819a7f2332cee3ac77b7f84d4e4b8c2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Pharmaceutical drugs: maintaining appropriate use while preventing diversion Dr Malcolm Dobbin Senior Medical Adviser Mental Health, Drugs and Regions Division Victorian Dept Health
Pharmaceutical drugs: maintaining appropriate use while preventing diversion Dr Malcolm Dobbin Senior Medical Adviser Mental Health, Drugs and Regions Division Victorian Dept Health
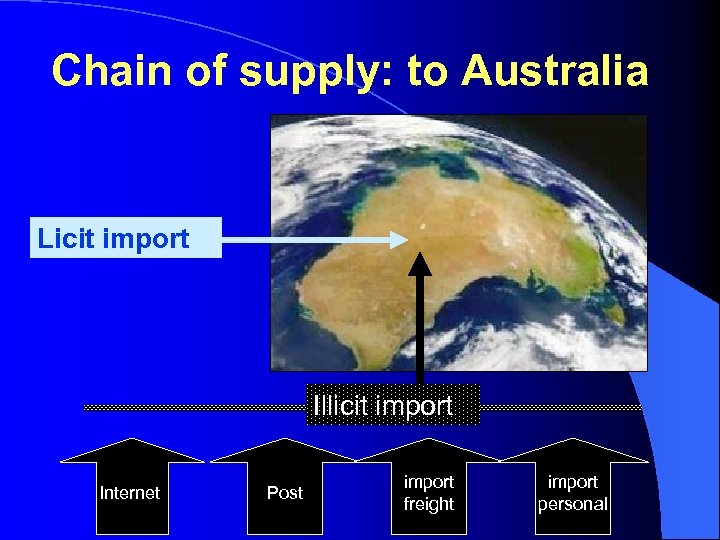 Chain of supply: to Australia Licit import Illicit import Internet Post import freight import personal
Chain of supply: to Australia Licit import Illicit import Internet Post import freight import personal
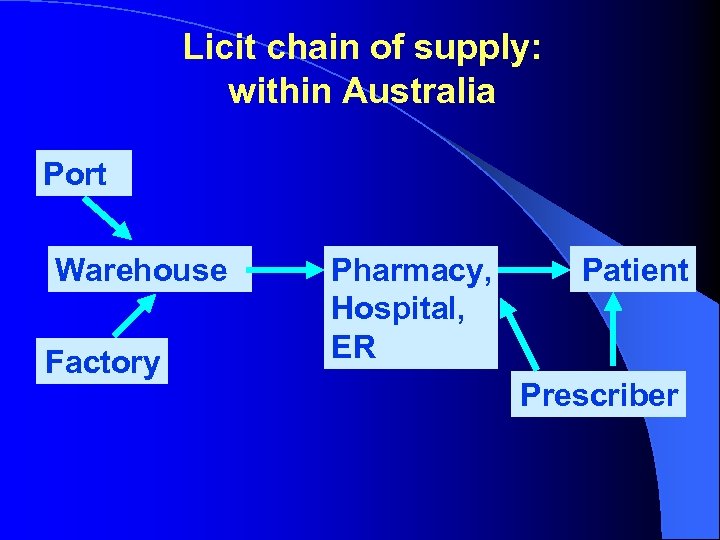 Licit chain of supply: within Australia Port Warehouse Factory Pharmacy, Hospital, ER Patient Prescriber
Licit chain of supply: within Australia Port Warehouse Factory Pharmacy, Hospital, ER Patient Prescriber
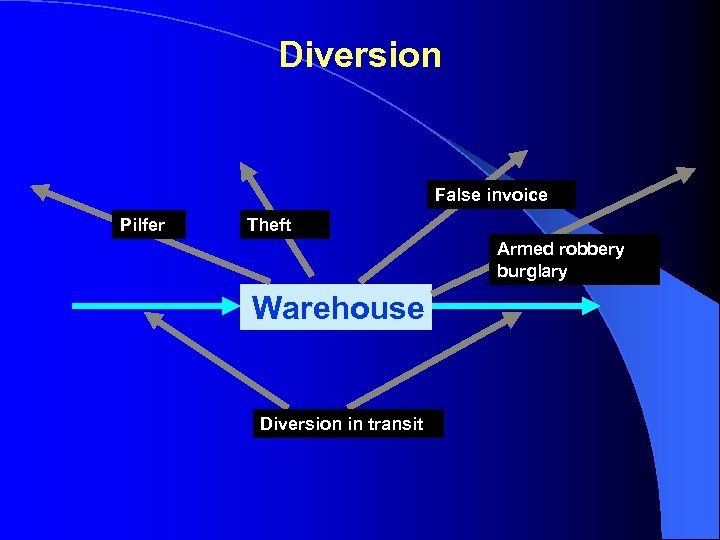 Diversion False invoice Pilfer Theft Armed robbery burglary Warehouse Diversion in transit
Diversion False invoice Pilfer Theft Armed robbery burglary Warehouse Diversion in transit
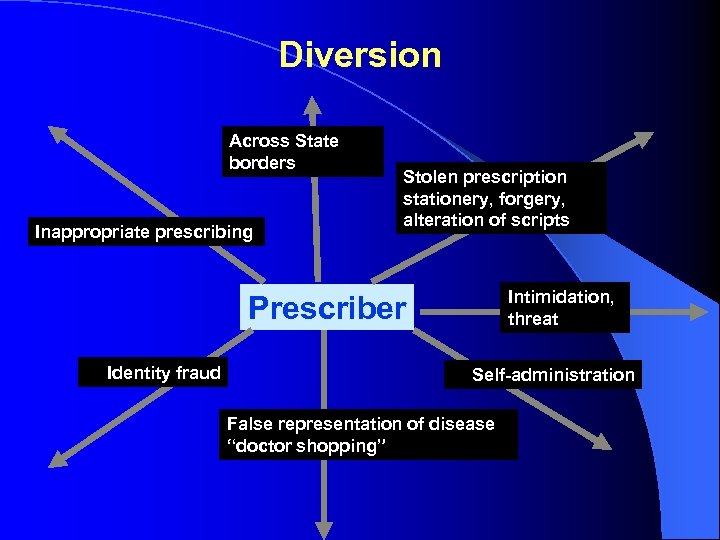 Diversion Across State borders Inappropriate prescribing Stolen prescription stationery, forgery, alteration of scripts Intimidation, threat Prescriber Identity fraud Self-administration False representation of disease “doctor shopping”
Diversion Across State borders Inappropriate prescribing Stolen prescription stationery, forgery, alteration of scripts Intimidation, threat Prescriber Identity fraud Self-administration False representation of disease “doctor shopping”
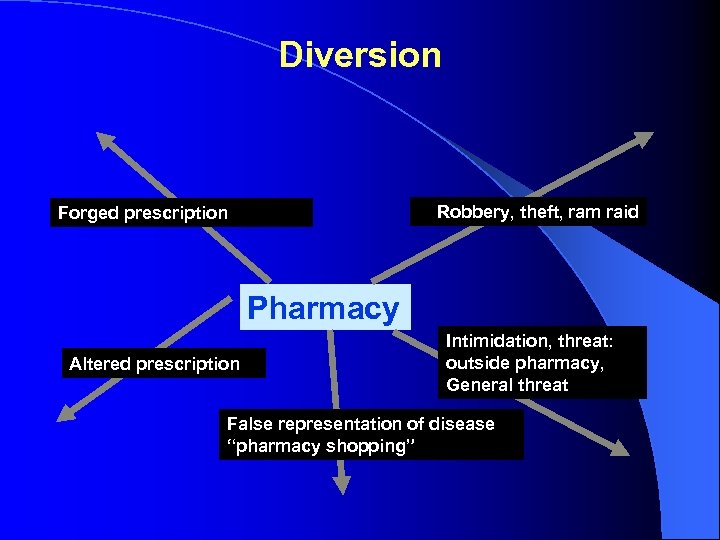 Diversion Robbery, theft, ram raid Forged prescription Pharmacy Altered prescription Intimidation, threat: outside pharmacy, General threat False representation of disease “pharmacy shopping”
Diversion Robbery, theft, ram raid Forged prescription Pharmacy Altered prescription Intimidation, threat: outside pharmacy, General threat False representation of disease “pharmacy shopping”
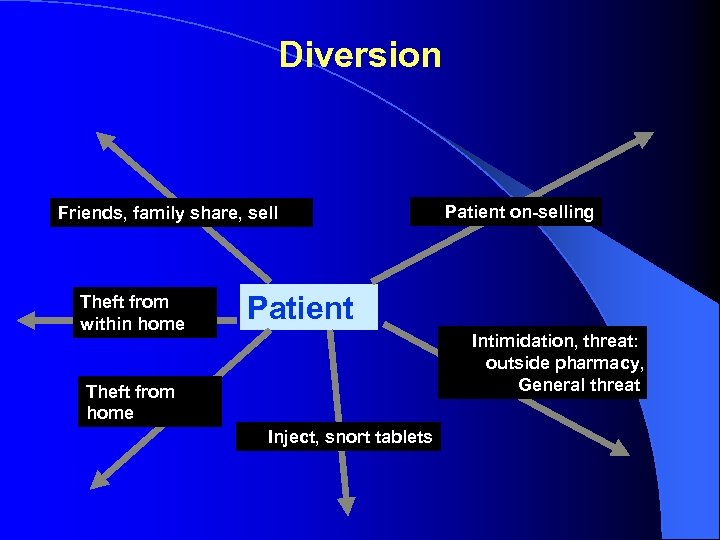 Diversion Friends, family share, sell Theft from within home Patient on-selling Patient Intimidation, threat: outside pharmacy, General threat Theft from home Inject, snort tablets
Diversion Friends, family share, sell Theft from within home Patient on-selling Patient Intimidation, threat: outside pharmacy, General threat Theft from home Inject, snort tablets
