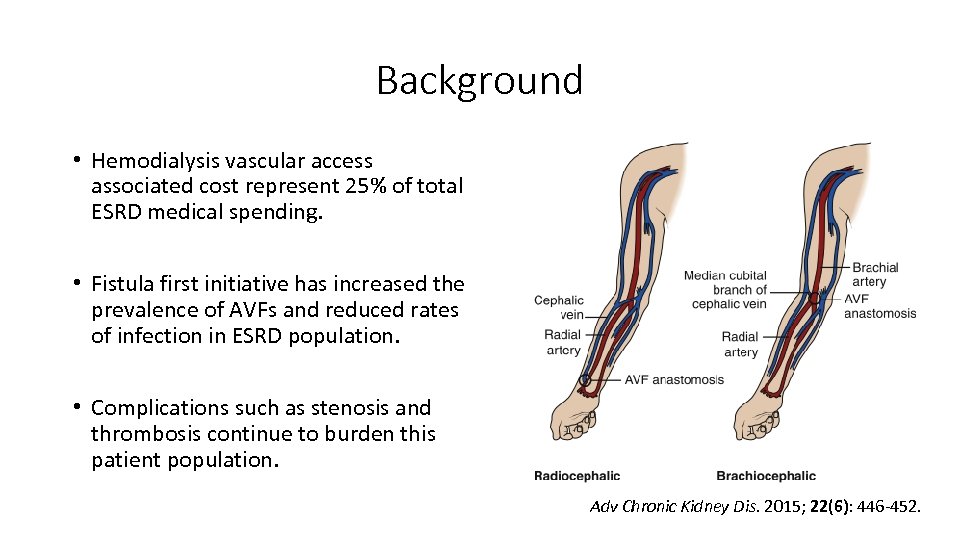
Background • Hemodialysis vascular access associated cost represent 25% of total ESRD medical spending. • Fistula first initiative has increased the prevalence of AVFs and reduced rates of infection in ESRD population. • Complications such as stenosis and thrombosis continue to burden this patient population. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015; 22(6): 446 -452.
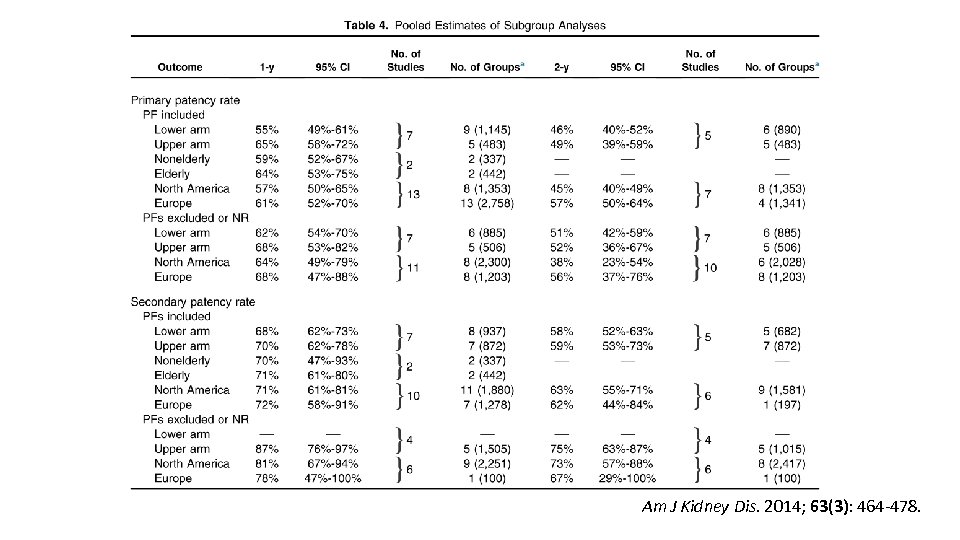
Am J Kidney Dis. 2014; 63(3): 464 -478.
