de8644a522e689342e3444cca2738fe1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Pharmacogenetics - difficult or just impossible? Stephen Senn (c) Stephen Senn 2007 1

Based on chapter 25 (with some additional material from chapter 24). (c) Stephen Senn 2007 2

“Statistics and the medicine of the future” Mass-market drugs have successfully treated millions, but they have a corollary: one size has to fit all. Every patient gets the same drug – yet every patient is different and responds differently to drugs, treatments and doses…Each drug each dose, each treatment will be tuned not to the average patient but to the individual. It is the difference between an off-thepeg suit and one made to measure. Chris Harbron, Significance, June 2006, p 67 (My italics) 3

Genes, Means and Screens It will soon be possible for patients in clinical trials to undergo genetic tests to identify those individuals who will respond favourably to the drug candidate, based on their genotype, and therefore the underlying mechanism of their disease. This will translate into smaller, more effective clinical trials with corresponding cost savings and ultimately better treatment in general practice. In addition, clinical trials will be capable of screening for genes involved in the absorption, metabolism and clearance of drugs and the genes which are likely to predispose a patient to drug-induced side-effects. In this way, individual patients will be targeted with specific treatment and personalised dosing regimens to maximise efficacy and minimise pharmacokinetic problems and other side-effects. Sir Richard Sykes, FRS (c) Stephen Senn 2007 4

Claims for Pharmacogenomics • Clinical trials – Cleaner signal – Non-responders eliminated • Treatment strategies – “Theranostics” • Markets – Lower volume – Higher price per patient day (c) Stephen Senn 2007 5

Pharmacogenetics: A cutting-edge science that will start delivering miracle cures the year after next. (c) Stephen Senn 2007 6

Implicit Assumptions • Most variability seen in clinical trials is genetic – Furthermore it is not revealed in obvious phenotypes • Example: height and forced expiratory volume (FEV 1) in one second • Height predicts FEV 1 and height is partly genetically determined but you don’t need pharmacogenetics to measure height • We are going to be able to find it – Small number of genes responsible – Low (or no) interactive effects (genes act singly) – We will know where to look • In fact we simply don’t know if most variation in clinical trials is due to individual response let alone genetic variability (c) Stephen Senn 2007 7

Moerman and Placebos • Paper of 1984 • Investigated 31 placebo-controlled trials of cimetidine in ulcer • Found considerable variation in response • Considered placebo response rate was an important factor • Has been cited by others as proof of variation in treatment effect from trial to trial (c) Stephen Senn 2007 8
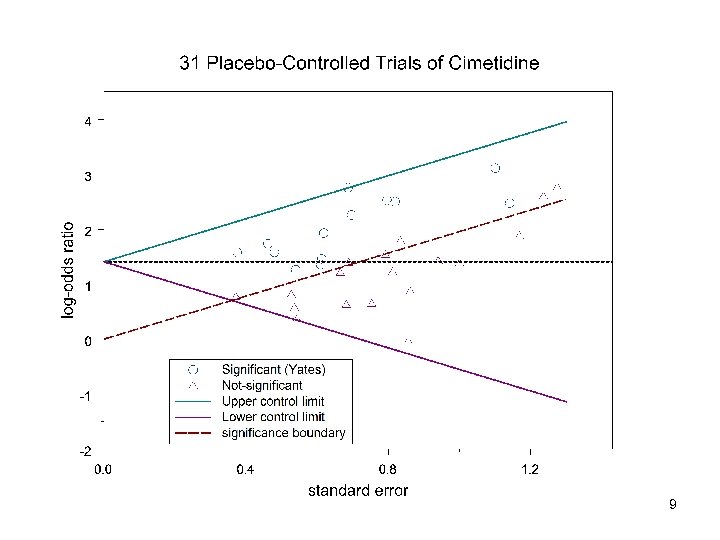
9
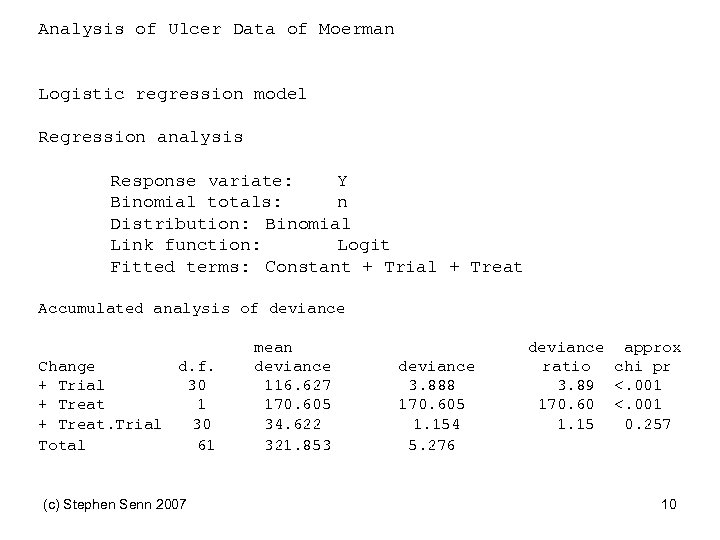
Analysis of Ulcer Data of Moerman Logistic regression model Regression analysis Response variate: Y Binomial totals: n Distribution: Binomial Link function: Logit Fitted terms: Constant + Trial + Treat Accumulated analysis of deviance Change d. f. + Trial 30 + Treat 1 + Treat. Trial 30 Total 61 (c) Stephen Senn 2007 mean deviance 116. 627 170. 605 34. 622 321. 853 deviance 3. 888 170. 605 1. 154 5. 276 deviance approx ratio chi pr 3. 89 <. 001 170. 60 <. 001 1. 15 0. 257 10

