9f6c19c355670d23f4ce333fdf69402a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 PFMEA Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis James Davis, General Dynamics
PFMEA Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis James Davis, General Dynamics
 Purpose The purpose of this presentation is to share the benefits of a detailed Process Flow Diagram, conducted during a Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis, that will ensure product quality in the manufacturing/assembly process. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 2
Purpose The purpose of this presentation is to share the benefits of a detailed Process Flow Diagram, conducted during a Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis, that will ensure product quality in the manufacturing/assembly process. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 2
 Introduction James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 3
Introduction James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 3
 Definition of FMEA A FMEA is an analytical tool that uses a disciplined technique to identify and help eliminate product and process potential failure modes. o o By ID of potential failures Assessing the risks caused by failure modes and Identify corrective actions Prioritizing corrective actions Carry out corrective actions James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 4
Definition of FMEA A FMEA is an analytical tool that uses a disciplined technique to identify and help eliminate product and process potential failure modes. o o By ID of potential failures Assessing the risks caused by failure modes and Identify corrective actions Prioritizing corrective actions Carry out corrective actions James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 4
 Most COMMON Types of FMEA's Design (Potential) Failure Modes and Effects Analysis-DFMEA • Focus is on potential design- related failures and their causes. Process (Potential) Failures Modes and Effects Analysis-PFMEA • Focuses is on potential process failures and their causes. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 5
Most COMMON Types of FMEA's Design (Potential) Failure Modes and Effects Analysis-DFMEA • Focus is on potential design- related failures and their causes. Process (Potential) Failures Modes and Effects Analysis-PFMEA • Focuses is on potential process failures and their causes. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 5
 Value of FMEA's l Aids in improving designs for products and process § Increased safety § Enhances Customer Satisfaction o o Better Quality Higher Reliability l Contributes to cost savings § Decreases warranty costs § Decreases waste, non-value added operations James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 6
Value of FMEA's l Aids in improving designs for products and process § Increased safety § Enhances Customer Satisfaction o o Better Quality Higher Reliability l Contributes to cost savings § Decreases warranty costs § Decreases waste, non-value added operations James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 6
 PFMEA's l Focus is on potential process –related failures and their causes. §Main drive is to understand the process through the identification of as many potential failures as possible. o e. g. Incorrect material used l PFMEA typically assumes that the design is sound. l Development of Recommended Actions is targeted at eliminating the Root Cause of the potential failures. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 7
PFMEA's l Focus is on potential process –related failures and their causes. §Main drive is to understand the process through the identification of as many potential failures as possible. o e. g. Incorrect material used l PFMEA typically assumes that the design is sound. l Development of Recommended Actions is targeted at eliminating the Root Cause of the potential failures. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 7
 PFMEA Three Parts: l. Process Flow Diagram (PFD) l. Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) l. Process Control Plan (PCP) James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 8
PFMEA Three Parts: l. Process Flow Diagram (PFD) l. Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) l. Process Control Plan (PCP) James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 8