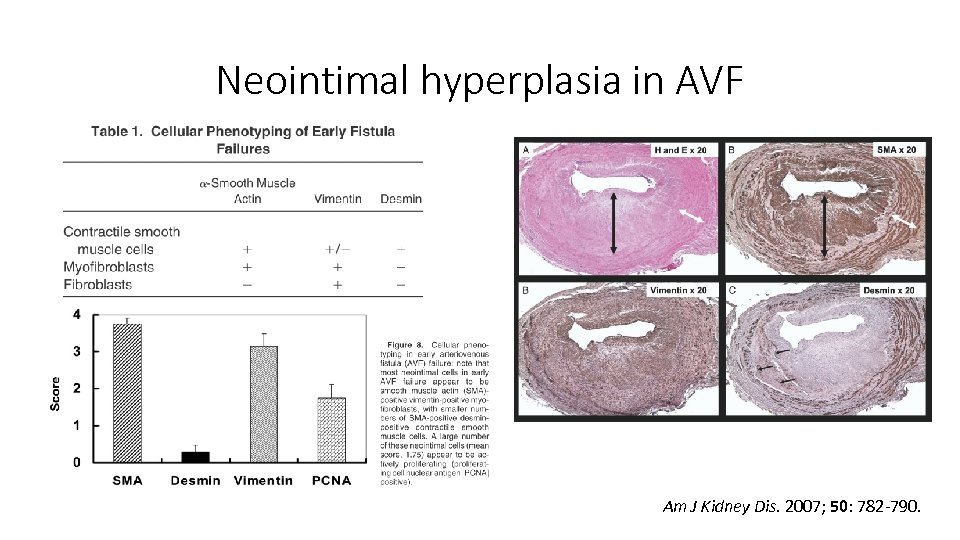
Neointimal hyperplasia in AVF Am J Kidney Dis. 2007; 50: 782 -790.
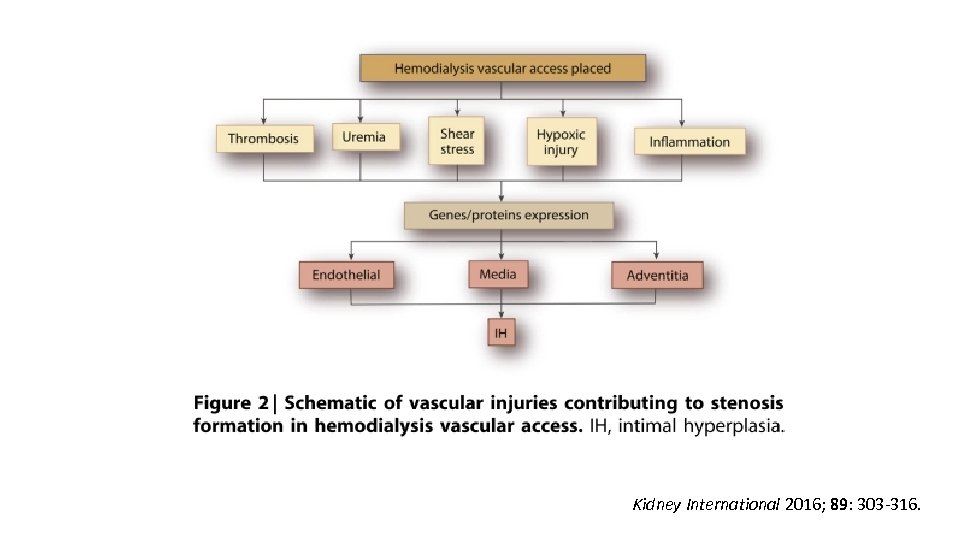
Kidney International 2016; 89: 303 -316.
