c1dd2fe99506a0f34d4b291caea04d5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Pharmaceutical Industry Mark Shigihara R. Ph. , CMR Account Manager UW Affiliate Faculty
Pharmaceutical Industry Mark Shigihara R. Ph. , CMR Account Manager UW Affiliate Faculty
 Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical Industry
 Pharmaceutical Innovation
Pharmaceutical Innovation
 What is a Medical Science Liaison (MSL)?
What is a Medical Science Liaison (MSL)?
 st 1 Generation Medical Science Liaisons
st 1 Generation Medical Science Liaisons
 MSL Roles & Responsibilities l MSL is a medical representative in the field for Wyeth. l Provide fair-balanced scientific clinical information, including full scientific data on products in response to unsolicited requests
MSL Roles & Responsibilities l MSL is a medical representative in the field for Wyeth. l Provide fair-balanced scientific clinical information, including full scientific data on products in response to unsolicited requests
 A Typical MSL Question
A Typical MSL Question
 MSLs educate pharmacists on XR dosage forms
MSLs educate pharmacists on XR dosage forms
 MSL Profile Example l USC – Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm. D. ) l Post – School of Pharmacy Doctoral Residency Primary Care / Ambulatory Medicine l UCLA – - Santa Monica Medical Center Director of Pharmacology Education and Research & Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine l Research - Internal Medicine & Primary Care, Journal Club l P&T Committee l Resident Education - Pharmacology l Patient Care- Inpatient Medicine Rounds & Outpatient Clinic
MSL Profile Example l USC – Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm. D. ) l Post – School of Pharmacy Doctoral Residency Primary Care / Ambulatory Medicine l UCLA – - Santa Monica Medical Center Director of Pharmacology Education and Research & Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine l Research - Internal Medicine & Primary Care, Journal Club l P&T Committee l Resident Education - Pharmacology l Patient Care- Inpatient Medicine Rounds & Outpatient Clinic
 General MSL Characteristics l l l l Apply the science Responsive to inquiries Prepare Medical Community for new therapies Educate Support research Develop relationships-internal and external colleagues Facilitate the acceptance and understanding of Wyeth-Ayerst products and assure their optimum use
General MSL Characteristics l l l l Apply the science Responsive to inquiries Prepare Medical Community for new therapies Educate Support research Develop relationships-internal and external colleagues Facilitate the acceptance and understanding of Wyeth-Ayerst products and assure their optimum use
 Pharmaceutical Representative The Untold Story. . . .
Pharmaceutical Representative The Untold Story. . . .
 Sales… The world’s oldest profession
Sales… The world’s oldest profession
 The Art of Selling
The Art of Selling
 Pharmaceutical Sales Candidates
Pharmaceutical Sales Candidates
 What people used to say about Pharmaceutical Representatives. . l “Oh no. . . not him again. . I don’t have the time” l “ He would have made a great used car salesman” l “ I can’t remember what he said about this product but this pen is really cool”
What people used to say about Pharmaceutical Representatives. . l “Oh no. . . not him again. . I don’t have the time” l “ He would have made a great used car salesman” l “ I can’t remember what he said about this product but this pen is really cool”
 Representative role is to provide value for the customer l Product education - fair balance/ethical l Address contract/pricing issues l Serve as a liaison to home office departments: medical affairs, product quality, product marketing, clinical studies. . . l Meet customer needs: speakers, grants, copromotion. .
Representative role is to provide value for the customer l Product education - fair balance/ethical l Address contract/pricing issues l Serve as a liaison to home office departments: medical affairs, product quality, product marketing, clinical studies. . . l Meet customer needs: speakers, grants, copromotion. .
 Office Based Representatives l Works in private practice setting with MD s and RNs. l Calls on chain and or independent pharmacies. l The majority of pharmaceutical representatives are in office based roles.
Office Based Representatives l Works in private practice setting with MD s and RNs. l Calls on chain and or independent pharmacies. l The majority of pharmaceutical representatives are in office based roles.
 Medical Center Representatives l Works in hospital/academic medical center environment. l Audience: MD, residents, pharmacists, RN. . . l Key responsibility- to identify and develop academic thought leaders.
Medical Center Representatives l Works in hospital/academic medical center environment. l Audience: MD, residents, pharmacists, RN. . . l Key responsibility- to identify and develop academic thought leaders.