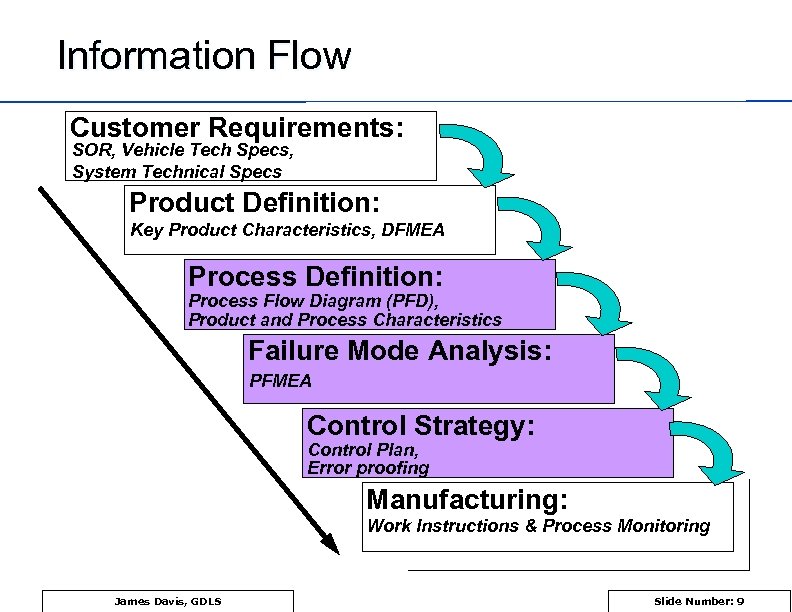 Information Flow Customer Requirements: SOR, Vehicle Tech Specs, System Technical Specs Product Definition: Key Product Characteristics, DFMEA Process Definition: Process Flow Diagram (PFD), Product and Process Characteristics Failure Mode Analysis: PFMEA Control Strategy: Control Plan, Error proofing Manufacturing: Work Instructions & Process Monitoring James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 9
Information Flow Customer Requirements: SOR, Vehicle Tech Specs, System Technical Specs Product Definition: Key Product Characteristics, DFMEA Process Definition: Process Flow Diagram (PFD), Product and Process Characteristics Failure Mode Analysis: PFMEA Control Strategy: Control Plan, Error proofing Manufacturing: Work Instructions & Process Monitoring James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 9
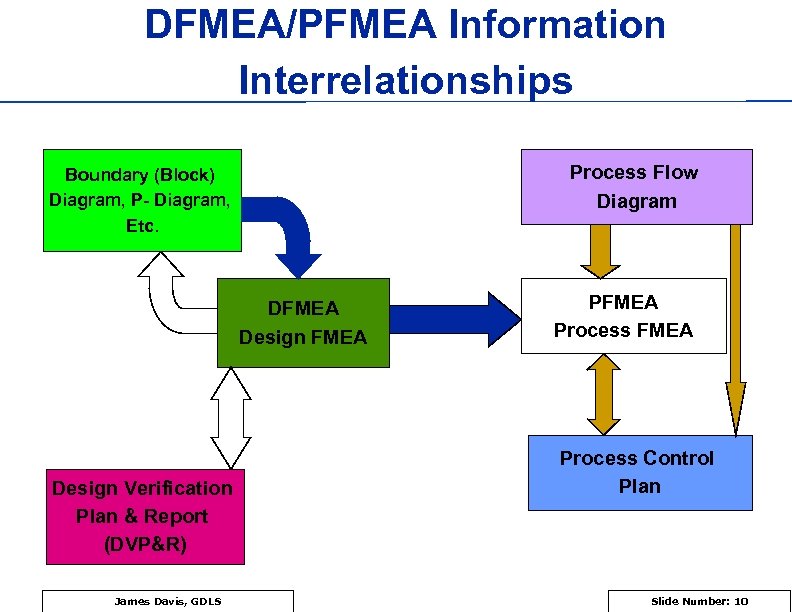 DFMEA/PFMEA Information Interrelationships Process Flow Diagram Boundary (Block) Diagram, P- Diagram, Etc. DFMEA Design Verification Plan & Report (DVP&R) James Davis, GDLS PFMEA Process Control Plan Slide Number: 10
DFMEA/PFMEA Information Interrelationships Process Flow Diagram Boundary (Block) Diagram, P- Diagram, Etc. DFMEA Design Verification Plan & Report (DVP&R) James Davis, GDLS PFMEA Process Control Plan Slide Number: 10
 Process Flow Diagrams l The Process Flow Diagram provides a logical (visual) depiction of the process that is being analyzed. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 11
Process Flow Diagrams l The Process Flow Diagram provides a logical (visual) depiction of the process that is being analyzed. James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 11
 Process Function / Requirement l The SAE/AIAG PFMEA guidelines describe two methods of defining process functions. Either or both may be used. l Process Functions may be described in terms of: § The product features/characteristics that are created or § The process actions that are performed l Process functions should be identified in detail as necessary to provide information for the PFMEA to develop effective Process Controls James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 12 12
Process Function / Requirement l The SAE/AIAG PFMEA guidelines describe two methods of defining process functions. Either or both may be used. l Process Functions may be described in terms of: § The product features/characteristics that are created or § The process actions that are performed l Process functions should be identified in detail as necessary to provide information for the PFMEA to develop effective Process Controls James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 12 12
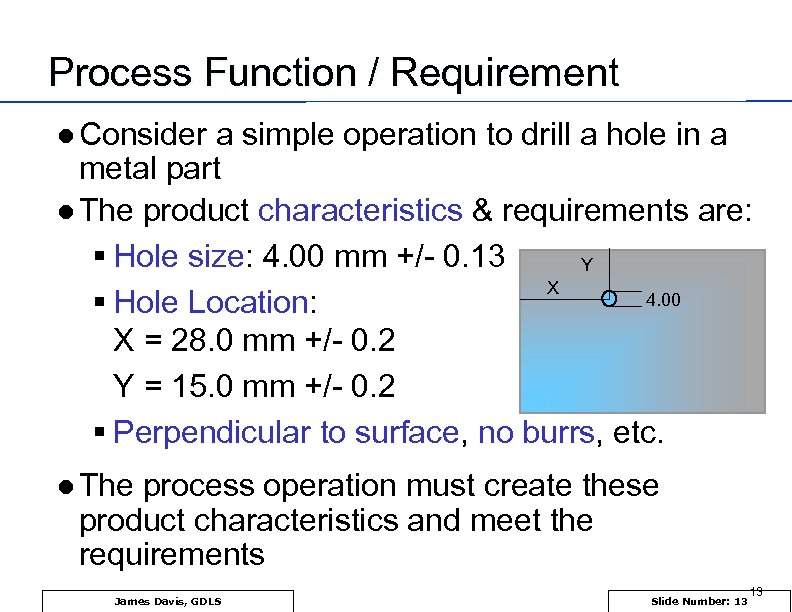 Process Function / Requirement l Consider a simple operation to drill a hole in a metal part l The product characteristics & requirements are: § Hole size: 4. 00 mm +/- 0. 13 Y X 4. 00 § Hole Location: X = 28. 0 mm +/- 0. 2 Y = 15. 0 mm +/- 0. 2 § Perpendicular to surface, no burrs, etc. l The process operation must create these product characteristics and meet the requirements James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 13 13
Process Function / Requirement l Consider a simple operation to drill a hole in a metal part l The product characteristics & requirements are: § Hole size: 4. 00 mm +/- 0. 13 Y X 4. 00 § Hole Location: X = 28. 0 mm +/- 0. 2 Y = 15. 0 mm +/- 0. 2 § Perpendicular to surface, no burrs, etc. l The process operation must create these product characteristics and meet the requirements James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 13 13
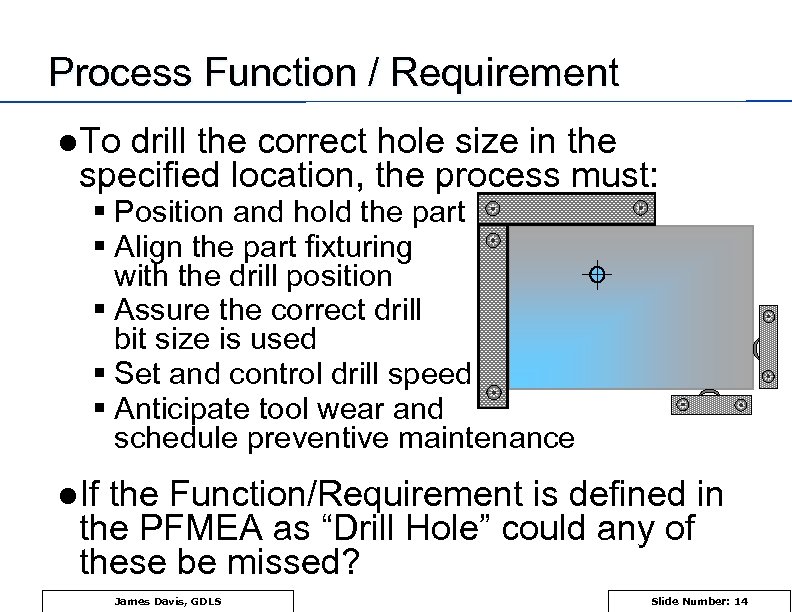 Process Function / Requirement l To drill the correct hole size in the specified location, the process must: § Position and hold the part § Align the part fixturing with the drill position § Assure the correct drill bit size is used § Set and control drill speed § Anticipate tool wear and schedule preventive maintenance l If the Function/Requirement is defined in the PFMEA as “Drill Hole” could any of these be missed? James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 14