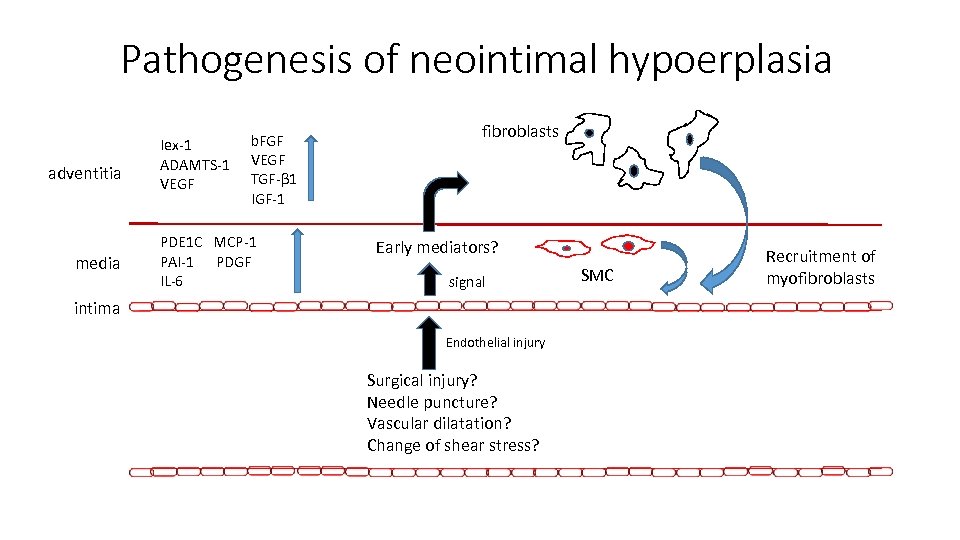
Pathogenesis of neointimal hypoerplasia adventitia media Iex-1 ADAMTS-1 VEGF b. FGF VEGF TGF-β 1 IGF-1 PDE 1 C MCP-1 PAI-1 PDGF IL-6 fibroblasts Early mediators? signal intima Endothelial injury Surgical injury? Needle puncture? Vascular dilatation? Change of shear stress? SMC Recruitment of myofibroblasts
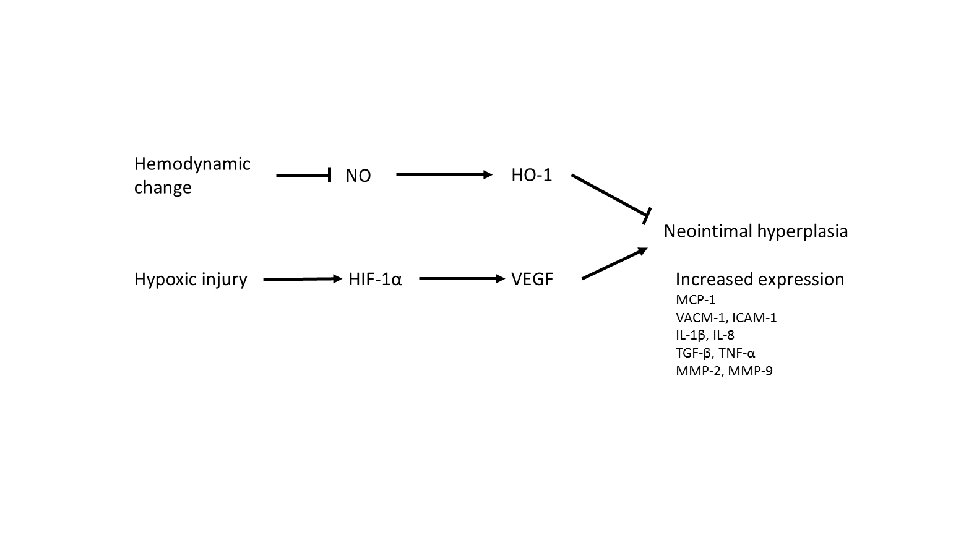

Fibroblast growth factor 21 • FGF 21, along with FGF 19 and FGF 23, are endocrine factors structurally belong to FGF superfamily. • The three members of FGF lack heparin-binding property and can be released into circulation. • FGF 21 modulate glucose and lipid metabolism and its expression increased in response to fasting. Diabetes Metab J 2016; 40: 22 -31.
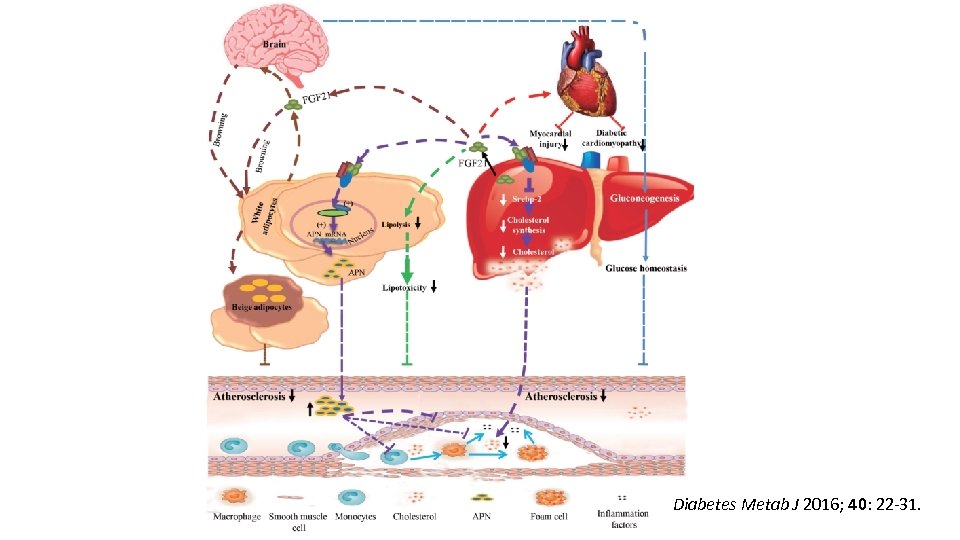
Diabetes Metab J 2016; 40: 22 -31.