 Representative Benefits Reward-recognition for individual achievement. l The “master of your own destiny”- strategy, time allocation, priority. . l Customer relationships l
Representative Benefits Reward-recognition for individual achievement. l The “master of your own destiny”- strategy, time allocation, priority. . l Customer relationships l
 Representative Benefits l Guaranteed Salary l Bonus plan - matched to performance l Stock Options l Car / Insurance / Gas l 401 K l Medical / Dental coverage
Representative Benefits l Guaranteed Salary l Bonus plan - matched to performance l Stock Options l Car / Insurance / Gas l 401 K l Medical / Dental coverage
 Representative Challenges Customers with different points of view. l Travel l Relocation? l Good bye to the 40 hour work week. . . l
Representative Challenges Customers with different points of view. l Travel l Relocation? l Good bye to the 40 hour work week. . . l
 Representative opportunities: l Multiple career options- home office, sales management, training. . . l Multiple company options: Wyeth, Ayerst, Robins, Lederle, Genetics Institute. . . l The pharmacy degree is a tremendous asset in the pharmaceutical industry.
Representative opportunities: l Multiple career options- home office, sales management, training. . . l Multiple company options: Wyeth, Ayerst, Robins, Lederle, Genetics Institute. . . l The pharmacy degree is a tremendous asset in the pharmaceutical industry.
 Mark Shigihara Managed Care Area Account Manager l Job responsibility l Work responsibilities and impact on pharmacists. l Real life questions/quiz
Mark Shigihara Managed Care Area Account Manager l Job responsibility l Work responsibilities and impact on pharmacists. l Real life questions/quiz
 Managed Care Environment
Managed Care Environment
 Managed Care RAM l Work with managed care health plans. Premera Blue Cross, Group Health, Pacifi. Care, Kaiser…. l Offer product information to accountsinfluence formulary /reimbursement position of products. l Co promote- initiatives with customers
Managed Care RAM l Work with managed care health plans. Premera Blue Cross, Group Health, Pacifi. Care, Kaiser…. l Offer product information to accountsinfluence formulary /reimbursement position of products. l Co promote- initiatives with customers
 Reimbursement Role
Reimbursement Role
 Real Life Quiz What causes the most complaints from patients regarding their prescriptions? Your typing speed on labels B) You can not decode the prescriber handwriting and fill the Viagra prescription with Valium. C) The COST of pharmaceuticals A)