 High risk - low value drugs: characteristics l Euphorigenic, sedating l Intoxicating l Rapid onset of effect l Low margin – therapeutic & toxic dose l Low therapeutic advantage l Formulation problem - high dose, gelcap
High risk - low value drugs: characteristics l Euphorigenic, sedating l Intoxicating l Rapid onset of effect l Low margin – therapeutic & toxic dose l Low therapeutic advantage l Formulation problem - high dose, gelcap
 High risk - low value drugs: removed l chloral hydrate l barbiturates l methaqualone l temazepam gelcaps (UK, Australia) l flunitrazepam 2 mg l dextromoramide l propoxyphene (UK, NZ, EU, USA)
High risk - low value drugs: removed l chloral hydrate l barbiturates l methaqualone l temazepam gelcaps (UK, Australia) l flunitrazepam 2 mg l dextromoramide l propoxyphene (UK, NZ, EU, USA)
 High risk - low value drugs: current concerns l Compound analgesics – opioid + simple analgesic (US, UK, NZ, Aust) l midazolam oral tablets (Asia), l quetiapine (antipsychotic) l alprazolam (e. g. Xanax®) l propoxyphene l pethidine (meperidine)
High risk - low value drugs: current concerns l Compound analgesics – opioid + simple analgesic (US, UK, NZ, Aust) l midazolam oral tablets (Asia), l quetiapine (antipsychotic) l alprazolam (e. g. Xanax®) l propoxyphene l pethidine (meperidine)
![Toolbox Problem High risk, low value drugs [change registration & review process] countermeasure • Toolbox Problem High risk, low value drugs [change registration & review process] countermeasure •](https://present5.com/presentation/819a7f2332cee3ac77b7f84d4e4b8c2d/image-11.jpg) Toolbox Problem High risk, low value drugs [change registration & review process] countermeasure • Registration process – assess diversion risk • Enhanced information systems to monitor drugs subject to diversion • Early identification of adverse trends • Agile and adaptable regulatory system • Review and remove • Reschedule to more restrictive
Toolbox Problem High risk, low value drugs [change registration & review process] countermeasure • Registration process – assess diversion risk • Enhanced information systems to monitor drugs subject to diversion • Early identification of adverse trends • Agile and adaptable regulatory system • Review and remove • Reschedule to more restrictive
 High risk - high value drugs: characteristics l l l Clinically important Commonly misused, diverted Dependence-producing, intoxicating effect Criminal activity - to obtain & under-the-influence Contribute to severe morbidity, mortality Heterogeneous, hidden sub-populations – Include non-injectors, not from drug subculture