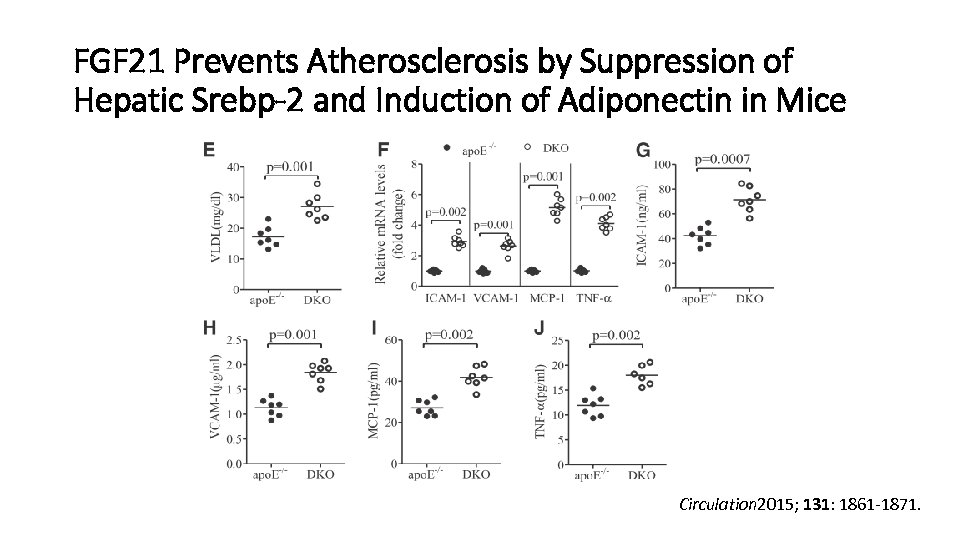
FGF 21 Prevents Atherosclerosis by Suppression of Hepatic Srebp-2 and Induction of Adiponectin in Mice Circulation 2015; 131: 1861 -1871.
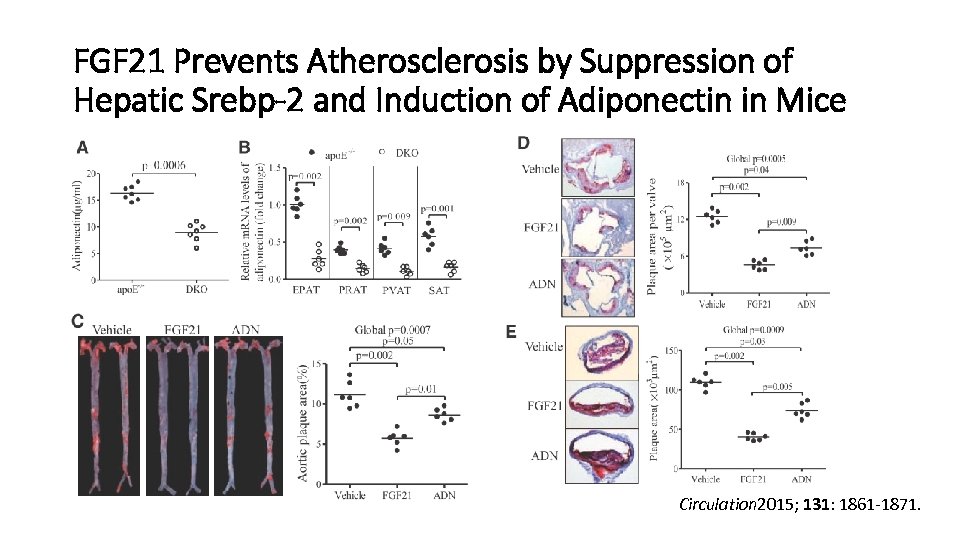
FGF 21 Prevents Atherosclerosis by Suppression of Hepatic Srebp-2 and Induction of Adiponectin in Mice Circulation 2015; 131: 1861 -1871.