Real Life Quiz What causes the most complaints from patients regarding their prescriptions? Your typing speed on labels B) You can not decode the prescriber handwriting and fill the Viagra prescription with Valium. C) The COST of pharmaceuticals A)
 COST Putting it into perspective
COST Putting it into perspective
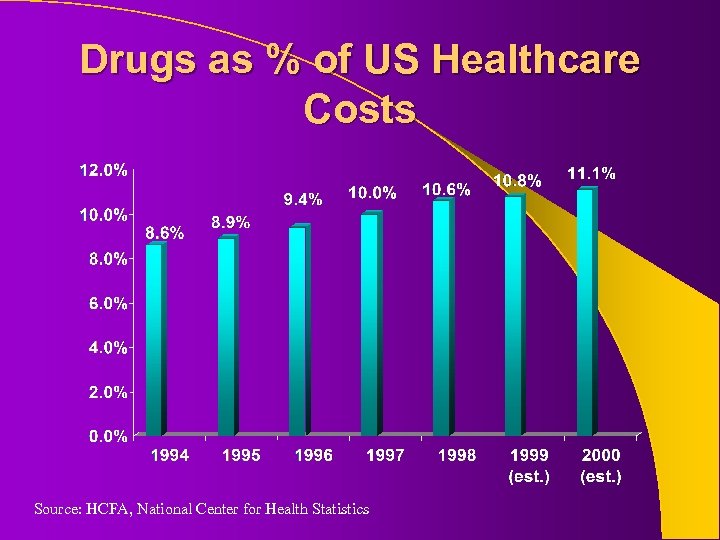 Drugs as % of US Healthcare Costs Source: HCFA, National Center for Health Statistics
Drugs as % of US Healthcare Costs Source: HCFA, National Center for Health Statistics
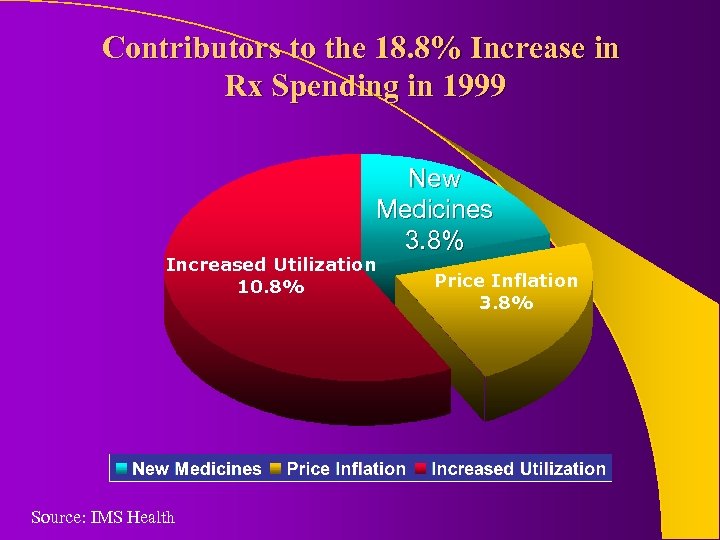 Contributors to the 18. 8% Increase in Rx Spending in 1999 New Medicines 3. 8% Increased Utilization 10. 8% Source: IMS Health Price Inflation 3. 8%
Contributors to the 18. 8% Increase in Rx Spending in 1999 New Medicines 3. 8% Increased Utilization 10. 8% Source: IMS Health Price Inflation 3. 8%
 COST But what about other countries…. . Pharmaceutical products cost less there….
COST But what about other countries…. . Pharmaceutical products cost less there….
 Mc Answer
Mc Answer
 Many Costs Are Lower in Canada From Higher Education. . . U. S. Canada Yale University Mc. Gill University (Undergraduate Tuition, Books, Room and Board) (Undergraduate Tuition, Books, Room and Board, Student Services) One Year: $32, 000 One Year: $12, 566 …to Fast Food Mc. Donald’s Big Mac $2. 43 Source: Published University Data, 2000 $1. 98
Many Costs Are Lower in Canada From Higher Education. . . U. S. Canada Yale University Mc. Gill University (Undergraduate Tuition, Books, Room and Board) (Undergraduate Tuition, Books, Room and Board, Student Services) One Year: $32, 000 One Year: $12, 566 …to Fast Food Mc. Donald’s Big Mac $2. 43 Source: Published University Data, 2000 $1. 98
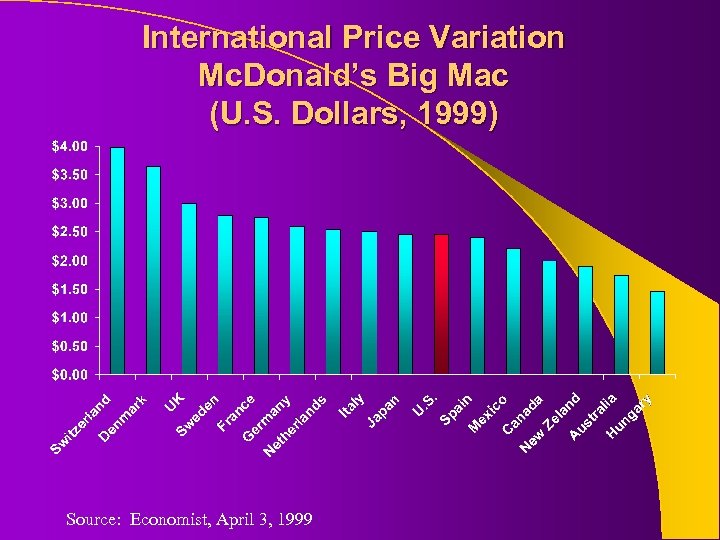 International Price Variation Mc. Donald’s Big Mac (U. S. Dollars, 1999) Source: Economist, April 3, 1999
International Price Variation Mc. Donald’s Big Mac (U. S. Dollars, 1999) Source: Economist, April 3, 1999
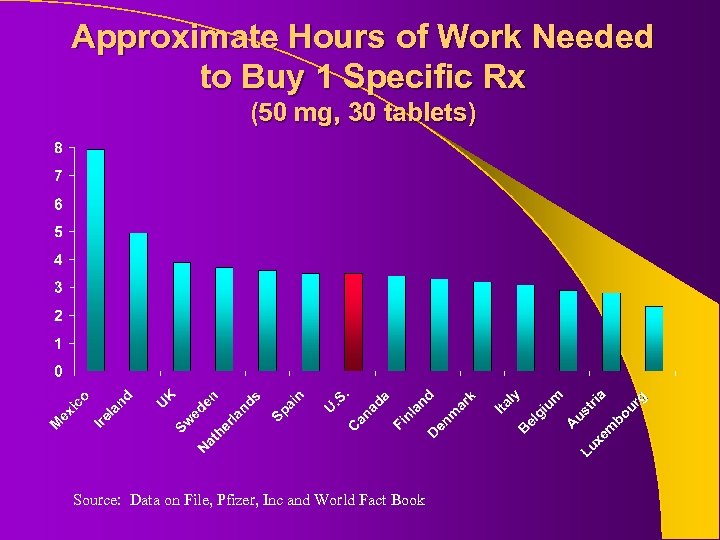 Approximate Hours of Work Needed to Buy 1 Specific Rx (50 mg, 30 tablets) Source: Data on File, Pfizer, Inc and World Fact Book
Approximate Hours of Work Needed to Buy 1 Specific Rx (50 mg, 30 tablets) Source: Data on File, Pfizer, Inc and World Fact Book
 COSTS What about some detailed United States perspective…. .