High risk - high value drugs: characteristics l l l Clinically important Commonly misused, diverted Dependence-producing, intoxicating effect Criminal activity - to obtain & under-the-influence Contribute to severe morbidity, mortality Heterogeneous, hidden sub-populations – Include non-injectors, not from drug subculture
 High risk - high value drugs: categories l Opioids l Benzodiazepines & other sedatives l l l Antipsychotic, antidepressant drugs Pharmacotherapies (opioid dependence) Precursor drugs Other (e. g. anti-Parkinson’s drugs, appetite suppressants, stimulants) Performance-enhancing - veterinary & human
High risk - high value drugs: categories l Opioids l Benzodiazepines & other sedatives l l l Antipsychotic, antidepressant drugs Pharmacotherapies (opioid dependence) Precursor drugs Other (e. g. anti-Parkinson’s drugs, appetite suppressants, stimulants) Performance-enhancing - veterinary & human
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Regulatory control countermeasure • Appropriate regulatory control && enforcement • Prescription - quantities in words & figures • Pharmacist know handwriting • No. items, cross out blank • Pharmacist to know handwriting or contact prescriber • Special prescription pads • Electronic prescribing replace paper • Oversight - problematic prescribing – automated analysis • National uniformity
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Regulatory control countermeasure • Appropriate regulatory control && enforcement • Prescription - quantities in words & figures • Pharmacist know handwriting • No. items, cross out blank • Pharmacist to know handwriting or contact prescriber • Special prescription pads • Electronic prescribing replace paper • Oversight - problematic prescribing – automated analysis • National uniformity
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Insufficient information about HRHV drug supply to individuals -> unsafe supply countermeasure • Coordinated medication management • Real time, for prescribers, pharmacists, at time of prescribing, dispensing • available to regulators – detect injudicious supply, diversion • Automated real-time analysis • Software to detect forged or altered scripts, drug-seeker, at-risk individuals • Privacy safeguards, audit trail of access • Encryption • Unique health-care identifiers • National – across State/Provinces • Include OTC high risk drugs