Lessons from Moerman • There is no evidence of variation in the treatment effect from trial to trial We should be wary about concluding that apparent variation signals true variation We need to be cautious and think carefully about analysis Of course…it is always possible that there was exactly the same genetic mix in each trial • • • – • in which case gene by treatment would not manifest itself as trial by treatment interaction We need to understand components of variation (c) Stephen Senn 2007 11

What you learn in your first ANOVA course • Completely randomised design – One way ANOVA • Randomised blocks design – Two way ANOVA • Randomised blocks design with replication – Two way ANOVA with interaction • No replication, no interaction (c) Stephen Senn 2007 12
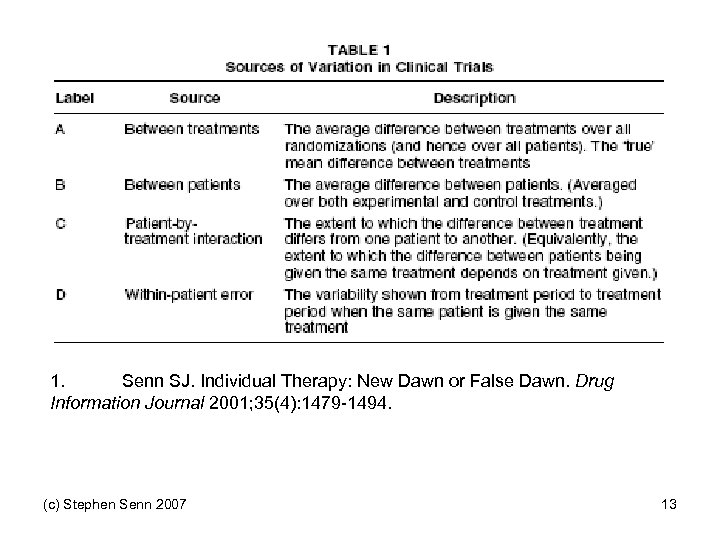
1. Senn SJ. Individual Therapy: New Dawn or False Dawn. Drug Information Journal 2001; 35(4): 1479 -1494. (c) Stephen Senn 2007 13
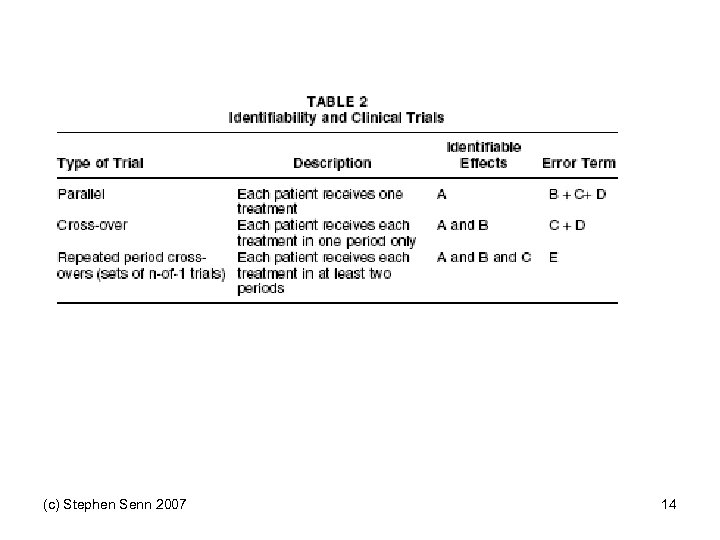
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 14