COSTS What about some detailed United States perspective…. .
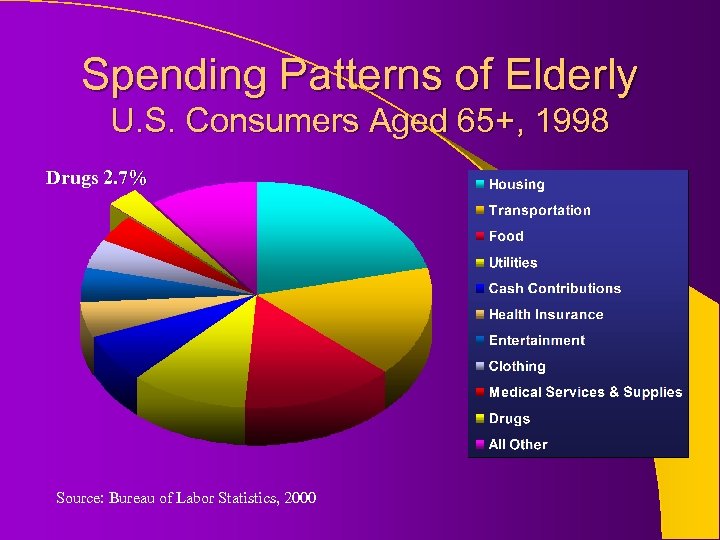 Spending Patterns of Elderly U. S. Consumers Aged 65+, 1998 Drugs 2. 7% Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2000
Spending Patterns of Elderly U. S. Consumers Aged 65+, 1998 Drugs 2. 7% Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2000
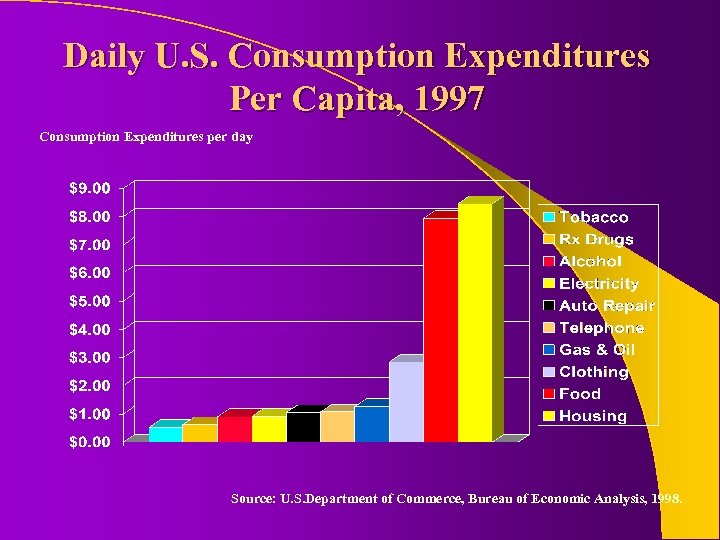 Daily U. S. Consumption Expenditures Per Capita, 1997 Consumption Expenditures per day Source: U. S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis, 1998.
Daily U. S. Consumption Expenditures Per Capita, 1997 Consumption Expenditures per day Source: U. S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis, 1998.
 COSTS But what about pharmaceutical companies… Are they just trying to price gouge the customer….
COSTS But what about pharmaceutical companies… Are they just trying to price gouge the customer….