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Insufficient information about HRHV drug supply to individuals -> unsafe supply countermeasure • Coordinated medication management • Real time, for prescribers, pharmacists, at time of prescribing, dispensing • available to regulators – detect injudicious supply, diversion • Automated real-time analysis • Software to detect forged or altered scripts, drug-seeker, at-risk individuals • Privacy safeguards, audit trail of access • Encryption • Unique health-care identifiers • National – across State/Provinces • Include OTC high risk drugs
 Coordinated medication mgmt “Prescription monitoring” l 1 st generation: inspecting pharmacies l 2 nd generation: paper based scripts to central point l 3 rd generation: electronic transmission l 4 th generation: real time information for prescribers, pharmacists, regulators
Coordinated medication mgmt “Prescription monitoring” l 1 st generation: inspecting pharmacies l 2 nd generation: paper based scripts to central point l 3 rd generation: electronic transmission l 4 th generation: real time information for prescribers, pharmacists, regulators
 Coordinated medication mgmt “Prescription monitoring” l 3 rd generation deficiencies – Historical, after-the-event – Limited capacity to identify individuals – Responsibility of operators to notify on limited information – How? Criteria? Delay – Difficult access for professionals needing immediate information for safe supply decisions
Coordinated medication mgmt “Prescription monitoring” l 3 rd generation deficiencies – Historical, after-the-event – Limited capacity to identify individuals – Responsibility of operators to notify on limited information – How? Criteria? Delay – Difficult access for professionals needing immediate information for safe supply decisions
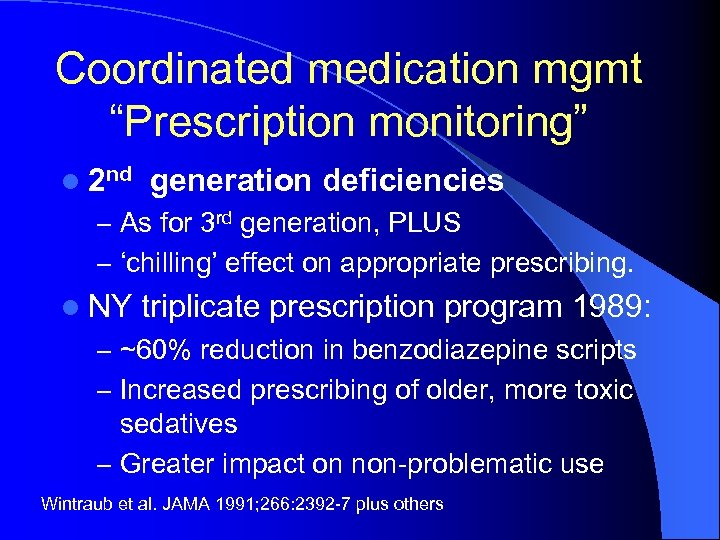 Coordinated medication mgmt “Prescription monitoring” l 2 nd generation deficiencies – As for 3 rd generation, PLUS – ‘chilling’ effect on appropriate prescribing. l NY triplicate prescription program 1989: – ~60% reduction in benzodiazepine scripts – Increased prescribing of older, more toxic sedatives – Greater impact on non-problematic use Wintraub et al. JAMA 1991; 266: 2392 -7 plus others
Coordinated medication mgmt “Prescription monitoring” l 2 nd generation deficiencies – As for 3 rd generation, PLUS – ‘chilling’ effect on appropriate prescribing. l NY triplicate prescription program 1989: – ~60% reduction in benzodiazepine scripts – Increased prescribing of older, more toxic sedatives – Greater impact on non-problematic use Wintraub et al. JAMA 1991; 266: 2392 -7 plus others
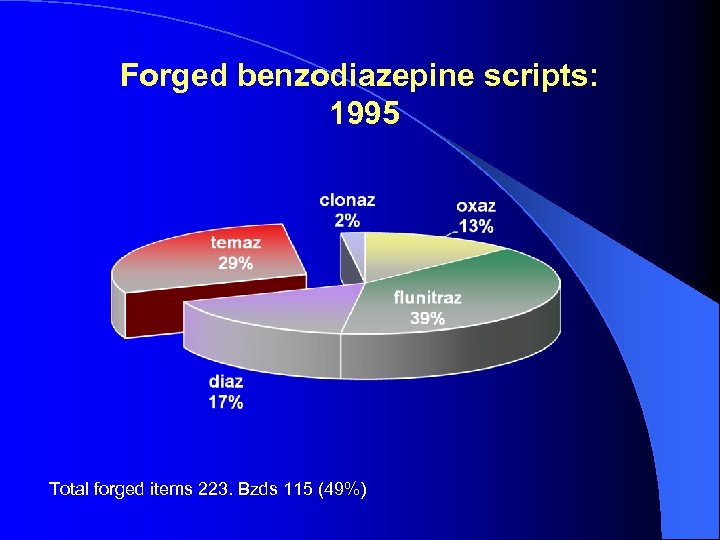 Forged benzodiazepine scripts: 1995 Total forged items 223. Bzds 115 (49%)