Process Function / Requirement l To drill the correct hole size in the specified location, the process must: § Position and hold the part § Align the part fixturing with the drill position § Assure the correct drill bit size is used § Set and control drill speed § Anticipate tool wear and schedule preventive maintenance l If the Function/Requirement is defined in the PFMEA as “Drill Hole” could any of these be missed? James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 14
 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) l Process Flow Diagram is the foundation § The process must be defined step by step, including interfaces § The PFD provides the structure to document what product characteristics and requirements (OUTPUTS) are affected by a given operation and how these characteristics and sources of variation are controlled (INPUTS) § PFD is a graphical representation of every possible path a part can take through the anticipated manufacturing process § A well defined PFD establishes the foundation for the PFMEA l Helps in developing equipment specifications. § How will the process control non-conforming material? § How and when will inspections be performed, what is required? § How and when will parts be re-introduced into the process? James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 15
Process Flow Diagram (PFD) l Process Flow Diagram is the foundation § The process must be defined step by step, including interfaces § The PFD provides the structure to document what product characteristics and requirements (OUTPUTS) are affected by a given operation and how these characteristics and sources of variation are controlled (INPUTS) § PFD is a graphical representation of every possible path a part can take through the anticipated manufacturing process § A well defined PFD establishes the foundation for the PFMEA l Helps in developing equipment specifications. § How will the process control non-conforming material? § How and when will inspections be performed, what is required? § How and when will parts be re-introduced into the process? James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 15
 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) l Hidden Factories: § Interfacing Processes Quality Audits Rework Processes Alternative Processes Scrap Part Buffers Part Movement Product/tooling Changeovers Part Ident. /Labeling Teardown Gauging Stations Reject Handling § Interface process issues affect quality performance o o l Rework and scrap parts bypass process controls Mixed parts in the manufacturing process at changeovers Need for common systems § Part of the overall Quality Strategy must include o Common content, common format, common approach § Quality strategy must extend to suppliers o Considered an extension of the Total Quality processes James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 16
Process Flow Diagram (PFD) l Hidden Factories: § Interfacing Processes Quality Audits Rework Processes Alternative Processes Scrap Part Buffers Part Movement Product/tooling Changeovers Part Ident. /Labeling Teardown Gauging Stations Reject Handling § Interface process issues affect quality performance o o l Rework and scrap parts bypass process controls Mixed parts in the manufacturing process at changeovers Need for common systems § Part of the overall Quality Strategy must include o Common content, common format, common approach § Quality strategy must extend to suppliers o Considered an extension of the Total Quality processes James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 16
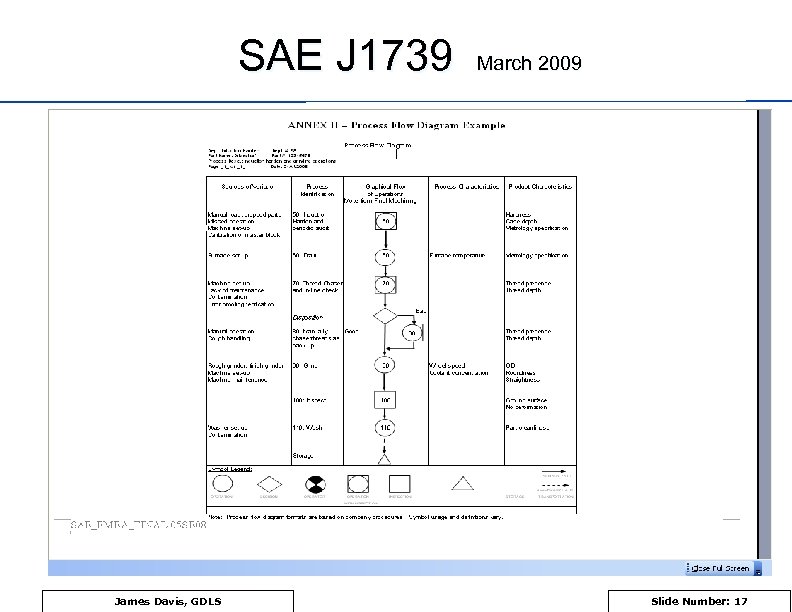 SAE J 1739 James Davis, GDLS March 2009 Slide Number: 17
SAE J 1739 James Davis, GDLS March 2009 Slide Number: 17
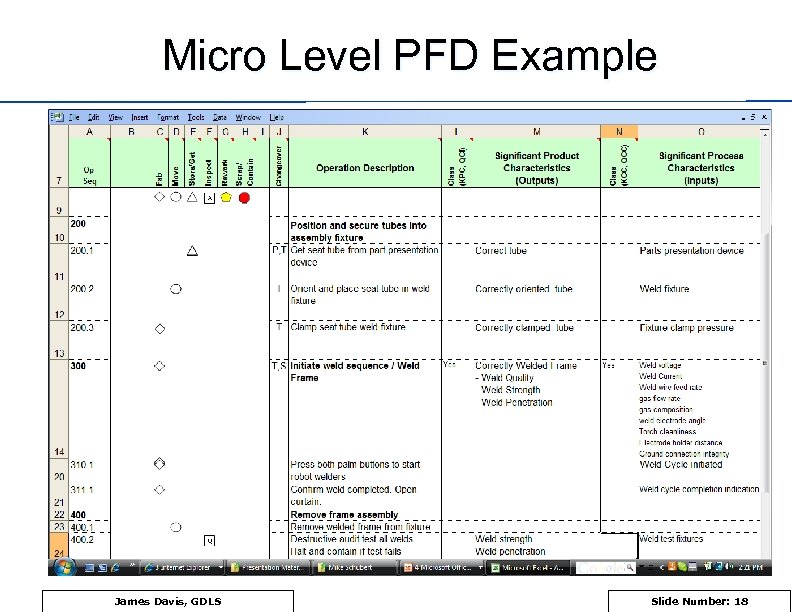 Micro Level PFD Example James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 18
Micro Level PFD Example James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 18
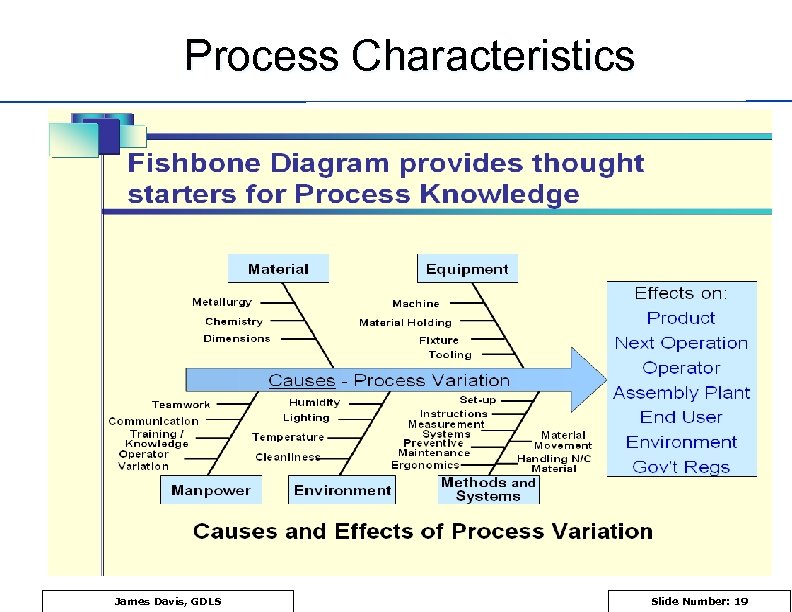 Process Characteristics James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 19
Process Characteristics James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 19
 PFD Feeds PFMEA Identify the Function(s) l Function is a description of what the Process does to meet the requirements Ø Related to process specification and product characteristics Ø Comes from the PFD operation description column l Functions can be described as: Ø Do this operation… Ø To this part or material… Ø With this tooling or equipment… James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 20