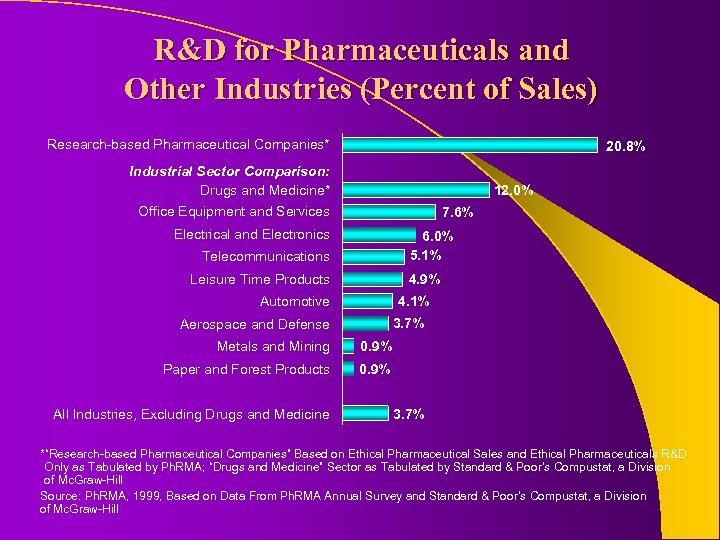 R&D for Pharmaceuticals and Other Industries (Percent of Sales) Research-based Pharmaceutical Companies* 20. 8% Industrial Sector Comparison: Drugs and Medicine* 12. 0% Office Equipment and Services 7. 6% Electrical and Electronics 6. 0% 5. 1% Telecommunications Leisure Time Products 4. 9% Automotive 4. 1% 3. 7% Aerospace and Defense Metals and Mining 0. 9% Paper and Forest Products 0. 9% All Industries, Excluding Drugs and Medicine 3. 7% *“Research-based Pharmaceutical Companies” Based on Ethical Pharmaceutical Sales and Ethical Pharmaceuticals R&D Only as Tabulated by Ph. RMA; “Drugs and Medicine” Sector as Tabulated by Standard & Poor’s Compustat, a Division of Mc. Graw-Hill Source: Ph. RMA, 1999, Based on Data From Ph. RMA Annual Survey and Standard & Poor’s Compustat, a Division of Mc. Graw-Hill
R&D for Pharmaceuticals and Other Industries (Percent of Sales) Research-based Pharmaceutical Companies* 20. 8% Industrial Sector Comparison: Drugs and Medicine* 12. 0% Office Equipment and Services 7. 6% Electrical and Electronics 6. 0% 5. 1% Telecommunications Leisure Time Products 4. 9% Automotive 4. 1% 3. 7% Aerospace and Defense Metals and Mining 0. 9% Paper and Forest Products 0. 9% All Industries, Excluding Drugs and Medicine 3. 7% *“Research-based Pharmaceutical Companies” Based on Ethical Pharmaceutical Sales and Ethical Pharmaceuticals R&D Only as Tabulated by Ph. RMA; “Drugs and Medicine” Sector as Tabulated by Standard & Poor’s Compustat, a Division of Mc. Graw-Hill Source: Ph. RMA, 1999, Based on Data From Ph. RMA Annual Survey and Standard & Poor’s Compustat, a Division of Mc. Graw-Hill
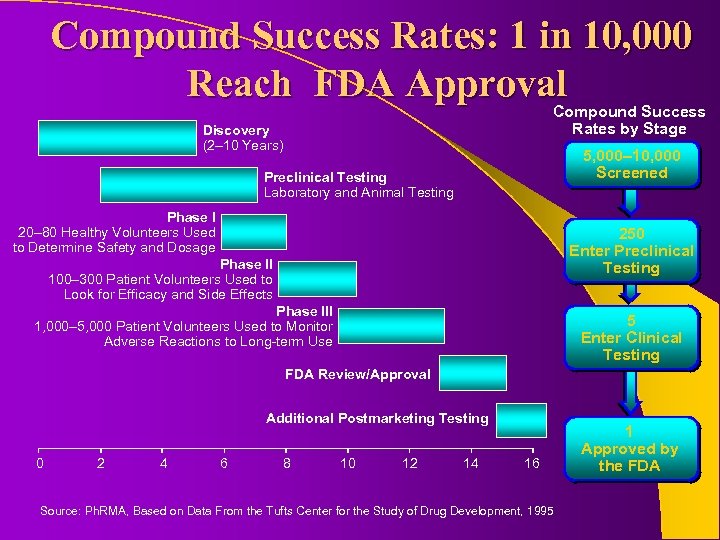 Compound Success Rates: 1 in 10, 000 Reach FDA Approval Compound Success Rates by Stage Discovery (2– 10 Years) 5, 000– 10, 000 Screened Preclinical Testing Laboratory and Animal Testing Phase I 20– 80 Healthy Volunteers Used to Determine Safety and Dosage 250 Enter Preclinical Testing Phase II 100– 300 Patient Volunteers Used to Look for Efficacy and Side Effects Phase III 1, 000– 5, 000 Patient Volunteers Used to Monitor Adverse Reactions to Long-term Use 5 Enter Clinical Testing FDA Review/Approval Additional Postmarketing Testing 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Source: Ph. RMA, Based on Data From the Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development, 1995 1 Approved by the FDA