Forged benzodiazepine scripts: 1995 Total forged items 223. Bzds 115 (49%)
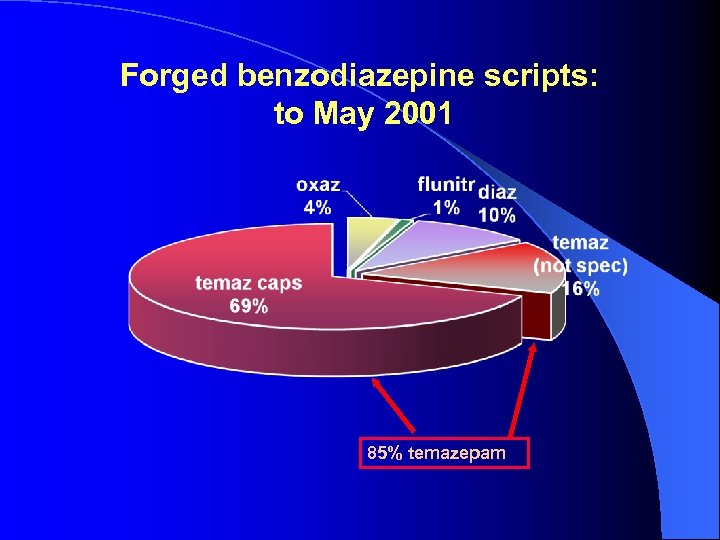 Forged benzodiazepine scripts: to May 2001 85% temazepam
Forged benzodiazepine scripts: to May 2001 85% temazepam
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Forged, altered prescriptions countermeasure • Tamper-proof, dedicated prescriptions for HRHV drugs • Secure storage stationery • Software programs to detect at time of supply (automated) • Electronic prescribing • Specify number of items on script • Words and figures • Cross out unmarked space
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Forged, altered prescriptions countermeasure • Tamper-proof, dedicated prescriptions for HRHV drugs • Secure storage stationery • Software programs to detect at time of supply (automated) • Electronic prescribing • Specify number of items on script • Words and figures • Cross out unmarked space
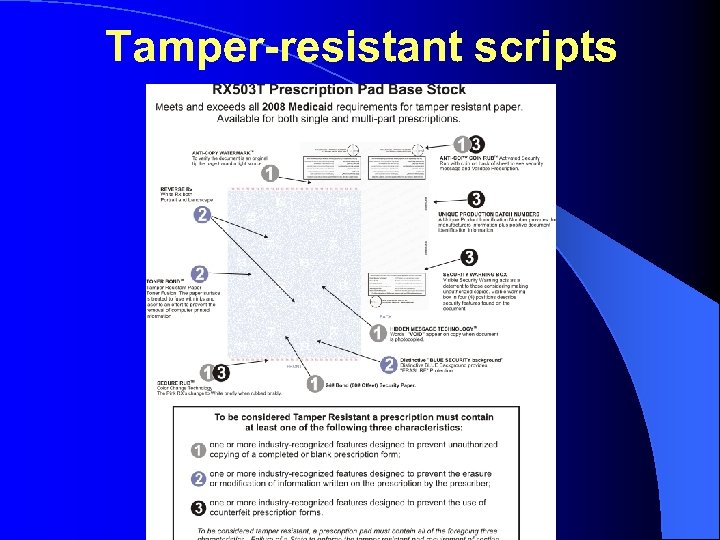 Tamper-resistant scripts
Tamper-resistant scripts
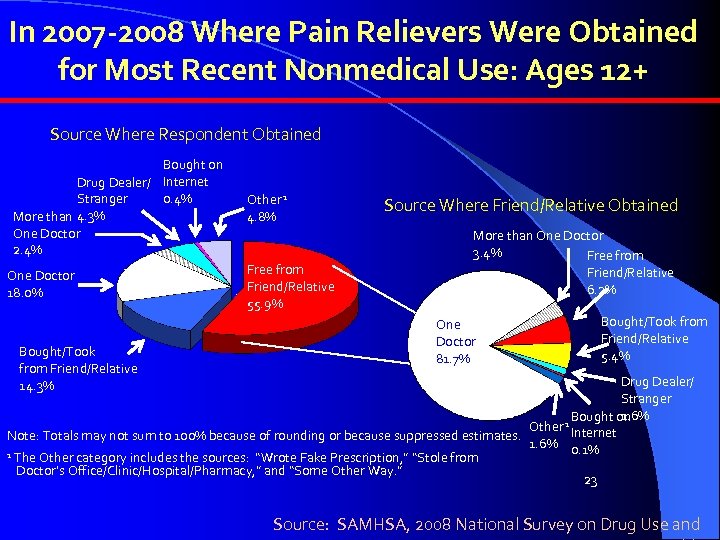 In 2007 -2008 Where Pain Relievers Were Obtained for Most Recent Nonmedical Use: Ages 12+ Source Where Respondent Obtained Bought on Drug Dealer/ Internet 0. 4% Stranger More than 4. 3% One Doctor 2. 4% One Doctor 18. 0% Bought/Took from Friend/Relative 14. 3% Other 1 4. 8% Free from Friend/Relative 55. 9% Source Where Friend/Relative Obtained More than One Doctor 3. 4% Free from Friend/Relative 6. 2% One Doctor 81. 7% Bought/Took from Friend/Relative 5. 4% Drug Dealer/ Stranger 1. 6% Bought on Other 1 Internet Note: Totals may not sum to 100% because of rounding or because suppressed estimates. 1. 6% 0. 1% 1 The Other category includes the sources: “Wrote Fake Prescription, ” “Stole from Doctor’s Office/Clinic/Hospital/Pharmacy, ” and “Some Other Way. ” 23 Source: SAMHSA, 2008 National Survey on Drug Use and
In 2007 -2008 Where Pain Relievers Were Obtained for Most Recent Nonmedical Use: Ages 12+ Source Where Respondent Obtained Bought on Drug Dealer/ Internet 0. 4% Stranger More than 4. 3% One Doctor 2. 4% One Doctor 18. 0% Bought/Took from Friend/Relative 14. 3% Other 1 4. 8% Free from Friend/Relative 55. 9% Source Where Friend/Relative Obtained More than One Doctor 3. 4% Free from Friend/Relative 6. 2% One Doctor 81. 7% Bought/Took from Friend/Relative 5. 4% Drug Dealer/ Stranger 1. 6% Bought on Other 1 Internet Note: Totals may not sum to 100% because of rounding or because suppressed estimates. 1. 6% 0. 1% 1 The Other category includes the sources: “Wrote Fake Prescription, ” “Stole from Doctor’s Office/Clinic/Hospital/Pharmacy, ” and “Some Other Way. ” 23 Source: SAMHSA, 2008 National Survey on Drug Use and