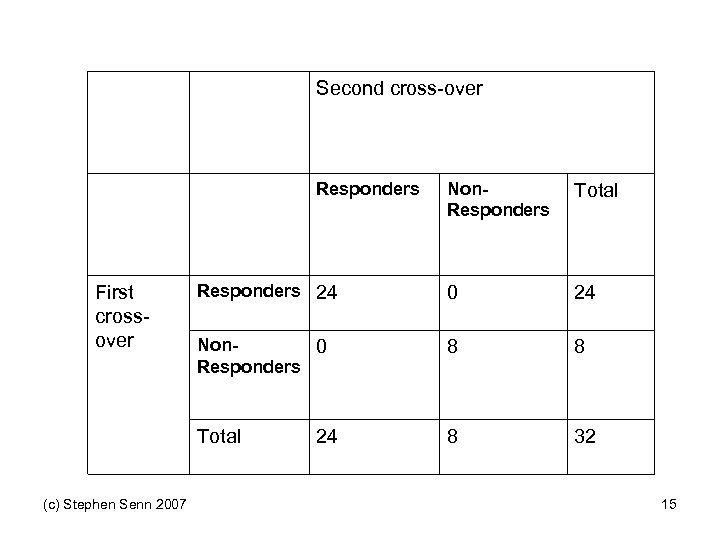
Second cross-over Responders (c) Stephen Senn 2007 Total Responders 24 0 24 Non 0 Responders 8 8 Total First crossover Non. Responders 8 32 24 15
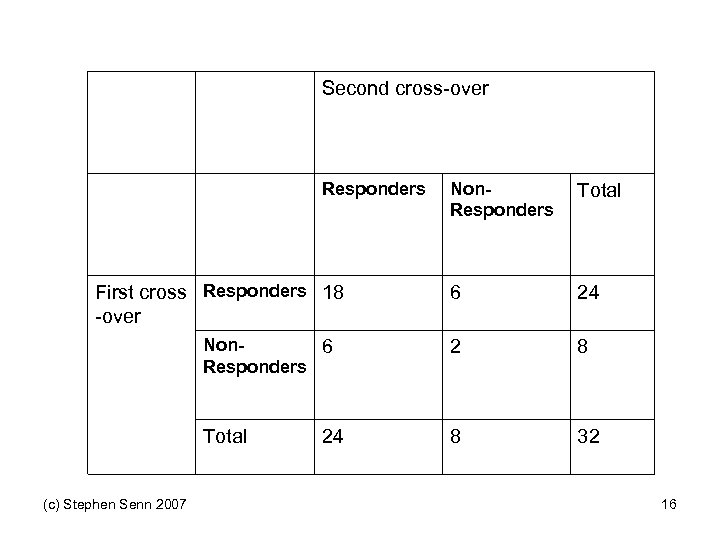
Second cross-over Responders Non. Responders Total 6 24 Non 6 Responders 2 8 Total 8 32 First cross Responders 18 -over (c) Stephen Senn 2007 24 16
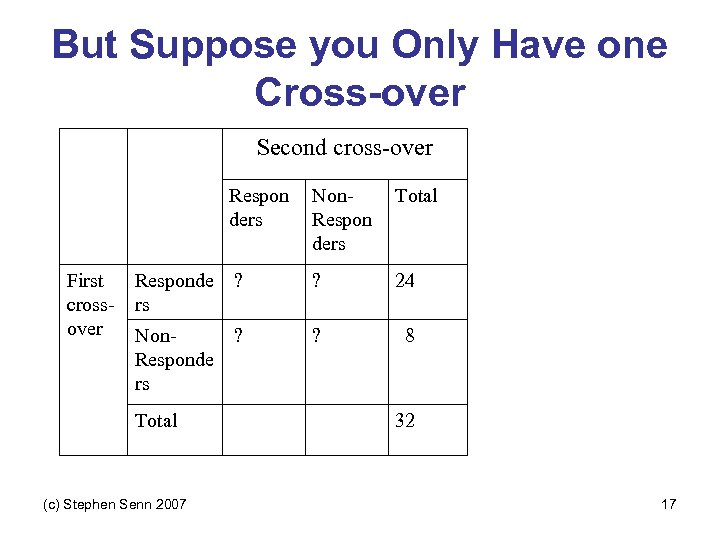
But Suppose you Only Have one Cross-over Second cross-over Respon ders First crossover Non. Respon ders Total Responde rs ? ? 24 Non. Responde rs ? ? 8 Total (c) Stephen Senn 2007 32 17
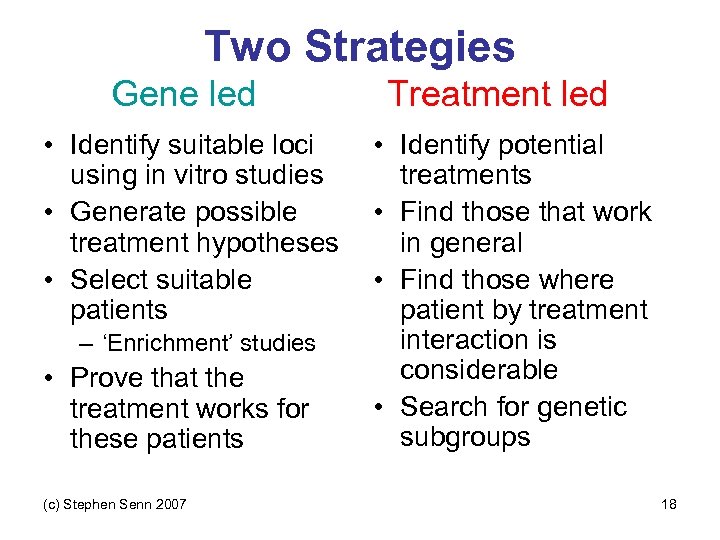
Two Strategies Gene led • Identify suitable loci using in vitro studies • Generate possible treatment hypotheses • Select suitable patients – ‘Enrichment’ studies • Prove that the treatment works for these patients (c) Stephen Senn 2007 Treatment led • Identify potential treatments • Find those that work in general • Find those where patient by treatment interaction is considerable • Search for genetic subgroups 18