PFD Feeds PFMEA Identify the Function(s) l Function is a description of what the Process does to meet the requirements Ø Related to process specification and product characteristics Ø Comes from the PFD operation description column l Functions can be described as: Ø Do this operation… Ø To this part or material… Ø With this tooling or equipment… James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 20
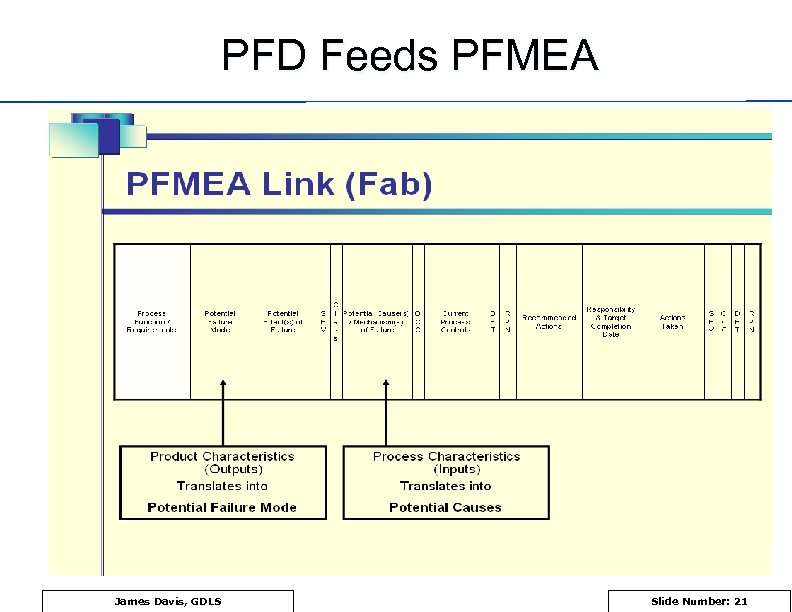 PFD Feeds PFMEA James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 21
PFD Feeds PFMEA James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 21
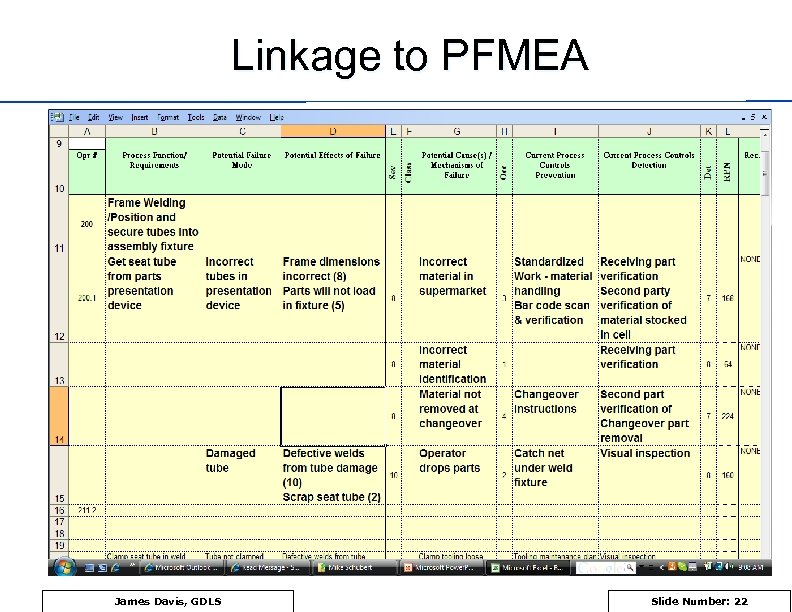 Linkage to PFMEA James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 22
Linkage to PFMEA James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 22
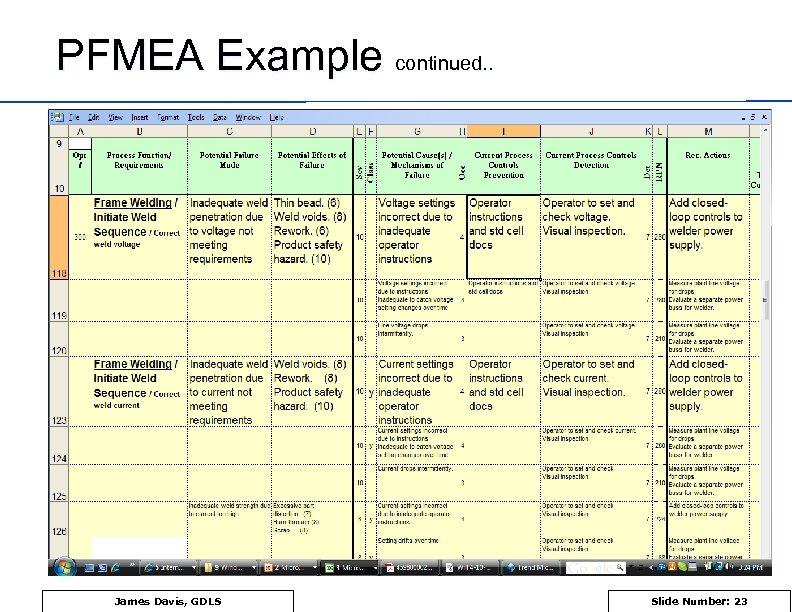 PFMEA Example continued. . James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 23
PFMEA Example continued. . James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 23
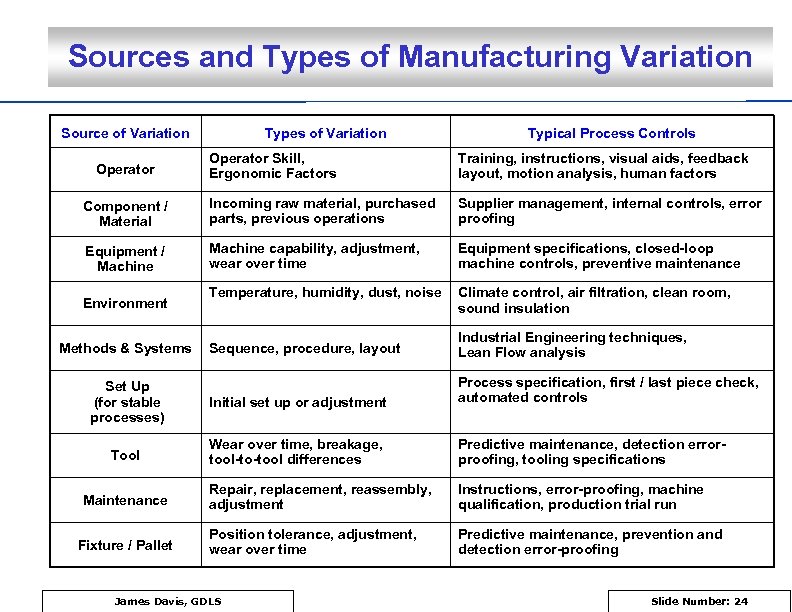 Sources and Types of Manufacturing Variation Source of Variation Types of Variation Typical Process Controls Operator Skill, Ergonomic Factors Training, instructions, visual aids, feedback layout, motion analysis, human factors Component / Material Incoming raw material, purchased parts, previous operations Supplier management, internal controls, error proofing Equipment / Machine capability, adjustment, wear over time Equipment specifications, closed-loop machine controls, preventive maintenance Temperature, humidity, dust, noise Climate control, air filtration, clean room, sound insulation Operator Environment Sequence, procedure, layout Industrial Engineering techniques, Lean Flow analysis Set Up (for stable processes) Initial set up or adjustment Process specification, first / last piece check, automated controls Tool Wear over time, breakage, tool-to-tool differences Predictive maintenance, detection errorproofing, tooling specifications Repair, replacement, reassembly, adjustment Instructions, error-proofing, machine qualification, production trial run Position tolerance, adjustment, wear over time Predictive maintenance, prevention and detection error-proofing Methods & Systems Maintenance Fixture / Pallet James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 24
Sources and Types of Manufacturing Variation Source of Variation Types of Variation Typical Process Controls Operator Skill, Ergonomic Factors Training, instructions, visual aids, feedback layout, motion analysis, human factors Component / Material Incoming raw material, purchased parts, previous operations Supplier management, internal controls, error proofing Equipment / Machine capability, adjustment, wear over time Equipment specifications, closed-loop machine controls, preventive maintenance Temperature, humidity, dust, noise Climate control, air filtration, clean room, sound insulation Operator Environment Sequence, procedure, layout Industrial Engineering techniques, Lean Flow analysis Set Up (for stable processes) Initial set up or adjustment Process specification, first / last piece check, automated controls Tool Wear over time, breakage, tool-to-tool differences Predictive maintenance, detection errorproofing, tooling specifications Repair, replacement, reassembly, adjustment Instructions, error-proofing, machine qualification, production trial run Position tolerance, adjustment, wear over time Predictive maintenance, prevention and detection error-proofing Methods & Systems Maintenance Fixture / Pallet James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 24
 Process Control Plan l PCP will be based on the previous activities in PFD and PFMEA. l Review the PFMEA information developed & supplied and use to identify: § Specific controls that may be needed due to the information added § Identify which controls are Product or Process o Note any Special Characteristics o Identify evaluation methods, frequency and Control Methods o Note Reaction Plans (particularly related to NC parts) James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 25