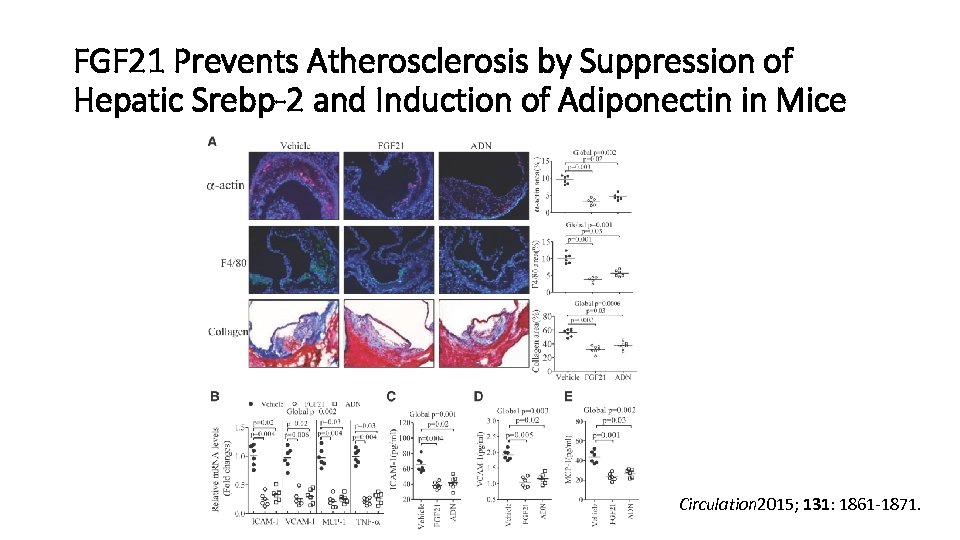
FGF 21 Prevents Atherosclerosis by Suppression of Hepatic Srebp-2 and Induction of Adiponectin in Mice Circulation 2015; 131: 1861 -1871.
Direct effect of FGF 21 on pathogenesis of athrosclerosis? • FGF 21 exerts its actions by binding to FGFR and co-receptor β-klotho. Circulation 2015; 131: 1861 -1871. • Expression of β-klotho is hardly detectable in any type of blood vessel cells. Z. L. and A. X. , unpublished data, 2014.
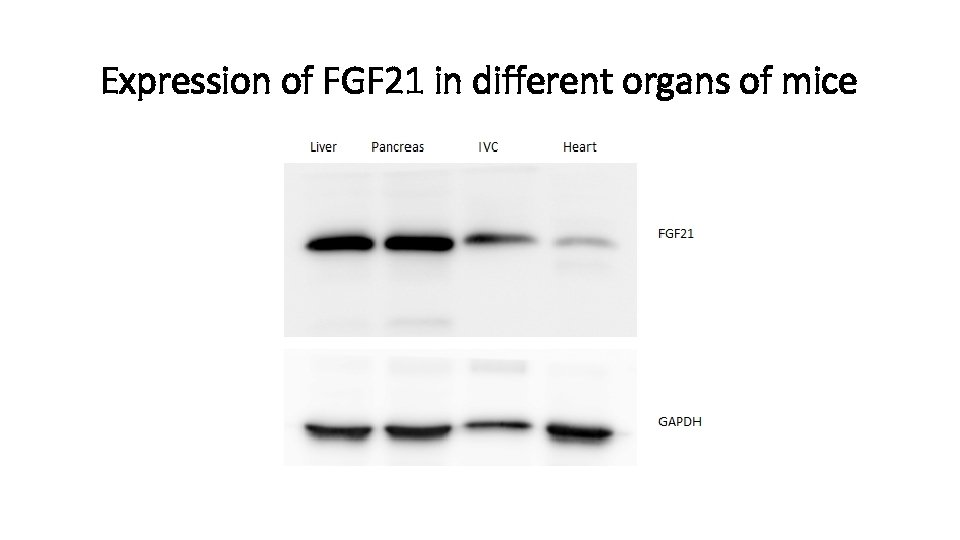