Strategy 1 (Treatment led) Whole genome matching “Drug responses are not persistent affairs; they are temporary characteristics. One therefore may ask whether twin studies are necessary to assess the genetic element in pharmacological responsiveness. To measure the genetic component contributing to their variability, it seems logical to investigate the response variation by repeated drug administration to given individuals, and to compare the variability of the responses within and between individuals. ” Kalow et al, Pharmacogenetics, 8, 283 -289, 1998. (c) Stephen Senn 2007 19

Physicians like within patient studies but statisticians get cross over them The Sayings of Confuseus (c) Stephen Senn 2007 20

Possible Strategy • Run multi-period cross-overs • Patient by treatment interaction becomes identifiable • This provides an upper bound for gene by treatment interaction – Because patients differ by more than their genes (c) Stephen Senn 2007 21
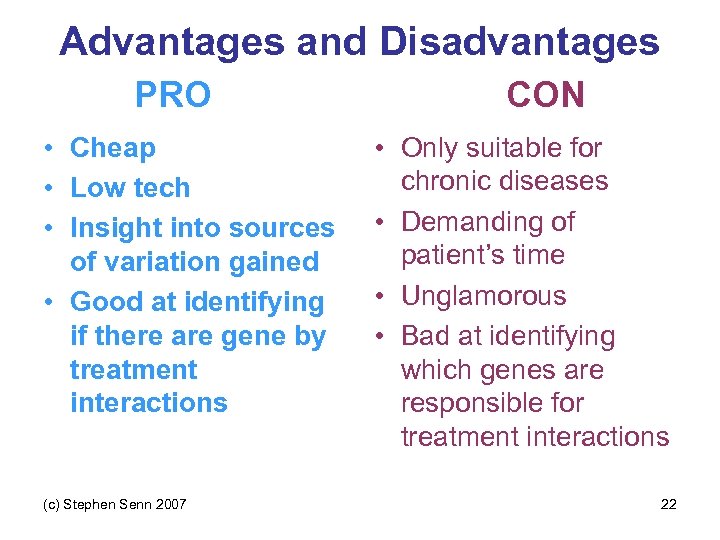
Advantages and Disadvantages PRO • Cheap • Low tech • Insight into sources of variation gained • Good at identifying if there are gene by treatment interactions (c) Stephen Senn 2007 CON • Only suitable for chronic diseases • Demanding of patient’s time • Unglamorous • Bad at identifying which genes are responsible for treatment interactions 22