Process Control Plan l PCP will be based on the previous activities in PFD and PFMEA. l Review the PFMEA information developed & supplied and use to identify: § Specific controls that may be needed due to the information added § Identify which controls are Product or Process o Note any Special Characteristics o Identify evaluation methods, frequency and Control Methods o Note Reaction Plans (particularly related to NC parts) James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 25
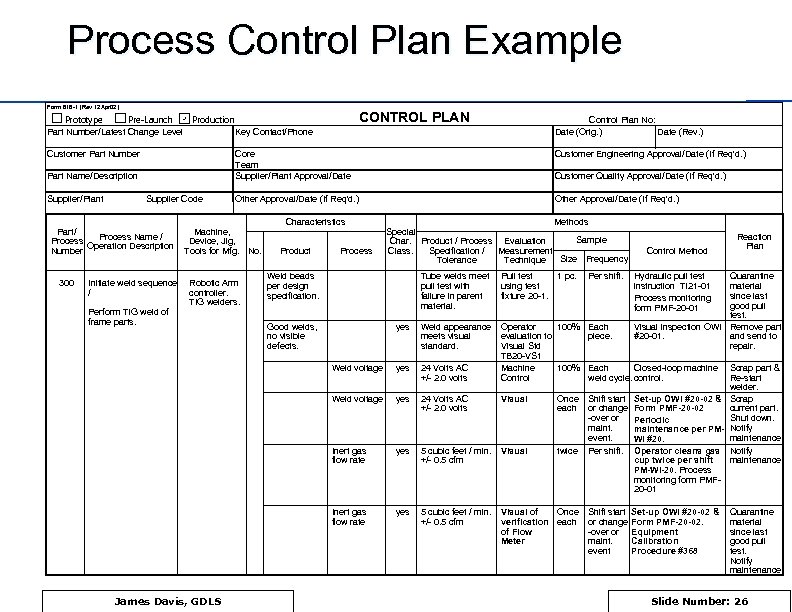 Process Control Plan Example Form 818 -1 (Rev 12 Apr 02) CONTROL PLAN Prototype Pre-Launch Production Part Number/Latest Change Level Key Contact/Phone Customer Part Number Core Team Supplier/Plant Approval/Date Part Name/Description Supplier/Plant Supplier Code Part/ Process Name / Process Operation Description Number 300 Control Plan No: Date (Orig. ) Date (Rev. ) Customer Engineering Approval/Date (If Req'd. ) Other Approval/Date (If Req'd. ) Machine, Device, Jig, Tools for Mfg. No. Characteristics Product Process Customer Quality Approval/Date (If Req'd. ) Methods Special Sample Char. Product / Process Evaluation Specification / Measurement Class. Size Frequency Tolerance Technique yes Weld appearance meets visual standard. yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Operator 100% Each evaluation to piece. Visual Std TB 20 -VS 1 Machine 100% Each Closed-loop machine Control weld cycle. control. yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Visual Once each Inert gas flow rate yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual twice Inert gas flow rate James Davis, GDLS Pull test using test fixture 20 -1. Weld voltage Perform TIG weld of frame parts. Robotic Arm controller. TIG welders. Tube welds meet pull test with failure in parent material. Weld voltage Initiate weld sequence / Weld beads per design specification. yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual of Once verification each of Flow Meter Good welds, no visible defects. 1 pc. Per shift. Control Method Reaction Plan Hydraulic pull test instruction TI 21 -01 Process monitoring form PMF-20 -01 Quarantine material since last good pull test. Visual inspection OWI Remove part #20 -01. and send to repair. Scrap part & Re-start welder. Shift start Set-up OWI #20 -02 & Scrap or change Form PMF-20 -02 current part. -over or Shut down. Periodic maintenance per PM- Notify event. maintenance. WI #20. Per shift. Operator cleans gas Notify cup twice per shift maintenance. PM-WI-20. Process monitoring form PMF 20 -01 Shift start or change -over or maint. event Set-up OWI #20 -02 & Form PMF-20 -02. Equipment Calibration Procedure #368 Quarantine material since last good pull test. Notify maintenance. Slide Number: 26
Process Control Plan Example Form 818 -1 (Rev 12 Apr 02) CONTROL PLAN Prototype Pre-Launch Production Part Number/Latest Change Level Key Contact/Phone Customer Part Number Core Team Supplier/Plant Approval/Date Part Name/Description Supplier/Plant Supplier Code Part/ Process Name / Process Operation Description Number 300 Control Plan No: Date (Orig. ) Date (Rev. ) Customer Engineering Approval/Date (If Req'd. ) Other Approval/Date (If Req'd. ) Machine, Device, Jig, Tools for Mfg. No. Characteristics Product Process Customer Quality Approval/Date (If Req'd. ) Methods Special Sample Char. Product / Process Evaluation Specification / Measurement Class. Size Frequency Tolerance Technique yes Weld appearance meets visual standard. yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Operator 100% Each evaluation to piece. Visual Std TB 20 -VS 1 Machine 100% Each Closed-loop machine Control weld cycle. control. yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Visual Once each Inert gas flow rate yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual twice Inert gas flow rate James Davis, GDLS Pull test using test fixture 20 -1. Weld voltage Perform TIG weld of frame parts. Robotic Arm controller. TIG welders. Tube welds meet pull test with failure in parent material. Weld voltage Initiate weld sequence / Weld beads per design specification. yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual of Once verification each of Flow Meter Good welds, no visible defects. 1 pc. Per shift. Control Method Reaction Plan Hydraulic pull test instruction TI 21 -01 Process monitoring form PMF-20 -01 Quarantine material since last good pull test. Visual inspection OWI Remove part #20 -01. and send to repair. Scrap part & Re-start welder. Shift start Set-up OWI #20 -02 & Scrap or change Form PMF-20 -02 current part. -over or Shut down. Periodic maintenance per PM- Notify event. maintenance. WI #20. Per shift. Operator cleans gas Notify cup twice per shift maintenance. PM-WI-20. Process monitoring form PMF 20 -01 Shift start or change -over or maint. event Set-up OWI #20 -02 & Form PMF-20 -02. Equipment Calibration Procedure #368 Quarantine material since last good pull test. Notify maintenance. Slide Number: 26