Expression of FGF 21 in different organs of mice
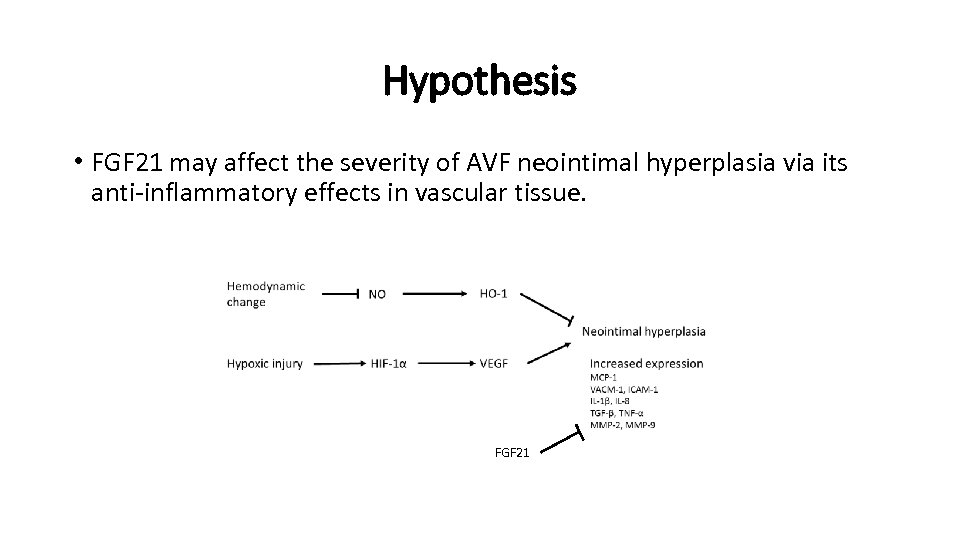
Hypothesis • FGF 21 may affect the severity of AVF neointimal hyperplasia via its anti-inflammatory effects in vascular tissue. FGF 21
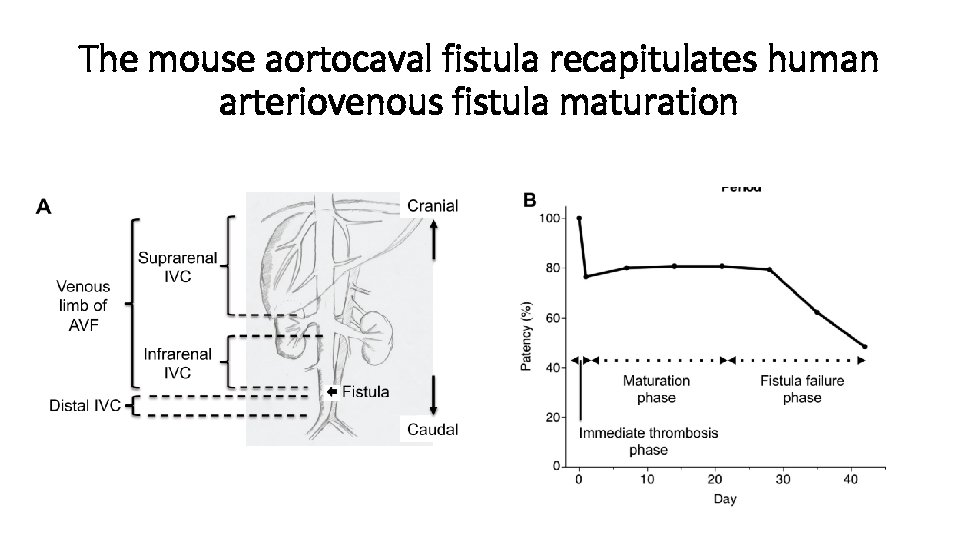
The mouse aortocaval fistula recapitulates human arteriovenous fistula maturation

Ongoing experiments • Expression of FGF 21 protein in IVC s/p aortocaval puncture compared with sham mice.
b1881709db82c53b33b879b429843897.ppt