In Practice • We hardly ever run repeated cross-over designs • Hence we are incapable of telling formally which of the two cases applies • Most researchers simply assume by default that case 1 is the case that applies • They assume that variation in response is a permanent feature of patients • This is what might be called patient-by-treatment interaction and provides an upper bound for gene-bytreatment interaction • Strangely enough, an area in which such repeated crossovers have been applied is one in which interaction is unlikely to be important: bioequivalence (c) Stephen Senn 2007 23
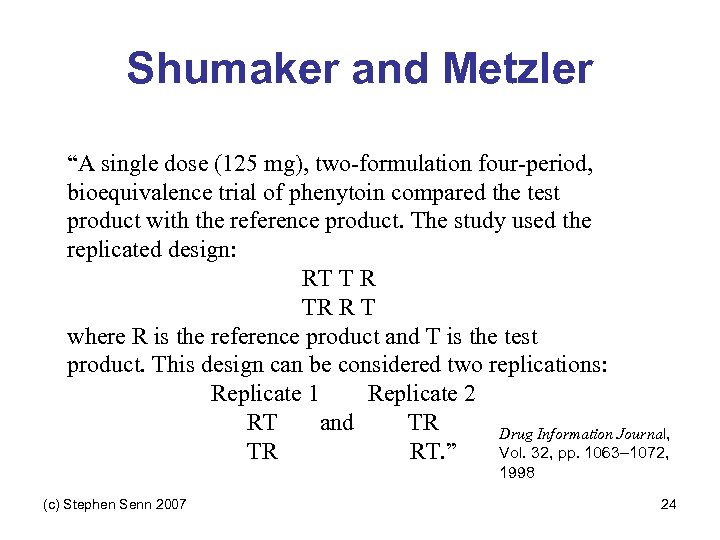
Shumaker and Metzler “A single dose (125 mg), two-formulation four-period, bioequivalence trial of phenytoin compared the test product with the reference product. The study used the replicated design: RT T R TR R T where R is the reference product and T is the test product. This design can be considered two replications: Replicate 1 Replicate 2 RT and TR Drug Information Journal, Vol. 32, pp. 1063– 1072, TR RT. ” 1998 (c) Stephen Senn 2007 24
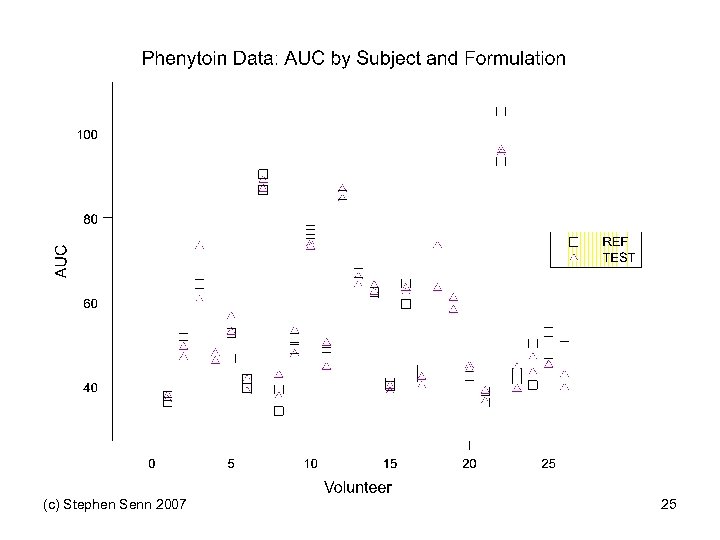
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 25
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 26
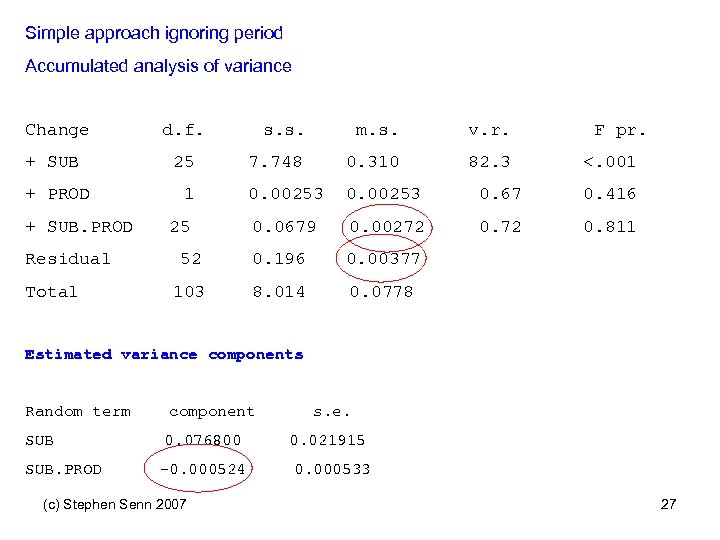
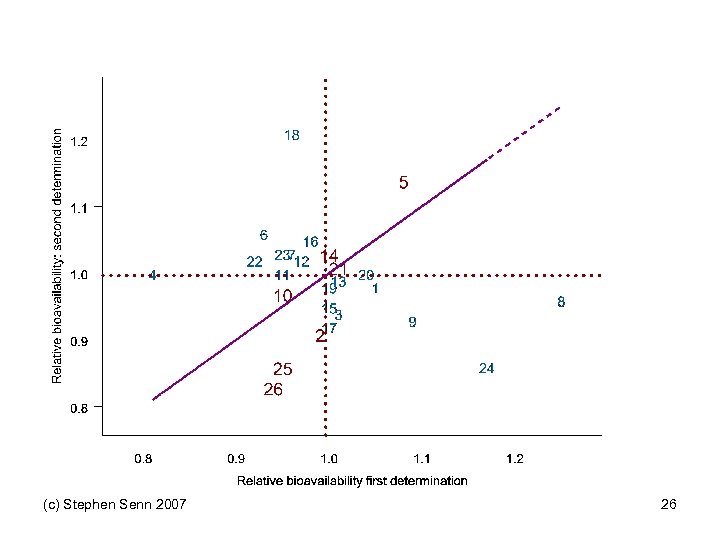
Simple approach ignoring period Accumulated analysis of variance Change d. f. + SUB 25 + PROD + SUB. PROD Residual Total s. s. m. s. v. r. 7. 748 0. 310 82. 3 0. 00253 0. 67 0. 416 0. 0679 0. 00272 0. 811 52 0. 196 0. 00377 103 8. 014 0. 0778 1 25 F pr. <. 001 Estimated variance components Random term component SUB 0. 076800 SUB. PROD -0. 000524 (c) Stephen Senn 2007 s. e. 0. 021915 0. 000533 27