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Patient selection Management of request countermeasure • Identify higher risk patients – MHD, SUD-personal or family history • Examination for evidence of SUD • Screening tools • Universal precautions • Inherited patients special precautions – confirm with previous prescriber directly • Borrowed protection • Scripted responses • Broken record, use “we”
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Patient selection Management of request countermeasure • Identify higher risk patients – MHD, SUD-personal or family history • Examination for evidence of SUD • Screening tools • Universal precautions • Inherited patients special precautions – confirm with previous prescriber directly • Borrowed protection • Scripted responses • Broken record, use “we”
 Pharmacy robbery
Pharmacy robbery
 Oxy. Contin in time-delay safe
Oxy. Contin in time-delay safe
 Ram raid
Ram raid
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem countermeasure Crime to obtain: pharmacy, warehouse, transit, domestic robbery • Requirement to keep in original pack • Indelibly marked or embossed blister packs • Hotline for law enforcement to track to whom dispensed, by whom prescribed and dispensed • ‘Pedigree’ chain records
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem countermeasure Crime to obtain: pharmacy, warehouse, transit, domestic robbery • Requirement to keep in original pack • Indelibly marked or embossed blister packs • Hotline for law enforcement to track to whom dispensed, by whom prescribed and dispensed • ‘Pedigree’ chain records
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Theft, robbery countermeasure • time-release safes, segmented • software to access, PIN no. or biometric ID to prevent pilfering • Mandatory high quality CCTV • indelibly labelled blister packs • Keep small quantities • Keep none, get on consignment • Crime prevention – visibility, layout, lighting, hours of opening
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Theft, robbery countermeasure • time-release safes, segmented • software to access, PIN no. or biometric ID to prevent pilfering • Mandatory high quality CCTV • indelibly labelled blister packs • Keep small quantities • Keep none, get on consignment • Crime prevention – visibility, layout, lighting, hours of opening
 Blister pack
Blister pack
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Identity fraud countermeasure • unique health-care identifiers • ‘inherited’ patients: special precautions