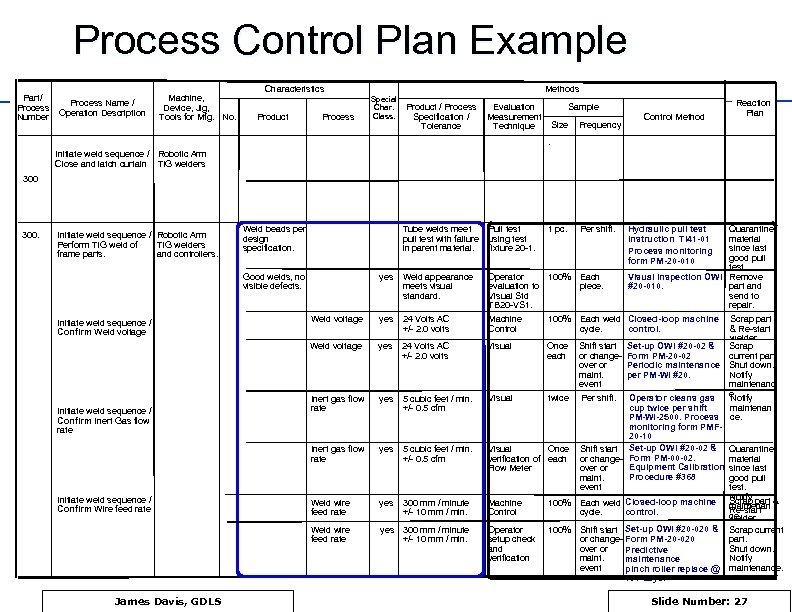 Process Control Plan Example Part/ Process Number Process Name / Operation Description Machine, Device, Jig, Tools for Mfg. No. Characteristics Product Process Methods Special Char. Class. Product / Process Specification / Tolerance Sample Evaluation Measurement Technique Size Frequency 1 pc. Per shift. Control Method Reaction Plan . Initiate weld sequence / Robotic Arm Close and latch curtain TIG welders 300. Tube welds meet pull test with failure in parent material. Pull test using test fixture 20 -1. yes Weld appearance meets visual standard. Operator 100% evaluation to Visual Std TB 20 -VS 1. Each piece. Weld voltage yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Machine Control 100% Each weld Closed-loop machine cycle. control. Weld voltage yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Visual Once each Shift start or changeover or maint. event Inert gas flow rate yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual twice Per shift. Inert gas flow rate yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual Once verification of each Flow Meter Weld wire feed rate yes 300 mm / minute +/- 10 mm / min. Machine Control 100% Each weld Closed-loop machine control. cycle. Weld wire feed rate Initiate weld sequence / Robotic Arm Perform TIG weld of TIG welders frame parts. and controllers. Weld beads per design specification. yes 300 mm / minute +/- 10 mm / min. Operator setup check and verification 100% Shift start Set-up OWI #20 -020 & or change- Form PM-20 -020 over or Predictive maintenance event pinch roller replace @ 180 days. Good welds, no visible defects. Initiate weld sequence / Confirm Weld voltage Initiate weld sequence / Confirm Inert Gas flow rate Initiate weld sequence / Confirm Wire feed rate James Davis, GDLS Hydraulic pull test instruction TI 41 -01 Process monitoring form PM-20 -010 Quarantine material since last good pull test. Visual inspection OWI Remove #20 -010. part and send to repair. Set-up OWI #20 -02 & Form PM-20 -02 Periodic maintenance per PM-WI #20. Operator cleans gas cup twice per shift PM-WI-2500. Process monitoring form PMF 20 -10 Shift start Set-up OWI #20 -02 & or change- Form PM-00 -02. Equipment Calibration over or Procedure #368 maint. event Scrap part & Re-start welder Scrap current part. Shut down. Notify maintenanc e. Notify maintenan ce. Quarantine material since last good pull test. Notify Scrap part & maintenan Re-start ce. welder Scrap current part. Shut down. Notify maintenance. Slide Number: 27
Process Control Plan Example Part/ Process Number Process Name / Operation Description Machine, Device, Jig, Tools for Mfg. No. Characteristics Product Process Methods Special Char. Class. Product / Process Specification / Tolerance Sample Evaluation Measurement Technique Size Frequency 1 pc. Per shift. Control Method Reaction Plan . Initiate weld sequence / Robotic Arm Close and latch curtain TIG welders 300. Tube welds meet pull test with failure in parent material. Pull test using test fixture 20 -1. yes Weld appearance meets visual standard. Operator 100% evaluation to Visual Std TB 20 -VS 1. Each piece. Weld voltage yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Machine Control 100% Each weld Closed-loop machine cycle. control. Weld voltage yes 24 Volts AC +/- 2. 0 volts Visual Once each Shift start or changeover or maint. event Inert gas flow rate yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual twice Per shift. Inert gas flow rate yes 5 cubic feet / min. +/- 0. 