Pharmacogenomics: A subject with great promise. (c) Stephen Senn 2007 28

Strategy Two (Gene Led) Genetic Subgroups • In many indications cross-over trials are impossible • This means that we have to investigate interaction not by whole genome matching (each patient his or her own control) but by genetic subgroups • Patients provide replication of the subgroup – Which genes should we use? – How should we group genotypes? – Will we have the statistical power to investigate subgroup interactions? (c) Stephen Senn 2007 29
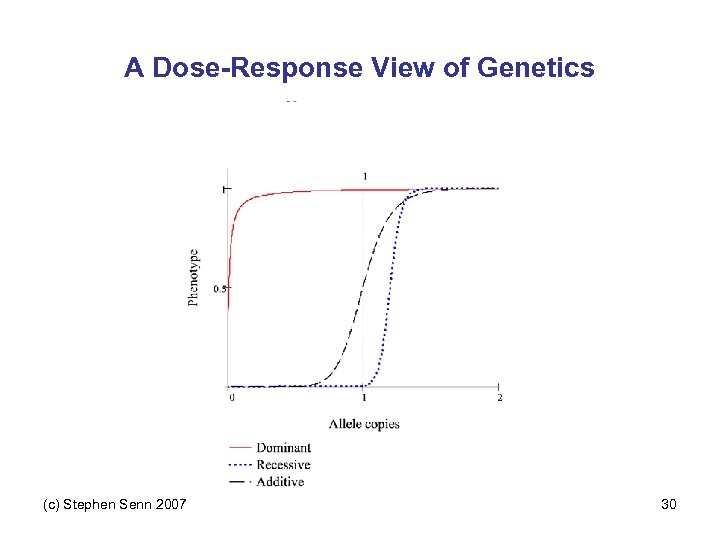
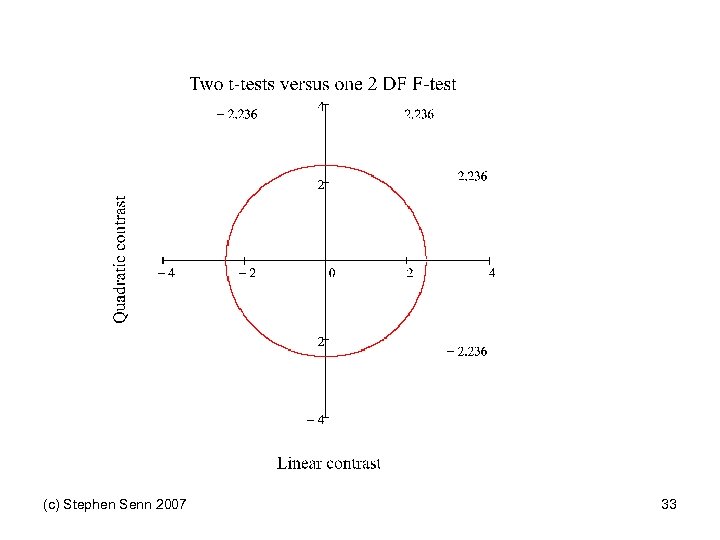
A Dose-Response View of Genetics (c) Stephen Senn 2007 30
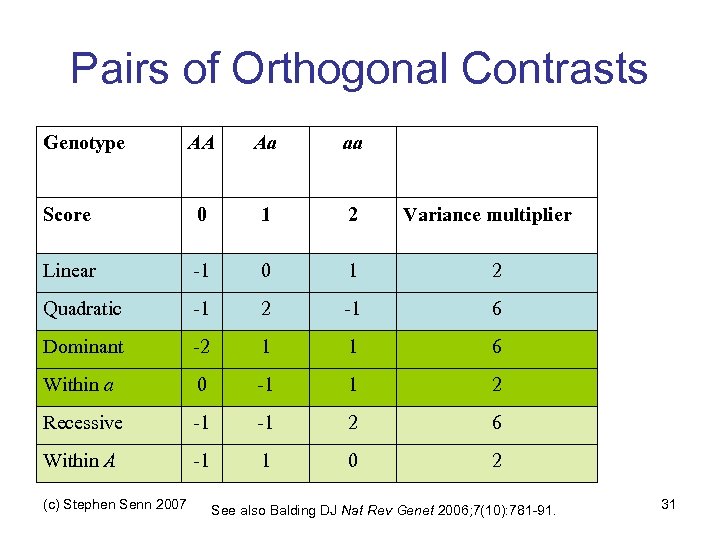
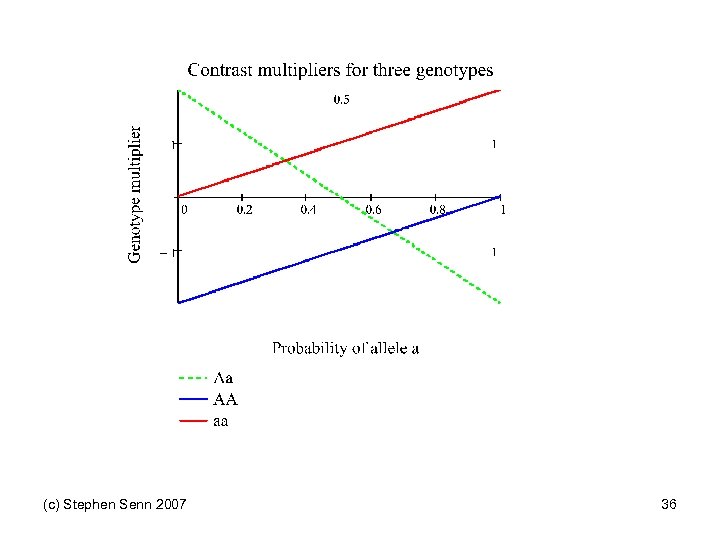
Pairs of Orthogonal Contrasts Genotype AA Aa aa Score 0 1 2 Linear -1 0 1 2 Quadratic -1 2 -1 6 Dominant -2 1 1 6 Within a 0 -1 1 2 Recessive -1 -1 2 6 Within A -1 1 0 2 (c) Stephen Senn 2007 Variance multiplier See also Balding DJ Nat Rev Genet 2006; 7(10): 781 -91. 31
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 32
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 33

