Petroleum (Organic Chemistry)
Petroleum (Organic Chemistry)
 What is Petroleum? In it’s natural state, it is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons and other substances, such as water, sulfides, metals and salts. Pumped from the ground Called crude oil A greenish-brown to black liquid Viscosity varies from high to low A mixture that must be refined before it can be used It is a nonrenewable resource
What is Petroleum? In it’s natural state, it is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons and other substances, such as water, sulfides, metals and salts. Pumped from the ground Called crude oil A greenish-brown to black liquid Viscosity varies from high to low A mixture that must be refined before it can be used It is a nonrenewable resource
 Where does petroleum come from? Petroleum comes from the ground and we transport it to refineries
Where does petroleum come from? Petroleum comes from the ground and we transport it to refineries
 What is petroleum made of? Hydrocarbons are the simplest of the organic compounds. As the name suggests, hydrocarbons are made from hydrogen and carbon.
What is petroleum made of? Hydrocarbons are the simplest of the organic compounds. As the name suggests, hydrocarbons are made from hydrogen and carbon.
 What can we do with petroleum? Burning it provides over ½ of the total annual U.S. energy needs Most of it is used as fuel in the form of gasoline Other petroleum based fuels heat homes, generate electricity, power diesel engines and jet aircraft. Other uses include the production of plastics, sports equipment, clothing, auto parts, medications, cosmetics, artificial limbs etc.
What can we do with petroleum? Burning it provides over ½ of the total annual U.S. energy needs Most of it is used as fuel in the form of gasoline Other petroleum based fuels heat homes, generate electricity, power diesel engines and jet aircraft. Other uses include the production of plastics, sports equipment, clothing, auto parts, medications, cosmetics, artificial limbs etc.
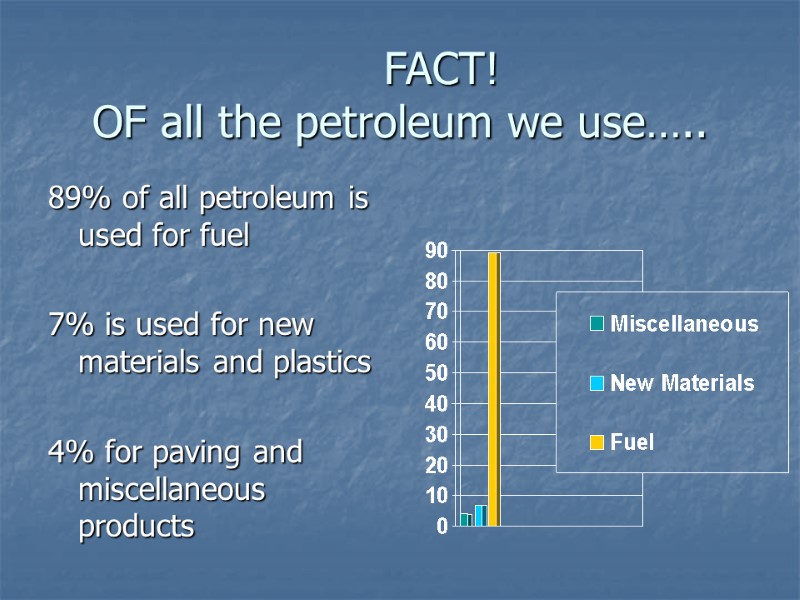 FACT! OF all the petroleum we use….. 89% of all petroleum is used for fuel 7% is used for new materials and plastics 4% for paving and miscellaneous products
FACT! OF all the petroleum we use….. 89% of all petroleum is used for fuel 7% is used for new materials and plastics 4% for paving and miscellaneous products
 For every gallon used to produce useful products, 5 are burned for fuel! Fuel: All other plastics and useful products:
For every gallon used to produce useful products, 5 are burned for fuel! Fuel: All other plastics and useful products:
 What happens to petroleum that makes it so valuable? When Petroleum is burned, a chemical reaction occurs. The atoms are rearranged to form new molecules. The burning hydrocarbons produce water and carbon dioxide (combustion reaction) The gases disperse into the air . It will take millions of years to replace it
What happens to petroleum that makes it so valuable? When Petroleum is burned, a chemical reaction occurs. The atoms are rearranged to form new molecules. The burning hydrocarbons produce water and carbon dioxide (combustion reaction) The gases disperse into the air . It will take millions of years to replace it
 Combustion reaction of hydrocarbons
Combustion reaction of hydrocarbons
 Who Has it? It is not spread equally
Who Has it? It is not spread equally
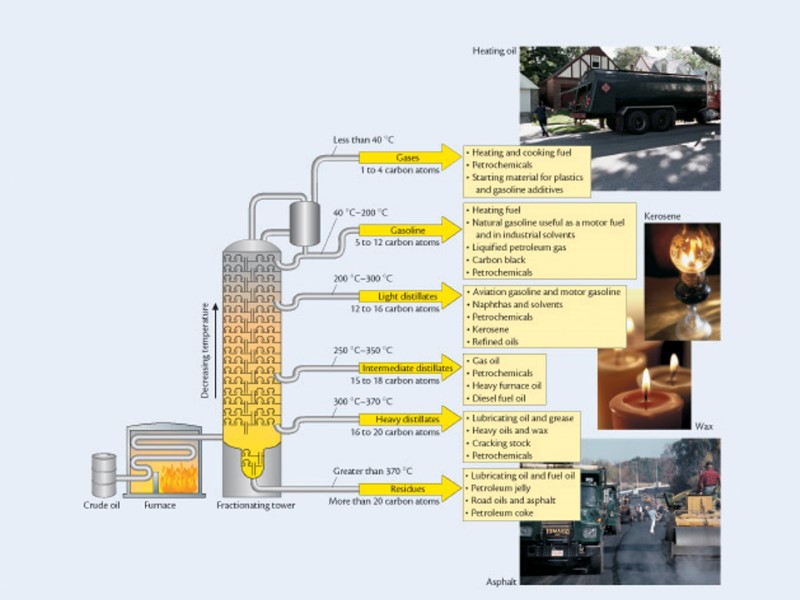
 Separation Taking out the good in the goo “fractional distillation” Separation by differences in boiling points
Separation Taking out the good in the goo “fractional distillation” Separation by differences in boiling points
 Simple Distillation All based on what temperature something vaporizes at The distillates are what is collected at differing time intervals
Simple Distillation All based on what temperature something vaporizes at The distillates are what is collected at differing time intervals
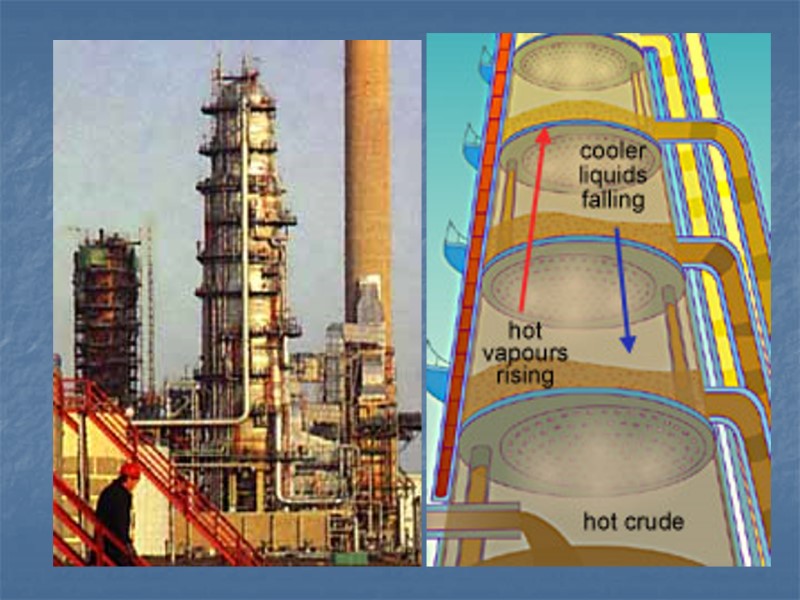
 Steps to refining crude oil The crude oil is heated to about 400 degrees. The crude is then pumped into a fractional tower, which is about 100 feet tall. Some of the crude oil vaporize. Trays at different heights collect the condensed fractions. The thickest and heaviest molecules never vaporize, they sink to the base and are drained.
Steps to refining crude oil The crude oil is heated to about 400 degrees. The crude is then pumped into a fractional tower, which is about 100 feet tall. Some of the crude oil vaporize. Trays at different heights collect the condensed fractions. The thickest and heaviest molecules never vaporize, they sink to the base and are drained.
 Petroleum Refining Crude oil is made up of hundreds of different hydrocarbons In oil the different groups of similar hydrocarbons are fractions Obtaining fractions at a large scale Large scale refineries process 3 million barrels a day
Petroleum Refining Crude oil is made up of hundreds of different hydrocarbons In oil the different groups of similar hydrocarbons are fractions Obtaining fractions at a large scale Large scale refineries process 3 million barrels a day
 Thank you ! Zavotpayeva Gaukhar
Thank you ! Zavotpayeva Gaukhar