5 cfm Visual Once verification of each Flow Meter Weld wire feed rate yes 300 mm / minute +/- 10 mm / min. Machine Control 100% Each weld Closed-loop machine control. cycle. Weld wire feed rate Initiate weld sequence / Robotic Arm Perform TIG weld of TIG welders frame parts. and controllers. Weld beads per design specification. yes 300 mm / minute +/- 10 mm / min. Operator setup check and verification 100% Shift start Set-up OWI #20 -020 & or change- Form PM-20 -020 over or Predictive maintenance event pinch roller replace @ 180 days. Good welds, no visible defects. Initiate weld sequence / Confirm Weld voltage Initiate weld sequence / Confirm Inert Gas flow rate Initiate weld sequence / Confirm Wire feed rate James Davis, GDLS Hydraulic pull test instruction TI 41 -01 Process monitoring form PM-20 -010 Quarantine material since last good pull test. Visual inspection OWI Remove #20 -010. part and send to repair. Set-up OWI #20 -02 & Form PM-20 -02 Periodic maintenance per PM-WI #20. Operator cleans gas cup twice per shift PM-WI-2500. Process monitoring form PMF 20 -10 Shift start Set-up OWI #20 -02 & or change- Form PM-00 -02. Equipment Calibration over or Procedure #368 maint. event Scrap part & Re-start welder Scrap current part. Shut down. Notify maintenanc e. Notify maintenan ce. Quarantine material since last good pull test. Notify Scrap part & maintenan Re-start ce. welder Scrap current part. Shut down. Notify maintenance. Slide Number: 27
 Case Studies – Supplier A l l l Not ISO Certified, Primarily Defense business base Sole Source - Unique Technology No Process Flow § Operator work instruction for 100 piece component o o l 20 process steps on a single piece of paper (included machining) Building the component relied on Tribal Knowledge Diagramming the Process Flow § 20 steps turned into 951 steps to produce the component § 22 manufacturing related issues (from DFMEA) were incorporated in the PFD/PFMEA l Supplier A used PFD - FMEA to § Develop work instructions § Determine the requirement to developed training programs for assemblers / machinists, QC personnel § Develop safety program / training James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 28
Case Studies – Supplier A l l l Not ISO Certified, Primarily Defense business base Sole Source - Unique Technology No Process Flow § Operator work instruction for 100 piece component o o l 20 process steps on a single piece of paper (included machining) Building the component relied on Tribal Knowledge Diagramming the Process Flow § 20 steps turned into 951 steps to produce the component § 22 manufacturing related issues (from DFMEA) were incorporated in the PFD/PFMEA l Supplier A used PFD - FMEA to § Develop work instructions § Determine the requirement to developed training programs for assemblers / machinists, QC personnel § Develop safety program / training James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 28
 Case Studies – Supplier B l l l ISO Certified, Primarily Defense business base Sole Source - Unique Design “Fair” Documented Process Flow § Relied on a combination of operator knowing what should be done next with operator work instructions. o l However it did allow for repeatable assembly of component with skilled employee Diagramming the Process Flow § 270 step PFD became 1, 170 steps o l FMEA analysis determined: work instructions that needed improvement and new work instructions were required Supplier B used PFD- FMEA to § Update work instructions to error proof build process James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 29
Case Studies – Supplier B l l l ISO Certified, Primarily Defense business base Sole Source - Unique Design “Fair” Documented Process Flow § Relied on a combination of operator knowing what should be done next with operator work instructions. o l However it did allow for repeatable assembly of component with skilled employee Diagramming the Process Flow § 270 step PFD became 1, 170 steps o l FMEA analysis determined: work instructions that needed improvement and new work instructions were required Supplier B used PFD- FMEA to § Update work instructions to error proof build process James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 29