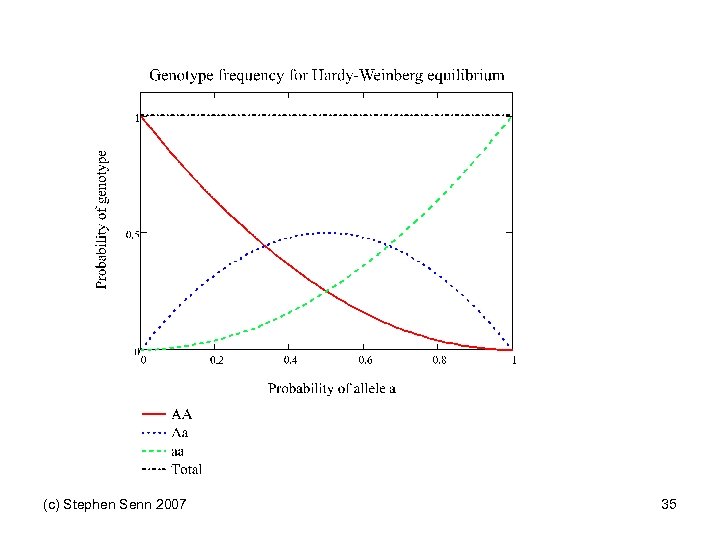
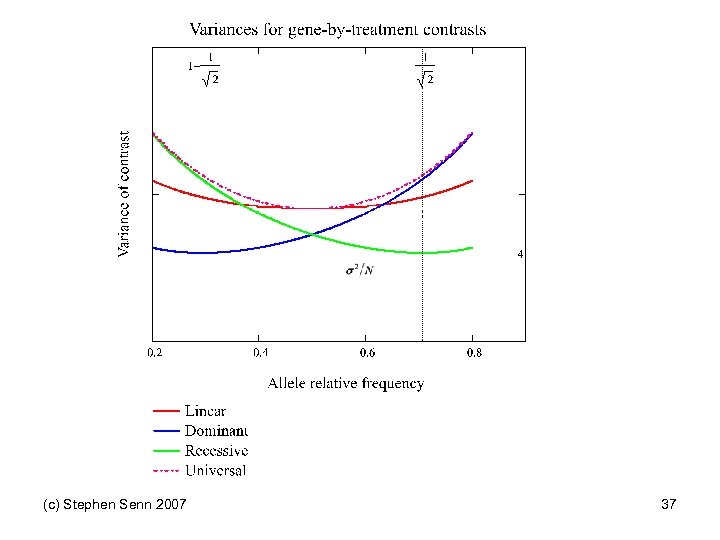
Impact on trial design • Suppose that you know that a dominant (with a as dominant allele) model applies • Then optimal clinical trial design implies that you should have half the patients on AA and the other half on Aa or aa • But if HW equilibrium applies this will only happen naturally if the probability of allele A is √ 2 • Of course, since disease is a selection process HW equilibrium may not apply anyway but this does not get around the problem • The distribution of genotypes may be very unfavourable for efficient investigation (c) Stephen Senn 2007 34
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 35
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 36
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 37

‘Enrichment’ studies? • Could we fix enrollment so that we have optimal genotype frequencies? • Problems – Recruitment time increases – Only optimal for one given locus – Requires knowledge of allele copy response • Dominant, recessive, linear etc – Requires knowledge of relevant locus – Interferes with other purposes of trial (c) Stephen Senn 2007 38