Compound Success Rates: 1 in 10, 000 Reach FDA Approval Compound Success Rates by Stage Discovery (2– 10 Years) 5, 000– 10, 000 Screened Preclinical Testing Laboratory and Animal Testing Phase I 20– 80 Healthy Volunteers Used to Determine Safety and Dosage 250 Enter Preclinical Testing Phase II 100– 300 Patient Volunteers Used to Look for Efficacy and Side Effects Phase III 1, 000– 5, 000 Patient Volunteers Used to Monitor Adverse Reactions to Long-term Use 5 Enter Clinical Testing FDA Review/Approval Additional Postmarketing Testing 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Source: Ph. RMA, Based on Data From the Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development, 1995 1 Approved by the FDA
 Pharmaceutical Industry Facts l Revenues from approved drugs (1 of 5 to 10, 000) must cover the “dry holes” of non approved compounds. l Average cost of bringing a drug to market is 500 to 800 million dollars. l Average approval time is 12 to 15 years. l Time to recoup investment is shrinkinggeneric drugs and limited patent life
Pharmaceutical Industry Facts l Revenues from approved drugs (1 of 5 to 10, 000) must cover the “dry holes” of non approved compounds. l Average cost of bringing a drug to market is 500 to 800 million dollars. l Average approval time is 12 to 15 years. l Time to recoup investment is shrinkinggeneric drugs and limited patent life
 COST Perspective What is the cost if pharmaceutical manufacturers did not create revolutionary drugs……. .
COST Perspective What is the cost if pharmaceutical manufacturers did not create revolutionary drugs……. .
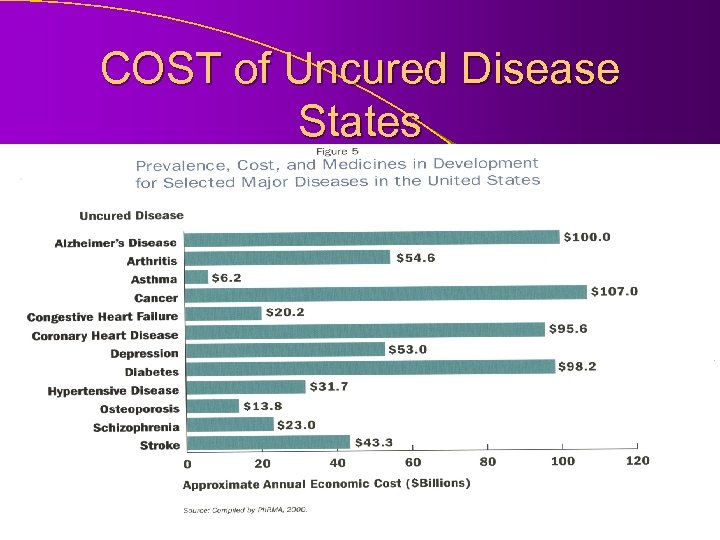 COST of Uncured Disease States
COST of Uncured Disease States
 COST And this does not even take into consideration… patient quality of life
COST And this does not even take into consideration… patient quality of life
 MSL or AAM l Consider signing up for our rotation. l In depth exposure to our positions. l Advantages l Disadvantages l Answers the question – “Is the pharmaceutical industry a viable career option for me ? ”
MSL or AAM l Consider signing up for our rotation. l In depth exposure to our positions. l Advantages l Disadvantages l Answers the question – “Is the pharmaceutical industry a viable career option for me ? ”
 Questions?
Questions?