 Case Studies – Supplier C l l ISO Certified, Defense/Civil business base Well Documented Process Flow § Operator work instructions allowed for repeatable assembly § Error Proofing allows for assembly with “average” employees l Diagramming the Process Flow § 263 step PFD became 268 steps § 32 manufacturing related issues (from DFMEA) were incorporated in the PFD/PFMEA o l FMEA analysis determined: work instructions that needed improvement and new work instructions were required Supplier C used PFD- FMEA to § Update work instructions James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 30
Case Studies – Supplier C l l ISO Certified, Defense/Civil business base Well Documented Process Flow § Operator work instructions allowed for repeatable assembly § Error Proofing allows for assembly with “average” employees l Diagramming the Process Flow § 263 step PFD became 268 steps § 32 manufacturing related issues (from DFMEA) were incorporated in the PFD/PFMEA o l FMEA analysis determined: work instructions that needed improvement and new work instructions were required Supplier C used PFD- FMEA to § Update work instructions James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 30
 Case Studies – Supplier D l l ISO Certified, Aerospace business base Very Small Company § 2 Master Assemblers (1 of which was the Assembly & Test Manager) l l Unique Technology “Fair” Documented Process Flow § Relied on a combination of operator knowing what should be done next with broad operator work instructions. o l However it did allow for repeatable assembly of component with highly skilled employee Diagramming the Process Flow § 5 page PFD became 22 pages § FMEA analysis determined: work instructions needed improvement to allow for production of more than 1 component at a time l Supplier D used PFD - FMEA to § Develop work instructions with boundary photos § Recall non-compliant parts § Determine the requirement to developed training programs for assemblers, QC personnel § Develop detailed ATP James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 31
Case Studies – Supplier D l l ISO Certified, Aerospace business base Very Small Company § 2 Master Assemblers (1 of which was the Assembly & Test Manager) l l Unique Technology “Fair” Documented Process Flow § Relied on a combination of operator knowing what should be done next with broad operator work instructions. o l However it did allow for repeatable assembly of component with highly skilled employee Diagramming the Process Flow § 5 page PFD became 22 pages § FMEA analysis determined: work instructions needed improvement to allow for production of more than 1 component at a time l Supplier D used PFD - FMEA to § Develop work instructions with boundary photos § Recall non-compliant parts § Determine the requirement to developed training programs for assemblers, QC personnel § Develop detailed ATP James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 31
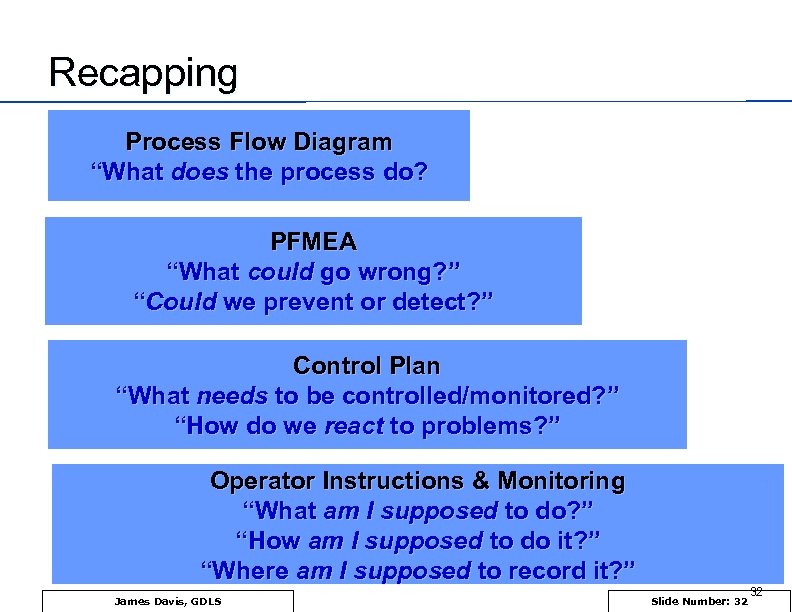 Recapping Process Flow Diagram “What does the process do? PFMEA “What could go wrong? ” “Could we prevent or detect? ” Control Plan “What needs to be controlled/monitored? ” “How do we react to problems? ” Operator Instructions & Monitoring “What am I supposed to do? ” “How am I supposed to do it? ” “Where am I supposed to record it? ” James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 32 32
Recapping Process Flow Diagram “What does the process do? PFMEA “What could go wrong? ” “Could we prevent or detect? ” Control Plan “What needs to be controlled/monitored? ” “How do we react to problems? ” Operator Instructions & Monitoring “What am I supposed to do? ” “How am I supposed to do it? ” “Where am I supposed to record it? ” James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 32 32
 References AIAG FMEA Fourth Edition June 2008 l SAE J 1739 March 2009 l James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 33
References AIAG FMEA Fourth Edition June 2008 l SAE J 1739 March 2009 l James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 33
 Vocabulary l l l AIAG FMEA Fourth Edition Published June 2008 SAE FMEA J 1739 Published March 2009 PFD, Process Flow Diagram PFMEA, Process Failure Modes and Effects Analysis PCP, Process Control Plan James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 34
Vocabulary l l l AIAG FMEA Fourth Edition Published June 2008 SAE FMEA J 1739 Published March 2009 PFD, Process Flow Diagram PFMEA, Process Failure Modes and Effects Analysis PCP, Process Control Plan James Davis, GDLS Slide Number: 34