Pharmacoeconomics and genotyping • Finding a subset of patients who benefit has the potential to make the market smaller • This might imply that it is not in the economic interests of sponsors to do so • In fact models can be produced that suggest subsetting is valuable • An adaptation of a model of Kwerel(1980), which was originally applied to another situation, will be considered (c) Stephen Senn 2007 39
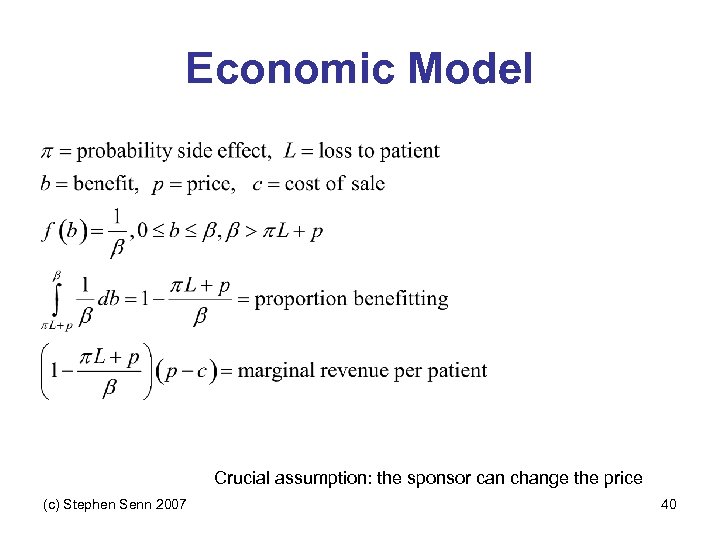
Economic Model Crucial assumption: the sponsor can change the price (c) Stephen Senn 2007 40
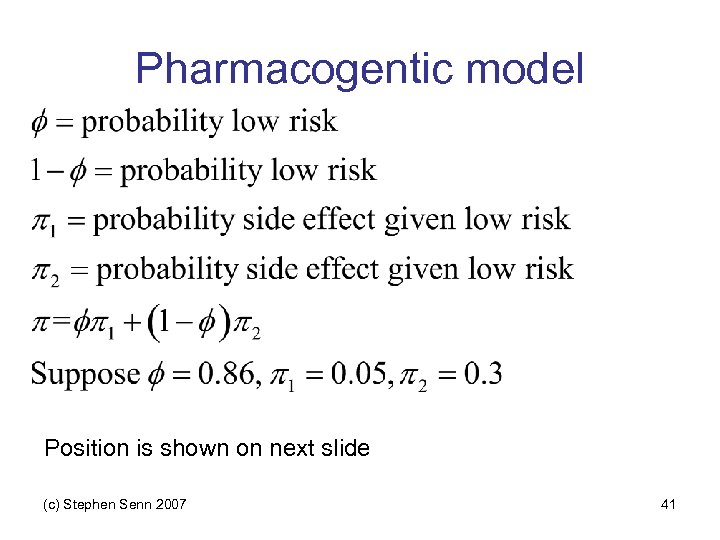
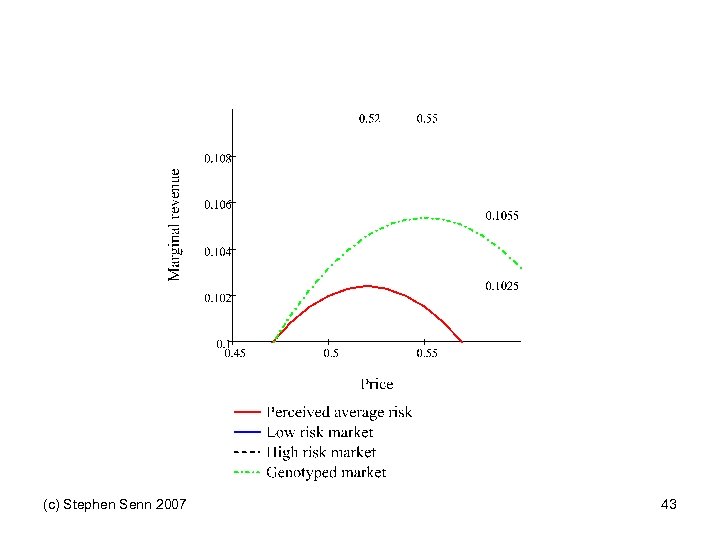
Pharmacogentic model Position is shown on next slide (c) Stephen Senn 2007 41
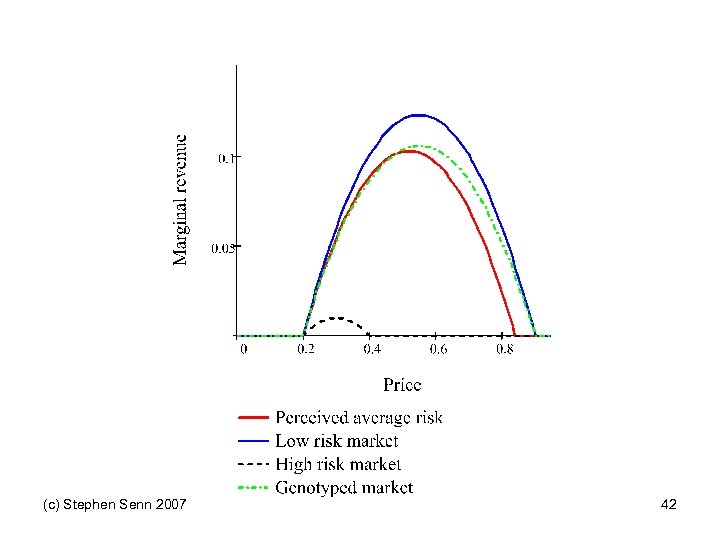
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 42
(c) Stephen Senn 2007 43

An Issue with Covariates • Covariate adjustment in clinical trials is generally beneficial and to be recommended – However a point to note is that the covariates in question should be measured prior to allocation of treatment – Otherwise problems arise with causal inference – Some of the treatment effect may be removed • However, when looking at gene-by-treatment interaction there is a potential problem • Covariates can be pre treatment allocation and hence unaffected by treatment but can be affected by genetics • Hence fitting the covariate could remove some of the gene effect • Will inference about gene-by-treatment interaction still be sound? • This issue requires careful thought (c) Stephen Senn 2007 44

An Overlooked Source of Genetic Variability • Humans may be classified into two important genetic subtypes • One of these suffers from a massive chromosomal deficiency • This is expressed in – important phenotypic differences – a huge disadvantage in life expectancy • Many treatment strategies take no account of this • The names of these subtypes are. . . (c) Stephen Senn 2007 45

Males and females (c) Stephen Senn 2007 46
de8644a522e689342e3444cca2738fe1.ppt