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Identity fraud countermeasure • unique health-care identifiers • ‘inherited’ patients: special precautions
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Patient onselling countermeasure • Requirement to keep in original indelibly marked or embossed pack • Coordinated medication management system to detect unusually high doses • Pill counts • Urine drug screen
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Patient onselling countermeasure • Requirement to keep in original indelibly marked or embossed pack • Coordinated medication management system to detect unusually high doses • Pill counts • Urine drug screen
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Trafficking, brokering countermeasure • Requirement to keep in original indelibly marked or embossed pack • Pedigree trail - audit • Supported by hotline for law enforcement • Penalty for unauthorised possession, or not in original pack • Coordinated medication management system to detect unusually high dose supply, potential on-selling •
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Trafficking, brokering countermeasure • Requirement to keep in original indelibly marked or embossed pack • Pedigree trail - audit • Supported by hotline for law enforcement • Penalty for unauthorised possession, or not in original pack • Coordinated medication management system to detect unusually high dose supply, potential on-selling •
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Sharing, domestic source, medicine cabinet countermeasure • Patient information – risks, safe storage • Never share • Limited quantity of supply • Return unused HRHV medicines • Safe storage
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Sharing, domestic source, medicine cabinet countermeasure • Patient information – risks, safe storage • Never share • Limited quantity of supply • Return unused HRHV medicines • Safe storage
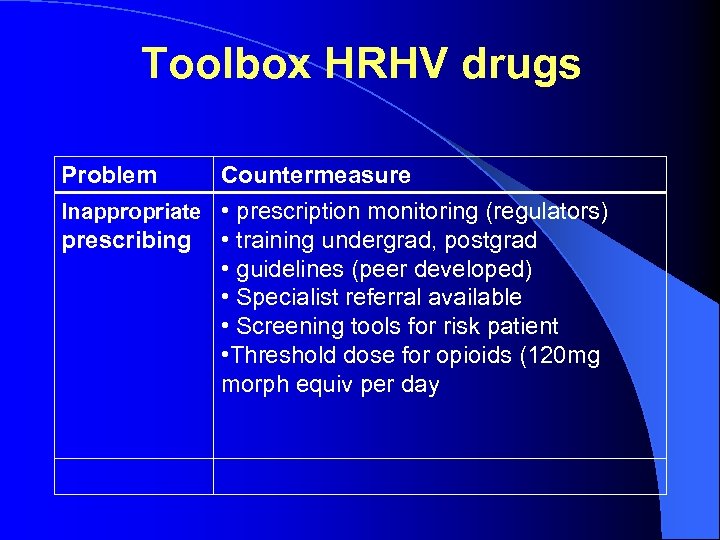 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Countermeasure Inappropriate • prescription monitoring (regulators) prescribing • training undergrad, postgrad • guidelines (peer developed) • Specialist referral available • Screening tools for risk patient • Threshold dose for opioids (120 mg morph equiv per day
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Countermeasure Inappropriate • prescription monitoring (regulators) prescribing • training undergrad, postgrad • guidelines (peer developed) • Specialist referral available • Screening tools for risk patient • Threshold dose for opioids (120 mg morph equiv per day
 Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Poisoning risk countermeasure • Patient information – risks, safe use, storage • Labelling, package inserts, leaflets advice – prescribers & pharmacists • Return unused drugs • Information about recognition of coma • Advice about use of other CNS depressants (inc alcohol)
Toolbox HRHV drugs Problem Poisoning risk countermeasure • Patient information – risks, safe use, storage • Labelling, package inserts, leaflets advice – prescribers & pharmacists • Return unused drugs • Information about recognition of coma • Advice about use of other CNS depressants (inc alcohol)
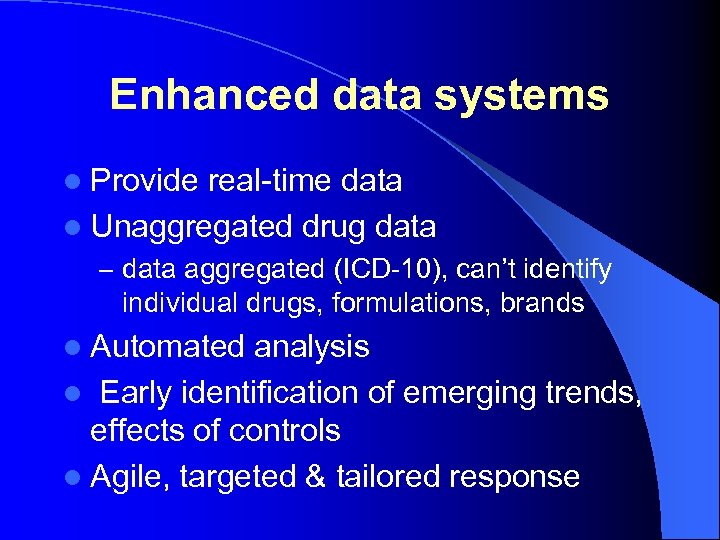 Enhanced data systems l Provide real-time data l Unaggregated drug data – data aggregated (ICD-10), can’t identify individual drugs, formulations, brands l Automated analysis l Early identification of emerging trends, effects of controls l Agile, targeted & tailored response
Enhanced data systems l Provide real-time data l Unaggregated drug data – data aggregated (ICD-10), can’t identify individual drugs, formulations, brands l Automated analysis l Early identification of emerging trends, effects of controls l Agile, targeted & tailored response
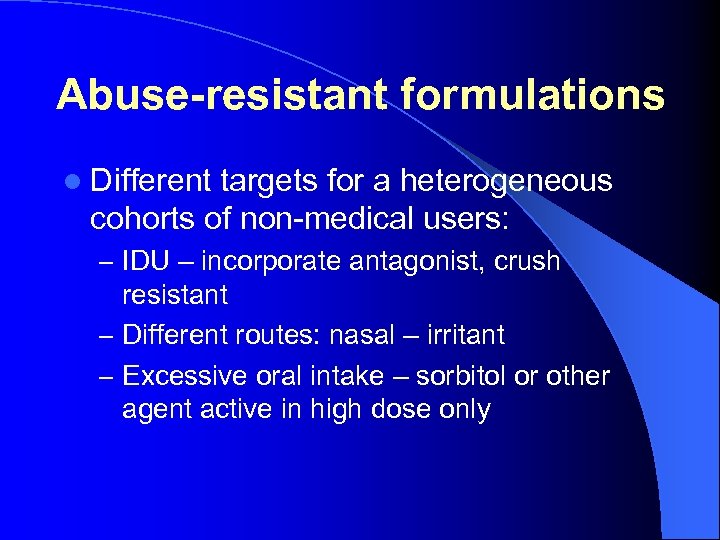 Abuse-resistant formulations l Different targets for a heterogeneous cohorts of non-medical users: – IDU – incorporate antagonist, crush resistant – Different routes: nasal – irritant – Excessive oral intake – sorbitol or other agent active in high dose only
Abuse-resistant formulations l Different targets for a heterogeneous cohorts of non-medical users: – IDU – incorporate antagonist, crush resistant – Different routes: nasal – irritant – Excessive oral intake – sorbitol or other agent active in high dose only
 DEMAND CONTROL l Prescriber/pharmacist education about optimal use of high risk high value drugs l -use non-drug, non-risk drug to max l Patient information about safe use, risks l Reconfigure services to attract and retain individuals in treatment l Reconfigure treatment regimes tailored to needs. l Integrated multi-disciplinary care
DEMAND CONTROL l Prescriber/pharmacist education about optimal use of high risk high value drugs l -use non-drug, non-risk drug to max l Patient information about safe use, risks l Reconfigure services to attract and retain individuals in treatment l Reconfigure treatment regimes tailored to needs. l Integrated multi-disciplinary care


